DNA合成、组装与纠错技术研究进展
Advances in technologies for de novo DNA synthesis, assembly and error correction
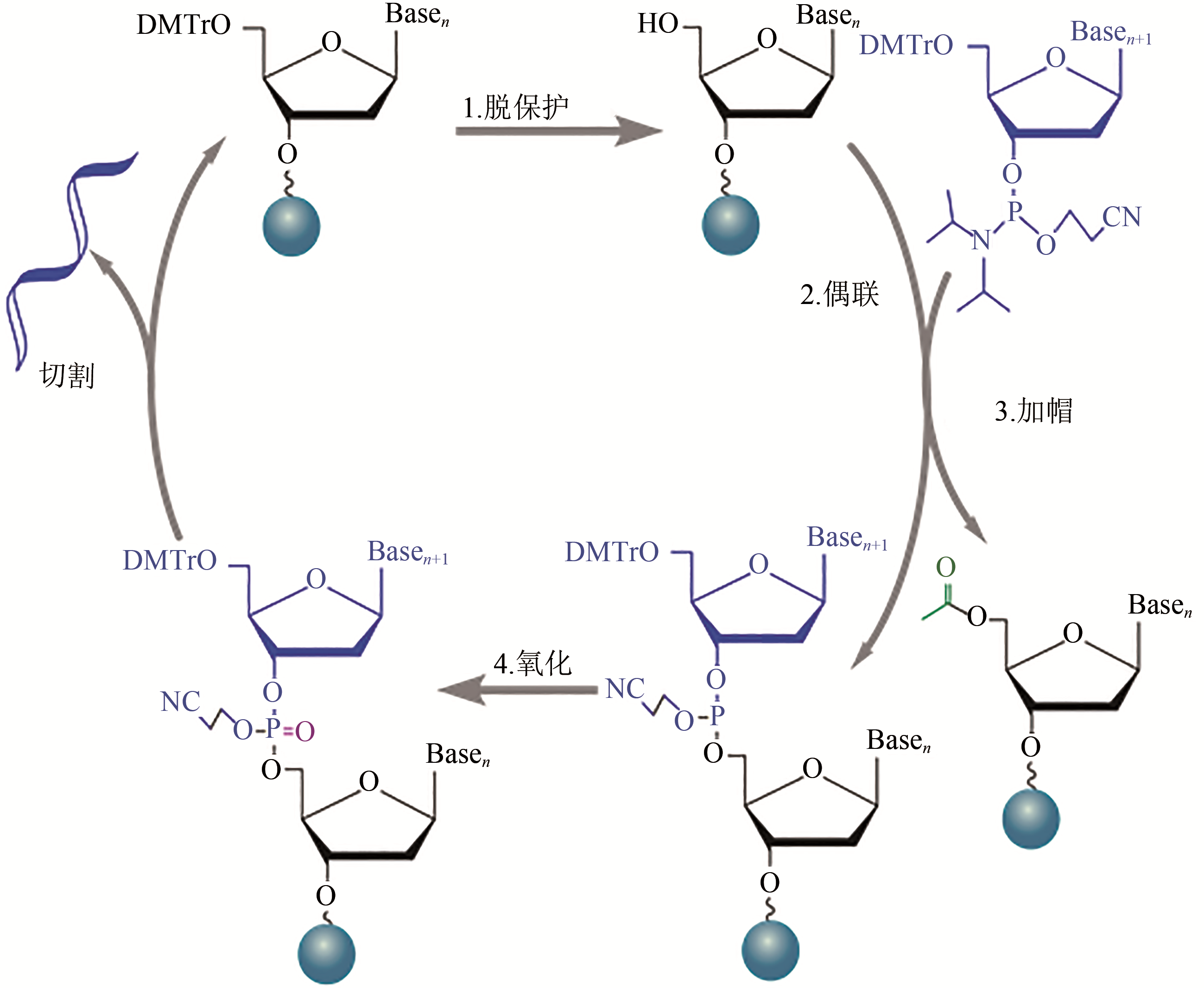
[1—脱保护,用三氯乙酸脱去固相载体上核苷酸5' 位的DMT(dimethoxytrityl)保护基团,获得供下一步缩合反应的游离5' 羟基;2—偶联,将亚磷酰胺保护的核苷酸单体与四氮唑活化剂混合,形成亚磷酰胺四唑活性中间体(其3' 端已被活化,但5' 端仍受DMT保护),与脱保护后生成的5' 羟基发生缩合反应,寡核苷酸链向前延长一个核苷酸;3—加帽,缩合反应后,通过乙酰化来封闭未参与反应的5' 羟基,防止其在随后的循环反应中被延伸,以减少产物中单核苷酸缺失片段的比例;4—氧化,用碘的四氢呋喃溶液将连接3',5' 的不稳定亚磷酰胺三酯氧化为磷酸三酯,得到稳定的寡核苷酸链]
[1—Deprotection. The dimethoxytrityl (DMT) ether capping group on the 5’ end of the previous nucleotide is removed to generate the 5’ end hydroxyl group on the growing chain. 2—Coupling. The desired phosphoramidite monomer couples to the chain via the 5’ end hydroxyl group generated in the deprotection step. 3—Capping. Uncoupled 5’ end hydroxyl group is blocked by acylating molecules to prevent further reactions. 4—Oxidation. An oxidizer agent is used to converte phosphite triester linkage to a more stable phosphotriester bond prior to the start of the next cycle. Cleavage: final oligonucleotides are cleaved from their solid support at the end of synthesis]