虫生真菌非核糖体多肽活性产物生物合成潜力预测
Potential biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides by hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungi
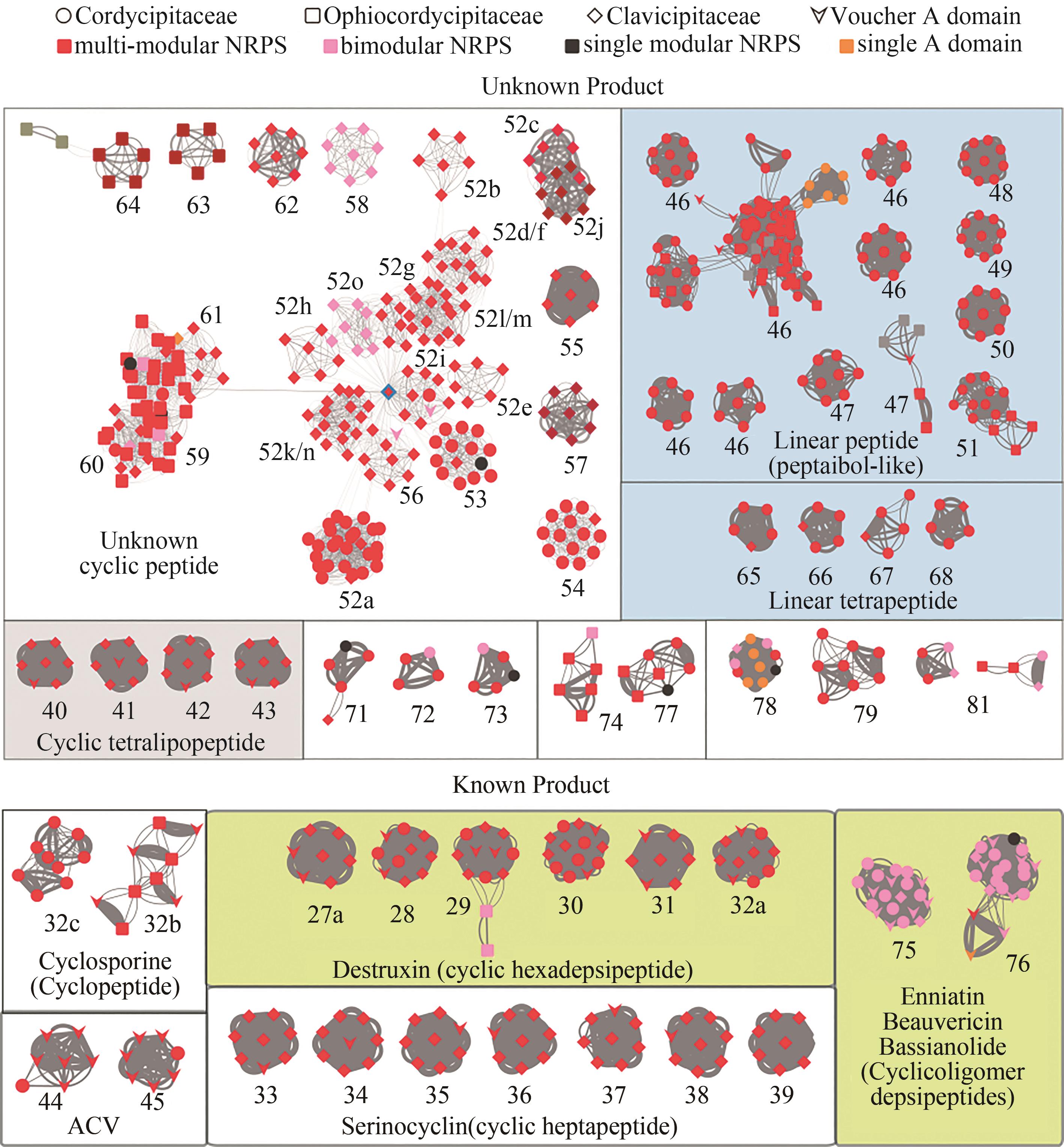
[其中每个节点代表一个腺苷酰化结构域,连接线粗细与相似性成正比。节点颜色显示非核糖体多肽合成酶的类型,形状表示肉座菌目虫生真菌的种类(科),已知功能的结构域用箭头表示。灰色边框中显示来自同一酶的腺苷酰化结构域的分支(如DtxS1),或由密切相关的结构域分支(如52~64)形成的超级分支(详见正文)。底色显示预测的产物类型。腺苷酰化结构域的亚分支用数字字母组合表示,例如52a]
(Nodes in the network represent A domains, and the line boldness is proportional to the identity. The nodes are colored according to the domain composition of NRPS. Referenced A domains from voucher NRPSs with known products are indicated by arrowheads. The predicted products/functions of the enzymes are listed below the clades. Boxed groups show A domains from the group of enzymes that also contain DtxS1, or superclades that are formed by closely related A domain clades such as clades #52~64 (see text for details). Sub-clades of A domains are indicated with a number-letter combination, for example 52a. NRPSs of the BGCs that contain the voucher A domains include: #27a~32a, destruxin synthetase DtxS1[