合成生物学视角下的基因功能探索与酵母工程菌株文库构建
Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective
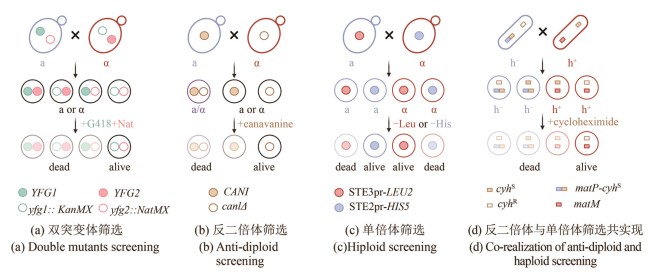
[(a)双突变体筛选策略。两种交配型的细胞分别在各自的突变位点携带不同抗性标签KanMX(绿色空心圆点)和NatMX(粉色空心圆点)用于筛选双突变体子代(黑线框细胞);YFG (your favourite gene):目的基因。(b)反二倍体筛选策略。含有野生型CAN1基因的单倍体细胞(蓝色细胞,a型)或二倍体细胞(紫色细胞)会摄入有毒的刀豆氨酸(canavanine),从而被杀死,而can1Δ突变体无法将刀豆氨酸运转入体内,因此能够存活(黑线框细胞)。(c) 单倍体筛选策略。在某一细胞型的母本菌株中,构建另一细胞型特异性启动子与营养缺陷筛选标签的表达盒,用于选择任一性别的单倍体子代细胞。例如在a型细胞(蓝色)中,携带只能在α型细胞中表达的STE3pr-LEU2基因线路(红色实心圆点),只有细胞交配使STE3pr-LEU2基因线路存在于α型细胞中时,该细胞存活(含有红色实心圆点的红线框细胞)。(d)反二倍体与单倍体筛选共实现。通过将一个显性致死的抗性基因cyhS(棕色实心方块)“镶嵌”在裂殖酵母交配位点mat1(在蓝色的h-细胞中为蓝色方块表示的matP)附近,使得某一单倍体表型与抗性基因的表达偶联(matP-cyhS)]
[(a) Double mutant selection strategy. Two mating-type cells each carry different resistance markers at their respective mutation sites: KanMX (green hollow circle) and NatMX (pink hollow circle). These allow for the selection of double mutant progeny (outlined in black). YFG (your favorite gene): target gene of interest.(b) Counter-diploid selection strategy. Haploid cells carrying a wild-type CAN1 gene (blue, a-type) and diploid cells (purple) can uptake the toxic analog canavanine and are killed, while can1Δ mutants cannot transport canavanine and thus survive (outlined in black).(c) Haploid selection strategy. A mating-type-specific promoter is used to drive the expression of a nutritional selection marker in the opposite mating type, allowing selection of haploid progeny of a specific mating type. For example, when an a-type parent cell (blue), harboring a gene cassette expressing STE3pr-LEU2 (red solid circle) — which is only active in α-type cell — mates with another cell, only the α-type progeny that inherit this construct (outlined in red with a red solid circle) will survive.(d) Combined counter-diploid and haploid selection strategy. A dominant-lethal resistance gene, cyhS (brown solid square), is inserted near the mat1 mating-type locus to link its expression with a specific haploid phenotype. For example, insertion near matP (blue square) in h- cells (blue) leads to the death of cyhS -containing h- haploids and diploids, enabling selection of h+ haploids.]