合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (6): 1277-1291.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-004
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
庆大霉素及其相关产物在工业底盘细胞中的高效合成
吴亮亮1, 常莹莹1, 邓子新1,2, 刘天罡1,2
- 1.武汉大学药学院,组合生物合成与新药发现教育部重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430071
2.武汉生物技术研究院,合成微生物技术湖北省工程实验室,湖北 武汉 430075
-
收稿日期:2022-01-05修回日期:2022-02-23出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2023-01-17 -
通讯作者:刘天罡 -
作者简介:吴亮亮 (1996—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为定向合成代谢指导工业菌株中庆大霉素的产量提升。E-mail:wuliangliang@whu.edu.cn常莹莹 (1994—),女,工程师。研究方向为定向合成代谢指导工业菌株中庆大霉素的产量提升。E-mail:yingyingchang@whu.edu.cn刘天罡 (1979—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为天然产物高效合成与创新发现。E-mail:liutg@whu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2018YFA0900400)
Efficient synthesis of gentamicin and its related products in industrial chassis cells
WU Liangliang1, CHANG Yingying1, DENG Zixin1,2, LIU Tiangang1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery,Ministry of Education,Wuhan University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China
2.Hubei Engineering Laboratory for Synthetic Microbiology,Wuhan Institute of Biotechnology,Wuhan 430075,Hubei,China
-
Received:2022-01-05Revised:2022-02-23Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:LIU Tiangang
摘要:
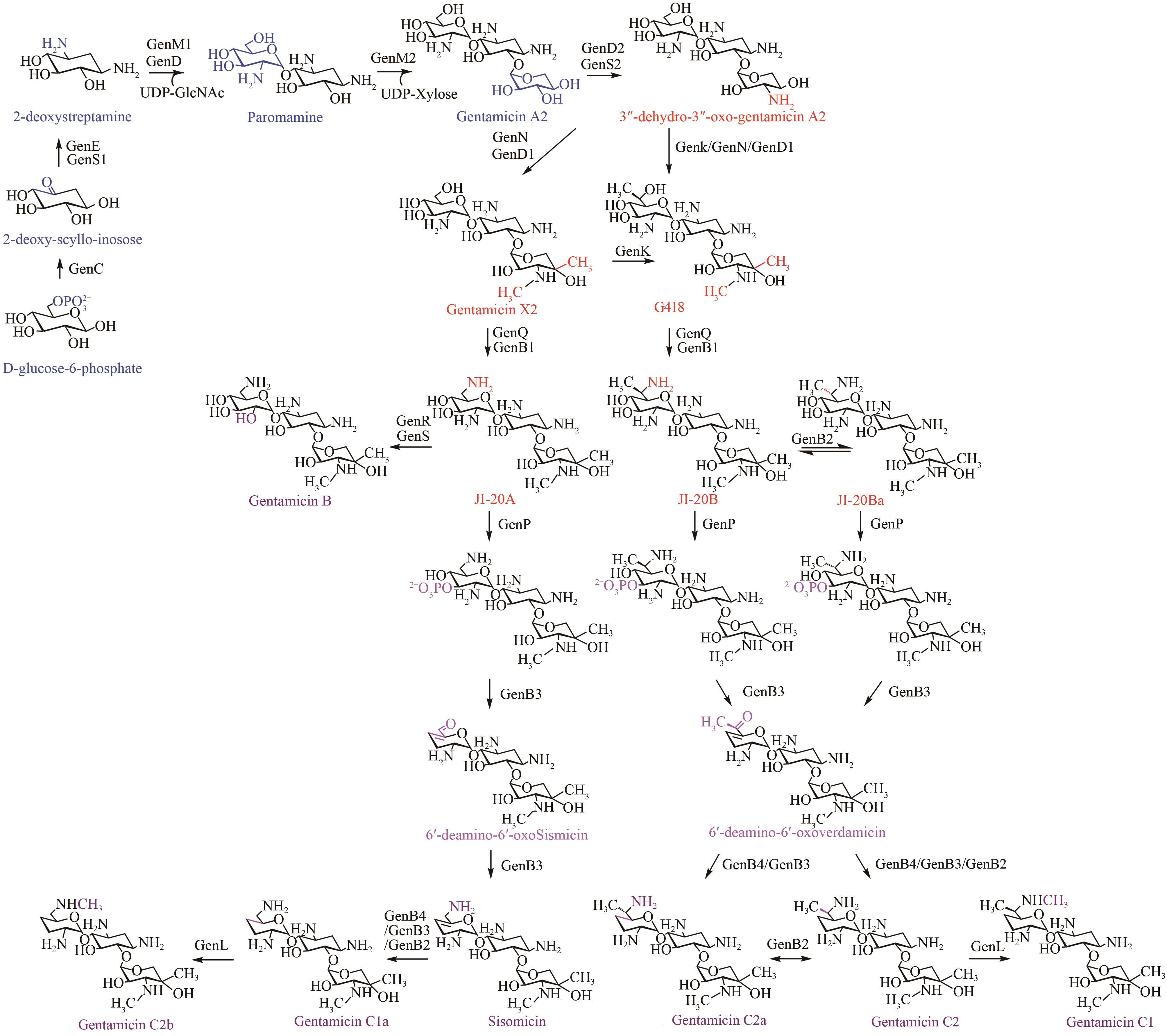
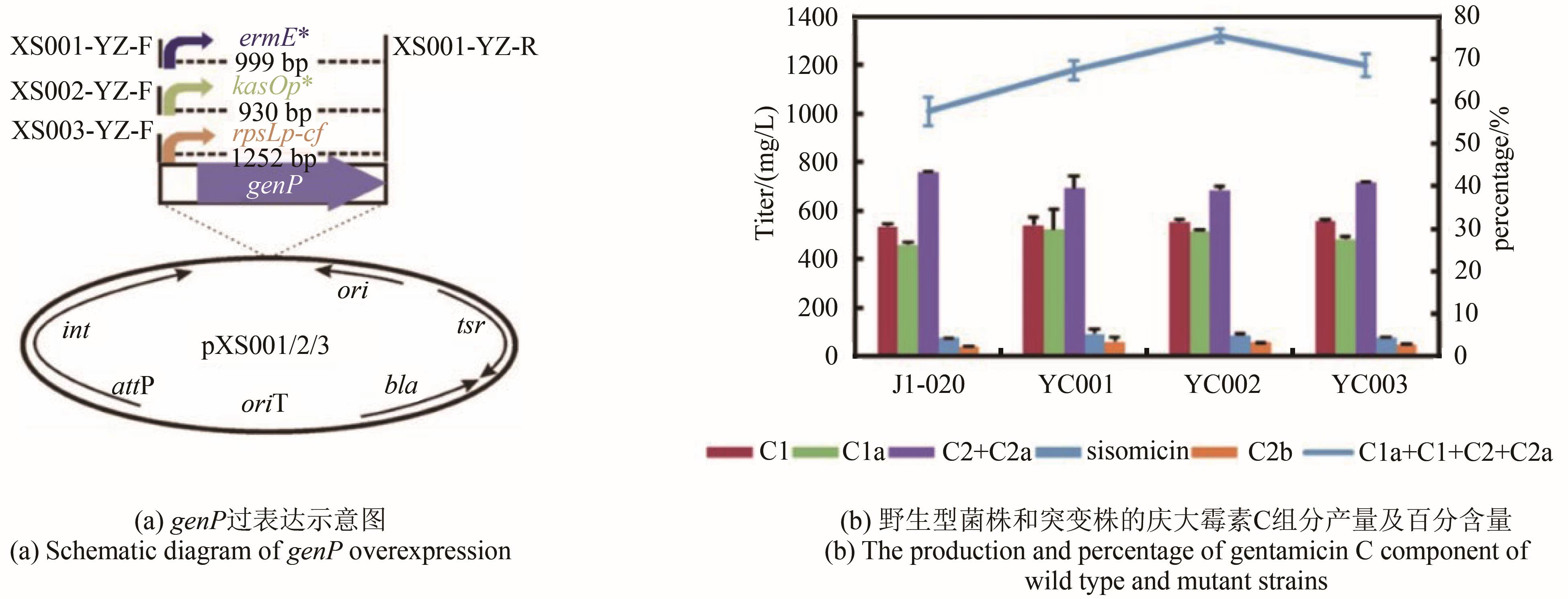
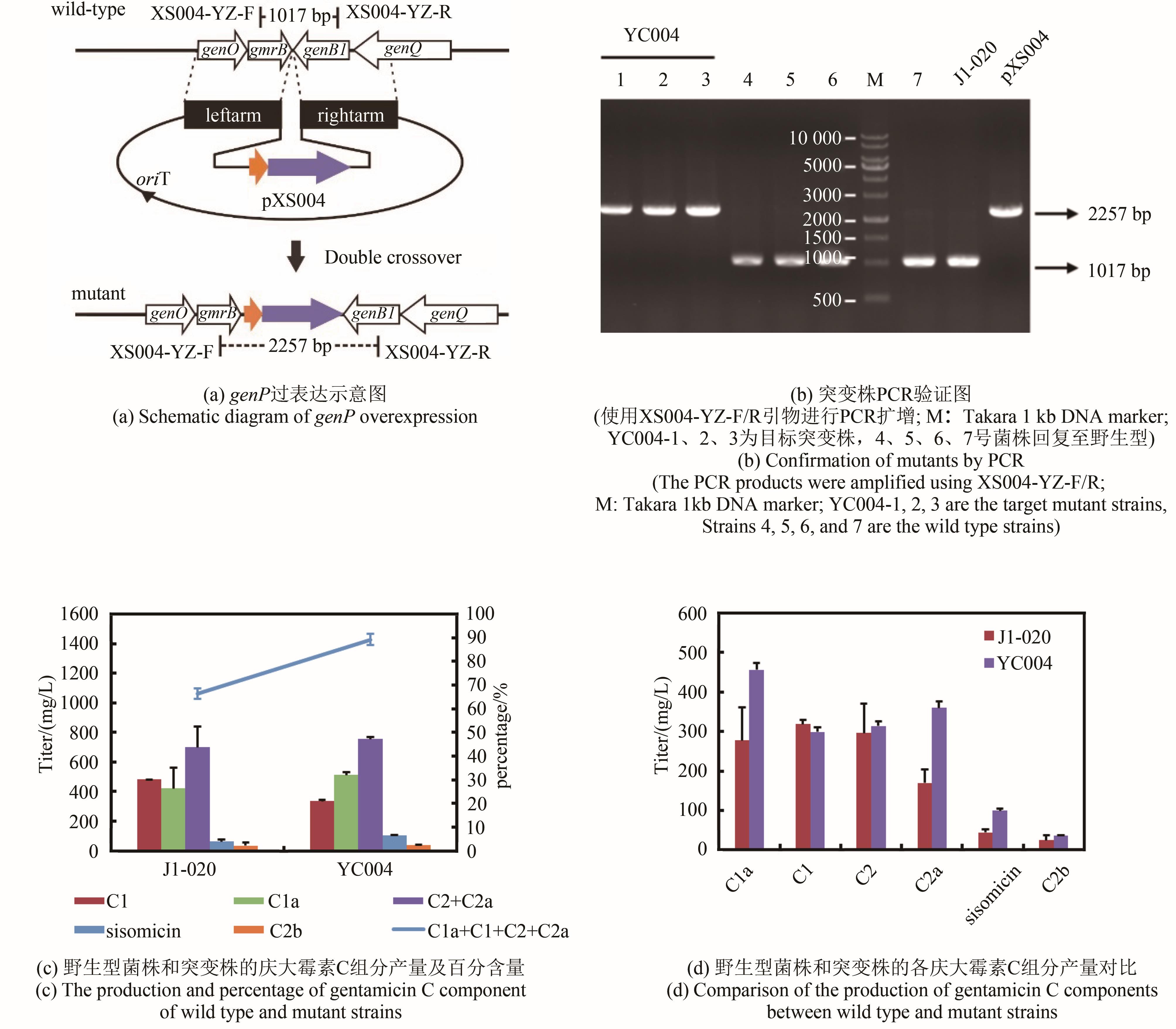
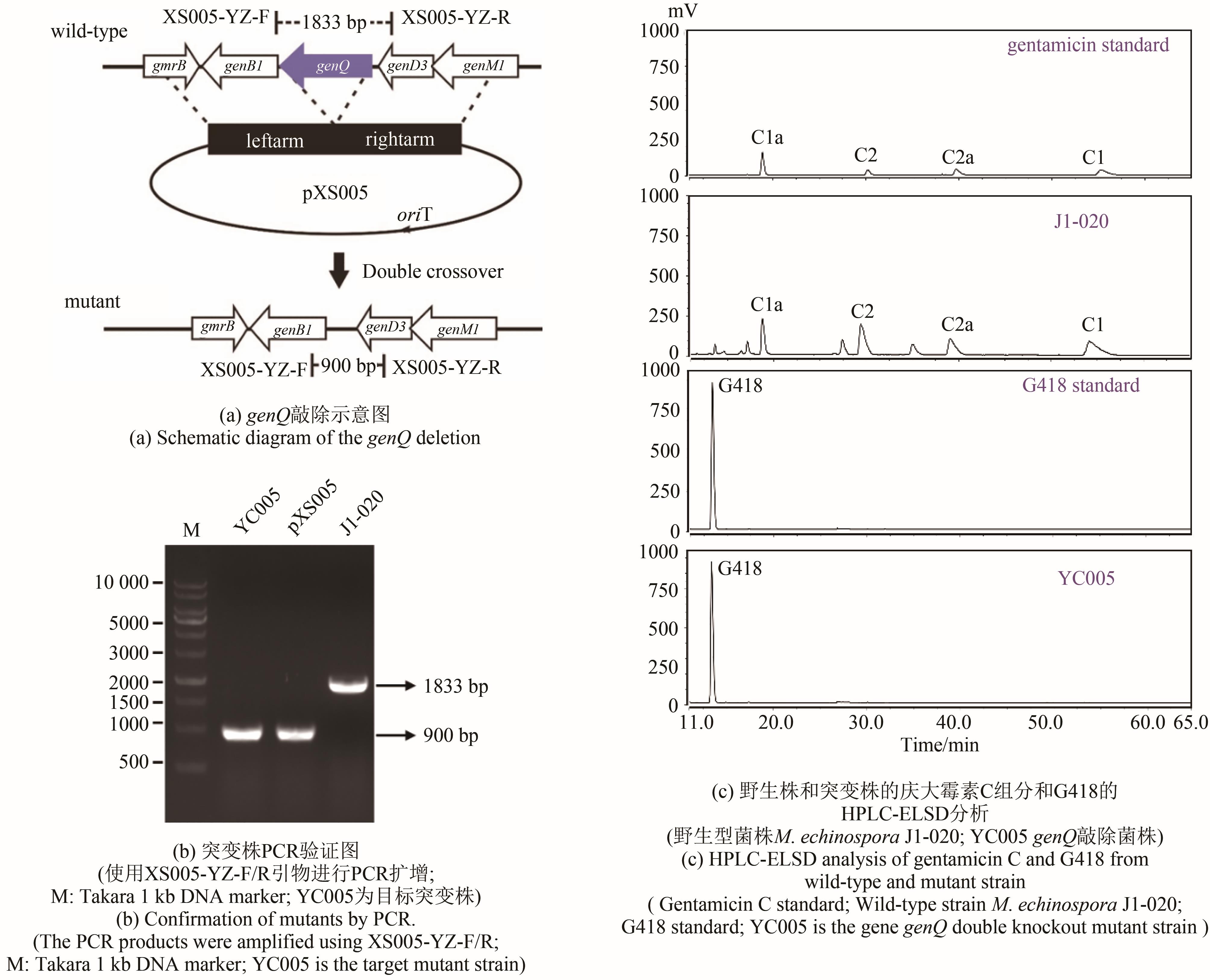
庆大霉素是一种氨基糖苷类抗生素,在临床上广泛应用于治疗由革兰氏阴性菌引起的严重感染。它可由棘孢小单孢菌Micromonospora echinospora产生,生物合成途径清晰。为了提高庆大霉素的产量,本文以工业菌株M. echinospora J1-020为基础,确定庆大霉素合成基因簇信息,建立了稳定的遗传操作方法。在此基础上,使用强(kasOp*)、中(rpsLp-cf)、弱(ermE*)三种强度的启动子评估磷酸转移酶GenP的最适过表达水平,构建对应attB/attP位点整合突变株YC002、YC003、YC001。摇瓶发酵结果显示,YC001、YC002、YC003菌株的庆大霉素C组分的产量较原始菌株[(1008±57) mg/L]分别提高了16.9%[(1178±39) mg/L]、30.8 %[(1319±29) mg/L]和18.8 %[(1198±46) mg/L];同时,结合杂质含量,在以上三株菌株中确定了中强度启动子控制genP过表达的效果最佳,以此构建对应的稳定整合在基因组上的genP过表达菌株YC004。使得庆大霉素C组分摇瓶发酵产量提高了34.5 %[(1427±37) mg/L]。此外,以工业菌株M. echinospora J1-020为底盘,构建genQ敲除菌株,获得了只产生G418单一组分的菌株YC005,其摇瓶发酵产量为460 mg/L。以YC004为出发菌株,依次敲除genB4、genK,获得了只产生西索米星单一组分的菌株YC007,其摇瓶发酵产量达1046 mg/L。综上,以该工业菌株M. echinospora J1-020为底盘,借助合理的代谢工程策略有望快速获得多种氨基糖苷类抗生素的高产菌株。
引用本文
吴亮亮, 常莹莹, 邓子新, 刘天罡. 庆大霉素及其相关产物在工业底盘细胞中的高效合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1277-1291.
WU Liangliang, CHANG Yingying, DENG Zixin, LIU Tiangang. Efficient synthesis of gentamicin and its related products in industrial chassis cells[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1277-1291.
| Strain | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| M. echinospora J1-020 | Wild-type | This study |
| DH10B | F–mcrA ∆(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) | Gibco-BRL |
| ET12567(pUZ8002) | damdcmhsdS/pUZ8002, for intergeneric conjugation | [ |
| ET12567(pUB307) | dam dcm hsdS/pUB307, for intergeneric conjugation | [ |
| YC001 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC002 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC003 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC004 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC005 | genQ gene knockout strain | This study |
| YC006 | genB4 gene knockout strain | This study |
| YC007 | genB4 and genK gene knockout strain | This study |
| Plasmid | ||
| pWHU77 | int, att, tsr, ermE* | [ |
| pYH7 | sti-, rep*, orf85-, R1-, tsr, aac(3)IV | [ |
| pXS001 | E.coli-actinomycete integrated shuttle plasmid, pWHU77 carries genP under the control of the ermE* promoter | This study |
| pXS002 | E.coli-actinomycete integrated shuttle plasmid, pWHU77 carries genP under the control of the kasOp* promoter | This study |
| pXS003 | E.coli-actinomycete integrated shuttle plasmid, pWHU77 carries genP under the control of the rpsLp-cf promoter | This study |
| pXS004 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, pYH7 carries genP under the control of the rpsLp-cf promoter | This study |
| pXS005 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, genQ gene knockout plasmid | This study |
| pXS006 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, genB4 gene knockout plasmid | This study |
| pXS007 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, genK gene knockout plasmid | This study |
表1 本研究中使用的菌株和质粒
Tab. 1 Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| M. echinospora J1-020 | Wild-type | This study |
| DH10B | F–mcrA ∆(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) | Gibco-BRL |
| ET12567(pUZ8002) | damdcmhsdS/pUZ8002, for intergeneric conjugation | [ |
| ET12567(pUB307) | dam dcm hsdS/pUB307, for intergeneric conjugation | [ |
| YC001 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC002 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC003 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC004 | genP gene overexpression strain | This study |
| YC005 | genQ gene knockout strain | This study |
| YC006 | genB4 gene knockout strain | This study |
| YC007 | genB4 and genK gene knockout strain | This study |
| Plasmid | ||
| pWHU77 | int, att, tsr, ermE* | [ |
| pYH7 | sti-, rep*, orf85-, R1-, tsr, aac(3)IV | [ |
| pXS001 | E.coli-actinomycete integrated shuttle plasmid, pWHU77 carries genP under the control of the ermE* promoter | This study |
| pXS002 | E.coli-actinomycete integrated shuttle plasmid, pWHU77 carries genP under the control of the kasOp* promoter | This study |
| pXS003 | E.coli-actinomycete integrated shuttle plasmid, pWHU77 carries genP under the control of the rpsLp-cf promoter | This study |
| pXS004 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, pYH7 carries genP under the control of the rpsLp-cf promoter | This study |
| pXS005 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, genQ gene knockout plasmid | This study |
| pXS006 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, genB4 gene knockout plasmid | This study |
| pXS007 | E.coli-actinomycete replicating shuttle plasmid, genK gene knockout plasmid | This study |
| Primers | Sequence(5′ to 3′) | Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| XS001-genP-F | CCA | NdeⅠ |
| XS001-genP-R | TAC | EcoRⅠ |
| XS001-YZ-F | GCGAGTGTCCGTTCGAGTGG | |
| XS001-YZ-R | TCAGAGAAATTCGTCCAGCAG | |
| XS002-kasOp*-F | GCAGGTCGACTCTAGTATGCAT | XbaⅠ |
| XS002- kasOp*-R | GTGCTGCAACCATCTTCATATGGCGTATCCCCTTTCAGATACC | |
| XS002-genP-F | TCTGAAAGGGGATACGCCATATGAAGATGGTTGCAGCACC | |
| XS002-genP-R | GGAAACAGCTATGACATGATTAC | EcoRⅠ |
| XS002-YZ-F | GGAACGATCGTTGGCTGTGTTC | |
| XS003-rpsLp-cf-F | AGGTCGACTCTAGTATGCAT | XbaⅠ |
| XS003-rpsLp-cf-R | GGTGCTGCAACCATCTTCATATGGCGTATCCCCTTTCAGATAC | |
| XS003-genP-F | TCTGAAAGGGGATACGCCATATGAAGATGGTTGCAGCACC | |
| XS003-genP-R | TTTCACACAGGAAACAGCTATGACATGATTAC | EcoRⅠ |
| XS003-YZ-F | GGAACGATCGTTGGCTGCCCGCCGCGGGCGCTG | |
| XS004-leftarm-F | ACCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGACACGTCTGAA | NheⅠ |
| XS004-leftarm-R | CCTCCAGCGCCCGCGGCGGGCAGCCAACGATCGTTCCTCACGCCTTGTGGATCGCCACC | |
| XS004-rpsLp-cf-F | CCTGGTGGCGATCCACAAGGCGTGAGGAACGATCGTTGGCTGCCCGCCGCGGGCGCTGG | |
| XS004-genP-R | AGACCACCGCGATCGTCGAGCGCCTCTGGGAGGACTGATCAGAGAAATTCGTCCAGCAG | |
| XS004-rightarm-F | GCTGACCTACATCCAACTGCTGGACGAATTTCTCTGATCAGTCCTCCCAGAGGCGCTCG | |
| XS004-rightarm-R | TAGGCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGTCTTCAA | EcoRⅠ |
| XS004-YZ-F | CCGTTCACCGTGCCCTGGCTGCGCGAGGTG | |
| XS004-YZ-R | CTCGACCCGGCCGTCTGGATCGTGGCGAAG | |
| XS005-leftarm-F | CGGCCATCGTGCCTCCCCACTCCTGC | HindⅢ |
| XS005-leftarm-R | GTGCGGCCTTCCGCGAATTCCGGGACCGGGCCCGACTGGAG | |
| XS005-rightarm-F | CGGGCCCGGTCCCGGAATTCGCGGAAGGCCGCACCGCCGAAG | |
| XS005-rightarm-R | AGCGGAAAAGATCCGTCGACCTGCAGGCATGC | BglⅡ |
| XS005-YZ-F | TCCGCTCGATTCGTTCCGTTCCGAC | |
| XS005-YZ-R | GCACGGGACCACCGGGCAGGTGCTC | |
| XS006-leftarm-F | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGACACGTCTGAA | NheⅠ |
| XS006-leftarm-R | AAGCTGACCTACATCCAACTGCTGGACGAATTTCTCTGATCAGCGCTGGTAGGTGCTCG | |
| XS006-rightarm-F | AGCGCTGGCGGCTGCGCGCACCTACCAGCGCTGCTAAGAGAAATTCGTCCAGCAGTTGG | |
| XS006-rightarm-R | GGCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGTCTTCAA | EcoRⅠ |
| XS006-YZ-F | GGCAGCCGGACTGGGCGACCATCCGGATCG | |
| XS006-YZ-R | CCGAGGACGATCTCGTCGTCTGCCACGGTG | |
| XS007-leftarm-F | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGACACGTCTGAA | NheⅠ |
| XS007-leftarm-R | CCCCCTACTACGAGAGCGCCTACGAGCTGGCCCGGATGATGGCGCAGCTCGACCCGGAG | |
| XS007-rightarm-F | GTTCCTCCGGGCTCTCCGGGTCGAGCtGCGCCATCATCCGGGCCAGCTCGAGGCGCTC | |
| XS007-rightarm-R | ATAGGCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGTCTTCAA | EcoRⅠ |
| XS007-YZ-F | CGTCACGCGATGGGAGCAGGGCGGAGTATC | |
| XS007-YZ-R | CCGAGCATCACGCTGCCGAAGGAGTTGGAG |
表2 本研究中使用的寡核苷酸引物
Tab. 2 Oligonucleotide primers used in this study
| Primers | Sequence(5′ to 3′) | Restriction site |
|---|---|---|
| XS001-genP-F | CCA | NdeⅠ |
| XS001-genP-R | TAC | EcoRⅠ |
| XS001-YZ-F | GCGAGTGTCCGTTCGAGTGG | |
| XS001-YZ-R | TCAGAGAAATTCGTCCAGCAG | |
| XS002-kasOp*-F | GCAGGTCGACTCTAGTATGCAT | XbaⅠ |
| XS002- kasOp*-R | GTGCTGCAACCATCTTCATATGGCGTATCCCCTTTCAGATACC | |
| XS002-genP-F | TCTGAAAGGGGATACGCCATATGAAGATGGTTGCAGCACC | |
| XS002-genP-R | GGAAACAGCTATGACATGATTAC | EcoRⅠ |
| XS002-YZ-F | GGAACGATCGTTGGCTGTGTTC | |
| XS003-rpsLp-cf-F | AGGTCGACTCTAGTATGCAT | XbaⅠ |
| XS003-rpsLp-cf-R | GGTGCTGCAACCATCTTCATATGGCGTATCCCCTTTCAGATAC | |
| XS003-genP-F | TCTGAAAGGGGATACGCCATATGAAGATGGTTGCAGCACC | |
| XS003-genP-R | TTTCACACAGGAAACAGCTATGACATGATTAC | EcoRⅠ |
| XS003-YZ-F | GGAACGATCGTTGGCTGCCCGCCGCGGGCGCTG | |
| XS004-leftarm-F | ACCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGACACGTCTGAA | NheⅠ |
| XS004-leftarm-R | CCTCCAGCGCCCGCGGCGGGCAGCCAACGATCGTTCCTCACGCCTTGTGGATCGCCACC | |
| XS004-rpsLp-cf-F | CCTGGTGGCGATCCACAAGGCGTGAGGAACGATCGTTGGCTGCCCGCCGCGGGCGCTGG | |
| XS004-genP-R | AGACCACCGCGATCGTCGAGCGCCTCTGGGAGGACTGATCAGAGAAATTCGTCCAGCAG | |
| XS004-rightarm-F | GCTGACCTACATCCAACTGCTGGACGAATTTCTCTGATCAGTCCTCCCAGAGGCGCTCG | |
| XS004-rightarm-R | TAGGCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGTCTTCAA | EcoRⅠ |
| XS004-YZ-F | CCGTTCACCGTGCCCTGGCTGCGCGAGGTG | |
| XS004-YZ-R | CTCGACCCGGCCGTCTGGATCGTGGCGAAG | |
| XS005-leftarm-F | CGGCCATCGTGCCTCCCCACTCCTGC | HindⅢ |
| XS005-leftarm-R | GTGCGGCCTTCCGCGAATTCCGGGACCGGGCCCGACTGGAG | |
| XS005-rightarm-F | CGGGCCCGGTCCCGGAATTCGCGGAAGGCCGCACCGCCGAAG | |
| XS005-rightarm-R | AGCGGAAAAGATCCGTCGACCTGCAGGCATGC | BglⅡ |
| XS005-YZ-F | TCCGCTCGATTCGTTCCGTTCCGAC | |
| XS005-YZ-R | GCACGGGACCACCGGGCAGGTGCTC | |
| XS006-leftarm-F | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGACACGTCTGAA | NheⅠ |
| XS006-leftarm-R | AAGCTGACCTACATCCAACTGCTGGACGAATTTCTCTGATCAGCGCTGGTAGGTGCTCG | |
| XS006-rightarm-F | AGCGCTGGCGGCTGCGCGCACCTACCAGCGCTGCTAAGAGAAATTCGTCCAGCAGTTGG | |
| XS006-rightarm-R | GGCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGTCTTCAA | EcoRⅠ |
| XS006-YZ-F | GGCAGCCGGACTGGGCGACCATCCGGATCG | |
| XS006-YZ-R | CCGAGGACGATCTCGTCGTCTGCCACGGTG | |
| XS007-leftarm-F | CTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGACACGTCTGAA | NheⅠ |
| XS007-leftarm-R | CCCCCTACTACGAGAGCGCCTACGAGCTGGCCCGGATGATGGCGCAGCTCGACCCGGAG | |
| XS007-rightarm-F | GTTCCTCCGGGCTCTCCGGGTCGAGCtGCGCCATCATCCGGGCCAGCTCGAGGCGCTC | |
| XS007-rightarm-R | ATAGGCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGTCTTCAA | EcoRⅠ |
| XS007-YZ-F | CGTCACGCGATGGGAGCAGGGCGGAGTATC | |
| XS007-YZ-R | CCGAGCATCACGCTGCCGAAGGAGTTGGAG |
| Type | Morphology of actinomycetes | Plasmid | The mixing ratio (Donor: Receptor) | Incubation time/h | Number of conjugants (Cultivate to 9d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diparental conjugation | mycelia | pWHU77 | 10∶1、4∶1、1∶1 | 14、16 | 100~200 |
| mycelia | pYH7 | 20∶1、10∶1 | 1 | ||
| Triparental conjugation | mycelia | pWHU77 | 4∶4∶1、1∶1∶1 | 100~200 | |
| mycelia | pYH7 | 4∶4∶1、1∶1∶1 | 50~100 | ||
| spore | pYH7 | 10∶10∶1、1∶1∶1 | 13 | >200 |
表3 M. echinospora J1-020接合转移条件摸索
Tab. 3 Exploration of the conjugation conditions of M. echinospora J1-020
| Type | Morphology of actinomycetes | Plasmid | The mixing ratio (Donor: Receptor) | Incubation time/h | Number of conjugants (Cultivate to 9d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diparental conjugation | mycelia | pWHU77 | 10∶1、4∶1、1∶1 | 14、16 | 100~200 |
| mycelia | pYH7 | 20∶1、10∶1 | 1 | ||
| Triparental conjugation | mycelia | pWHU77 | 4∶4∶1、1∶1∶1 | 100~200 | |
| mycelia | pYH7 | 4∶4∶1、1∶1∶1 | 50~100 | ||
| spore | pYH7 | 10∶10∶1、1∶1∶1 | 13 | >200 |
| 1 | LLEWELLYN N M, SPENCER J B. Biosynthesis of 2-deoxystreptamine-containing aminoglycoside antibiotics[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2006, 23(6): 864-874. |
| 2 | Waksman SA. Antibiotics and chemotherapy[J]. California medicine, 1953,78(5):417-423. |
| 3 | SWART E A, HUTCHISON D, WAKSMAN S A. Neomycin, recovery and purification[J]. Archives of Biochemistry, 1949, 24(1): 92-103. |
| 4 | UMEZAWA H, UEDA M, MAEDA K, et al. Production and isolation of a new antibiotic: kanamycin[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1957, 10(5): 181-188. |
| 5 | WEINSTEIN M J, LUEDEMANN G M, ODEN E M, et al. Gentamicin, a new antibiotic complex from micromonospora[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1963, 6: 463-464. |
| 6 | FOURMY D, RECHT M I, BLANCHARD S C, et al. Structure of the A site of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA complexed with an aminoglycoside antibiotic[J]. Science, 1996, 274(5291): 1367-1371. |
| 7 | TESTA R T, TILLEY B C. Biotransformation, a new approach to aminoglycoside biosynthesis: II. Gentamicin[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1976, 29(2): 140-146. |
| 8 | KHAREL M K, BASNET D B, LEE H C, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a 2-deoxystreptamine biosynthetic gene cluster in gentamicin-producing Micromonospora echinospora ATCC 15835[J]. Molecules and Cells, 2004, 18(1): 71-78. |
| 9 | PARK J W, HONG J S J, PARAJULI N, et al. Genetic dissection of the biosynthetic route to gentamicin A2 by heterologous expression of its minimal gene set[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(24): 8399-8404. |
| 10 | KIM J Y, SUH J W, KANG S H, et al. Gene inactivation study of gntE reveals its role in the first step of pseudotrisaccharide modifications in gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2008, 372(4): 730-734. |
| 11 | HONG W R, YAN L B. Identification of gntK, a gene required for the methylation of purpurosamine C-6' in gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 2012, 58(5): 349-356. |
| 12 | KIM H J, MCCARTY R M, OGASAWARA Y, et al. GenK-catalyzed C-6′ methylation in the biosynthesis of gentamicin: isolation and characterization of a cobalamin-dependent radical SAM enzyme[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(22): 8093-8096. |
| 13 | HUANG C, HUANG F L, MOISON E, et al. Delineating the biosynthesis of gentamicin X2, the common precursor of the gentamicin C antibiotic complex[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2015, 22(2): 251-261. |
| 14 | GUO J H, HUANG F L, HUANG C, et al. Specificity and promiscuity at the branch point in gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2014, 21(5): 608-618. |
| 15 | SHAO L, CHEN J S, WANG C X, et al. Characterization of a key aminoglycoside phosphotransferase in gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2013, 23(5): 1438-1441. |
| 16 | ZHOU S T, CHEN X T, NI X P, et al. Pyridoxal-5′-phosphate-dependent enzyme GenB3 catalyzes C-3′, 4′-dideoxygenation in gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 65. |
| 17 | CHEN X T, ZHANG H, ZHOU S T, et al. The bifunctional enzyme, GenB4, catalyzes the last step of gentamicin 3′, 4′-di-deoxygenation via reduction and transamination activities[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 62. |
| 18 | LI S, GUO J, REVA A, et al. Methyltransferases of gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(6): 1340-1345. |
| 19 | BAN Y H, SONG M C, HWANG J Y, et al. Complete reconstitution of the diverse pathways of gentamicin B biosynthesis[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(3): 295-303. |
| 20 | CHANG Y Y, CHAI B Z, DING Y K, et al. Overproduction of gentamicin B in industrial strain Micromonospora echinospora CCTCC M 2018898 by cloning of the missing genes genR and genS [J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2019, 9: e00096. |
| 21 | MACNEIL D J, OCCI J L, GEWAIN K M, et al. Complex organization of the Streptomyces avermitilis genes encoding the avermectin polyketide synthase[J]. Gene, 1992, 115(1/2): 119-125. |
| 22 | FLETT F, MERSINIAS V, SMITH C P. High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 1997, 155(2): 223-229. |
| 23 | SUN Y H, HONG H, SAMBORSKYY M, et al. Organization of the biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces sp. DSM 4137 for the novel neuroprotectant polyketide meridamycin[J]. Microbiology, 2006, 152(Pt 12): 3507-3515. |
| 24 | WEBER T, BLIN K, DUDDELA S, et al. antiSMASH 3.0—a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(W1): W237-W243. |
| 25 | BILYK O, LUZHETSKYY A. Metabolic engineering of natural product biosynthesis in actinobacteria[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 42: 98-107. |
| 26 | SASAKI K, MIZUSAWA H, ISHIDATE M, et al. Regulation of G418 selection efficiency by cell-cell interaction in transfection[J]. Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics, 1992, 18(6): 517-527. |
| 27 | BAIAZITOV R Y, FRIESEN W, JOHNSON B, et al. Chemical modifications of G418 (geneticin): synthesis of novel readthrough aminoglycosides results in an improved in vitro safety window but no improvements in vivo [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2020, 495: 108058. |
| 28 | NI X P, SUN Z P, ZHANG H Y, et al. Genetic engineering combined with random mutagenesis to enhance G418 production in Micromonospora echinospora [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2014, 41(9): 1383-1390. |
| 29 | SHAEER K M, ZMARLICKA M T, CHAHINE E B, et al. Plazomicin: a next-generation aminoglycoside[J]. Pharmacotherapy, 2019, 39(1): 77-93. |
| 30 | NI X P, SUN Z P, GU Y W, et al. Assembly of a novel biosynthetic pathway for gentamicin B production in Micromonospora echinospora [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15: 1. |
| 31 | WU Z, GAO W L, ZHOU S T, et al. Improving gentamicin B and gentamicin C1a production by engineering the glycosyltransferases that transfer primary metabolites into secondary metabolites biosynthesis[J]. Microbiological Research, 2017, 203: 40-46. |
| 32 | LI D, LI H, NI X P, et al. Construction of a gentamicin C1a-overproducing strain of Micromonospora purpurea by inactivation of the gacD gene[J]. Microbiological research, 2013, 168(5): 263-267. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||