合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (5): 815-825.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-005
虫生真菌非核糖体多肽活性产物生物合成潜力预测
张礼文1, MOLNÁR István2, 徐玉泉1
- 1.中国农业科学院生物技术研究所,北京 100081
2.美国亚利桑那大学西南天然产物研究中心,亚利桑那州 图森 85706,美国
-
收稿日期:2021-01-12修回日期:2021-04-16出版日期:2021-10-31发布日期:2021-11-19 -
通讯作者:MOLNáR István,徐玉泉 -
作者简介:张礼文 (1985—),女,副研究员。研究方向为从真菌中挖掘具有农用生物活性的次生代谢产物及其合成基因元件,再用于组合生物合成新骨架、改进活性的化合物。E-mail:zhangliwen@caas.cnIstván Molnár (1963—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为真菌天然产物生物合成与组合合成生物学。E-mail:imolnar@arizona.edu徐玉泉 (1971—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为发现真菌合成的新型生物活性天然产物,阐明其生物合成机制,利用合成生物学的方法对目标产物进行高效生物合成及结构修饰。E-mail:xuyuquan@caas.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32070064);中国农业科学院基本科研业务费专项(Y2020XK20);中国农业科学院科技创新工程
Potential biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides by hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungi
ZHANG Liwen1, MOLNÀR István2, XU Yuquan1
- 1.Biotechnology Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100081,China
2.Southwest Center for Natural Products Research,University of Arizona,Tucson,AZ 85706,USA
-
Received:2021-01-12Revised:2021-04-16Online:2021-10-31Published:2021-11-19 -
Contact:MOLNàR István, XU Yuquan
摘要:
肉座菌目虫生真菌合成的非核糖体多肽类天然产物具有抗菌、杀虫、抗癌、调节免疫等生物活性,在临床和农业等领域有重要应用价值。近年来,随着真菌基因组测序数量的迅速增加、注释和分析工具的不断进步,人们发现真菌基因组中存在大量产物未知的天然产物合成基因。准确有效地预测这些基因的功能,筛选最有潜力合成新颖天然产物的基因簇,可以提高天然产物挖掘的效率。本研究选取40株肉座菌目虫生真菌基因组,系统分析了编码非核糖体多肽合成酶的基因及基因簇。基于隐马尔可夫模型,预测了445个模块型非核糖体多肽合成酶和1243个类非核糖体多肽合成酶;通过提取腺苷酰化结构域,构建序列相似性网络,以已知功能的非核糖体多肽合成酶作为标签,利用马尔可夫聚类算法,分析了非核糖体多肽产物的主要类别,发现了可能合成线性多肽、环缩肽、脂多肽、生物碱等新型结构化合物的基因簇。研究结果不仅揭示了肉座菌目虫生真菌合成非核糖体多肽活性产物的巨大潜力,而且为通过激活沉默基因簇挖掘新产物、利用合成生物学手段改造合成途径提供参考。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张礼文, MOLNÁR István, 徐玉泉. 虫生真菌非核糖体多肽活性产物生物合成潜力预测[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 815-825.
ZHANG Liwen, MOLNÀR István, XU Yuquan. Potential biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides by hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungi[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 815-825.
| Description | Function with HMM | Source | Cutoff (Score) | Length | Domains (SwissProt) | Domains (HEF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenylation domain | AMP-binding | PFAM00501.21 | 55 | 418 | 280 | 2297 |
| Condensation domain | Condensation | PFAM00668.13 | 50 | 301 | 255 | 1483 |
| Thiolation domain | PP-binding | PFAM0050.20 | 30 | 67 | 312 | 2775 |
表1 非核糖体多肽合成酶结构域注释
Tab. 1 Annotion for NRPS domains in hypocrealean entomopathotenic fungi (HEF)
| Description | Function with HMM | Source | Cutoff (Score) | Length | Domains (SwissProt) | Domains (HEF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenylation domain | AMP-binding | PFAM00501.21 | 55 | 418 | 280 | 2297 |
| Condensation domain | Condensation | PFAM00668.13 | 50 | 301 | 255 | 1483 |
| Thiolation domain | PP-binding | PFAM0050.20 | 30 | 67 | 312 | 2775 |
| Subtype | Definition (Proteins that contain…) | Number(SwissProt) | Number(HEF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-modular | more than one A AND C domains | 57 | 280 |
| Single-modular | ONE A AND C domains | 21 | 165 |
| Pseudo | A OR C domain | 86 | 1243 |
表2 非核糖体多肽合成酶统计信息
Tab. 2 Statistic summary of NRPSs in hypocrealean entomopathotenic fungi (HEF)
| Subtype | Definition (Proteins that contain…) | Number(SwissProt) | Number(HEF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-modular | more than one A AND C domains | 57 | 280 |
| Single-modular | ONE A AND C domains | 21 | 165 |
| Pseudo | A OR C domain | 86 | 1243 |
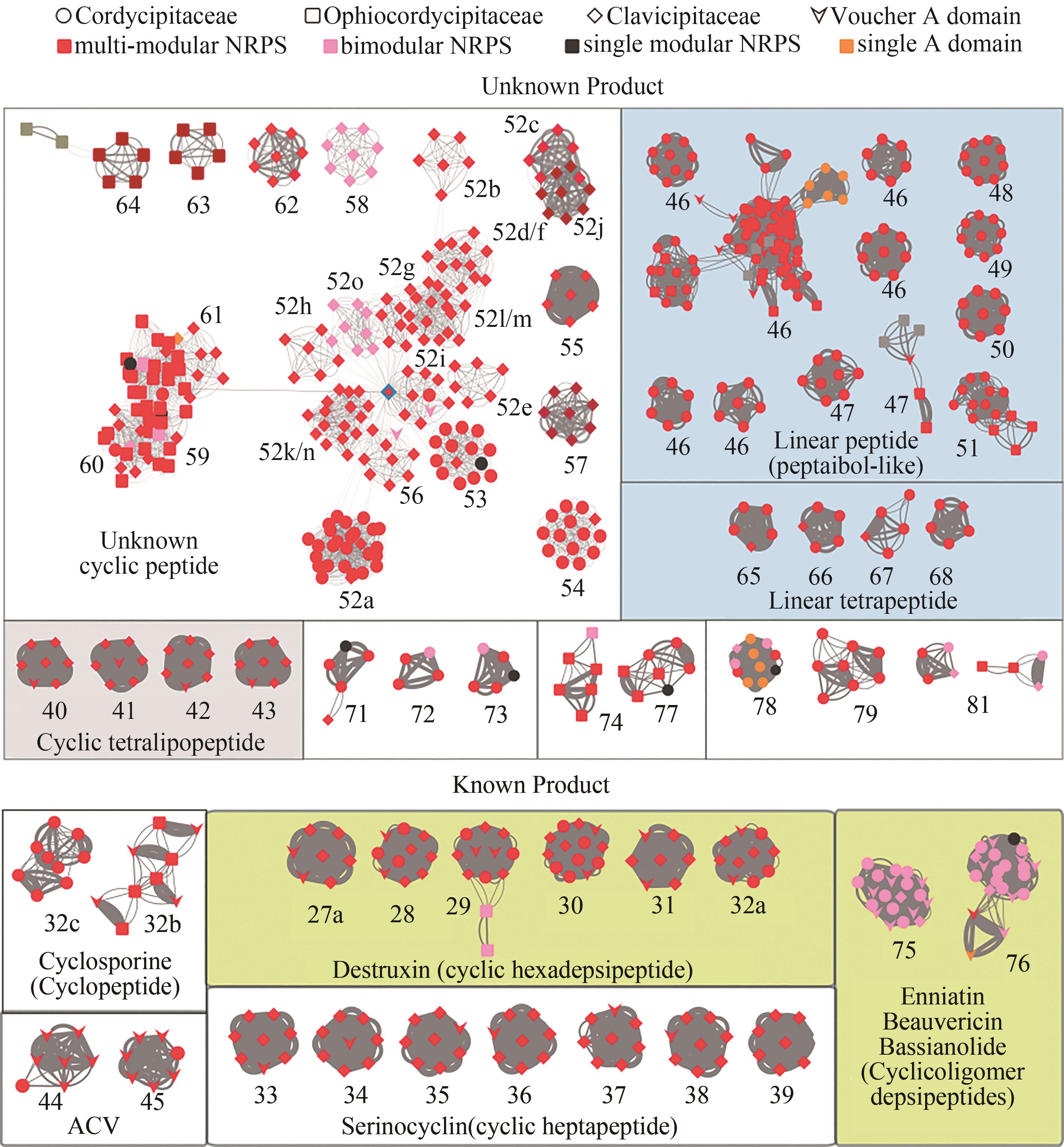
图1 肉座菌目虫生真菌多模块非核糖体多肽合成酶的相似性网络图[其中每个节点代表一个腺苷酰化结构域,连接线粗细与相似性成正比。节点颜色显示非核糖体多肽合成酶的类型,形状表示肉座菌目虫生真菌的种类(科),已知功能的结构域用箭头表示。灰色边框中显示来自同一酶的腺苷酰化结构域的分支(如DtxS1),或由密切相关的结构域分支(如52~64)形成的超级分支(详见正文)。底色显示预测的产物类型。腺苷酰化结构域的亚分支用数字字母组合表示,例如52a]
Fig. 1 Network for the subgroups of multi-modular NRPSs in Hypocrealean Entomopathogenic fungi(Nodes in the network represent A domains, and the line boldness is proportional to the identity. The nodes are colored according to the domain composition of NRPS. Referenced A domains from voucher NRPSs with known products are indicated by arrowheads. The predicted products/functions of the enzymes are listed below the clades. Boxed groups show A domains from the group of enzymes that also contain DtxS1, or superclades that are formed by closely related A domain clades such as clades #52~64 (see text for details). Sub-clades of A domains are indicated with a number-letter combination, for example 52a. NRPSs of the BGCs that contain the voucher A domains include: #27a~32a, destruxin synthetase DtxS1[9]; #32b, cyclosporine synthetase[29]; #33~39, serinocyclin synthetase[13-14]; #44~45, ACVS: N-(5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase in penicillin/cephalosporin biosynthesis; #46~51, Tex1: a peptaibol synthetase from Trichoderma virens[30]; #75~76, beauvericin and bassianolide synthetase[11-12].)
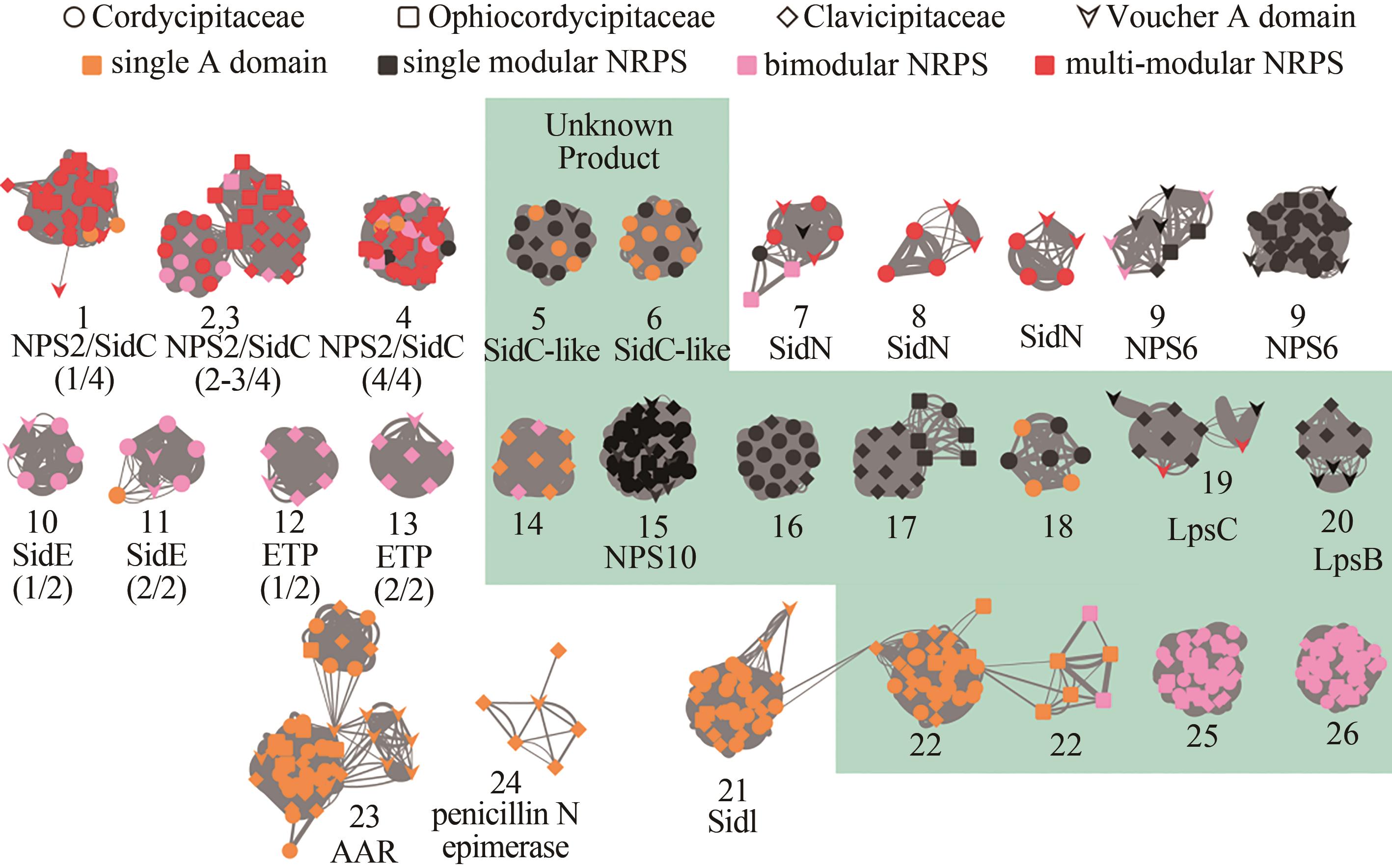
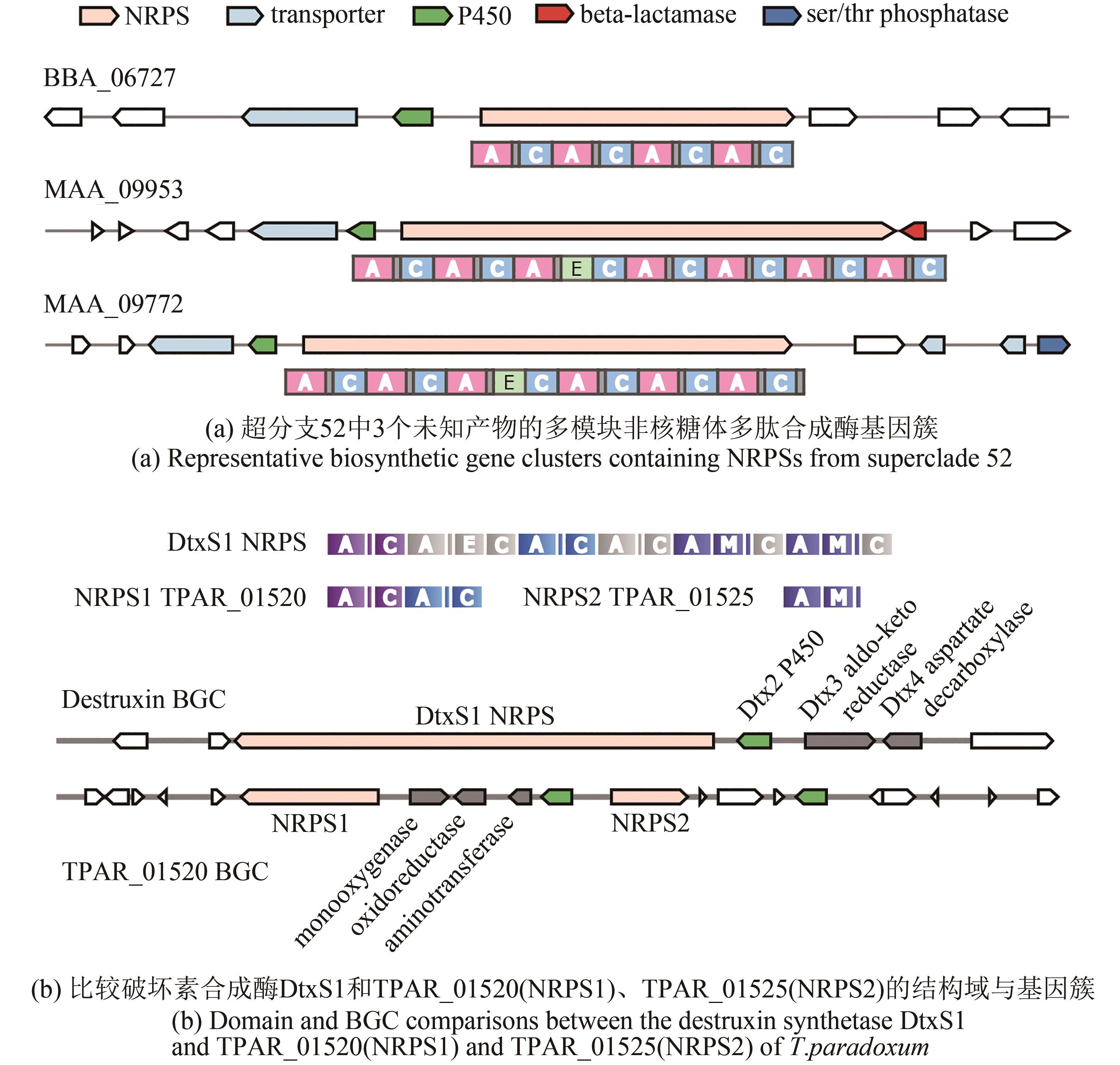
图3 肉座菌目虫生真菌单模块和双模块非核糖体多肽合成酶的相似性网络图[其中每个节点代表一个腺苷酰化结构域,连接线粗细与相似性成正比。节点颜色显示非核糖体多肽合成酶的类型,形状表示肉座菌目虫生真菌的种类(科),已知功能的结构域用箭头表示。绿色阴影标注产物未知的非核糖体多肽合成酶腺苷酰化结构域。括号中的数字表示腺苷酰化结构域在标签非核糖体多肽合成酶中的位置,例如(1/3)表示该结构域是一个具有3个模块的非核糖体多肽合成酶的第1个腺苷酰化结构域。AAR—L-氨基己二酸半醛脱氢酶[24];LpsC和LpsB—D-麦角酰肽合成酶亚基1和2,参与麦角生物碱的生物合成[32];ChNPS10—参与真菌形态发育[33-34];NPS2/SidC[35-36]和SidI[37]—胞内铁载体合成酶;SidN[38]和NPS6[39]:胞外铁载体合成酶]
Fig. 3 Overview of the A domain distance network for monomodular, bimodular or siderophore-like NRPSs in Hypocrealean entomopathogenic fungal species(Nodes in the network represent A domains, and the line boldness is proportional to the identity. Nodes are colored according to the domain composition of NRPS. Referenced A domains from voucher NRPSs with known products are indicated by arrowheads. The predicted products/functions of the enzymes are listed below the clades. NRPSs that contain the voucher A domains include: AAR, L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase[24]; LpsC and LpsB: D-lysergyl-peptide synthetase subunit 1 and 2, respectively, involved in ergot alkaloid biosynthesis[32]; ChNPS10[33-34]: an NRPS-like protein involved in morphological development; NPS2/SidC[35-36] and SidI[37]: synthetases for intracellular siderophores; SidN[38] and NPS6[39]: synthetases for extracellular siderophores. Numbers in parentheses indicate the position of the A domain in the voucher NRPS, for example (1/3) indicates the first A domain out of the three housed in the NRPS.)
| 1 | LÜ H N, LIU H W, KELLER N P, et al. Harnessing diverse transcriptional regulators for natural product discovery in fungi[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(1): 6-16. |
| 2 | WANG H, FEWER D P, HOLM L, et al. Atlas of nonribosomal peptide and polyketide biosynthetic pathways reveals common occurrence of nonmodular enzymes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(25): 9259-9264. |
| 3 | MOLNÁR I, GIBSON D M, KRASNOFF S B. Secondary metabolites from entomopathogenic Hypocrealean fungi[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2010, 27(9): 1241-1275. |
| 4 | GIBSON D M, DONZELLI B G G, KRASNOFF S B, et al. Discovering the secondary metabolite potential encoded within entomopathogenic fungi[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(10): 1287-1305. |
| 5 | ZHANG X, WEI W, TAN R X. Symbionts, a promising source of bioactive natural products[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2015, 58(7): 1097-1109. |
| 6 | BEEMELMANNS C, GUO H J, RISCHER M, et al. Natural products from microbes associated with insects[J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2016, 12: 314-327. |
| 7 | PEDRINI N. Molecular interactions between entomopathogenic fungi (Hypocreales) and their insect host: perspectives from stressful cuticle and hemolymph battlefields and the potential of dual RNA sequencing for future studies[J]. Fungal Biology, 2018, 122(6): 538-545. |
| 8 | OLATUNJI O J, TANG J, TOLA A, et al. The genus Cordyceps: an extensive review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology[J]. Fitoterapia, 2018, 129: 293-316. |
| 9 | WANG B, KANG Q J, LU Y Z, et al. Unveiling the biosynthetic puzzle of destruxins in Metarhizium species[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(4): 1287-1292. |
| 10 | DONZELLI B G G, KRASNOFF S B, YONG S M, et al. Genetic basis of destruxin production in the entomopathogen Metarhizium robertsii [J]. Current Genetics, 2012, 58(2): 105-116. |
| 11 | XU Y Q, OROZCO R, WIJERATNE E M K, et al. Biosynthesis of the cyclooligomer depsipeptide beauvericin, a virulence factor of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2008, 15(9): 898-907. |
| 12 | XU Y Q, OROZCO R, WIJERATNE E M K, et al. Biosynthesis of the cyclooligomer depsipeptide bassianolide, an insecticidal virulence factor of Beauveria bassiana [J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2009, 46(5): 353-364. |
| 13 | MOON Y S, DONZELLI B G, KRASNOFF S B, et al. Agrobacterium-mediated disruption of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene in the invertebrate pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae reveals a peptide spore factor[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(14): 4366-4380. |
| 14 | SBARAINI N, GUEDES R L M, ANDREIS F C, et al. Secondary metabolite gene clusters in the entomopathogen fungus Metarhizium anisopliae: genome identification and patterns of expression in a cuticle infection model[J]. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17(8): 399-417. |
| 15 | DE BEKKER C, OHM R A, LORETO R G, et al. Gene expression during zombie ant biting behavior reflects the complexity underlying fungal parasitic behavioral manipulation[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16: 620. |
| 16 | LIN H Z, LÜ H N, ZHOU S, et al. Deletion of a global regulator LaeB leads to the discovery of novel polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2018, 16(27): 4973-4976. |
| 17 | RUTLEDGE P J, CHALLIS G L. Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2015, 13(8): 509-523. |
| 18 | COPP J N, ANDERSON D W, AKIVA E, et al. Exploring the sequence, function, and evolutionary space of protein superfamilies using sequence similarity networks and phylogenetic reconstructions[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2019, 620: 315-347. |
| 19 | COPP J N, AKIVA E, BABBITT P C, et al. Revealing unexplored sequence-function space using sequence similarity networks[J]. Biochemistry, 2018, 57(31): 4651-4662. |
| 20 | AKIVA E, BROWN S, ALMONACID D E, et al. The structure-function linkage database[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42: D521-D530. |
| 21 | NIELSEN J C, GRIJSEELS S, PRIGENT S, et al. Global analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters reveals vast potential of secondary metabolite production in Penicillium species[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2: 17044. |
| 22 | ZIEMERT N, LECHNER A, WIETZ M, et al. Diversity and evolution of secondary metabolism in the marine actinomycete genus Salinispora [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(12): E1130-E1139. |
| 23 | GALLO A, FERRARA M, PERRONE G. Phylogenetic study of polyketide synthases and nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the biosynthesis of mycotoxins[J]. Toxins, 2013, 5(4): 717-742. |
| 24 | BUSHLEY K E, TURGEON B G. Phylogenomics reveals subfamilies of fungal nonribosomal peptide synthetases and their evolutionary relationships[J]. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 2010, 10: 26. |
| 25 | KROKEN S, GLASS N L, TAYLOR J W, et al. Phylogenomic analysis of type I polyketide synthase genes in pathogenic and saprobic ascomycetes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(26): 15670-15675. |
| 26 | RAUSCH C, HOOF I, WEBER T, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of condensation domains in NRPS sheds light on their functional evolution[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2007, 7: 78. |
| 27 | LIU H, XIE L N, WANG J, et al. The stress-responsive and host-oriented role of nonribosomal peptide synthetases in an entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 27(3): 439-449. |
| 28 | AGRAWAL Y, NARWANI T, SUBRAMANIAN S. Genome sequence and comparative analysis of clavicipitaceous insect-pathogenic fungus Aschersonia badia with Metarhizium spp[J]. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17: 367. |
| 29 | YANG X Q, FENG P, YIN Y, et al. Cyclosporine biosynthesis in Tolypocladium inflatum benefits fungal adaptation to the environment[J]. MBio, 2018, 9 (5): e01211-18. |
| 30 | WIEST A, GRZEGORSKI D, XU B W, et al. Identification of peptaibols from Trichoderma virens and cloning of a peptaibol synthetase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277 (23): 20862-20868. |
| 31 | XU Y Q, ZHAN J X, WIJERATNE E M K, et al. Cytotoxic and antihaptotactic beauvericin analogues from precursor-directed biosynthesis with the insect pathogen Beauveria bassiana ATCC 7159[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2007, 70(9): 1467-1471. |
| 32 | FLEETWOOD D J, SCOTT B, LANE G A, et al. A complex ergovaline gene cluster in epichloe endophytes of grasses[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(8): 2571-2579. |
| 33 | TURGEON B G, OIDE S, BUSHLEY K. Creating and screening Cochliobolus heterostrophus non-ribosomal peptide synthetase mutants[J]. Mycological Research, 2008, 112(2): 200-206. |
| 34 | OHM R A, FEAU N, HENRISSAT B, et al. Diverse lifestyles and strategies of plant pathogenesis encoded in the genomes of eighteen dothideomycetes fungi[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2012, 8(12): e1003037. |
| 35 | GREENSHIELDS D L, LIU G S, FENG J, et al. The siderophore biosynthetic gene SID1, but not the ferroxidase gene FET3, is required for full Fusarium graminearum virulence[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2007, 8(4): 411-421. |
| 36 | WALLNER A, BLATZER M, SCHRETTL M, et al. Ferricrocin, a siderophore involved in intra- and transcellular iron distribution in Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75 (12): 4194-4196. |
| 37 | YASMIN S, ALCAZAR-FUOLI L, GRÜNDLINGER M, et al. Mevalonate governs interdependency of ergosterol and siderophore biosyntheses in the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(8): E497-E504. |
| 38 | JOHNSON L J, KOULMAN A, CHRISTENSEN M, et al. An extracellular siderophore is required to maintain the mutualistic interaction of Epichloë festucae with Lolium perenne [J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2013, 9(5): e1003332. |
| 39 | OIDE S, MOEDER W, KRASNOFF S, et al. NPS6, encoding a nonribosomal peptide synthetase involved in siderophore-mediated iron metabolism, is a conserved virulence determinant of plant pathogenic ascomycetes[J]. The Plant Cell, 2006, 18(10): 2836-2853. |
| 40 | BUSHLEY K E, RAJA R, JAISWAL P, et al. The genome of Tolypocladium inflatum: Evolution, organization, and expression of the cyclosporin biosynthetic gene cluster[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2013, 9 (6): e1003496. |
| 41 | DOPSTADT J, NEUBAUER L, TUDZYNSKI P, et al. The epipolythiodiketopiperazine gene cluster in claviceps purpurea: Dysfunctional cytochrome P450 enzyme prevents formation of the previously unknown clapurines[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(7): e0158945. |
| 42 | STEINCHEN W, LACKNER G, YASMIN S, et al. Bimodular peptide synthetase SidE produces fumarylalanine in the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(21): 6670-6676. |
| 43 | DONZELLI B G G, KRASNOFF S B, Molecular genetics of secondary chemistry in Metarhizium fungi[M]LOVETTB//, LEGERR JST.Genetics and molecular biology of entomopathogenic fungi[M]// Advances in Genetics, 2016, 94: 365-436. |
| [1] | 赖奇龙, 姚帅, 查毓国, 白虹, 宁康. 微生物组生物合成基因簇发掘方法及应用前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 611-627. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||