合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (1): 209-223.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-101
细胞培养肉商业化的法律规范与监管:外国经验及对我国启示
李玉娟1,2, 傅雄飞2, 杜立1
- 1.澳门大学法学院,澳门 999078
2.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,中国科学院定量工程生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2021-11-02修回日期:2022-01-14出版日期:2022-02-28发布日期:2022-03-14 -
通讯作者:杜立 -
作者简介:李玉娟 (1989—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为生物科技法与医疗法、国际法。E-mail:yc17213@um.edu.mo杜立 (1982—),男,博士生导师,助理教授。研究方向为生物科技法律与政策、国际法、卫生法。E-mail:stephendu@um.edu.mo -
基金资助:深圳合成生物学创新研究院创新项目(CP-030-2021)
Regulating the commercialization of cell-cultured meat: practices in selected jurisdictions and their implications for China
LI Yujuan1,2, FU Xiongfei2, DU Li1
- 1.Faculty of Law,University of Macau,Macau SAR 999078,China
2.CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2021-11-02Revised:2022-01-14Online:2022-02-28Published:2022-03-14 -
Contact:DU Li
摘要:
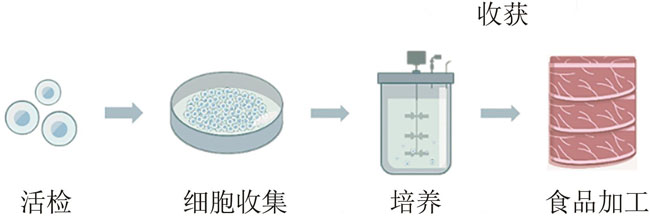
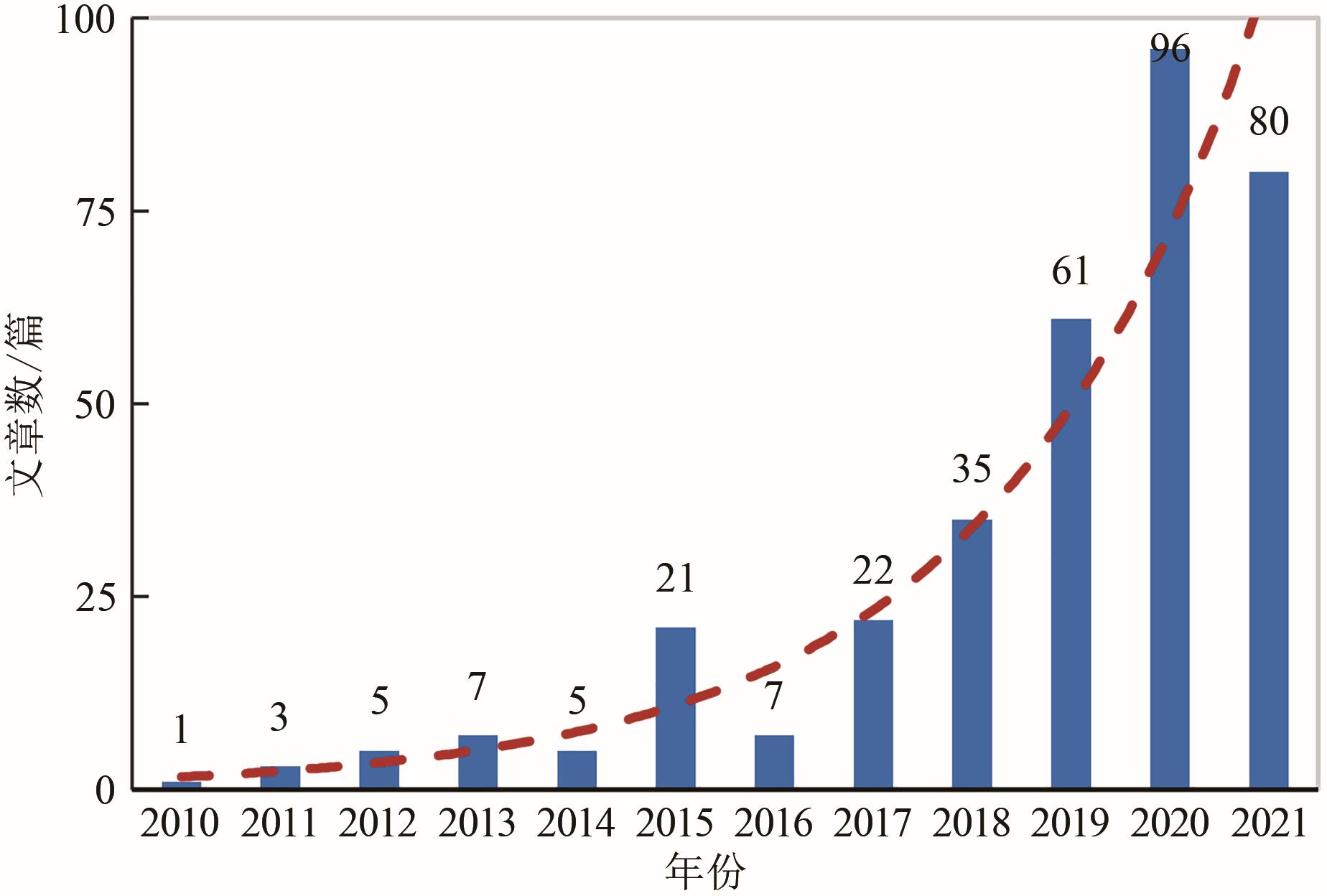
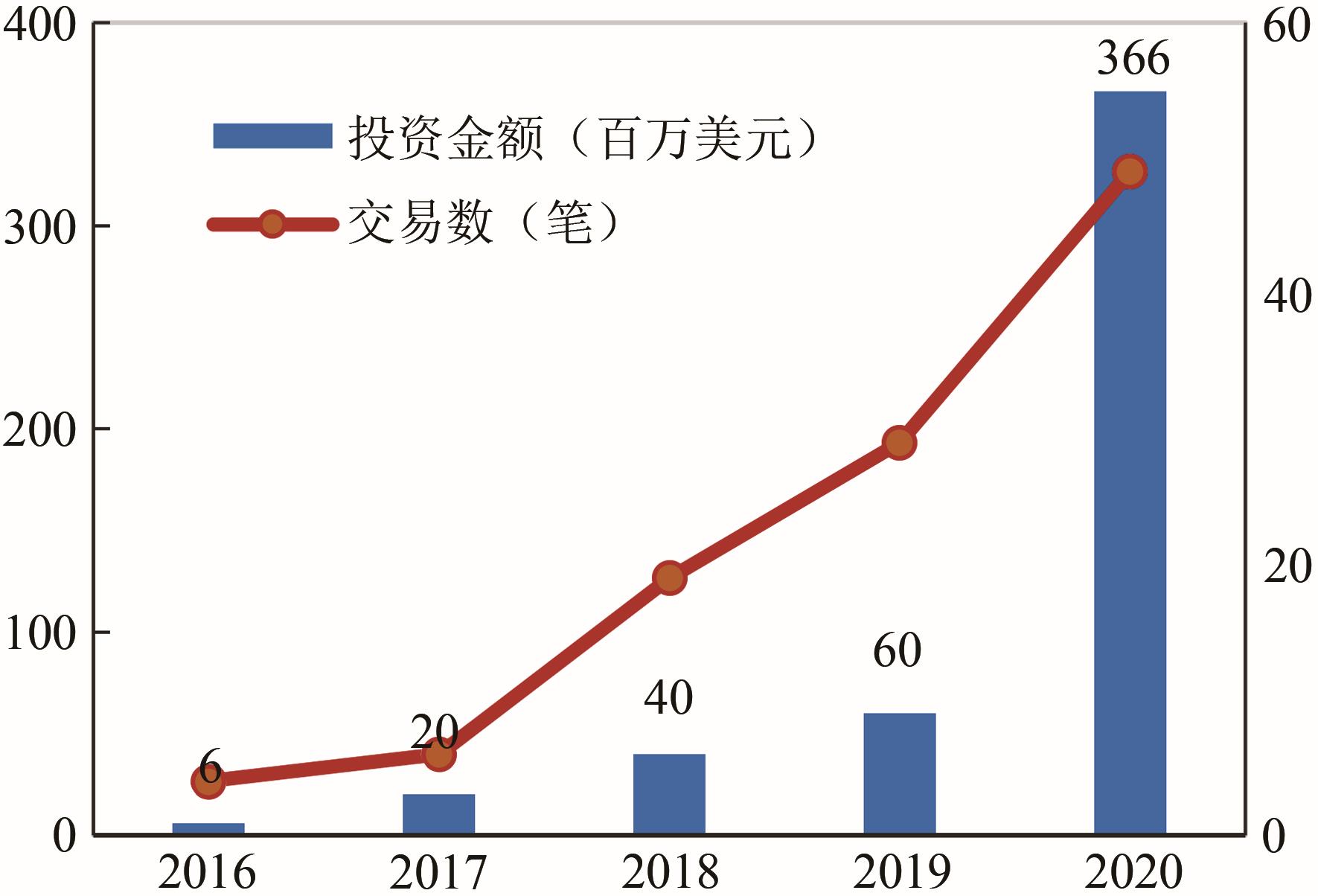
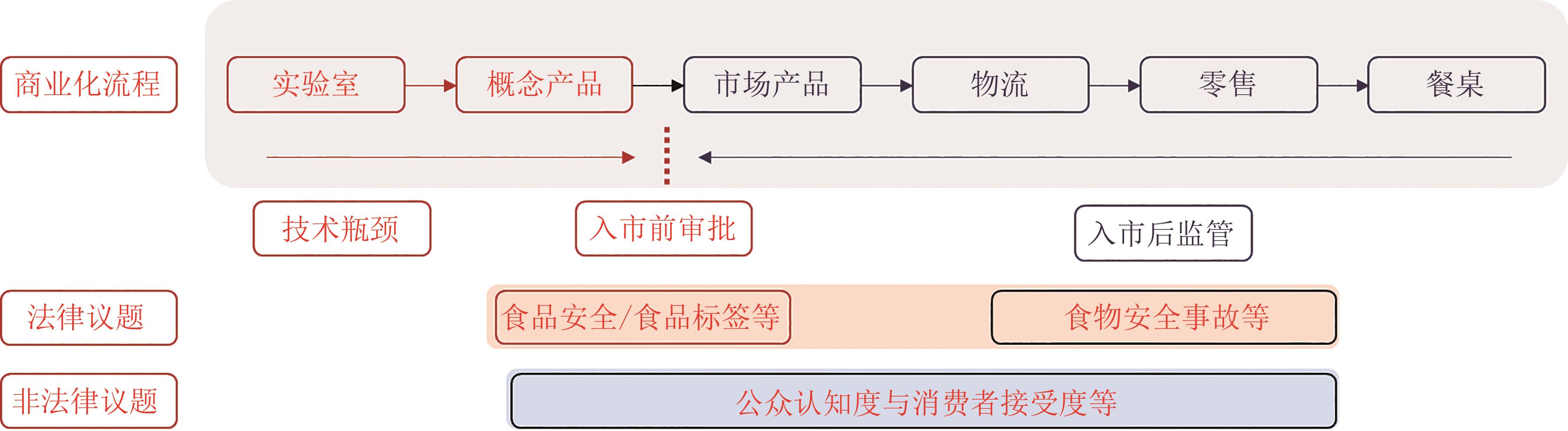
细胞培养肉有望改进当前肉类生产体系,缓解未来粮食资源短缺、公共卫生及动物福利等问题。无论是在研究领域还是在产业市场,细胞培养肉已成为当前热点。欧美国家纷纷启动相关战略部署,大力推动细胞培养肉的发展。然而,细胞培养肉的研发与商业化过程对现行相关法律规范与监管制度带来挑战。欧盟、美国及新加坡等国家及地区积极探寻细胞培养肉在法律规范与监管制度方面的完善与更新。2020年,新加坡更是率先批准细胞培养肉产品入市并发布具体监管措施。我国细胞培养肉在生产技术研发方面已不断取得突破,但在法律规范与监管制度方面的研究探讨相对不足。在此背景下,本文结合细胞培养肉的研究进展与发展现状,重点考察欧美及新加坡细胞培养肉商业化相关法律规范,识别法律法规挑战,并为我国细胞培养肉的研发与商业化法律规范、监管制度建设提供建议。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李玉娟, 傅雄飞, 杜立. 细胞培养肉商业化的法律规范与监管:外国经验及对我国启示[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 209-223.
LI Yujuan, FU Xiongfei, DU Li. Regulating the commercialization of cell-cultured meat: practices in selected jurisdictions and their implications for China[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(1): 209-223.
| 评估内容 | 备注说明 |
|---|---|
| 关于整个制造过程的描述 | 所需信息可能会随着细胞培养肉的生产技术发展而变化 |
| 培养肉制品的特征 | |
| 所使用的细胞系和培养基的相关信息 | |
| 关于支架材料的信息(如有使用) | |
| 关于在制造过程中如何保存细胞培养物的纯度和遗传稳定性的信息 | |
| 安全评估,涵盖培养肉类生产过程中可能产生的危害 | |
| 支撑安全性的其他评估,如消化率测定、过敏原分析、基因测序等 |
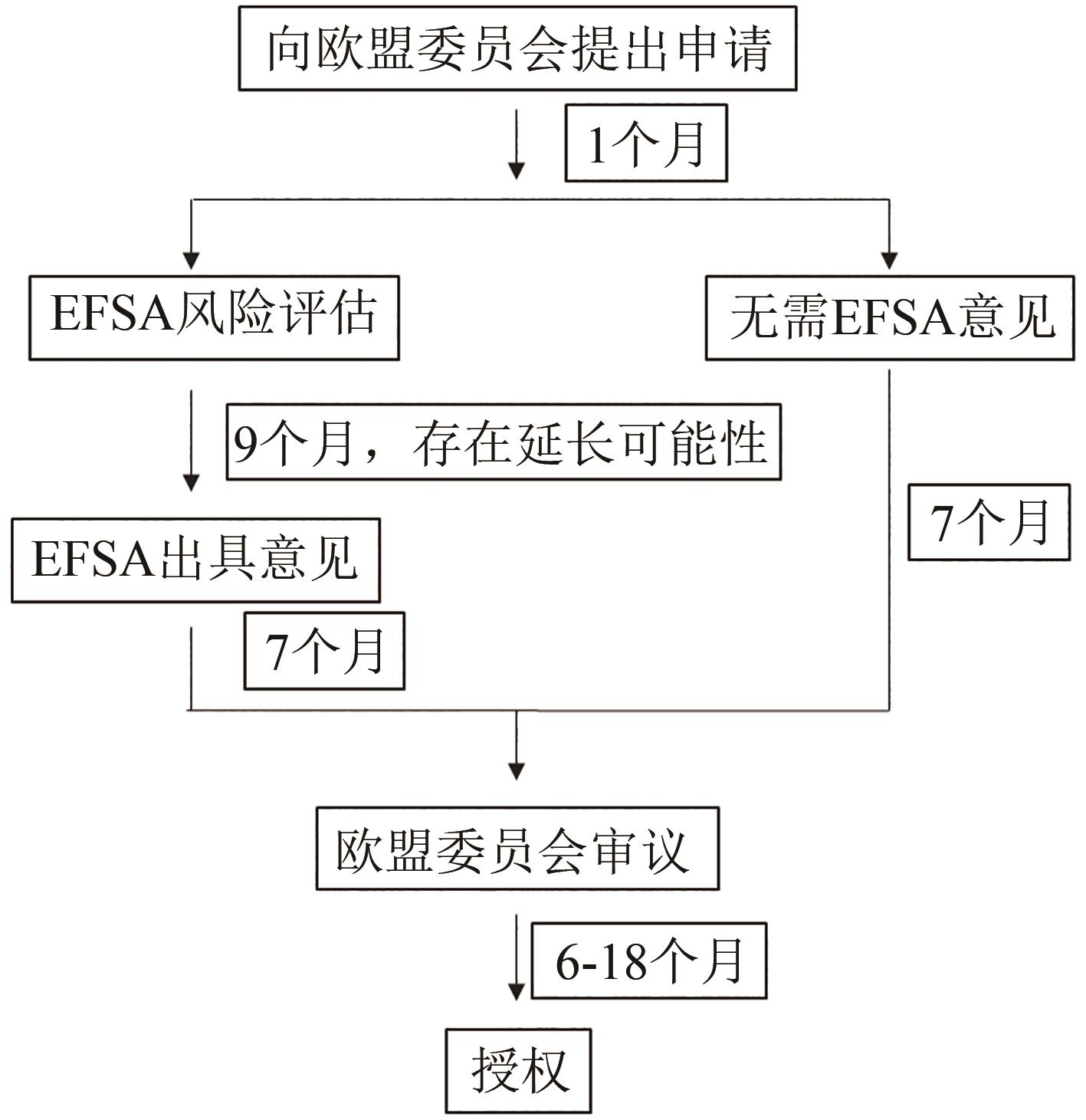
表1 新加坡新型食品安全评估要求[47]
Tab. 1 Requirements for Safety Assessment of Novel Foods in Singapore[47]
| 评估内容 | 备注说明 |
|---|---|
| 关于整个制造过程的描述 | 所需信息可能会随着细胞培养肉的生产技术发展而变化 |
| 培养肉制品的特征 | |
| 所使用的细胞系和培养基的相关信息 | |
| 关于支架材料的信息(如有使用) | |
| 关于在制造过程中如何保存细胞培养物的纯度和遗传稳定性的信息 | |
| 安全评估,涵盖培养肉类生产过程中可能产生的危害 | |
| 支撑安全性的其他评估,如消化率测定、过敏原分析、基因测序等 |
| 机构 | 肉 | 肉制品 |
|---|---|---|
| 欧盟[ | 动物的任何可食用部分,包括家养和野味动物的血液 | 加工肉类或进一步加工而产生的加工产品。此类加工产品不再具有鲜肉的特性 |
| 美国[ | 牛、绵羊、猪或山羊肌肉的任何一部分 | 能够用作人类食品的产品,其全部或部分由肉类任何部分制成……牛、绵羊、猪或山羊的尸体的任何一部分 |
| 新加坡[ | 供人食用的屠宰家禽、牛、羊、羊、猪、野味或其他动物的任何部分 | 供人食用的以下任何产品:胴体的内脏或其他部分;加工或保存肉类而制成的任何产品;任何含有肉类的产品 |
| 中国[ | 活畜(猪、牛、羊、兔等)、禽(鸡、鸭、鹅等)宰杀、加工后的肉 | 以畜禽肉及其他食用副产品为主要原料,添加或者不添加辅料,经过腌、卤、酱、蒸、煮、熏、烤、烘焙、干燥、油炸、成型、发酵、调制等有关生产工艺加工而成的生或者熟的肉类制品 |
表2 肉与肉制品的定义[49]
Tab. 2 Definitions of meat and meat products
| 机构 | 肉 | 肉制品 |
|---|---|---|
| 欧盟[ | 动物的任何可食用部分,包括家养和野味动物的血液 | 加工肉类或进一步加工而产生的加工产品。此类加工产品不再具有鲜肉的特性 |
| 美国[ | 牛、绵羊、猪或山羊肌肉的任何一部分 | 能够用作人类食品的产品,其全部或部分由肉类任何部分制成……牛、绵羊、猪或山羊的尸体的任何一部分 |
| 新加坡[ | 供人食用的屠宰家禽、牛、羊、羊、猪、野味或其他动物的任何部分 | 供人食用的以下任何产品:胴体的内脏或其他部分;加工或保存肉类而制成的任何产品;任何含有肉类的产品 |
| 中国[ | 活畜(猪、牛、羊、兔等)、禽(鸡、鸭、鹅等)宰杀、加工后的肉 | 以畜禽肉及其他食用副产品为主要原料,添加或者不添加辅料,经过腌、卤、酱、蒸、煮、熏、烤、烘焙、干燥、油炸、成型、发酵、调制等有关生产工艺加工而成的生或者熟的肉类制品 |
| 1 | HALABOWSKI D, RZYMSKI P. Taking a lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic: Preventing the future outbreaks of viral zoonoses through a multi-faceted approach[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 757: 143723. |
| 2 | BHAT Z F, MORTON J D, MASON S L, et al. Technological, regulatory, and ethical aspects of in vitro meat: a future slaughter-free harvest[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2019, 18(4): 1192-1208. |
| 3 | 中华人民共和国国务院. 国务院关于印发2030年前碳达峰行动方案的通知,国发〔2021〕23号[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 4 | Parliament European.What is carbon neutrality and how can it be achieved by 2050?[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 5 | Nations United. The sustainable development goals[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 6 | POST M J, LEVENBERG S, KAPLAN D L, et al. Scientific, sustainability and regulatory challenges of cultured meat[J]. Nature Food, 2020, 1(7): 403-415. |
| 7 | STEPHENS N, DI SILVIO L, DUNSFORD I, et al. Bringing cultured meat to market: Technical, socio-political, and regulatory challenges in cellular agriculture[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2018, 78: 155-166. |
| 8 | ZHANG G Q, ZHAO X R, LI X L, et al. Challenges and possibilities for bio-manufacturing cultured meat[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2020, 97: 443-450. |
| 9 | 周光宏, 丁世杰, 徐幸莲. 培养肉的研究进展与挑战[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(5): 1-11. |
| ZHOU G H, DING S J, XU X L. Progress and challenges in cultured meat[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(5): 1-11. | |
| 10 | Government Accountability Office. USA. Food safety: FDA and USDA could strengthen existing efforts to prepare for oversight of cell-cultured meat[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 11 | Food and Drug Administration, USA. Impossible Foods, Inc.; Filing of Color Additive Petition. [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 12 | STOUT A J, MIRLIANI A B, SOULE-ALBRIDGE E L, et al. Engineering carotenoid production in mammalian cells for nutritionally enhanced cell-cultured foods[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 62: 126-137. |
| 13 | HALDANE J B S. Possible worlds, and other essays[J]. Nature, 1928, 121(3055): 785-786. |
| 14 | CHURCHILL W. Fifty years hence[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 15 | BENJAMINSON M A, GILCHRIEST J A, LORENZ M. In vitro edible muscle protein production system (MPPS): Stage 1, fish[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2002, 51(12): 879-889. |
| 16 | STEPHENS N, SEXTON A E, DRIESSEN C. Making sense of making meat: key moments in the first 20 years of tissue engineering muscle to make food[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2019, 3: 45. |
| 17 | NISSIN Group. [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 18 | 周子未来食品科技有限公司[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| Joes Future Food Ltd[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . | |
| 19 | KANG D H, LOUIS F, LIU H, et al. Engineered whole cut meat-like tissue by the assembly of cell fibers using tendon-gel integrated bioprinting[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5059. |
| 20 | 李东巧, 谢华玲, 杨艳萍, 等. 人造肉领域国际创新发展态势分析[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2021, 43(1): 43-53. |
| LI D Q, XIE H L, YANG Y P, et al. Analysis of the development trend of international innovation in artificial meat[J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 2021, 43(1): 43-53. | |
| 21 | BYRNE B, MURRAY S, IGNASZEWSKI E. 2020 State of the industry report cultivated meat[R]. Good Food Institute, 2020: 1-54. |
| 22 | CHOUDHURY D, TSENG T W, SWARTZ E. The business of cultured meat[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(6): 573-577. |
| 23 | KUMAR P, SHARMA N, SHARMA S, et al. In-vitro meat: a promising solution for sustainability of meat sector[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 2021, 63(4): 693-724. |
| 24 | Prnewswire. Future meat technologies launches world's first industrial cultured meat production facility[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 25 | Aster Esco. Esco aster receives food processing license to manufacture cell-based cultivated meat from Singapore authorities[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 26 | Nestlé explores emerging technologies for cultured meat[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 27 | Fisher Thermo. Cell culture, tissue culture & transfection solutions.[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 28 | 启信宝.南京周子未来食品科技有限公司融资信息[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 29 | 肖鹏. 欧美转基因食品标识制度的趋同化及我国的应对——兼评美国S.764法[J]. 法学杂志, 2018, 39(10): 134-140. |
| XIAO P. Convergent trend of genetically modified food labeling systems in European Union and the United States and the countermeasures of China[J]. Law Science Magazine, 2018, 39(10): 134-140. | |
| 30 | European Parliament. Regulation (EC) No. 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council laying down the general principles and requirements of food law, establishing the European Food Safety Authority and laying down procedures in matters of food safety[Z]. EU: European Parliament, 2002. |
| 31 | European Parliament. Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council on novel foods[Z]. EU: European Parliament, 2018. |
| 32 | European Food Safety Authority. Guidance on the preparation and submission of an application for authorisation of a novel food in the context of Regulation (EU) 2015/2283(Revision 1). [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 33 | STANTON M M, TZATZALOS E, DONNE M, et al. Prospects for the use of induced pluripotent stem cells in animal conservation and environmental protection[J]. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 2019, 8(1): 7-13. |
| 34 | European Court of Justice. Case C-528/16, Confédération Paysanne and others v. Premier Ministre and Ministre de l'Agriculture, de l'Agroalimentaire et de la Forêt, ECLI:EU:C: 2018:583[Z]. EU: European Court of Justice, 2018. |
| 35 | Commission European. Study on the status of new genomic techniques under Union law and in light of the Court of Justice ruling in Case C- 528/16. [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 36 | MOHORČICH J, REESE J. Cell-cultured meat: Lessons from GMO adoption and resistance[J]. Appetite, 2019, 143: 104408. |
| 37 | European Parliament. Regulation (EU) No. 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the provision of food information to consumers[Z]. EU: European Parliament, 2011. |
| 38 | Food and Drug Administration, USA. What does FDA regulate?[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 39 | USDA and FDA Announce a Formal Agreement to Regulate Cell-Cultured Food Products from Cell Lines of Livestock and Poultry. [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 40 | Senate, USA. S.1056 Cell-Cultured Meat and Poultry Regulation Act of 2019[Z]. USA: Senate, 2019. |
| 41 | Missouri Revised Statutes, USA. Section 265.494-Prohibited practices, required disclosures[Z]. USA: Missouri, 2021. |
| 42 | South Dakota Codified Laws, USA. Section 39-4-26 Misbranding as meat food product, meat by-product, or poultry[Z]. USA: South Dakota, 2019. |
| 43 | New Mexico Statutes 1978, USA. Section 25-2-11-When food deemed misbranded[Z]. USA: New Mexico Statutes, 2021. |
| 44 | Meat Institute and AMPS Innovation Send Joint Letter to USDA on Mandatory Labeling for Cell-Based/Cultured Meat & Poultry Products. [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 45 | United States Department of Agriculture, USA. Labeling of meat or poultry products comprised of or containing cultured animal cells. a proposed rule by the food safety and inspection service on 2021-03-09[Z]. USA: United States Department of Agriculture, 2021. |
| 46 | Singapore Food Agency. Risk at a glance safety of alternative protein[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 47 | Singapore Food Agency. Requirements for the Safety Assessment of Novel Foods. Version dated 23 November 2020[Z]. Singapore: Singapore Food Agency, 2020. |
| 48 | KREIS K, ZOBRIST S, PARKER M E, et al. PATH. Cultured proteins: an analysis of the policy and regulatory environment in selected geographies[R]. Seattle: Path, International Food Policy Research Institute, 2019: 5-6. |
| 49 | ONG S, CHOUDHURY D, NAING M W. Cell-based meat: current ambiguities with nomenclature[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2020, 102: 223-231. |
| 50 | United States Congress. The Federal Meat Inspection Act, as amended[Z]. USA: United States Congress, 2018. |
| 51 | Singapore Statutes. Sale of Food Act (Chapter 283)[Z]. Singapore: Singapore Statutes, 2021. |
| 52 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准肉和肉制品经营卫生规范: [S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. |
| National Health Commission of People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration of People's Republic of China. Food safety national standard of meat and meat products business hygiene code: [S].Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016. | |
| 53 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准鲜(冻)畜、禽产品: [S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. |
| National Health Commission of People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration of People's Republic of China. Food safety national standard of fresh (frozen) livestock and poultry products: [S].Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016. | |
| 54 | The constitution of the United States: a transcription. [EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 55 | BRYANT C J, ANDERSON J E, ASHER K E, et al. Strategies for overcoming aversion to unnaturalness: the case of clean meat[J]. Meat Science, 2019, 154: 37-45. |
| 56 | BRYANT C, BARNETT J. Consumer acceptance of cultured meat: a systematic review[J]. Meat Science, 2018, 143: 8-17. |
| 57 | SZEJDA K, BRYANT C J, URBANOVICH T. US and UK consumer adoption of cultivated meat: a segmentation study[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(5): 1050. |
| 58 | ZHANG M, LI L, BAI J F. Consumer acceptance of cultured meat in urban areas of three cities in China[J]. Food Control, 2020, 118: 107390. |
| 59 | BRYANT C, SZEJDA K, PAREKH N, et al. A survey of consumer perceptions of plant-based and clean meat in the USA, India, and China[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2019, 3: 11. |
| 60 | ANDERSON J, BRYANT C. Messages to overcome naturalness concerns in clean meat acceptance: primary findings[R]. Olympia, WA, USA: Faunalytics, 2018. https://faunalytics.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Clean-Meat-Acceptance-Primary-Findings.pdf. |
| 61 | 张忠民. 论转基因食品标识制度的法理基础及其完善[J]. 政治与法律, 2016(5): 118-131. |
| ZHANG Z M. Discussion on the legal basis and perfection of GMO labeling system[J]. Policital Science and Law, 2016(5): 118-131. | |
| 62 | DU L. GMO labelling and the consumer's right to know: a comparative review of the legal bases for the consumer's right to genetically modified food labelling[J]. McGill Journal of Law and Health. 2015, 8(01):1-42. |
| 63 | KETELINGS L, KREMERS S, DE BOER A. The barriers and drivers of a safe market introduction of cultured meat: a qualitative study[J]. Food Control, 2021, 130: 108299. |
| 64 | 杜立, 王萌. 合成生物学技术制造食品的商业化法律规范[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 593-608. |
| DU L, WANG M. The legal issues about commercialization of food products employing synthetic biology strategies[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 593-608. | |
| 65 | GUAN X, LEI Q Z, YAN Q Y, et al. Trends and ideas in technology, regulation and public acceptance of cultured meat[J]. Future Foods, 2021, 3: 100032. |
| 66 | 汪超, 刘元法, 周景文. 细胞培养肉的生物伦理学思考[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(2): 378-383. |
| WANG C, LIU Y F, ZHOU J W. Bioethical considerations of cell-cultured meat[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(2): 378-383. | |
| 67 | CHRIKI S, HOCQUETTE J F. The myth of cultured meat: a review[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2020, 7: 7. |
| 68 | 刘芳, 王盼娣, 熊小娟, 等. 人造肉技术发展现状、安全性评价和监管以及消费者接受度[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2021, 27(9):47-52. |
| LIU F, WANG P D, XIONG X J, et al. Development status of artificial meat technology, safety evaluation and supervision and consumer acceptance[J]. Food and Nutrition in China., 2021, 27(9): 47-52. | |
| 69 | HOCQUETTE J F. Is in vitro meat the solution for the future?[J]. Meat Science, 2016, 120: 167-176. |
| 70 | 王守伟, 孙宝国, 李石磊, 等. 生物培育肉发展现状及战略思考[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(15): 1-9. |
| WANG S W, SUN B G, LI S L, et al. Development status and strategic thinking of cultivated meat[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(15): 1-9. | |
| 71 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会.新食品原料安全性审查管理办法(2017年修正)[Z]. 中国: 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 2017. |
| 72 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会.食品添加剂新品种管理办法(2017年修正)[Z]. 中国: 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 2017. |
| 73 | 中华人民共和国农业农村部.农业转基因生物(植物、动物、动物用微生物)安全评价指南[Z]. 中国: 中华人民共和国农业农村部, 2017. |
| 74 | 中华人民共和国农业农村部.农业转基因生物加工审批办法(2019修正)[Z]. 中国: 中华人民共和国农业农村部, 2019. |
| 75 | 中华人民共和国国务院.农业转基因生物安全管理条例(2017修订)[Z]. 中国: 中华人民共和国国务院, 2017. |
| 76 | 中华人民共和国农业农村部.农业转基因生物标识管理办法(2017修订)[Z]. 中国: 中华人民共和国农业农村部, 2017. |
| 77 | 中华人民共和国农业农村部.关于《农业农村部关于修改〈农业转基因生物安全评价管理办法〉的决定(征求意见稿)》公开征求意见的通知[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 78 | 国家卫生健康委员会职能配置、内设机构和人员编制规定[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 79 | 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局食品审评中心[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 80 | 中华人民共和国农业农村部.职能配置[EB/OL]. [2021-11-11]. . |
| 81 | 李德茂, 曾艳, 周桔, 等. 生物制造食品原料市场准入政策比较及对我国的建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(8): 1041-1052. |
| LI D M, ZENG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Regulation and guidance for marketing of food ingredients from biomanufacturing and policy suggestions for China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(8): 1041-1052. | |
| 82 | 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局.行业标准管理办法[Z]. 中国:中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局, 1990. |
| 83 | 中国食品科学技术分会. 植物基肉制品团体标准: T/CI [S].中国: 中国食品科学技术分会, 2020. |
| Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology. Plant-based meat products group standard: T/CI [S]. China: Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020. |
| [1] | 张璨, 施李杨, 戴建武. 细胞培养肉用生物材料的设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 676-689. |
| [2] | 杜立, 王萌. 合成生物学技术制造食品的商业化法律规范[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 593-608. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||