合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (4): 813-830.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-064
肝器官芯片在生物医学研究中的应用进展
陈汐玥1,2, 王亚清3,4, 包芳3,4, 秦建华1
- 1.中国科学院大连化学物理研究所,辽宁 大连 116023
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3.中国科学技术大学,安徽 合肥 230026
4.中国科学技术大学苏州高等研究院,江苏 苏州 215123
-
收稿日期:2024-08-16修回日期:2024-08-30出版日期:2024-08-31发布日期:2024-09-19 -
通讯作者:秦建华 -
作者简介:陈汐玥 ,博士研究生。研究方向为肝器官芯片、类器官及其生物医学应用研究。E-mail:xiyue@dicp.ac.cn秦建华 ,中国科学院大连化学物理研究所首席研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为器官芯片、干细胞与类器官工程、疾病建模与创新药物评估。E-mail:jhqin@dicp.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32171406);国家重点研发计划(2022YFA1104700)
Advances in the application of liver on a chip in biomedical research
CHEN Xiyue1,2, WANG Yaqing3,4, BAO Fang3,4, QIN Jianhua1
- 1.Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Dalian 116023,Liaoning,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
3.University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,Anhui,China
4.Suzhou Institute for Advanced Research,University of Science and Technology of China,Suzhou 215123,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2024-08-16Revised:2024-08-30Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-19 -
Contact:QIN Jianhua
摘要:
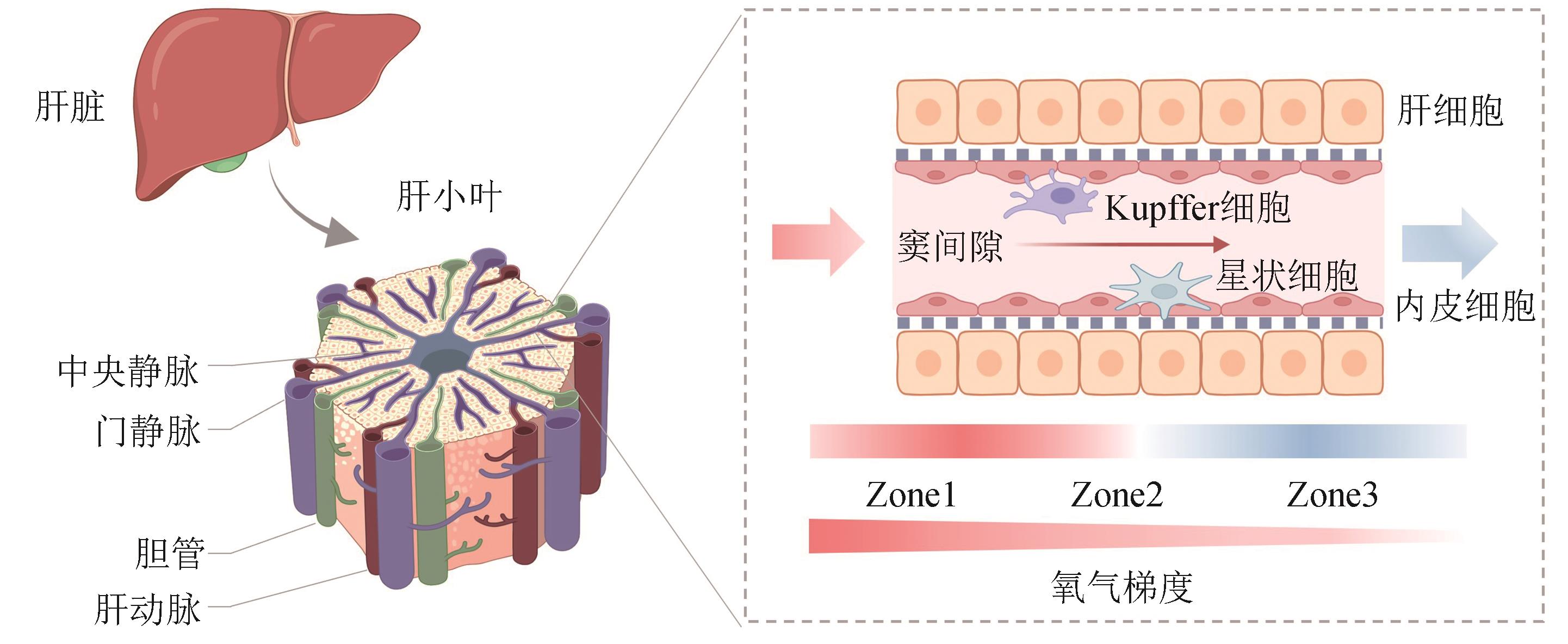
肝脏具有复杂结构和多种功能,包括血糖调控、蛋白合成、解毒和药物代谢等,在维持人体正常生理活动中起着重要作用。传统的二维细胞培养和动物模型已被广泛用于肝脏生理或疾病研究,但它们在反映人体组织真实微环境和对药物反应等方面仍存在一定局限。因此,建立高仿真度肝脏体外模型对于肝病研究、药效与毒性评价至关重要。本文概述了传统肝脏体外模型在实现近生理复杂微环境模拟、肝组织特异性功能准确复现等方面的局限性,总结了以器官芯片为代表的新型肝脏体外模型的设计策略、技术特点及其在生物医学领域的研究进展。文中重点介绍了肝器官芯片仿生构筑和实现肝组织微环境模拟的关键要素,包括多细胞组分、肝窦/肝小叶结构、生化因子梯度和流体因素等,并对未来结合其他先进手段(如类器官、生物材料和基因编辑等)等,建立高度生理相关性的肝器官芯片和微生理系统的发展前景予以展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈汐玥, 王亚清, 包芳, 秦建华. 肝器官芯片在生物医学研究中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 813-830.
CHEN Xiyue, WANG Yaqing, BAO Fang, QIN Jianhua. Advances in the application of liver on a chip in biomedical research[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 813-830.
| 39 | SGODDA M, DAI Z, ZWEIGERDT R, et al. A scalable approach for the generation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatic organoids with sensitive hepatotoxicity features[J]. Stem Cells and Development, 2017, 26(20): 1490-1504. |
| 40 | HUCH M, GEHART H, VAN BOXTEL R, et al. Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(1-2): 299-312. |
| 41 | SUDO R, MITAKA T, IKEDA M, et al. Reconstruction of 3D stacked-up structures by rat small hepatocytes on microporous membranes[J]. FASEB Journal, 2005, 19(12): 1695-1697. |
| 42 | SCOTT M J, LIU S B, SU G L, et al. Hepatocytes enhance effects of lipopolysaccharide on liver nonparenchymal cells through close cell interactions[J]. Shock, 2005, 23(5): 453-458. |
| 43 | OSTROVIDOV S, JIANG J L, SAKAI Y, et al. Membrane-based PDMS microbioreactor for perfused 3D primary rat hepatocyte cultures[J]. Biomedical Microdevices, 2004, 6(4): 279-287. |
| 44 | FOSTER E, YOU J, SILTANEN C, et al. Heparin hydrogel sandwich cultures of primary hepatocytes[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2015, 72: 726-735. |
| 45 | THOMAS R J, BHANDARI R, BARRETT D A, et al. The effect of three-dimensional co-culture of hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells on key hepatocyte functions in vitro [J]. Cells, Tissues, Organs, 2005, 181(2): 67-79. |
| 46 | ZINCHENKO Y S, SCHRUM L W, CLEMENS M, et al. Hepatocyte and Kupffer cells co-cultured on micropatterned surfaces to optimize hepatocyte function[J]. Tissue Engineering, 2006, 12(4): 751-761. |
| 47 | FREVERT U, ENGELMANN S, ZOUGBÉDÉ S, et al. Intravital observation of Plasmodium berghei sporozoite infection of the liver[J]. PLoS Biology, 2005, 3(6): e192. |
| 48 | SHIH M C, TSENG S H, WENG Y S, et al. A microfluidic device mimicking acinar concentration gradients across the liver acinus[J]. Biomedical Microdevices, 2013, 15(5): 767-780. |
| 49 | HEGDE M, JINDAL R, BHUSHAN A, et al. Dynamic interplay of flow and collagen stabilizes primary hepatocytes culture in a microfluidic platform[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(12): 2033-2039. |
| 50 | ASAI A, AIHARA E, WATSON C, et al. Paracrine signals regulate human liver organoid maturation from induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Development, 2017, 144(6): 1056-1064. |
| 51 | TAKEBE T, SEKINE K, ENOMURA M, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant[J]. Nature, 2013, 499(7459): 481-484. |
| 52 | ZHANG B Y, MONTGOMERY M, CHAMBERLAIN M D, et al. Biodegradable scaffold with built-in vasculature for organ-on-a-chip engineering and direct surgical anastomosis[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(6): 669-678. |
| 53 | FRITSCHEN A, LINDNER N, SCHOLPP S, et al. High-scale 3D-bioprinting platform for the automated production of vascularized organs-on-a-chip[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2024, 13(17): e2304028. |
| 54 | HO C T, LIN R Z, CHEN R J, et al. Liver-cell patterning lab chip: mimicking the morphology of liver lobule tissue[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2013, 13(18): 3578-3587. |
| 55 | POISSON J, LEMOINNE S, BOULANGER C, et al. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: physiology and role in liver diseases[J]. Journal of Hepatology, 2017, 66(1): 212-227. |
| 56 | HOEHME S, BRULPORT M, BAUER A, et al. Prediction and validation of cell alignment along microvessels as order principle to restore tissue architecture in liver regeneration[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(23): 10371-10376. |
| 57 | DU K, LI S B, LI C P, et al. Modeling nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on a liver lobule chip with dual blood supply[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2021, 134: 228-239. |
| 58 | LEE P J, HUNG P J, LEE L P. An artificial liver sinusoid with a microfluidic endothelial-like barrier for primary hepatocyte culture[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2007, 97(5): 1340-1346. |
| 59 | PRODANOV L, JINDAL R, BALE S S, et al. Long-term maintenance of a microfluidic 3D human liver sinusoid[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(1): 241-246. |
| 60 | RENNERT K, STEINBORN S, GRÖGER M, et al. A microfluidically perfused three dimensional human liver model[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 71: 119-131. |
| 61 | NAKAO Y, KIMURA H, SAKAI Y, et al. Bile canaliculi formation by aligning rat primary hepatocytes in a microfluidic device[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2011, 5(2): 22212. |
| 62 | MATSUMOTO K, IMASATO M, YAMAZAKI Y, et al. Claudin 2 deficiency reduces bile flow and increases susceptibility to cholesterol gallstone disease in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 147(5): 1134-1145.e10. |
| 1 | HUH D, MATTHEWS B D, MAMMOTO A, et al. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5986): 1662-1668. |
| 2 | BHATIA S N, INGBER D E. Microfluidic organs-on-chips[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(8): 760-772. |
| 3 | MAHLER G J, ESCH M B, GLAHN R P, et al. Characterization of a gastrointestinal tract microscale cell culture analog used to predict drug toxicity[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2009, 104(1): 193-205. |
| 4 | WANG L, TAO T T, SU W T, et al. A disease model of diabetic nephropathy in a Glomerulus-on-a-chip microdevice[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(10): 1749-1760. |
| 5 | 秦建华, 张敏, 于浩, 等. 人体器官芯片[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(12): 1281-1289. |
| QIN J H, ZHANG M, YU H, et al. Human organs-on-a-chip[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(12): 1281-1289. | |
| 6 | LI Z Y, SU W T, ZHU Y J, et al. Drug absorption related nephrotoxicity assessment on an intestine-kidney chip[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2017, 11(3): 034114. |
| 7 | MORADI E, JALILI-FIROOZINEZHAD S, SOLATI-HASHJIN M. Microfluidic organ-on-a-chip models of human liver tissue[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2020, 116: 67-83. |
| 8 | YOON NO D, LEE K H, LEE J, et al. 3D liver models on a microplatform: well-defined culture, engineering of liver tissue and liver-on-a-chip[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(19): 3822-3837. |
| 9 | BECKWITT C H, CLARK A M, WHEELER S, et al. Liver ‘organ on a chip’[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2018, 363(1): 15-25. |
| 10 | MATERNE E M, TONEVITSKY A G, MARX U. Chip-based liver equivalents for toxicity testing: organotypicalness versus cost-efficient high throughput[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2013, 13(18): 3481-3495. |
| 11 | SØRENSEN K K, SIMON-SANTAMARIA J, MCCUSKEY R S, et al. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells[J]. Comprehensive Physiology, 2015, 5(4): 1751-1774. |
| 12 | SENOO H. Structure and function of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Medical Electron Microscopy, 2004, 37(1): 3-15. |
| 13 | DIXON L J, BARNES M, TANG H, et al. Kupffer cells in the liver[J]. Comprehensive Physiology, 2013, 3(2): 785-797. |
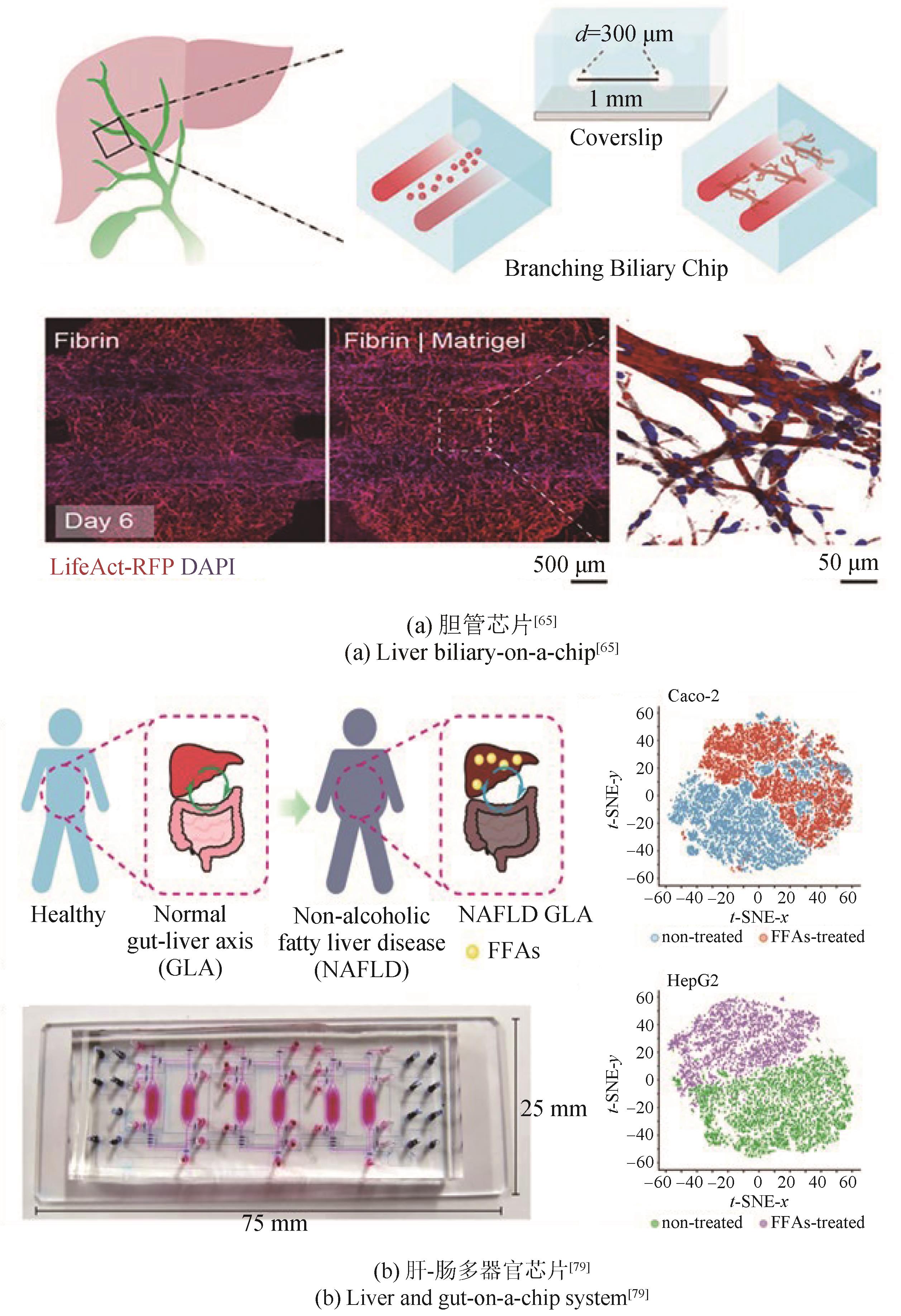
| 63 | DU Y, KHANDEKAR G, LLEWELLYN J, et al. A bile duct-on-a-chip with organ-level functions[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(4): 1350-1363. |
| 64 | LIU Q, MILLE L S, VILLALOBOS C, et al. 3D-bioprinted cholangiocarcinoma-on-a-chip model for evaluating drug responses[J]. Bio-Design and Manufacturing, 2023, 6(4): 373-389. |
| 65 | SMITH Q, BAYS J, LI L Q, et al. Directing cholangiocyte morphogenesis in natural biomaterial scaffolds[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(3): e2102698. |
| 66 | HUCH M, DORRELL C, BOJ S F, et al. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7436): 247-250. |
| 67 | NANTASANTI S, SPEE B, KRUITWAGEN H S, et al. Disease modeling and gene therapy of copper storage disease in canine hepatic organoids[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2015, 5(5): 895-907. |
| 68 | KRUITWAGEN H S, OOSTERHOFF L A, VERNOOIJ I G W H, et al. Long-term adult feline liver organoid cultures for disease modeling of Hepatic steatosis[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2017, 8(4): 822-830. |
| 69 | KAFTANOVSKAYA E M, NG H H, SOULA M, et al. Therapeutic effects of a small molecule agonist of the relaxin receptor ML290 in liver fibrosis[J]. FASEB Journal, 2019, 33(11): 12435-12446. |
| 70 | GÓMEZ-MARIANO G, MATAMALA N, MARTÍNEZ S, et al. Liver organoids reproduce alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency-related liver disease[J]. Hepatology International, 2020, 14(1): 127-137. |
| 71 | NIE Y Z, ZHENG Y W, MIYAKAWA K, et al. Recapitulation of hepatitis B virus-host interactions in liver organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 35: 114-123. |
| 72 | GURAL N, MANCIO-SILVA L, HE J, et al. Engineered livers for infectious diseases[J]. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2018, 5(2): 131-144. |
| 73 | PARK S E, GEORGESC A, HUH D E. Organoids-on-a-chip[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6444): 960-965. |
| 74 | WANG Y Q, WANG L, ZHU Y J, et al. Human brain organoid-on-a-chip to model prenatal nicotine exposure[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(6): 851-860. |
| 75 | ZHU Y J, WANG L, YU H, et al. In situ generation of human brain organoids on a micropillar array[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(17): 2941-2950. |
| 14 | EHRLICH A, DUCHE D, OUEDRAOGO G, et al. Challenges and opportunities in the design of liver-on-chip microdevices[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 21: 219-239. |
| 15 | BAUDY A R, OTIENO M A, HEWITT P, et al. Liver microphysiological systems development guidelines for safety risk assessment in the pharmaceutical industry[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20(2): 215-225. |
| 16 | HUGHES D J, KOSTRZEWSKI T, SCEATS E L. Opportunities and challenges in the wider adoption of liver and interconnected microphysiological systems[J]. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 2017, 242(16): 1593-1604. |
| 17 | BHUSHAN A, SENUTOVITCH N, BALE S S, et al. Towards a three-dimensional microfluidic liver platform for predicting drug efficacy and toxicity in humans[J]. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 2013, 4(): S16. |
| 18 | ZHANG J W, ZHAO X, LIANG L G, et al. A decade of progress in liver regenerative medicine[J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 157: 161-176. |
| 19 | HEYDARI Z, NAJIMI M, MIRZAEI H, et al. Tissue engineering in liver regenerative medicine: insights into novel translational technologies[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(2): 304. |
| 20 | GEBHARDT R, MATZ-SOJA M. Liver zonation: novel aspects of its regulation and its impact on homeostasis[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2014, 20(26): 8491-8504. |
| 21 | HEWITT N J, LECHÓN M J, HOUSTON J B, et al. Primary hepatocytes: current understanding of the regulation of metabolic enzymes and transporter proteins, and pharmaceutical practice for the use of hepatocytes in metabolism, enzyme induction, transporter, clearance, and hepatotoxicity studies[J]. Drug Metabolism Reviews, 2007, 39(1): 159-234. |
| 22 | LECLUYSE E L. Human hepatocyte culture systems for the in vitro evaluation of cytochrome P450 expression and regulation[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2001, 13(4): 343-368. |
| 23 | LÜBBERSTEDT M, MÜLLER-VIEIRA U, MAYER M, et al. HepaRG human hepatic cell line utility as a surrogate for primary human hepatocytes in drug metabolism assessment in vitro [J]. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods, 2011, 63(1): 59-68. |
| 24 | WILKENING S, STAHL F, BADER A. Comparison of primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hepg2 with regard to their biotransformation properties[J]. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 2003, 31(8): 1035-1042. |
| 25 | GUGUEN-GUILLOUZO C, GUILLOUZO A. General review on in vitro hepatocyte models and their applications[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2010, 640: 1-40. |
| 26 | LECLUYSE E L, WITEK R P, ANDERSEN M E, et al. Organotypic liver culture models: meeting current challenges in toxicity testing[J]. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 2012, 42(6): 501-548. |
| 27 | INOUE H, NAGATA N, KUROKAWA H, et al. iPS cells: a game changer for future medicine[J]. EMBO Journal, 2014, 33(5): 409-417. |
| 76 | TAKEBE T, ZHANG B Y, RADISIC M. Synergistic engineering: organoids meet organs-on-a-chip[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2017, 21(3): 297-300. |
| 77 | WANG Y Q, WANG H, DENG P W, et al. In situ differentiation and generation of functional liver organoids from human iPSCs in a 3D perfusable chip system[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(23): 3606-3616. |
| 78 | ARTEGIANI B, VAN VOORTHUIJSEN L, LINDEBOOM R G H, et al. Probing the tumor suppressor function of BAP1 in CRISPR-engineered human liver organoids[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2019, 24(6): 927-943.e6. |
| 79 | YANG J D, HIRAI Y, IIDA K, et al. Integrated-gut-liver-on-a-chip platform as an in vitro human model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Communications Biology, 2023, 6(1): 310. |
| 80 | MASCHMEYER I, LORENZ A K, SCHIMEK K, et al. A four-organ-chip for interconnected long-term co-culture of human intestine, liver, skin and kidney equivalents[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(12): 2688-2699. |
| 81 | BOVARD D, SANDOZ A, LUETTICH K, et al. A lung/liver-on-a-chip platform for acute and chronic toxicity studies[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(24): 3814-3829. |
| 82 | YIN F C, ZHANG X, WANG L, et al. HiPSC-derived multi-organoids-on-chip system for safety assessment of antidepressant drugs[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2021, 21(3): 571-581. |
| 83 | LUCCHETTI M, AINA K O, GRANDMOUGIN L, et al. An organ-on-chip platform for simulating drug metabolism along the gut-liver axis[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2024, 13(20): e2303943. |
| 84 | AIZENSHTADT A, WANG C C, ABADPOUR S, et al. Pump-less, recirculating organ-on-chip (rOoC) platform to model the metabolic crosstalk between islets and liver[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2024, 13(13): e2303785. |
| 85 | HASSAN S, SEBASTIAN S, MAHARJAN S, et al. Liver-on-a-chip models of fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(2): 733-740. |
| 86 | LASLI S, KIM H J, LEE K J, et al. A human liver-on-a-chip platform for modeling nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Advanced Biosystems, 2019, 3(8): e1900104. |
| 87 | LEE J S, CHOI B H, NO D Y, et al. A 3D alcoholic liver disease model on a chip[J]. Integrative Biology, 2016, 8(3): 302-308. |
| 88 | KOSTRZEWSKI T, CORNFORTH T, SNOW S A, et al. Three-dimensional perfused human in vitro model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2017, 23(2): 204-215. |
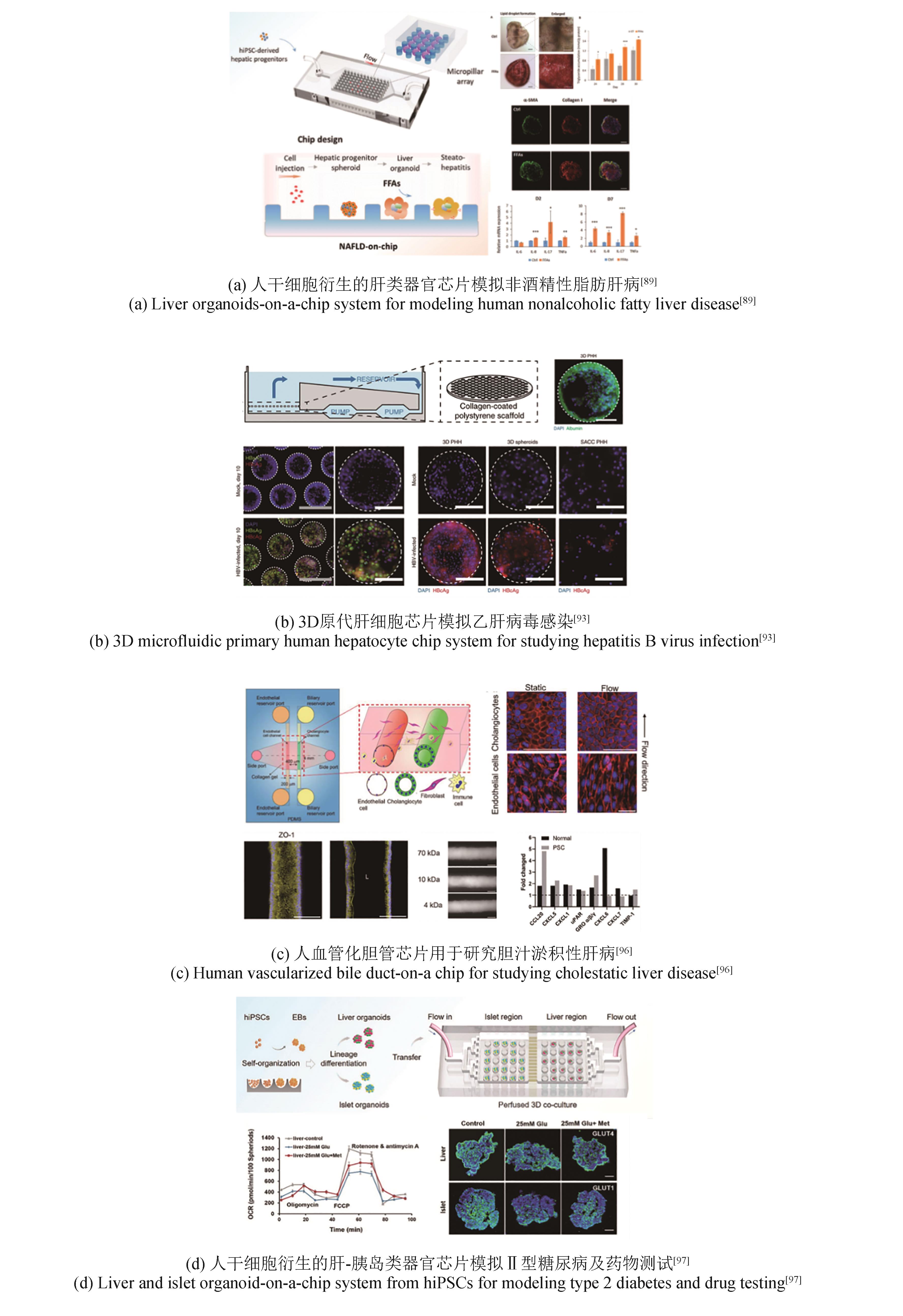
| 89 | WANG Y Q, WANG H, DENG P W, et al. Modeling human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with an organoids-on-a-chip system[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2020, 6(10): 5734-5743. |
| 90 | SLAUGHTER V L, RUMSEY J W, BOONE R, et al. Validation of an adipose-liver human-on-a-chip model of NAFLD for preclinical therapeutic efficacy evaluation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 13159. |
| 91 | LIN C L, KAO J H. Review article: novel therapies for hepatitis B virus cure-advances and perspectives[J]. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2016, 44(3): 213-222. |
| 92 | ORTEGA-PRIETO A M, CHERRY C, GUNN H, et al. In vivo model systems for hepatitis B virus research[J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2019, 5(5): 688-702. |
| 93 | ORTEGA-PRIETO A M, SKELTON J K, WAI S N, et al. 3D microfluidic liver cultures as a physiological preclinical tool for hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 682. |
| 94 | SODUNKE T R, BOUCHARD M J, NOH H M. Microfluidic platform for hepatitis B viral replication study[J]. Biomedical Microdevices, 2008, 10(3): 393-402. |
| 95 | KANG Y, RAWAT S, DUCHEMIN N, et al. Human liver sinusoid on a chip for hepatitis B virus replication study[J]. Micromachines, 2017, 8(1): 27. |
| 96 | DU Y, DE JONG I E M, GUPTA K, et al. Human vascularized bile duct-on-a chip: a multi-cellular micro-physiological system for studying cholestatic liver disease[J]. Biofabrication, 2023, 16(1): 015004. |
| 97 | TAO T T, DENG P W, WANG Y Q, et al. Microengineered multi-organoid system from hiPSCs to recapitulate human liver-islet axis in normal and type 2 diabetes[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(5): e2103495. |
| 98 | LI L, KNUTSDOTTIR H, HUI K, et al. Human primary liver cancer organoids reveal intratumor and interpatient drug response heterogeneity[J]. JCI Insight, 2019, 4(2): e121490. |
| 99 | BROUTIER L, MASTROGIOVANNI G, VERSTEGEN M M, et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening[J]. Nature Medicine, 2017, 23(12): 1424-1435. |
| 28 | ROBINTON D A, DALEY G Q. The promise of induced pluripotent stem cells in research and therapy[J]. Nature, 2012, 481(7381): 295-305. |
| 29 | SAMPAZIOTIS F, SEGERITZ C P, VALLIER L. Potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells in studies of liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62(1): 303-311. |
| 30 | SCOTT C W, PETERS M F, DRAGAN Y P. Human induced pluripotent stem cells and their use in drug discovery for toxicity testing[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2013, 219(1): 49-58. |
| 31 | SCHWARTZ R E, FLEMING H E, KHETANI S R, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2014, 32(2): 504-513. |
| 32 | SI-TAYEB K, NOTO F K, NAGAOKA M, et al. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(1): 297-305. |
| 33 | SONG Z H, CAI J, LIU Y X, et al. Efficient generation of hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Cell Research, 2009, 19(11): 1233-1242. |
| 34 | TAKATA A, OTSUKA M, KOGISO T, et al. Direct differentiation of hepatic cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells using a limited number of cytokines[J]. Hepatology International, 2011, 5(4): 890-898. |
| 35 | BANAEIYAN A A, THEOBALD J, PAUKŠTYTE J, et al. Design and fabrication of a scalable liver-lobule-on-a-chip microphysiological platform[J]. Biofabrication, 2017, 9(1): 015014. |
| 36 | CLEVERS H. Modeling development and disease with organoids[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(7): 1586-1597. |
| 37 | FATEHULLAH A, TAN S H, BARKER N. Organoids as an in vitro model of human development and disease[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2016, 18(3): 246-254. |
| 38 | GUAN Y, XU D, GARFIN P M, et al. Human hepatic organoids for the analysis of human genetic diseases[J]. JCI Insight, 2017;2(17):e94954.. |
| 100 | HENDRIKS D, BROUWERS J F, HAMER K, et al. Engineered human hepatocyte organoids enable CRISPR-based target discovery and drug screening for steatosis[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(11): 1567-1581. |
| 101 | ZHU Y X, JIANG D M, QIU Y, et al. Dynamic microphysiological system chip platform for high-throughput, customizable, and multi-dimensional drug screening[J]. Bioactive Materials, 2024, 39: 59-73. |
| 102 | LI Z Y, JIANG L, ZHU Y J, et al. Assessment of hepatic metabolism-dependent nephrotoxicity on an organs-on-a-chip microdevice[J]. Toxicology in Vitro, 2018, 46: 1-8. |
| 103 | SUNG J H, KAM C, SHULER M L. A microfluidic device for a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model on a chip[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2010, 10(4): 446-455. |
| 104 | HERLAND A, MAOZ B M, DAS D, et al. Quantitative prediction of human pharmacokinetic responses to drugs via fluidically coupled vascularized organ chips[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 4(4): 421-436. |
| 105 | RONALDSON-BOUCHARD K, TELES D, YEAGER K, et al. A multi-organ chip with matured tissue niches linked by vascular flow[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 6(4): 351-371. |
| 106 | MA C, ZHAO L, ZHOU E M, et al. On-chip construction of liver lobule-like microtissue and its application for adverse drug reaction assay[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(3): 1719-1727. |
| 107 | KOSTADINOVA R, BOESS F, APPLEGATE D, et al. A long-term three dimensional liver co-culture system for improved prediction of clinically relevant drug-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2013, 268(1): 1-16. |
| 108 | LEE-MONTIEL F T, GEORGE S M, GOUGH A H, et al. Control of oxygen tension recapitulates zone-specific functions in human liver microphysiology systems[J]. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 2017, 242(16): 1617-1632. |
| 109 | VERNETTI L A, SENUTOVITCH N, BOLTZ R, et al. A human liver microphysiology platform for investigating physiology, drug safety, and disease models[J]. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 2016, 241(1): 101-114. |
| 110 | BIRCSAK K M, DEBIASIO R, MIEDEL M, et al. A 3D microfluidic liver model for high throughput compound toxicity screening in the OrganoPlate®[J]. Toxicology, 2021, 450: 152667. |
| 111 | JANG K J, OTIENO M A, RONXHI J, et al. Reproducing human and cross-species drug toxicities using a Liver-Chip[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2019, 11(517): eaax5516. |
| 112 | EWART L, APOSTOLOU A, BRIGGS S A, et al. Performance assessment and economic analysis of a human Liver-Chip for predictive toxicology[J]. Communications Medicine, 2022, 2(1): 154. |
| 113 | DEY S, BHAT A, JANANI G, et al. Microfluidic human physiomimetic liver model as a screening platform for drug induced liver injury[J]. Biomaterials, 2024, 310: 122627. |
| 114 | ZHANG C J, MEYER S R, O’MEARA M J, et al. A human liver organoid screening platform for DILI risk prediction[J]. Journal of Hepatology, 2023, 78(5): 998-1006. |
| 115 | 中国生物工程学会. 器官芯片通用术语: T/C [S]. 北京: 中国生物工程学会, 2024. |
| Chinese Society of Biotechnology. General terminology of organs-on-chips: T/C [S]. Beijing: Chinese Society of Biotechnology, 2024. | |
| 116 | 中国生物工程学会. 器官芯片 肝 第1部分:模型构建规范: T/C [S]. 北京: 中国生物工程学会, 2024. |
| Chinese Society of Biotechnology. Organs-on-chips: liver—Part 1: Specification of model construction. : T/C [S]. Beijing: Chinese Society of Biotechnology, 2024. |
| [1] | 王达庆, 陶婷婷, 张旭, 李洪敬. 骨骼肌芯片及其在生物医学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 867-882. |
| [2] | 曹荣凯, 秦建华, 王亚清. 胎盘芯片及其在生殖医学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 831-850. |
| [3] | 洪源, 刘妍. 脑类器官在再生医学中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 754-769. |
| [4] | 陈倩文, 赵思琪, 彭耀进. 类器官:技术创新与伦理争议[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 898-907. |
| [5] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [6] | 张博航, 祁晓萱, 袁艳. 睾丸类器官在体外精子发生中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 770-781. |
| [7] | 李石开, 曾东鳌, 杜方舟, 张京钟, 余爽. 血管化类器官的构建方法及生物材料[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 851-866. |
| [8] | 胡可儿, 王汉奇, 黄儒麒, 张灿阳, 邢新会, 马少华. 整合设计策略下的工程化类器官与类器官芯片技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 883-897. |
| [9] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [10] | 艾宗勇, 张成庭, 牛宝华, 尹宇, 杨洁, 李天晴. 人胚胎早期发育与干细胞[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 700-718. |
| [11] | 孟倩, 尹聪, 黄卫人. 肿瘤类器官及其在合成生物学中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 191-201. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||