合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (3): 267-284.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-040
人工多细胞体系设计与构建研究进展
钱秀娟1, 陈琳1, 章文明1,2, 周杰1,2, 董维亮1,2, 信丰学1,2, 姜岷1,2
- 1.南京工业大学材料化学工程国家重点实验室,江苏 南京 211816
2.南京工业大学江苏先进生物与化学制造协同创新中心(SICAM),江苏 南京 211816
-
收稿日期:2020-04-05修回日期:2020-08-03出版日期:2020-06-30发布日期:2020-09-29 -
通讯作者:信丰学,姜岷 -
作者简介:钱秀娟(1992—),女,博士,博士后,研究方向为代谢工程及合成生物学。E-mail:xiujuanqian@njtech.edu.cn
信丰学(1982—),男,博士,教授, 研究方向为生物化工与生物能源。E-mail:xinfengxue@njtech.edu.cn
姜岷(1972—),男,博士,教授,研究方向为生物转化与生物催化。E-mail:jiangmin@njtech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2018YFA0902200);国家自然科学基金项目(31961133017)
Recent research progress in the design and construction of synthetic microbial consortia
QIAN Xiujuan1, CHEN Lin1, ZHANG Wenming1,2, ZHOU Jie1,2, DONG Weiliang1,2, XIN Fengxue1,2, JIANG Min1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering,College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering,Nanjing Tech University,Nanjing 211816,Jiangsu,China
2.Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials (SICAM),Nanjing Tech University,Nanjing 211816,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2020-04-05Revised:2020-08-03Online:2020-06-30Published:2020-09-29 -
Contact:XIN Fengxue, JIANG Min
摘要:
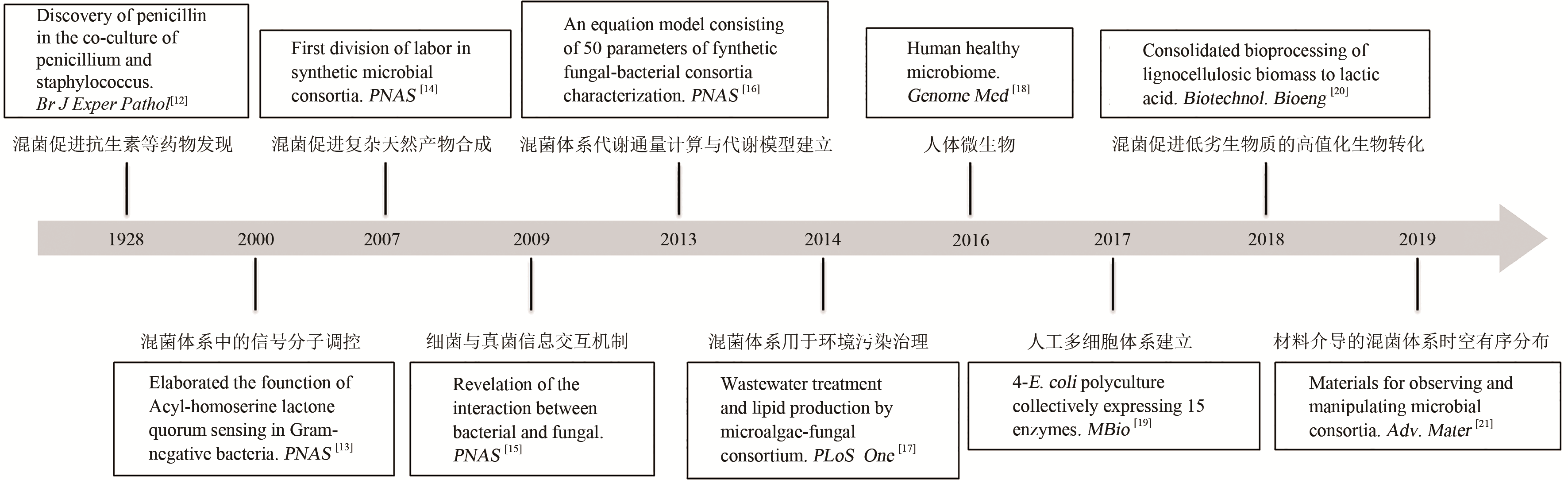
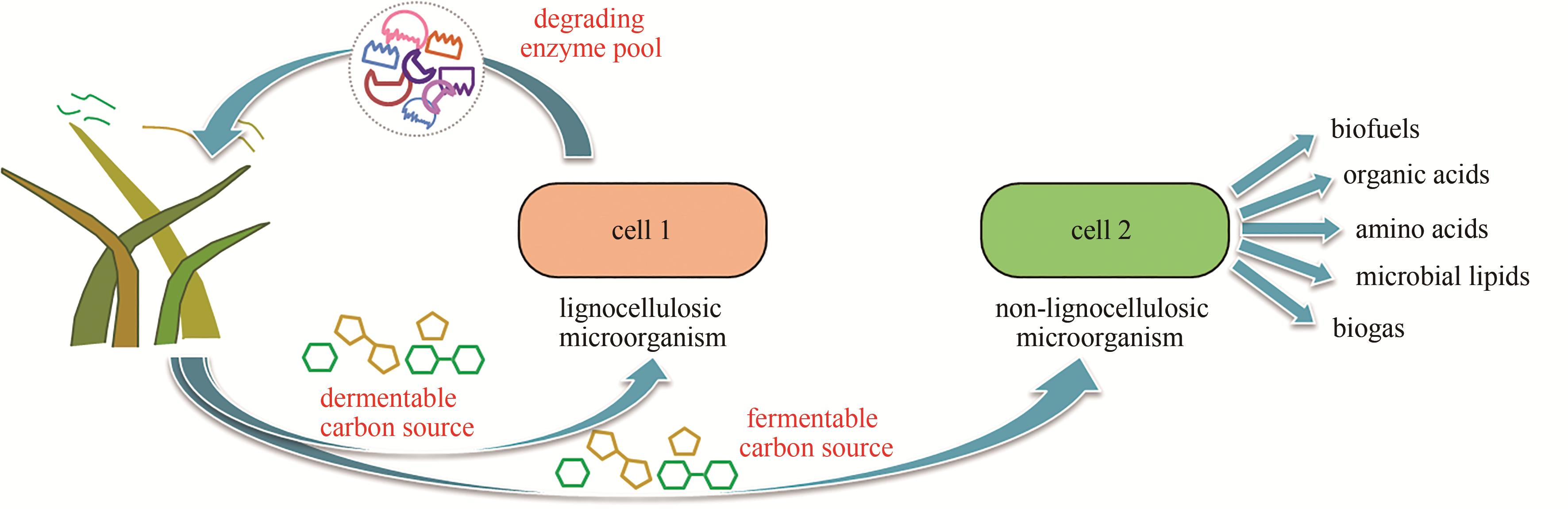
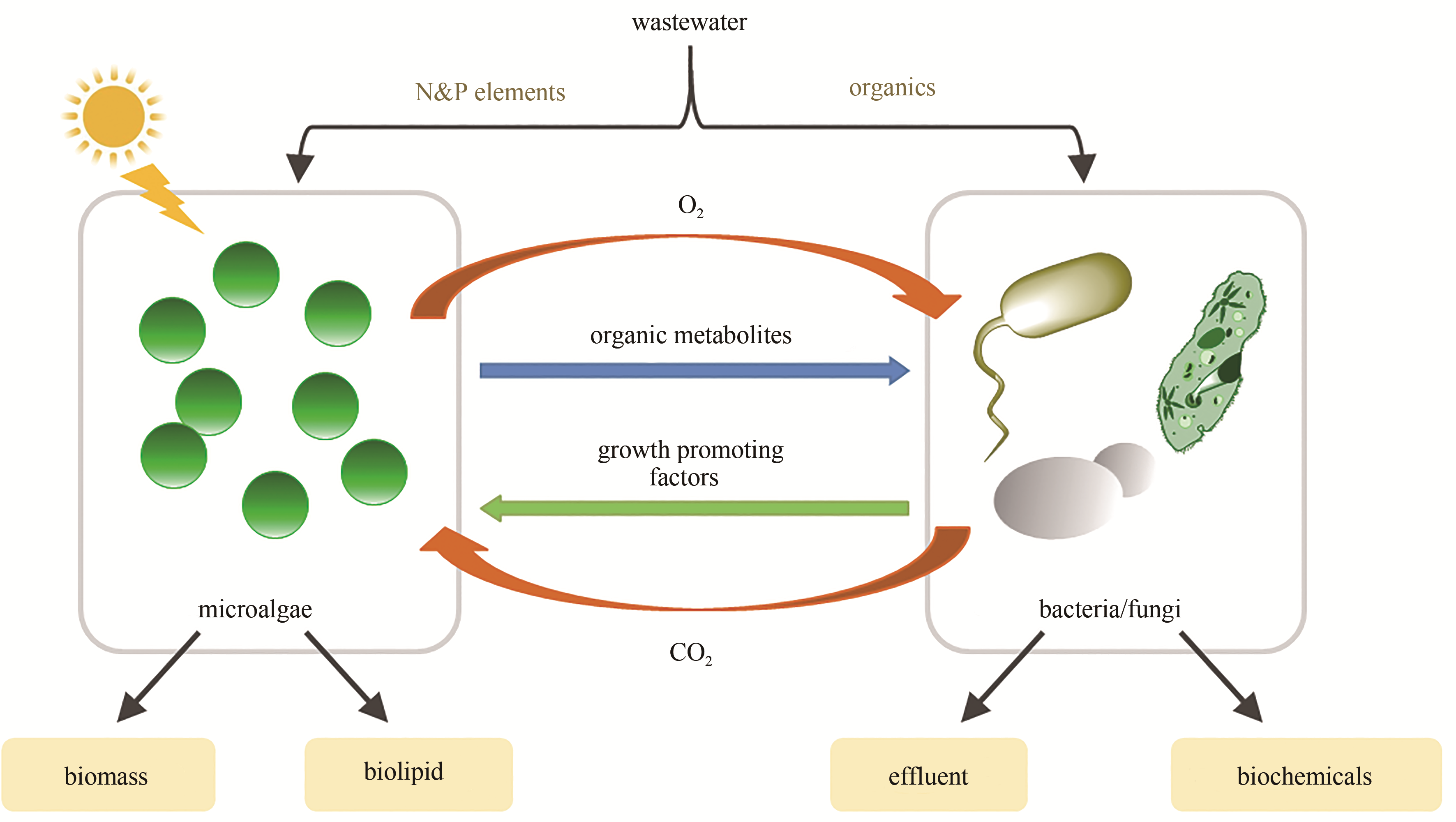
合成生物学的发展正从优化基因元件与模块走向从头设计复杂代谢线路。多细胞体系因可实现代谢功能分工、复杂底物多组分利用及耐受复杂环境等,在医药、食品、化工、环境及能源等领域发挥着不可替代的作用,并已成为合成生物学发展的新方向。然而,多细胞体系的研究还处于起步阶段,理性设计与构建人工多细胞体系、解析细胞间信息互作机制及调控多细胞体系结构等方面还面临诸多挑战。本文综述了人工多细胞体系在医药开发与医疗健康、天然产物合成、木质纤维素一体化生物加工以及环境修复等领域的应用,总结了人工多细胞体系的构建原理,阐述了多细胞体系内细胞间的交流机制,并剖析了人工多细胞体系面临的诸多挑战以及针对性的解决方案,为构建系统鲁棒、稳定、可控的人工多细胞体系提供理论指导。
中图分类号:
引用本文
钱秀娟, 陈琳, 章文明, 周杰, 董维亮, 信丰学, 姜岷. 人工多细胞体系设计与构建研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 267-284.
QIAN Xiujuan, CHEN Lin, ZHANG Wenming, ZHOU Jie, DONG Weiliang, XIN Fengxue, JIANG Min. Recent research progress in the design and construction of synthetic microbial consortia[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 267-284.
| 微生物组合 | 新产物 | 活性 | 是否可单独 培养获得 | 年份 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria tenuissima &Nigrospora sphaerica | 间苯甲酚,异戊二烯醇 | 抗真菌 | 是 | 2013 | [ |
| Aspergillus fumigates &Streptomyces rapamycinicus | 富马环素A, B | 抗生素 | 否 | 2013 | [ |
| A. fumigatus & S. bullii | 麦角甾醇、二酮哌嗪生物碱 | 抗菌和抗原虫 | 否 | 2013 | [ |
| Fusarium tricinctum &Fusarium begoniae | 亚苯甲酸甲酯,亚苯甲酸乙酯 | 抗生素 | 否 | 2013 | [ |
| Trichophyton rubrum &Bionectria ochroleuca | 4″-羟基亚砜-2,2″-二甲基硫丙氨酸P | N/A | 否 | 2014 | [ |
| Streptomyces clavuligerus & Staphylococcus aureus | 全霉素 | 抗微生物 | 否 | 2012 | [ |
| Penicillium pinophilum &Trichoderma harzianum | 二氯戊菊酯C 青霉素、MC-141和施托美霉素 | N/A | 否 是 | 2011 | [ |
| A. fumigates & Streptomyces peucetius | 烟酰胺(1),N,N′-[(1Z,3Z)-1,4-双(4-甲氧基苯基)丁烷-1,3-二烯-2,3-二基]二甲酰胺(2) | (1)无活性 (2)细胞毒素 | 否 | 2011 | [ |
表1 混合培养鉴定新的次生代谢物的最新研究
Tab. 1 Recent studies on mixed cultures identifying novel secondary metabolites
| 微生物组合 | 新产物 | 活性 | 是否可单独 培养获得 | 年份 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria tenuissima &Nigrospora sphaerica | 间苯甲酚,异戊二烯醇 | 抗真菌 | 是 | 2013 | [ |
| Aspergillus fumigates &Streptomyces rapamycinicus | 富马环素A, B | 抗生素 | 否 | 2013 | [ |
| A. fumigatus & S. bullii | 麦角甾醇、二酮哌嗪生物碱 | 抗菌和抗原虫 | 否 | 2013 | [ |
| Fusarium tricinctum &Fusarium begoniae | 亚苯甲酸甲酯,亚苯甲酸乙酯 | 抗生素 | 否 | 2013 | [ |
| Trichophyton rubrum &Bionectria ochroleuca | 4″-羟基亚砜-2,2″-二甲基硫丙氨酸P | N/A | 否 | 2014 | [ |
| Streptomyces clavuligerus & Staphylococcus aureus | 全霉素 | 抗微生物 | 否 | 2012 | [ |
| Penicillium pinophilum &Trichoderma harzianum | 二氯戊菊酯C 青霉素、MC-141和施托美霉素 | N/A | 否 是 | 2011 | [ |
| A. fumigates & Streptomyces peucetius | 烟酰胺(1),N,N′-[(1Z,3Z)-1,4-双(4-甲氧基苯基)丁烷-1,3-二烯-2,3-二基]二甲酰胺(2) | (1)无活性 (2)细胞毒素 | 否 | 2011 | [ |
| 混菌体系 | 产物 | 相对单菌体系提升效果 | 发表年份 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli-E. coli | 黏康酸 | 产量提高19倍 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 4-羟基苯甲酸 | 产量提高8.6倍 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 乙酸苏氨酯 | 产量提高3.3倍,生产强度提高34倍 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 3-氨基苯甲酸 | 产量提高15倍 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 白藜芦醇 | 22.6 mg/L,以甘油为底物从头合成首次报道 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 类黄酮 | 产量提高970倍 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 水杨酸酯2-O-β-d-葡萄糖苷 | 2.5 g/L,首次混菌高产 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 柚皮素 | 产量提高1.5倍 | 2017 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 咖啡醇 | 产量提高12倍 | 2017 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 卡达维林 | 产量提高3倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 芹菜素 | 产量提高2.1倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 咖啡酰苹果酸 | 产量提高5倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 红景天苷 | 产量提高20多倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 白藜芦醇苷 | 产量提高2.9倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 双去甲氧基姜黄素 | 6.28 mg/L,以葡萄糖为底物从头合成首次报道 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 蒎烯 | 产量提高1.9倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 吡喃花青素 | 优于植物提取 | 2019 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 3-羟基苯甲酸 | 产量提高5.3倍 | 2019 | [ |
| G. oxydans-K. vulgare | 2-酮-L-古洛糖酸 | 89.7% 的理论转化率,与双阶段发酵相当 | 2016 | [ |
| P. putida-P. putida | 2-羟基联苯 | 50%转化率 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-B. subtilis- | 电 | 0.28 g葡萄糖产生约550 mV电压供电15天 | 2017 | [ |
| S. oneidensis | ||||
| E. coli-E. coli-E. coli- E. coli | 花葵素 | 9.5 mg/L,微生物体系首次合成 | 2017 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli-E. coli | 迷迭香酸 | 产量提高38倍 | 2019 | [ |
| P. pastoris-P. pastoris | 莫那可林J,洛伐他汀 | 莫那可林J产量提升55%,洛伐他汀产量提升71% | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-S.cerevisiae | 氧化紫杉烷 | 33 mg/L,单细胞体系无法合成 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-S.cerevisiae | 柚皮素 | 产量提高8倍 | 2017 | [ |
表2 人工多细胞体系在高附加值化合物生产中的最新研究成果
Tab. 2 Summary of recent progress in valuable compound production applying synthetic microbial consortia
| 混菌体系 | 产物 | 相对单菌体系提升效果 | 发表年份 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli-E. coli | 黏康酸 | 产量提高19倍 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 4-羟基苯甲酸 | 产量提高8.6倍 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 乙酸苏氨酯 | 产量提高3.3倍,生产强度提高34倍 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 3-氨基苯甲酸 | 产量提高15倍 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 白藜芦醇 | 22.6 mg/L,以甘油为底物从头合成首次报道 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 类黄酮 | 产量提高970倍 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 水杨酸酯2-O-β-d-葡萄糖苷 | 2.5 g/L,首次混菌高产 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 柚皮素 | 产量提高1.5倍 | 2017 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 咖啡醇 | 产量提高12倍 | 2017 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 卡达维林 | 产量提高3倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 芹菜素 | 产量提高2.1倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 咖啡酰苹果酸 | 产量提高5倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 红景天苷 | 产量提高20多倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 白藜芦醇苷 | 产量提高2.9倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 双去甲氧基姜黄素 | 6.28 mg/L,以葡萄糖为底物从头合成首次报道 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 蒎烯 | 产量提高1.9倍 | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 吡喃花青素 | 优于植物提取 | 2019 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli | 3-羟基苯甲酸 | 产量提高5.3倍 | 2019 | [ |
| G. oxydans-K. vulgare | 2-酮-L-古洛糖酸 | 89.7% 的理论转化率,与双阶段发酵相当 | 2016 | [ |
| P. putida-P. putida | 2-羟基联苯 | 50%转化率 | 2016 | [ |
| E. coli-B. subtilis- | 电 | 0.28 g葡萄糖产生约550 mV电压供电15天 | 2017 | [ |
| S. oneidensis | ||||
| E. coli-E. coli-E. coli- E. coli | 花葵素 | 9.5 mg/L,微生物体系首次合成 | 2017 | [ |
| E. coli-E. coli-E. coli | 迷迭香酸 | 产量提高38倍 | 2019 | [ |
| P. pastoris-P. pastoris | 莫那可林J,洛伐他汀 | 莫那可林J产量提升55%,洛伐他汀产量提升71% | 2018 | [ |
| E. coli-S.cerevisiae | 氧化紫杉烷 | 33 mg/L,单细胞体系无法合成 | 2015 | [ |
| E. coli-S.cerevisiae | 柚皮素 | 产量提高8倍 | 2017 | [ |
| 12 | FLEMING A. On the antibacterial action of cultures of a penicillium with special reference to their use in isolation of B. influenzae [J]. Bull World Health Org, 2001,79:780-90 (reprinted from the Br J Exper Pathol, 1929,10:226-236). |
| 13 | PARSEK MR, Greenberg EP. Colloquium Paper: Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(16): 8789-8793. |
| 14 | SHOU W, RAM S, VILAR JMG. Synthetic cooperation in engineered yeast populations [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104 (6) :1877-1882. |
| 15 | SCHROECKH V, SCHERLACH K, H-W NÜTZMANN, et al. Intimate bacterial-fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009,106:14558-63. |
| 16 | MINTY JJ, SINGER ME, SCHOLZ SA, et al. Design and characterization of synthetic fungal-bacterial consortia for direct production of isobutanol from cellulosic biomass [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110:14592-7. |
| 17 | PLOS ONE STAFF THE. Correction: applications and comparisons of four time series models in epidemiological surveillance data [J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(2):e91629. |
| 18 | LLOYD-PRICE J, ABU-ALI G, HUTTENHOWER C. The healthy human microbiome [J]. Genome Medicine, 2016,8:51. |
| 19 | JONES JA, VERNACCHIO VR, COLLINS SM, et al. Complete biosynthesis of anthocyanins using E. coli polycultures [J]. MBio. 2017;8: e00621-17. |
| 20 | SHAHAB RL, LUTERBACHER JS, BRETHAUER S, et al. Consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulosic biomass to lactic acid by a synthetic fungal-bacterial consortium [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115. |
| 21 | JIAO F, XU B: Electrochemical ammonia synthesis and ammonia fuel cells [J]. Advanced materials, 2019, 31:1970221. |
| 22 | NETZKER T, FLAK M, KRESPACH M K, et al. Microbial interactions trigger the production of antibiotics [J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2018, 45: 117-123. |
| 23 | TURNBAUGH P J, LEY R E, HAMADY M, et al. The human microbiome project [J]. Nature, 2007, 449: 804-810. |
| 24 | ZHOU K, QIAO K, EDGAR S, et al. Distributing a metabolic pathway among a microbial consortium enhances production of natural products [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33: 377. |
| 25 | HAYS S G, PATRICK W G, ZIESACK M, et al. Better together: engineering and application of microbial symbioses [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 36: 40-49. |
| 26 | MCCARTY N S, LEDESMA-AMARO R. Synthetic biology tools to engineer microbial communities for biotechnology [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37: 181-197. |
| 27 | WANG J, LIN W, WRAY V, et al. Induced production of depsipeptides by co-culturing Fusarium tricinctum and Fusarium begoniae [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2013, 54: 2492-2496. |
| 28 | CHARUSANTI P, FONG N L, NAGARAJAN H, et al. Exploiting adaptive laboratory evolution of Streptomyces clavuligerus for antibiotic discovery and overproduction [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7: e33727. |
| 29 | MARMANN A, ALY A, LIN Wenhan, et al. Co-cultivation-a powerful emerging tool for enhancing the chemical diversity of microorganisms [J]. Marine Drugs, 2014, 12: 1043-1065. |
| 30 | SPOHN M, KIRCHNER N, KULIK A, et al. Overproduction of ristomycin A by activation of a silent gene cluster in Amycolatopsis japonicum MG417-CF17 [J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2014, 58: 6185-6196. |
| 31 | BERTRAND S, BOHNI N, SCHNEE S, et al. Metabolite induction via microorganism co-culture: a potential way to enhance chemical diversity for drug discovery [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2014, 32: 1180-1204. |
| 32 | CHAGAS F O, DIAS L G, PUPO M T. A mixed culture of endophytic fungi increases production of antifungal polyketides [J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2013, 39: 1335-1342. |
| 33 | KÖNIG CC, SCHERLACH K, SCHROECKH V, et al. Bacterium induces cryptic meroterpenoid pathway in the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. ChemBioChem, 2013, 14: 938-942. |
| 34 | RATEB M E, HALLYBURTON I, HOUSSEN W E, et al. Induction of diverse secondary metabolites in Aspergillus fumigatus by microbial co-culture [J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3: 14444-14450. |
| 35 | NONAKA K, ABE T, IWATSUKI M, et al. Enhancement of metabolites productivity of Penicillium pinophilum FKI-5653, by co-culture with Trichoderma harzianum FKI-5655 [J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2011, 64: 769. |
| 36 | ZUCK KM, SHIPLEY S, NEWMAN DJ. Induced production of N-formyl alkaloids from Aspergillus fumigatus by co-culture with Streptomyces peucetius [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2011, 74: 1653-1657. |
| 37 | TACCONELLI E, CARRARA E, SAVOLDI A, et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis [J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2018, 18(3): 318-327. |
| 38 | GILBERT J A, BLASER M J, CAPORASO J G, et al. Current understanding of the human microbiome [J]. Nature Medicine, 2013, 24: 392-400. |
| 39 | LLOYD-PRICE J, ABU-ALI G, HUTTENHOWER C. The healthy human microbiome [J]. Genome Medicine, 2016, 8: 51. |
| 40 | CHEN L, GARMAEVA S, ZHERANKOVA A, et al. A system biology perspective on environment-host-microbe interactions [J]. Human Molecular Genetics, 2018, 27(R2): R187-R194. |
| 41 | AJIKUMAR PK, XIAO W, KE TYO, et al. Isoprenoid pathway optimization for taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli [J]. Science, 2010, 330: 70-74. |
| 42 | ZHANG H, PEREIRA B, LI Z, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli coculture systems for the production of biochemical products [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112: 8266-8271. |
| 43 | SENGUPTA S, JONNALAGADDA S, GOONEWARDENA L, et al. Metabolic engineering of a novel muconic acid biosynthesis pathway via 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(23): 8037-8043. |
| 44 | WANG S, BILAL M, HU H, et al. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid-a versatile platform intermediate for value-added compounds [J]. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2018, 102(8): 3561-3571. |
| 45 | WANG J, LU X, YING H, et al. A novel process for cadaverine bio-production using a consortium of two engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1312. |
| 46 | LIU X, LI X, JIANG J, et al. Convergent engineering of syntrophic Escherichia coli coculture for efficient production of glycosides [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 243-253. |
| 47 | ZHANG H, LI Z, PEREIRA B, et al. Engineering E. coli-E. coli cocultures for production of muconic acid from glycerol [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 134. |
| 48 | AKDEMIR H, SILVA A, ZHA J, et al. Production of pyranoanthocyanins using Escherichia coli co-cultures [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 55: 290-298. |
| 49 | LI T, ZHOU W, BI H, et al. Production of caffeoylmalic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2018, 40: 1057-1065. |
| 50 | NIU F, HE X, WU Y, et al. Enhancing production of pinene in Escherichia coli by using a combination of tolerance, evolution, and modular co-culture engineering [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9. |
| 1 | HALL G M, HOWE J. The impact of synthetic biology in chemical engineering-educational issues [J]. Education for Chemical Engineers, 2012, 7: e51-e55. |
| 2 | BHATIA S K, BHATIA R K, CHOI Yong-Keun, et al. Biotechnological potential of microbial consortia and future perspectives [J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2018, 38: 1209-1229. |
| 3 | SHONG J, DIAZ M R J, COLLINS C H. Towards synthetic microbial consortia for bioprocessing [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2012, 23: 798-802. |
| 4 | KAEBERLEIN T, LEWIS K, EPSTEIN S S. Isolating "uncultivable" microorganisms in pure culture in a simulated natural environment [J]. Science, 2002, 296: 1127-1129. |
| 5 | HANEMAAIJER M, RÖLING W F M, OLIVIER B G, ET AL. Systems modeling approaches for microbial community studies: from metagenomics to inference of the community structure [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 6: 213. |
| 6 | WANG Xin, SU Rui, CHEN Kequan, et al. Engineering a microbial consortium based whole-cell system for efficient production of glutarate from L-lysine [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 341. |
| 7 | ZHANG H, WANG X. Modular co-culture engineering, a new approach for metabolic engineering [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 37: 114-121. |
| 8 | WANG E, LIU Y, MA Q, et al. Synthetic cell-cell communication in a three-species consortium for one-step vitamin C fermentation [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2019, 41(8/9): 951-961. |
| 9 | ROELL G W, ZHA J, CARR R R, et al. Engineering microbial consortia by division of labor [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18: 35. |
| 10 | LI F, AN X, WU D, et al. Engineering microbial consortia for high-performance cellulosic hydrolyzates-fed microbial fuel cells [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 409. |
| 11 | SONG H, DING M, JIA X, et al. Synthetic microbial consortia: from systematic analysis to construction and applications [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43: 6954-6981. |
| 51 | CAMACHO-ZARAGOZA J M, HERNÁNDEZ-CHÁVEZ G, MORENO-AVITIA F, et al. Engineering of a microbial coculture of Escherichia coli strains for the biosynthesis of resveratrol [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15: 163. |
| 52 | WILLRODT C, HOSCHEK A, BÜHLER B, et al. Coupling limonene formation and oxyfunctionalization by mixed‐culture resting cell fermentation [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112: 1738-1750. |
| 53 | ZHANG H, STEPHANOPOULOS G. Co‐culture engineering for microbial biosynthesis of 3‐amino‐benzoic acid in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 11: 981-987. |
| 54 | JONES J A, VERNACCHIO V R, SINKOE A L, et al. Experimental and computational optimization of an Escherichia coli co-culture for the efficient production of flavonoids [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 35: 55-63. |
| 55 | AHMADI M K, FANG Lei, MOSCATELLO N, et al. E. coli metabolic engineering for gram scale production of a plant-based anti-inflammatory agent [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 382-388. |
| 56 | GANESAN V, LI Z, WANG X, et al. Heterologous biosynthesis of natural product naringenin by co-culture engineering [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2: 236-242. |
| 57 | CHEN Z, SUN X, LI Ye, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial synthesis of monolignols [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 39: 102-109. |
| 58 | THUAN N H, CHAUDHARY A K, CUONG D VAN, et al. Engineering co-culture system for production of apigetrin in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2018, 45: 175-185. |
| 59 | THUAN N H, TRUNG N T, CUONG N X, et al. Escherichia coli modular coculture system for resveratrol glucosides production [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 34: 75. |
| 60 | FANG Z, JONES J A, ZHOU J, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli co‐cultures for production of curcuminoids from glucose [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13: 1700576. |
| 61 | ZHOU YY, LI ZH, WANG XN, et al. Establishing microbial co‐cultures for 3‐hydroxybenzoic acid biosynthesis on glycerol [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2019, 19: 389-395. |
| 62 | WANG EX, DING MZ, MA Q, et al. Reorganization of a synthetic microbial consortium for one-step vitamin C fermentation [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15: 21. |
| 63 | MARTÍNEZ I, E-S MOHAMED M, ROZAS D, et al. Engineering synthetic bacterial consortia for enhanced desulfurization and revalorization of oil sulfur compounds [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 35: 46-54. |
| 64 | LIU Y, DING MZ, LING W, et al. A three-species microbial consortium for power generation [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10: 1600-1609. |
| 65 | JONES JA, VERNACCHIO VR, COLLINS SM, et al. Complete biosynthesis of anthocyanins using E. coli polycultures [J]. mBio, 2017, 8(3): 28588129. |
| 66 | LI ZH, WANG XN, ZHANG HR. Balancing the non-linear rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway by modular co-culture engineering [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 54: 1-11. |
| 67 | LIU YQ, TU XH, XU Q, et al. Engineered monoculture and co-culture of methylotrophic yeast for de novo production of monacolin J and lovastatin from methanol [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 45: 189-199. |
| 68 | ZHANG W, LIU H, LI X, et al. Production of naringenin from D‐xylose with co‐culture of E. coli and S. cerevisiae [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2017, 17: 1021-1029. |
| 69 | CAMPBELL CD, VEDERAS JC. Biosynthesis of lovastatin and related metabolites formed by fungal iterative PKS enzymes [J]. Biopolymers, 2010, 93: 755-763. |
| 70 | RODRÍGUEZ-BUSTAMANTE E, MALDONADO-ROBLEDO G, ORTIZ M A, et al. Bioconversion of lutein using a microbial mixture-maximizing the production of tobacco aroma compounds by manipulation of culture medium [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2005, 68: 174-182. |
| 71 | KLEIN-MARCUSCHAMER D, OLESKOWICZ-POPIEL P, SIMMONS B A, et al. The challenge of enzyme cost in the production of lignocellulosic biofuels [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2012, 109: 1083-1087. |
| 72 | OLSON DG, MCBRIDE JE, SHAW AJ, et al. Recent progress in consolidated bioprocessing [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2012, 23: 396-405. |
| 73 | XIN FX, CHEN TP, JIANG YJ, et al. Strategies for improved isopropanol-butanol production by a Clostridium strain from glucose and hemicellulose through consolidated bioprocessing [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 118. |
| 74 | Y-S JANG, LEE JY, LEE JM, et al. Enhanced butanol production obtained by reinforcing the direct butanol-forming route in Clostridium acetobutylicum [J]. mBio, 2012, 3(5): e00314-12. |
| 75 | YANG XR, XU MM, YANG ST. Metabolic and process engineering of Clostridium cellulovorans for biofuel production from cellulose [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 32: 39-48. |
| 76 | ZHANG XZ, SATHITSUKSANOH N, ZHU ZG, et al. One-step production of lactate from cellulose as the sole carbon source without any other organic nutrient by recombinant cellulolytic Bacillus subtilis [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13: 364-372. |
| 77 | EDWARDS MC, HENRIKSEN ED, YOMANO LP, et al. Addition of genes for cellobiase and pectinolytic activity in Escherichia coli for fuel ethanol production from pectin-rich lignocellulosic biomass [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(15): 5184-5191. |
| 78 | FAVARO L, VIKTOR MJ, ROSE SH, et al. Consolidated bioprocessing of starchy substrates into ethanol by industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains secreting fungal amylases [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112: 1751-1760. |
| 79 | HASUNUMA T, KONDO A. Development of yeast cell factories for consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulose to bioethanol through cell surface engineering [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30: 1207-1218. |
| 80 | VECCHIO DD, QIAN YL, MURRAY RM, et al. Future systems and control research in synthetic biology [J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2018, 45: 5-17. |
| 81 | VAN ZYL W H, HAAN R DEN, GRANGE DC LA. Developing cellulolytic organisms for consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulosics [M]// GUPTA V K, TUOHY M G. Biofuel technologies. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 189-220. |
| 82 | HAAN R DEN, RENSBURG E VAN, ROSE S H, et al. Progress and challenges in the engineering of non-cellulolytic microorganisms for consolidated bioprocessing [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 33: 32-38. |
| 83 | GUO ZP, JULIEN R, SOPHIE D, et al. Developing cellulolytic Yarrowia lipolytica as a platform for the production of valuable products in consolidated bioprocessing of cellulose [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 141. |
| 84 | SINGH N, MATHUR AS, GUPTA RP, et al. Enhanced cellulosic ethanol production via consolidated bioprocessing by Clostridium thermocellum ATCC 31924 [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 250: 860-867. |
| 85 | SHAHAB R L, LUTERBACHER J S, BRETHAUER S, et al. Consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulosic biomass to lactic acid by a synthetic fungal‐bacterial consortium [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115: 1207-1215. |
| 86 | BUZZINI P. Batch and fed‐batch carotenoid production by Rhodotorula glutinis-Debaryomyces castellii co‐cultures in corn syrup [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2001, 90: 843-847. |
| 87 | BAYER TS, WIDMAIER DM, TEMME K, et al. Synthesis of methyl halides from biomass using engineered microbes [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131: 6508-6515. |
| 88 | SGOBBA E, STUMPF AK, VORTMANN M, et al. Synthetic Escherichia coli-Corynebacterium glutamicum consortia for L-lysine production from starch and sucrose [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 260: 302-310. |
| 89 | PATLE S, LAL B. Ethanol production from hydrolysed agricultural wastes using mixed culture of Zymomonas mobilis and Candida tropicalis [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2007, 29: 1839-1843. |
| 90 | BRETHAUER S, STUDER MH. Consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulose by a microbial consortium [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7: 1446-1453. |
| 91 | MINTY JJ, SINGER ME, SCHOLZ SA, et al. Design and characterization of synthetic fungal-bacterial consortia for direct production of isobutanol from cellulosic biomass [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110: 14592-14597. |
| 92 | SURIYACHAI N, WEERASAIA K, LAOSIRIPOJANA N, et al. Optimized simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of rice straw for ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Scheffersomyces stipitis co-culture using design of experiments [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 142: 171-178. |
| 93 | ZUROFF T R, XIQUES S B, CURTIS W R. Consortia-mediated bioprocessing of cellulose to ethanol with a symbiotic Clostridium phytofermentans/yeast co-culture [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2013, 6: 59. |
| 94 | VALDEZ-VAZQUEZ I, PÉREZ-RANGEL M, TAPIA A, et al. Hydrogen and butanol production from native wheat straw by synthetic microbial consortia integrated by species of Enterococcus and Clostridium [J]. Fuel, 2015, 159: 214-222. |
| 95 | PAPONE T, KOOKHUNTHOD S, PAUNGBUT M, et al. Producing of microbial oil by mixed culture of microalgae and oleaginous yeast using sugarcane molasses as carbon substrate [J]. Journal of Clean Energy Technologies, 2016, 4: 253-256. |
| 96 | IKE A, MURAKAWA T, KAWAGUCHI H, et al. Photoproduction of hydrogen from raw starch using a halophilic bacterial community [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 1999, 88: 72-77. |
| 97 | PACHAPUR VL, SARMA SJ, BRAR SK, et al. Co‐culture strategies for increased biohydrogen production [J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2015, 39: 1479-1504. |
| 98 | MASSET J, CALUSINSKA M, HAMILTON C, et al. Fermentative hydrogen production from glucose and starch using pure strains and artificial co-cultures of Clostridium spp . [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2012, 5: 35. |
| 99 | KUMAR R, SINGH S, SINGH O V. Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass: biochemical and molecular perspectives [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2008, 35: 377-391. |
| 100 | GUPTE A, MADAMWAR D. Solid state fermentation of lignocellulosic waste for cellulase and β‐Glucosidase production by cocultivation of Aspergillus ellipticus and Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Biotechnology Progress, 1997, 13: 166-169. |
| 101 | VERMA P, MADAMWAR D. Production of ligninolytic enzymes for dye decolorization by cocultivation of white-rot fungi Pleurotus ostreatus and Phanerochaete chrysosporium under solid-state fermentation [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2002, 102: 109-118. |
| 102 | HU HL, BRINK J VAN DEN, GRUBEN B S, et al. Improved enzyme production by co-cultivation of Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae and with other fungi [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2011, 65: 248-252. |
| 103 | AHMED N, THOMPSON S, GLASER M. Global aquaculture productivity, environmental sustainability, and climate change adaptability [J]. Environmental Management, 2019, 63: 159-172. |
| 104 | CAMPBELL-LENDRUM D, PRÜSS-USTÜN A. Climate change, air pollution and noncommunicable diseases [J]. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 2019, 97: 160. |
| 105 | WALKER D, BAUMGARTNER D, GERBA C, et al. Surface water pollution [M]// BRUSSEAU M L, PEPPER I L, GERBA C P. Environmental and pollution science. 3rd ed. Cambridge, Massachusetts:Elsevier, 2019: 261-292. |
| 106 | AZUBUIKE C C, CHIKERE C B, OKPOKWASILI G C. Bioremediation techniques-classification based on site of application: principles, advantages, limitations and prospects [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 32: 180. |
| 107 | VILLEGAS L B, MARTÍNEZ M A, RODRÍGUEZ A, et al. consortia Microbial, a viable alternative for cleanup of contaminated soils [M]// ALVAREZ A, POLTI M A. Bioremediation in Latin America. Berlin, Germany:Springer, 2014: 135-148. |
| 108 | MUJTABA G, LEE K. Advanced treatment of wastewater using symbiotic co-culture of microalgae and bacteria [J]. Applied Chemistry for Engineering, 2016, 27(1): 1-9. |
| 109 | GONÇALVES A L, PIRES J C, SIMÕES M. A review on the use of microalgal consortia for wastewater treatment [J]. Algal Research, 2017, 24(B): 403-415. |
| 110 | K-J CHOI, HAN T H, YOO G, et al. Co-culture consortium of Scenedesmus dimorphus and nitrifiers enhances the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from artificial wastewater [J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2018, 22: 3215-3221. |
| 111 | MUJTABA G, RIZWAN M, LEE K. Removal of nutrients and COD from wastewater using symbiotic co-culture of bacterium Pseudomonas putida and immobilized microalga Chlorella vulgaris [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2017, 49: 145-151. |
| 112 | REN HY, LIU BF, KONG FY, et al. Hydrogen and lipid production from starch wastewater by co-culture of anaerobic sludge and oleaginous microalgae with simultaneous COD, nitrogen and phosphorus removal [J]. Water Research, 2015, 85: 404-412. |
| 113 | ABINANDAN S, SUBASHCHANDRABOSE S R, VENKATESWARLU K, et al. Nutrient removal and biomass production: advances in microalgal biotechnology for wastewater treatment [J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2018, 38: 1244-1260. |
| 114 | BORDEL S, GUIEYSSE B, MUNOZ R. Mechanistic model for the reclamation of industrial wastewaters using algal-bacterial photobioreactors [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43: 3200-3207. |
| 115 | BHATIA S K, BHATIA R K, YANG Y-H. An overview of microdiesel-a sustainable future source of renewable energy [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 79: 1078-1090. |
| 116 | WREDE D, TAHA M, MIRANDA A F, et al. Co-cultivation of fungal and microalgal cells as an efficient system for harvesting microalgal cells, lipid production and wastewater treatment [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9: e113497. |
| 117 | STILES W A, STYLES D, CHAPMAN S P, et al. Using microalgae in the circular economy to valorise anaerobic digestate: challenges and opportunities [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 267: 732-742. |
| 118 | OSUNDEKO O, ANSOLIA P, GUPTA S K, et al. Promises and challenges of growing microalgae in wastewater [M]// SINGH R P, KOLOK A S, BARTELT-HUNT S L. Water Conservation, Recycling and Reuse: Issues and Challenges. Singapore: Springer, 2019: 29-53. |
| 119 | SATHIYANARAYANAN G, BHATIA S K, KIM H J, et al. Metal removal and reduction potential of an exopolysaccharide produced by Arctic psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. PAMC 28620 [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6: 96870-96881. |
| 120 | SHAFIQUE M, JAWAID A, REHMAN Y. As(V) reduction, As (III) oxidation, and Cr (VI) reduction by multi-metal-resistant Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus safensis, and Bacillus cereus species isolated from wastewater treatment plant [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2017, 34: 687-694. |
| 121 | KIPIGROCH K, JANOSZ-RAJCZYK M, WYKROTA L. Biosorption of heavy metals with the use of mixed algal population [J]. Archives of Environmental Protection, 2012, 38: 3-10. |
| 122 | ILAMATHI R, NIRMALA G, MURUGANANDAM L. Heavy metals biosorption in liquid solid fluidized bed by immobilized consortia in alginate beads [J]. International Journal of Chem Tech Research, 2014, 6: 652-662. |
| 123 | SENAN R C, ABRAHAM T E. Bioremediation of textile azo dyes by aerobic bacterial consortium aerobic degradation of selected azo dyes by bacterial consortium [J]. Biodegradation, 2004, 15: 275-280. |
| 124 | KHAN R, BHAWANA P, FULEKAR M. Microbial decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes: a review [J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2013, 12: 75-97. |
| 125 | SOLÍS M, SOLÍS A, PÉREZ H I, al et, Microbial decolouration of azo dyes : a review [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2012, 47: 1723-1748. |
| 126 | SHANMUGAM B K, EASWARAN S N, LAKRA R, et al. Metabolic pathway and role of individual species in the bacterial consortium for biodegradation of azo dye: a biocalorimetric investigation [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 188: 81-89. |
| 127 | CHAN G F, RASHID N A, KOAY L L, et al. Identification and optimization of novel NAR-1 bacterial consortium for the biodegradation of Orange II [J]. Insight Biotechnol, 2011, 1: 7-16. |
| 128 | SARATALE R, SARATALE G, KALYANI D, et al. Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of textile azo dye Scarlet R by using developed microbial consortium-GR [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100: 2493-2500. |
| 129 | SARATALE R, SARATALE G, CHANG J, et al. Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive dyes and dye wastewater by a developed bacterial consortium [J]. Biodegradation, 2010, 21: 999-1015. |
| 130 | SENTHILVELAN T, KANAGARAJ J, PANDA R C, et al. Biodegradation of phenol by mixed microbial culture: an eco-friendly approach for the pollution reduction [J]. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 2014, 16: 113-126. |
| 131 | XU GM, LI YY, ZHENG W, et al. Mineralization of chlorpyrifos by co-culture of Serratia and Trichosporon spp [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2007, 29: 1469-1473. |
| 132 | JIN D F, HU H, LIU D F, et al. Optimization of a bacterial consortium for nitrobenzene degradation [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2012, 65: 795-801. |
| 133 | GONZÁLEZ N, SIMARRO R, MOLINA M, et al. Effect of surfactants on PAH biodegradation by a bacterial consortium and on the dynamics of the bacterial community during the process [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 9438-9446. |
| 134 | JOINT I, TAIT K, CALLOW ME, et al. Cell-to-cell communication across the prokaryote-eukaryote boundary [J]. Science, 2002, 298: 1207-1207. |
| 135 | W-L NG, BASSLER B L. Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures [J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2009, 43: 197-222. |
| 136 | BALAGADDÉ F K, SONG Hao, OZAKI J, et al. A synthetic Escherichia coli predator-prey ecosystem [J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4. |
| 137 | BASU S, MEHREJA R, THIBERGE S, et al. Spatiotemporal control of gene expression with pulse-generating networks [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101: 6355-6360. |
| 138 | YOU Lingchong, COX R S, WEISS R, et al. Programmed population control by cell-cell communication and regulated killing [J]. Nature, 2004, 428: 868-871. |
| 139 | THOENDEL M, HORSWILL A R. Biosynthesis of peptide signals in gram-positive bacteria [J]. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2010, 71: 91-112. |
| 140 | MICHIE K L, CORNFORTH D M, WHITELEY M. Bacterial Tweets and Podcasts #signaling#eavesdropping#microbialfightclub [J]. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology, 2016, 208(1): 41-48. |
| 141 | FISCHER J, MUELLER S Y, NETZKER T, et al. Fungal chromatin mapping identifies BasR, as the regulatory node of bacteria-induced fungal secondary metabolism [J/OL]. BioRxiv, 2018, 211979. |
| 142 | SCHROECKH V, SCHERLACH K, H-W NÜTZMANN, et al. Intimate bacterial-fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106: 14558-14563. |
| 143 | TOYOFUKU M. Bacterial communication through membrane vesicles [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2019, 83: 1-7. |
| 144 | NÜTZMANN H W, REYES-DOMINGUEZ Y, SCHERLACH K, et al. Bacteria-induced natural product formation in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans requires Saga/Ada-mediated histone acetylation [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108: 14282-14287. |
| 145 | KUROSAWA K, GHIVIRIGA I, SAMBANDAN T, et al. Rhodostreptomycins, antibiotics biosynthesized following horizontal gene transfer from Streptomyces padanus to Rhodococcus fascians [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130: 1126-1127. |
| 146 | SHAHAB R L, LUTERBACHER J S, BRETHAUER, et al. Labor division in engineered cross-kingdom consortia: consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulosic biomass to carboxylic acids [D]. Lausanne, Switzerland:École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne(EPFL), 2019. |
| 147 | WANG C, LI YZ, TAN H, et al. A novel microbe consortium, nano-visible light photocatalyst and microcapsule system to degrade PAHs [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 1065-1074. |
| 148 | LINDEMANN S R, BERNSTEIN H C, SONG Hyun-Seob, et al l. Engineering microbial consortia for controllable outputs [J]. The ISME Journal, 2016, 10: 2077. |
| 149 | SHAHAB R L, BRETHAUER S, LUTERBACHER J S, et al. Engineering of ecological niches to create stable artificial consortia for complex biotransformations [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 62: 129-136. |
| 150 | AGAPAKIS C M, BOYLE P M, SILVER P A. Natural strategies for the spatial optimization of metabolism in synthetic biology [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2012, 8: 527. |
| 151 | JOHNS N I, BLAZEJEWSKI T, GOMES A L, et al. Principles for designing synthetic microbial communities [J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2016, 31: 146-153. |
| 152 | MACLEOD F, GUIOT S, COSTERTON J. Layered structure of bacterial aggregates produced in an upflow anaerobic sludge bed and filter reactor [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1990, 56: 1598-1607. |
| 153 | DAS A A, BOVILL J, AYESH M, et al. Fabrication of living soft matter by symbiotic growth of unicellular microorganisms [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2016, 4: 3685-3694. |
| 154 | AZEREDO J, AZEVEDO N F, BRIANDET R, et al. Critical review on biofilm methods [J]. Critical reviews in Microbiology, 2017, 43: 313-351. |
| 155 | H-C FLEMMING, WINGENDER J. The biofilm matrix [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8: 623. |
| 156 | WONDRACZEK L, POHNERT G, SCHACHER F H, et al. Artificial microbial arenas: materials for observing and manipulating microbial consortia [J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(24): 1900284. |
| 157 | KIM H J, BOEDICKER J Q, CHOI Jang Wook, et al. Defined spatial structure stabilizes a synthetic multispecies bacterial community [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105: 18188-18193. |
| 158 | CONNELL J L, RITSCHDORFF E T, WHITELEY M, et al. 3D printing of microscopic bacterial communities [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110: 18380-18385. |
| [1] | 程中玉, 李付琸. 基于P450选择性氧化的天然产物化学-酶法合成进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 960-980. |
| [2] | 施茜, 吴园园, 杨洋. DNA纳米技术与合成生物学[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 302-319. |
| [3] | 刘裕, 韦惠玲, 刘骥翔, 王少杰, 苏海佳. 人工多菌体系的设计与构建:合成生物学研究新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 635-650. |
| [4] | 丁明珠, 李炳志, 王颖, 谢泽雄, 刘夺, 元英进. 合成生物学重要研究方向进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||