合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (6): 1061-1080.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-021
基因回路型全细胞微生物传感器的设计、优化与应用
杨璐1, 吴楠1, 白茸茸1, 董维亮1,2, 周杰1,2, 姜岷1,2
- 1.南京工业大学生物与制药工程学院,江苏 南京 211816
2.南京工业大学材料化学工程国家重点实验室,江苏 南京 211816
-
收稿日期:2021-02-07修回日期:2021-04-23出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2023-01-17 -
通讯作者:周杰,姜岷 -
作者简介:杨璐 (1997—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为合成生物传感器的设计与应用。E-mail:luyang97@njtech.edu.cn周杰 (1991—),男,博士,副教授。研究方向为合成生物传感器的设计与应用。E-mail:jayzhou@njtech.edu.cn姜岷 (1972—),男,博士,教授。研究方向为人工多细胞体系设计与构建。E-mail:bioengine@njtech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2018YFA0902200);国家自然科学基金(21727818)
Design, optimization and application of whole-cell microbial biosensors with engineered genetic circuits
YANG Lu1, WU Nan1, BAI Rongrong1, DONG Weiliang1,2, ZHOU Jie1,2, JIANG Min1,2
- 1.College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering,Nanjing Tech University,Nanjing 211816,Jiangsu,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering,Nanjing Tech University,Nanjing 211816,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2021-02-07Revised:2021-04-23Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:ZHOU Jie, JIANG Min
摘要:
基于合成生物学理念构建的基因回路型全细胞微生物传感器作为生物传感器的一大重要分支,能够感知环境中特定的待测物质,并按照一定规律将其转换成特定的信号输出,在生物制造过程监控、环境监测与食品安全、医疗诊断与监护等领域的检测应用中显现出巨大的潜力。随着合成生物学各项技术的日益完善和遗传元件的逐渐丰富,越来越多的基于不同响应机制、不同逻辑门与逻辑回路的全细胞微生物传感器已被陆续开发。然而,目前基因回路型全细胞微生物传感器的设计与构建仍主要依靠假设-试错循环的经验性方法。如何设计与构建具有高响应特性的基因回路型全细胞传感器,以及如何对元件、基因回路的优化提高其传感检测性能以满足不同实际应用场景的检测需求,是目前亟需解决的瓶颈问题。本文将主要对基因回路型全细胞生物传感器的原理、分类以及发展历程进行综述,着重介绍全细胞微生物传感器基因回路的设计与构建原则、传感检测性能的优化策略以及在不同检测领域的应用进展,最后剖析了目前全细胞微生物传感器面临的生物安全性、设计构建烦琐、缺乏高效便捷性、难以进入传感器市场等诸多挑战,以及对人工智能、合成生物学、液滴微流控等新兴技术将加速遗传传感元件的开发和生物传感器的人工设计与构建进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨璐, 吴楠, 白茸茸, 董维亮, 周杰, 姜岷. 基因回路型全细胞微生物传感器的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1061-1080.
YANG Lu, WU Nan, BAI Rongrong, DONG Weiliang, ZHOU Jie, JIANG Min. Design, optimization and application of whole-cell microbial biosensors with engineered genetic circuits[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1061-1080.
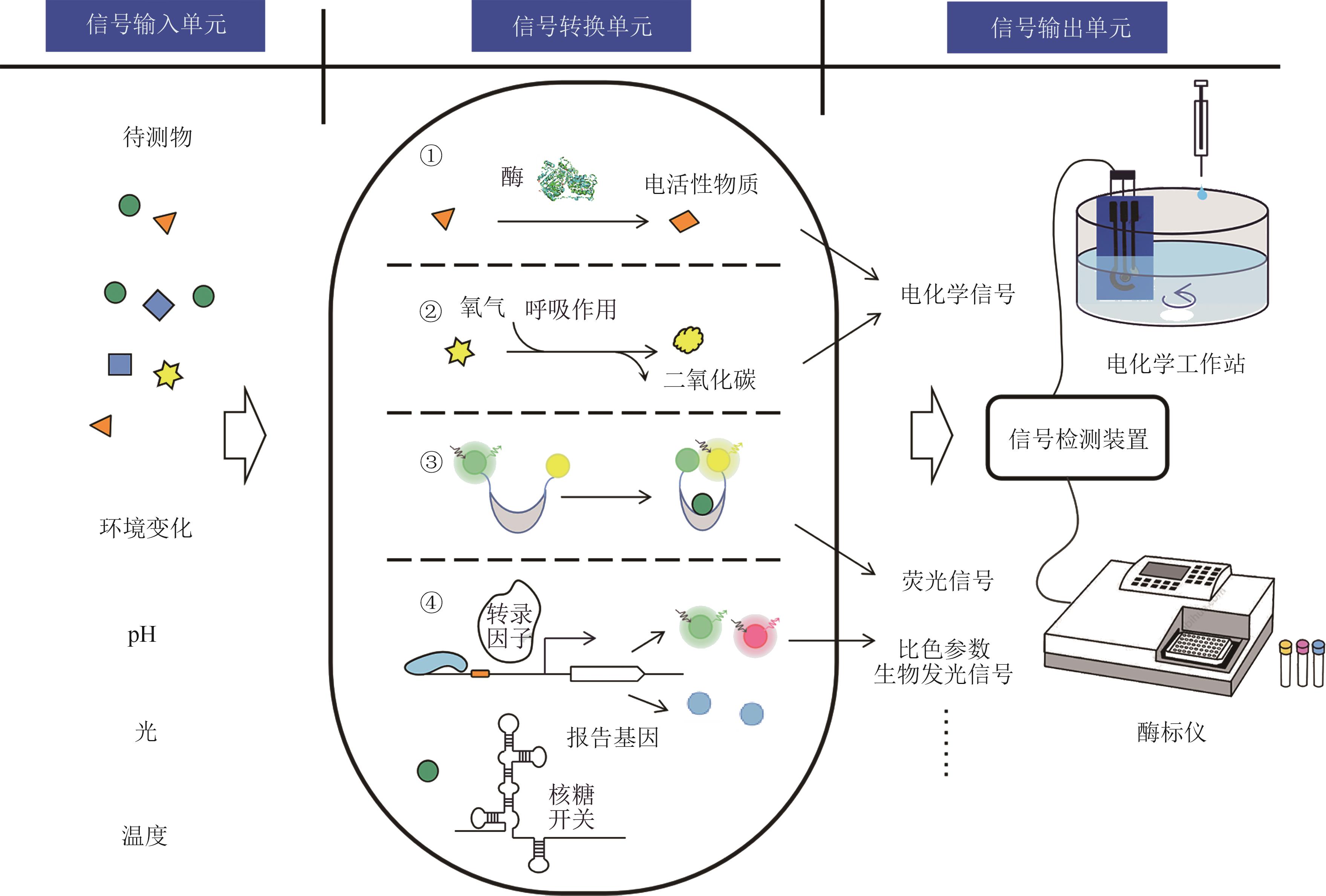
图1 全细胞微生物传感器的分类Signal input: metabolites, environmental change, pH, light, temperature. Signal conversion: ① microbial biosensor for electroactive substances, ② microbial biosensor for respiratory activity, ③ fluorescence resonance energy transfer biosensor, ④ microbial biosensor with genetic circuit. Signal output: electron, fluorescence, colorimetry, bioluminescence that can be detected by electrochemical workstations microplate reader system.
Fig. 1 Classification of whole-cell microbial biosensor
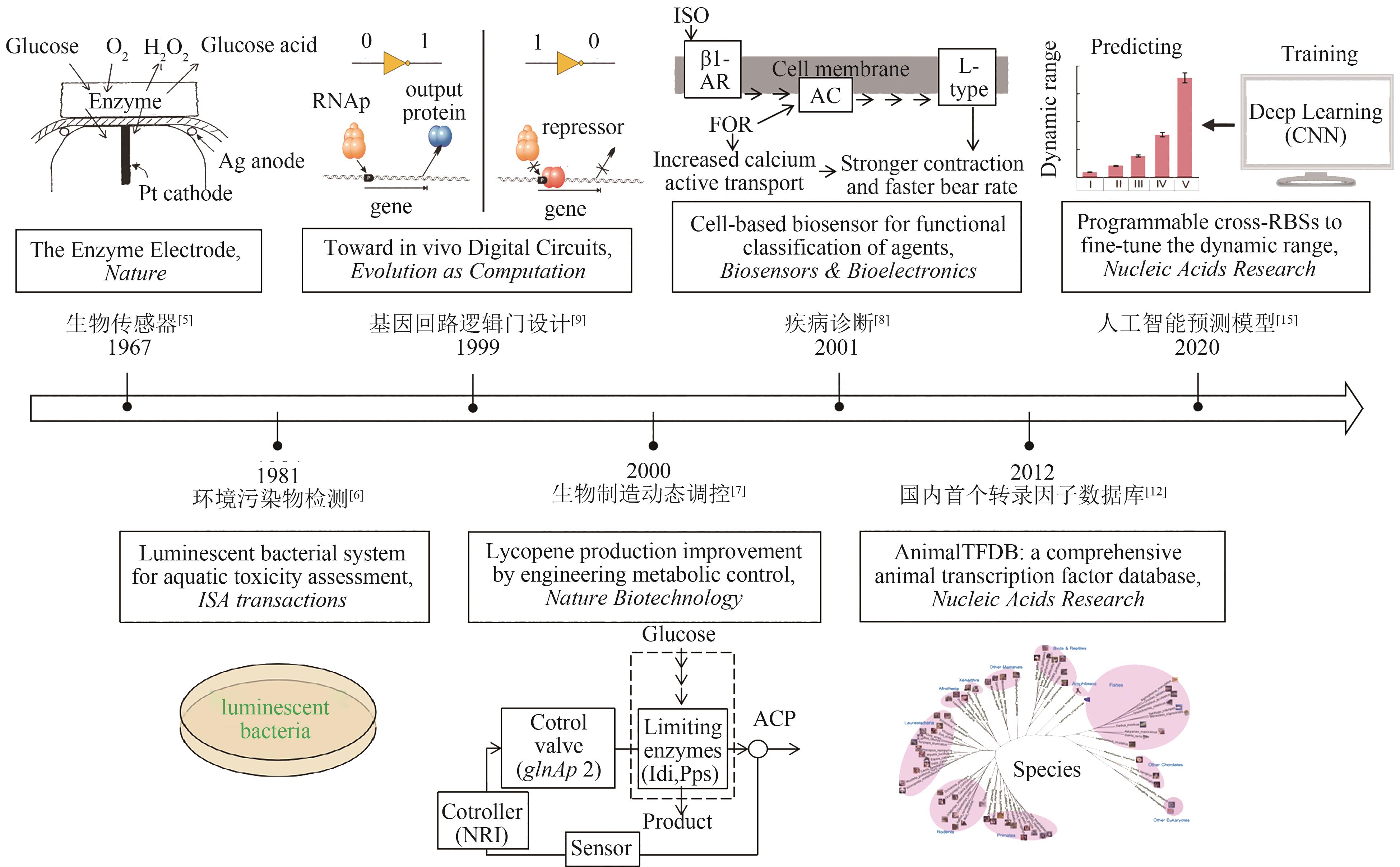
图2 全细胞微生物传感器研究进展及重要成果(biosensors invention, environmental pollutants detection, logic gate design of genetic circuits, dynamic control in fermentation process, disease diagnosis, Transcription factor database, artificial intelligence prediction model.)
Fig. 2 A brief timeline and important achievements in whole-cell microbial biosensor

图 3 基于转录因子全细胞微生物传感器构建原理[Transcription factors (TFs) preferentially bind to ligands and induce conformational changes in the DNA binding domain (DBD). TFs, via their DBD, recognize and bind to a particular DNA-regulatory sequences called binding sites. This may result in increased or decreased reporter gene transcription by promoting or blocking the recruitment of RNA polymerase.]
Fig. 3 Construction principle of whole-cell microbial biosensor based on TFs
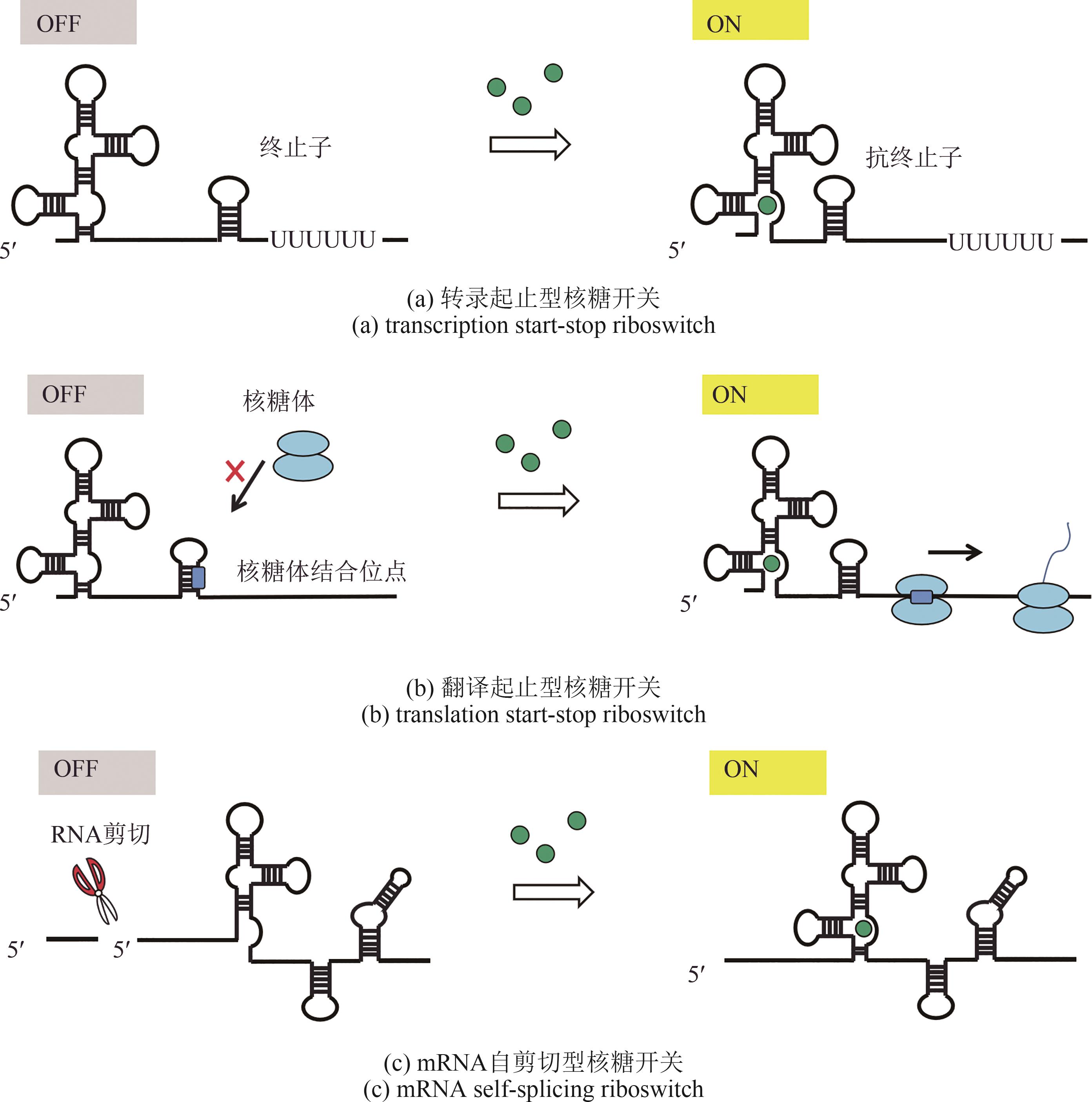
图4 基于核糖开关全细胞微生物传感器构建原理[Regulation by riboswitch. The riboswitch binds with a metabolite (a) to breaks formation of a terminator hairpin, leading to promote transcription of the reporter gene; (b) to activate translation of a reporter gene via its conformational change; or (c) to stabilize mRNA by blocking cleavage site in mRNA, leading to active translation of a reporter gene.]
Fig. 4 Construction principle of whole-cell microbial biosensor based on riboswitches
| 评价指标 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 特异性 | 在复杂环境中专一性识别待测底物的能力 |
| 灵敏度 | 对待测物浓度变化的敏感程度 |
| 动态范围 | 最大输出信号和最小输出信号的比例 |
| 操作范围 | 输入与输出呈单一正相关或负相关的输入信号浓度范围 |
| 稳定性 | 样品检测过程中保持性能恒定的能力 |
| 响应时间 | 信号输入到信号输出的总时间 |
| 安全性 | 是否存在基因泄露转移、吸收外源DNA或潜在有害突变等风险 |
表1 全细胞微生物传感器性能参数[44]
Tab. 1 Evaluation of whole cell microbial sensor [44]
| 评价指标 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 特异性 | 在复杂环境中专一性识别待测底物的能力 |
| 灵敏度 | 对待测物浓度变化的敏感程度 |
| 动态范围 | 最大输出信号和最小输出信号的比例 |
| 操作范围 | 输入与输出呈单一正相关或负相关的输入信号浓度范围 |
| 稳定性 | 样品检测过程中保持性能恒定的能力 |
| 响应时间 | 信号输入到信号输出的总时间 |
| 安全性 | 是否存在基因泄露转移、吸收外源DNA或潜在有害突变等风险 |

图5 全细胞生物传感器的Hill方程曲线(Main response performance parameters: maximum output signal a, background level b, dynamic range a/b, sensitivity c/d, operational range e .)
Fig. 5 Response curve of whole-cell microbial biosensor

图6 全细胞微生物传感器响应性能优化原则(The major impact factors of the performance of whole-cell microbial biosensor include the binding affinity of metabolites to TFs or riboswitches, and TFs to operators, functional domains position, TFs expression level, promoter strength, plasmid copy number, etc.)
Fig. 6 Optimization principles of whole-cell microbial biosensor response performance
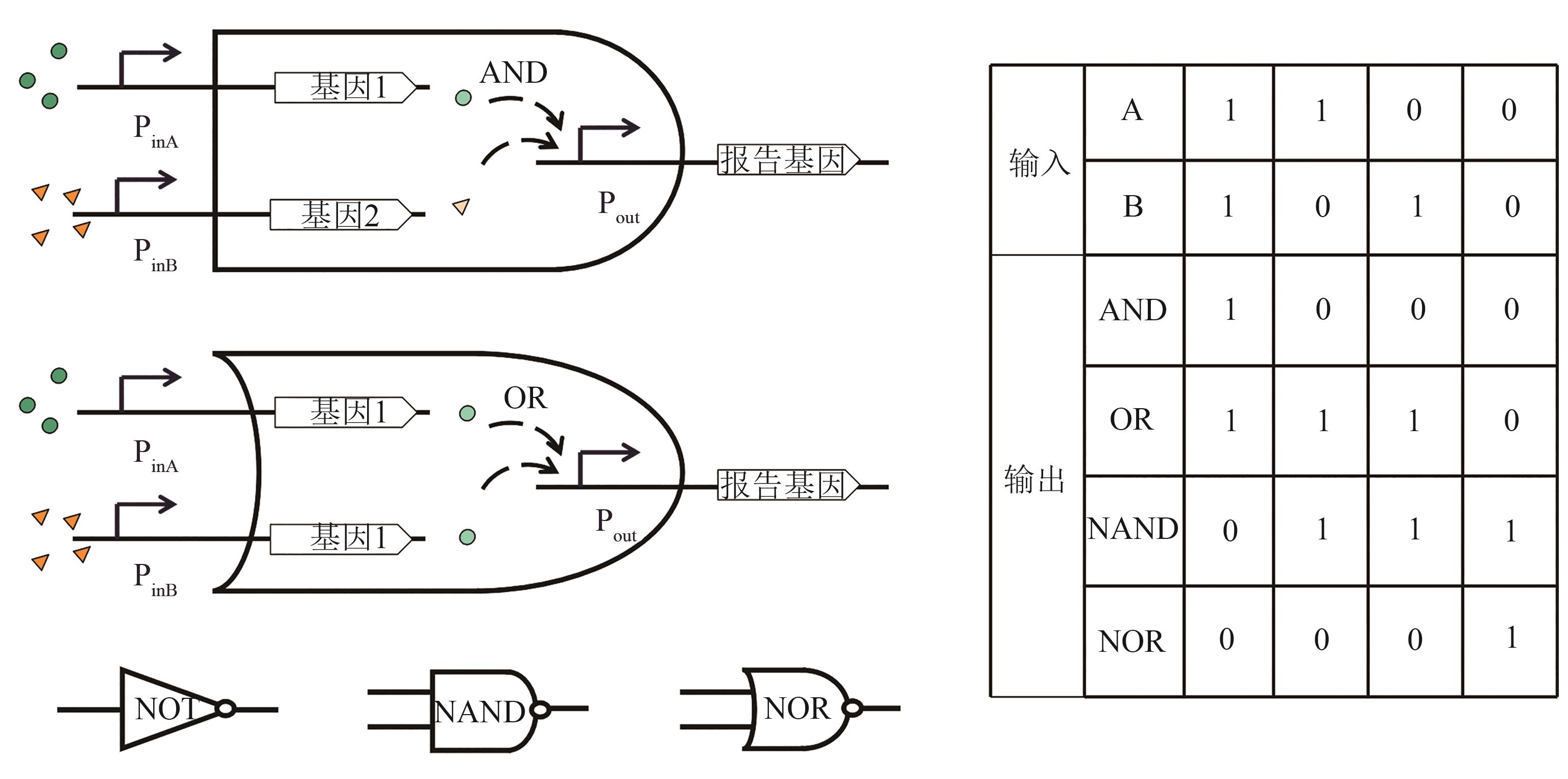
图7 全细胞微生物传感器基因回路逻辑门的设计(AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR gate design and signal input/output change.)
Fig. 7 Design of logic gate in whole-cell microbial biosensor
| 领域 | 检测物 | 传感元件 | 操作范围 | 应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物制造过程监控 | 木糖 | XylR | 0~20 g/L | 木糖转运蛋白筛选 | [ |
| 甘氨酸 | 甘氨酸核糖开关 | 20~200 μmol/L | 动态调控5-氨基乙酰丙酸合成 | [ | |
| 丙酮酸 | PdhR | 10~35 nmol/g | 动态调控葡萄糖二酸合成 | [ | |
| 衣康酸 | YpLysR | 16~160 μmol/L | 衣康酸高产菌株筛选 | [ | |
| 环境监测食品安全 | 4-甲基苯二酚 | ChpR | 25~500 nmol/L | 农药毒死蜱检测 | [ |
| As3+ /As5+ | ArsR | 0.74~60 μg/L | 水样重金属离子检测 | [ | |
四环素 土霉素 | TetR | >20 μg/kg >50 μg/kg | 鱼肉四环素、土霉素含量检测 | [ | |
| 医疗诊断与监护 | 硫代硫酸盐 | ThsR | 0.1~1 mmol/L | 小鼠结肠炎诊断 | [ |
| 茶碱 | 茶碱核糖开关 | 0~5 mmol/L | 支气管扩张剂药物摄取监测 | [ | |
| 尿酸 | HucR | 0~5 mmol/L | 血液中尿酸稳态维持 | [ | |
| 葡萄糖 | GBP | 1~10 mmol/L | 糖尿病患者血糖监测 | [ |
表2 全细胞微生物传感器的应用实例
Tab. 2 Application examples of whole-cell microbial biosensor
| 领域 | 检测物 | 传感元件 | 操作范围 | 应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物制造过程监控 | 木糖 | XylR | 0~20 g/L | 木糖转运蛋白筛选 | [ |
| 甘氨酸 | 甘氨酸核糖开关 | 20~200 μmol/L | 动态调控5-氨基乙酰丙酸合成 | [ | |
| 丙酮酸 | PdhR | 10~35 nmol/g | 动态调控葡萄糖二酸合成 | [ | |
| 衣康酸 | YpLysR | 16~160 μmol/L | 衣康酸高产菌株筛选 | [ | |
| 环境监测食品安全 | 4-甲基苯二酚 | ChpR | 25~500 nmol/L | 农药毒死蜱检测 | [ |
| As3+ /As5+ | ArsR | 0.74~60 μg/L | 水样重金属离子检测 | [ | |
四环素 土霉素 | TetR | >20 μg/kg >50 μg/kg | 鱼肉四环素、土霉素含量检测 | [ | |
| 医疗诊断与监护 | 硫代硫酸盐 | ThsR | 0.1~1 mmol/L | 小鼠结肠炎诊断 | [ |
| 茶碱 | 茶碱核糖开关 | 0~5 mmol/L | 支气管扩张剂药物摄取监测 | [ | |
| 尿酸 | HucR | 0~5 mmol/L | 血液中尿酸稳态维持 | [ | |
| 葡萄糖 | GBP | 1~10 mmol/L | 糖尿病患者血糖监测 | [ |
| 1 | 周益康, 吴亦楠, 王天民, 等. 代谢物生物传感器:微生物细胞工厂构建中的合成生物学工具[J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(1): 1-11. |
| ZHOU Y K, WU Y N, WANG T M, et al. Metabolite biosensor: a useful synthetic biology tool to assist the construction of microbial cell factory[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(1): 1-11. | |
| 2 | 秦伟彤, 田健, 伍宁丰. 全细胞生物传感器的设计及其在环境监测中的应用[J]. 生物技术进展, 2018, 8(5): 369-375. |
| QIN W T, TIAN J, WU N F. Design of the whole-cell biosenor and its application in environmental monitoring[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2018, 8(5): 369-375. | |
| 3 | 张静, 吕雪飞,邓玉林. 基因工程微生物传感器及其应用研究进展[J]. 生命科学仪器, 2019, 17(1): 11-16. |
| ZHANG J, LV X F, DENG Y L. Application research of genetically engineered microbial biosensors[J]. Life Science Instruments, 2019, 17(1): 11-16. | |
| 4 | 施冬艳, 何珣, 陈怡露. 合成生物学在微生物传感器中的应用[J]. 东南大学学报, 2012, 31(3): 363-369. |
| SHI D Y, HE X, CHEN Y L. Application of synthetic biology in microbial sensors[J]. Journal of Southeast University, 2012, 31(3): 363-369. | |
| 5 | UPDIKE S J, HICKS G P. The enzyme electrode[J]. Nature, 1967, 214(5092): 986-988. |
| 6 | BULICH A A, ISENBERG D L. Use of the luminescent bacterial system for the rapid assessment of aquatic toxicity[J]. ISA transactions, 1981, 20(1): 29-33. |
| 7 | FARMER W R, LIAO J C. Improving lycopene production in Escherichia coli by engineering metabolic control[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2000, 18(5): 533-537. |
| 8 | ARAVANIS A M, DE BUSSCHERE B D, CHRUSCINSKI A J, et al. A genetically engineered cell-based biosensor for functional classification of agents[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2001, 16(7/8): 571-577. |
| 9 | WEISS R, HOMSY G E, KNIGHT T F. Toward in vivo digital circuits[C]//LANDWEBER L F, WINFREE E. Evolution as Computation. Berlin: Springer, 2002:275-295. |
| 10 | SALTEPE B, KEHRIBAR E S, YIRMIBESOGLU S S S, et al. Cellular biosensors with engineered genetic circuits[J]. ACS Sensors, 2018, 3(1): 13-26. |
| 11 | AUSLANDER S, AUSLANDER D, MULLER M, et al. Programmable single-cell mammalian biocomputers[J]. Nature, 2012, 487(7405): 123-127. |
| 12 | ZHANG H M, CHEN H, LIU W, et al. AnimalTFDB: a comprehensive animal transcription factor database[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 40(D1): D144-D149. |
| 13 | ANG J, HARRIS E, HUSSEY B J, et al. Tuning response curves for synthetic biology[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(10): 547-567. |
| 14 | RICCI F, VALLEE-BELISLE A, SIMON A J, et al. Using nature's "tricks" to rationally tune the binding properties of biomolecular receptors[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49(9): 1884-1892. |
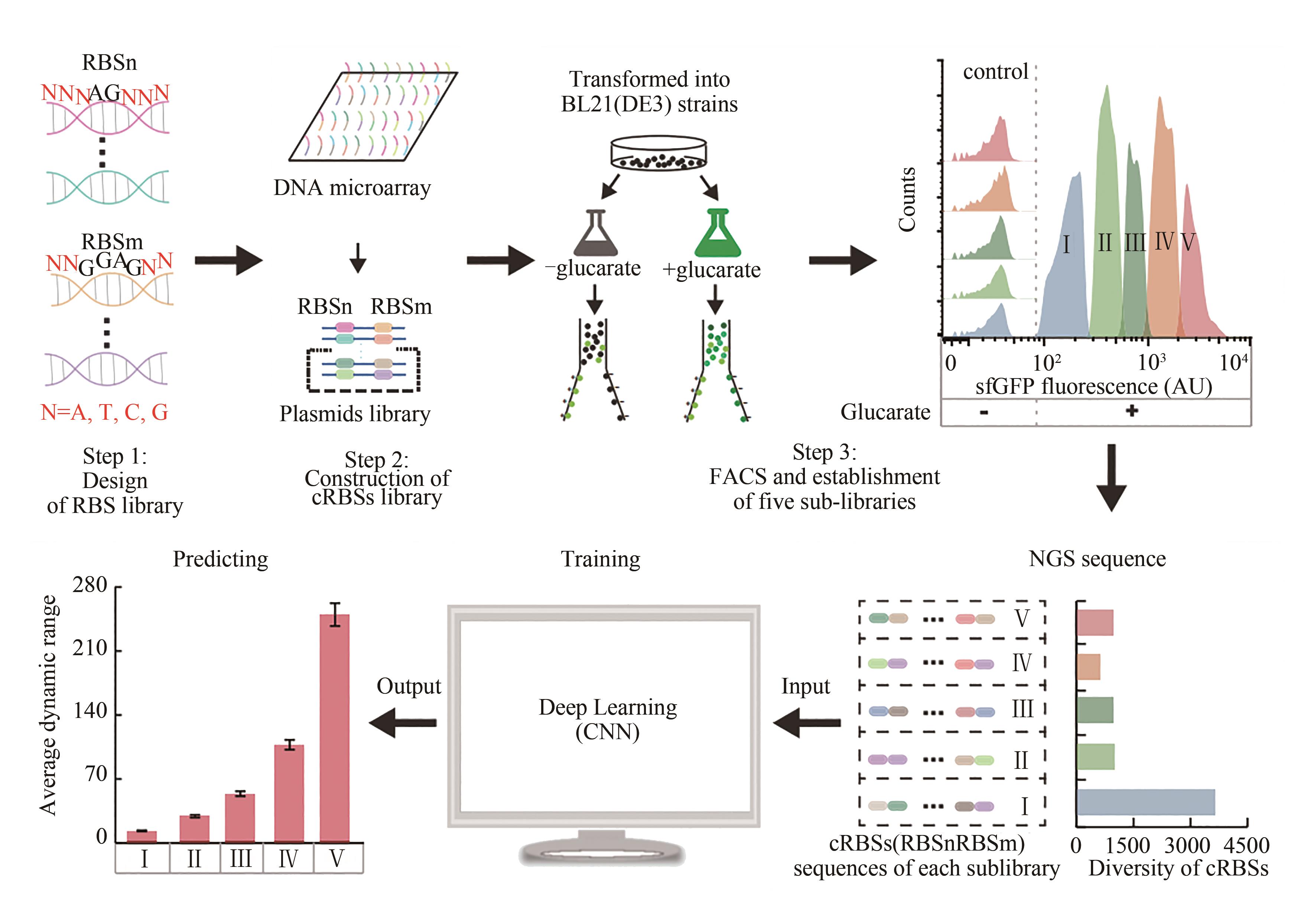
| 15 | DING N N, YUAN Z Q, ZHANG X J, et al. Programmable cross-ribosome-binding sites to fine-tune the dynamic range of transcription factor-based biosensor[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(18): 10602-10613. |
| 16 | DE PAEPE B, PETERS G, COUSSEMENT P, et al. Tailor-made transcriptional biosensors for optimizing microbial cell factories[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 44(4/5): 623-645. |
| 17 | XU X H, LI X L, LIU Y F, et al. Pyruvate-responsive genetic circuits for dynamic control of central metabolism[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(11): 1261-1268. |
| 18 | TANG R Q, WAGNER J M, ALPER H S, et al. Design, evolution, and characterization of a xylose biosensor in Escherichia coli using the XylR/xylO system with an expanded operating range[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(10): 2714-2722. |
| 19 | TANG S Y, FAZELINIA H, CIRINO P C. AraC regulatory protein mutants with altered effector specificity[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(15): 5267-5271. |
| 20 | XU P, LI L Y, ZHANG F M, et al. Improving fatty acids production by engineering dynamic pathway regulation and metabolic control[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(31): 11299-11304. |
| 21 | YANG Y P, LIN Y H, WANG J, et al. Sensor-regulator and RNAi based bifunctional dynamic control network for engineered microbial synthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3043-3052. |
| 22 | WU Y K, CHEN T C, LIU Y F, et al. Design of a programmable biosensor-CRISPRi genetic circuits for dynamic and autonomous dual-control of metabolic flux in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(2): 996-1009. |
| 23 | TUNGTUR S, EGAN S M, SWINT-KRUSE L. Functional consequences of exchanging domains between LacI and PurR are mediated by the intervening linker sequence[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2007, 68(1): 375-388. |
| 24 | WINKLER W, NAHVI A, BREAKER R R. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression[J]. Nature, 2002, 419(6910): 952-956. |
| 25 | ZHOU L B, REN J, LI Z D, et al. Characterization and engineering of a clostridium glycine riboswitch and its use to control a novel metabolic pathway for 5-aminolevulinic acid production in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(10): 2327-2335. |
| 26 | ZHOU L B, ZENG A P. Exploring lysine riboswitch for metabolic flux control and improvement of L-lysine synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(6): 729-734. |
| 27 | ONTIVEROS-PALACIOS N, SMITH A M, GRUNDY F J, et al. Molecular basis of gene regulation by the THI-box riboswitch [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2008, 67(4): 793-803. |
| 28 | WINKLER W C, COHEN-CHALAMISH S, BREAKER R R. An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(25): 15908-15913. |
| 29 | CROMIE M J, SHI Y X, LATIFI T, et al. An RNA sensor for intracellular Mg2+ [J]. Cell, 2006, 125(1): 71-84. |
| 30 | SHI Y X, ZHAO G, KONG W. Genetic analysis of riboswitch-mediated transcriptional regulation responding to Mn2+ in Salmonella [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(16): 11353-11366. |
| 31 | SUESS B, HANSON S, BERENS C, et al. Conditional gene expression by controlling translation with tetracycline-binding aptamers[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, 31(7): 1853-1858. |
| 32 | TRAUSCH J J, CERES P, REYES F E, et al. The structure of a tetrahydrofolate-sensing riboswitch reveals two ligand binding sites in a single aptamer[J]. Structure, 2011, 19(10): 1413-1423. |
| 33 | DESAI S K, GALLIVAN J P. Genetic screens and selections for small molecules based on a synthetic riboswitch that activates protein translation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(41): 13247-13254. |
| 34 | BEREZA-MALCOLM L T, MANN G, FRANKS A E. Environmental sensing of heavy metals through whole cell microbial biosensors: a synthetic biology approach[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(5): 535-546. |
| 35 | TAO H C, PENG Z W, LI P S, et al. Optimizing cadmium and mercury specificity of CadR-based E. coli biosensors by redesign of CadR[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2013, 35(8): 1253-1258. |
| 36 | HANKO E K R, MINTON N P, MALYS N. A Transcription factor-based biosensor for detection of itaconic acid[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(5): 1436-1446. |
| 37 | YAGI K. Applications of whole-cell bacterial sensors in biotechnology and environmental science[J]. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2007, 73(6): 1251-1258. |
| 38 | FUJIMOTO H, WAKABAYASHI M, YAMASHIRO H, et al. Whole-cell arsenite biosensor using photosynthetic bacterium Rhodovulum sulfidophilum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 73(2): 332-338. |
| 39 | ALEKSIC J, BIZZARI F, CAI Y, et al. Development of a novel biosensor for the detection of arsenic in drinking water[J]. IET Synthetic Biology, 2007, 1(1/2): 87-90. |
| 40 | FEENEY K A, PUTKER M, BRANCACCIO M, et al. In-depth characterization of firefly luciferase as a reporter of circadian gene expression in mammalian cells[J]. Journal of Biological Rhythms, 2016, 31(6): 540-550. |
| 41 | TINIKUL R, CHUNTHABOON P, PHONBUPPHA J, et al. Bacterial luciferase: molecular mechanisms and applications[J]. The Enzymes, 2020, 47: 427-455. |
| 42 | LOPRESIDE A, CALABRETTA M M, MONTALI L, et al. Prêt-à-porter nanoYESα and nanoYESβ bioluminescent cell biosensors for ultrarapid and sensitive screening of endocrine-disrupting chemicals[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 411(19): 4937-4949. |
| 43 | LOPRESIDE A, WAN X Y, MICHELINI E, et al. Comprehensive profiling of diverse genetic reporters with application to whole-cell and cell-free biosensors[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(23): 15284-15292. |
| 44 | DIETRICH J A, MCKEE A E, KEASLING J D. High-throughput metabolic engineering: advances in small-molecule screening and selection[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2010, 79:563-590. |
| 45 | CHONG H Q, CHING C B. Development of colorimetric-based whole-cell biosensor for organophosphorus compounds by engineering transcription regulator DmpR [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(11): 1290-1298. |
| 46 | SHIN H J. Development of highly-sensitive microbial biosensors by mutation of the nahR regulatory gene[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 150(2): 246-250. |
| 47 | TEO W S, HEE K S, CHANG M W. Bacterial FadR and synthetic promoters function as modular fatty acid sensor- regulators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2013, 13(5): 456-463. |
| 48 | TEO W S, CHANG M W. Bacterial XylRs and synthetic promoters function as genetically encoded xylose biosensors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 10(2): 315-322. |
| 49 | LIANG C N, ZHANG X X, WU J Y, et al. Dynamic control of toxic natural product biosynthesis by an artificial regulatory circuit[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 57: 239-246. |
| 50 | TANG S Y, CIRINO P C. Design and application of a mevalonate-responsive regulatory protein[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2011, 50(5): 1084-1086. |
| 51 | TANG S Y, QIAN S, AKINTERINWA O, et al. Screening for enhanced triacetic acid lactone production by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing a designed triacetic acid lactone reporter[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(27): 10099-10103. |
| 52 | FREI C S, WANG Z Q, QIAN S, et al. Analysis of amino acid substitutions in AraC variants that respond to triacetic acid lactone[J]. Protein Science, 2016, 25(4): 804-814. |
| 53 | CHEN W, ZHANG S, JIANG P X, et al. Design of an ectoine-responsive AraC mutant and its application in metabolic engineering of ectoine biosynthesis[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 30: 149-155. |
| 54 | XIONG D D, LU S K, WU J Y, et al. Improving key enzyme activity in phenylpropanoid pathway with a designed biosensor[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 40: 115-123. |
| 55 | YEOM S J, KIM M, KWON K K, et al. A synthetic microbial biosensor for high-throughput screening of lactam biocatalysts[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 5053. |
| 56 | MEINHARDT S, MANLEY M W, BECKER N A, et al. Novel insights from hybrid LacI/GalR proteins: family-wide functional attributes and biologically significant variation in transcription repression[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(21): 11139-11154. |
| 57 | CHOU H H, KEASLING J D. Programming adaptive control to evolve increased metabolite production[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2595. |
| 58 | ZHANG F Z, CAROTHERS J M, KEASLING J D. Design of a dynamic sensor-regulator system for production of chemicals and fuels derived from fatty acids[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(4): 354-359. |
| 59 | DABIRIAN Y, LI X W, CHEN Y, et al. Expanding the dynamic range of a transcription factor-based biosensor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(9): 1968-1975. |
| 60 | DAVID F, NIELSEN J, SIEWERS V. Flux control at the malonyl-CoA node through hierarchical dynamic pathway regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(3): 224-233. |
| 61 | CHEN Y, HO J M L, SHIS D L, et al. Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 64. |
| 62 | LI S J, SI T, WANG M, et al. Development of a synthetic malonyl-CoA sensor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for intracellular metabolite monitoring and genetic screening [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(12): 1308-1315. |
| 63 | PANG Q X, HAN H, LIU X Q, et al. In vivo evolutionary engineering of riboswitch with high-threshold for N-acetylneuraminic acid production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 59: 36-43. |
| 64 | JANG S H, JANG S Y, XIU Y, et al. Development of artificial riboswitches for monitoring of naringenin in vivo [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(11): 2077-2085. |
| 65 | JANG S Y, JANG S H, IM D K, et al. Artificial caprolactam-specific riboswitch as an intracellular metabolite sensor[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(6): 1276-1283. |
| 66 | DWIDAR M, SEIKE Y, KOBORI S, et al. Programmable artificial cells using histamine-responsive synthetic riboswitch[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(28): 11103-11114. |
| 67 | YANG J, SEO S W, JANG S H, et al. Synthetic RNA devices to expedite the evolution of metabolite-producing microbes[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1413. |
| 68 | WEIGAND J E, SANCHEZ M, GUNNESCH EB, et al. Screening for engineered neomycin riboswitches that control translation initiation[J]. RNA, 2008, 14(1): 89-97. |
| 69 | GROHER F, BOFILL-BOSCH C, SCHNEIDER C, et al. Riboswitching with ciprofloxacin-development and characterization of a novel RNA regulator[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(4): 2121-2132. |
| 70 | BOUSSEBAYLE A, TORKA D, OLLIVAUD S, et al. Next-level riboswitch development-implementation of Capture-SELEX facilitates identification of a new synthetic riboswitch[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(9): 4883-4895. |
| 71 | WERSTUCK G, GREEN M R. Controlling gene expression in living cells through small molecule-RNA interactions[J]. Science, 1998, 282(5387): 296-298. |
| 72 | GRATE D, WILSON C. Inducible regulation of the S. cerevisiae cell cycle mediated by an RNA aptamer-ligand complex[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2001, 9(10): 2565-2570. |
| 73 | HARVEY I, GARNEAU P, PELLETIER J. Inhibition of translation by RNA-small molecule interactions[J]. RNA, 2002, 8(4): 452-463. |
| 74 | SUESS B, FINK B, BERENS C, et al. A theophylline responsive riboswitch based on helix slipping controls gene expression in vivo [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(4): 1610-1614. |
| 75 | WIELAND M, BENZ A, KLAUSER B, et al. Artificial ribozyme switches containing natural riboswitch aptamer domains[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2009, 48: 2715-2718. |
| 76 | WACHSMUTH M, FINDEISS S, WEISSHEIMER N, et al. De novo design of a synthetic riboswitch that regulates transcription termination[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(4): 2541-2551. |
| 77 | TEO W S, CHANG M W. Development and characterization of AND-gate dynamic controllers with a modular synthetic GAL1 core promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2014, 111(1): 144-151. |
| 78 | ANDERSON J C, VOIGT C A, ARKIN A P. Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2007, 3: 133. |
| 79 | WANG B J, KITNEY R I, JOLY N, et al. Engineering modular and orthogonal genetic logic gates for robust digital-like synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2: 508. |
| 80 | TAMSIR A, TABOR J J, VOIGT C A. Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical 'wires' [J]. Nature, 2011, 469(7329): 212-215. |
| 81 | WHANGSUK W, THIENGMAG S, DUBBS J, et al. Specific detection of the pesticide chlorpyrifos by a sensitive genetic-based whole cell biosensor[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2016, 493: 11-13. |
| 82 | HU Q, LI L, WANG Y J, et al. Construction of WCB-11: a novel phiYFP arsenic-resistant whole-cell biosensor[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 9(22): 1469-1474. |
| 83 | PELLINEN T, BYLUND G, VIRTA M, et al. Detection of traces of tetracyclines from fish with a bioluminescent sensor strain incorporating bacterial luciferase reporter genes[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2002, 50(17): 4812-4815. |
| 84 | DAEFFLER K N M, GALLEY J D, SHETH R U, et al. Engineering bacterial thiosulfate and tetrathionate sensors for detecting gut inflammation[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2017, 13(4): 923. |
| 85 | JO J J, SHIN J S. Construction of intragenic synthetic riboswitches for detection of a small molecule[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2009, 31(10): 1577-1581. |
| 86 | KEMMER C, GITZINGER M, DAOUD-EL BABA M, et al. Self-sufficient control of urate homeostasis in mice by a synthetic circuit[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(4): 355-360. |
| 87 | PICKUP J C, KHAN F, ZHI Z L. Fluorescence intensity- and lifetime-based glucose sensing using glucose/galactose-binding protein[J]. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 2013, 7(1): 62-71. |
| 88 | 于政, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 等. 动态调控策略在代谢工程中的应用研究进[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 440-453. |
| YU Z, SHEN X L, SUN X X, et al. Application of dynamic regulation strategies in metabolic engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(4): 440-453. | |
| 89 | LIU D, XIAO Y, EVANS B S, et al. Negative feedback regulation of fatty acid production based on a malonyl-CoA sensor-actuator [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(2): 132-140. |
| 90 | DE LAS HERAS A, MARTINEZ-GARCIA E, DOMINGO-SANANES M R, et al. Rationally rewiring the connectivity of the XylR/Pu regulatory node of the m-xylene degradation pathway in Pseudomonas putida [J]. Integrative Biology, 2016, 8(4): 571-576. |
| 91 | WERLEN C, JASPERS M C M, VAN DER MEER J R. Measurement of biologically available naphthalene in gas and aqueous phases by use of a Pseudomonas putida biosensor [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(1): 43-51. |
| 92 | MADHUSHANI A, DEL PESO-SANTOS T, MORENO R, et al. Transcriptional and translational control through the 5'-leader region of the dmpR master regulatory gene of phenol metabolism[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(1): 119-133. |
| 93 | JOE M H, LEE K H, LIM S Y, et al. Pigment-based whole-cell biosensor system for cadmium detection using genetically engineered Deinococcus radiodurans [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2012, 35(1/2): 265-272. |
| 94 | RAVIKUMAR S, GANESH I, YOO I K, et al. Construction of a bacterial biosensor for zinc and copper and its application to the development of multifunctional heavy metal adsorption bacteria[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2012, 47(5): 758-765. |
| 95 | KISKER C, HINRICHS W, TOVAR K, et al. The complex formed between Tet repressor and tetracycline-Mg2+ reveals mechanism of antibiotic resistance[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1995, 247(2): 260-280. |
| 96 | CHANG Y M, CHEN C K M, KO T P, et al. Structural analysis of the antibiotic-recognition mechanism of MarR proteins[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D-Structural Biology, 2013, 69(6): 1138-1149. |
| 97 | WANG B J, BARAHONA M, BUCK M. A modular cell-based biosensor using engineered genetic logic circuits to detect and integrate multiple environmental signals[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2013, 40(1): 368-376. |
| 98 | FERNANDEZ-LOPEZ R, RUIZ R, DE LA CRUZ F, et al. Transcription factor-based biosensors enlightened by the analyte[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 648. |
| 99 | CHEN X, LV Y, WU R Q. Current technologies of synthetic biosensors for disease detection: design, classification and future perspectives[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(4): 240-251. |
| 100 | AUSLANDER D, EGGERSCHWILER B, KEMMER C, et al. A designer cell-based histamine-specific human allergy profiler[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4408. |
| 101 | BAI P, YE H F, XIE M Q, et al. A synthetic biology-based device prevents liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Hepatology, 2016, 65(1): 84-94. |
| 102 | YE H F, XIE M Q, XUE S, et al. Self-adjusting synthetic gene circuit for correcting insulin resistance[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 1: 0005. |
| 103 | SAXENA P, CHARPIN-EL HAMRI G, FOLCHER M, et al. Synthetic gene network restoring endogenous pituitary-thyroid feedback control in experimental Graves' disease[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(5): 1244-1249. |
| 104 | SMOLE A, LAINSCEK D, BEZELJAK U, et al. A synthetic mammalian therapeutic gene circuit for sensing and suppressing inflammation[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2017, 25(1): 102-119. |
| 105 | ZAGER V, CEMAZAR M, HRELJAC I, et al. Development of human cell biosensor system for genotoxicity detection based on DNA damage-induced gene expression[J]. Radiology and Oncology, 2010, 44(1): 42-51. |
| 106 | 刘泽辉, 张亚同, 胡欣. 我院茶碱血药浓度监测及其影响因素综合性评[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2016, 25(21): 2514-2520. |
| LIU Z H, ZHANG Y T, HU X. Analysis of influence factors on blood concentration monitoring of theophylline in our hospital [J]. Chinese Journal of New Drug, 2016, 25(21): 2514-2520. | |
| 107 | TIAN J Z, YANG G H, GU Y, et al. Developing an endogenous quorum-sensing based CRISPRi circuit for autonomous and tunable dynamic regulation of multiple targets in Streptomyces[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(14): 8188-8202. |
| 108 | CUNNINGHAM-BRYANT D, SUN J W, FERNANDEZ B, et al. CRISPR-Cas-mediated chemical control of transcriptional dynamics in yeast[J]. ChemBioChem, 2019, 20(12): 1519-1523. |
| 109 | WAN X Y, VOLPETTI F, PETROVA E, et al. Cascaded amplifying circuits enable ultrasensitive cellular sensors for toxic metals[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(5): 540-548. |
| [1] | 孙智, 杨宁, 娄春波, 汤超, 杨晓静. 功能拓扑的理性设计及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 444-463. |
| [2] | 储攀, 朱静雯, 黄文琦, 刘陈立, 傅雄飞. 底盘-回路耦合:合成基因回路设计新挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 91-105. |
| [3] | 林璐, 吕雪芹, 刘延峰, 堵国成, 陈坚, 刘龙. 枯草芽孢杆菌底盘细胞的设计、构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 247-265. |
| [4] | 张博, 马永硕, 尚轶, 黄三文. 植物合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 121-140. |
| [5] | 丁明珠, 李炳志, 王颖, 谢泽雄, 刘夺, 元英进. 合成生物学重要研究方向进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||