合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (6): 1081-1108.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-025
定向进化在蛋白质工程中的应用研究进展
祁延萍1,2, 朱晋1,2, 张凯1,2, 刘彤1, 王雅婕1,2
- 1.西湖大学工学院,浙江 杭州 310024
2.西湖大学合成生物学与生物智造中心,浙江 杭州 331712
-
收稿日期:2022-01-12修回日期:2022-01-20出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2023-01-17 -
通讯作者:王雅婕 -
作者简介:祁延萍 (1995—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为酿酒酵母代谢工程。E-mail:qiyanping@westlake.edu.cn
除通讯作者外,其他作者贡献相同。王雅婕 (1989—),女,西湖大学特聘研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为化学-酶偶联协同催化体系的构建、酶定向进化、代谢工程等。E-mail:wangyajie@westlake.edu.cn -
基金资助:西湖大学王雅婕实验室人才引进专项(103110456022101)
Recent development of directed evolution in protein engineering
QI Yanping1,2, ZHU Jin1,2, ZHANG Kai1,2, LIU Tong1, WANG Yajie1,2
- 1.School of Engineering,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310024,Zhejiang,China
2.Synthetic Biology and Biomanufacturing Center,Westlake University,Hangzhou 331712,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2022-01-12Revised:2022-01-20Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:WANG Yajie
摘要:
定向进化旨在通过基因多样化和突变体库筛选的迭代循环,加速实现在胞内或胞外进行的自然进化过程。近年来,因其强大的功能而被广泛应用于酶工程当中。本文概述了近十年助力定向进化发展的最新技术,包括胞外和胞内高效构建基因突变体库的方法、高通量筛选突变体库的方法、连续定向进化策略、自动化生物合成平台助力定向进化的策略、计算机技术辅助定向进化的应用实例。为了阐述定向进化在酶工程中的应用价值,本文着重讨论了利用定向进化技术对酶进行改造的代表性案例,其中包括改善酶在有机溶剂中的耐受性、提高酶的热稳定性、增强天然酶对非天然底物的催化能力、提高酶催化化学反应的选择性(包括区域选择性、立体选择性和对映选择性)以及拓展酶催化的反应类型。最后,本文对定向进化在未来可能遇到的挑战及应用前景进行了归纳总结。
引用本文
祁延萍, 朱晋, 张凯, 刘彤, 王雅婕. 定向进化在蛋白质工程中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108.
QI Yanping, ZHU Jin, ZHANG Kai, LIU Tong, WANG Yajie. Recent development of directed evolution in protein engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108.
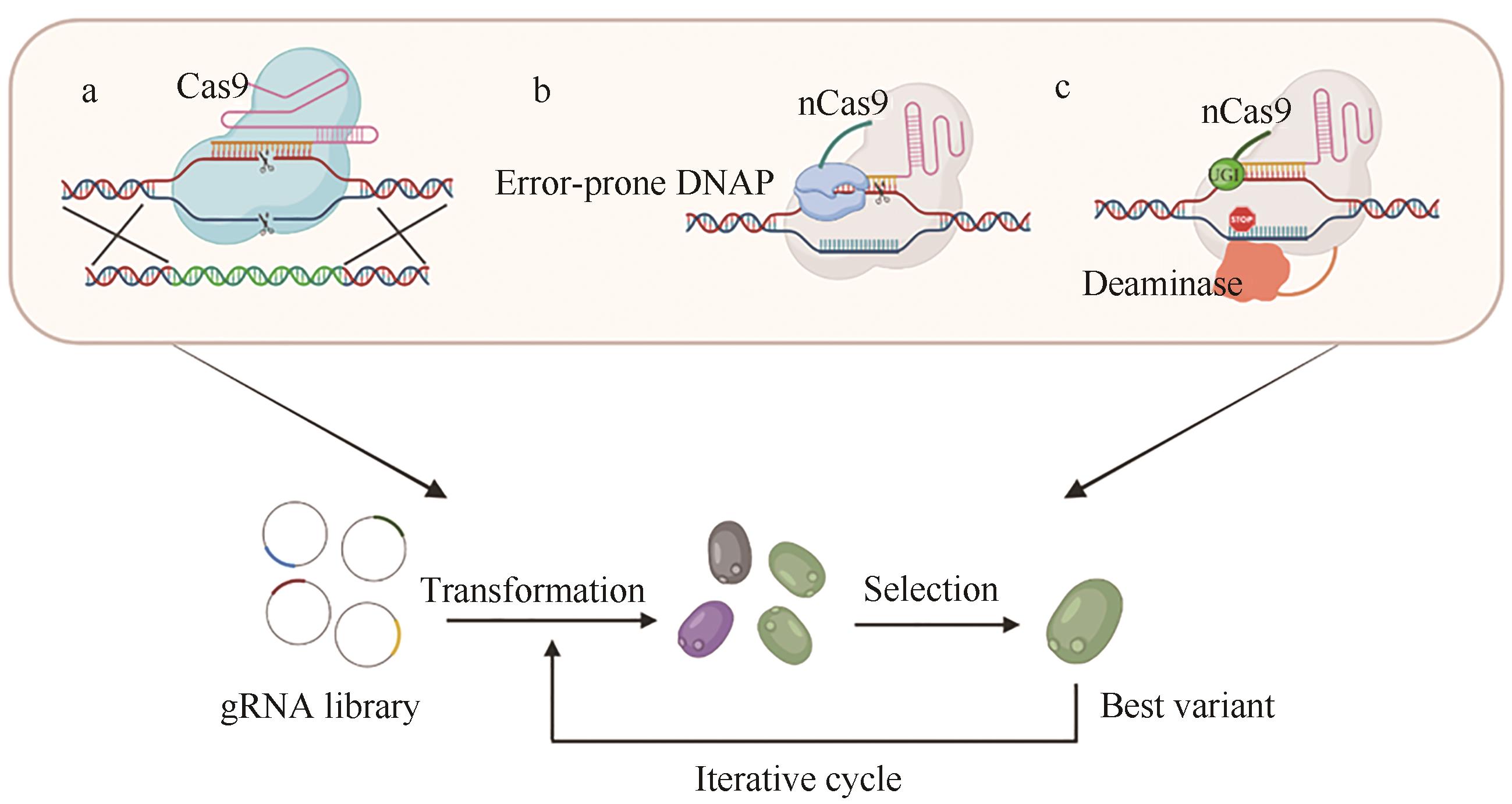
图2 基于CRISPR的体内突变方法[7]a—基于CRISPR-Cas9同源重组的突变;b—基于nCas9和DNA聚合酶I的突变;c—基于nCas9和碱基编辑器的突变
Fig. 2 CRISPR-assisted in vivo mutagenesis[7]a—CRISPR-Cas9-HDR; b—Random mutagenesis induced by nCas9-E. coli DNA PolI (error-prone) hybrid proteins; c—Gene mutangenesis caused by nCas9-deaminase hybrid proteins
目标蛋白 Target protein | 目标性状 Target phenotype | 基因回路设计 Genetic circuit design | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T7聚合酶 | 拓宽可识别的启动子范围[ | 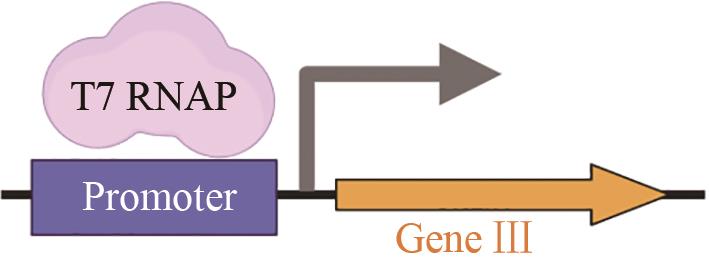 | |
| T7聚合酶 | 增强识别人工启动子的特异性[ | 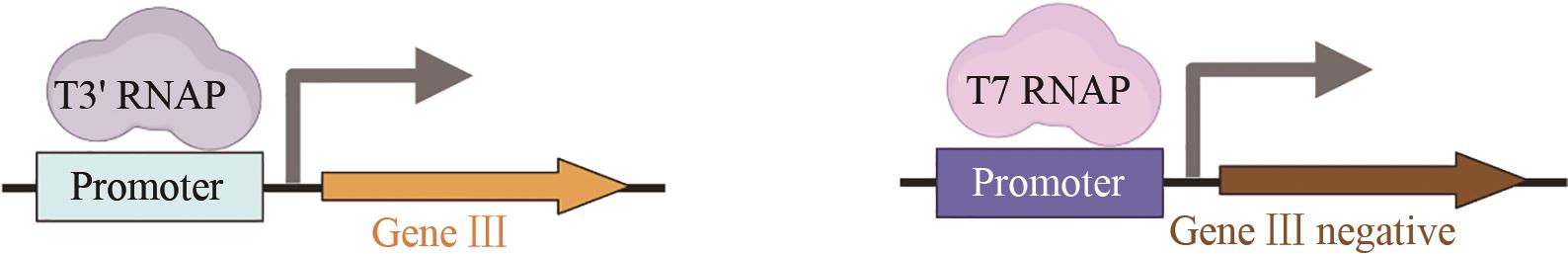 | |
| TALEN | DNA序列识别特异性[ | 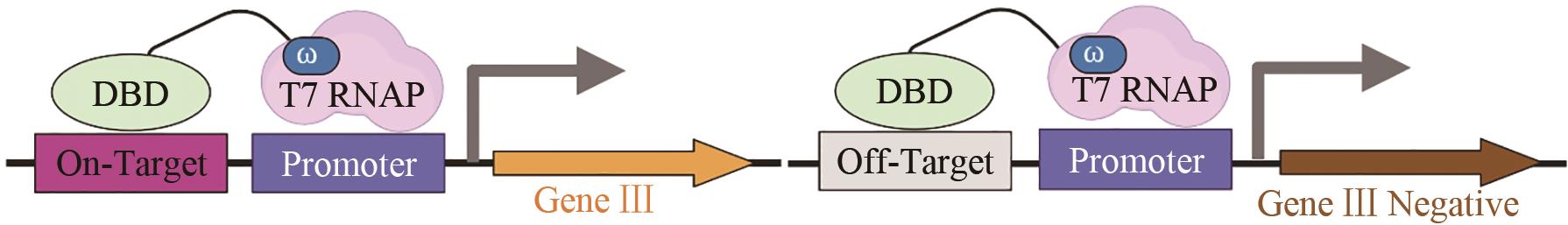 | |
| spCas9 | 拓宽可识别的PAM序列[ | 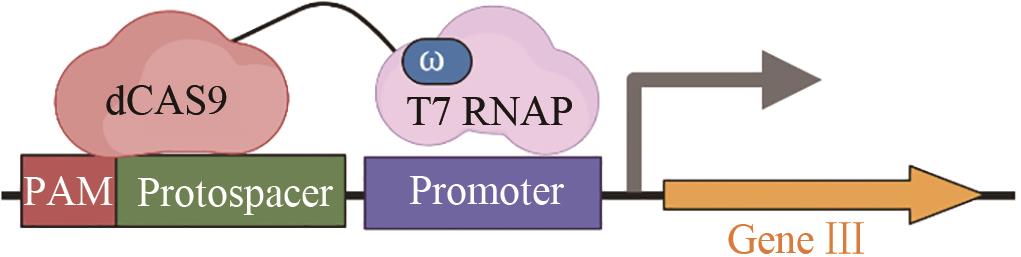 | |
| 胞嘧啶碱基编 辑器(CBEs) | 拓宽可编辑的基因序列范围(例如GC丰富的序列)[ | 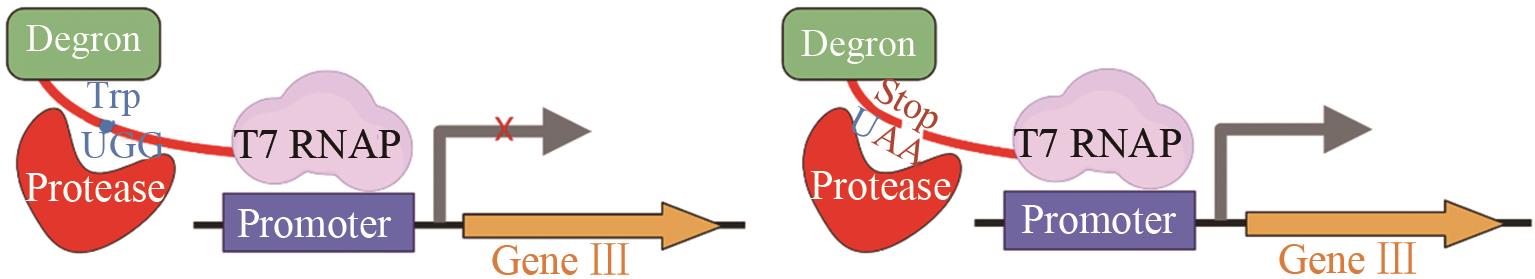 | |
| 腺嘌呤碱基编 辑器(ABEs) | 提高与Cas结构域的兼容性和编辑活性[ | 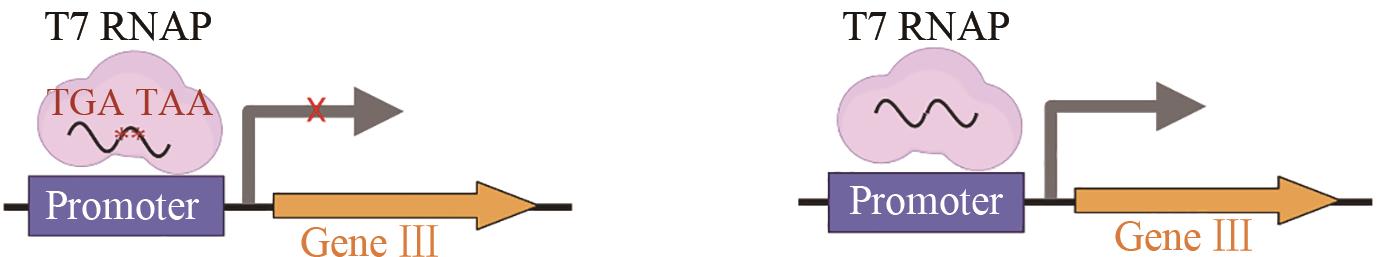 | |
| 苏云金芽孢杆菌δ-内毒素 | 增强与毛滴虫的钙黏蛋白样受体结合亲和力[ | 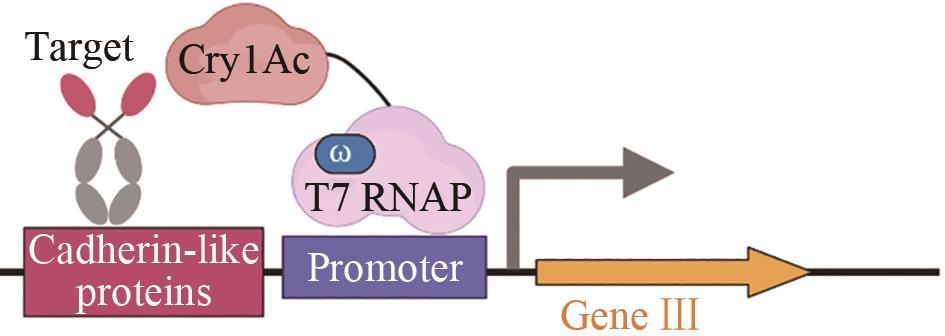 | |
| 抗体、麦芽糖 结合蛋白 | 增强目标蛋白 可溶性表达[ | 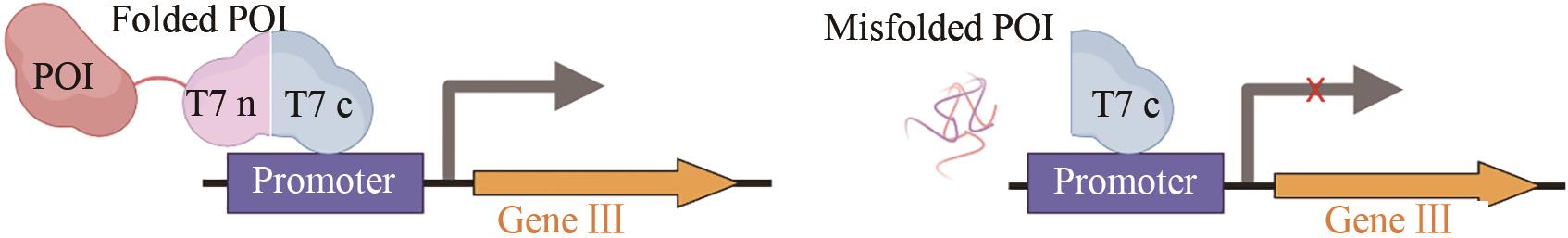 | |
| 蛋白水解酶 | 提高水解酶催化活性及底物特异性[ |  | |
| 肉毒神 经毒素 | 使肉毒神经毒素有可编程的特异性[ | ||
| 氨酰-tRNA 合成酶 | 生产高活性和选择性的正交氨基酰-tRNA合成酶[ |  | |
表1 PACE系统改造蛋白实例
Tab. 1 Cases for engineering proteins through PACE
目标蛋白 Target protein | 目标性状 Target phenotype | 基因回路设计 Genetic circuit design | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T7聚合酶 | 拓宽可识别的启动子范围[ |  | |
| T7聚合酶 | 增强识别人工启动子的特异性[ | 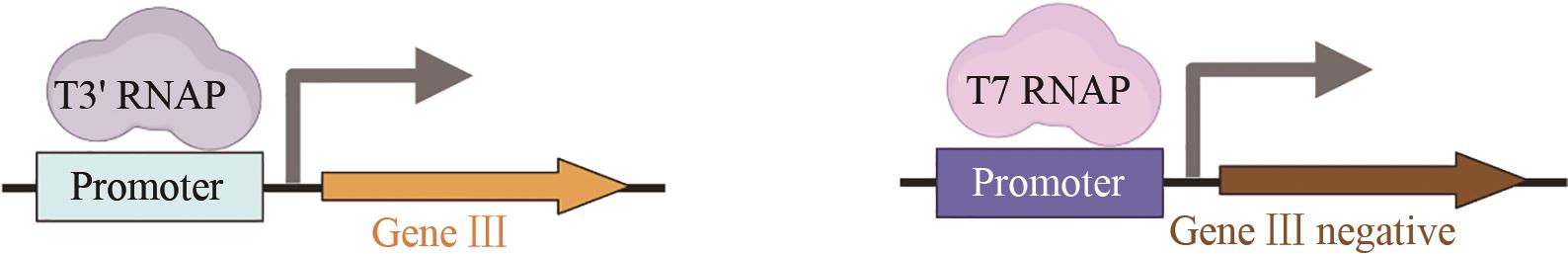 | |
| TALEN | DNA序列识别特异性[ |  | |
| spCas9 | 拓宽可识别的PAM序列[ |  | |
| 胞嘧啶碱基编 辑器(CBEs) | 拓宽可编辑的基因序列范围(例如GC丰富的序列)[ |  | |
| 腺嘌呤碱基编 辑器(ABEs) | 提高与Cas结构域的兼容性和编辑活性[ | 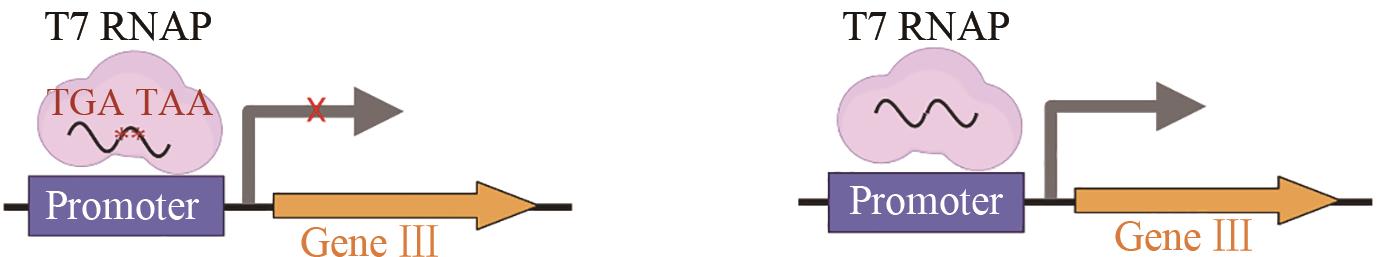 | |
| 苏云金芽孢杆菌δ-内毒素 | 增强与毛滴虫的钙黏蛋白样受体结合亲和力[ |  | |
| 抗体、麦芽糖 结合蛋白 | 增强目标蛋白 可溶性表达[ |  | |
| 蛋白水解酶 | 提高水解酶催化活性及底物特异性[ |  | |
| 肉毒神 经毒素 | 使肉毒神经毒素有可编程的特异性[ | ||
| 氨酰-tRNA 合成酶 | 生产高活性和选择性的正交氨基酰-tRNA合成酶[ |  | |
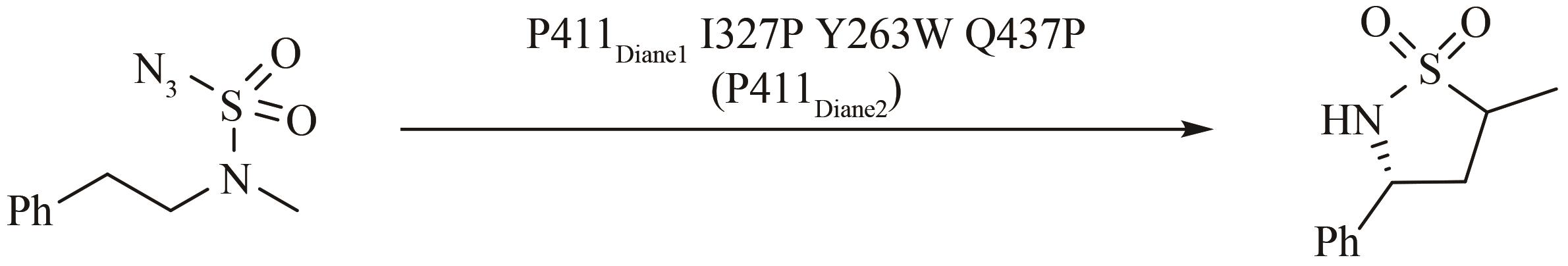
图10 P411Diane2催化的不对称C(sp3)—H氨基化
Fig. 10 P411Diane2 catalyzed asymmetric amination of primary, secondary and tertiary C(sp3)—H bonds via nitrene insertion

图 13 Aldolase催化的可逆羟醛缩合反应及β-羰基酮与氨基酸残基形成乙烯基酰胺的催化抑制机理
Fig. 13 Aldolase-catalyzed reversible aldol condensation reaction and the catalytic inhibition mechanism of β-carbonyl ketones with amino acid residues to form vinyl amides

图17 (a) Ir-Cyp119催化的柠檬烯的环丙化;(b) Ir-Cyp119催化的对映选择性、区域选择性C—H活化
Fig. 17 (a) Ir-Cyp119 catalyzed cyclopropanation of limonene; (b) Ir-Cyp119 catalyzed enantioselective and site-selective C—H activation
| 1 | ZUIN V G, EILKS I, ELSCHAMI M, et al. Education in green chemistry and in sustainable chemistry: perspectives towards sustainability[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(4): 1594-1608. |
| 2 | ARNOLD F H. Directed evolution: creating biocatalysts for the future[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1996, 51(23): 5091-5102. |
| 3 | CAMPOS K R, COLEMAN P J, ALVAREZ J C, et al. The importance of synthetic chemistry in the pharmaceutical industry[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6424): eaat0805. |
| 4 | BORNSCHEUER U T, HAUER B, JAEGER K E, et al. Directed evolution empowered redesign of natural proteins for the sustainable production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(1): 36-40. |
| 5 | ARNOLD F H, VOLKOV A A. Directed evolution of biocatalysts[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 1999, 3(1): 54-59. |
| 6 | PACKER M S, LIU D R. Methods for the directed evolution of proteins[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2015, 16(7): 379-394. |
| 7 | WANG Y J, XUE P, CAO M F, et al. Directed evolution: methodologies and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(20): 12384-12444. |
| 8 | LEUNG D W, CHEN E Y, GOEDDEL D V. A method for random mutagenesis of a defined DNA segment using a modified polymerase chain reaction[J]. Technique, 1989, 1(1): 11-15. |
| 9 | STEMMER W P. DNA shuffling by random fragmentation and reassembly: in vitro recombination for molecular evolution [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(22): 10747-10751. |
| 10 | MATTEUCCI M D, HEYNEKER H L. Targeted random mutagenesis: the use of ambiguously synthesized oligonucleotides to mutagenize sequences immediately 5' of an ATG initiation codon[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1983, 11(10): 3113-3121. |
| 11 | CHICA R A, DOUCET N, PELLETIER J N. Semi-rational approaches to engineering enzyme activity: combining the benefits of directed evolution and rational design[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2005, 16(4): 378-384. |
| 12 | YANG G Y, WITHERS S G. Ultrahigh-throughput FACS-based screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. ChemBioChem, 2009, 10(17): 2704-2715. |
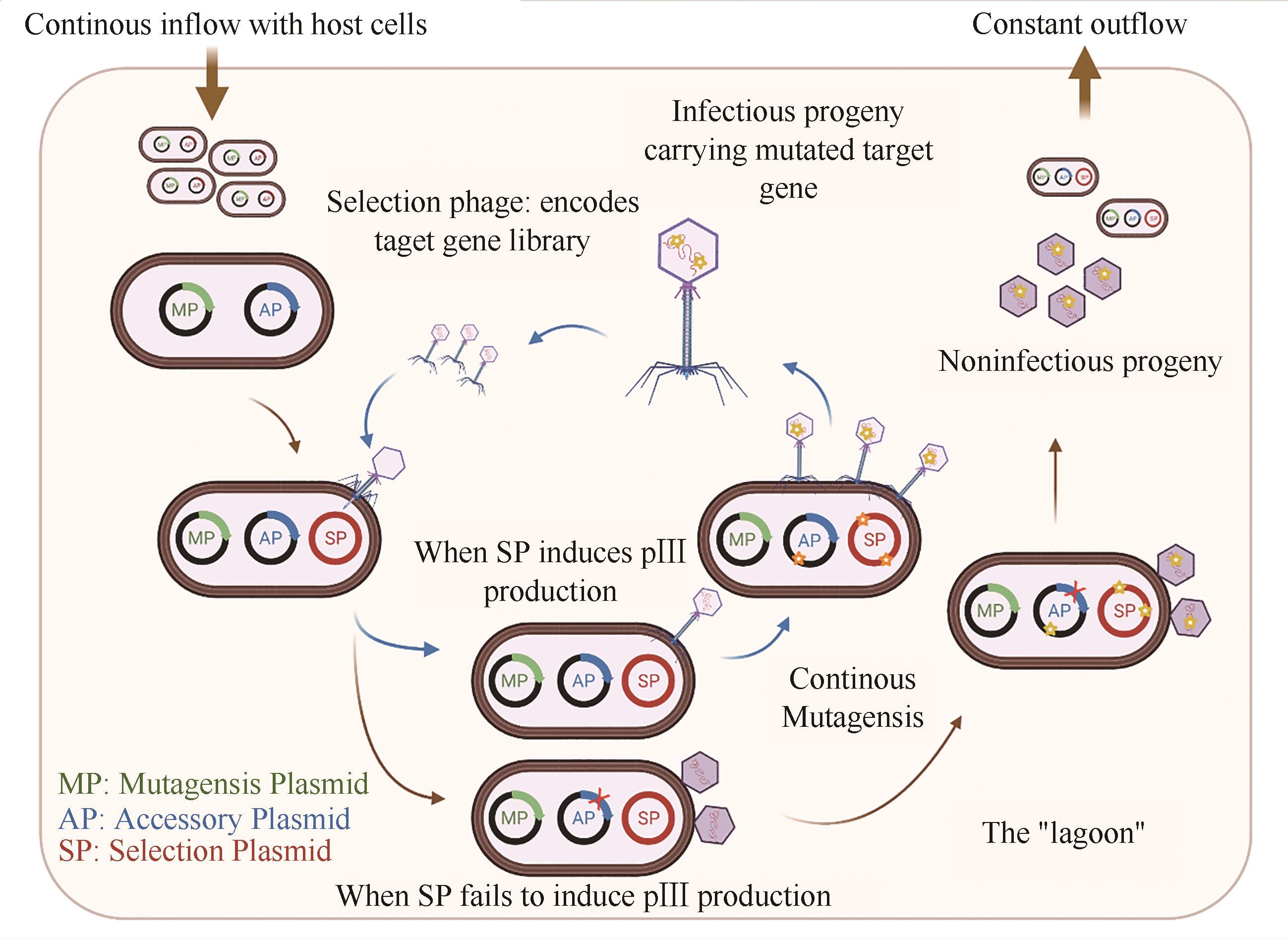
| 13 | SI T, LI B, COMI T J, et al. Profiling of microbial colonies for high-throughput engineering of multistep enzymatic reactions via optically guided matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(36): 12466-12473. |
| 14 | DIEFENBACH X W, FARASAT I, GUETSCHOW E D, et al. Enabling biocatalysis by high-throughput protein engineering using droplet microfluidics coupled to mass spectrometry[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(2): 1498-1508. |
| 15 | WU Z, KAN S B J, LEWIS R D, et al. Machine learning-assisted directed protein evolution with combinatorial libraries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(18): 8852-8858. |
| 16 | VOLK M J, LOURENTZOU I, MISHRA S, et al. Biosystems design by machine learning[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(7): 1514-1533. |
| 17 | WONG T S, TEE K L, HAUER B, et al. Sequence saturation mutagenesis (SeSaM): a novel method for directed evolution[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(3): e26. |
| 18 | LI A T, ACEVEDO-ROCHA C G, SUN Z T, et al. Beating bias in the directed evolution of proteins: combining high-fidelity on-chip solid-phase gene synthesis with efficient gene assembly for combinatorial library construction[J]. ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(3): 221-228. |
| 19 | 王未未, 张永昌, 刘明杰. 通过原位易错PCR一步构建基因突变文库[J]. 微生物学通报, 2014, 41(4): 719-724. |
| WANG W W, ZHANG Y C, LIU M J. One-step construction of mutagenesis libraries via in situ error-prone PCR[J]. Microbiology China, 2014, 41(4): 719-724. | |
| 20 | 佘文文, 倪静, 马立新. 一种改进的基于PCR的建立饱和突变库的方法[J]. 湖北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(1): 1-4, 9. |
| SHE W W, NI J, MA L X. An improved PCR-based method to create saturated mutagenic library[J]. Journal of Hubei University(Natural Sicence), 2019, 41(1): 1-4, 9. | |
| 21 | REETZ M T, BOCOLA M, CARBALLEIRA J D, et al. Expanding the range of substrate acceptance of enzymes: combinatorial active-site saturation test[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(27): 4192-4196. |
| 22 | REETZ M T, CARBALLEIRA J D. Iterative saturation mutagenesis (ISM) for rapid directed evolution of functional enzymes[J]. Nature Protocols, 2007, 2(4): 891-903. |
| 23 | XU J, CEN Y X, SINGH W, et al. Stereodivergent protein engineering of a lipase to access all possible stereoisomers of chiral esters with two stereocenters[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(19): 7934-7945. |
| 24 | SUN Z T, LONSDALE R, WU L, et al. Structure-guided triple-code saturation mutagenesis: efficient tuning of the stereoselectivity of an epoxide hydrolase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(3): 1590-1597. |
| 25 | ELLIS H M, YU D, DITIZIO T, et al. High efficiency mutagenesis, repair, and engineering of chromosomal DNA using single-stranded oligonucleotides[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(12): 6742-6746. |
| 26 | ANZALONE A V, KOBLAN L W, LIU D R. Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 824-844. |
| 27 | BAO Z H, XIAO H, LIANG J, et al. Homology-integrated CRISPR-Cas (HI-CRISPR) system for one-step multigene disruption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(5): 585-594. |
| 28 | RONDA C, PEDERSEN L E, SOMMER M O A, et al. CRMAGE: CRISPR optimized MAGE recombineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19452. |
| 29 | JAKOČIŪNAS T, PEDERSEN L E, LIS A V, et al. CasPER, a method for directed evolution in genomic contexts using mutagenesis and CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 48: 288-296. |
| 30 | HALPERIN S O, TOU C J, WONG E B, et al. CRISPR-guided DNA polymerases enable diversification of all nucleotides in a tunable window[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7717): 248-252. |
| 31 | TOU C J, SCHAFFER D V, DUEBER J E. Targeted diversification in the S. cerevisiae genome with CRISPR-guided DNA polymerase I[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(7): 1911-1916. |
| 32 | RAVIKUMAR A, ARZUMANYAN G A, OBADI M K A, et al. Scalable, continuous evolution of genes at mutation rates above genomic error thresholds[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(7): 1946-1957.e13. |
| 33 | RIX G, WATKINS-DULANEY E J, ALMHJELL P J, et al. Scalable continuous evolution for the generation of diverse enzyme variants encompassing promiscuous activities[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5644. |
| 34 | YI X, KHEY J, KAZLAUSKAS R J, et al. Plasmid hypermutation using a targeted artificial DNA replisome[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(29): eabg8712. |
| 35 | MASON D M, WEBER C R, PAROLA C, et al. High-throughput antibody engineering in mammalian cells by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology-directed mutagenesis[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(14): 7436-7449. |
| 36 | CHEN H Q, LIU S, PADULA S, et al. Efficient, continuous mutagenesis in human cells using a pseudo-random DNA editor[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(2): 165-168. |
| 37 | LI C, ZHANG R, MENG X B, et al. Targeted, random mutagenesis of plant genes with dual cytosine and adenine base editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 875-882. |
| 38 | CROOK N, ABATEMARCO J, SUN J, et al. In vivo continuous evolution of genes and pathways in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 13051. |
| 39 | AL'ABRI I S, HALLER D J, LI Z D, et al. Inducible directed evolution of complex phenotypes in bacteria[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(10): e58. |
| 40 | 杨建花, 苏晓岚, 朱蕾蕾. 高通量筛选系统在定向改造中的新进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. |
| YANG J H, SU X L, ZHU L L. Advances of high-throughput screening system in reengineering of biological entities[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. | |
| 41 | PASCHKE M. Phage display systems and their applications[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 70(1): 2-11. |
| 42 | LEE S Y, CHOI J H, XU Z H. Microbial cell-surface display[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2003, 21(1): 45-52. |
| 43 | VALENCIA C A, ZOU J W, LIU R H. In vitro selection of proteins with desired characteristics using mRNA-display[J]. Methods, 2013, 60(1): 55-69. |
| 44 | PARMLEY S F, SMITH G P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes[J]. Gene, 1988, 73(2): 305-318. |
| 45 | VICHIER-GUERRE S, FERRIS S, AUBERGER N, et al. A population of thermostable reverse transcriptases evolved from Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase I by phage display[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(37): 6133-6137. |
| 46 | LEVIN A M, WEISS G A. Optimizing the affinity and specificity of proteins with molecular display[J]. Molecular BioSystems, 2006, 2(1): 49-57. |
| 47 | GRINDEL B J, ENGEL B J, ONG J N, et al. Directed evolution of PD-L1-targeted affibodies by mRNA display[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2022, 17(6): 1543-1555. |
| 48 | TAN Y M, ZHANG Y, HAN Y B, et al. Directed evolution of an α1,3-fucosyltransferase using a single-cell ultrahigh-throughput screening method[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(10): eaaw8451. |
| 49 | XIAO H, BAO Z H, ZHAO H M. High throughput screening and selection methods for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(16): 4011-4020. |
| 50 | AGRESTI J J, ANTIPOV E, ABATE A R, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(9): 4004-4009. |
| 51 | OBEXER R, GODINA A, GARRABOU X, et al. Emergence of a catalytic tetrad during evolution of a highly active artificial aldolase[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(1): 50-56. |
| 52 | MA F Q, CHUNG M T, YAO Y, et al. Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1030. |
| 53 | FANG X N, ZHENG Y Z, DUAN Y K, et al. Recent advances in design of fluorescence-based assays for high-throughput screening[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(1): 482-504. |
| 54 | NISHIYAMA K, TAKAHASHI K, FUKUYAMA M, et al. Facile and rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibody based on a noncompetitive fluorescence polarization immunoassay in human serum samples[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2021, 190: 113414. |
| 55 | CAMARA A, GEORGE A, HEBNER E, et al. A fluorescence polarization-based high-throughput screen to identify the first small-molecule modulators of the human adenylyltransferase HYPE/FICD[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(19): 7128. |
| 56 | SHIROMA Y, FUJITA G, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Identification of a selective RelA inhibitor based on DSE-FRET screening methods[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(23): 9150. |
| 57 | FENN J B, MANN M, MENG C K, et al. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules[J]. Science, 1989, 246(4926): 64-71. |
| 58 | KARAS M, BACHMANN D, BAHR U, et al. Matrix-assisted ultraviolet laser desorption of non-volatile compounds[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 1987, 78: 53-68. |
| 59 | KARAS M, HILLENKAMP F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10, 000 daltons[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1988, 60(20): 2299-2301. |
| 60 | BAN L, PETTIT N, LI L, et al. Discovery of glycosyltransferases using carbohydrate arrays and mass spectrometry[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2012, 8(9): 769-773. |
| 61 | DE ROND T, DANIELEWICZ M, NORTHEN T. High throughput screening of enzyme activity with mass spectrometry imaging[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 31: 1-9. |
| 62 | GREVING M, CHENG X L, REINDL W, et al. Acoustic deposition with NIMS as a high-throughput enzyme activity assay[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 403(3): 707-711. |
| 63 | MRKSICH M. Mass spectrometry of self-assembled monolayers: a new tool for molecular surface science[J]. ACS Nano, 2008, 2(1): 7-18. |
| 64 | PLUCHINSKY A J, WACKELIN D J, HUANG X Y, et al. High throughput screening with SAMDI mass spectrometry for directed evolution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(47): 19804-19808. |
| 65 | LIU C, VAN BERKEL G J, KOVARIK P, et al. Fluid dynamics of the open port interface for high-speed nanoliter volume sampling mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(24): 8559-8567. |
| 66 | REETZ M T, BECKER M H, LIEBL M, et al. IR-thermographic screening of thermoneutral or endothermic transformations: the ring-closing olefin metathesis reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2000, 39(7): 1236-1239. |
| 67 | 任重远, 吴玉清. 生物酶活力的原位红外光谱测定[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(8): 2087-2093. |
| REN Z Y, WU Y Q. In situ infrared spectroscopic determination of enzyme activity[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(8): 2087-2093. | |
| 68 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 69 | YU X J, HUANG C Y, CHEN H, et al. High-throughput biochemical fingerprinting of oleaginous Aurantiochytrium sp. strains by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) for lipid and carbohydrate productions[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(8): 1593. |
| 70 | KOSA G, SHAPAVAL V, KOHLER A, et al. FTIR spectroscopy as a unified method for simultaneous analysis of intra-and extracellular metabolites in high-throughput screening of microbial bioprocesses[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 195. |
| 71 | ESVELT K M, CARLSON J C, LIU D R. A system for the continuous directed evolution of biomolecules[J]. Nature, 2011, 472(7344): 499-503. |
| 72 | CARLSON J C, BADRAN A H, GUGGIANA-NILO D A, et al. Negative selection and stringency modulation in phage-assisted continuous evolution[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(3): 216-222. |
| 73 | HUBBARD B P, BADRAN A H, ZURIS J A, et al. Continuous directed evolution of DNA-binding proteins to improve TALEN specificity[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(10): 939-942. |
| 74 | HU J H, MILLER S M, GEURTS M H, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 57-63. |
| 75 | THURONYI B W, KOBLAN L W, LEVY J M, et al. Continuous evolution of base editors with expanded target compatibility and improved activity[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(9): 1070-1079. |
| 76 | RICHTER M F, ZHAO K T, ETON E, et al. Phage-assisted evolution of an adenine base editor with improved Cas domain compatibility and activity[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 883-891. |
| 77 | BADRAN A H, GUZOV V M, HUAI Q, et al. Continuous evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins overcomes insect resistance[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7601): 58-63. |
| 78 | WANG T N, BADRAN A H, HUANG T P, et al. Continuous directed evolution of proteins with improved soluble expression[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(10): 972-980. |
| 79 | DICKINSON B C, PACKER M S, BADRAN A H, et al. A system for the continuous directed evolution of proteases rapidly reveals drug-resistance mutations[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5352. |
| 80 | PACKER M S, REES H A, LIU D R. Phage-assisted continuous evolution of proteases with altered substrate specificity[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 956. |
| 81 | BLUM T R, LIU H, PACKER M S, et al. Phage-assisted evolution of botulinum neurotoxin proteases with reprogrammed specificity[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6531): 803-810. |
| 82 | BRYSON D I, FAN C G, GUO L T, et al. Continuous directed evolution of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(12): 1253-1260. |
| 83 | WONG B G, MANCUSO C P, KIRIAKOV S, et al. Precise, automated control of conditions for high-throughput growth of yeast and bacteria with eVOLVER[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 614-623. |
| 84 | ZHONG Z W, WONG B G, RAVIKUMAR A, et al. Automated continuous evolution of proteins in vivo [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(6): 1270-1276. |
| 85 | DEBENEDICTIS E A, CHORY E J, GRETTON D W, et al. Systematic molecular evolution enables robust biomolecule discovery[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(1): 55-64. |
| 86 | SI T, CHAO R, MIN Y H, et al. Automated multiplex genome-scale engineering in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15187. |
| 87 | WANG Y, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. MACBETH: Multiplex automated Corynebacterium glutamicum base editing method[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 200-210. |
| 88 | YU H R, MA S, LI Y W, et al. Hot spots-making directed evolution easier[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 56: 107926. |
| 89 | MITCHELL A L, ALMEIDA A, BERACOCHEA M, et al. MGnify: the microbiome analysis resource in 2020[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(D1): D570-D578. |
| 90 | CONSORTIUM W, BURLEY S K, BERMAN H M, et al. Protein data bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 47(D1): D520-D528. |
| 91 | PEARCE R, ZHANG Y. Deep learning techniques have significantly impacted protein structure prediction and protein design[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2021, 68: 194-207. |
| 92 | WEBB B, SALI A. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER[J]. Current Protocols in Protein Science, 2016, 86(1): 2.9.1-2.9.37. |
| 93 | LEMAN J K, WEITZNER B D, LEWIS S M, et al. Macromolecular modeling and design in Rosetta: recent methods and frameworks[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(7): 665-680. |
| 94 | JUMPER J, EVANS R, PRITZEL A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 583-589. |
| 95 | DONALDSON L W. Molecular modeling the proteins from the exo-xis region of Lambda and Shigatoxigenic bacteriophages[J]. Antibiotics, 2021, 10(11): 1282. |
| 96 | ESPOSITO L, BALASCO N, SMALDONE G, et al. AlphaFold-predicted structures of KCTD proteins unravel previously undetected relationships among the members of the family[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(12): 1862. |
| 97 | PARK Y, STUKEY G J, JOG R, et al. Mutant phosphatidate phosphatase Pah1-W637A exhibits altered phosphorylation, membrane association, and enzyme function in yeast[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2022, 298(2): 101578. |
| 98 | WANG T W, LIANG C, HOU Y J, et al. Small design from big alignment: engineering proteins with multiple sequence alignment as the starting point[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2020, 42(8): 1305-1315. |
| 99 | MOTOYAMA T, HIRAMATSU N, ASANO Y, et al. Protein sequence selection method that enables full consensus design of artificial L-threonine 3-dehydrogenases with unique enzymatic properties[J]. Biochemistry, 2020, 59(40): 3823-3833. |
| 100 | STERNKE M, TRIPP K W, BARRICK D. Consensus sequence design as a general strategy to create hyperstable, biologically active proteins[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(23): 11275-11284. |
| 101 | HUNG J H, WENG Z. Sequence alignment and homology search with BLAST and ClustalW[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2016(11): 1-6. |
| 102 | TROTT O, OLSON A J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2010, 31(2): 455-461. |
| 103 | MOORE E J, ZORINE D, HANSEN W A, et al. Enzyme stabilization via computationally guided protein stapling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(47): 12472-12477. |
| 104 | BADILLO S, BANFAI B, BIRZELE F, et al. An introduction to machine learning[J]. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2020, 107(4): 871-885. |
| 105 | MAZURENKO S, PROKOP Z, DAMBORSKY J. Machine learning in enzyme engineering[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(2): 1210-1223. |
| 106 | ALQURAISHI M. Machine learning in protein structure prediction[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2021, 65: 1-8. |
| 107 | PRESNELL K V, ALPER H S. Systems metabolic engineering meets machine learning: a new era for data-driven metabolic engineering[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 14(9): 1800416. |
| 108 | WITTMANN B J, JOHNSTON K E, WU Z, et al. Advances in machine learning for directed evolution[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2021, 69: 11-18. |
| 109 | YANG K K, WU Z, ARNOLD F H. Machine-learning-guided directed evolution for protein engineering[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(8): 687-694. |
| 110 | ALLEY E C, KHIMULYA G, BISWAS S, et al. Unified rational protein engineering with sequence-based deep representation learning[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(12): 1315-1322. |
| 111 | LUO Y N, JIANG G D, YU T H, et al. ECNet is an evolutionary context-integrated deep learning framework for protein engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5743. |
| 112 | HUANG B, XU Y, HU X H, et al. A backbone-centred energy function of neural networks for protein design[J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7897): 523-528. |
| 113 | CHEN K, ARNOLD F H. Tuning the activity of an enzyme for unusual environments: sequential random mutagenesis of subtilisin E for catalysis in dimethylformamide[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1993, 90(12): 5618-5622. |
| 114 | YOU L, ARNOLD F H. Directed evolution of subtilisin E in Bacillus subtilis to enhance total activity in aqueous dimethylformamide[J]. Protein Engineering Design & Selection, 1996, 9(1): 77-83. |
| 115 | MOORE J C, ARNOLD F H. Directed evolution of a para-nitrobenzyl esterase for aqueous-organic solvents[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1996, 14(4): 458-467. |
| 116 | ZHAO H M, ARNOLD F H. Directed evolution converts subtilisin E into a functional equivalent of thermitase[J]. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 1999, 12(1): 47-53. |
| 117 | WU Y W, HU L, LI Z, et al. Catalytic asymmetric umpolung reactions of imines[J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7561): 445-450. |
| 118 | WALSH M P, PHELPS J M, LENNON M E, et al. Enantioselective synthesis of ammonium cations[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7874): 70-76. |
| 119 | SAVILE C K, JANEY J M, MUNDORFF E C, et al. Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5989): 305-309. |
| 120 | HUFFMAN M A, FRYSZKOWSKA A, ALVIZO O, et al. Design of an in vitro biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of islatravir[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6470): 1255-1259. |
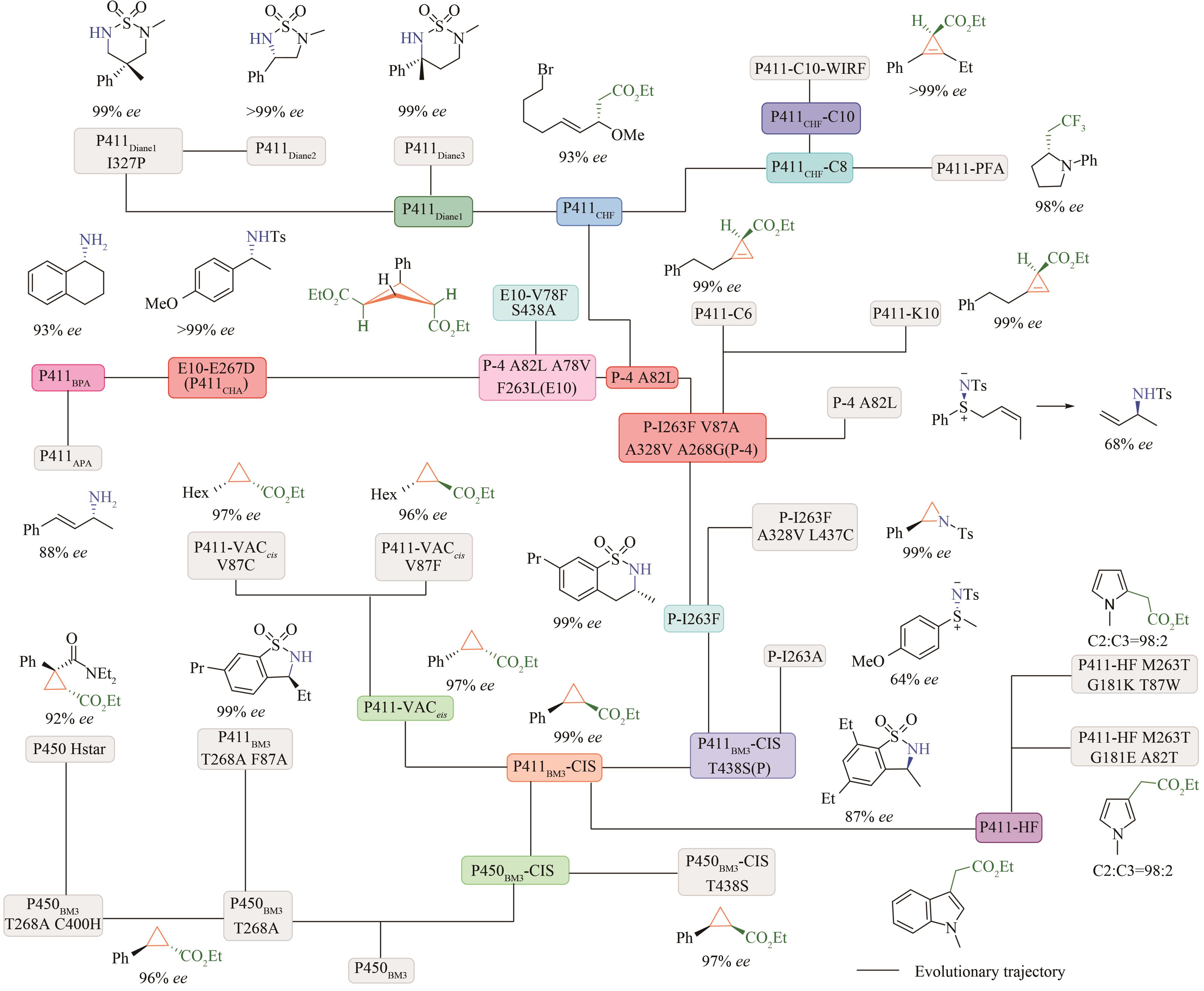
| 121 | YANG Y, ARNOLD F H. Navigating the unnatural reaction space: directed evolution of heme proteins for selective carbene and nitrene transfer[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2021, 54(5): 1209-1225. |
| 122 | CHEN K, ARNOLD F H. Engineering new catalytic activities in enzymes[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(3): 203-213. |
| 123 | COELHO P S, BRUSTAD E M, KANNAN A, et al. Olefin cyclopropanation via carbene transfer catalyzed by engineered cytochrome P450 enzymes[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6117): 307-310. |
| 124 | KAN S B J, LEWIS R D, CHEN K, et al. Directed evolution of cytochrome c for carbon-silicon bond formation: bringing silicon to life[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6315): 1048-1051. |
| 125 | HUANG X Y, GARCIA-BORRÀS M, MIAO K, et al. A biocatalytic platform for synthesis of chiral α- trifluoromethylated organoborons[J]. ACS Central Science, 2019, 5(2): 270-276. |
| 126 | YANG Y, CHO I, QI X T, et al. An enzymatic platform for the asymmetric amination of primary, secondary and tertiary C(sp3)-H bonds[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(11): 987-993. |
| 127 | CHEN K, HUANG X Y, KAN S B J, et al. Enzymatic construction of highly strained carbocycles[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6384): 71-75. |
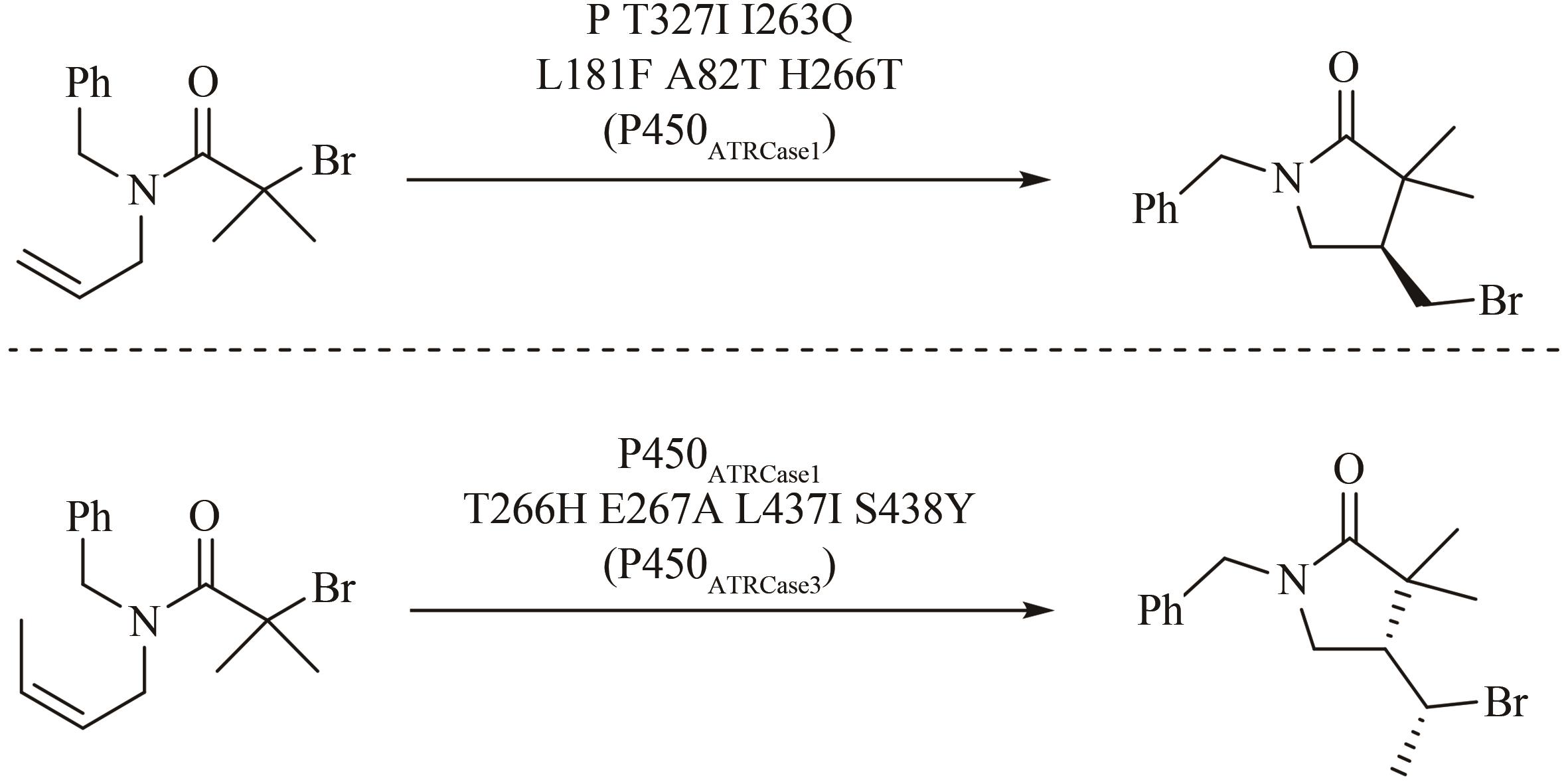
| 128 | ZHOU Q, CHIN M, FU Y, et al. Stereodivergent atom-transfer radical cyclization by engineered cytochromes P450[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6575): 1612-1616. |
| 129 | ZHOU P P, DU Y, XU N N, et al. Improved linalool production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by combining directed evolution of linalool synthase and overexpression of the complete mevalonate pathway[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 161: 107655. |
| 130 | SCHWIZER F, OKAMOTO Y, HEINISCH T, et al. Artificial metalloenzymes: reaction scope and optimization strategies[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(1): 142-231. |
| 131 | CHRISTOFFEL F, IGARETA N V, PELLIZZONI M M, et al. Design and evolution of chimeric streptavidin for protein-enabled dual gold catalysis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(8): 643-653. |
| 132 | ANISHCHENKO I, PELLOCK S J, CHIDYAUSIKU T M, et al. De novo protein design by deep network hallucination[J]. Nature, 2021, 600(7889): 547-552. |
| 133 | KEY H M, DYDIO P, CLARK D S, et al. Abiological catalysis by artificial haem proteins containing noble metals in place of iron[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7608): 534-537. |
| 134 | RICHTER F, BLOMBERG R, KHARE S D, et al. Computational design of catalytic dyads and oxyanion holes for ester hydrolysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(39): 16197-16206. |
| 135 | THOMPSON S K, HOYE T R. The aza-hexadehydro-diels-alder reaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(50): 19575-19580. |
| 136 | PREISWERK N, BECK T, SCHULZ J D, et al. Impact of scaffold rigidity on the design and evolution of an artificial Diels-Alderase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(22): 8013-8018. |
| 137 | JESCHEK M, REUTER R, HEINISCH T, et al. Directed evolution of artificial metalloenzymes for in vivo metathesis[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7622): 661-665. |
| 138 | CHATTERJEE A K, GRUBBS R H. Synthesis of trisubstituted alkenes via olefin cross-metathesis[J]. Organic Letters, 1999, 1(11): 1751-1753. |
| 139 | HUANG J, LIU Z N, BLOOMER B J, et al. Unnatural biosynthesis by an engineered microorganism with heterologously expressed natural enzymes and an artificial metalloenzyme[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2021, 13(12): 1186-1191. |
| 140 | GU Y, BLOOMER B J, LIU Z N, et al. Directed evolution of artificial metalloenzymes in whole cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 134(5): e202110519. |
| 141 | MARKEL U, ESSANI K D, BESIRLIOGLU V, et al. Advances in ultrahigh-throughput screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(1): 233-262. |
| 142 | CHAO R, MISHRA S, SI T, et al. Engineering biological systems using automated biofoundries[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 98-108. |
| 143 | BRYANT D H, BASHIR A, SINAI S, et al. Deep diversification of an AAV capsid protein by machine learning[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(6): 691-696. |
| 144 | WITTMANN B J, YUE Y S, ARNOLD F H. Informed training set design enables efficient machine learning-assisted directed protein evolution[J]. Cell Systems, 2021, 12(11): 1026-1045.e7. |
| [1] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [2] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [3] | 程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [4] | 付雨, 钟芳锐. 化学原理驱动的光生物不对称催化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [5] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [6] | 汤志军, 胡友财, 刘文. 酶促4+2和2+2环加成反应:区域与立体选择性的理解与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [7] | 张俊, 金诗雪, 云倩, 瞿旭东. 聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [8] | 孙梦楚, 陆亮宇, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 基于荧光检测的高通量筛选技术和装备助力细胞工厂构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| [9] | 明阳, 陈彬, 黄小强. 光酶催化合成进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 651-675. |
| [10] | 陈志航, 季梦麟, 戚逸飞. 人工智能蛋白质结构设计算法研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 464-487. |
| [11] | 康里奇, 谈攀, 洪亮. 人工智能时代下的酶工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. |
| [12] | 阮青云, 黄莘, 孟子钧, 全舒. 蛋白质稳定性计算设计与定向进化前沿工具[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. |
| [13] | 梁丽亚, 刘嵘明. 靶向DNA的Ⅱ类CRISPR/Cas系统的蛋白工程化改造[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| [14] | 崔馨予, 吴冉冉, 王园明, 朱之光. 酶促生物电催化系统的设计构建与强化[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 1006-1030. |
| [15] | 涂涛, 罗会颖, 姚斌. 蛋白质工程在饲料用酶研发中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 487-499. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||