合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 561-570.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-093
聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用
张俊1, 金诗雪2, 云倩2, 瞿旭东1
- 1.上海交通大学张江高等研究院,上海 201204
2.复旦大学药学院,上海 201203
-
收稿日期:2023-11-30修回日期:2024-01-08出版日期:2024-06-30发布日期:2024-07-12 -
通讯作者:瞿旭东 -
作者简介:张俊 (1992—),女,博士后。研究方向为聚酮化合物的生物合成与结构改造。E-mail:zhangjun2021@sjtu.edu.cn瞿旭东 (1980—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为天然产物生物合成与生物催化,通过生物合成与化学合成结合的方式,发展针对各类天然产物骨架的普适、高效的合成与编辑策略,用于拓展结构多样性和提高药物的生产效率,实现对天然产物资源的深度开发及天然药物的高效创制。E-mail:quxd19@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年科学基金(32200033)
Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines
ZHANG Jun1, JIN Shixue2, YUN Qian2, QU Xudong1
- 1.Zhangjiang Institute for Advanced Study,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 201204,China
2.School of Pharmacy,Fudan University,Shanghai 201203,China
-
Received:2023-11-30Revised:2024-01-08Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-12 -
Contact:QU Xudong
摘要:
聚酮天然产物包括10 000多种具有广泛生物活性的分子,是获批临床药物中最著名的类别之一。已知活性先导化合物通常需要经过结构修饰改良其吸收、分布、代谢和排泄等特性,从而促进成药开发,但针对聚酮化合物的结构修饰极具挑战,需要应对聚酮骨架中大量的立体中心以及多个惰性碳原子,导致化学合成手段难以对聚酮骨架进行精准和高效的衍生化,因此,通过合成生物学方法实现其结构优化就成为了研究者们关注的热点。自然界中,绝大多数聚酮化合物主要由简单的乙酸盐和丙酸盐结构单元通过聚酮合酶组装而成,而少数存在的具有特殊结构单元的聚酮案例给了研究者以灵感——通过设置和引入非天然结构单元从而有选择性地高效改造聚酮结构。聚酮骨架的生物合成有赖于一个起始单元与多个延伸单元的组装,因此,通过人工设计延伸单元向聚酮引入预期结构被认为是精准高效改造聚酮的有力突破点。本文在此总结了近十年来报道的聚酮非天然延伸单元的三种重要的酶促合成方法,通过挖掘新颖的延伸单元合成酶并探索其底物宽泛性,或利用酶工程手段改造延伸单元合成酶的底物催化范围,获得了大量自然界不存在的延伸单元。此外,本文还归纳了利用非天然延伸单元对聚酮结构进行改造的案例,借助聚酮的天然合成途径或利用改造的合成途径达到预期目的。最后,作者讨论了该研究领域内存在的一些制约因素以及可优化的研究方向,包括聚酮合酶对非天然延伸单元的兼容性问题、非天然延伸单元的前体供给等。近年来,利用非天然延伸单元改造聚酮结构的研究兴趣和热度日益高涨,本文绘制了一份基于延伸单元改造聚酮结构研究的简明清晰的图谱,期望为加速聚酮类药物的高效开发打下坚实基础。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张俊, 金诗雪, 云倩, 瞿旭东. 聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 561-570.
ZHANG Jun, JIN Shixue, YUN Qian, QU Xudong. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570.

图1 代表性聚酮类药物(a)和经典的聚酮天然产物红霉素A的生物合成途径(b)AT—酰基转移酶;ACP—酰基载体蛋白;DEBS—6-脱氧红霉内酯合酶;DH—脱水酶;ER—烯基还原酶;KR—酮还原酶;KS—酮缩合酶;TE—硫酯酶
Fig. 1 Selected polyketide drugs (a) and the classical polyketide synthase assembly line for the biosynthesis of erythromycin A (b)AT—acyltransferase; ACP—acyl carrier protein; DEBS—6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase; DH—dehydratase; ER—enoylreductase; KR—ketoreductase; KS—ketosynthase; TE—thioesterase
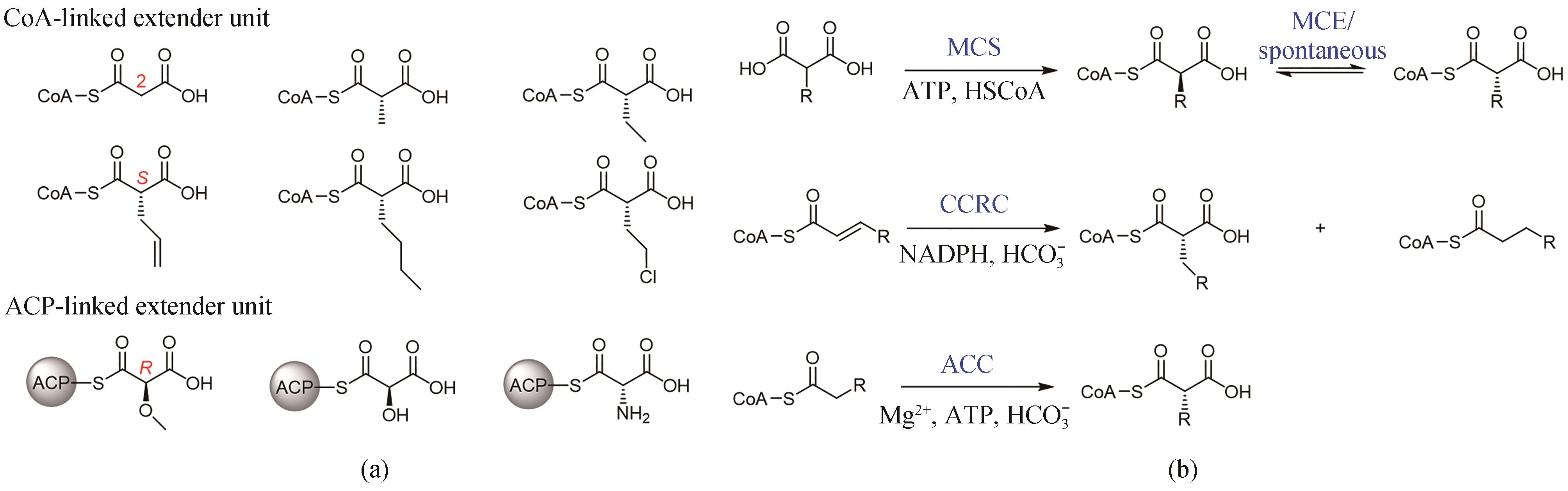
图2 天然延伸单元结构分类(a)和丙二酰辅酶A类延伸单元生物合成途径(b)MCS—丙二酰辅酶A合酶;CCRC—巴豆酰辅酶A还原/羧化酶;ACC—酰基辅酶A羧化酶;MCE—甲基丙二酰辅酶A异构酶;CoA—辅酶A;ACP—酰基载体蛋白
Fig. 2 Two classes of natural extender units (a) and the biosynthesis of malonyl-CoA extender units (b)MCS—malonyl-CoA synthetase; CCRC—crotonyl-CoA reductase/carboxylase; ACC—acyl-CoA carboxylase; MCE—methyl malonyl-CoA epimerase; CoA—coenzyme A; ACP—acyl carrier protein
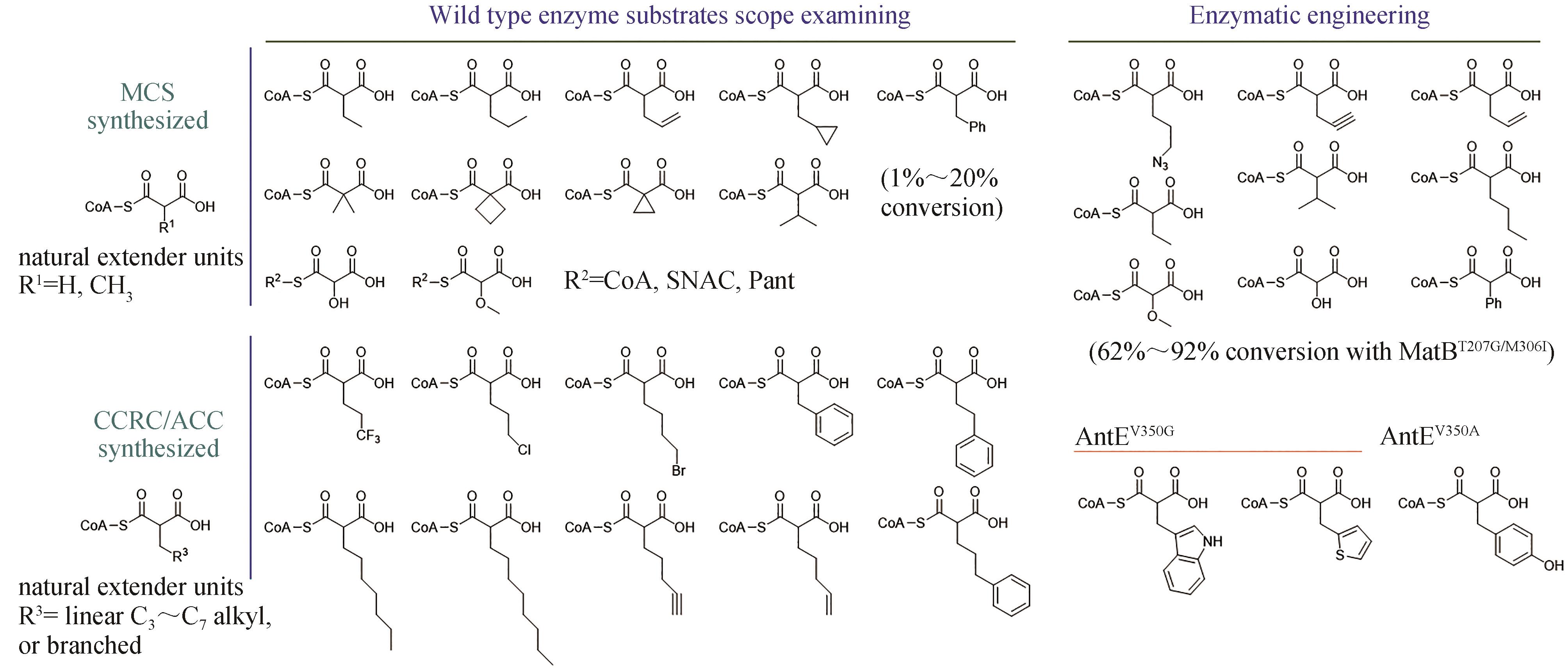
图3 通过酶底物谱探索或酶工程改造途径合成的非天然延伸单元MCS—丙二酰辅酶A合酶;CCRC—巴豆酰辅酶A还原/羧化酶;ACC—酰基辅酶A羧化酶;CoA—辅酶A;SNAC—N-乙酰半胱胺;Pant—泛硫乙胺
Fig. 3 Biosynthesis of unnatural extender units through engineering substrate spectrum or the enzymesMCS—malonyl-CoA synthetase; CCRC—crotonyl-CoA reductase/carboxylase; ACC—acyl-CoA carboxylase; CoA—Coenzyme A; SNAC—N-acetylcysteamine; Pant—pantetheine

图4 利用天然底物混杂性的AT改造聚酮侧链案例(蓝色为非天然延伸单元引入的非天然侧链)
Fig. 4 Modifications of polyketide sidechains through the biosynthesis of unnatural extender units with a natural promiscuous AT(Blue represents unnatural sidechains introduced by unnatural extender units)
| 1 | ROBERTSEN H L, MUSIOL-KROLL E M. Actinomycete-derived polyketides as a source of antibiotics and lead structures for the development of new antimicrobial drugs[J]. Antibiotics, 2019, 8(4): 157. |
| 2 | DAVISON E K, BRIMBLE M A. Natural product derived privileged scaffolds in drug discovery[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2019, 52: 1-8. |
| 3 | NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(3): 770-803. |
| 4 | LI G, LOU H X. Strategies to diversify natural products for drug discovery[J]. Medicinal Research Reviews, 2018, 38(4): 1255-1294. |
| 5 | KENNEDY J. Mutasynthesis, chemobiosynthesis, and back to semi-synthesis: combining synthetic chemistry and biosynthetic engineering for diversifying natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2008, 25(1): 25-34. |
| 6 | LIN Z, QU X D. Emerging diversity in polyketide synthase[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2022, 110: 154183. |
| 7 | YAN X L, ZHANG J, TAN H Q, et al. A pair of atypical KAS Ⅲ homologues with initiation and elongation functions program the polyketide biosynthesis in Asukamycin[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(19): e202200879. |
| 8 | KEATINGE-CLAY A T. The structures of type Ⅰ polyketide synthases[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2012, 29(10): 1050-1073. |
| 9 | ROBBINS T, LIU Y C, CANE D E, et al. Structure and mechanism of assembly line polyketide synthases[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2016, 41: 10-18. |
| 10 | HERTWECK C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(26): 4688-4716. |
| 11 | FISCHBACH M A, WALSH C T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2006, 106(8): 3468-3496. |
| 12 | WALKER P D, WEIR A N M, WILLIS C L, et al. Polyketide β-branching: diversity, mechanism and selectivity[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(4): 723-756. |
| 13 | CHAN Y A, PODEVELS A M, KEVANY B M, et al. Biosynthesis of polyketide synthase extender units[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2009, 26(1): 90-114. |
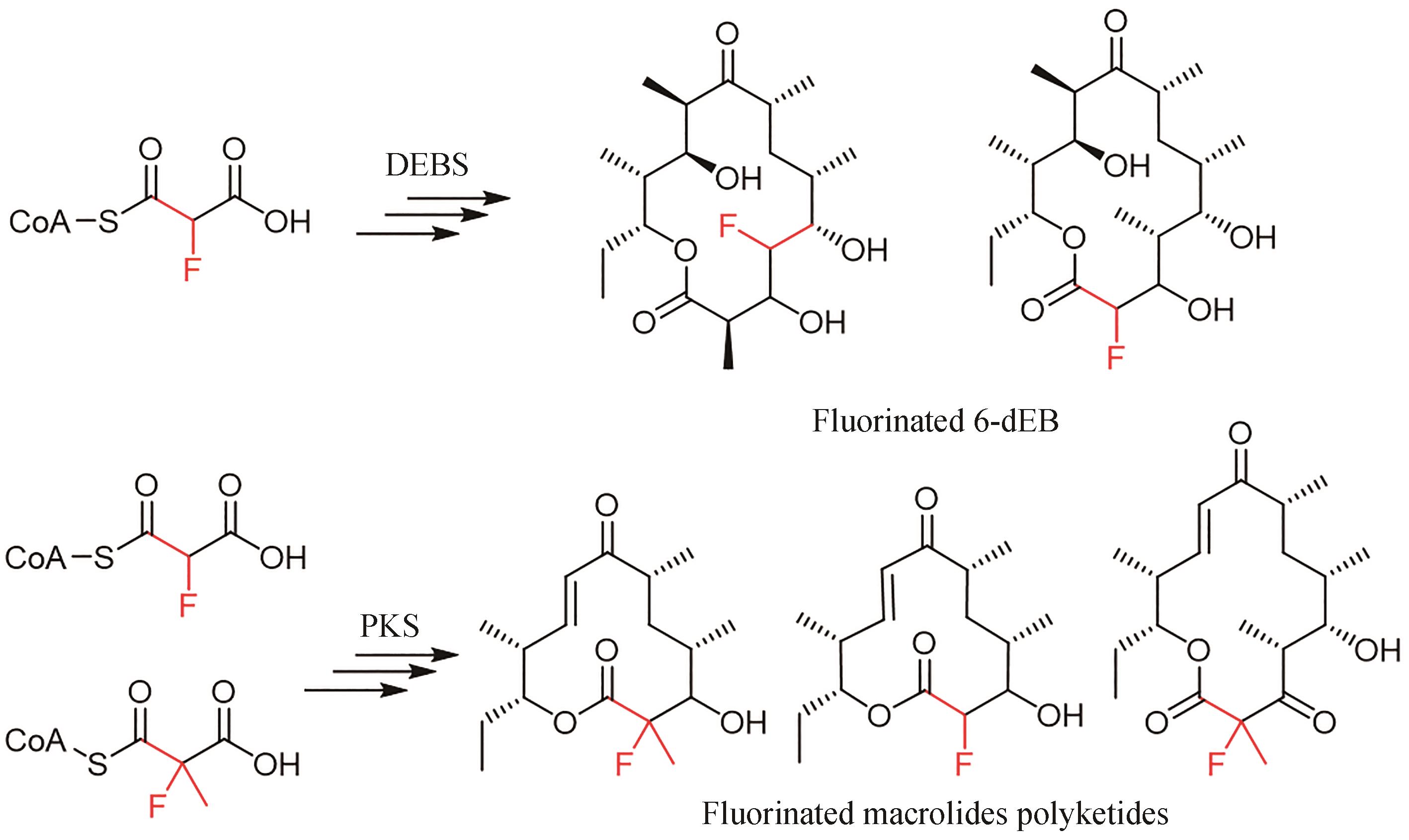
| 14 | LITTLE R F, HERTWECK C. Chain release mechanisms in polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide biosynthesis[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2022, 39(1): 163-205. |
| 15 | MOORE B S, HERTWECK C. Biosynthesis and attachment of novel bacterial polyketide synthase starter units[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2002, 19(1): 70-99. |
| 16 | WILSON M C, MOORE B S. Beyond ethylmalonyl-CoA: the functional role of crotonyl-CoA carboxylase/reductase homologs in expanding polyketide diversity[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2012, 29(1): 72-86. |
| 17 | RAY L, MOORE B S. Recent advances in the biosynthesis of unusual polyketide synthase substrates[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(2): 150-161. |
| 18 | BISSELL A U, RAUTSCHEK J, HOEFGEN S, et al. Biosynthesis of the sphingolipid inhibitors sphingofungins in filamentous fungi requires aminomalonate as a metabolic precursor[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2022, 17(2): 386-394. |
| 19 | ZHAO C H, COUGHLIN J M, JU J H, et al. Oxazolomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces albus JA3453 featuring an “acyltransferase-less” type Ⅰ polyketide synthase that incorporates two distinct extender units[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(26): 20097-20108. |
| 20 | CHEN D D, ZHANG Q, ZHANG Q L, et al. Improvement of FK506 production in Streptomyces tsukubaensis by genetic enhancement of the supply of unusual polyketide extender units via utilization of two distinct site-specific recombination systems[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(15): 5093-5103. |
| 21 | KATO Y, BAI L Q, XUE Q, et al. Functional expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of the novel polyketide chain extension unit, methoxymalonyl-acyl carrier protein, and engineered biosynthesis of 2-desmethyl-2-methoxy-6-deoxyerythronolide B[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(19): 5268-5269. |
| 22 | CARPENTER S M, WILLIAMS G J. Extender unit promiscuity and orthogonal protein interactions of an aminomalonyl-ACP utilizing trans-acyltransferase from zwittermicin biosynthesis[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2018, 13(12): 3361-3373. |
| 23 | DODGE G J, MALONEY F P, SMITH J L. Protein-protein interactions in “cis-AT” polyketide synthases[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2018, 35(10): 1082-1096. |
| 24 | KOSOL S, JENNER M, LEWANDOWSKI J R, et al. Protein-protein interactions in trans-AT polyketide synthases[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2018, 35(10): 1097-1109. |
| 25 | ZHANG F, JI H N, ALI I, et al. Structural and biochemical insight into the recruitment of acyl carrier protein-linked extender units in ansamitocin biosynthesis[J]. Chembiochem, 2020, 21(9): 1309-1314. |
| 26 | ZHENG M M, ZHANG J, ZHANG W, et al. An atypical acyl-CoA synthetase enables efficient biosynthesis of extender units for engineering a polyketide carbon scaffold[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(43): e202208734. |
| 27 | AN J H, KIM Y S. A gene cluster encoding malonyl-CoA decarboxylase (MatA), malonyl-CoA synthetase (MatB) and a putative dicarboxylate carrier protein (MatC) in Rhizobium trifolii: cloning, sequencing, and expression of the enzymes in Escherichia coli [J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1998, 257(2): 395-402. |
| 28 | POHL N L, HANS M, LEE H Y, et al. Remarkably broad substrate tolerance of malonyl-CoA synthetase, an enzyme capable of intracellular synthesis of polyketide precursors[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(24): 5822-5823. |
| 29 | HUGHES A J, KEATINGE-CLAY A. Enzymatic extender unit generation for in vitro polyketide synthase reactions: structural and functional showcasing of Streptomyces coelicolor MatB[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2011, 18(2): 165-176. |
| 30 | ERB T J, BERG I A, BRECHT V, et al. Synthesis of C5-dicarboxylic acids from C2-units involving crotonyl-CoA carboxylase/reductase: the ethylmalonyl-CoA pathway[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(25): 10631-10636. |
| 31 | YAN Y, CHEN J, ZHANG L H, et al. Multiplexing of combinatorial chemistry in antimycin biosynthesis: expansion of molecular diversity and utility[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(47): 12308-12312. |
| 32 | VÖGELI B, GEYER K, GERLINGER P D, et al. Combining promiscuous acyl-CoA oxidase and enoyl-CoA carboxylase/reductases for atypical polyketide extender unit biosynthesis[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2018, 25(7): 833-839.e4. |
| 33 | RAY L, VALENTIC T R, MIYAZAWA T, et al. A crotonyl-CoA reductase-carboxylase independent pathway for assembly of unusual alkylmalonyl-CoA polyketide synthase extender units[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 13609. |
| 34 | ZHANG J, ZHENG M M, YAN J Y, et al. A permissive medium chain acyl-CoA carboxylase enables the efficient biosynthesis of extender units for engineering polyketide carbon scaffolds[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(19): 12179-12185. |
| 35 | TRAN T H, HSIAO Y S, JO J, et al. Structure and function of a single-chain, multi-domain long-chain acyl-CoA carboxylase[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7537): 120-124. |
| 36 | FARINAS E T, BULTER T, ARNOLD F H. Directed enzyme evolution[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2001, 12(6): 545-551. |
| 37 | NODA-GARCIA L, TAWFIK D S. Enzyme evolution in natural products biosynthesis: target- or diversity-oriented?[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2020, 59: 147-154. |
| 38 | KORYAKINA I, WILLIAMS G J. Mutant malonyl-CoA synthetases with altered specificity for polyketide synthase extender unit generation[J]. Chembiochem, 2011, 12(15): 2289-2293. |
| 39 | KORYAKINA I, MCARTHUR J, RANDALL S, et al. Poly specific trans-acyltransferase machinery revealed via engineered acyl-CoA synthetases[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2013, 8(1): 200-208. |
| 40 | ZHANG L H, MORI T, ZHENG Q F, et al. Rational control of polyketide extender units by structure-based engineering of a crotonyl-CoA carboxylase/reductase in antimycin biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(45): 13462-13465. |
| 41 | QUADE N, HUO L J, RACHID S, et al. Unusual carbon fixation gives rise to diverse polyketide extender units[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2012, 8(1): 117-124. |
| 42 | TIAN W Y, CHEN X R, ZHANG J, et al. Biosynthesis of tetronates by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase-polyketide synthase system[J]. Organic Letters, 2023, 25(10): 1628-1632. |
| 43 | AWAKAWA T, FUJIOKA T, ZHANG L H, et al. Reprogramming of the antimycin NRPS-PKS assembly lines inspired by gene evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3534. |
| 44 | WALKER M C, THURONYI B W, CHARKOUDIAN L K, et al. Expanding the fluorine chemistry of living systems using engineered polyketide synthase pathways[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6150): 1089-1094. |
| 45 | SIRIRUNGRUANG S, AD O, PRIVALSKY T M, et al. Engineering site-selective incorporation of fluorine into polyketides[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(8): 886-893. |
| 46 | RITTNER A, JOPPE M, SCHMIDT J J, et al. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated polyketides[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2022, 14(9): 1000-1006. |
| 47 | LI Y, ZHANG W, ZHANG H, et al. Structural basis of a broadly selective acyltransferase from the polyketide synthase of splenocin[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(20): 5823-5827. |
| 48 | KALKREUTER E, CROWETIPTON J M, LOWELL A N, et al. Engineering the substrate specificity of a modular polyketide synthase for installation of consecutive non-natural extender units[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(5): 1961-1969. |
| 49 | ENGLUND E, SCHMIDT M, NAVA A A, et al. Expanding extender substrate selection for unnatural polyketide biosynthesis by acyltransferase domain exchange within a modular polyketide synthase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(16): 8822-8832. |
| 50 | MUSIOL-KROLL E M, WOHLLEBEN W. Acyltransferases as tools for polyketide synthase engineering[J]. Antibiotics, 2018, 7(3): 62. |
| 51 | CHANG C C, HUANG R, YAN Y, et al. Uncovering the formation and selection of benzylmalonyl-CoA from the biosynthesis of splenocin and enterocin reveals a versatile way to introduce amino acids into polyketide carbon scaffolds[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(12): 4183-4190. |
| 52 | ZHU X J, LIU J, ZHANG W J. De novo biosynthesis of terminal alkyne-labeled natural products[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(2): 115-120. |
| [1] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [2] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [3] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [4] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [5] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [6] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [7] | 程中玉, 李付琸. 基于P450选择性氧化的天然产物化学-酶法合成进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 960-980. |
| [8] | 刘子健, 穆柏杨, 段志强, 王璇, 陆晓杰. 与核酸兼容的化学反应开发进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [9] | 张守祺, 王涛, 孔尧, 邹家胜, 刘元宁, 徐正仁. 天然产物的化学-酶法合成:方法与策略的演进[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [10] | 谢向前, 郭雯, 王欢, 李进. 含氨基乙烯半胱氨酸核糖体肽的生物合成与化学合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [11] | 汤志军, 胡友财, 刘文. 酶促4+2和2+2环加成反应:区域与立体选择性的理解与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [12] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [13] | 虞旭昶, 吴辉, 李雷. 文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选驱动的微生物天然产物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| [14] | 冯金, 潘海学, 唐功利. 近十年天然产物药物的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 408-446. |
| [15] | 奚萌宇, 胡逸灵, 顾玉诚, 戈惠明. 基因组挖掘指导天然药物分子的发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||