合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 492-506.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-083
文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选驱动的微生物天然产物高效发现
虞旭昶1,2, 吴辉2, 李雷1
- 1.上海交通大学生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,上海 200240
2.华东理工大学生物工程学院,生物反应器工程国家重点实验室,上海 200237
-
收稿日期:2023-11-27修回日期:2024-01-26出版日期:2024-06-30发布日期:2024-07-12 -
通讯作者:吴辉,李雷 -
作者简介:虞旭昶 (2000—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为微生物天然产物创新发现与高效制造。E-mail:yxc@ecust.edu.cn吴辉 (1982—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为微生物代谢设计与重编程。E-mail:hwu@ecust.edu.cn李雷 (1989—),男,长聘教轨副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为微生物天然药物化学与合成生物学。E-mail:lei.li@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFA0914200);国家自然科学基金面上项目(32370070)
Library construction and targeted BGC screening for more efficient discovery of microbial natural products
YU Xuchang1,2, WU Hui2, LI Lei1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
2.State key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering,School of Biological Engineering,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
-
Received:2023-11-27Revised:2024-01-26Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-12 -
Contact:WU Hui, LI Lei
摘要:
微生物天然产物作为小分子药物的主要来源,已被广泛应用于医药与农业等领域。随着全球抗生素耐药性与其他公共健康问题的加剧,新结构、新靶点微生物天然产物发现迫在眉睫。大规模(宏)基因组测序揭示微生物蕴含了巨大的生物合成潜力,相继催生了多种不同类型的天然产物挖掘策略。然而,目前仍然缺乏将天然产物合成基因簇与编码产物快速关联的高效方案。近年来,(宏)基因组文库构建在获取批量天然产物合成基因簇方面展现出明显优势,结合高效的基因簇靶向筛选方法,显著加速了新结构天然产物系统发现。本文综述了三类基于(宏)基因组文库构建与靶向筛选驱动天然产物创新发现的策略,主要从克隆载体类型、文库构建方式、基因簇靶向筛选方法等角度进行了阐述,并对Cosmid/Fosmid文库、BAC/PAC文库、FAC/YAC文库等不同文库类型的优缺点及应用范围进行了对比,最后对这些策略的发展前景进行了展望。未来,基于文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选策略将极大驱动不同生境微生物来源的活性天然产物挖掘,预期大量新靶点、新结构天然产物将不断涌现。
中图分类号:
引用本文
虞旭昶, 吴辉, 李雷. 文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选驱动的微生物天然产物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 492-506.
YU Xuchang, WU Hui, LI Lei. Library construction and targeted BGC screening for more efficient discovery of microbial natural products[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 492-506.

图1 土壤宏基因组Cosmid文库构建驱动新化合物高效挖掘(NPST—天然产物序列标签。采用基于共现网络的CONKAT-Seq策略或基于eSNaPD软件的谱系分析获取感兴趣的基因簇,通过异源表达或化学合成方法获取新化合物。)
Fig. 1 Construction of soil metagenomic cosmid libraries for the discovery of novel compounds(NPST—Natural Products Sequence Tag. The CONKAT-Seq strategy based on co-occurrence network or phylogenetic analysis strategy based on eSNaPD software is used to identify BGCs of interest. Then, novel NPs are obtained by heterologous expression or chemical synthesis.)
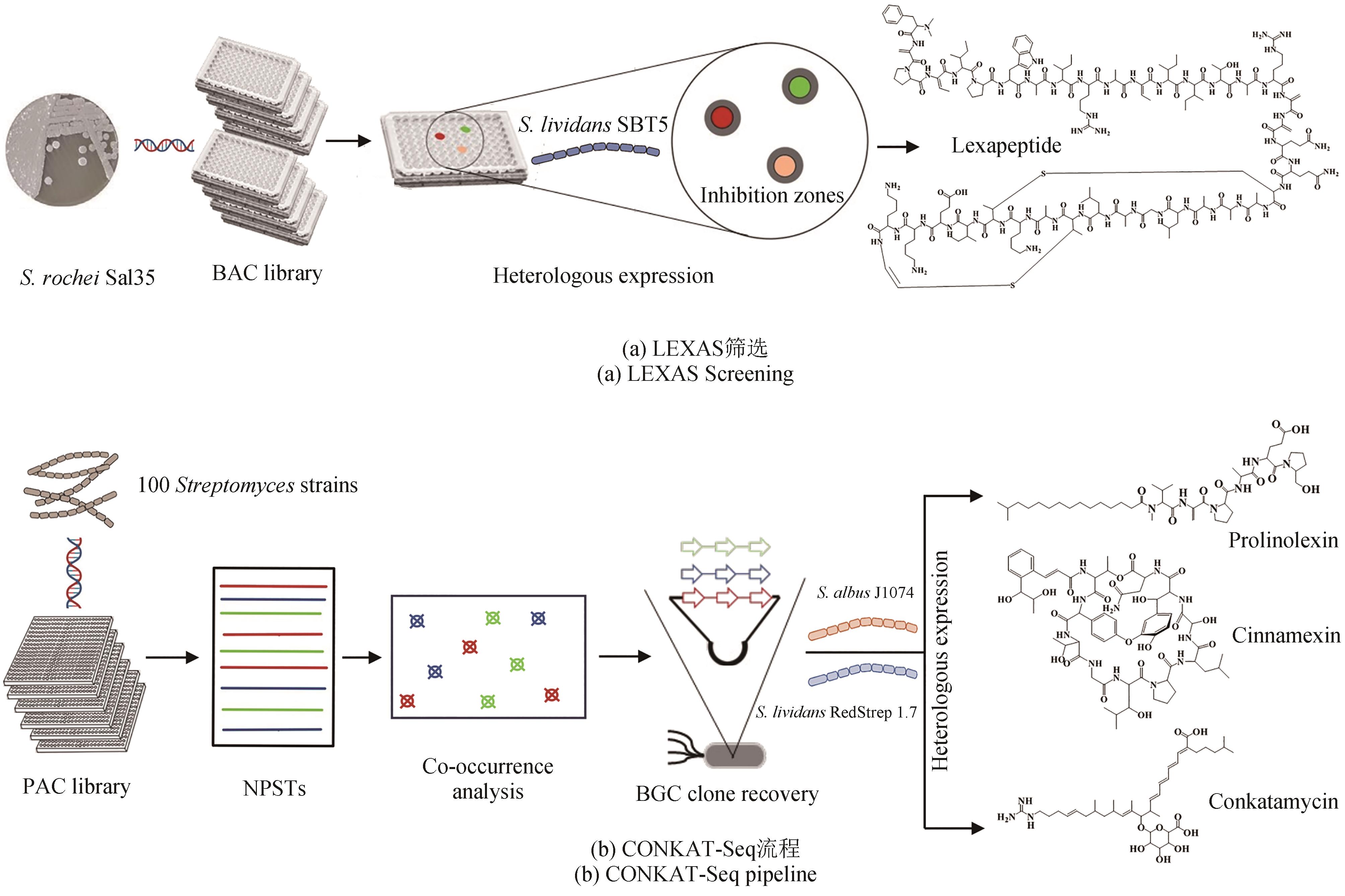
图2 细菌基因组BAC/PAC文库构建加速活性天然产物高通量挖掘。(a)构建娄彻氏链霉菌Streptomyces rochei Sal35基因组BAC文库,建立LEXAS筛选系统,高效挖掘新化合物;(b)构建100株链霉菌基因组PAC文库,采用基于共现网络的CONKAT-Seq策略大规模获取新的非核糖体或聚酮类化合物合成基因簇,并在不同宿主中异源表达,高效获取新化合物
Fig. 2 Construction of bacterial genome BAC/PAC libraries for the high-throughput mining of bioactive natural products.(a) BAC library construction for the genome of S. rochei Sal35 combined with the LEXAS screening system is used for the high-efficient mining of novel compounds; (b) PAC library construction for the genomes of 100 Streptomyces combined with the CONKAT-Seq strategy based on co-occurrence network is used to identify novel BGCs encoding NRP and PK, and then heterologous expression can be performed in different hosts to discover novel compounds.

图3 真菌基因组FAC文库构建驱动真菌天然产物创新发现(采用非靶向代谢组学打分系统,精准实现新化合物的筛选与分离)
Fig. 3 Construction of fungal genome FAC libraries for discovering fungal natural products(An untargeted metabolomics scoring system was used to accurately screen and separate novel compounds.)
| 文库 类型 | 插入 大小 | 核心 元件 | 筛选方法 | 文库针对 类型 | 基因簇获取通量 | 获得化合物 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cosmid | 约40 kb | COS位点 质粒元件 | CONKAT-seq | 宏基因组 | 107个 克隆 | Omnipeptin(NRP) | 适合宏基因组挖掘 | 克隆片段大小相对较小,在克隆大尺度BGC(>40 kb)方面存在局限 | Libis等(2019)[ |
| 约40 kb | eSNaPD | 宏基因组 | >2×107个 克隆 | MBA3(NRP) | Li等 (2022)[ | ||||
| Fosmid | 约40 kb | COS位点 F因子元件 | 序列引导的PCR筛选 | (宏) 基因组 | 2880个 克隆 | Actinonin(NRP) | Wolf等(2018)[ | ||
| BAC | 约100 kb | loxP F因子元件 | LEXAS | 基因组 | 784个克隆 | Lexapeptide (羊毛硫肽)等 | ①转化效率高 ②克隆100~300 kb片段 | 不适合宏基因组挖掘 | 徐敏 (2017)[ |
| PAC | 约140 kb | F因子元件 P1噬菌体元件 | CONKAT-seq | 基因组 | 60 000个 克隆 | Prolinolexin(NRP) Cinnamexin(NRP) Conkatamycin(PK) | Libis等(2022)[ | ||
| FAC | 约100 kb | F因子元件 真菌ARS | FAC-MS | 基因组 | 156个FAC | Benzomalvin A/D(NRP) Sesterterpenoid(Terpene) Valactamide A(Hybrid NRP-PK) | ①克隆100~300 kb片段 ②适合真菌基因组挖掘 | 克隆稳定性差 | Clevenger等(2017)[ |
| YAC | 100~ 2000 kb | 着丝粒 端粒 酵母ARS | NA | 基因组 | 1896个YAC | NA | 克隆100~2000 kb片段 | ①克隆稳定性差 ②转化效率低 ③重组率、嵌合率高 | Saji等(2001)[ |
表1 不同类型文库构建策略用于新化合物高通量发现的比较
Table 1 Comparison of strategies for constructing different libraries for high-throughput screening of novel natural products
| 文库 类型 | 插入 大小 | 核心 元件 | 筛选方法 | 文库针对 类型 | 基因簇获取通量 | 获得化合物 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cosmid | 约40 kb | COS位点 质粒元件 | CONKAT-seq | 宏基因组 | 107个 克隆 | Omnipeptin(NRP) | 适合宏基因组挖掘 | 克隆片段大小相对较小,在克隆大尺度BGC(>40 kb)方面存在局限 | Libis等(2019)[ |
| 约40 kb | eSNaPD | 宏基因组 | >2×107个 克隆 | MBA3(NRP) | Li等 (2022)[ | ||||
| Fosmid | 约40 kb | COS位点 F因子元件 | 序列引导的PCR筛选 | (宏) 基因组 | 2880个 克隆 | Actinonin(NRP) | Wolf等(2018)[ | ||
| BAC | 约100 kb | loxP F因子元件 | LEXAS | 基因组 | 784个克隆 | Lexapeptide (羊毛硫肽)等 | ①转化效率高 ②克隆100~300 kb片段 | 不适合宏基因组挖掘 | 徐敏 (2017)[ |
| PAC | 约140 kb | F因子元件 P1噬菌体元件 | CONKAT-seq | 基因组 | 60 000个 克隆 | Prolinolexin(NRP) Cinnamexin(NRP) Conkatamycin(PK) | Libis等(2022)[ | ||
| FAC | 约100 kb | F因子元件 真菌ARS | FAC-MS | 基因组 | 156个FAC | Benzomalvin A/D(NRP) Sesterterpenoid(Terpene) Valactamide A(Hybrid NRP-PK) | ①克隆100~300 kb片段 ②适合真菌基因组挖掘 | 克隆稳定性差 | Clevenger等(2017)[ |
| YAC | 100~ 2000 kb | 着丝粒 端粒 酵母ARS | NA | 基因组 | 1896个YAC | NA | 克隆100~2000 kb片段 | ①克隆稳定性差 ②转化效率低 ③重组率、嵌合率高 | Saji等(2001)[ |
| 1 | HUTCHINGS M I, TRUMAN A W, WILKINSON B. Antibiotics: past, present and future[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2019, 51: 72-80. |
| 2 | MULLOWNEY M W, DUNCAN K R, ELSAYED S S, et al. Artificial intelligence for natural product drug discovery[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2023, 22(11): 895-916. |
| 3 | ATANASOV A G, ZOTCHEV S B, DIRSCH V M, et al. Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(3): 200-216. |
| 4 | KWON M J, STEINIGER C, CAIRNS T C, et al. Beyond the biosynthetic gene cluster paradigm: genome-wide coexpression networks connect clustered and unclustered transcription factors to secondary metabolic pathways[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2021, 9(2): e00898-21. |
| 5 | WOOLEY J C, YE Y Z. Metagenomics: facts and artifacts, and computational challenges[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2010, 25(1): 71-81. |
| 6 | SIMON C, DANIEL R. Metagenomic analyses: past and future trends[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(4): 1153-1161. |
| 7 | SCHERLACH K, HERTWECK C. Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3864. |
| 8 | ZIEMERT N, ALANJARY M, WEBER T. The evolution of genome mining in microbes—a review[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(8): 988-1005. |
| 9 | GAVRIILIDOU A, KAUTSAR S A, ZABURANNYI N, et al. Compendium of specialized metabolite biosynthetic diversity encoded in bacterial genomes[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2022, 7(5): 726-735. |
| 10 | BALTZ R H. Gifted microbes for genome mining and natural product discovery[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 44(4/5): 573-588. |
| 11 | LI L. Next-generation synthetic biology approaches for the accelerated discovery of microbial natural products[J]. Engineering Microbiology, 2023, 3(1): 100060. |
| 12 | HUO L J, HUG J J, FU C Z, et al. Heterologous expression of bacterial natural product biosynthetic pathways[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(10): 1412-1436. |
| 13 | HAO T T, XIE Z J, WANG M, et al. An anaerobic bacterium host system for heterologous expression of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3665. |
| 14 | GALM U, SHEN B. Expression of biosynthetic gene clusters in heterologous hosts for natural product production and combinatorial biosynthesis[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 2006, 1(5): 409-437. |
| 15 | LI L, JIANG W H, LU Y H. New strategies and approaches for engineering biosynthetic gene clusters of microbial natural products[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(8): 936-949. |
| 16 | GIBSON D G, YOUNG L, CHUANG R Y, et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases[J]. Nature Methods, 2009, 6(5): 343-345. |
| 17 | KOUPRINA N, LARIONOV V. Transformation-associated recombination (TAR) cloning for genomics studies and synthetic biology[J]. Chromosoma, 2016, 125(4): 621-632. |
| 18 | ZHANG Y, BUCHHOLZ F, MUYRERS J P, et al. A new logic for DNA engineering using recombination in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Genetics, 1998, 20(2): 123-128. |
| 19 | JIANG W J, ZHAO X J, GABRIELI T, et al. Cas9-assisted targeting of chromosome segments CATCH enables one-step targeted cloning of large gene clusters[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8101. |
| 20 | LIANG M D, LIU L S, XU F, et al. Activating cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster through a CRISPR-Cas12a-mediated direct cloning approach[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(6): 3581-3592. |
| 21 | DU D Y, WANG L, TIAN Y Q, et al. Genome engineering and direct cloning of antibiotic gene clusters via phage ϕBT1 integrase-mediated site-specific recombination in Streptomyces [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8740. |
| 22 | 戴岩, 吴旭日, 陈依军. 链霉菌沉默生物合成基因簇激活策略的研究进展[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2019, 50(4): 379-388. |
| DAI Y, WU X R, CHEN Y J. Advances in strategies for activating silent biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces [J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 2019, 50(4): 379-388. | |
| 23 | 戴钊钊. 基于PacBio的高通量Fosmid文库克隆长配对末端测序技术的开发[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019. |
| DAI Z Z. High-throughput long paired-end sequencing of a Fosmid library by PacBio[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 24 | PETERSON D G, TOMKINS J P, FRISCH D A, et al. Construction of plant bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) libraries: an illustrated guide[J/OL]. Journal of Agricultural Genomics, 2000, 5: 1-100[2023-12-01]. . |
| 25 | 樊颖伦, 赵开军. 大片段克隆载体研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2004, 24(3): 12-16. |
| FAN Y L, ZHAO K J. Progress in development of large DNA fragment cloning vectors[J]. China Biotechnology, 2004, 24(3): 12-16. | |
| 26 | HOSODA F, NISHIMURA S, UCHIDA H, et al. An F factor based cloning system for large DNA fragments[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1990, 18(13): 3863-3869. |
| 27 | DANIEL R. The metagenomics of soil[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2005, 3(6): 470-478. |
| 28 | 高花花, 胡娟, 刘玲丽. 基因簇大片段克隆技术研究进展及挑战[J]. 微生物学通报, 2023, 50(1): 351-367. |
| GAO H H, HU J, LIU L L. Research progress and challenges in cloning large gene clusters[J]. Microbiology China, 2023, 50(1): 351-367. | |
| 29 | 王凯, 张燕洁, 关兵, 等. 棉花细菌人工染色体的荧光原位杂交(BAC-FISH)技术[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2007, 34(11): 1216-1222. |
| WANG K, ZHANG Y J, GUAN B, et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization of bacterial artificial chromosome in cotton[J]. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2007, 34(11): 1216-1222. | |
| 30 | 池淏甜, 陈实. 基因组学技术解码天然产物合成[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 1889-1900. |
| CHI H T, CHEN S. Genomics approaches decode natural products synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 1889-1900. | |
| 31 | SUMMERS W C. Plasmids: histories of a concept[M/OL]//Reticulate evolution: symbiogenesis, lateral gene transfer, hybridization and infectious heredity. Cham: Springer, 2015: 179-190 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 32 | LEDERBERG E M, LEDERBERG J. Genetic studies of lysogenicity in Escherichia coli [J]. Genetics, 1953, 38(1): 51-64. |
| 33 | COLLINS J, HOHN B. Cosmids: a type of plasmid gene-cloning vector that is packageable in vitro in bacteriophage lambda heads[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1978, 75(9): 4242-4246. |
| 34 | WENZEL R, HERRMANN R. Cosmid cloning with small genomes[M/OL]//Nonmammalian genomic analysis. San Diego, CA, USA: Academic Press, 1996: 197-222 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 35 | LI J E, GUO Z Y, HUANG W, et al. Mining of a streptothricin gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. TP-A0356 genome via heterologous expression[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2013, 56(7): 619-627. |
| 36 | 杨其会. 基于基因组挖掘策略研究Streptomyces netropsis DSM 40846中天然产物生物合成基因簇[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2022. |
| YANG Q H. Exploring natural product biosynthesis gene clusters in Streptomyces netropsis DSM 40846 by genome mining[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| 37 | 张巧燕. 基于genome mining技术的TRM 15522次级代谢产物研究[D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学, 2021. |
| ZHANG Q Y. Study on secondary metabolites of TRM 15522 based on genome mining technology[D]. Alaer: Tarim University, 2021. | |
| 38 | GAO Y S, WALT C, BADER C D, et al. Genome-guided discovery of the myxobacterial thiolactone-containing sorangibactins[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2023, 18(4): 924-932. |
| 39 | LIU J Y, YANG L, KJELLERUP B V, et al. Viable but nonculturable (VBNC) state, an underestimated and controversial microbial survival strategy[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2023, 31(10): 1013-1023. |
| 40 | PINTO D, SANTOS M A, CHAMBEL L. Thirty years of viable but nonculturable state research: unsolved molecular mechanisms[J]. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 2015, 41(1): 61-76. |
| 41 | EKKERS D M, CRETOIU M S, KIELAK A M, et al. The great screen anomaly: a new frontier in product discovery through functional metagenomics[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(3): 1005-1020. |
| 42 | HANDELSMAN J. Metagenomics: application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2004, 68(4): 669-685. |
| 43 | COURTOIS S, CAPPELLANO C M, BALL M, et al. Recombinant environmental libraries provide access to microbial diversity for drug discovery from natural products[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(1): 49-55. |
| 44 | BRADY S F, CHAO C J, HANDELSMAN J, et al. Cloning and heterologous expression of a natural product biosynthetic gene cluster from eDNA[J]. Organic Letters, 2001, 3(13): 1981-1984. |
| 45 | BRADY S F, CLARDY J. Cloning and heterologous expression of isocyanide biosynthetic genes from environmental DNA[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 117(43): 7225-7227. |
| 46 | BAUER J D, KING R W, BRADY S F. Utahmycins A and B, azaquinones produced by an environmental DNA clone[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2010, 73(5): 976-979. |
| 47 | KALLIFIDAS D, KANG H S, BRADY S F. Tetarimycin A, an MRSA-active antibiotic identified through induced expression of environmental DNA gene clusters[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(48): 19552-19555. |
| 48 | KANG H S, BRADY S F. Arimetamycin A: improving clinically relevant families of natural products through sequence-guided screening of soil metagenomes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(42): 11063-11067. |
| 49 | PEEK J, LILIC M, MONTIEL D, et al. Rifamycin congeners kanglemycins are active against rifampicin-resistant bacteria via a distinct mechanism[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 4147. |
| 50 | HOVER B M, KIM S H, KATZ M, et al. Culture-independent discovery of the malacidins as calcium-dependent antibiotics with activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-positive pathogens[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2018, 3(4): 415-422. |
| 51 | LIBIS V, ANTONOVSKY N, ZHANG M Y, et al. Uncovering the biosynthetic potential of rare metagenomic DNA using co-occurrence network analysis of targeted sequences[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3848. |
| 52 | LI L, KOIRALA B, HERNANDEZ Y, et al. Identification of structurally diverse menaquinone-binding antibiotics with in vivo activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2022, 7(1): 120-131. |
| 53 | 刘建喜, 林爱星, 丁翔, 等. DNA克隆载体的发展和应用[J]. 遗传, 1997, 19(6): 41-44. |
| LIU J X, LIN A X, DING X, et al. The development and application of DNA cloning vectors[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 1997, 19(6): 41-44. | |
| 54 | EVANS G A, LEWIS K A. Physical mapping of complex genomes by cosmid multiplex analysis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1989, 86(13): 5030-5034. |
| 55 | KIM U J, SHIZUYA H, DE JONG P J, et al. Stable propagation of cosmid sized human DNA inserts in an F factor based vector[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1992, 20(5): 1083-1085. |
| 56 | 李昂, 张安, 唐君, 等. Fosmid基因组文库构建及应用现状[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(6): 28-30. |
| LI A, ZHANG A, TANG J, et al. Fosmid genomic library construction and its application status[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(6): 28-30. | |
| 57 | LIU C X, LIU X L, LEI L, et al. Fosmid library construction and screening for the maize mutant gene Vestigial glume 1 [J]. The Crop Journal, 2016, 4(1): 55-60. |
| 58 | FELCZYKOWSKA A, DYDECKA A, BOHDANOWICZ M, et al. The use of fosmid metagenomic libraries in preliminary screening for various biological activities[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2014, 13: 105. |
| 59 | WOLF F, LEIPOLDT F, KULIK A, et al. Characterization of the actinonin biosynthetic gene cluster[J]. ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(11): 1189-1195. |
| 60 | JIAO Y J, LIU Y, WANG H X, et al. Expression of the clifednamide biosynthetic pathway in Streptomyces generates 27, 28-seco-derivatives[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(9): 2803-2808. |
| 61 | UFARTÉ L, BOZONNET S, LAVILLE E, et al. Functional metagenomics: construction and high-throughput screening of Fosmid libraries for discovery of novel carbohydrate-active enzymes[M/OL]//Methods in molecular biology: microbial environmental genomics. New York: Humana Press, 2016, 1399: 257-271 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 62 | RIESENFELD C S, SCHLOSS P D, HANDELSMAN J. Metagenomics: genomic analysis of microbial communities[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2004, 38: 525-552. |
| 63 | 芦晓飞, 赵志祥, 谢丙炎, 等. 西藏米拉山高寒草甸土壤微生物DNA提取及宏基因组Fosmid文库构建[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2009, 15(6): 824-829. |
| LU X F, ZHAO Z X, XIE B Y, et al. DNA extraction and construction of a metagenomic Fosmid library of alpine meadow soil from the Mila mountains in Tibet, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2009, 15(6): 824-829. | |
| 64 | NEGRI T, MANTRI S, ANGELOV A, et al. A rapid and efficient strategy to identify and recover biosynthetic gene clusters from soil metagenomes[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 106(8): 3293-3306. |
| 65 | SHIZUYA H, BIRREN B, KIM U J, et al. Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(18): 8794-8797. |
| 66 | KIM U J, BIRREN B W, SLEPAK T, et al. Construction and characterization of a human bacterial artificial chromosome library[J]. Genomics, 1996, 34(2): 213-218. |
| 67 | LIU Y G, SHIRANO Y, FUKAKI H, et al. Complementation of plant mutants with large genomic DNA fragments by a transformation-competent artificial chromosome vector accelerates positional cloning[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(11): 6535-6540. |
| 68 | LUO M Z, WANG Y H, FRISCH D, et al. Melon bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library construction using improved methods and identification of clones linked to the locus conferring resistance to melon Fusarium wilt (Fom-2)[J]. Genome, 2001, 44(2): 154-162. |
| 69 | LUO M Z, WING R A. An improved method for plant BAC library construction[M/OL]//Methods in molecular biology: plant functional genomics. New York: Human Press, 2003, 236: 3-20 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 70 | 黄胜, 李娜, 周俊, 等. 适用于链霉菌大片段基因组DNA克隆和异源表达的细菌人工染色体(BAC)载体的构建及应用[J]. 微生物学报, 2012, 52(1): 30-37. |
| HUANG S, LI N, ZHOU J, et al. Construction of a new bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) vector for cloning of large DNA fragments and heterologous expression in Streptomyces [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2012, 52(1): 30-37. | |
| 71 | 刘家栋, 王革娇, 罗美中. 阿维链霉菌BAC文库的构建及分析[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2016, 35(5): 45-50. |
| LIU J D, WANG G J, LUO M Z. Construction and analysis of a BAC library of Streptomyces avermitilis genome[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2016, 35(5): 45-50. | |
| 72 | RASCHER A, HU Z H, VISWANATHAN N, et al. Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster for geldanamycin production in Streptomyces hygroscopicus NRRL 3602[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2003, 218(2): 223-230. |
| 73 | PENN J, LI X, WHITING A, et al. Heterologous production of daptomycin in Streptomyces lividans [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2006, 33(2): 121-128. |
| 74 | LIU H B, JIANG H, HALTLI B, et al. Rapid cloning and heterologous expression of the meridamycin biosynthetic gene cluster using a versatile Escherichia coli-Streptomyces artificial chromosome vector, pSBAC[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2009, 72(3): 389-395. |
| 75 | DENG Q, ZHOU L, LUO M Z, et al. Heterologous expression of avermectins biosynthetic gene cluster by construction of a Bacterial Artificial Chromosome library of the producers[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2(1): 59-64. |
| 76 | HASHIMOTO T, HASHIMOTO J, KOZONE I, et al. Biosynthesis of quinolidomicin, the largest known macrolide of terrestrial origin: identification and heterologous expression of a biosynthetic gene cluster over 200 kb[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20(24): 7996-7999. |
| 77 | HASHIMOTO T, KOZONE I, HASHIMOTO J, et al. Novel macrolactam compound produced by the heterologous expression of a large cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces rochei IFO12908[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2020, 73(3): 171-174. |
| 78 | 徐敏. 高通量异源表达辅助的活性天然产物挖掘与新型羊毛硫肽Lexapeptide的生物合成研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017. |
| XU M. Discovery of bioactive natural products enabled by high throughput heterologous expression and biosynthesis of a novel lantibiotic, lexapeptide[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017. | |
| 79 | XU M, ZHANG F, CHENG Z, et al. Functional genome mining reveals a class Ⅴ lanthipeptide containing a D-amino acid introduced by an F420 H2-dependent reductase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(41): 18029-18035. |
| 80 | STERNBERG N. Bacteriophage P1 cloning system for the isolation, amplification, and recovery of DNA fragments as large as 100 kilobase pairs[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1990, 87(1): 103-107. |
| 81 | IOANNOU P A, AMEMIYA C T, GARNES J, et al. A new bacteriophage P1-derived vector for the propagation of large human DNA fragments[J]. Nature Genetics, 1994, 6(1): 84-89. |
| 82 | JONES A C, GUST B, KULIK A, et al. Phage p1-derived artificial chromosomes facilitate heterologous expression of the FK506 gene cluster[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e69319. |
| 83 | CASTRO J F, RAZMILIC V, GOMEZ-ESCRIBANO J P, et al. Identification and heterologous expression of the chaxamycin biosynthesis gene cluster from Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(17): 5820-5831. |
| 84 | TU J J, LI S T, CHEN J, et al. Characterization and heterologous expression of the neoabyssomicin/abyssomicin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 28. |
| 85 | LIBIS V, MACINTYRE L W, MEHMOOD R, et al. Multiplexed mobilization and expression of biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 5256. |
| 86 | BÉRDY J. Bioactive microbial metabolites[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2005, 58(1): 1-26. |
| 87 | CHIANG C Y, OHASHI M, TANG Y. Deciphering chemical logic of fungal natural product biosynthesis through heterologous expression and genome mining[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2023, 40(1): 89-127. |
| 88 | KELLER N P. Translating biosynthetic gene clusters into fungal armor and weaponry[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9): 671-677. |
| 89 | ROKAS A, WISECAVER J H, LIND A L. The birth, evolution and death of metabolic gene clusters in fungi[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2018, 16(12): 731-744. |
| 90 | VAN DEN BERG M A, ALBANG R, ALBERMANN K, et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(10): 1161-1168. |
| 91 | ALBERTS A W, CHEN J, KURON G, et al. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1980, 77(7): 3957-3961. |
| 92 | STIERLE A, STROBEL G, STIERLE D. Taxol and taxane production by Taxomyces andreanae, an endophytic fungus of Pacific yew[J]. Science, 1993, 260(5105): 214-216. |
| 93 | HÜTTEL W. Echinocandins: structural diversity, biosynthesis, and development of antimycotics[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(1): 55-66. |
| 94 | 林继聪, 邹根, 刘宏民, 等. CRISPR/Cas基因组编辑技术在丝状真菌次级代谢产物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. |
| LIN J C, ZOU G, LIU H M, et al. Application of CRISPR/Cas genome editing technology in the synthesis of secondary metabolites of filamentous fungi[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. | |
| 95 | BOK J W, YE R, CLEVENGER K D, et al. Fungal artificial chromosomes for mining of the fungal secondary metabolome[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 343. |
| 96 | CLEVENGER K D, BOK J W, YE R, et al. A scalable platform to identify fungal secondary metabolites and their gene clusters[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(8): 895-901. |
| 97 | MURRAY A W, SZOSTAK J W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast[J]. Nature, 1983, 305(5931): 189-193. |
| 98 | SANTRA D K, SANDHU D, TAI T, et al. Construction and characterization of a soybean yeast artificial chromosome library and identification of clones for the Rps6 region[J]. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2003, 3(4): 153-159. |
| 99 | KURATA N, UMEHARA Y, TANOUE H, et al. Physical mapping of the rice genome with YAC clones[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1997, 35(1/2): 101-113. |
| 100 | BURKE D T, CARLE G F, OLSON M V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors[J]. Science, 1987, 236(4803): 806-812. |
| 101 | SAJI S, UMEHARA Y, ANTONIO B A, et al. A physical map with yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones covering 63% of the 12 rice chromosomes[J]. Genome, 2001, 44(1): 32-37. |
| 102 | BLIN K, SHAW S, KLOOSTERMAN A M, et al. antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(W1): W29-W35. |
| 103 | TERLOUW B R, BLIN K, NAVARRO-MUÑOZ J C, et al. MIBiG 3.0: a community-driven effort to annotate experimentally validated biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(D1): D603-D610. |
| 104 | NAVARRO-MUÑOZ J C, SELEM-MOJICA N, MULLOWNEY M W, et al. A computational framework to explore large-scale biosynthetic diversity[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(1): 60-68. |
| 105 | KAUTSAR S A, VAN DER HOOFT J J J, RIDDER D D, et al. BiG-SLiCE: a highly scalable tool maps the diversity of 1.2 million biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. GigaScience, 2021, 10(1): giaa154. |
| 106 | 赖奇龙, 姚帅, 查毓国, 等. 微生物组生物合成基因簇发掘方法及应用前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 611-627. |
| LAI Q L, YAO S, ZHA Y G, et al. Microbiome-based biosynthetic gene cluster data mining techniques and application potentials[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 611-627. | |
| 107 | LI L. Accessing hidden microbial biosynthetic potential from underexplored sources for novel drug discovery[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2023, 66: 108176. |
| 108 | BALTZ R H. Marcel Faber Roundtable: is our antibiotic pipeline unproductive because of starvation, constipation or lack of inspiration?[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2006, 33(7): 507-513. |
| 109 | SHU W S, HUANG L N. Microbial diversity in extreme environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 20(4): 219-235. |
| 110 | LI S, DONG L, LIAN W H, et al. Exploring untapped potential of Streptomyces spp. in Gurbantunggut Desert by use of highly selective culture strategy[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 790: 148235. |
| 111 | LAZZARINI A, CAVALETTI L, TOPPO G, et al. Rare Genera of actinomycetes as potential producers of new antibiotics[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2000, 78(3/4): 399-405. |
| 112 | XIE F Y, PATHOM-AREE W. Actinobacteria from desert: diversity and biotechnological applications[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 765531. |
| 113 | WANASINGHE D N, MORTIMER P E, XU J C. Insight into the systematics of microfungi colonizing dead woody twigs of Dodonaea viscosa in Honghe (China)[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2021, 7(3): 180. |
| 114 | LEWIS K, EPSTEIN S, D’ONOFRIO A, et al. Uncultured microorganisms as a source of secondary metabolites[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2010, 63(8): 468-476. |
| [1] | 宋永相, 张秀凤, 李艳芹, 肖华, 闫岩. 自抗性基因导向的活性天然产物挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 474-491. |
| [2] | 赖奇龙, 姚帅, 查毓国, 白虹, 宁康. 微生物组生物合成基因簇发掘方法及应用前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 611-627. |
| [3] | 张礼文, MOLNÁR István, 徐玉泉. 虫生真菌非核糖体多肽活性产物生物合成潜力预测[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 815-825. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
