合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 1006-1030.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-018
酶促生物电催化系统的设计构建与强化
崔馨予1,2, 吴冉冉1, 王园明1, 朱之光1,2,3
- 1.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,天津 300308
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3.国家合成生物技术创新中心,天津 300308
-
收稿日期:2022-04-01修回日期:2022-06-22出版日期:2022-10-31发布日期:2022-11-16 -
通讯作者:朱之光 -
作者简介:崔馨予 (1996—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为氧化还原酶改造、生物电子传递。E-mail:cuixy@tib.cas.cn吴冉冉 (1988—),女,副研究员。研究方向为生物燃料电池、生物电化学合成、微生物电化学。E-mail:wu_rr@tib.cas.cn朱之光 (1985—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为体外合成生物学、生物电催化、生物燃料电池、生物电化学合成、生物传感、酶工程。E-mail:zhu_zg@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFA0910400);国家自然科学基金(21878324)
Construction and enhancement of enzymatic bioelectrocatalytic systems
CUI Xinyu1,2, WU Ranran1, WANG Yuanming1, ZHU Zhiguang1,2,3
- 1.Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
3.National Synthesis of Biotechnology Innovation Center,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2022-04-01Revised:2022-06-22Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-16 -
Contact:ZHU Zhiguang
摘要:
酶促生物电催化是一种绿色高效的催化技术,充分结合了生物酶催化和电催化的优点,可实现化学能和电能的相互转换,目前已在生物发电、电能存储、CO2固定、传感与监测等方面受到广泛关注。本综述分析了酶促生物电催化的发展现状与当前面临的挑战,从合成生物学的角度详细介绍了氧化还原酶的结构功能和酶促生物电催化系统的基本要素,探讨了酶的改造,包括定向进化、理性设计和引入非天然组件等,以及通过构建多酶复合体模块和强化生物-非生物界面电子传递等方法以提高系统性能。围绕电子传递和能量转化效率等问题,阐述了酶的定向固定方法、电子传递机制以及电极材料设计原则。此外,总结了酶促生物电催化技术在酶燃料电池、生物传感器、化学品酶电合成等合成生物学相关领域的前沿应用。最后,本文展望了未来前景,并提出了从设计改造电活性生物元件、拓宽反应电势、放大反应系统等方面进一步提升酶促生物电催化系统的性能和可应用性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
崔馨予, 吴冉冉, 王园明, 朱之光. 酶促生物电催化系统的设计构建与强化[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 1006-1030.
CUI Xinyu, WU Ranran, WANG Yuanming, ZHU Zhiguang. Construction and enhancement of enzymatic bioelectrocatalytic systems[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 1006-1030.
| 策略 | 氧化 还原酶 | 氧化还 原中心 | 酶元件的构建 | 改造结果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设计酶元件提高其催化性能 | |||||
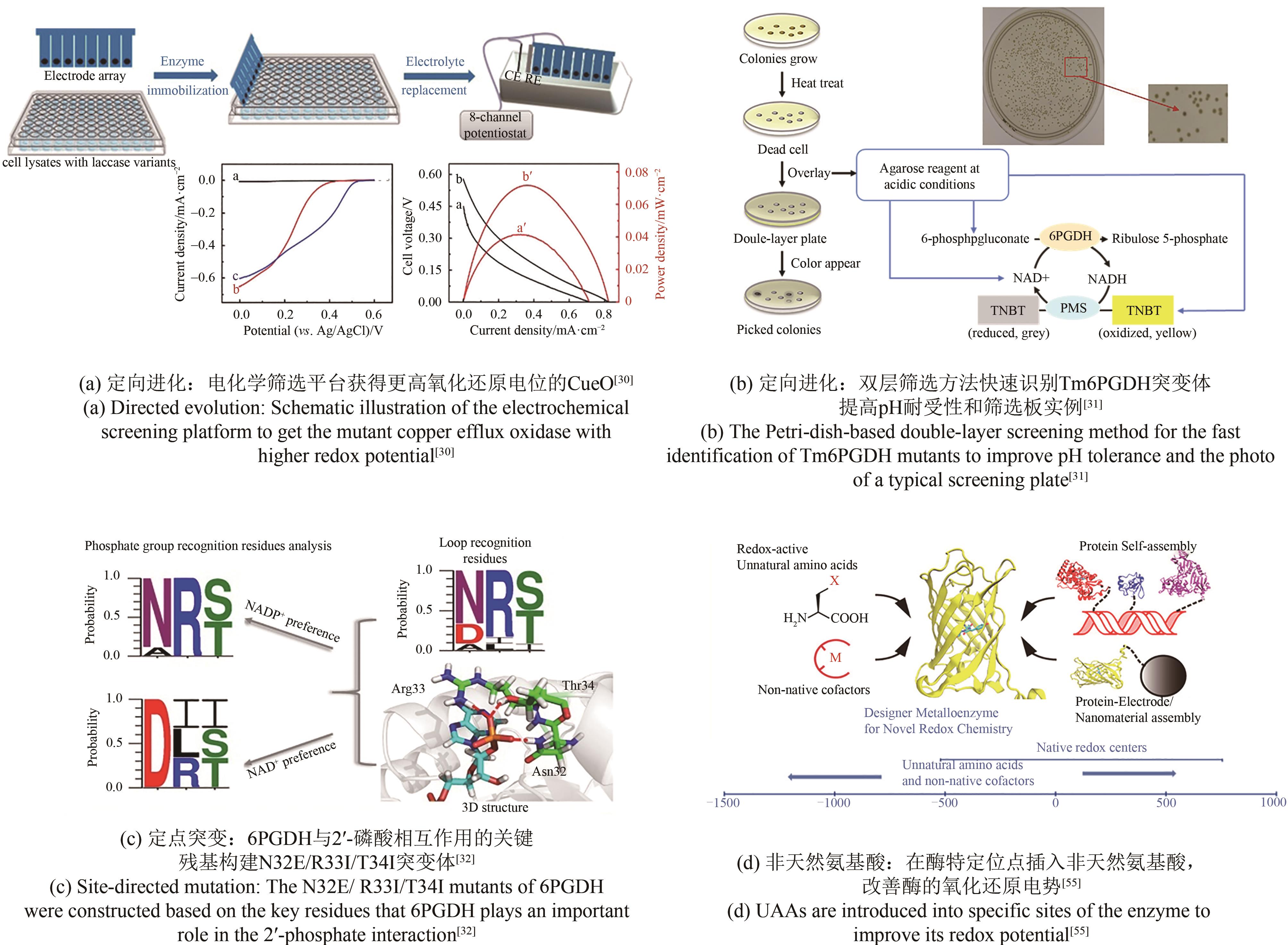
| 定向进化 | GOx | FAD | 利用中介体二茂铁甲醇的筛选系统在96孔板中进行筛选 | 酶活性增加1.9倍,电流密度提高23% | [ |
| CueO | T1 Cu | 利用多通道恒电位仪搭载多电极阵列评估氧还原过电位 | 降低了阴极过电位,提高1.72倍电池输出功率 | [ | |
| G6PDH | NADH | 多轮随机诱变与双层平板筛选相结合 | 低pH下催化效率提高42倍,最大功率密度0.5 mW/cm2 | [ | |
| 定点突变 | 6PGDH | NADP | 改造与辅酶结合相关位点 | 辅酶偏好性从NADP+转变为NAD+,并实现1.75 mW/cm2的高功率密度 | [ |
| MADH | TTQ | 将Phe55替换为更小位阻的丙氨酸 | Km为野生型的1/400 | [ | |
| Cyt C | heme | 引入带正电荷的赖氨酸 | 对超氧化物的灵敏度提高40% | [ | |
| LOx | FMN | 设计阻断氧通路的突变位点 | O2干扰减少30%,传感器检测范围扩大10倍 | [ | |
| GDH | FAD | 预测与葡萄糖底物结合的残基构建双突变体 | 底物特异性提高30倍 | [ | |
| UAA | Mb | heme | 非天然氨基酸MtTyr替代Tyr-Cys辅助因子 | 还原羟胺的速率提高3倍 | [ |
| P450 | heme | 用人工Ir代替了细胞色素P450血红素基团中的Fe | 实现卡宾反应形成C—C,催化C—H功能化 | [ | |
| Mb | heme | 人工OmeY的掺入复制了细胞色素c氧化酶的重要特征 | 降低了还原电位,提高2倍的周转率 | [ | |
| 设计酶元件的定向固定 | |||||
| 引入接头 | GOx | NADH | C端添加精氨酸标记形成SAM | 将传感器检测范围扩大为0.01~100 mmol/L | [ |
| C端与聚赖氨酸亲水链相连 | 将更多的中介体锚定在酶上,电流增加了2倍 | ||||
| HRP | heme | C端添加了His-tag | 实现DET,电子传递速率提高60% | [ | |
| GDH | FAD | N端或C端添加金结合肽 | 实现DET,催化电流高达249 μA | [ | |
| 定点突变 | BOD | Cu | 特定位置引入的半胱氨酸残基耦联形成新共价键 | 形成巯基,加快DET速率 | [ |
| GOx | FAD | 活性位点的附近突变带负电氨基酸 | 增加Os和酶之间的相互作用,电流增加2.4倍 | [ | |
| 化学修饰 | NiFe氢酶 | Fe-S | 将4-甲基苄胺修饰在氨基化MWCNT上 | 酶空间构象改变并且在电极上重新定向固定 | [ |
| CDH | FAD heme | 根据静电作用构建带电的硫醇SAM | 亲水性带电的硫醇SAM电流密度增加两倍 | [ | |
| GDH | FAD | 在金电极上修饰SWCNT | 实现DET和传感器110 μA·L/(mmol·cm2)的高灵敏度 | [ | |
| Apo-酶 | GOx | FAD | PQQ作为中继单元,用配体与FAD连接作用 | 减少干扰物的影响,施加电位从-0.4 V减少到-0.6 V | [ |
| 改造酶元件以强化界面电子传递 | |||||
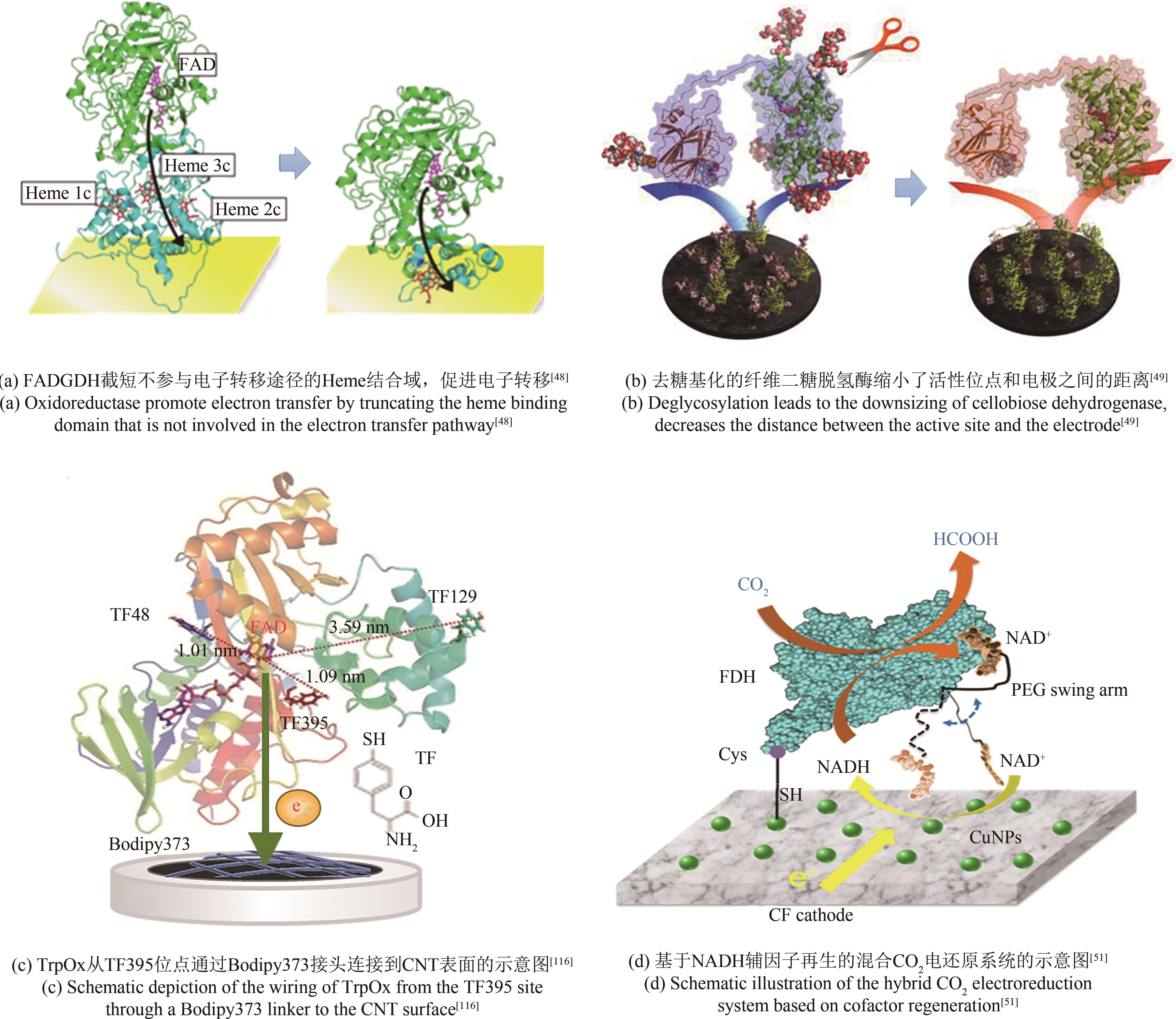
| 截短 | NiFe氢酶 | Fe-S | 4亚基截短成2亚基 | 缩短电极与酶的距离,电子转移速率提高约20倍 | [ |
| GDH | FAD | 构建仅含有电子转移功能trβ亚基 | 实现DET | [ | |
| 去糖基化 | CDH | FAD heme | 利用糖苷酶脱糖基化 | 酶尺寸的减小促进DET且电流密度增加60% | [ |
| GOx | FAD | 黑曲霉表达纯化几乎完全脱糖基化 | 电流响应从0提高到235 μA/cm2 | [ | |
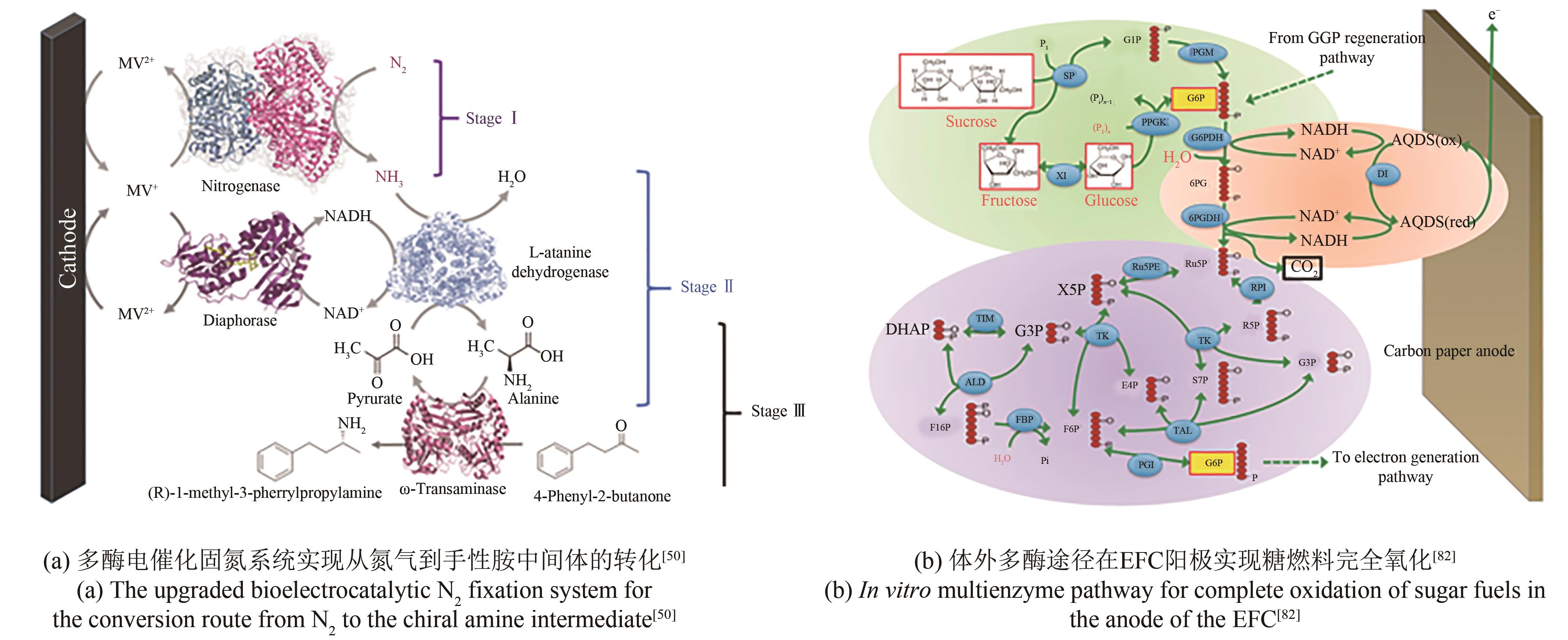
| 辅酶再生 | 固氮酶 | MoFe | 通过ω-TA与DI升级N2固定系统 | 实现NADH再生,电合成手性胺浓度达到0.54 mmol/L | [ |
| FDH | NADH | 与NAD构建交联体聚合物 | 促进电子穿梭,固定CO2法拉第效率达到22.8% | [ | |
表1 酶元件设计策略及典型示例
Tab. 1 Design strategies for oxidoreductases as well as typical examples
| 策略 | 氧化 还原酶 | 氧化还 原中心 | 酶元件的构建 | 改造结果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设计酶元件提高其催化性能 | |||||
| 定向进化 | GOx | FAD | 利用中介体二茂铁甲醇的筛选系统在96孔板中进行筛选 | 酶活性增加1.9倍,电流密度提高23% | [ |
| CueO | T1 Cu | 利用多通道恒电位仪搭载多电极阵列评估氧还原过电位 | 降低了阴极过电位,提高1.72倍电池输出功率 | [ | |
| G6PDH | NADH | 多轮随机诱变与双层平板筛选相结合 | 低pH下催化效率提高42倍,最大功率密度0.5 mW/cm2 | [ | |
| 定点突变 | 6PGDH | NADP | 改造与辅酶结合相关位点 | 辅酶偏好性从NADP+转变为NAD+,并实现1.75 mW/cm2的高功率密度 | [ |
| MADH | TTQ | 将Phe55替换为更小位阻的丙氨酸 | Km为野生型的1/400 | [ | |
| Cyt C | heme | 引入带正电荷的赖氨酸 | 对超氧化物的灵敏度提高40% | [ | |
| LOx | FMN | 设计阻断氧通路的突变位点 | O2干扰减少30%,传感器检测范围扩大10倍 | [ | |
| GDH | FAD | 预测与葡萄糖底物结合的残基构建双突变体 | 底物特异性提高30倍 | [ | |
| UAA | Mb | heme | 非天然氨基酸MtTyr替代Tyr-Cys辅助因子 | 还原羟胺的速率提高3倍 | [ |
| P450 | heme | 用人工Ir代替了细胞色素P450血红素基团中的Fe | 实现卡宾反应形成C—C,催化C—H功能化 | [ | |
| Mb | heme | 人工OmeY的掺入复制了细胞色素c氧化酶的重要特征 | 降低了还原电位,提高2倍的周转率 | [ | |
| 设计酶元件的定向固定 | |||||
| 引入接头 | GOx | NADH | C端添加精氨酸标记形成SAM | 将传感器检测范围扩大为0.01~100 mmol/L | [ |
| C端与聚赖氨酸亲水链相连 | 将更多的中介体锚定在酶上,电流增加了2倍 | ||||
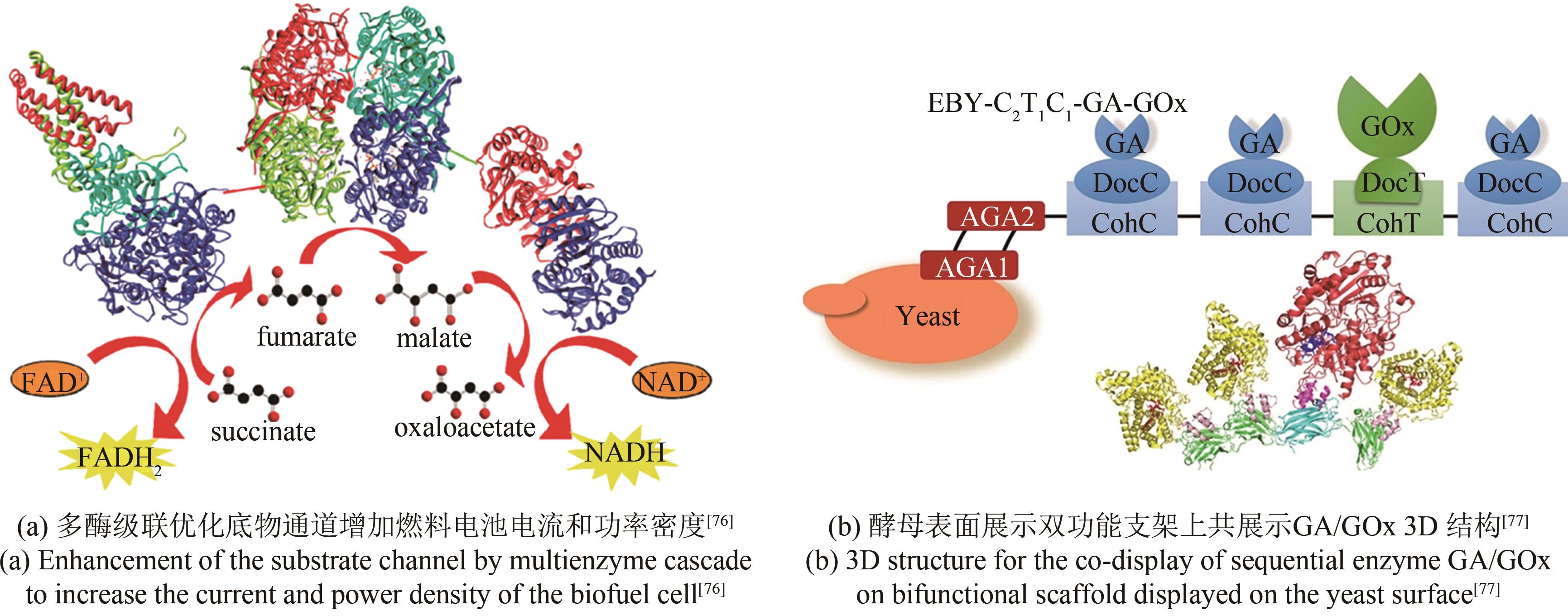
| HRP | heme | C端添加了His-tag | 实现DET,电子传递速率提高60% | [ | |
| GDH | FAD | N端或C端添加金结合肽 | 实现DET,催化电流高达249 μA | [ | |
| 定点突变 | BOD | Cu | 特定位置引入的半胱氨酸残基耦联形成新共价键 | 形成巯基,加快DET速率 | [ |
| GOx | FAD | 活性位点的附近突变带负电氨基酸 | 增加Os和酶之间的相互作用,电流增加2.4倍 | [ | |
| 化学修饰 | NiFe氢酶 | Fe-S | 将4-甲基苄胺修饰在氨基化MWCNT上 | 酶空间构象改变并且在电极上重新定向固定 | [ |
| CDH | FAD heme | 根据静电作用构建带电的硫醇SAM | 亲水性带电的硫醇SAM电流密度增加两倍 | [ | |
| GDH | FAD | 在金电极上修饰SWCNT | 实现DET和传感器110 μA·L/(mmol·cm2)的高灵敏度 | [ | |
| Apo-酶 | GOx | FAD | PQQ作为中继单元,用配体与FAD连接作用 | 减少干扰物的影响,施加电位从-0.4 V减少到-0.6 V | [ |
| 改造酶元件以强化界面电子传递 | |||||
| 截短 | NiFe氢酶 | Fe-S | 4亚基截短成2亚基 | 缩短电极与酶的距离,电子转移速率提高约20倍 | [ |
| GDH | FAD | 构建仅含有电子转移功能trβ亚基 | 实现DET | [ | |
| 去糖基化 | CDH | FAD heme | 利用糖苷酶脱糖基化 | 酶尺寸的减小促进DET且电流密度增加60% | [ |
| GOx | FAD | 黑曲霉表达纯化几乎完全脱糖基化 | 电流响应从0提高到235 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 辅酶再生 | 固氮酶 | MoFe | 通过ω-TA与DI升级N2固定系统 | 实现NADH再生,电合成手性胺浓度达到0.54 mmol/L | [ |
| FDH | NADH | 与NAD构建交联体聚合物 | 促进电子穿梭,固定CO2法拉第效率达到22.8% | [ | |
| 应用领域 | 主要策略 | 主要效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酶生物燃料电池 | |||
| MET型 | 基于氢酶/MV/为阳极、固氮酶/MV为阴极的H2/N2燃料电池 | 最大电流和功率密度分别为48.0 μA/cm2和1.50 μW/cm2,OCP为0.23 V | [ |
| 基于氢酶/MV/Nafion为阳极、ADO/TBO/Nafion为阴极的H2/庚醛燃料电池 | 最大电流密度和功率密度为25 μA/cm2和4.7 μW/cm2,OCP最高达到0.6 V | [ | |
| 基于氢酶/MV/C为阳极、BOD/Nafion/C为阴极的H2/O2燃料电池 | 最大功率密度为3.6×103 μW/cm2,OCP的值为1.13 V。 | [ | |
| 基于氢酶/MV/GCE为阳极、BOD/C为阴极的H2/O2燃料电池 | 最大电流密度和功率密度为6.3×103 μA/cm2和4.4 ×103 μW/cm2,OCP最高达到1.14 V | [ | |
| 基于FDH/Cc-PAA/C为阳极的甲酸盐/O2燃料电池 | 最大电流密度62 μA/cm2,OCP为 1.28 V | [ | |
| FDH/BPV-LPEI/C为阳极、Lc/MWCNT/Nafion/C为阴极的HCOO-/O2酶燃料电池 | 最大电流和功率密度为17 μA/cm2和18 μW/cm2,OCP为1.28 V | [ | |
| FDH/MV/聚乙二醇/GCE为阳极、BOD/ABTS/GCE为阴极的HCOO-/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度达到2×104 μA/cm2,功率密度为1.2×103 μW/cm2,OCP为0.78 V | [ | |
| 基于多酶/CNT/AQDS/C阳极、Pt为阴极的多糖燃料电池酶 | 最大功率密度为108 μW/cm2,电流密度为 2.56×103 μA/cm2,法拉第效率为95% | [ | |
| DET型 | 基于Lc/CNT/Ta高性能生物阴极组成的O2燃料电池 | 电流密度840 μA/cm2,在168 h的使用寿命期间能保持75%的电流 | [ |
| GOx/对苯二酚/SWNT/Au为阴极、Lc/SWNT/Au为阳极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度790 μA/cm2,功率密度240 μW/cm2,OCP为0.52 V,在低pH下可有效工作 | [ | |
| 基于Py2Ox/CAT/GC为阳极、Py2Ox/HRP/CNT-CMF-CC为阴极的H2/葡萄糖燃料电池 | 功率密度530 μW/cm2,OCP为1.15 V,在10 h的使用寿命期间保留50%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于GDH/PANI/AuNP/Au为作用在人体血液中的高效生物阳极的葡萄糖燃料电池 | 电流密度1×103 μA/cm2,在10 h的使用寿命期间能保持79%的电流 | [ | |
| GOx/NQ/MWNT为阳极、HRP/MWNT为阴极的葡萄糖/H2O2燃料电池 | 功率密度700 μW/cm2,OCP为0.6 V | [ | |
| 基于GOx/TPA/PEI/CNT为阳极、Pt/C为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度78.6 μA/cm2,功率密度1.62×103 μW/cm2,在672 h的使用寿命期间能保持75.8%的电流 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PANI/GC为阳极、Lc/PANI/GC为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 功率密度1.12×103 μW/cm2,OCP为0.78 V,在336 h的使用寿命期间能保持82.9%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于FAD-GDH/Th-AuNP/CNT/GC为阳极、BOD/GR/CNT/GC为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度925 μA/cm2,功率密度269 μW/cm2,OCP为0.71 V | [ | |
| 基于GOx/Naph-SH/AgNP/PEI/CNT为阳极、Pt/C为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度1.46×103 μA/cm2,在840 h的使用寿命期间能保持83%的电流 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/3D石墨烯为阳极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 功率密度164 μW/cm2,OCP为0.44 V,在168 h的使用寿命期间能保持60%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PVP-RPPy/NiF为阳极、Lc/PVP-RPPy/NiF为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 功率密度350 μW/cm2,OCP为1.16 V,在336 h的使用寿命期间能保持82%的功率 | [ | |
| Zn为阳极、BOD/MWNT/rGO/PG为阴极的O2燃料电池 | 电流密度650 μA/cm2,功率密度775 μW/cm2,OCP为1.68 V | [ | |
| BOD/MWCNT为阴极的O2燃料电池 | 功率密度4×103 μW/cm2,在24 h的使用寿命期间能保持73%的功率 | [ | |
| GDH/GO/GC为阳极、Lc/AuNP/Au为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度1.1×103 μA/cm2,功率密度400 μW/cm2,OCP为0.86 V,在576 h的使用寿命期间能保持93%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于NiFe氢酶/MWCNT/NQ/GCE为阴极的H2/O2燃料电池 | 最大功率密度为 890 μW/cm2,OCP为1.1 V | [ | |
| 自供电可穿戴电子设备 | 基于LOx/TTF-MDB/Pt/Co设计的由汗液驱动的集成电子皮肤检测乳酸 | 功率密度350 µW/cm2,具有良好的稳定性能 | [ |
| 基于LOx/CNT/1,4-NQ/GA/CHI为阳极、Box/CNT/PPIX/Nafion为阴极制备的电子纺织微电网 | 功率密度21.5 µW/cm2,电流密度5.8 µA/cm2监测汗液中的乳酸 | [ | |
| 基于LOx/CNT/NQ/Pt/Cu/Nafion检测汗液中的乳酸 | 可以从静止状态下指尖汗液中收集400 mJ/cm2能量 | [ | |
| 基于LOx/NQ/液态金属组成的可伸缩电化学组件检测汗液中的乳酸浓度 | 最大功率密度为270 μW/cm2和0.50 V的OCP | [ | |
| 酶生物传感器 | |||
| 表皮检测 | 附着在皮肤上以形成皮下电化学双通道利用GOx检测血糖 | 实现无创血管内血糖测量,具有130.4 μA·L/mmol高灵敏度 | [ |
| 尿酸酶/C制备的新型纸质智能绷带检测伤口尿酸水平 | 降低更换伤口敷料的频率,检测范围为100~800 μmol/L,精确监测伤口长达3 d | [ | |
| 将LOx与硼酸盐形成外聚合层同Nafion固定在电极上检测乳酸 | 检测范围0.22~0.75 mmol/L,灵敏度为0.1 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于Au/rGO/PtNP/CHI/GOx制备的葡萄糖生物传感器 | 汗液葡萄糖水平分析和心电图的同时监测,检测范围0~200 μmol/L,灵敏度29.1 μA·L/(mmol·cm2) | [ | |
| 基于PVA/GOx/PB/C/PET制备的触摸指尖无创血糖监测 | 检测范围0~50 μmol/L,灵敏度2.89 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PB/Au和LOx/PB/Au/GA/Nafion的多功能电化学分析,同时测量葡萄糖和乳酸 | 葡萄糖检测范围1~600 μmol/L,灵敏度26.3 μA·L/(mmol·cm2),乳酸盐检测范围1~40 mmol/L,灵敏度1.49 μA·L/(mmol·cm2) | [ | |
| 基于紫外介导的化学电镀技术制备的GOx/PB/Au/PET葡萄糖传感器 | 检测范围0~2.7 μmol/L,灵敏度22.05 μA·L/(mmol·cm2),抗干扰性强 | [ | |
| 基于Nafion/GOx/PB/porous Au制备的一次性汗液的血糖监测设备 | 检测范围0~10 μmol/L,1 μL汗液即可检测,并实现多级透皮药物释放 | [ | |
| 基于GOx-CNT/PB/Au/PET的葡糖糖传感器与LOx-CNT/PB/Au/CHI乳酸传感器制备的多功能微流体检测 | 葡萄糖检测范围为0~200 μmol/L,灵敏度2.35 μA·L/mmol,乳酸检测范围0~30 mmol/L,灵敏度0.22 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于GOx-CNT/PB/Au制备的实时检测血糖设备 | 检测范围0~25 μmol/L,灵敏度2.1 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于化学气相沉积制备GOx/PB/石墨烯的血糖传感器 | 检测范围0~10 μmol/L,灵敏度1.0 μA·L/mmol,并具有经皮药物释放功能 | [ | |
| 泪液检测 | GOx/水凝胶/Pt制备的下眼睑NovioSense葡萄糖传感器 | 检测范围0~20 mmol/L,稳定信号长达4.5 h | [ |
| 基于GOx/CAT/石墨烯制备的智能隐形眼镜葡萄糖传感器 | 检测范围0.1~0.9 mmol/L,灵敏度22.72%·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于AOx/CHI/PB/PET;GOx/PB的眼睛生物传感器检测酒精、维生素和血糖水平 | 检测范围0.011~0.08 μmol/L,9 h的测试期间显示出高稳定性 | [ | |
| 唾液检测 | 基于GOx/PB/Au/PET/CHI制备的安抚奶嘴用于葡萄糖监测 | 检测范围0.1~1.4 mmol/L,灵敏度0.69 nA·L/mmol | [ |
| 通过尿酸酶/PB/GA/聚邻苯二胺制备的护牙生物传感器检测尿酸 | 检测范围0~600 μmol/L,灵敏度为2.45 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 配件检测 | OPH/Nafion/碳电极制备的手套传感器快速检测有机磷神经毒剂 | 检测范围0~200 μmol/L,平均电阻值为480 Ω | [ |
| 基于OPH/PB/PET/碳电极制备的戒指式样传感器检测空气和液体中的爆炸性和神经毒剂威胁 | 气体检测范围0~100 mL/m3,灵敏度高达4.55 μA·m3/mL;液体检测范围2~10 mmol/L,灵敏度高达1.8 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| GOx/LOx/COD/CHI/Au/PtNP/PPD制备的一次性独立式智能手表,监测久坐和高强度运动环境中个体的汗液代谢物特征 | 葡萄糖检测范围0~1000 μmol/L,灵敏度22.8 μA·L/(mmol·cm2);乳酸检测范围0~20 mmol/L,灵敏度4.1 μA·L/(mmol·cm2);胆碱检测范围0~350 μmol/L,灵敏度9.4 μA·L/(mmol·cm2) | [ | |
| 间质液 检测 | 利用普鲁士蓝修饰的GOx传感器在低电位下检测葡萄糖 | 跟踪食物消耗引起的血糖水平变化,检测范围0~100 μmol/L | [ |
| 构建通过PEG-二酰肼交联剂用GOx修饰的纳米纤维垫的葡萄糖生物传感器 | 检测范围95~2000 μmol/L,灵敏度0.8 μA·L/(mmol·cm2),可以在8周内多次重复使用 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PB/CHI制备的检测食用食物后的血糖水平传感器 | 检测范围0~160 μmol/L,灵敏度300 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 基于PPD/AOx-CHI/Nafion/Pt制备的微针生物传感器 | 检测范围0~80 mmol/L,灵敏度0.045 nA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 食品检测 | 基于FDHb/MPA/CMC/NPG制备的果糖生物传感器,用于检测在天然甜味剂和饮料 | 检测范围0.05~0.3 mmol/L,灵敏度145 μA/cm2,6天后剩余40%活性 | [ |
| 基于CDH/PEI-AuNP/RDE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围1~100 μmol/L,灵敏度196.5 μA/cm2,电流密度为10 μA/cm2,响应时间小于5 s | [ | |
| 基于CDH/AuNPs/BPDT/AuE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围5~400 μmol/L,灵敏度27.5 μA/cm2,20天后仍可保持85%活性 | [ | |
| 基于CDH/AuNPs/GCE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围10~300 mmol/L,灵敏度5.4 μA/cm2,1周后保留了约50%的初始活性 | [ | |
| 基于CDH/Co-hemin/CHI/GCE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围10~100 mmol/L,灵敏度102.3 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 酶电合成 | |||
| CO2固定 | 基于FNR/乙酰辅酶A羧化酶/MV/GCE构建的辅因子再生系统 | 碳产品中间体生成速率为160 nmol/(cm2·h),法拉第效率为91% | [ |
| 基于FDH/Cc-PAA/C氧化甲酸的生物阳极 | 还原甲酸盐酸产率为431 nmol/h,法拉第效率高达99% | [ | |
| 基于MoFe-Fe固氮酶/Cc/GDE/GCE将CO2还原为甲酸盐 | 电流密度350 μA/cm2,MoFe-Fe固氮酶法拉第效率分别为9%和32% | [ | |
| 基于FDH/MV/Nafion的三室结构使二氧化碳还原为甲酸盐 | 在20 mV负向可逆电极电位下产生甲酸盐,产量高达97% | [ | |
| 基于FDH/Rh/Nafion/C为阴极的双室反应器的NADH再生系统将CO2还原为甲酸 | 电流密度80 μA/cm2,法拉第效率可达到46% | [ | |
| N2固定 | 基于氢酶/MV为阳极,固氮酶/MV为阴极的体系将N2还原为NH3 | 生成286 nmol NH3,法拉第效率为26.4% | [ |
| 固氮酶/AlaDH/DI/HN-ωTA/MV构建的辅酶再生系统在厌氧H形双室反应器生产手性胺 | 实现MV再生,反应10 h后,胺化产物达到0.61 mmol/L的最高浓度,法拉第效率为27% | [ | |
| 基于Lc/LPEI/MWCNT/C制备的不依赖 ATP的DET系统将 N2 还原到 NH3 | NH3的产量为180 nmol,最大催化电流密度1.88×103 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 氢酶/MV为阳极,固氮酶/MV/DI/LeuDH为阴极制备的H2/α-酮酸燃料电池用于将N2转化为手性氨基酸 | 实现了92%的NH3转化率和87.1%的法拉第效率,OCP为0.25 V | [ | |
| 增值化学品合成 | 基于氢酶/MV/Nafion/为阳极,ADO/TBO/Nafion为阴极,催化脂肪醛脱羰基化为烷烃和甲酸 | 最大电流密度为25 μA/cm2在0.6 V下产生己烷,法拉第效率为24% | [ |
| 基于BPV-LPEI/DH/C8-LPEI/PHA/GC再生NADH系统,可持续合成PHB | NADH再生的法拉第效率为52%,最大电流密度为27.9 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 基于氢酶/MV为阳极,Alk/TBO为阴极利用石油衍生物生成烷烃 | 电流密度为 318 μA/cm2,OCP为0.65 V,法拉第效率为23%,生成辛烷产率为690 nmol/cm2 | [ | |
| 基于GDH/DI/VK3/CF为阳极,利用葡萄糖生成L-DOPA | L-DOPA生产率为118.3 mg/(h·L)和90%的法拉第效率 | [ | |
| 酪氨酸酶/Fe3O4-COOH-NP/Nafion/Ni/C为阴极构建的微生物-酶电合成系统将废水转化为增值化学品 | 合成药物油酸和CPMA的转化率达到78.9%和86.8%,法拉第效率分别达到91%和102.4% | [ | |
表2 酶生物电催化应用系统
Tab. 2 Application systems of enzymatic bioelectrocatalysis
| 应用领域 | 主要策略 | 主要效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酶生物燃料电池 | |||
| MET型 | 基于氢酶/MV/为阳极、固氮酶/MV为阴极的H2/N2燃料电池 | 最大电流和功率密度分别为48.0 μA/cm2和1.50 μW/cm2,OCP为0.23 V | [ |
| 基于氢酶/MV/Nafion为阳极、ADO/TBO/Nafion为阴极的H2/庚醛燃料电池 | 最大电流密度和功率密度为25 μA/cm2和4.7 μW/cm2,OCP最高达到0.6 V | [ | |
| 基于氢酶/MV/C为阳极、BOD/Nafion/C为阴极的H2/O2燃料电池 | 最大功率密度为3.6×103 μW/cm2,OCP的值为1.13 V。 | [ | |
| 基于氢酶/MV/GCE为阳极、BOD/C为阴极的H2/O2燃料电池 | 最大电流密度和功率密度为6.3×103 μA/cm2和4.4 ×103 μW/cm2,OCP最高达到1.14 V | [ | |
| 基于FDH/Cc-PAA/C为阳极的甲酸盐/O2燃料电池 | 最大电流密度62 μA/cm2,OCP为 1.28 V | [ | |
| FDH/BPV-LPEI/C为阳极、Lc/MWCNT/Nafion/C为阴极的HCOO-/O2酶燃料电池 | 最大电流和功率密度为17 μA/cm2和18 μW/cm2,OCP为1.28 V | [ | |
| FDH/MV/聚乙二醇/GCE为阳极、BOD/ABTS/GCE为阴极的HCOO-/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度达到2×104 μA/cm2,功率密度为1.2×103 μW/cm2,OCP为0.78 V | [ | |
| 基于多酶/CNT/AQDS/C阳极、Pt为阴极的多糖燃料电池酶 | 最大功率密度为108 μW/cm2,电流密度为 2.56×103 μA/cm2,法拉第效率为95% | [ | |
| DET型 | 基于Lc/CNT/Ta高性能生物阴极组成的O2燃料电池 | 电流密度840 μA/cm2,在168 h的使用寿命期间能保持75%的电流 | [ |
| GOx/对苯二酚/SWNT/Au为阴极、Lc/SWNT/Au为阳极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度790 μA/cm2,功率密度240 μW/cm2,OCP为0.52 V,在低pH下可有效工作 | [ | |
| 基于Py2Ox/CAT/GC为阳极、Py2Ox/HRP/CNT-CMF-CC为阴极的H2/葡萄糖燃料电池 | 功率密度530 μW/cm2,OCP为1.15 V,在10 h的使用寿命期间保留50%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于GDH/PANI/AuNP/Au为作用在人体血液中的高效生物阳极的葡萄糖燃料电池 | 电流密度1×103 μA/cm2,在10 h的使用寿命期间能保持79%的电流 | [ | |
| GOx/NQ/MWNT为阳极、HRP/MWNT为阴极的葡萄糖/H2O2燃料电池 | 功率密度700 μW/cm2,OCP为0.6 V | [ | |
| 基于GOx/TPA/PEI/CNT为阳极、Pt/C为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度78.6 μA/cm2,功率密度1.62×103 μW/cm2,在672 h的使用寿命期间能保持75.8%的电流 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PANI/GC为阳极、Lc/PANI/GC为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 功率密度1.12×103 μW/cm2,OCP为0.78 V,在336 h的使用寿命期间能保持82.9%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于FAD-GDH/Th-AuNP/CNT/GC为阳极、BOD/GR/CNT/GC为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度925 μA/cm2,功率密度269 μW/cm2,OCP为0.71 V | [ | |
| 基于GOx/Naph-SH/AgNP/PEI/CNT为阳极、Pt/C为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度1.46×103 μA/cm2,在840 h的使用寿命期间能保持83%的电流 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/3D石墨烯为阳极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 功率密度164 μW/cm2,OCP为0.44 V,在168 h的使用寿命期间能保持60%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PVP-RPPy/NiF为阳极、Lc/PVP-RPPy/NiF为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 功率密度350 μW/cm2,OCP为1.16 V,在336 h的使用寿命期间能保持82%的功率 | [ | |
| Zn为阳极、BOD/MWNT/rGO/PG为阴极的O2燃料电池 | 电流密度650 μA/cm2,功率密度775 μW/cm2,OCP为1.68 V | [ | |
| BOD/MWCNT为阴极的O2燃料电池 | 功率密度4×103 μW/cm2,在24 h的使用寿命期间能保持73%的功率 | [ | |
| GDH/GO/GC为阳极、Lc/AuNP/Au为阴极的葡萄糖/O2燃料电池 | 电流密度1.1×103 μA/cm2,功率密度400 μW/cm2,OCP为0.86 V,在576 h的使用寿命期间能保持93%的功率 | [ | |
| 基于NiFe氢酶/MWCNT/NQ/GCE为阴极的H2/O2燃料电池 | 最大功率密度为 890 μW/cm2,OCP为1.1 V | [ | |
| 自供电可穿戴电子设备 | 基于LOx/TTF-MDB/Pt/Co设计的由汗液驱动的集成电子皮肤检测乳酸 | 功率密度350 µW/cm2,具有良好的稳定性能 | [ |
| 基于LOx/CNT/1,4-NQ/GA/CHI为阳极、Box/CNT/PPIX/Nafion为阴极制备的电子纺织微电网 | 功率密度21.5 µW/cm2,电流密度5.8 µA/cm2监测汗液中的乳酸 | [ | |
| 基于LOx/CNT/NQ/Pt/Cu/Nafion检测汗液中的乳酸 | 可以从静止状态下指尖汗液中收集400 mJ/cm2能量 | [ | |
| 基于LOx/NQ/液态金属组成的可伸缩电化学组件检测汗液中的乳酸浓度 | 最大功率密度为270 μW/cm2和0.50 V的OCP | [ | |
| 酶生物传感器 | |||
| 表皮检测 | 附着在皮肤上以形成皮下电化学双通道利用GOx检测血糖 | 实现无创血管内血糖测量,具有130.4 μA·L/mmol高灵敏度 | [ |
| 尿酸酶/C制备的新型纸质智能绷带检测伤口尿酸水平 | 降低更换伤口敷料的频率,检测范围为100~800 μmol/L,精确监测伤口长达3 d | [ | |
| 将LOx与硼酸盐形成外聚合层同Nafion固定在电极上检测乳酸 | 检测范围0.22~0.75 mmol/L,灵敏度为0.1 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于Au/rGO/PtNP/CHI/GOx制备的葡萄糖生物传感器 | 汗液葡萄糖水平分析和心电图的同时监测,检测范围0~200 μmol/L,灵敏度29.1 μA·L/(mmol·cm2) | [ | |
| 基于PVA/GOx/PB/C/PET制备的触摸指尖无创血糖监测 | 检测范围0~50 μmol/L,灵敏度2.89 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PB/Au和LOx/PB/Au/GA/Nafion的多功能电化学分析,同时测量葡萄糖和乳酸 | 葡萄糖检测范围1~600 μmol/L,灵敏度26.3 μA·L/(mmol·cm2),乳酸盐检测范围1~40 mmol/L,灵敏度1.49 μA·L/(mmol·cm2) | [ | |
| 基于紫外介导的化学电镀技术制备的GOx/PB/Au/PET葡萄糖传感器 | 检测范围0~2.7 μmol/L,灵敏度22.05 μA·L/(mmol·cm2),抗干扰性强 | [ | |
| 基于Nafion/GOx/PB/porous Au制备的一次性汗液的血糖监测设备 | 检测范围0~10 μmol/L,1 μL汗液即可检测,并实现多级透皮药物释放 | [ | |
| 基于GOx-CNT/PB/Au/PET的葡糖糖传感器与LOx-CNT/PB/Au/CHI乳酸传感器制备的多功能微流体检测 | 葡萄糖检测范围为0~200 μmol/L,灵敏度2.35 μA·L/mmol,乳酸检测范围0~30 mmol/L,灵敏度0.22 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于GOx-CNT/PB/Au制备的实时检测血糖设备 | 检测范围0~25 μmol/L,灵敏度2.1 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于化学气相沉积制备GOx/PB/石墨烯的血糖传感器 | 检测范围0~10 μmol/L,灵敏度1.0 μA·L/mmol,并具有经皮药物释放功能 | [ | |
| 泪液检测 | GOx/水凝胶/Pt制备的下眼睑NovioSense葡萄糖传感器 | 检测范围0~20 mmol/L,稳定信号长达4.5 h | [ |
| 基于GOx/CAT/石墨烯制备的智能隐形眼镜葡萄糖传感器 | 检测范围0.1~0.9 mmol/L,灵敏度22.72%·L/mmol | [ | |
| 基于AOx/CHI/PB/PET;GOx/PB的眼睛生物传感器检测酒精、维生素和血糖水平 | 检测范围0.011~0.08 μmol/L,9 h的测试期间显示出高稳定性 | [ | |
| 唾液检测 | 基于GOx/PB/Au/PET/CHI制备的安抚奶嘴用于葡萄糖监测 | 检测范围0.1~1.4 mmol/L,灵敏度0.69 nA·L/mmol | [ |
| 通过尿酸酶/PB/GA/聚邻苯二胺制备的护牙生物传感器检测尿酸 | 检测范围0~600 μmol/L,灵敏度为2.45 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 配件检测 | OPH/Nafion/碳电极制备的手套传感器快速检测有机磷神经毒剂 | 检测范围0~200 μmol/L,平均电阻值为480 Ω | [ |
| 基于OPH/PB/PET/碳电极制备的戒指式样传感器检测空气和液体中的爆炸性和神经毒剂威胁 | 气体检测范围0~100 mL/m3,灵敏度高达4.55 μA·m3/mL;液体检测范围2~10 mmol/L,灵敏度高达1.8 μA·L/mmol | [ | |
| GOx/LOx/COD/CHI/Au/PtNP/PPD制备的一次性独立式智能手表,监测久坐和高强度运动环境中个体的汗液代谢物特征 | 葡萄糖检测范围0~1000 μmol/L,灵敏度22.8 μA·L/(mmol·cm2);乳酸检测范围0~20 mmol/L,灵敏度4.1 μA·L/(mmol·cm2);胆碱检测范围0~350 μmol/L,灵敏度9.4 μA·L/(mmol·cm2) | [ | |
| 间质液 检测 | 利用普鲁士蓝修饰的GOx传感器在低电位下检测葡萄糖 | 跟踪食物消耗引起的血糖水平变化,检测范围0~100 μmol/L | [ |
| 构建通过PEG-二酰肼交联剂用GOx修饰的纳米纤维垫的葡萄糖生物传感器 | 检测范围95~2000 μmol/L,灵敏度0.8 μA·L/(mmol·cm2),可以在8周内多次重复使用 | [ | |
| 基于GOx/PB/CHI制备的检测食用食物后的血糖水平传感器 | 检测范围0~160 μmol/L,灵敏度300 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 基于PPD/AOx-CHI/Nafion/Pt制备的微针生物传感器 | 检测范围0~80 mmol/L,灵敏度0.045 nA·L/mmol | [ | |
| 食品检测 | 基于FDHb/MPA/CMC/NPG制备的果糖生物传感器,用于检测在天然甜味剂和饮料 | 检测范围0.05~0.3 mmol/L,灵敏度145 μA/cm2,6天后剩余40%活性 | [ |
| 基于CDH/PEI-AuNP/RDE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围1~100 μmol/L,灵敏度196.5 μA/cm2,电流密度为10 μA/cm2,响应时间小于5 s | [ | |
| 基于CDH/AuNPs/BPDT/AuE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围5~400 μmol/L,灵敏度27.5 μA/cm2,20天后仍可保持85%活性 | [ | |
| 基于CDH/AuNPs/GCE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围10~300 mmol/L,灵敏度5.4 μA/cm2,1周后保留了约50%的初始活性 | [ | |
| 基于CDH/Co-hemin/CHI/GCE制备的乳糖传感器 | 检测范围10~100 mmol/L,灵敏度102.3 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 酶电合成 | |||
| CO2固定 | 基于FNR/乙酰辅酶A羧化酶/MV/GCE构建的辅因子再生系统 | 碳产品中间体生成速率为160 nmol/(cm2·h),法拉第效率为91% | [ |
| 基于FDH/Cc-PAA/C氧化甲酸的生物阳极 | 还原甲酸盐酸产率为431 nmol/h,法拉第效率高达99% | [ | |
| 基于MoFe-Fe固氮酶/Cc/GDE/GCE将CO2还原为甲酸盐 | 电流密度350 μA/cm2,MoFe-Fe固氮酶法拉第效率分别为9%和32% | [ | |
| 基于FDH/MV/Nafion的三室结构使二氧化碳还原为甲酸盐 | 在20 mV负向可逆电极电位下产生甲酸盐,产量高达97% | [ | |
| 基于FDH/Rh/Nafion/C为阴极的双室反应器的NADH再生系统将CO2还原为甲酸 | 电流密度80 μA/cm2,法拉第效率可达到46% | [ | |
| N2固定 | 基于氢酶/MV为阳极,固氮酶/MV为阴极的体系将N2还原为NH3 | 生成286 nmol NH3,法拉第效率为26.4% | [ |
| 固氮酶/AlaDH/DI/HN-ωTA/MV构建的辅酶再生系统在厌氧H形双室反应器生产手性胺 | 实现MV再生,反应10 h后,胺化产物达到0.61 mmol/L的最高浓度,法拉第效率为27% | [ | |
| 基于Lc/LPEI/MWCNT/C制备的不依赖 ATP的DET系统将 N2 还原到 NH3 | NH3的产量为180 nmol,最大催化电流密度1.88×103 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 氢酶/MV为阳极,固氮酶/MV/DI/LeuDH为阴极制备的H2/α-酮酸燃料电池用于将N2转化为手性氨基酸 | 实现了92%的NH3转化率和87.1%的法拉第效率,OCP为0.25 V | [ | |
| 增值化学品合成 | 基于氢酶/MV/Nafion/为阳极,ADO/TBO/Nafion为阴极,催化脂肪醛脱羰基化为烷烃和甲酸 | 最大电流密度为25 μA/cm2在0.6 V下产生己烷,法拉第效率为24% | [ |
| 基于BPV-LPEI/DH/C8-LPEI/PHA/GC再生NADH系统,可持续合成PHB | NADH再生的法拉第效率为52%,最大电流密度为27.9 μA/cm2 | [ | |
| 基于氢酶/MV为阳极,Alk/TBO为阴极利用石油衍生物生成烷烃 | 电流密度为 318 μA/cm2,OCP为0.65 V,法拉第效率为23%,生成辛烷产率为690 nmol/cm2 | [ | |
| 基于GDH/DI/VK3/CF为阳极,利用葡萄糖生成L-DOPA | L-DOPA生产率为118.3 mg/(h·L)和90%的法拉第效率 | [ | |
| 酪氨酸酶/Fe3O4-COOH-NP/Nafion/Ni/C为阴极构建的微生物-酶电合成系统将废水转化为增值化学品 | 合成药物油酸和CPMA的转化率达到78.9%和86.8%,法拉第效率分别达到91%和102.4% | [ | |
| 164 | SIN M L Y, MACH K E, WONG P K, et al. Advances and challenges in biosensor-based diagnosis of infectious diseases[J]. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 2014, 14(2): 225-244. |
| 165 | GATTANI A, SINGH S V, AGRAWAL A, et al. Recent progress in electrochemical biosensors as point of care diagnostics in livestock health[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2019, 579: 25-34. |
| 166 | HARRAD L EL, BOURAIS I, MOHAMMADI H, et al. Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors based on enzyme inhibition for clinical and pharmaceutical applications[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 164. |
| 167 | NGUYEN H H, LEE S H, LEE U J, et al. Immobilized enzymes in biosensor applications[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(1): 121. |
| 168 | REYES-DE-CORCUERA J I, OLSTAD H E, GARCÍA-TORRES R. Stability and stabilization of enzyme biosensors: the key to successful application and commercialization[J]. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 9: 293-322. |
| 169 | HAMMOND J L, FORMISANO N, ESTRELA P, et al. Electrochemical biosensors and nanobiosensors[J]. Essays in Biochemistry, 2016, 60(1): 69-80. |
| 170 | JAFFREZIC-RENAULT N, DZYADEVYCH S V. Conductometric microbiosensors for environmental monitoring[J]. Sensors, 2008, 8(4): 2569-2588. |
| 171 | RANDVIIR E P, BANKS C E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: an overview of bioanalytical applications[J]. Analytical Methods, 2013, 5(5): 1098. |
| 172 | GUO X W. Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor technique: a review[J]. Journal of Biophotonics, 2012, 5(7): 483-501. |
| 173 | DING J W, QIN W. Recent advances in potentiometric biosensors[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 124: 115803. |
| 174 | GARG S K, AKTURK H K. Flash glucose monitoring: the future is here[J]. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 2017, 19(S2): S1-S3. |
| 175 | Lactose biosensor assay kit system. [Z]. 2021. www.lactosens.com |
| 176 | FERAPONTOVA E E, GRIGORENKO V G, EGOROV A M, et al. Mediatorless biosensor for H2O2 based on recombinant forms of horseradish peroxidase directly adsorbed on polycrystalline gold[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2001, 16(3): 147-157. |
| 177 | GASPAR S, ZIMMERMANN H, GAZARYAN I, et al. Hydrogen peroxide biosensors based on direct electron transfer from plant peroxidases immobilized on self-assembled thiol-monolayer modified gold electrodes[J]. Electroanalysis, 2001, 13(4): 284-288. |
| 178 | GAZARYAN I G, GORTON L, RUZGAS T, et al. Tobacco peroxidase as a new reagent for amperometric biosensors[J]. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 60(6): 558-566. |
| 179 | SHIPOVSKOV S, FERAPONTOVA E E. Biocatalysis of theophylline oxidation by microbial theophylline oxidase in the presence of non-physiological electron acceptors[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 2008, 26(6): 455-465. |
| 180 | FORT C I, ORTIZ R, COTET L C, et al. Carbon aerogel as electrode material for improved direct electron transfer in biosensors incorporating cellobiose dehydrogenase[J]. Electroanalysis, 2016, 28(10): 2311-2319. |
| 181 | KHOKHAR S, MOHD ZIN A A, BHAYO M A, et al. Automated recognition of single & hybrid power quality disturbances using wavelet transform based support vector machine[J]. Jurnal Teknologi, 2016, 79(1). . |
| 182 | BOLLELLA P, GORTON L, ANTIOCHIA R. Direct electron transfer of dehydrogenases for development of 3rd generation biosensors and enzymatic fuel cells[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1319. |
| 183 | LE BORGNE S, PANIAGUA D, VAZQUEZ-DUHALT R. Biodegradation of organic pollutants by halophilic bacteria and Archaea[J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 15(2/3): 74-92. |
| 184 | DOMINGUEZ-BENETTON X, SANDIPAM S, SATYAWALI Y, et al. Enzymatic electrosynthesis: an overview on the progress in enzyme-electrodes for the production of electricity, fuels and chemicals[J/OL]. Journal of Microbial and Biochemical Technology, 2013, S6: 009. |
| 185 | YUAN M W, SAHIN S, CAI R, et al. Creating a low-potential redox polymer for efficient electroenzymatic CO2 reduction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(22): 6582-6586. |
| 186 | BASSEGODA A, MADDEN C, WAKERLEY D W, et al. Reversible interconversion of CO2 and formate by a molybdenum-containing formate dehydrogenase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(44): 15473-15476. |
| 187 | KUK S K, GOPINATH K, SINGH R K, et al. NADH-free electroenzymatic reduction of CO2 by conductive hydrogel-conjugated formate dehydrogenase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(6): 5584-5589. |
| 188 | SAKAI K, KITAZUMI Y, SHIRAI O, et al. Efficient bioelectrocatalytic CO2 reduction on gas-diffusion-type biocathode with tungsten-containing formate dehydrogenase[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2016, 73: 85-88. |
| 189 | KUK S K, SINGH R K, NAM D H, et al. Photoelectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol through a highly efficient enzyme cascade[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(14): 3827-3832. |
| 1 | HILL H A O, HIGGINS I J. Bioelectrocatalysis[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1981, 302: 267-273. |
| 2 | IKEDA T, KANO K. An electrochemical approach to the studies of biological redox reactions and their applications to biosensors, bioreactors, and biofuel cells[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2001, 92(1): 9-18. |
| 3 | CADOUX C, MILTON R D. Recent enzymatic electrochemistry for reductive reactions[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(9): 1974-1986. |
| 4 | CHEN H, DONG F Y, MINTEER S D. The progress and outlook of bioelectrocatalysis for the production of chemicals, fuels and materials[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(3): 225-244. |
| 5 | GAJDA I, OBATA O, GREENMAN J, et al. Electroosmotically generated disinfectant from urine as a by-product of electricity in microbial fuel cell for the inactivation of pathogenic species[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5533. |
| 6 | INAMUDDIN, SHAKEEL N, IMRAN AHAMED M, et al. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles decorated on polyindole functionalized-MCNTs and used as anode material for enzymatic biofuel cell applications[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5052. |
| 7 | FREGUIA S, VIRDIS B, HARNISCH F, et al. Bioelectrochemical systems: microbial versus enzymatic catalysis[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 82: 165-174. |
| 8 | HICKEY D P, MILTON R D, RASMUSSEN M A, et al. Fundamentals and applications of bioelectrocatalysis [M]// BANKS C, MORTIMER R, MCINTOSH S. Electrochemistry: Volume 13. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2016. |
| 9 | HAQUE S U, DUTEANU N, CIOCAN S, et al. A review: evolution of enzymatic biofuel cells[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 298: 113483. |
| 10 | WU R R, MA C L, ZHU Z G. Enzymatic electrosynthesis as an emerging electrochemical synthesis platform[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2020, 19: 1-7. |
| 11 | VLASITS J, JAKOPITSCH C, BERNROITNER M, et al. Mechanisms of catalase activity of heme peroxidases[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2010, 500(1): 74-81. |
| 12 | ZHANG W, DU L, LI F W, et al. Mechanistic insights into interactions between bacterial class I P450 enzymes and redox partners[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(11): 9992-10003. |
| 190 | MILTON R D, MINTEER S D. Enzymatic bioelectrosynthetic ammonia production: recent electrochemistry of nitrogenase, nitrate reductase, and nitrite reductase[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2017, 82(4): 513-521. |
| 191 | LEE Y S, RUFF A, CAI R, et al. Electroenzymatic nitrogen fixation using a MoFe protein system immobilized in an organic redox polymer[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(38): 16511-16516. |
| 192 | HICKEY D P, LIM K, CAI R, et al. Pyrene hydrogel for promoting direct bioelectrochemistry: ATP-independent electroenzymatic reduction of N2 [J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(23): 5172-5177. |
| 193 | ABDELLAOUI S, MACAZO F C, CAI R, et al. Enzymatic electrosynthesis of alkanes by bioelectrocatalytic decarbonylation of fatty aldehydes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(9): 2404-2408. |
| 194 | NAM D H, RYU G M, KUK S K, et al. Water oxidation-coupled, photoelectrochemical redox biocatalysis toward mimicking natural photosynthesis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 198: 311-317. |
| 195 | LEE S M, CHOE H, CHO D H, et al. Communication-highly efficient electroenzymatic NADH regeneration by an electron-relay flavoenzyme[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(5): G50-G52. |
| 196 | ZOR C, REEVE H A, QUINSON J, et al. H2-Driven biocatalytic hydrogenation in continuous flow using enzyme-modified carbon nanotube columns[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(71): 9839-9841. |
| 197 | LEE Y W, BOONMONGKOLRAS P, SON E J, et al. Unbiased biocatalytic solar-to-chemical conversion by FeOOH/BiVO4/perovskite tandem structure[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 4208. |
| 198 | WU R R, ZHU Z G. Self-powered enzymatic electrosynthesis of l-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in a hybrid bioelectrochemical system[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(10): 12593-12597. |
| 199 | SON E, LEE S, KUK S, et al. Carbon nanotube-graphitic carbon nitride hybrid films for flavoenzyme-catalyzed photoelectrochemical cells[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 28: 1705232. |
| 200 | CHEN X L, CAO Y X, LI F, et al. Enzyme-assisted microbial electrosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) via CO2 bioreduction by engineered Ralstonia eutropha [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(5): 4429-4437. |
| 201 | CHOI D S, NI Y, FERNáNDEZ-FUEYO E, et al. Photoelectroenzymatic oxyfunctionalization on flavin-hybridized carbon nanotube electrode platform[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(3): 1563-7. |
| 13 | BETANCOR L, JOHNSON G R, LUCKARIFT H R. Stabilized laccases as heterogeneous bioelectrocatalysts[J]. ChemCatChem, 2013, 5(1): 46-60. |
| 14 | HUIJBERS M M E, MONTERSINO S, WESTPHAL A H, et al. Flavin dependent monooxygenases[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2014, 544: 2-17. |
| 15 | LAURINAVICIUS V, RAZUMIENE J, RAMANAVICIUS A, et al. Wiring of PQQ-dehydrogenases[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2004, 20(6): 1217-1222. |
| 16 | MAYO S L, ELLIS W R JR, CRUTCHLEY R J, et al. Long-range electron transfer in heme proteins[J]. Science, 1986, 233(4767): 948-952. |
| 17 | MEYER J. Iron-sulfur protein folds, iron-sulfur chemistry, and evolution[J]. JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 13(2): 157-170. |
| 18 | LILL R. Function and biogenesis of iron-sulphur proteins[J]. Nature, 2009, 460(7257): 831-838. |
| 19 | EVANS D J, PICKETT C J. Chemistry and the hydrogenases[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2003, 32(5): 268-275. |
| 20 | CAI R, MINTEER S D. Nitrogenase bioelectrocatalysis: from understanding electron-transfer mechanisms to energy applications[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(11): 2736-2742. |
| 21 | SEEFELDT L C, HOFFMAN B M, PETERS J W, et al. Energy transduction in nitrogenase[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(9): 2179-2186. |
| 22 | SHLEEV S, TKAC J, CHRISTENSON A, et al. Direct electron transfer between copper-containing proteins and electrodes[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2005, 20(12): 2517-2554. |
| 23 | ROMERO E, CASTELLANOS J R G, GADDA G, et al. Same substrate, many reactions: oxygen activation in flavoenzymes[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(4): 1742-1769. |
| 24 | GOODWIN P M, ANTHONY C. The biochemistry, physiology and genetics of PQQ and PQQ-containing enzymes [M]//POOLE R K. Advances in microbial physiology. Academic Press. 1998: 1-80. |
| 25 | RAZUMIENE J, NICULESCU M, RAMANAVICIUS A, et al. Direct bioelectrocatalysis at carbon electrodes modified with quinohemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter sp. 33[J]. Electroanalysis, 2002, 14(1): 43-49. |
| 26 | TREMEY E, STINES-CHAUMEIL C, GOUNEL S, et al. Designing an O2-insensitive glucose oxidase for improved electrochemical applications[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2017, 4(10): 2520-2526. |
| 27 | MASAKARI Y, HARA C, ARAKI Y, et al. Improvement in the thermal stability of Mucor prainii-derived FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase via protein chimerization[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2020, 132: 109387. |
| 28 | 王世珍, 刘凯泷, 詹东平. 氧化还原酶电催化反应研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(10): 1240-1249. |
| WANG S Z, LIU L L, ZHAN D P. Advances of bioelectrocatalysis by oxidoreductases[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(10): 1240-1249. | |
| 29 | MANO N. Engineering glucose oxidase for bioelectrochemical applications[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2019, 128: 218-240. |
| 30 | ZHANG L L, CUI H Y, ZOU Z, et al. Directed evolution of a bacterial laccase (CueO) for enzymatic biofuel cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(14): 4562-4565. |
| 31 | MA C, WU R, HUANG R, et al. Directed evolution of a 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase for operating an enzymatic fuel cell at lowered anodic pHs [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 851: 113444. |
| 32 | CHEN H, ZHU Z G, HUANG R, et al. Coenzyme engineering of a hyperthermophilic 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from NADP+ to NAD+ with its application to biobatteries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 36311. |
| 33 | BAO L L, SUN D P, TACHIKAWA H, et al. Improved sensitivity of a histamine sensor using an engineered methylamine dehydrogenase[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 74(5): 1144-1148. |
| 34 | WEGERICH F, TURANO P, ALLEGROZZI M, et al. Cytochrome C mutants for superoxide biosensors[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(8): 2976-2984. |
| 35 | HIRAKA K, KOJIMA K, LIN C E, et al. Minimizing the effects of oxygen interference on L-lactate sensors by a single amino acid mutation in Aerococcus viridans l-lactate oxidase[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2018, 103: 163-170. |
| 36 | YAMASHITA Y, FERRI S, HUYNH M L, et al. Direct electron transfer type disposable sensor strip for glucose sensing employing an engineered FAD glucose dehydrogenase[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2013, 52(2): 123-128. |
| 37 | ZHOU Q, HU M R, ZHANG W, et al. Probing the function of the Tyr-Cys cross-link in metalloenzymes by the genetic incorporation of 3-methylthiotyrosine[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(4): 1203-1207. |
| 38 | DYDIO P, KEY H M, NAZARENKO A, et al. An artificial metalloenzyme with the kinetics of native enzymes[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6308): 102-106. |
| 39 | YANG Y, ZHOU Q, WANG L, et al. Significant improvement of oxidase activity through the genetic incorporation of a redox-active unnatural amino acid[J]. Chemical Science, 2015, 6(7): 3881-3885. |
| 40 | PRESNOVA G, GRIGORENKO V, EGOROV A, et al. Direct heterogeneous electron transfer of recombinant horseradish peroxidases on gold[J]. Faraday Discussions, 2000(116): 281-289. |
| 41 | LEE Y S, BAEK S, LEE H, et al. Construction of uniform monolayer-and orientation-tunable enzyme electrode by a synthetic glucose dehydrogenase without electron-transfer subunit via optimized site-specific gold-binding peptide capable of direct electron transfer[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(34): 28615-28626. |
| 42 | AL-LOLAGE F, BARTLETT P N, GOUNEL S, et al. Site-directed immobilization of bilirubin oxidase for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(3): 2068-2078. |
| 43 | WANG Y M, KANG Z P, ZHANG L L, et al. Elucidating the interactions between a [NiFe]-hydrogenase and carbon electrodes for enhanced bioelectrocatalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(2): 1415-1427. |
| 44 | LAMBERG P, HAMIT-EMINOVSKI J, TOSCANO M D, et al. Electrical activity of cellobiose dehydrogenase adsorbed on thiols: influence of charge and hydrophobicity[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2017, 115: 26-32. |
| 45 | MUGURUMA H, IWASA H, HIDAKA H, et al. Mediatorless direct electron transfer between flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent glucose dehydrogenase and single-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(1): 725-734. |
| 46 | ZAYATS M, KATZ E, WILLNER I. Electrical contacting of glucose oxidase by surface-reconstitution of the apo-protein on a relay-boronic acid-FAD cofactor monolayer[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(10): 2120-2121. |
| 47 | WANG Y M, SONG Y H, MA C L, et al. Electrochemical characterization of a truncated hydrogenase from Pyrococcus furiosus [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 387: 138502. |
| 48 | OKUDA-SHIMAZAKI J, LOEW N, HIROSE N, et al. Construction and characterization of flavin adenine dinucleotide glucose dehydrogenase complex harboring a truncated electron transfer subunit[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 277: 276-286. |
| 49 | ORTIZ R, MATSUMURA H, TASCA F, et al. Effect of deglycosylation of cellobiose dehydrogenases on the enhancement of direct electron transfer with electrodes[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(23): 10315-10323. |
| 50 | CHEN H, CAI R, PATEL J, et al. Upgraded bioelectrocatalytic N2 fixation: from N2 to chiral amine intermediates[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(12): 4963-4971. |
| 51 | SONG H Y, MA C L, LIU P, et al. A hybrid CO2 electroreduction system mediated by enzyme-cofactor conjugates coupled with Cu nanoparticle-catalyzed cofactor regeneration[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2019, 34: 568-575. |
| 52 | ZEYMER C, HILVERT D. Directed evolution of protein catalysts[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2018, 87: 131-157. |
| 53 | PACKER M S, LIU D R. Methods for the directed evolution of proteins[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2015, 16(7): 379-394. |
| 54 | HORAGUCHI Y, SAITO S, KOJIMA K, et al. Engineering glucose oxidase to minimize the influence of oxygen on sensor response[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 126: 158-161. |
| 55 | YU Y, LIU X H, WANG J Y. Expansion of redox chemistry in designer metalloenzymes[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(3): 557-565. |
| 56 | ZHU Z G, MA C L, PERCIVAL ZHANG Y H. Co-utilization of mixed sugars in an enzymatic fuel cell based on an in vitro enzymatic pathway[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 263: 184-191. |
| 57 | XIA L, HAN M J, ZHOU L, et al. S-click reaction for isotropic orientation of oxidases on electrodes to promote electron transfer at low potentials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(46): 16480-16484. |
| 58 | 曲戈, 赵晶, 郑平, 等. 定向进化技术的最新进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(1): 1-11. |
| QU G, ZHAO J, ZHENG P, et al. Recent advances in directed evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 34(1): 1-11. | |
| 59 | ADACHI T, KATAOKA K, KITAZUMI Y, et al. A bio-solar cell with thylakoid membranes and bilirubin oxidase[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2019, 48(7): 686-689. |
| 60 | HU C, CHAN S I, SAWYER E B, et al. Metalloprotein design using genetic code expansion[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(18): 6498-6510. |
| 61 | AGOSTINI F, VÖLLER J S, KOKSCH B, et al. Biocatalysis with unnatural amino acids: enzymology meets xenobiology[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(33): 9680-9703. |
| 62 | HU C, YU Y, WANG J Y. Improving artificial metalloenzymes' activity by optimizing electron transfer[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(30): 4173-4186. |
| 63 | KEY H M, DYDIO P, CLARK D S, et al. Abiological catalysis by artificial haem proteins containing noble metals in place of iron[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7608): 534-537. |
| 64 | ARDAOI, HWANGE T, ZENGA-P. In vitro multienzymatic reaction systems for biosynthesis [M]// ZENG A-P. Fundamentals and application of new bioproduction systems. Berlin, Heidelberg; Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2013: 153-184. |
| 65 | WU R R, SONG H Y, WANG Y M, et al. Multienzyme co-immobilization-based bioelectrode: design of principles and bioelectrochemical applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020, 28(8): 2037-2050. |
| 66 | ZHU Z G, SUN F F, ZHANG X Z, et al. Deep oxidation of glucose in enzymatic fuel cells through a synthetic enzymatic pathway containing a cascade of two thermostable dehydrogenases[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2012, 36(1): 110-115. |
| 67 | ALIM S, KAFI A K M, RAJAN J, et al. Application of polymerized multiporous nanofiber of SnO2 for designing a bienzyme glucose biosensor based on HRP/GOx[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 123: 1028-1034. |
| 68 | ZHANG L L, LIU J, FU Z L, et al. A wearable biosensor based on bienzyme gel-membrane for sweat lactate monitoring by mounting on eyeglasses[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2020, 20(3): 1495-1503. |
| 69 | ALKOTAINI B, ABDELLAOUI S, HASAN K, et al. Sustainable bioelectrosynthesis of the bioplastic polyhydroxybutyrate: overcoming substrate requirement for NADH regeneration[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(4): 4909-4915. |
| 70 | WANG L L, GONG W C, WANG F, et al. Efficient bienzyme nanocomposite film for chiral recognition of L-tryptophan, L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine[J]. Analytical Methods, 2016, 8(17): 3481-3487. |
| 71 | VARGAS E, RUIZ M A, FERRERO F J, et al. Automatic bionalyzer using an integrated amperometric biosensor for the determination of L-malic acid in wines[J]. Talanta, 2016, 158: 6-13. |
| 72 | SAKAMOTO H, KOMATSU T, YAMASAKI K, et al. Design of a multi-enzyme reaction on an electrode surface for an L-glutamate biofuel anode[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2017, 39(2): 235-240. |
| 73 | HIRANO Y, IKEGAMI M, KOWATA K, et al. Bienzyme reactions on cross-linked DNA scaffolds for electrochemical analysis[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2017, 113: 15-19. |
| 74 | HWANG E T, LEE S. Multienzymatic cascade reactions via enzyme complex by immobilization[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(5): 4402-4425. |
| 75 | ZUCCA P, SANJUST E. Inorganic materials as supports for covalent enzyme immobilization: methods and mechanisms[J]. Molecules, 2014, 19(9): 14139-14194. |
| 76 | MOEHLENBROCK M J, MEREDITH M T, MINTEER S D. Bioelectrocatalytic oxidation of glucose in CNT impregnated hydrogels: advantages of synthetic enzymatic metabolon formation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2012, 2(1): 17-25. |
| 77 | MOEHLENBROCK M J, TOBY T K, PELSTER L N, et al. Metabolon catalysts: an efficient model for multi-enzyme cascades at electrode surfaces[J]. ChemCatChem, 2011, 3(3): 561-570. |
| 78 | MOEHLENBROCK M J, TOBY T K, WAHEED A, et al. Metabolon catalyzed pyruvate/air biofuel cell[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(18): 6288-6289. |
| 79 | FAN S Q, LIANG B, XIAO X X, et al. Controllable display of sequential enzymes on yeast surface with enhanced biocatalytic activity toward efficient enzymatic biofuel cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(6): 3222-3230. |
| 80 | BEHRENDORFF J B Y H, BORRÀS-GAS G, PRIBIL M. Synthetic protein scaffolding at biological membranes[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(4): 432-446. |
| 81 | MENG D D, WU R R, WANG J, et al. Acceleration of cellodextrin phosphorolysis for bioelectricity generation from cellulosic biomass by integrating a synthetic two-enzyme complex into an in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystem[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 267. |
| 82 | SZCZUPAK A, AIZIK D, MORAÏS S, et al. The electrosome: a surface-displayed enzymatic cascade in a biofuel cell's anode and a high-density surface-displayed biocathodic enzyme[J]. Nanomaterials, 2017, 7(7): 153. |
| 83 | FU J L, LIU M H, LIU Y, et al. Interenzyme substrate diffusion for an enzyme cascade organized on spatially addressable DNA nanostructures[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(12): 5516-5519. |
| 84 | KIM Y H, CAMPBELL E, YU J, et al. Complete oxidation of methanol in biobattery devices using a hydrogel created from three modified dehydrogenases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(5): 1437-1440. |
| 85 | PAGE C C, MOSER C C, CHEN X X, et al. Natural engineering principles of electron tunnelling in biological oxidation-reduction[J]. Nature, 1999, 402(6757): 47-52. |
| 86 | STEINBUSCH K J J, HAMELERS H V M, SCHAAP J D, et al. Bioelectrochemical ethanol production through mediated acetate reduction by mixed cultures[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(1): 513-517. |
| 87 | HATCH J L, FINNERAN K T. Influence of reduced electron shuttling compounds on biological H2 production in the fermentative pure culture Clostridium beijerinckii [J]. Current Microbiology, 2008, 56(3): 268-273. |
| 88 | PARK D H, ZEIKUS J G. Utilization of electrically reduced neutral red by Actinobacillus succinogenes: physiological function of neutral red in membrane-driven fumarate reduction and energy conservation[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1999, 181(8): 2403-2410. |
| 89 | MINTEER S D. Enzyme stabilization and immobilization[M]. Springer, 2017. |
| 90 | JESIONOWSKI T, ZDARTA J, KRAJEWSKA B. Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: a review[J]. Adsorption, 2014, 20(5/6): 801-821. |
| 91 | CHRISTWARDANA M, CHUNG Y, KWON Y. Co-immobilization of glucose oxidase and catalase for enhancing the performance of a membraneless glucose biofuel cell operated under physiological conditions[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(5): 1993-2002. |
| 92 | WU R R, MA C L, YONG Y C, et al. Composition and distribution of internal resistance in an enzymatic fuel cell and its dependence on cell design and operating conditions[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(13): 7292-7300. |
| 93 | SHARMA S K, SINGHAL R, MALHOTRA B D, et al. Biosensor based on Langmuir-Blodgett films of poly(3-hexyl thiophene) for detection of galactose in human blood[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2004, 26(8): 645-647. |
| 94 | MOHAMAD N R, MARZUKI N H C, BUANG N A, et al. An overview of technologies for immobilization of enzymes and surface analysis techniques for immobilized enzymes[J]. Biotechnology, Biotechnological Equipment, 2015, 29(2): 205-220. |
| 95 | DENG L, SHANG L, WEN D, et al. A membraneless biofuel cell powered by ethanol and alcoholic beverage[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2010, 26(1): 70-73. |
| 96 | ZHU Z G, MA C L, PERCIVAL ZHANG Y H. Co-utilization of mixed sugars in an enzymatic fuel cell based on an in vitro enzymatic pathway[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 263: 184-191. |
| 97 | MACAZO F C, MINTEER S D. Enzyme cascades in biofuel cells[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 5(1): 114-120. |
| 98 | DATTA S, CHRISTENA L R, RAJARAM Y R S. Enzyme immobilization: an overview on techniques and support materials[J]. 3 Biotech, 2013, 3(1): 1-9. |
| 99 | VAN NGUYEN K, MINTEER S D. Investigating DNA hydrogels as a new biomaterial for enzyme immobilization in biobatteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(66): 13071-13073. |
| 100 | SATOMURA T, HORINAGA K, TANAKA S, et al. Construction of a novel bioanode for amino acid powered fuel cells through an artificial enzyme cascade pathway[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2019, 41(4/5): 605-611. |
| 101 | HYUN K, KANG S, KIM J, et al. New biocatalyst including a 4-nitrobenzoic acid mediator embedded by the cross-linking of chitosan and genipin and its use in an energy device[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(20): 23635-23643. |
| 102 | CHANG H C, WOHLSCHLAGER L, CSARMAN F, et al. Real-time measurement of cellobiose and glucose formation during enzymatic biomass hydrolysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(21): 7732-7738. |
| 103 | WANG F, GONG W C, WANG L L, et al. Enhanced amperometric response of a glucose oxidase and horseradish peroxidase based bienzyme glucose biosensor modified with a film of polymerized toluidine blue containing reduced graphene oxide[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2015, 182(11/12): 1949-1956. |
| 104 | GRIJALVA-BUSTAMANTE G A, EVANS-VILLEGAS A G, DEL CASTILLO-CASTRO T, et al. Enzyme mediated synthesis of polypyrrole in the presence of chondroitin sulfate and redox mediators of natural origin[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2016, 63: 650-656. |
| 105 | SO K, KITAZUMI Y, SHIRAI O, et al. Direct electron transfer-type dual gas diffusion H2/O2biofuel cells[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(22): 8742-8749. |
| 106 | TAKAMURA E, OHNISHI T, SAKAMOTO H, et al. Promoting of direct electron transfer of multicopper oxidase by control of enzyme molecule density on multi-walled carbon nanotube[J]. Journal of Physics: Energy, 2021, 3(1): 014006. |
| 107 | LAI B, TANG X H, LI H R, et al. Power production enhancement with a polyaniline modified anode in microbial fuel cells[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2011, 28(1): 373-377. |
| 108 | SAITO T, MEHANNA M, WANG X, et al. Effect of nitrogen addition on the performance of microbial fuel cell anodes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(1): 395-398. |
| 109 | ZHU N W, CHEN X, ZHANG T, et al. Improved performance of membrane free single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cells with nitric acid and ethylenediamine surface modified activated carbon fiber felt anodes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(1): 422-426. |
| 110 | ZHOU M H, CHI M L, WANG H Y, et al. Anode modification by electrochemical oxidation: a new practical method to improve the performance of microbial fuel cells[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 60: 151-155. |
| 111 | CHUMILLAS S, MAESTRO B, FELIU J M, et al. Comprehensive study of the enzymatic catalysis of the electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) by immobilized copper efflux oxidase (CueO) from Escherichia coli [J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2018, 6: 358. |
| 112 | KALIMUTHU P, BELAIDI A A, SCHWARZ G, et al. Chitosan-promoted direct electrochemistry of human sulfite oxidase[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2017, 121(39): 9149-9159. |
| 113 | WILLNER I, KATZ E, WILLNER B. Electrical contact of redox enzyme layers associated with electrodes: routes to amperometric biosensors[J]. Electroanalysis, 1997, 9(13): 965-977. |
| 114 | KATZ E, WILLNER I. Biomolecule-functionalized carbon nanotubes: applications in nanobioelectronics [J]. ChemPhysChem, 2004, 5(8): 1084-1104. |
| 115 | COURJEAN O, GAO F, MANO N. Deglycosylation of glucose oxidase for direct and efficient glucose electrooxidation on a glassy carbon electrode[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(32): 5897-5899. |
| 116 | PRÉVOTEAU A, COURJEAN O, MANO N. Deglycosylation of glucose oxidase to improve biosensors and biofuel cells[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12(2): 213-215. |
| 117 | LEE H J, LEE S H, PARK C B, et al. Coenzyme analogs: excellent substitutes (not poor imitations) for electrochemical regeneration[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(46): 12538-12540. |
| 118 | SONG H Y, MA C L, ZHOU W, et al. Construction of enzyme-cofactor/mediator conjugates for enhanced in vitro bioelectricity generation[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2018, 29(12): 3993-3998. |
| 119 | BARSAN M M, GHICA M E, BRETT C M A. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on redox polymer/carbon nanotube modified electrodes: a review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2015, 881: 1-23. |
| 120 | KUMAR S A, CHEN S M. Electroanalysis of NADH using conducting and redox active polymer/carbon nanotubes modified electrodes-a review[J]. Sensors, 2008, 8(2): 739-766. |
| 121 | YUAN M W, MINTEER S D. Redox polymers in electrochemical systems: from methods of mediation to energy storage[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2019, 15: 1-6. |
| 202 | SHI T, HAN P P, YOU C, et al. An in vitro synthetic biology platform for emerging industrial biomanufacturing: bottom-up pathway design[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2018, 3(3): 186-195. |
| 203 | CHEN X L, LI S B, LIU L M. Engineering redox balance through cofactor systems[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2014, 32(6): 337-343. |
| 204 | SHARP R E, CHAPMAN S K. Mechanisms for regulating electron transfer in multi-centre redox proteins[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 1999, 1432(2): 143-158. |
| 205 | SHITANDA I, NOHARA S, HOSHI Y, et al. A screen-printed circular-type paper-based glucose/O2 biofuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 360: 516-519. |
| 206 | SURANITI E, MERZEAU P, ROCHE J, et al. Uphill production of dihydrogen by enzymatic oxidation of glucose without an external energy source[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3229. |
| 207 | VERMA S, LU S, KENIS P J A. Co-electrolysis of CO2 and glycerol as a pathway to carbon chemicals with improved technoeconomics due to low electricity consumption[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(6): 466-474. |
| 208 | DU J, CATANIA C, BAZAN G C. Modification of abiotic-biotic interfaces with small molecules and nanomaterials for improved bioelectronics[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(1): 686-697. |
| 209 | AJO-FRANKLIN C M, NOY A. Crossing over: nanostructures that move electrons and ions across cellular membranes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(38): 5797-5804. |
| 210 | KRIEG T, MADJAROV J, ROSA L F M, et al. Reactors for microbial electrobiotechnology [M]//HARNISCH F, HOLTMANN D. Bioelectrosynthesis. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 231-271. |
| 211 | ENZMANN F, MAYER F, STÖCKL M, et al. Transferring bioelectrochemical processes from H-cells to a scalable bubble column reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 193: 133-143. |
| 122 | MAO F, MANO N, HELLER A. Long tethers binding redox centers to polymer backbones enhance electron transport in enzyme “wiring” hydrogels[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(16): 4951-4957. |
| 123 | WALCARIUS A, MINTEER S D, WANG J, et al. Nanomaterials for bio-functionalized electrodes: recent trends[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(38): 4878-4908. |
| 124 | ZHAO C E, GAI P P, SONG R B, et al. Nanostructured material-based biofuel cells: recent advances and future prospects[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(5): 1545-1564. |
| 125 | SABOE P O, CONTE E, FARELL M, et al. Biomimetic and bioinspired approaches for wiring enzymes to electrode interfaces[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(1): 14-42. |
| 126 | MAZURENKO I, DE POULPIQUET A, LOJOU E. Recent developments in high surface area bioelectrodes for enzymatic fuel cells[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 5(1): 74-84. |
| 127 | HOLZINGER M, LE GOFF A, COSNIER S. Carbon nanotube/enzyme biofuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 82: 179-190. |
| 128 | LAHEÄÄR A, DELPEUX-OULDRIANE S, LUST E, et al. Ammonia treatment of activated carbon powders for supercapacitor electrode application[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(4): A568-A575. |
| 129 | FRANZOI A C, VIEIRA I C, DUPONT J, et al. Biosensor for luteolin based on silver or gold nanoparticles in ionic liquid and laccase immobilized in chitosan modified with cyanuric chloride[J]. The Analyst, 2009, 134(11): 2320-2328. |
| 130 | CAVALCANTI I T, SILVA B V M, PERES N G, et al. A disposable chitosan-modified carbon fiber electrode for dengue virus envelope protein detection[J]. Talanta, 2012, 91: 41-46. |
| 131 | WANG L, ZHENG Y L, LU X P, et al. Dendritic copper-cobalt nanostructures/reduced graphene oxide-chitosan modified glassy carbon electrode for glucose sensing[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 195: 1-7. |
| 132 | XIE Y E, MA Z K, SONG H H, et al. Melamine modified carbon felts anode with enhanced electrogenesis capacity toward microbial fuel cells[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2017, 26(1): 81-86. |
| 133 | WINDMILLER J R, WANG J. Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review[J]. Electroanalysis, 2013, 25(1): 29-46. |
| 134 | XIAO X X, XIA H Q, WU R R, et al. Tackling the challenges of enzymatic (bio)fuel cells[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(16): 9509-9558. |
| 135 | HERNÁNDEZ-IBÁÑEZ N, GOMIS-BERENGUER A, MONTIEL V, et al. Fabrication of a biocathode for formic acid production upon the immobilization of formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii on a nanoporous carbon[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291(Pt 3): 133117. |
| 136 | CHEN H, SIMOSKA O, LIM K, et al. Fundamentals, applications, and future directions of bioelectrocatalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(23): 12903-12993. |
| 137 | YU S, MYUNG N V. Recent advances in the direct electron transfer-enabled enzymatic fuel cells[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 8: 620153. |
| 138 | PARRILLA M, DE WAEL K. Wearable self-powered electrochemical devices for continuous health management [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(50): 2107042. |
| 139 | MINJ H, SEMPIONATTOJ R, TEYMOURIANH, et al. Wearable electrochemical biosensors in North America[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2021, 172: 112750. |
| 140 | XUAN X, PÉREZ-RÀFOLS C, CHEN C, et al. Lactate biosensing for reliable on-body sweat analysis[J]. ACS Sensors, 2021, 6(7): 2763-2771. |
| 141 | YOON S, YOON H, ZAHED M A, et al. Multifunctional hybrid skin patch for wearable smart healthcare applications[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022, 196: 113685. |
| 142 | KEMP E, PALOMÄKI T, RUUTH I A, et al. Influence of enzyme immobilization and skin-sensor interface on non-invasive glucose determination from interstitial fluid obtained by magnetohydrodynamic extraction[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022, 206: 114123. |
| 143 | SCHACHINGER F, CHANG H C, SCHEIBLBRANDNER S, et al. Amperometric biosensors based on direct electron transfer enzymes[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(15): 4525. |
| 144 | CAIR, MILTONR D, ABDELLAOUIS, et al. Electroenzymatic C-C bond formation from CO2 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(15): 5041-5044. |
| 145 | WU R R, YU Y Y, WANG Y M, et al. Wastewater-powered high-value chemical synthesis in a hybrid bioelectrochemical system[J]. iScience, 2021, 24(12): 103401. |
| 146 | UEKI T, WALKER D J F, TREMBLAY P L, et al. Decorating the outer surface of microbially produced protein nanowires with peptides[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(8): 1809-1817. |
| 147 | TAN Y, ADHIKARI R Y, MALVANKAR N S, et al. The low conductivity of geobacter uraniireducens pili suggests a diversity of extracellular electron transfer mechanisms in the genus geobacter[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 980. |
| 148 | HARTSHORNE R S, REARDON C L, ROSS D, et al. Characterization of an electron conduit between bacteria and the extracellular environment[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(52): 22169-22174. |
| 149 | ROSS D E, FLYNN J M, BARON D B, et al. Towards electrosynthesis in Shewanella: energetics of reversing the Mtr pathway for reductive metabolism[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2): e16649. |
| 150 | HALÁMKOVÁ L, HALÁMEK J, BOCHAROVA V, et al. Implanted biofuel cell operating in a living snail[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(11): 5040-5043. |
| 151 | BANDODKAR A J, GUTRUF P, CHOI J, et al. Battery-free, skin-interfaced microfluidic/electronic systems for simultaneous electrochemical, colorimetric, and volumetric analysis of sweat[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(1): eaav3294. |
| 152 | SAKAI H, NAKAGAWA T, TOKITA Y, et al. A high-power glucose/oxygen biofuel cell operating under quiescent conditions [J]. Energy and Environmental Science, 2009, 2(1): 133-138. |
| 153 | COSNIER S, SHAN D, DING S N. An easy compartment-less biofuel cell construction based on the physical co-inclusion of enzyme and mediator redox within pressed graphite discs[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12(2): 266-269. |
| 154 | SHI P K, WU R R, WANG J, et al. Biomass sugar-powered enzymatic fuel cells based on a synthetic enzymatic pathway[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2022, 144: 108008. |
| 155 | CHEN H, HUANG R, KIM E J, et al. Building a thermostable metabolon for facilitating coenzyme transport and in vitro hydrogen production at elevated temperature[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(18): 3120-3130. |
| 156 | MOEHLENBROCK M J, MINTEER S D. Extended lifetime biofuel cells[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 37(6): 1188-1196. |
| 157 | CASTILLO-ORTEGA M M, RODRIGUEZ D E, ENCINAS J C, et al. Conductometric uric acid and urea biosensor prepared from electroconductive polyaniline-poly(n-butyl methacrylate) composites[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2002, 85(1/2): 19-25. |
| 158 | MILTON R D, LIM K, HICKEY D P, et al. Employing FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase within a glucose/oxygen enzymatic fuel cell operating in human serum[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2015, 106: 56-63. |
| 159 | LEE I, LOEW N, TSUGAWA W, et al. The electrochemical behavior of a FAD dependent glucose dehydrogenase with direct electron transfer subunit by immobilization on self-assembled monolayers[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2018, 121: 1-6. |
| 160 | YOSHIDA H, SAKAI G, MORI K, et al. Structural analysis of fungus-derived FAD glucose dehydrogenase[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 13498. |
| 161 | SCHEIBLBRANDNER S, CSARMAN F, LUDWIG R. Cellobiose dehydrogenase in biofuel cells[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 73: 205-212. |
| 162 | XU M, OBODO D, YADAVALLI V K. The design, fabrication, and applications of flexible biosensing devices[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2019, 124/125: 96-114. |
| 163 | ROTARIU L, LAGARDE F, JAFFREZIC-RENAULT N, et al. Electrochemical biosensors for fast detection of food contaminants-trends and perspective[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 79: 80-87. |
| [1] | 李怡霏, 陈艾, 孙俊松, 张以恒. 体外多酶分子机器产氢应用中的氢酶研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1461-1484. |
| [2] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [3] | 张俊, 金诗雪, 云倩, 瞿旭东. 聚酮化合物非天然延伸单元的生物合成与结构改造应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [4] | 陈雅如, 曹英秀, 宋浩. 电活性微生物基因编辑与转录调控技术进展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [5] | 朱华伟, 李寅. 生物光伏:环境友好的新型太阳能利用技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1259-1280. |
| [6] | 康里奇, 谈攀, 洪亮. 人工智能时代下的酶工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. |
| [7] | 祁延萍, 朱晋, 张凯, 刘彤, 王雅婕. 定向进化在蛋白质工程中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. |
| [8] | 由紫暄, 李锋, 宋浩. 电能细胞的合成生物学设计构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 1031-1059. |
| [9] | 杨璐, 瞿旭东. 亚胺还原酶在手性胺合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 516-529. |
| [10] | 张以恒. 忆王义翘教授对生物炼制的贡献和我对此领域未来发展的观点[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 497-508. |
| [11] | 史然, 江正强. 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖的酶法合成研究进展和展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 481-494. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||