合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 1031-1059.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-014
• 特约评述 • 上一篇
电能细胞的合成生物学设计构建
由紫暄1,2,3, 李锋1,2,3, 宋浩1,2,3
- 1.天津大学化工学院,天津 300072
2.天津大学合成生物学前沿科学中心和系统生物工程教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
3.天津大学化工协同创新中心合成生物学研究平台,天津 300072
-
收稿日期:2022-03-01修回日期:2022-04-19出版日期:2022-10-31发布日期:2022-11-16 -
通讯作者:李锋,宋浩 -
作者简介:由紫暄(1997—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为电能细胞的合成生物学研究。由紫暄 (1997—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为电能细胞的合成生物学研究。E-mail:youzixuan_yzx@tju.edu.cn李锋 (1988—),男,助理教授,硕士生导师。研究方向为光电遗传学在物质、能量代谢中的应用。E-mail:messilifeng@163.com宋浩 (1973—),男 ,教授、博士生导师。研究方向为能量代谢与光-电遗传学,生物制药。E-mail:hsong@tju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0901300);国家自然科学基金(32071411);天津市科技计划(20JCQNJC00830);天津市教育部研究生科研创新项目(2020YJSB045)
Design and construction of electroactive cells by synthetic biology strategies
YOU Zixuan1,2,3, LI Feng1,2,3, SONG Hao1,2,3
- 1.School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2.Frontiers Science Center for Synthetic Biology (Ministry of Education),Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
3.Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin),School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
-
Received:2022-03-01Revised:2022-04-19Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-16 -
Contact:LI Feng, SONG Hao
摘要:
电能细胞具有与外界环境进行双向电子交换的能力,包括向外界环境释放电子的产电细胞,以及从外界环境获取电子的噬电细胞,在微生物电化学系统中发挥微生物电催化剂的核心作用。以电能细胞为核心的微生物电化学系统在生态环境治理、绿色能源开发、化学品高效合成等方面有着广泛应用。但是野生电能细胞因其摄取底物能力弱、胞内电子通量小、双向跨膜电子传递效率低、生物膜形成能力差等原因,化学能到电能的双向转化效率受到极大限制,是实现微生物电化学系统大规模产业化应用的核心瓶颈。本综述聚焦近5年电能细胞合成生物学改造的最新研究进展,通过分析双向电子传递的分子机制,分类汇总产电细胞和噬电细胞的合成生物学改造策略:①工程产电细胞(强化产电细胞的胞内电子生成、胞外传递效率,具体为拓宽底物谱、增强还原力转化,提高胞外传递能力、促进电极生物膜形成);②工程噬电细胞(强化噬电细胞胞外电子摄取、还原力转化、产物合成效率,包括提高噬电细胞电子摄取和还原力转化,调控细胞代谢路径电合成化学品和生物燃料)。最后,展望了未来高效电能细胞和微生物电化学系统的设计与构建。
中图分类号:
引用本文
由紫暄, 李锋, 宋浩. 电能细胞的合成生物学设计构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 1031-1059.
YOU Zixuan, LI Feng, SONG Hao. Design and construction of electroactive cells by synthetic biology strategies[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 1031-1059.

图1 双向电子传递机制由细胞色素或纳米线介导的直接电子传递机制(左);由电子传递载体介导的间接电子传递机制(右)
Fig. 1 Bi-directional electron transfer mechanism(Left) Direct electron transfer via cytochromes and conductive nanowires; (Right) Electron shuttles mediated electron transfer
| 电能细胞 | 合成生物学策略 | 工程结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 底物代谢效率的合成生物学改造 | ||
| S.oneidensis | 强化乳酸利用关键因子CRP表达,增强菌株对乳酸的利用能力[ | 最大电流密度约40 mA/m2 |
| 异源表达视紫红质基因,通过光驱动改变膜电位,增强乳酸的摄取[ | 平均电流密度达0.39 A/m2 | |
| 异源表达葡萄糖转运基因和葡萄糖激酶基因,增强菌株葡萄糖代谢能力[ | 最大电流输出0.085 mA | |
| 异源表达木糖转运蛋白、异构酶等构建木糖代谢途径[ | 最大功率密度2.1 mW/m2 | |
| 异源表达乙酸辅酶A基因(ato1,ato2),强化柠檬酸合酶基因gtlA,构建乙酸代谢路径[ | 最大功率密度8.3 mW/m2 | |
| 胞内可释放电子池的合成生物学改造 | ||
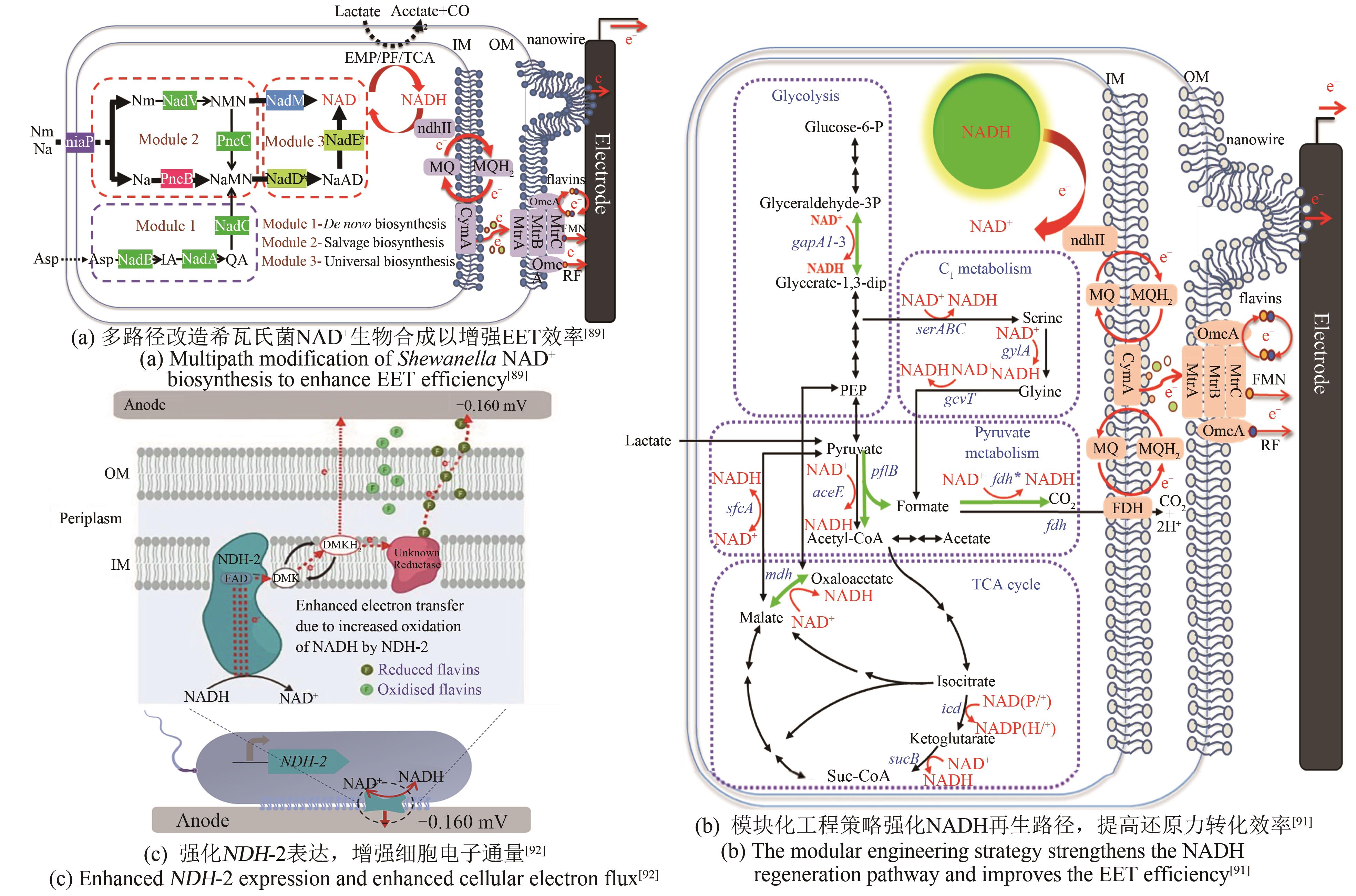
| P.aeruginosa | 过表达NAD+合成酶基因nadE,扩充胞内NAD(H/+)总量[ | 最大功率密度4.0 mW/m2 |
| S.oneidensis | 过表达ycel、pncB、nadM、nadD*、nadE*基因,增强NAD+的生物合成[ | 最大功率密度162.8 mW/m2 |
| 过表达gapA2、pflB、fdh*、mdh基因,强化NADH的合成[ | 最大功率密度105.8 mW/m2 | |
| E.coli | 破坏乳酸脱氢酶基因ldhA,释放储存在胞内中间代谢物的电子[ | 最大功率密度3.0 mW/m2 |
| 过表达非质子泵NADH脱氢酶NDH-2,使更多电子通过氧化呼吸链流入EET途径[ | 输出电流4.7 μA | |
| 构建C3N代谢通路,获得高效的NAD+代谢途径[ | NAD(H)浓度约6 mmol/L | |
| 胞外电子传递的合成生物学改造 | ||
| E.coli | 通过引入S.oneidensis的MtrCAB色素系统使得E.coli具备胞外电子传递能力[ | Fe(Ⅲ)还原速率达83 μmol/(L·d) |
| 构建S.oneidensis和E.coli细胞色素融合表达系统[ | 电流密度达到25.32 mA/m2 | |
| 异源表达PCA合成路径phzA1B1C1D1E1F1G1基因簇,以提高间接胞外电子传递速率[ | 最大功率密度为181.1 mW/m2 | |
| S.oneidensis | 过表达内膜细胞色素CymA,加速电子传递至末端周质还原酶[ | 功率达到0.13 mW |
| 敲除周质色素蛋白napB、fccA、tsdB并过表达细胞色素cctA,降低周质细胞色素复杂性[ | 最高功率密度达到436.5 mW/m2 | |
| 异源表达来自B.subtilis的核黄素合成基因簇ribADEHC,以提高菌株的胞外电子传递速率[ | 最大功率输出为233.0 mW/m2 | |
| 强化核黄素表达,结合孔蛋白增强分泌,添加材料rGO,构建三维杂合生物膜系统[ | 最大功率输出达2630 mW/m2 | |
| 异源构建PCA合成路径和ombB-omaB-omcB-omcS直接电子传递链[ | 最大电流密度达310.2 mA/m2 | |
| P.aeruginosa | 通过截断PaPilA C端并增加N端 α-螺旋区的芳香族氨基酸含量,提高菌毛导电率[ | 最大电流达130 μA |
| 过表达甲基转移酶基因phzM,增强菌株胞外电子传递载体-绿脓菌素的合成[ | 最大功率密度达16.67 mW/m2 | |
| G.sulfurreducens | 异源表达来自G.metallireducens的pilA基因,增强菌毛导电率[ | pili导电率为277 S/cm |
| 电活性生物膜的合成生物学改造 | ||
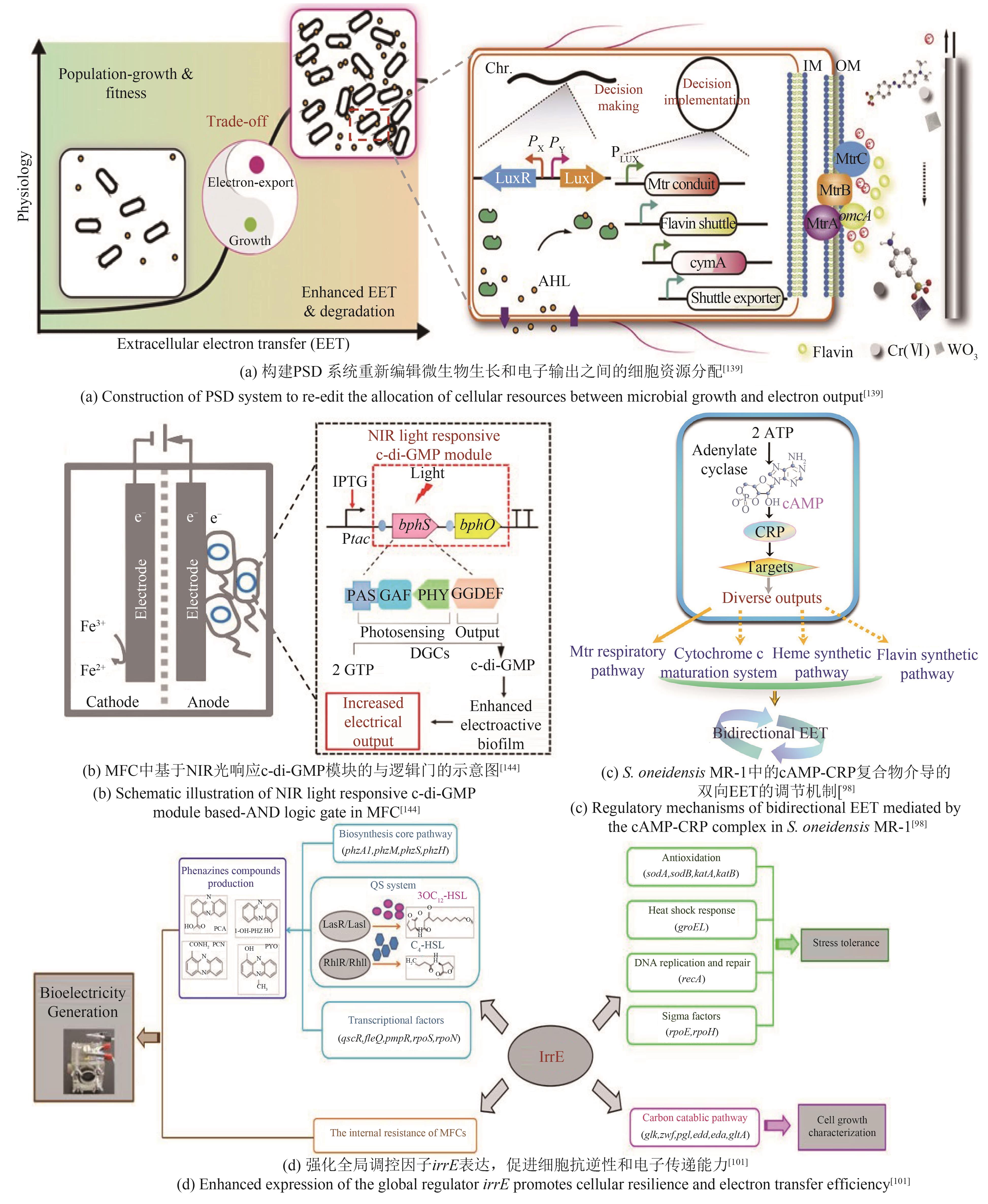
| S.oneidensis | 过表达ydeH基因,增强菌株生物膜形成能力[ | 最大功率密度达167.6 mW/m2 |
| 过表达cyaC基因增加菌株胞内cAMP浓度,提高菌株电流输出密度[ | 最大电流密度达356 mA/m2 | |
| G.sulfurreducens | 过表达GSU1501基因促进胞外多糖分泌,促进生物膜形成,提高c型细胞色素丰度[ | Fe(Ⅲ)还原速率达1.75 mmol/(L·d) |
| P.aeruginosa | 敲除RpoS基因促进吩嗪类物质合成,提高胞外电子通量[ | 最大电流密度达4.5 μA/cm2 |
| 过表达irrE基因,强化参与胞内代谢和EET过程[ | 最大功率密度达56.0 mW/m2 | |
| 构建irrE突变基因文库,增强细胞环境适应性和产电性能[ | 最大功率密度达149.2 mW/m2 | |
表1 产电细胞的合成生物学改造汇总
Tab. 1 Summary of engineering exoelectrogens by synthetic biology
| 电能细胞 | 合成生物学策略 | 工程结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 底物代谢效率的合成生物学改造 | ||
| S.oneidensis | 强化乳酸利用关键因子CRP表达,增强菌株对乳酸的利用能力[ | 最大电流密度约40 mA/m2 |
| 异源表达视紫红质基因,通过光驱动改变膜电位,增强乳酸的摄取[ | 平均电流密度达0.39 A/m2 | |
| 异源表达葡萄糖转运基因和葡萄糖激酶基因,增强菌株葡萄糖代谢能力[ | 最大电流输出0.085 mA | |
| 异源表达木糖转运蛋白、异构酶等构建木糖代谢途径[ | 最大功率密度2.1 mW/m2 | |
| 异源表达乙酸辅酶A基因(ato1,ato2),强化柠檬酸合酶基因gtlA,构建乙酸代谢路径[ | 最大功率密度8.3 mW/m2 | |
| 胞内可释放电子池的合成生物学改造 | ||
| P.aeruginosa | 过表达NAD+合成酶基因nadE,扩充胞内NAD(H/+)总量[ | 最大功率密度4.0 mW/m2 |
| S.oneidensis | 过表达ycel、pncB、nadM、nadD*、nadE*基因,增强NAD+的生物合成[ | 最大功率密度162.8 mW/m2 |
| 过表达gapA2、pflB、fdh*、mdh基因,强化NADH的合成[ | 最大功率密度105.8 mW/m2 | |
| E.coli | 破坏乳酸脱氢酶基因ldhA,释放储存在胞内中间代谢物的电子[ | 最大功率密度3.0 mW/m2 |
| 过表达非质子泵NADH脱氢酶NDH-2,使更多电子通过氧化呼吸链流入EET途径[ | 输出电流4.7 μA | |
| 构建C3N代谢通路,获得高效的NAD+代谢途径[ | NAD(H)浓度约6 mmol/L | |
| 胞外电子传递的合成生物学改造 | ||
| E.coli | 通过引入S.oneidensis的MtrCAB色素系统使得E.coli具备胞外电子传递能力[ | Fe(Ⅲ)还原速率达83 μmol/(L·d) |
| 构建S.oneidensis和E.coli细胞色素融合表达系统[ | 电流密度达到25.32 mA/m2 | |
| 异源表达PCA合成路径phzA1B1C1D1E1F1G1基因簇,以提高间接胞外电子传递速率[ | 最大功率密度为181.1 mW/m2 | |
| S.oneidensis | 过表达内膜细胞色素CymA,加速电子传递至末端周质还原酶[ | 功率达到0.13 mW |
| 敲除周质色素蛋白napB、fccA、tsdB并过表达细胞色素cctA,降低周质细胞色素复杂性[ | 最高功率密度达到436.5 mW/m2 | |
| 异源表达来自B.subtilis的核黄素合成基因簇ribADEHC,以提高菌株的胞外电子传递速率[ | 最大功率输出为233.0 mW/m2 | |
| 强化核黄素表达,结合孔蛋白增强分泌,添加材料rGO,构建三维杂合生物膜系统[ | 最大功率输出达2630 mW/m2 | |
| 异源构建PCA合成路径和ombB-omaB-omcB-omcS直接电子传递链[ | 最大电流密度达310.2 mA/m2 | |
| P.aeruginosa | 通过截断PaPilA C端并增加N端 α-螺旋区的芳香族氨基酸含量,提高菌毛导电率[ | 最大电流达130 μA |
| 过表达甲基转移酶基因phzM,增强菌株胞外电子传递载体-绿脓菌素的合成[ | 最大功率密度达16.67 mW/m2 | |
| G.sulfurreducens | 异源表达来自G.metallireducens的pilA基因,增强菌毛导电率[ | pili导电率为277 S/cm |
| 电活性生物膜的合成生物学改造 | ||
| S.oneidensis | 过表达ydeH基因,增强菌株生物膜形成能力[ | 最大功率密度达167.6 mW/m2 |
| 过表达cyaC基因增加菌株胞内cAMP浓度,提高菌株电流输出密度[ | 最大电流密度达356 mA/m2 | |
| G.sulfurreducens | 过表达GSU1501基因促进胞外多糖分泌,促进生物膜形成,提高c型细胞色素丰度[ | Fe(Ⅲ)还原速率达1.75 mmol/(L·d) |
| P.aeruginosa | 敲除RpoS基因促进吩嗪类物质合成,提高胞外电子通量[ | 最大电流密度达4.5 μA/cm2 |
| 过表达irrE基因,强化参与胞内代谢和EET过程[ | 最大功率密度达56.0 mW/m2 | |
| 构建irrE突变基因文库,增强细胞环境适应性和产电性能[ | 最大功率密度达149.2 mW/m2 | |
| 电能细胞 | 合成生物学策略 | 工程结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 工程强化噬电细胞电子摄取和转化 | ||
| S.oneidensis | 表达光驱动质子泵,强化丁二醇脱氢酶表达并敲除氢化酶基因hyaB、hydA,驱动丁二醇合成[ | 2,3-丁二醇合成量10.06 mmol/L |
| E.coli | 异源表达细胞色素蛋白MtrCAB、FccA、CymA碳酸氢盐转运蛋白和碳酸酐酶基因,构建产琥珀酸细胞工厂[ | 琥珀酸产电达30.56 mmol/L |
| S.elongatus PCC 7942 | 异源表达色素蛋白OmcS和nif基因,促进N2固定[ | NH3 20 h产率达295.7 μmol/L |
| 工程噬电细胞代谢路径电合成化学品和生物燃料 | ||
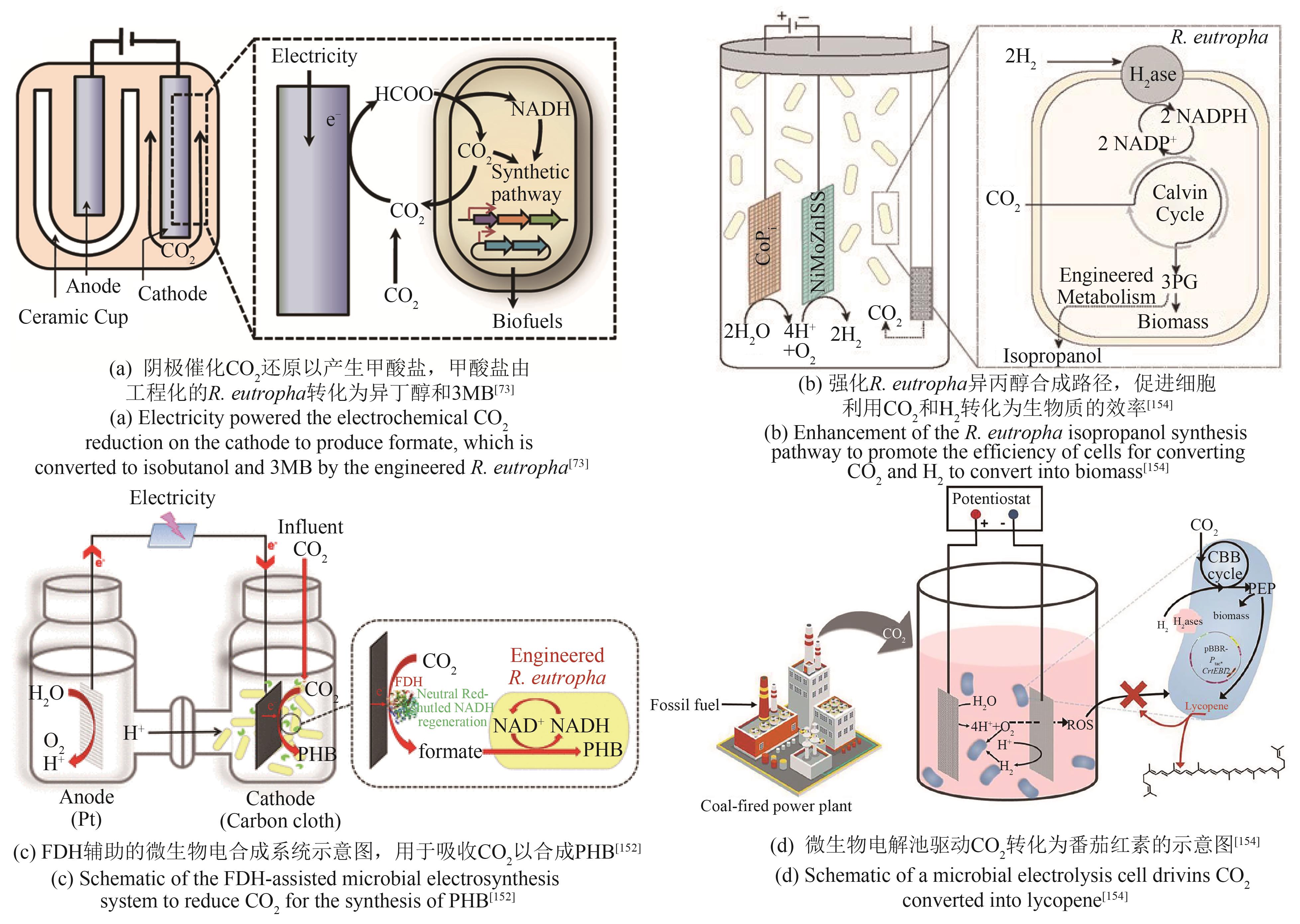
| R.eutropha | 敲除聚羟基丁酸合成基因簇,异源表达异丁醇合成路径关键基因alsS、ilvC、ilvD、kivd和yqhD,使代谢流向异丁醇和3-甲基-1-丁醇合成[ | 异丁醇、3-甲基-1-丁醇产量达140 mg/L |
| 破坏聚羟基丁酸酯合成,并强化异丙醇合成路径,使代谢流向异丙醇合成[ | 异丙醇产量达216 mg/L | |
| 异源表达核酮糖-1,5-二磷酸羧化酶,强化PHB合成[ | PHB产量达485 mg/L | |
| 异源过表达的甲羟戊酸途径酶法尼基焦磷酸合酶ERG20、IPP异构酶fni和α-葎草烯合酶(ZSSI),促进α-葎草烯合成[ | α-葎草烯产量达10.8 mg/L | |
| 表达番茄红素途径基因CrtEBI2,促进番茄红素合成[ | 番茄红素产量达1.73 mg/L | |
| S.cerevisiae | 异源表达氧甾醇7α-羟化酶,促进7α-OH-DHEA合成[ | 7α-OH-DHEA产量达288.6 mg/L |
| R.palustris | 异源引入丁醇生物合成途径phaABJ、ter、adhE2基因,强化丁醇合成[ | 丁醇产量达0.91 mg/L± 0.07 mg/L |
表2 噬电细胞的合成生物学改造汇总
Tab.2 Summary of engineering electrotrophs by synthetic biology
| 电能细胞 | 合成生物学策略 | 工程结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 工程强化噬电细胞电子摄取和转化 | ||
| S.oneidensis | 表达光驱动质子泵,强化丁二醇脱氢酶表达并敲除氢化酶基因hyaB、hydA,驱动丁二醇合成[ | 2,3-丁二醇合成量10.06 mmol/L |
| E.coli | 异源表达细胞色素蛋白MtrCAB、FccA、CymA碳酸氢盐转运蛋白和碳酸酐酶基因,构建产琥珀酸细胞工厂[ | 琥珀酸产电达30.56 mmol/L |
| S.elongatus PCC 7942 | 异源表达色素蛋白OmcS和nif基因,促进N2固定[ | NH3 20 h产率达295.7 μmol/L |
| 工程噬电细胞代谢路径电合成化学品和生物燃料 | ||
| R.eutropha | 敲除聚羟基丁酸合成基因簇,异源表达异丁醇合成路径关键基因alsS、ilvC、ilvD、kivd和yqhD,使代谢流向异丁醇和3-甲基-1-丁醇合成[ | 异丁醇、3-甲基-1-丁醇产量达140 mg/L |
| 破坏聚羟基丁酸酯合成,并强化异丙醇合成路径,使代谢流向异丙醇合成[ | 异丙醇产量达216 mg/L | |
| 异源表达核酮糖-1,5-二磷酸羧化酶,强化PHB合成[ | PHB产量达485 mg/L | |
| 异源过表达的甲羟戊酸途径酶法尼基焦磷酸合酶ERG20、IPP异构酶fni和α-葎草烯合酶(ZSSI),促进α-葎草烯合成[ | α-葎草烯产量达10.8 mg/L | |
| 表达番茄红素途径基因CrtEBI2,促进番茄红素合成[ | 番茄红素产量达1.73 mg/L | |
| S.cerevisiae | 异源表达氧甾醇7α-羟化酶,促进7α-OH-DHEA合成[ | 7α-OH-DHEA产量达288.6 mg/L |
| R.palustris | 异源引入丁醇生物合成途径phaABJ、ter、adhE2基因,强化丁醇合成[ | 丁醇产量达0.91 mg/L± 0.07 mg/L |
| 1 | LOVLEY D R, HOLMES D E. Electromicrobiology: the ecophysiology of phylogenetically diverse electroactive microorganisms [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 20(1): 1-15. |
| 2 | LOGAN B E, ROSSI R, RAGAB A, et al. Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2019, 17(5): 307-319. |
| 3 | KUMAR A, HSU L H-H, KAVANAGH P, et al. The ins and outs of microorganism-electrode electron transfer reactions [J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2017, 1(3): 0024. |
| 4 | KOCH C, HARNISCH F. Is there a specific ecological niche for electroactive microorganisms? [J]. ChemElectroChem, 2016, 3(9): 1282-1295. |
| 5 | CHEN H, SIMOSKA O, LIM K, et al. Fundamentals, applications, and future directions of bioelectrocatalysis [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(23): 12903-12993. |
| 6 | SUN M, ZHAI L F, LI W W, et al. Harvest and utilization of chemical energy in wastes by microbial fuel cells [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(10): 2847-2870. |
| 7 | LIANG P, DUAN R, JIANG Y, et al. Corrigendum to “one-year operation of 1000-L modularized microbial fuel cell for municipal wastewater treatment” [J]. Water Research, 2019, 166: 114878. |
| 8 | HUANG J J, FENG H J, HUANG L J, et al. Continuous hydrogen production from food waste by anaerobic digestion (AD) coupled single-chamber microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) under negative pressure [J]. Waste Management, 2020, 103: 61-66. |
| 9 | SEVDA S, ABU-REESH I M, YUAN H, et al. Bioelectricity generation from treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater with simultaneous seawater desalination in microbial desalination cells [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 141: 101-107. |
| 10 | CHANDRASEKHAR K, KUMAR A N, KUMAR G, et al. Electro-fermentation for biofuels and biochemicals production: Current status and future directions [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 323: 124598. |
| 11 | MOSCOVIZ R, TOLEDO-ALARCÓN J, TRABLY E, et al. Electro-fermentation: how to drive fermentation using electrochemical systems [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(11): 856-865. |
| 12 | SCHIEVANO A, PEPE SCIARRIA T, VANBROEKHOVEN K, et al. Electro-fermentation-merging electrochemistry with fermentation in industrial applications [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(11): 866-878. |
| 13 | PREVOTEAU A, CARVAJAL-ARROYO J M, GANIGUE R, et al. Microbial electrosynthesis from CO2: forever a promise? [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 62: 48-57. |
| 14 | JIANG Y, MAY H D, LU L, et al. Carbon dioxide and organic waste valorization by microbial electrosynthesis and electro-fermentation [J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 42-55. |
| 15 | SAKIMOTO K K, WONG A B, YANG P D. Self-photosensitization of nonphotosynthetic bacteria for solar-to-chemical production [J]. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 74-77. |
| 16 | WANG J W, CHEN Q W, LUO G F, et al. A self-driven bioreactor based on bacterium-metal-organic framework biohybrids for boosting chemotherapy via cyclic lactate catabolism [J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15: 17870-17884 |
| 17 | FAN G, DUNDAS C M, GRAHAM A J, et al. Shewanella oneidensis as a living electrode for controlled radical polymerization[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(18): 4559-4564. |
| 18 | SHARMA D, GULATI S S, SHARMA N, et al. Correction to: sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles using various biological sources and waste materials: a review[J/OL]. Emergent Materials, 2021. |
| 19 | KONG F Y, REN H Y, PAVLOSTATHIS S G, et al. Enhanced azo dye decolorization and microbial community analysis in a stacked bioelectrochemical system[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 354: 351-362. |
| 20 | 李锋, 宋浩. 微生物胞外电子传递效率的合成生物学强化[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 516-534. |
| LI F, SONG H. Promoting efficiency of microbial extracellular electron transfer by synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 516-534. | |
| 21 | 赵贞尧, 张保财, 李锋, 等. 产电细胞的合成生物学设计构建[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 468-482. |
| ZHAO Z Y, ZHANG B C, LI F, et al. Design and construction of exoelectrogens by synthetic biology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 468-482. | |
| 22 | 刘向, 张君奇, 张保财, 等. 强化产电微生物与电极间电子传递速率的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(2): 361-377. |
| LIU X, ZHANG J Q, ZHANG B C, et al. Progress in enhancing electron transfer rate between exoelectrogenic microorganisms and electrode interface[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(2): 361-377. | |
| 23 | RICHTER H, NEVIN K P, JIA H F, et al. Cyclic voltammetry of biofilms of wild type and mutant Geobacter sulfurreducens on fuel cell anodes indicates possible roles of OmcB, OmcZ, type IV pili, and protons in extracellular electron transfer[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2009, 2(5): 506-516. |
| 24 | BREUER M, ROSSO K M, BLUMBERGER J, et al. Multi-haem cytochromes in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: structures, functions and opportunities[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2015, 12(102): 20141117. |
| 25 | LIU Y C, ATANASSOV P. Charge transfer at biotic/abiotic interfaces in biological electrocatalysis[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2020, 19: 175-183. |
| 26 | TERAVEST M A, AJO-FRANKLIN C M. Transforming exoelectrogens for biotechnology using synthetic biology[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(4): 687-697. |
| 27 | ROSS D E, RUEBUSH S S, BRANTLEY S L, et al. Characterization of protein-protein interactions involved in iron reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(18): 5797-5808. |
| 28 | HARTSHORNE R S, REARDON C L, ROSS D, et al. Characterization of an electron conduit between bacteria and the extracellular environment [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(52): 22169-22174. |
| 29 | RICHARDSON D J, EDWARDS M J, WHITE G F, et al. Exploring the biochemistry at the extracellular redox frontier of bacterial mineral Fe(III) respiration[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2012, 40(3): 493-500. |
| 30 | RICHARDSON D J, BUTT J N, FREDRICKSON J K, et al. The 'porin-cytochrome' model for microbe-to-mineral electron transfer[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2012, 85(2): 201-212. |
| 31 | ZHAO J T, LI F, CAO Y X, et al. Microbial extracellular electron transfer and strategies for engineering electroactive microorganisms[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 53: 107682. |
| 32 | COURSOLLE D, GRALNICK J A. Modularity of the Mtr respiratory pathway of Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2010, 77(4): 995-1008. |
| 33 | LIU Y M, WANG Z M, LIU J, et al. A trans-outer membrane porin-cytochrome protein complex for extracellular electron transfer by Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2014, 6(6): 776-785. |
| 34 | SHI L, FREDRICKSON J K, ZACHARA J M. Genomic analyses of bacterial porin-cytochrome gene clusters[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2014, 5: 657. |
| 35 | MEHTA T, COPPI M V, CHILDERS S E, et al. Outer membrane c-type cytochromes required for Fe(Ⅲ) and Mn(Ⅳ) oxide reduction in Geobacter sulfurreducens [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(12): 8634-8641. |
| 36 | LEYS D, SCRUTTON N S. Electrical circuitry in biology: emerging principles from protein structure[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2004, 14(6): 642-647. |
| 37 | REGUERA G, MCCARTHY K D, MEHTA T, et al. Extracellular electron transfer via microbial nanowires[J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7045): 1098-1101. |
| 38 | WALKER D J, ADHIKARI R Y, HOLMES D E, et al. Electrically conductive pili from pilin genes of phylogenetically diverse microorganisms[J]. The ISME Journal, 2018, 12(1): 48-58. |
| 39 | LOVLEY D R, MALVANKAR N S. Seeing is believing: novel imaging techniques help clarify microbial nanowire structure and function[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(7): 2209-2215. |
| 40 | GORBY Y A, YANINA S, MCLEAN J S, et al. Electrically conductive bacterial nanowires produced by Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1 and other microorganisms[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(30): 11358-11363. |
| 41 | BHAYA D, BIANCO N R, BRYANT D, et al. Type IV pilus biogenesis and motility in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2000, 37(4): 941-951. |
| 42 | YANG Y G, WANG Z G, GAN C F, et al. Long-distance electron transfer in a filamentous Gram-positive bacterium[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 1709. |
| 43 | PIRBADIAN S, BARCHINGER S E, LEUNG K M, et al. Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 nanowires are outer membrane and periplasmic extensions of the extracellular electron transport components[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(35): 12883-12888. |
| 44 | REARDON P N, MUELLER K T. Structure of the type IVa major pilin from the electrically conductive bacterial nanowires of Geobacter sulfurreducens [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(41): 29260-29266. |
| 45 | LOVLEY D R. Electrically conductive pili: biological function and potential applications in electronics[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 4(1): 190-198. |
| 46 | LAMPA-PASTIRK S, VEAZEY J P, WALSH K A, et al. Thermally activated charge transport in microbial protein nanowires[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 23517. |
| 47 | CREASEY R C G, MOSTERT A B, NGUYEN T A H, et al. Microbial nanowires-electron transport and the role of synthetic analogues[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2018, 69: 1-30. |
| 48 | REGUERA G. Microbial nanowires and electroactive biofilms[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2018, 94(7): fiy086. |
| 49 | MALVANKAR N S, VARGAS M, NEVIN K P, et al. Tunable metallic-like conductivity in microbial nanowire networks[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2011, 6(9): 573-579. |
| 50 | STRYCHARZ-GLAVEN S M, SNIDER R M, GUISEPPI-ELIE A, et al. On the electrical conductivity of microbial nanowires and biofilms[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(11): 4366-4397. |
| 51 | GU Y Q, SRIKANTH V, SALAZAR-MORALES A I, et al. Structure of Geobacter pili reveals secretory rather than nanowire behaviour[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7876): 430-434. |
| 52 | VON CANSTEIN H, OGAWA J, SHIMIZU S, et al. Secretion of flavins by Shewanella species and their role in extracellular electron transfer[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(3): 615-623. |
| 53 | PHAM T H, BOON N, DE MAEYER K, et al. Use of Pseudomonas species producing phenazine-based metabolites in the anodes of microbial fuel cells to improve electricity generation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 80(6): 985-993. |
| 54 | MCANULTY M J, POOSARLA V G, KIM K Y, et al. Electricity from methane by reversing methanogenesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15419. |
| 55 | OKAMOTO A, SAITO K, INOUE K, et al. Uptake of self-secreted flavins as bound cofactors for extracellular electron transfer in Geobacter species[J]. Energy and Environmental Science, 2014, 7(4): 1357-1361. |
| 56 | OKAMOTO A, NAKAMURA R, NEALSON K H, et al. Bound flavin model suggests similar electron-transfer mechanisms in Shewanella and Geobacter [J]. ChemElectroChem, 2014, 1(11): 1808-1812. |
| 57 | OKAMOTO A, HASHIMOTO K, NEALSON K H, et al. Rate enhancement of bacterial extracellular electron transport involves bound flavin semiquinones[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(19): 7856-7861. |
| 58 | HUANG L Y, TANG J H, CHEN M, et al. Two modes of riboflavin-mediated extracellular electron transfer in Geobacter uraniireducens [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 2886. |
| 59 | BREUER M, ROSSO K M, BLUMBERGER J. Flavin binding to the deca-heme cytochrome MtrC: insights from computational molecular simulation[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2015, 109(12): 2614-2624. |
| 60 | MEVERS E, SU L, PISHCHANY G, et al. An elusive electron shuttle from a facultative anaerobe[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e48054. |
| 61 | RABAEY K, BOON N, HÖFTE M, et al. Microbial phenazine production enhances electron transfer in biofuel cells[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(9): 3401-3408. |
| 62 | ZHENG T, XU Y S, YONG X Y, et al. Endogenously enhanced biosurfactant production promotes electricity generation from microbial fuel cells[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 197: 416-421. |
| 63 | LIGHT S H, SU L, RIVERA-LUGO R, et al. A flavin-based extracellular electron transfer mechanism in diverse Gram-positive bacteria[J]. Nature, 2018, 562(7725): 140-144. |
| 64 | LU L, GUEST J S, PETERS C A, et al. Wastewater treatment for carbon capture and utilization[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2018, 1(12): 750-758. |
| 65 | LIU C, COLÓN B C, ZIESACK M, et al. Water splitting-biosynthetic system with CO2 reduction efficiencies exceeding photosynthesis[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6290): 1210-1213. |
| 66 | THAPA B S, KIM T, PANDIT S, et al. Overview of electroactive microorganisms and electron transfer mechanisms in microbial electrochemistry[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 347: 126579. |
| 67 | GONG Z Y, YU H, ZHANG J Q, et al. Microbial electro-fermentation for synthesis of chemicals and biofuels driven by bi-directional extracellular electron transfer[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2020, 5(4): 304-313. |
| 68 | TREMBLAY P L, ANGENENT L T, ZHANG T. Extracellular electron uptake: among autotrophs and mediated by surfaces[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2017, 35(4): 360-371. |
| 69 | JIANG Y, ZENG R J. Bidirectional extracellular electron transfers of electrode-biofilm: mechanism and application[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 271: 439-448. |
| 70 | ROSS D E, FLYNN J M, BARON D B, et al. Towards electrosynthesis in Shewanella: energetics of reversing the mtr pathway for reductive metabolism[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2): e16649. |
| 71 | STRYCHARZ S M, GLAVEN R H, COPPI M V, et al. Gene expression and deletion analysis of mechanisms for electron transfer from electrodes to Geobacter sulfurreducens [J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2011, 80(2): 142-150. |
| 72 | XIE Q Q, LU Y, TANG L, et al. The mechanism and application of bidirectional extracellular electron transport in the field of energy and environment[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 51(17): 1924-1969. |
| 73 | LI H, OPGENORTH P H, WERNICK D G, et al. Integrated electromicrobial conversion of CO2 to higher alcohols[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6076): 1596. |
| 74 | YANG Y, DING Y Z, HU Y D, et al. Enhancing bidirectional electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis by a synthetic flavin pathway[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(7): 815-823. |
| 75 | LEE C R, KIM C, SONG Y E, et al. Co-culture-based biological carbon monoxide conversion by Citrobacter amalonaticus Y19 and Sporomusa ovata via a reducing-equivalent transfer mediator[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 259: 128-135. |
| 76 | KASAI T, TOMIOKA Y, KOUZUMA A, et al. Overexpression of the adenylate cyclase gene cyaC facilitates current generation by Shewanella oneidensis in bioelectrochemical systems[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2019, 129: 100-105. |
| 77 | JOHNSON E T, BARON D B, NARANJO B, et al. Enhancement of survival and electricity production in an engineered bacterium by light-driven proton pumping[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(13): 4123-4129. |
| 78 | CHOI D, LEE S B, KIM S, et al. Metabolically engineered glucose-utilizing Shewanella strains under anaerobic conditions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 154: 59-66. |
| 79 | LI F, LI Y X, SUN L M, et al. Engineering Shewanella oneidensis enables xylose-fed microbial fuel cell[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 196. |
| 80 | ZHANG J Q, CHEN Z, LIU C J, et al. Construction of an acetate metabolic pathway to enhance electron generation of engineered Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 757953. |
| 81 | YONG X Y, FENG J, CHEN Y L, et al. Enhancement of bioelectricity generation by cofactor manipulation in microbial fuel cell[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2014, 56: 19-25. |
| 82 | LI F, LI Y X, CAO Y X, et al. Modular engineering to increase intracellular NAD(H/+) promotes rate of extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3637. |
| 83 | LI F, LI Y X, SUN L M, et al. Modular engineering intracellular NADH regeneration boosts extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(3): 885-895. |
| 84 | YONG Y C, YU Y Y, YANG Y, et al. Increasing intracellular releasable electrons dramatically enhances bioelectricity output in microbial fuel cells[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2012, 19: 13-16. |
| 85 | VAMSHI KRISHNA K, VENKATA MOHAN S. Purification and characterization of NDH-2 protein and elucidating its role in extracellular electron transport and bioelectrogenic activity[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 880. |
| 86 | DING Y, LI X L, HORSMAN G P, et al. Construction of an alternative NAD+ de novo biosynthesis pathway[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(9): 2004632. |
| 87 | JENSEN H M, ALBERS A E, MALLEY K R, et al. Engineering of a synthetic electron conduit in living cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(45): 19213-19218. |
| 88 | SU L, FUKUSHIMA T, AJO-FRANKLIN C M. A hybrid cyt cmaturation system enhances the bioelectrical performance of engineered Escherichia coli by improving the rate-limiting step[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2020, 165: 112312. |
| 89 | FENG J, QIAN Y, WANG Z, et al. Enhancing the performance of Escherichia coli-inoculated microbial fuel cells by introduction of the phenazine-1-carboxylic acid pathway[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 275: 1-6. |
| 90 | VELLINGIRI A, SONG Y E, MUNUSSAMI G, et al. Overexpression of c-type cytochrome, CymA in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for enhanced bioelectricity generation and cell growth in a microbial fuel cell[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2019, 94(7): 2115-2122. |
| 91 | SUN W N, LIN Z F, YU Q Z, et al. Promoting extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 by optimizing the periplasmic cytochrome c network[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 727709. |
| 92 | LIN T, DING W Q, SUN L M, et al. Engineered Shewanella oneidensis-reduced graphene oxide biohybrid with enhanced biosynthesis and transport of flavins enabled a highest bioelectricity output in microbial fuel cells[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 50: 639-648. |
| 93 | FAN Y Y, TANG Q, LI Y, et al. Rapid and highly efficient genomic engineering with a novel iEditing device for programming versatile extracellular electron transfer of electroactive bacteria[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 23(2): 1238-1255. |
| 94 | LIU X, WANG S W, XU A M, et al. Biological synthesis of high-conductive pili in aerobic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(3): 1535-1544. |
| 95 | YONG X Y, SHI D Y, CHEN Y L, et al. Enhancement of bioelectricity generation by manipulation of the electron shuttles synthesis pathway in microbial fuel cells[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 152: 220-224. |
| 96 | TAN Y, ADHIKARI R Y, MALVANKAR N S, et al. Expressing the Geobacter metallireducens PilA in Geobacter sulfurreducens yields pili with exceptional conductivity[J]. mBio, 2017, 8(1): e02203-e02216. |
| 97 | LIU T, YU Y Y, DENG X P, et al. Enhanced Shewanella biofilm promotes bioelectricity generation[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112(10): 2051-2059. |
| 98 | CHENG Z H, XIONG J R, MIN D, et al. Promoting bidirectional extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for hexavalent chromium reduction via elevating intracellular cAMP level[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(5): 1294-1303. |
| 99 | ZHUANG Z, YANG G Q, MAI Q J, et al. Physiological potential of extracellular polysaccharide in promoting Geobacter biofilm formation and extracellular electron transfer[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140365. |
| 100 | YU Y Y, FANG Z, GAO L, et al. Engineering of bacterial electrochemical activity with global regulator manipulation[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2018, 86: 117-120. |
| 101 | LUO J M, WANG T T, LI X, et al. Enhancement of bioelectricity generation via heterologous expression of IrrE in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-inoculated MFCs[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2018, 117: 23-31. |
| 102 | LUO J M, LI X, ZHANG J M, et al. Global regulator engineering enhances bioelectricity generation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-inoculated MFCs[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2020, 163: 112269. |
| 103 | KASAI T, KOUZUMA A, WATANABE K. CRP regulates D-lactate oxidation in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 869. |
| 104 | ISHIKI K, SHIIGI H. Kinetics of intracellular electron generation in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(22): 14401-14406. |
| 105 | HOWARD E C, HAMDAN L J, LIZEWSKI S E, et al. High frequency of glucose-utilizing mutants in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2012, 327(1): 9-14. |
| 106 | NAKAGAWA G, KOUZUMA A, HIROSE A, et al. Metabolic characteristics of a glucose-utilizing Shewanella oneidensis strain grown under electrode-respiring conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9): e0138813. |
| 107 | CHENG L, MIN D, HE R L, et al. Developing a base-editing system to expand the carbon source utilization spectra of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for enhanced pollutant degradation[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(8): 2389-2400. |
| 108 | FLYNN J M, ROSS D E, HUNT K A, et al. Enabling unbalanced fermentations by using engineered electrode-interfaced bacteria[J]. mBio, 2010, 1(5): e00190-e00110. |
| 109 | SEKAR R, SHIN H D, DICHRISTINA T J. Activation of an otherwise silent xylose metabolic pathway in Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 82(13): 3996-4005. |
| 110 | TAO L, XIE M S, CHIEW G G Y, et al. Improving electron trans-inner membrane movements in microbial electrocatalysts[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(37): 6292-6295. |
| 111 | GOLDBECK C P, JENSEN H M, TERAVEST M A, et al. Tuning promoter strengths for improved synthesis and function of electron conduits in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(3): 150-159. |
| 112 | DELGADO V P, PAQUETE C M, STURM G, et al. Improvement of the electron transfer rate in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 using a tailored periplasmic protein composition[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2019, 129: 18-25. |
| 113 | LOVLEY D R, YAO J. Intrinsically conductive microbial nanowires for 'green' electronics with novel functions[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(9): 940-952. |
| 114 | WANG F B, GU Y Q, O'BRIEN J P, et al. Structure of microbial nanowires reveals stacked hemes that transport electrons over micrometers[J]. Cell, 2019, 177(2): 361-369.e10. |
| 115 | SHAPIRO D M, MANDAVA G, YALCIN S E, et al. Protein nanowires with tunable functionality and programmable self-assembly using sequence-controlled synthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 829. |
| 116 | LIU X, ZHAN J, JING X Y, et al. A pilin chaperone required for the expression of electrically conductive Geobacter sulfurreducens pili[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2019, 21(7): 2511-2522. |
| 117 | LIU X M, GAO H Y, WARD J E, et al. Power generation from ambient humidity using protein nanowires[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7796): 550-554. |
| 118 | UEKI T, WALKER D J F, WOODARD T L, et al. An Escherichia coli chassis for production of electrically conductive protein nanowires[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(3): 647-654. |
| 119 | UEKI T, WALKER D J F, TREMBLAY P L, et al. Decorating the outer surface of microbially produced protein nanowires with peptides[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(8): 1809-1817. |
| 120 | LIU X B, SHI L, GU J D. Microbial electrocatalysis: redox mediators responsible for extracellular electron transfer[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(7): 1815-1827. |
| 121 | YONG Y C, YU Y Y, YANG Y, et al. Enhancement of extracellular electron transfer and bioelectricity output by synthetic porin[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2013, 110(2): 408-416. |
| 122 | MIN D, CHENG L, ZHANG F, et al. Enhancing extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 through coupling improved flavin synthesis and metal-reducing conduit for pollutant degradation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(9): 5082-5089. |
| 123 | SHI L, DONG H L, REGUERA G, et al. Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(10): 651-662. |
| 124 | FLEMMING H C, NEU T R, WOZNIAK D J. The EPS matrix: the "house of biofilm cells"[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2007, 189(22): 7945-7947. |
| 125 | SHENG G P, YU H Q, LI X Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2010, 28(6): 882-894. |
| 126 | FLEMMING H C, WINGENDER J. The biofilm matrix[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8(9): 623-633. |
| 127 | DAS T, SEHAR S, MANEFIELD M. The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2013, 5(6): 778-786. |
| 128 | FURST A L, SMITH M J, LEE M C, et al. DNA hybridization to interface current-producing cells with electrode surfaces[J]. ACS Central Science, 2018, 4(7): 880-884. |
| 129 | SAUNDERS S H, TSE E C M, YATES M D, et al. Extracellular DNA promotes efficient extracellular electron transfer by pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(4): 919-932.e19. |
| 130 | ZHANG J Y, POH C L. Regulating exopolysaccharide gene wcaF allows control of Escherichia coli biofilm formation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 13127. |
| 131 | CHARLES C J, ROUT S P, PATEL K A, et al. Floc formation reduces the pH stress experienced by microorganisms living in alkaline environments[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(6): e02985-e02916. |
| 132 | REICHHARDT C, WONG C, PASSOS DA SILVA D, et al. CdrA interactions within the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix safeguard it from proteolysis and promote cellular packing[J]. mBio, 2018, 9(5): e01376-e01318. |
| 133 | BARNHART M M, CHAPMAN M R. Curli biogenesis and function[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2006, 60: 131-147. |
| 134 | SUO D, FANG Z, YU Y-Y, et al. Synthetic curli enables efficient microbial electrocatalysis with stainless-steel electrode[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 66(4): e16897. |
| 135 | SHI M M, GAO T, JU L L, et al. Effects of FlrBC on flagellar biosynthesis of Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2014, 93(6): 1269-1283. |
| 136 | LIU X, ZHUO S Y, JING X Y, et al. Flagella act as Geobacter biofilm scaffolds to stabilize biofilm and facilitate extracellular electron transfer[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2019, 146: 111748. |
| 137 | READING N C, SPERANDIO V. Quorum sensing: the many languages of bacteria[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2006, 254(1): 1-11. |
| 138 | JING X Y, LIU X, DENG C S, et al. Chemical signals stimulate Geobacter soli biofilm formation and electroactivity[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2019, 127: 1-9. |
| 139 | LI F H, TANG Q, FAN Y Y, et al. Developing a population-state decision system for intelligently reprogramming extracellular electron transfer in Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(37): 23001-23010. |
| 140 | THORMANN K M, DUTTLER S, SAVILLE R M, et al. Control of formation and cellular detachment from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms by cyclic di-GMP[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2006, 188(7): 2681-2691. |
| 141 | GUINOTE I B, MOREIRA R N, BARAHONA S, et al. Breaking through the stress barrier: the role of BolA in Gram-negative survival[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2014, 30(10): 2559-2566. |
| 142 | FREIRE P, MOREIRA R N, ARRAIANO C M. BolA inhibits cell elongation and regulates MreB expression levels[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 385(5): 1345-1351. |
| 143 | MOREIRA R N, DRESSAIRE C, BARAHONA S, et al. BolA is required for the accurate regulation of c-di-GMP, a central player in biofilm formation[J]. mBio, 2017, 8(5): e00443-e00417. |
| 144 | HU Y D, WU Y C, MUKHERJEE M, et al. A near-infrared light responsive c-di-GMP module-based AND logic gate in Shewanella oneidensis [J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(10): 1646-1648. |
| 145 | HU Y D, LIU X B, REN A T M, et al. Optogenetic modulation of a catalytic biofilm for the biotransformation of indole into tryptophan[J]. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(23): 5142-5148. |
| 146 | SADHUKHAN J, LLOYD J R, SCOTT K, et al. A critical review of integration analysis of microbial electrosynthesis (MES) systems with waste biorefineries for the production of biofuel and chemical from reuse of CO2 [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 56: 116-132. |
| 147 | VIRDIS B, HOELZLE R D, MARCHETTI A, et al. Electro-fermentation: sustainable bioproductions steered by electricity[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 59: 107950. |
| 148 | TEFFT N M, TERAVEST M A. Reversing an extracellular electron transfer pathway for electrode-driven acetoin reduction[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(7): 1590-1600. |
| 149 | WU Z Q, WANG J S, LIU J, et al. Engineering an electroactive Escherichia coli for the microbial electrosynthesis of succinate from glucose and CO2 [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 15. |
| 150 | DONG F Y, LEE Y S, GAFFNEY E M, et al. Engineering cyanobacterium with transmembrane electron transfer ability for bioelectrochemical nitrogen fixation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(21): 13169-13179. |
| 151 | TORELLA J P, GAGLIARDI C J, CHEN J S, et al. Efficient solar-to-fuels production from a hybrid microbial-water-splitting catalyst system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(8): 2337-2342. |
| 152 | CHEN X L, CAO Y X, LI F, et al. Enzyme-assisted microbial electrosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) via CO2 bioreduction by engineered Ralstonia eutropha [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(5): 4429-4437. |
| 153 | KRIEG T, SYDOW A, FAUST S, et al. CO2 to terpenes: autotrophic and electroautotrophic α-humulene production with Cupriavidus necator [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(7): 1879-1882. |
| 154 | WU H L, PAN H J, LI Z J, et al. Efficient production of lycopene from CO2 via microbial electrosynthesis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 132943. |
| 155 | ZHANG Z Y, LI F, CAO Y X, et al. Electricity-driven 7α-hydroxylation of a steroid catalyzed by a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase in engineered yeast[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(18): 4877-4887. |
| 156 | BAI W, RANAIVOARISOA T O, SINGH R, et al. n-Butanol production by Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1[J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4: 1257. |
| 157 | FENG J, JIANG M J, LI K, et al. Direct electron uptake from a cathode using the inward Mtr pathway in Escherichia coli [J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, 134: 107498. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 雷航彬, 何宁, 李斐煊, 董玲玲, 王世珍. 氢化酶固定化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1485-1497. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||