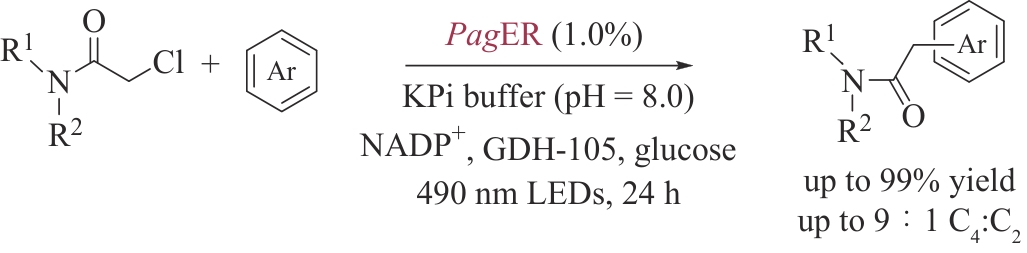
合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (5): 997-1020.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-012
光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展
夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起
- 浙江大学化学系,浙江 杭州 310058
-
收稿日期:2024-01-25修回日期:2024-04-28出版日期:2024-10-31发布日期:2024-11-20 -
通讯作者:徐维华,吴起 -
作者简介:夏孔晨 (2000—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为酶定向进化与催化多功能性。 E-mail:22337042@zju.edu.cn徐维华 (1991—),女,博士后。研究方向为酶定向进化、光酶催化多功能性、酶促混乱性反应。 E-mail:xuwh@zju.edu.cn吴起 (1976—),男,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为酶定向进化、合成生物学、生物催化等。 E-mail:wuqi1000@163.com,llc123@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2102000);国家自然科学基金(22277105);浙江省自然科学基金(LZ24B020003)
Recent advances in photo-induced promiscuous enzymatic reactions
XIA Kongchen, XU Weihua, WU Qi
- Department of Chemistry,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2024-01-25Revised:2024-04-28Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-20 -
Contact:XU Weihua, WU Qi
摘要:
光催化具有条件温和、可再生、反应性强等优点,然而由于自由基的高活性往往导致其选择性难以调控,限制了光催化在不对称有机合成中的广泛应用。酶催化虽具有高选择性和专一性的优势,但这也导致其存在反应类型单一和底物谱窄等缺陷。将反应性强的光催化与选择性高的酶催化相结合的光酶催化则可以提供一种全新的合成模式,实现优势互补,更加符合现代绿色有机合成的要求。狭义的光酶催化反应,也就是光酶协同反应一般包括以下四类:天然光酶反应,人工光酶反应,光催化与酶催化的偶联反应以及光酶催化混乱性反应。近年来,光酶催化的研究蓬勃发展,解决了许多传统有机合成中难以实现的问题,尤其是在不对称合成领域已占据重要地位。例如,脂肪酸光脱酸酶可以催化长链脂肪酸脱羧转化为相应烃类;结合光敏辅因子和蛋白骨架的人工光酶大大拓展了酶的应用范围,催化更多样化非天然有机化学品的生物合成;光催化剂催化光化学反应与酶催化反应的偶联方式可以实现一些复杂的有机合成过程;以及近年来一些含有光敏辅因子的氧化还原酶在光激发下催化新分子混乱性反应的功能。尽管已有许多文献对相关研究进行了总结,但是自2023年以来,光酶催化混乱性研究不断突破,涌现出许多全新的光酶催化反应类型和反应机理,立体选择性和区域选择性的精准调控更是满足了不对称合成的重大需求。对于这个飞速发展的领域,系统归纳其成果仍显得至关重要。因此本综述聚焦在光激发下光敏辅因子依赖型酶催化的混乱性反应最新研究成果,根据不同催化反应类型,分别介绍光酶通过自由基途径实现不对称脱卤、氢化、分子内环化、分子间C—C/C—N/C—S键交叉耦合等非天然反应。这些反应由于酶和底物的不同,展示了不同机理。例如在氧化还原起始过程中,包括单电子还原起始和单电子氧化起始两种类型;在自由基终止过程中,可能采用单电子还原终止和单电子氧化终止,而单电子还原终止方式中也存在氢原子转移和电子转移/质子转移耦合过程等不同情况。机理的多样性也为拓展更多的光酶催化混乱性反应提供了可能。在未来,新型的光酶催化方法将在快速发展的基因工程、合成生物学、酶工程,以及流动化学、人工智能等学科和技术的推动下,涌现出更多高效、高选择性的新分子新功能反应,显著拓展光酶催化方法在有机合成(尤其是绿色不对称合成)领域中的应用范围。
中图分类号:
引用本文
夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020.
XIA Kongchen, XU Weihua, WU Qi. Recent advances in photo-induced promiscuous enzymatic reactions[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020.
| 1 | CIAMICIAN G. The photochemistry of the future[J]. Science, 1912, 36(926): 385-394. |
| 2 | SCHULTZ D M, YOON T P. Solar synthesis: prospects in visible light photocatalysis[J]. Science, 2014, 343(6174): 1239176. |
| 3 | WEI H L, CHEN H, CHEN J Z, et al. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of α-substituted vinylphosphonates and diarylvinylphosphine oxides[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(6): e202214990. |
| 4 | SPRAGUE-KLEIN E A, HE X, MARA M W, et al. Photo-electrochemical effect in the amorphous cobalt oxide water oxidation catalyst cobalt-phosphate (CoPi)[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(9): 3129-3138. |
| 5 | JOHNSTON C P, SMITH R T, ALLMENDINGER S, et al. Metallaphotoredox-catalysed sp3-sp3 cross-coupling of carboxylic acids with alkyl halides[J]. Nature, 2016, 536(7616): 322-325. |
| 6 | CAO D W, ATAYA M, CHEN Z P, et al. Light-driven transition-metal-free direct decarbonylation of unstrained diaryl ketones via a dual C-C bond cleavage[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1805. |
| 7 | QUIRÓS I, MARTÍN M, GOMEZ-MENDOZA M, et al. Isonitriles as alkyl radical precursors in visible light mediated hydro- and deuterodeamination reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(7): e202317683. |
| 8 | ZHANG L, PFUND B, WENGER O S, et al. Oxidase-type C-H/C-H coupling using an isoquinoline-derived organic photocatalyst[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(20): e202202649. |
| 9 | BACKUS E H G, HOSSEINPOUR S, RAMANAN C, et al. Ultrafast surface-specific spectroscopy of water at a photoexcited TiO2 model water-splitting photocatalyst[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(8): e202312123. |
| 10 | HUANG J, KANG Y Y, LIU J N, et al. Gradient tungsten-doped Bi3TiNbO9 ferroelectric photocatalysts with additional built-in electric field for efficient overall water splitting[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 7948. |
| 11 | QU G, LI A T, ACEVEDO-ROCHA C G, et al. The crucial role of methodology development in directed evolution of selective enzymes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(32): 13204-13231. |
| 12 | SHELDON R A, WOODLEY J M. Role of biocatalysis in sustainable chemistry[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(2): 801-838. |
| 13 | MAESTRE-REYNA M, WANG P H, NANGO E, et al. Visualizing the DNA repair process by a photolyase at atomic resolution[J]. Science, 2023, 382(6674): eadd7795. |
| 14 | ZHANG S W, HEYES D J, FENG L L, et al. Structural basis for enzymatic photocatalysis in chlorophyll biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7780): 722-725. |
| 15 | SORIGUÉ D, LÉGERET B, CUINÉ S, et al. An algal photoenzyme converts fatty acids to hydrocarbons[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6354): 903-907. |
| 16 | SUN N N, HUANG J J, QIAN J Y, et al. Enantioselective [2+2]-cycloadditions with triplet photoenzymes[J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7937): 715-720. |
| 17 | TRIMBLE J S, CRAWSHAW R, HARDY F J, et al. A designed photoenzyme for enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions[J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7937): 709-714. |
| 18 | ALPHAND V, VAN BERKEL W J H, JURKAŠ V, et al. Exciting enzymes: current state and future perspective of photobiocatalysis[J]. ChemPhotoChem, 2023, 7(7): e202200325. |
| 19 | SINGH P P, SINHA S, NAINWAL P, et al. Novel applications of photobiocatalysts in chemical transformations[J]. RSC Advances, 2024, 14(4): 2590-2601. |
| 20 | LI S H, SHI J F, LIU S S, et al. Molecule-electron-proton transfer in enzyme-photo-coupled catalytic system[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 44: 96-110. |
| 21 | YANG N, TIAN Y, ZHANG M, et al. Photocatalyst-enzyme hybrid systems for light-driven biotransformation[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 54: 107808. |
| 22 | ROTH S, NIESE R, MÜLLER M, et al. Redox out of the box: catalytic versatility across NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(13): e202314740. |
| 23 | SELLÉS VIDAL L, KELLY C L, MORDAKA P M, et al. Review of NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases: properties, engineering and application[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Proteins and Proteomics, 2018, 1866(2): 327-347. |
| 24 | PAUL C E, EGGERICHS D, WESTPHAL A H, et al. Flavoprotein monooxygenases: versatile biocatalysts[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 51: 107712. |
| 25 | LEE S H, CHOI D S, KUK S K, et al. Photobiocatalysis: activating redox enzymes by direct or indirect transfer of photoinduced electrons[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(27): 7958-7985. |
| 26 | EMMANUEL M A, GREENBERG N R, OBLINSKY D G, et al. Accessing non-natural reactivity by irradiating nicotinamide-dependent enzymes with light[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7633): 414-417. |
| 27 | EMMANUEL M A, BENDER S G, BILODEAU C, et al. Photobiocatalytic strategies for organic synthesis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(9): 5459-5520. |
| 28 | HARRISON W, HUANG X Q, ZHAO H M. Photobiocatalysis for abiological transformations[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2022, 55(8): 1087-1096. |
| 29 | 明阳, 陈彬, 黄小强. 光酶催化合成进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 651-675. |
| MING Y, CHEN B, HUANG X Q. Recent advances in photoenzymatic synthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 651-675. | |
| 30 | SANDOVAL B A, MEICHAN A J, HYSTER T K. Enantioselective hydrogen atom transfer: discovery of catalytic promiscuity in flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(33): 11313-11316. |
| 31 | BIEGASIEWICZ K F, COOPER S J, EMMANUEL M A, et al. Catalytic promiscuity enabled by photoredox catalysis in nicotinamide-dependent oxidoreductases[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2018, 10(7): 770-775. |
| 32 | PENG Y Z, WANG Z G, CHEN Y, et al. Photoinduced promiscuity of cyclohexanone monooxygenase for the enantioselective synthesis of α-fluoroketones[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(50): e202211199. |
| 33 | XU J, CEN Y X, SINGH W, et al. Stereodivergent protein engineering of a lipase to access all possible stereoisomers of chiral esters with two stereocenters[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(19): 7934-7945. |
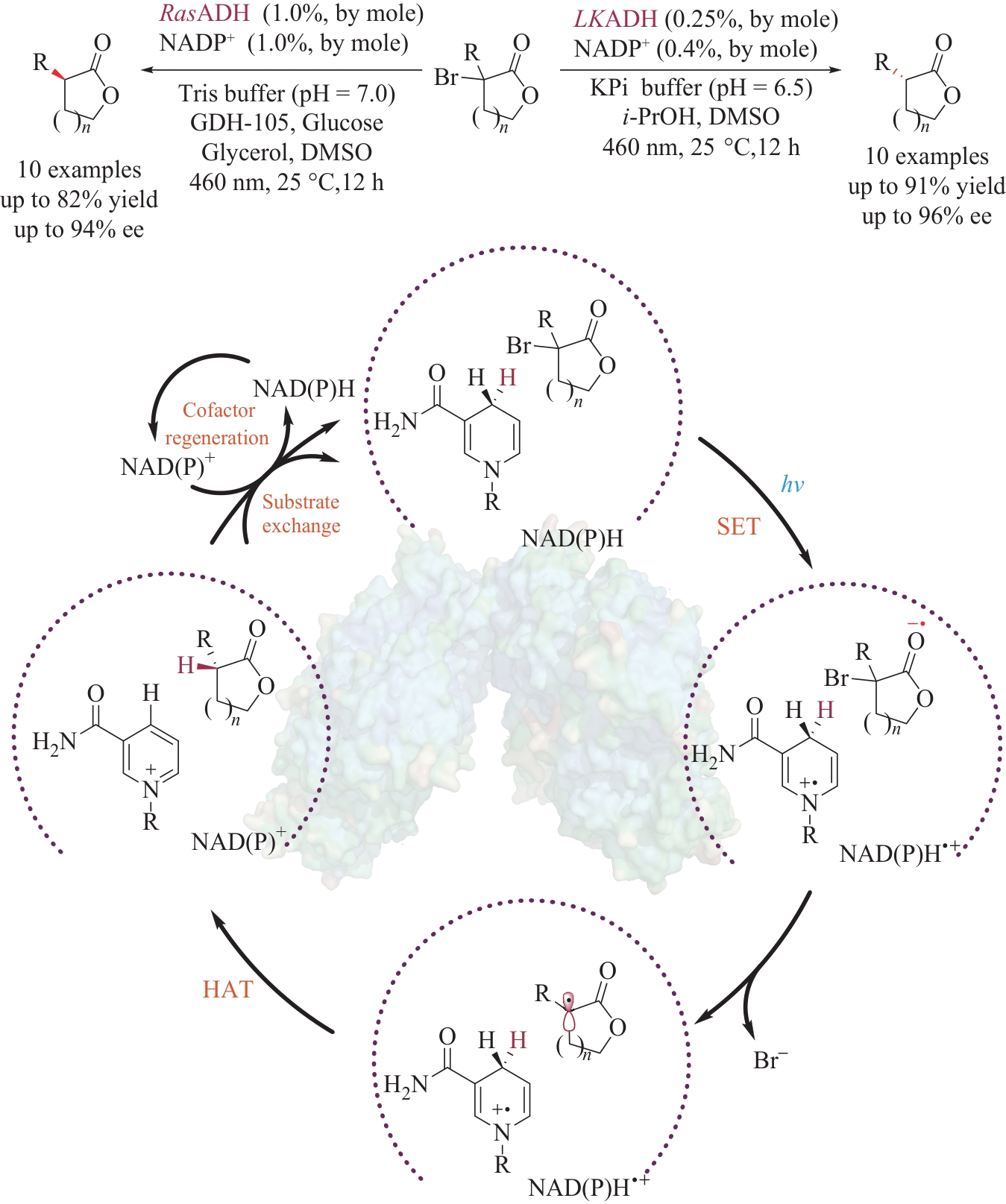
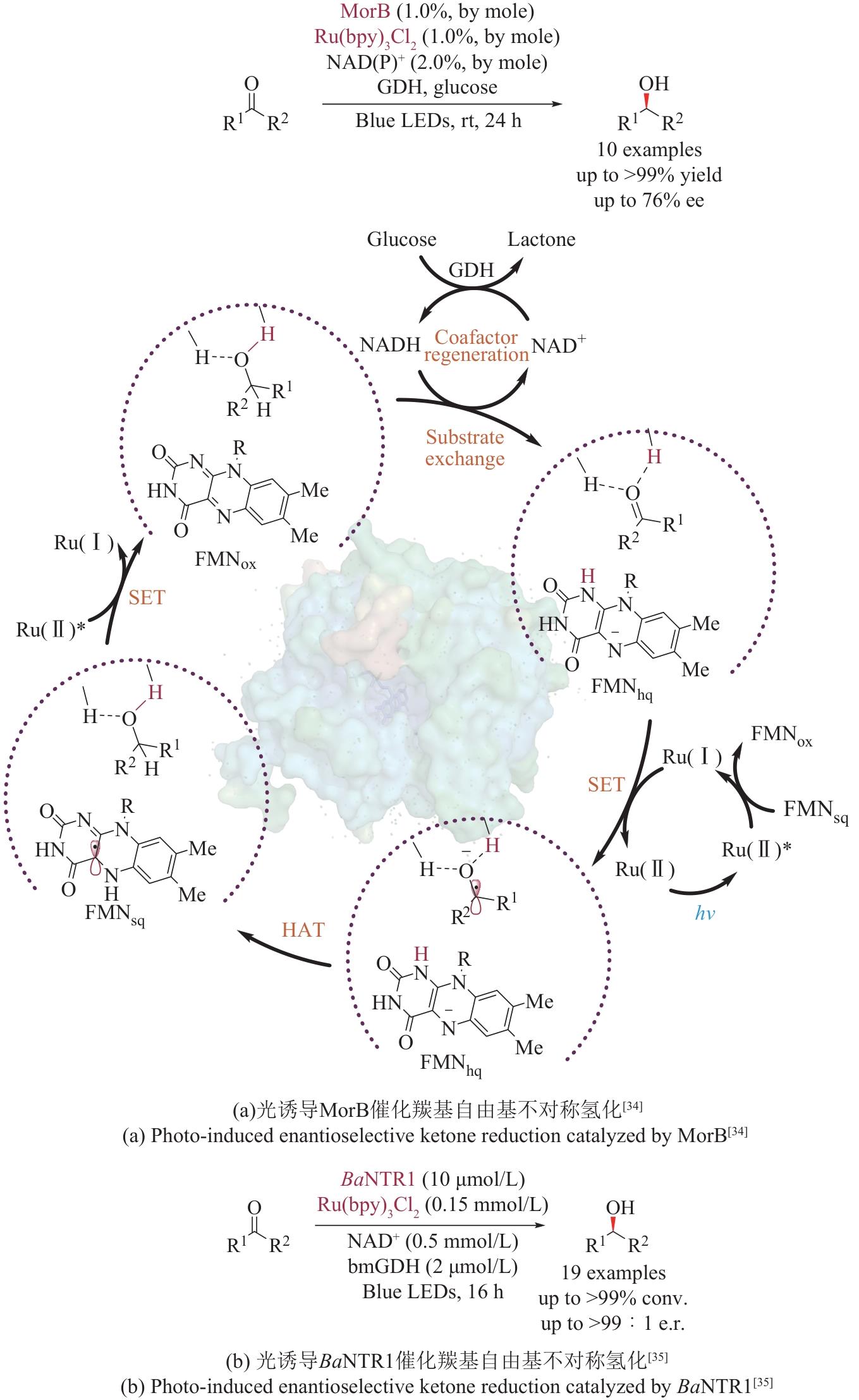
| 34 | SANDOVAL B A, KURTOIC S I, CHUNG M M, et al. Photoenzymatic catalysis enables radical-mediated ketone reduction in ene-reductases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(26): 8714-8718. |
| 35 | PRATS LUJÁN A, BHAT M F, SARAVANAN T, et al. Chemo- and enantioselective photoenzymatic ketone reductions using a promiscuous flavin-dependent nitroreductase[J]. ChemCatChem, 2022, 14(8): e202200043. |
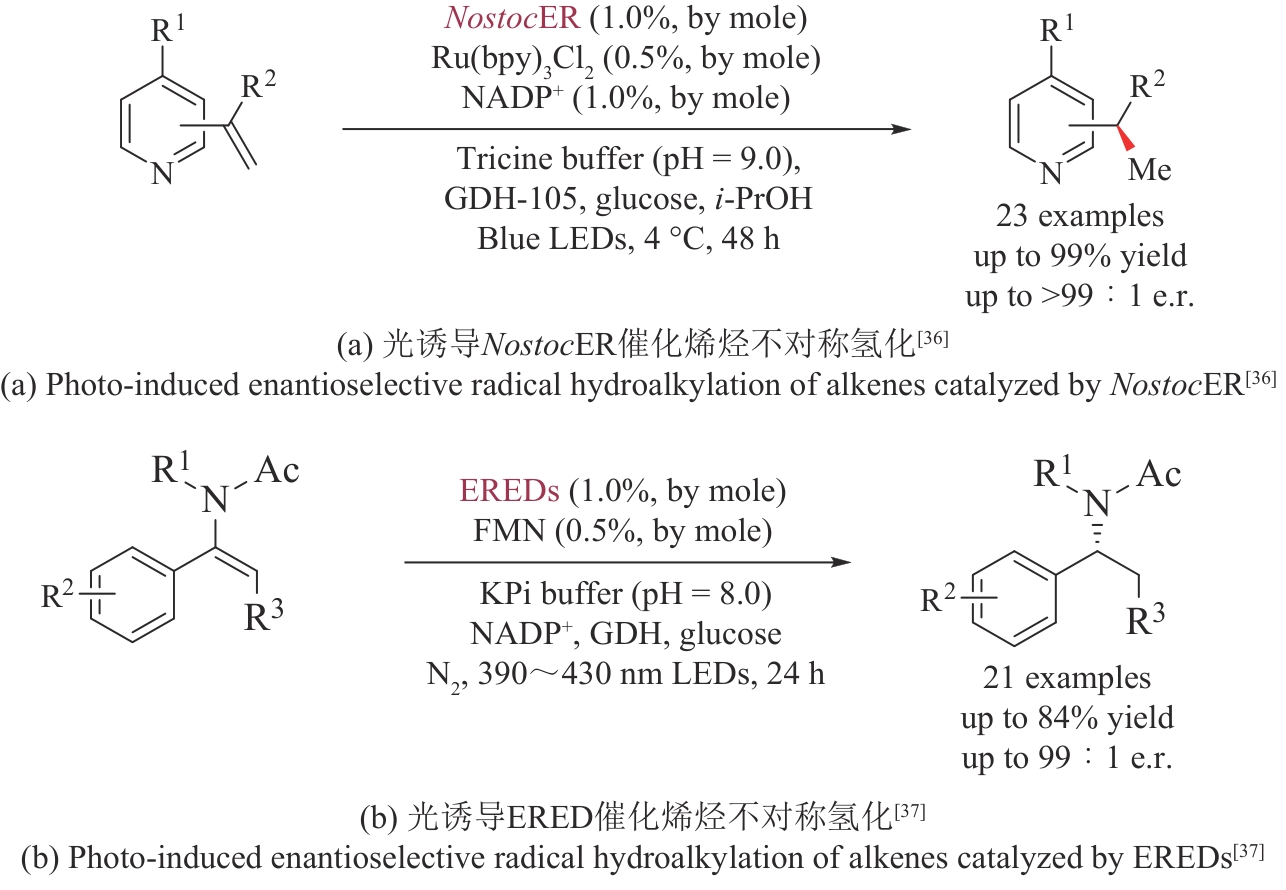
| 36 | NAKANO Y, BLACK M J, MEICHAN A J, et al. Photoenzymatic hydrogenation of heteroaromatic olefins using ‘ene’-reductases with photoredox catalysts[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(26): 10484-10488. |
| 37 | ZHANG J W, ZHANG Q Y, CHEN B, et al. Photoenzymatic conversion of enamides to enantioenriched benzylic amines enabled by visible-light-induced single-electron reduction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(24): 15682-15690. |
| 38 | BIEGASIEWICZ K F, COOPER S J, GAO X, et al. Photoexcitation of flavoenzymes enables a stereoselective radical cyclization[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6446): 1166-1169. |
| 39 | MONDAL S, DUMUR F, GIGMES D, et al. Enantioselective radical reactions using chiral catalysts[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(6): 5842-5976. |
| 40 | CLAYMAN P D, HYSTER T K. Photoenzymatic generation of unstabilized alkyl radicals: an asymmetric reductive cyclization[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(37): 15673-15677. |
| 41 | ZHU C T, YUAN Z B, DENG Z W, et al. Photoenzymatic enantioselective synthesis of oxygen-containing benzo-fused heterocycles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(50): e202311762. |
| 42 | CAPONE M, DELL’ORLETTA G, NICHOLLS B T, et al. Evidence of a distinctive enantioselective binding mode for the photoinduced radical cyclization of α-chloroamides in ene-reductases[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(23): 15310-15321. |
| 43 | COLEMAN T, KIRK A M, CHAO R R, et al. Understanding the mechanistic requirements for efficient and stereoselective alkene epoxidation by a cytochrome P450 enzyme[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(4): 1995-2010. |
| 44 | SCHMERMUND L, VALENTINA JURKAŠ V, ÖZGEN F F. Photo-biocatalysis: biotransformations in the presence of light[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(5): 4115-4144. |
| 45 | HUANG X Q, WANG B J, WANG Y J, et al. Photoenzymatic enantioselective intermolecular radical hydroalkylation[J]. Nature, 2020, 584(7819): 69-74. |
| 46 | OUYANG Y, TUREK-HERMAN J, QIAO T Z, et al. Asymmetric carbohydroxylation of alkenes using photoenzymatic catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(31): 17018-17022. |
| 47 | LI M L, HARRISON W, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Remote stereocontrol with azaarenes via enzymatic hydrogen atom transfer[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2024, 16(2): 277-284. |
| 48 | BEST D, LAM H W. C-N-containing azaarenes as activating groups in enantioselective catalysis[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2014, 79(3): 831-845. |
| 49 | GUO J, XIE Y, LAI Z M, et al. Enantioselective hydroalkylation of alkenylpyridines enabled by merging photoactive electron donor-acceptor complexes with chiral bifunctional organocatalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(20): 13065-13074. |
| 50 | BENDER S G, HYSTER T K. Pyridylmethyl radicals for enantioselective alkene hydroalkylation using “ene”-reductases[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(22): 14680-14684. |
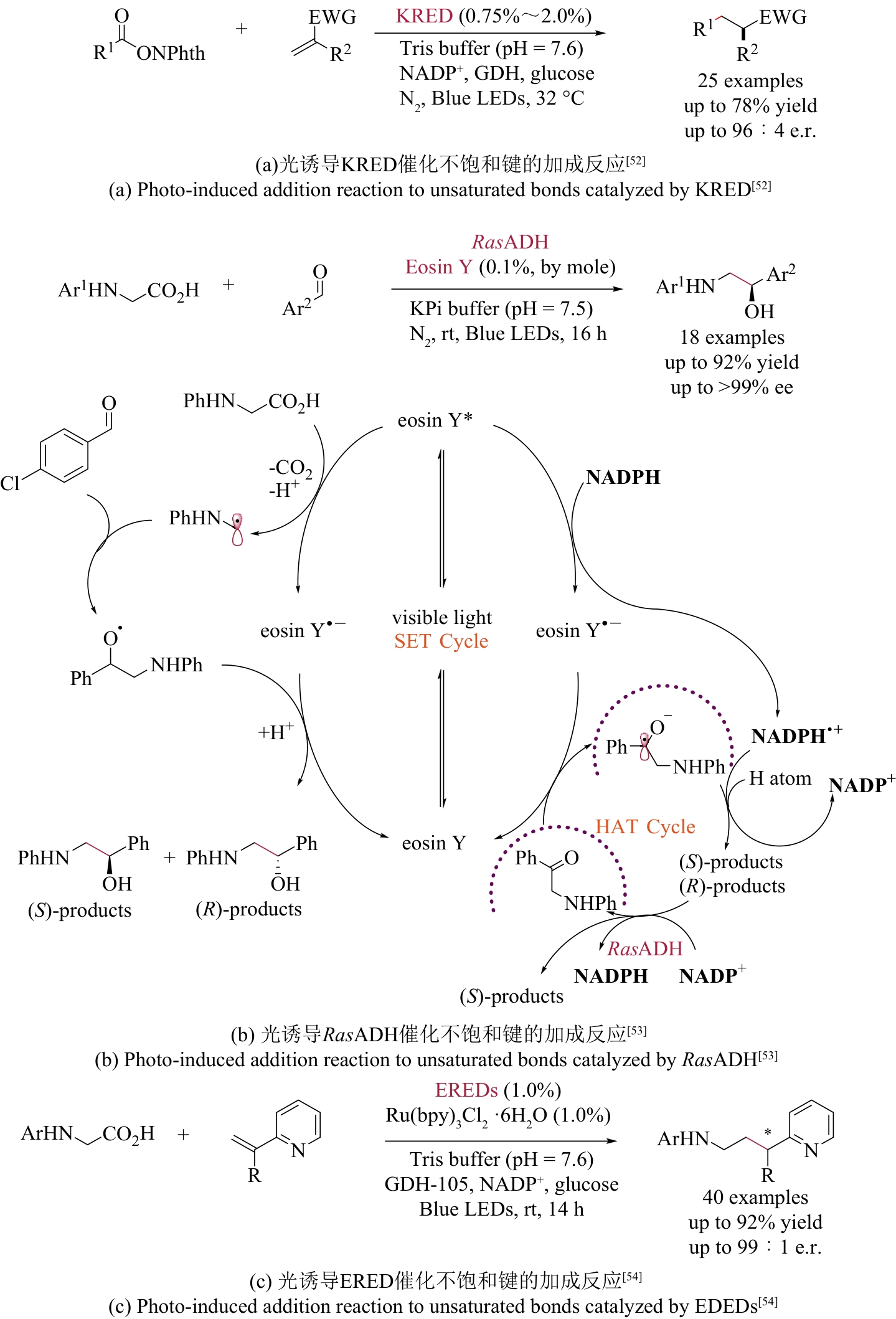
| 51 | DUAN X Y, CUI D, WANG Z G, et al. A photoenzymatic strategy for radical-mediated stereoselective hydroalkylation with diazo compounds[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(5): e202214135. |
| 52 | HUANG X Q, FENG J Q, CUI J W, et al. Photoinduced chemomimetic biocatalysis for enantioselective intermolecular radical conjugate addition[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5: 586-593. |
| 53 | LIU Y Y, ZHU L Y, LI X M, et al. Photoredox/enzymatic catalysis enabling redox-neutral decarboxylative asymmetric C-C coupling for asymmetric synthesis of chiral 1,2-amino alcohols[J]. JACS Au, 2023, 3(11): 3005-3013. |
| 54 | SUN S Z, NICHOLLS B T, BAIN D, et al. Enantioselective decarboxylative alkylation using synergistic photoenzymatic catalysis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2024, 7: 35-42. |
| 55 | XUE Y P, CAO C H, ZHENG Y G. Enzymatic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amino acids[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(4): 1516-1561. |
| 56 | BLASKOVICH M A T. Unusual amino acids in medicinal chemistry[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2016, 59(24): 10807-10836. |
| 57 | WANG Y W, DENG L F, ZHANG X, et al. A radical approach to making unnatural amino acids: conversion of C-S bonds in cysteine derivatives into C-C bonds[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(4): 2155-2159. |
| 58 | DUMAS A, LERCHER L, SPICER C D, et al. Designing logical codon reassignment — expanding the chemistry in biology[J]. Chemical Science, 2015, 6(1): 50-69. |
| 59 | ELIOT A C, KIRSCH J F. Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2004, 73: 383-415. |
| 60 | NAJERA C, SANSANO J M. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of alpha-amino acids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(11): 4584-4671. |
| 61 | CHENG L, LI D, MAI B K, et al. Stereoselective amino acid synthesis by synergistic photoredox-pyridoxal radical biocatalysis[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6656): 444-451. |
| 62 | ZHANG W, LU L X, ZHANG W, et al. Electrochemically driven cross-electrophile coupling of alkyl halides[J]. Nature, 2022, 604(7905): 292-297. |
| 63 | FU H G, CAO J Z, QIAO T Z, et al. An asymmetric sp3-sp3 cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases[J]. Nature, 2022, 610(7931): 302-307. |
| 64 | FU H G, QIAO T Z, CARCELLER J M, et al. Asymmetric C-alkylation of nitroalkanes via enzymatic photoredox catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(2): 787-793. |
| 65 | BALAKRISHNAN A, PARAMASIVAM S, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance studies delineate the role of the protein in activation of both aromatic rings of thiamin[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(1): 665-672. |
| 66 | BALAKRISHNAN A, GAO Y H, MOORJANI P, et al. Bifunctionality of the thiamin diphosphate cofactor: assignment of tautomeric/ionization states of the 4′-aminopyrimidine ring when various intermediates occupy the active sites during the catalysis of yeast pyruvate decarboxylase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(8): 3873-3885. |
| 67 | GAN M M, LIU J Q, ZHANG L, et al. Preparation and post-assembly modification of metallosupramolecular assemblies from poly(N-heterocyclic carbene) ligands[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(19): 9587-9641. |
| 68 | XU Y Y, CHEN H W, YU L, et al. A light-driven enzymatic enantioselective radical acylation[J]. Nature, 2024, 625(7993): 74-78. |
| 69 | XIONG T, ZHANG Q. New amination strategies based on nitrogen-centered radical chemistry[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(11): 3069-3087. |
| 70 | KWON K, SIMONS R T, NANDAKUMAR M, et al. Strategies to generate nitrogen-centered radicals that may rely on photoredox catalysis: development in reaction methodology and applications in organic synthesis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(2): 2353-2428. |
| 71 | YE Y X, CAO J Z, OBLINSKY D G, et al. Using enzymes to tame nitrogen-centred radicals for enantioselective hydroamination[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2023, 15(2): 206-212. |
| 72 | ZHANG Z Y, FENG J Q, YANG C, et al. Photoenzymatic enantioselective intermolecular radical hydroamination[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2023, 6(8): 687-694. |
| 73 | CHEN X Y, ZHENG D N, JIANG L Y, et al. Photoenzymatic hydrosulfonylation for the stereoselective synthesis of chiral sulfones[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(23): e202218140. |
| 74 | SHI Q L, KANG X W, LIU Z Y, et al. Single-electron oxidation-initiated enantioselective hydrosulfonylation of olefins enabled by photoenzymatic catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(4): 2748-2756. |
| 75 | DUTTA U, MAITI S, BHATTACHARYA T, et al. Arene diversification through distal C(sp2)-H functionalization[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6543): eabd5992. |
| 76 | WANG Y J, CHANG W J, QIN S M, et al. Diversification of aryl sulfonyl compounds through ligand-controlled meta- and para-C-H borylation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(34): e202206797. |
| 77 | LAUDER K, TOSCANI A, QI Y Y, et al. Photo-biocatalytic one-pot cascades for the enantioselective synthesis of 1,3-mercaptoalkanol volatile sulfur compounds[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(20): 5803-5807. |
| 78 | ZHAO B B, FENG J Q, YU L, et al. Direct visible-light-excited flavoproteins for redox-neutral asymmetric radical hydroarylation[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2023, 6(11): 996-1004. |
| 79 | COLGAN A C, PROCTOR R S J, GIBSON D C, et al. Hydrogen atom transfer driven enantioselective Minisci reaction of alcohols[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(25): e202200266. |
| 80 | PAGE C G, CAO J Z, OBLINSKY D G, et al. Regioselective radical alkylation of arenes using evolved photoenzymes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(21): 11866-11874. |
| 81 | LUJÁN A P, BHAT M F, TSATURYAN S, et al. Tailored photoenzymatic systems for selective reduction of aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds fueled by light[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 5442. |
| 82 | CHEN L, ZHANG Z Y, HOSHINO A, et al. NADPH production by the oxidative pentose-phosphate pathway supports folate metabolism[J]. Nature Metabolism, 2019, 1(3): 404-415. |
| 83 | BAUMANN S, PAUL W, CHOI T Y, et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance of individual atoms on a surface[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6259): 417-420. |
| 84 | WANG Y J, XUE P, CAO M F, et al. Directed evolution: methodologies and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(20): 12384-12444. |
| 85 | QIN Z Y, ZHOU Y, LI Z, et al. Production of biobased ethylbenzene by cascade biocatalysis with an engineered photodecarboxylase[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(8): e202314566. |
| 86 | FU Y, LIU X H, XIA Y, et al. Whole-cell-catalyzed hydrogenation/deuteration of aryl halides with a genetically repurposed photodehalogenase[J]. Chem, 2023, 9(7): 1897-1909. |
| 87 | YU T H, CUI H Y, LI J C, et al. Enzyme function prediction using contrastive learning[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6639): 1358-1363. |
| 88 | CHONG W Y, QI Y, JI L R, et al. Computer-aided tunnel engineering: a promising strategy for improving lipase applications in esterification reactions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(1): 67-83. |
| 89 | BENINCÁ L A D, FRANÇA A S, BRÊDA G C, et al. Continuous-flow CvFAP photodecarboxylation of palmitic acid under environmentally friendly conditions[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 528: 112469. |
| 90 | TAN C L, TAO F, XU P. Direct carbon capture for the production of high-performance biodegradable plastics by cyanobacterial cell factories[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(11): 4470-4483. |
| 91 | ÖZGEN F F, RUNDA M E, SCHMIDT S. Photo-biocatalytic cascades: combining chemical and enzymatic transformations fueled by light[J]. ChemBioChem, 2021, 22(5): 790-806. |
| 92 | TAYLOR A, HEYES D J, SCRUTTON N S. Catalysis by nature′s photoenzymes[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2022, 77: 102491. |
| 93 | COLLINS K D, GENSCH T, GLORIUS F. Contemporary screening approaches to reaction discovery and development[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6(10): 859-871. |
| 94 | VOLK M J, TRAN V G, TAN S I, et al. Metabolic engineering: methodologies and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(9): 5521-5570. |
| 95 | BULLER R, LUTZ S, KAZLAUSKAS R J, et al. From nature to industry: harnessing enzymes for biocatalysis[J]. Science, 2023, 382(6673): eadh8615. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||