合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (4): 808-823.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-020
重组胶原蛋白表达体系研究进展
潘家豪1, 潘炜松2, 邱健3, 谢东玲2, 邹奇4, 吴川1
- 1.中南大学冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙 410083
2.湖南诺合新生物科技有限公司,湖南 长沙 410001
3.中南大学湘雅医院,湖南 长沙 410008
4.华南师范大学生命科学学院,广东 广州 510631
-
收稿日期:2023-03-06修回日期:2023-05-17出版日期:2023-08-31发布日期:2023-09-14 -
通讯作者:吴川 -
作者简介:潘家豪 (2000—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为重组胶原蛋白在植物表达及其应用。E-mail:thekid123go@163.com吴川 (1983—),女,教授,博士生导师,湖湘青年英才,香港裘槎访问学者。研究方向为植物生物反应器、重金属污染生物修复等方面的研究。E-mail:wuchuan@csu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31670955);中南大学前沿交叉项目(2023QYJC035)
Research progress on recombinant collagen expression system
PAN Jiahao1, PAN Weisong2, QIU Jian3, XIE Donling2, ZOU Qi4, WU Chuan1
- 1.School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University,Changsha 410083,Hunan,China
2.Hunan Novomore Biotechnology Corporation,Changsha 410001,Hunan,China
3.Xiangya Hospital of Central South University,Changsha 410008,Hunan,China
4.School of Life Sciences,South China Normal University,Guangzhou 510631,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-03-06Revised:2023-05-17Online:2023-08-31Published:2023-09-14 -
Contact:WU Chuan
摘要:
胶原蛋白是哺乳动物中含量最多的蛋白质,至今已发现28种类型,主要分为纤维性胶原蛋白、网状胶原蛋白、珠状丝状胶原蛋白、锚定纤维蛋白、膜蛋白以及multiplexins胶原蛋白,其中纤维性胶原蛋白中Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白占人体胶原蛋白的80%~90%。目前,根据来源,胶原蛋白大致分为动物源胶原蛋白和重组胶原蛋白。动物源胶原蛋白主要来源于陆生动物以及海洋动物,而重组胶原蛋白是指将人胶原蛋白基因克隆到选定的表达载体并转化到表达细胞内,最后通过纯化技术所获得的蛋白质。本文简述了胶原蛋白的结构、类别和生物合成机制,重点阐述了重组胶原蛋白表达体系及特点,包括原核生物、酵母、植物、杆状病毒以及哺乳动物细胞等表达体系及其优势与局限性,介绍了重组胶原蛋白市场前景及在眼科、软骨工程、皮肤治疗等生物医药方面的实际应用,并对重组胶原蛋白的研究和产业发展进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
潘家豪, 潘炜松, 邱健, 谢东玲, 邹奇, 吴川. 重组胶原蛋白表达体系研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 808-823.
PAN Jiahao, PAN Weisong, QIU Jian, XIE Donling, ZOU Qi, WU Chuan. Research progress on recombinant collagen expression system[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 808-823.
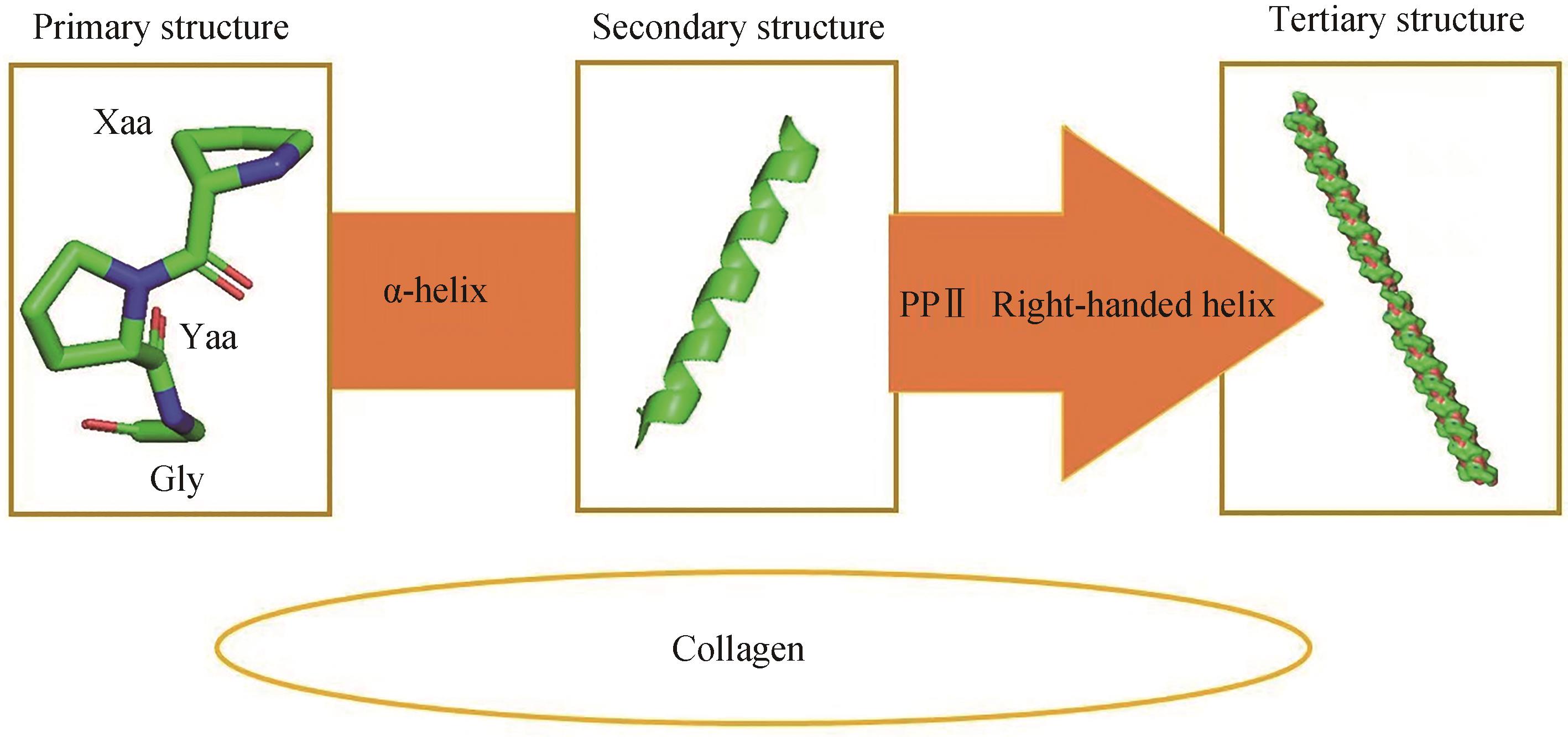
图1 胶原蛋白结构[20](胶原蛋白一级结构展示了胶原蛋白主要由脯氨酸、甘氨酸以及羟脯氨酸等氨基酸构成;二级结构则展示了脯氨酸、甘氨酸以及羟脯氨酸等氨基酸通过α螺旋使胶原蛋白二级结构趋于稳定;三级结构展示了3条α链经过左手螺旋构象形成原胶原)
Fig. 1 Structure of collagen[20](The primary structure of collagen shows that collagen is mainly composed of amino acids such as proline, glycine and hydroxyproline. The secondary structure shows that amino acids such as proline, glycine and hydroxyproline stabilize the secondary structure of collagen through α-helix. The tertiary structure shows that three α-chains passing through the left-hand helical conformation form procollagen.)
| 类型 | 组成 | 分布 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | α1[Ⅰ]2α2[Ⅰ] | 真皮、骨骼、肌腱、韧带 | 其变异会造成骨质疏松、牙齿异常、蓝色巩膜、皮肤薄、肌腱无力、听力丧失 |
| Ⅱ | α1[Ⅱ]3 | 软骨、玻璃体 | 与骨形态形成蛋白-2和转化因子P结合,有利于软骨的发育 |
| Ⅲ | α1[Ⅲ]3 | 皮肤、血管、肠 | 其突变会造成埃勒-丹洛斯综合征 |
| Ⅳ | α1[Ⅳ]2α2[Ⅳ] α3[Ⅳ]α4[Ⅳ] α5[Ⅳ]α5[Ⅳ]2α6[Ⅳ] | 基底膜 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构,细胞选择型过滤器,抑制血管生成与肿瘤生长 |
| Ⅴ | α1[Ⅴ]3 α1[Ⅴ]2α2[Ⅴ] α1[Ⅴ]α2[Ⅴ]α3[Ⅴ] | 骨、真皮、角膜、胎盘 | 神经发育与再生,其突变会造成埃勒-丹洛斯综合征 |
| Ⅵ | α1[Ⅵ]α2[Ⅵ] α3[Ⅵ] α1[Ⅵ]α2[Ⅵ] α4[Ⅵ] | 骨头、软骨、角膜、真皮层 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构,细胞选择型过滤器,肌功能主要贡献值 |
| Ⅶ | α1[Ⅶ]2α2[Ⅶ] | 真皮、膀胱 | 其突变会造成大疱性表皮松解症 |
| Ⅷ | α1[Ⅷ]3 α2[Ⅷ]3 α1[Ⅷ]2α2[Ⅷ] | 真皮、大脑、心脏、肾脏 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构、细胞选择型过滤器 |
| Ⅸ | α1[Ⅸ]α2[Ⅸ]α3[Ⅸ] | 软骨、角膜、玻璃体 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| Ⅹ | α1[Ⅹ]3 | 软骨 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构,细胞选择型过滤器,有利于软骨发育 |
| Ⅺ | α1[Ⅺ]α2[Ⅺ]α3[Ⅺ] | 软骨、椎间盘 | 有利于软骨发育 |
| Ⅻ | α1[Ⅻ]3 | 真皮、肌腱 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程,维持组织的完整性与机械性 |
| ⅩⅢ | α1[ⅩⅢ]3 | 内皮细胞、真皮、心脏、眼睛 | — |
| ⅩⅣ | α1[ⅩⅣ]3 | 骨、真皮、软骨 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程,维持组织的完整性与机械性 |
| ⅩⅤ | α1[ⅩⅤ]3 | 毛细血管、肾脏、睾丸、心脏 | 抑制血管生成与肿瘤生长 |
| ⅩⅥ | α1[ⅩⅥ]3 | 真皮、肾 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| ⅩⅦ | α1[ⅩⅦ]3 | 上皮细胞中半脂小体 | 其突变会造成大疱性表皮松解症 |
| ⅩⅧ | α1[ⅩⅧ]3 | 基底膜、肝脏 | 抑制血管生成与肿瘤生长,信息分子受体,维护肾脏形态 |
| ⅩⅨ | α1[ⅩⅨ]3 | 基底膜 | 调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| ⅩⅩ | α1[ⅩⅩ]3 | 角膜(小鸡) | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| ⅩⅪ | α1[ⅩⅪ]3 | 胃、肾 | — |
| ⅩⅫ | α1[ⅩⅫ]3 | 组织连接 | 软骨中结构和功能分离的基质聚集体,与软骨纤维外基质结合 |
| ⅩⅩⅢ | α1[ⅩⅩⅢ]3 | 心、视网膜 | 增殖区组织所必需,细胞外基质关键的结构作用 |
| ⅩⅩⅣ | α1[ⅩⅩⅣ]3 | 骨头、角膜 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅤ | α1[ⅩⅩⅤ]3 | 大脑、心脏、睾丸 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅥ | α1[ⅩⅩⅥ]3 | 睾丸、卵巢 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅦ | α1[ⅩⅩⅦ]3 | 软骨 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅧ | α1[ⅩⅩⅧ]3 | 真皮、坐骨神经 | — |
表1 胶原蛋白类型、分布及功能[23,29-30]
Table 1 Collagen type, distribution and function[23,29-30]
| 类型 | 组成 | 分布 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | α1[Ⅰ]2α2[Ⅰ] | 真皮、骨骼、肌腱、韧带 | 其变异会造成骨质疏松、牙齿异常、蓝色巩膜、皮肤薄、肌腱无力、听力丧失 |
| Ⅱ | α1[Ⅱ]3 | 软骨、玻璃体 | 与骨形态形成蛋白-2和转化因子P结合,有利于软骨的发育 |
| Ⅲ | α1[Ⅲ]3 | 皮肤、血管、肠 | 其突变会造成埃勒-丹洛斯综合征 |
| Ⅳ | α1[Ⅳ]2α2[Ⅳ] α3[Ⅳ]α4[Ⅳ] α5[Ⅳ]α5[Ⅳ]2α6[Ⅳ] | 基底膜 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构,细胞选择型过滤器,抑制血管生成与肿瘤生长 |
| Ⅴ | α1[Ⅴ]3 α1[Ⅴ]2α2[Ⅴ] α1[Ⅴ]α2[Ⅴ]α3[Ⅴ] | 骨、真皮、角膜、胎盘 | 神经发育与再生,其突变会造成埃勒-丹洛斯综合征 |
| Ⅵ | α1[Ⅵ]α2[Ⅵ] α3[Ⅵ] α1[Ⅵ]α2[Ⅵ] α4[Ⅵ] | 骨头、软骨、角膜、真皮层 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构,细胞选择型过滤器,肌功能主要贡献值 |
| Ⅶ | α1[Ⅶ]2α2[Ⅶ] | 真皮、膀胱 | 其突变会造成大疱性表皮松解症 |
| Ⅷ | α1[Ⅷ]3 α2[Ⅷ]3 α1[Ⅷ]2α2[Ⅷ] | 真皮、大脑、心脏、肾脏 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构、细胞选择型过滤器 |
| Ⅸ | α1[Ⅸ]α2[Ⅸ]α3[Ⅸ] | 软骨、角膜、玻璃体 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| Ⅹ | α1[Ⅹ]3 | 软骨 | 作为细胞和组织的支撑结构,细胞选择型过滤器,有利于软骨发育 |
| Ⅺ | α1[Ⅺ]α2[Ⅺ]α3[Ⅺ] | 软骨、椎间盘 | 有利于软骨发育 |
| Ⅻ | α1[Ⅻ]3 | 真皮、肌腱 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程,维持组织的完整性与机械性 |
| ⅩⅢ | α1[ⅩⅢ]3 | 内皮细胞、真皮、心脏、眼睛 | — |
| ⅩⅣ | α1[ⅩⅣ]3 | 骨、真皮、软骨 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程,维持组织的完整性与机械性 |
| ⅩⅤ | α1[ⅩⅤ]3 | 毛细血管、肾脏、睾丸、心脏 | 抑制血管生成与肿瘤生长 |
| ⅩⅥ | α1[ⅩⅥ]3 | 真皮、肾 | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| ⅩⅦ | α1[ⅩⅦ]3 | 上皮细胞中半脂小体 | 其突变会造成大疱性表皮松解症 |
| ⅩⅧ | α1[ⅩⅧ]3 | 基底膜、肝脏 | 抑制血管生成与肿瘤生长,信息分子受体,维护肾脏形态 |
| ⅩⅨ | α1[ⅩⅨ]3 | 基底膜 | 调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| ⅩⅩ | α1[ⅩⅩ]3 | 角膜(小鸡) | 参与细胞外基质的完整性和稳定性,调节胶原蛋白形成过程 |
| ⅩⅪ | α1[ⅩⅪ]3 | 胃、肾 | — |
| ⅩⅫ | α1[ⅩⅫ]3 | 组织连接 | 软骨中结构和功能分离的基质聚集体,与软骨纤维外基质结合 |
| ⅩⅩⅢ | α1[ⅩⅩⅢ]3 | 心、视网膜 | 增殖区组织所必需,细胞外基质关键的结构作用 |
| ⅩⅩⅣ | α1[ⅩⅩⅣ]3 | 骨头、角膜 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅤ | α1[ⅩⅩⅤ]3 | 大脑、心脏、睾丸 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅥ | α1[ⅩⅩⅥ]3 | 睾丸、卵巢 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅦ | α1[ⅩⅩⅦ]3 | 软骨 | — |
| ⅩⅩⅧ | α1[ⅩⅩⅧ]3 | 真皮、坐骨神经 | — |

图2 胶原蛋白合成机制图[26,41]P—脯氨酸残基;K—赖氨酸残基;P4H—脯氨酰4-羟化酶;LH—赖氨酰羟化酶;P3H1—脯氨酰3-羟化酶;HSP47—热休克蛋白47;PDI—二硫异构酶;FKPB65—免疫亲蛋白;PNP—原胶原N端酶;PCP—原胶原C端酶(首先胶原蛋白 α 链经内质网中P4H酶以及LH酶的作用下实现羟基化,随后,3条胶原蛋白α单链的C端前肽在内质网膜凝集素样分子伴侣、钙联蛋白和内质网氧化还原酶PDI的协同作用下形成二硫键。HSP47能有效防止前胶原蛋白局部展开和聚集形成。最后,前胶原蛋白经高尔基体运送至细胞质基质利用N端酶与C端酶将多余N端与C端进行切除,形成完整的胶原蛋白结构)
Fig. 2 Mechanism of collagen synthesis[26,41]P—proline residue; K—lysine residue; P4H—prolyl 4-hydroxylase; LH—lysyl hydroxylase; P3H1—prolyl 3-hydroxylase; HSP47—heat shock protein 47; PDI—disulfide isomerase; FKPB65—immunophilic proteins; PNP—procollagen N protease; PCP—procollagen C protease (Firstly, collagen genes form collagen α-chains through transcription and translation, and secondly, under the action of P4H enzymes and LH enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum, collagen α-chain is hydroxylated. Subsequently, three collagen α single-stranded C-terminal propeptides form disulfide bonds under the synergistic action of endoplasmic reticulum lectin-like chaperones, calcepiprotein, and endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase PDI. HSP47 effectively prevents the formation of local expansion and aggregation of pre-collagen. Finally, the cytoplasmic matrix of the procollagen is transported by the Golgi apparatus and the excess N-terminal and C-terminus of the precollagen are excised by N-terminal enzymes and C-terminal enzymes to form a complete collagen structure.)
| 重组胶原蛋白表达体系 | 表达量 | 类型 | 三螺旋结构 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 100~200 mg/L | 胶原蛋白聚合物 | 无 | Yin et al.[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 83.9 g/L | 重组类人Ⅱ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 常海燕[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 520 mg/L | 重组类人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 杨晶等[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 90 mg/L | 重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Rutschman et al.[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 0.8 g/L | 融合胶原蛋白 | 无 | Liu et al.[ |
| 酵母 | 2.15 g/kg | 重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Vuorela et al.[ |
| 酵母 | 60.1 mg/L | 重组类人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 高力虎 [ |
| 酵母 | 1.27 g/L | 重组人胶原Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Wang et al.[ |
| 酵母 | 4.7 g/L | 重组类人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 李伟娜等[ |
| 酵母 | 4.5 g/L | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | 侯增淼等[ |
| 植物 | 100 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Ruggiero et al.[ |
| 植物 | 50~100 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Merle et al.[ |
| 植物 | 200 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | CollPlant公司[ |
| 植物 | 羟基化:4 mg/kg; 未羟基化:12 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Xu et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 前胶原蛋白:60 mg/L 胶原蛋白:40 mg/L | 重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Lamberg et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 10~20 mg/L | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Myllyharju et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 70 mg融合蛋白质 | 前胶原蛋白Ⅲ型 | 无 | Tomita et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 1 mg/幼虫 | 重组人Ⅱ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Qi et al.[ |
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 50 mg/L | 重组人Ⅹ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Frischholz et al.[ |
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 8 g/L | 重组人胶原蛋Ⅰ型 | 有 | Toman et al.[ |
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 6.28 mg/L | 重组Ⅳ-α胶原蛋白 | 无 | 曾斐鸿 [ |
表2 不同表达体系产生胶原蛋白含量及种类
Table 2 Content and types of collagen produced by different expression systems
| 重组胶原蛋白表达体系 | 表达量 | 类型 | 三螺旋结构 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 100~200 mg/L | 胶原蛋白聚合物 | 无 | Yin et al.[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 83.9 g/L | 重组类人Ⅱ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 常海燕[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 520 mg/L | 重组类人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 杨晶等[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 90 mg/L | 重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Rutschman et al.[ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 0.8 g/L | 融合胶原蛋白 | 无 | Liu et al.[ |
| 酵母 | 2.15 g/kg | 重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Vuorela et al.[ |
| 酵母 | 60.1 mg/L | 重组类人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 高力虎 [ |
| 酵母 | 1.27 g/L | 重组人胶原Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Wang et al.[ |
| 酵母 | 4.7 g/L | 重组类人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 无 | 李伟娜等[ |
| 酵母 | 4.5 g/L | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | 侯增淼等[ |
| 植物 | 100 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Ruggiero et al.[ |
| 植物 | 50~100 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Merle et al.[ |
| 植物 | 200 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | CollPlant公司[ |
| 植物 | 羟基化:4 mg/kg; 未羟基化:12 mg/kg | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Xu et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 前胶原蛋白:60 mg/L 胶原蛋白:40 mg/L | 重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Lamberg et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 10~20 mg/L | 重组人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Myllyharju et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 70 mg融合蛋白质 | 前胶原蛋白Ⅲ型 | 无 | Tomita et al.[ |
| 昆虫杆状病毒 | 1 mg/幼虫 | 重组人Ⅱ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Qi et al.[ |
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 50 mg/L | 重组人Ⅹ型胶原蛋白 | 有 | Frischholz et al.[ |
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 8 g/L | 重组人胶原蛋Ⅰ型 | 有 | Toman et al.[ |
| 哺乳动物细胞 | 6.28 mg/L | 重组Ⅳ-α胶原蛋白 | 无 | 曾斐鸿 [ |
| 重组胶原蛋白表达体系 | 成本 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 植物表达体系 | 较低 | 可规模化,生产周期短,成本低,安全性高 | 产量较低,产能不足 |
| 大肠杆菌表达体系 | 较低 | 遗传背景清晰,发酵成本较低,生产周期短,效率高 | 产生胶原蛋白缺乏羟基化 |
| 酵母表达体系 | 较低 | 较高的安全性,发酵成本较低,产量高 | 多为同源性胶原蛋白,生产异源性胶原蛋白较为困难 |
| 昆虫杆状病毒表达体系 | 较高 | 背景干扰低,进行翻译后处理能力更强 | 周期较长、产量较低 |
| 哺乳动物细胞表达体系 | 较高 | 表达稳定,产量稳定 | 表达周期长,成本高,有病毒感染风险 |
表3 不同表达体系生产胶原蛋白成本及优缺点
Table 3 Costs, advantages and disadvantages of collagen production in different expression systems
| 重组胶原蛋白表达体系 | 成本 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 植物表达体系 | 较低 | 可规模化,生产周期短,成本低,安全性高 | 产量较低,产能不足 |
| 大肠杆菌表达体系 | 较低 | 遗传背景清晰,发酵成本较低,生产周期短,效率高 | 产生胶原蛋白缺乏羟基化 |
| 酵母表达体系 | 较低 | 较高的安全性,发酵成本较低,产量高 | 多为同源性胶原蛋白,生产异源性胶原蛋白较为困难 |
| 昆虫杆状病毒表达体系 | 较高 | 背景干扰低,进行翻译后处理能力更强 | 周期较长、产量较低 |
| 哺乳动物细胞表达体系 | 较高 | 表达稳定,产量稳定 | 表达周期长,成本高,有病毒感染风险 |
| 1 | AVILA RODRÍGUEZ M I, RODRÍGUEZ BARROSO L G, SÁNCHEZ M L. Collagen: a review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications[J]. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 2018, 17(1): 20-26. |
| 2 | KADLER K E, BALDOCK C, BELLA J, et al. Collagens at a glance[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2007, 120(12): 1955-1958. |
| 3 | VEIT G, KOBBE B, KEENE D R, et al. Collagen ⅩⅩⅧ, a novel von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein with many imperfections in the collagenous domain[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2006, 281(6): 3494-3504. |
| 4 | DI LULLO G A, SWEENEY S M, KÖRKKÖ J, et al. Mapping the ligand-binding sites and disease-associated mutations on the most abundant protein in the human, type Ⅰ collagen[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(6): 4223-4231. |
| 5 | FRIESS W. Collagen-biomaterial for drug delivery[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 1998, 45(2): 113-136. |
| 6 | SIONKOWSKA A, SKRZYŃSKI S, ŚMIECHOWSKI K, et al. The review of versatile application of collagen[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2017, 28(1): 4-9. |
| 7 | GRIFFITH M, JACKSON W B, LAGALI N, et al. Artificial corneas: a regenerative medicine approach[J]. Eye, 2009, 23(10): 1985-1989. |
| 8 | DUNN M G, DOILLON C J, BERG R A, et al. Wound healing using a collagen matrix: effect of DC electrical stimulation[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1988, 22(S13): 191-206. |
| 9 | RAO J R, KANTHIMATHI M, THANIKAIVELAN P, et al. Pickle-free chrome tanning using a polymeric synthetic tanning agent for cleaner leather processing[J]. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 2004, 6(4): 243-249. |
| 10 | INOUE T, TODA S, NARISAWA Y, et al. Subcutaneous adipocytes promote the differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma cell line (DJM-1) in collagen gel matrix culture[J]. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2001, 117(2): 244-250. |
| 11 | CHE Z M, JUNG T H, CHOI J H, et al. Collagen-based co-culture for invasive study on cancer cells-fibroblasts interaction[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2006, 346(1): 268-275. |
| 12 | GINGRAS M, BEAULIEU M M, GAGNON V, et al. In vitro study of axonal migration and myelination of motor neurons in a three-dimensional tissue-engineered model[J]. Glia, 2008, 56(3): 354-364. |
| 13 | CHAMBERLAIN L J, YANNAS I V, HSU H P, et al. Collagen-GAG substrate enhances the quality of nerve regeneration through collagen tubes up to level of autograft[J]. Experimental Neurology, 1998, 154(2): 315-329. |
| 14 | SEROR J, STERN M, ZARKA R, et al. The potential use of novel plant-derived recombinant human collagen in aesthetic medicine[J]. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 2021, 148(6S): 32S-38S. |
| 15 | SHOSEYOV O, POSEN Y, GRYNSPAN F. Human recombinant type Ⅰ collagen produced in plants[J]. Tissue Engineering Part A, 2013, 19(13/14): 1527-1533. |
| 16 | SHOSEYOV O, POSEN Y, GRYNSPAN F. Human collagen produced in plants: more than just another molecule[J]. Bioengineered, 2014, 5(1): 49-52. |
| 17 | XU N, PENG X L, LI H R, et al. Marine-derived collagen as biomaterials for human health[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2021, 8: 702108. |
| 18 | 傅容湛, 范代娣, 杨婉娟, 等. 重组胶原蛋白的产业发展历程和生物医学应用前景展望[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(9): 3228-3242. |
| FU R Z, FAN D D, YANG W J, et al. Industrial development and biomedical application prospect of recombinant collagen[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(9): 3228-3242. | |
| 19 | 中国国家药品监督管理局. 重组胶原蛋白生物材料命名指导原则 [S/OL]. 2021[2023-02-01]. . |
| China National Medical Products Administration. Guidelines for the naming of recombinant collagen biomaterials [S/OL]. 2021[2023-02-01]. . | |
| 20 | BERISIO R, VITAGLIANO L, MAZZARELLA L, et al. Crystal structure of the collagen triple helix model [(Pro-Pro-Gly)10]3 [J]. Protein Science, 2002, 11(2): 262-270. |
| 21 | NEUMAN R E, LOGAN M A. The determination of collagen and elastin in tissues[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1950, 186(2): 549-556. |
| 22 | BRODSKY B, RAMSHAW J A M. The collagen triple-helix structure[J]. Matrix Biology, 1997, 15(8/9): 545-554. |
| 23 | SHOULDERS M D, RAINES R T. Collagen structure and stability[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2009, 78: 929-958. |
| 24 | LEIKINA E, MERTTS M V, KUZNETSOVA N, et al. Type Ⅰ collagen is thermally unstable at body temperature[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(3): 1314-1318. |
| 25 | SAXENA T, KARUMBAIAH L, VALMIKINATHAN C M. Proteins and poly(amino acids)[M/OL]//Natural and Synthetic Biomedical Polymers. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 43-65 [2023-02-01]. . |
| 26 | JONES E Y, MILLER A. Analysis of structural design features in collagen[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1991, 218(1): 209-219. |
| 27 | ITO S, NAGATA K. Quality control of procollagen in cells[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2021, 90: 631-658. |
| 28 | ERDMANN R S, WENNEMERS H. Effect of sterically demanding substituents on the conformational stability of the collagen triple helix[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(41): 17117-17124. |
| 29 | LEÓN-LÓPEZ A, MORALES-PEÑALOZA A, MARTÍNEZ-JUÁREZ V M, et al. Hydrolyzed collagen—sources and applications[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(22): 4031. |
| 30 | RICHARDS A J, SNEAD M P. Molecular basis of pathogenic variants in the fibrillar collagens[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(7): 1199. |
| 31 | RICARD-BLUM S. The collagen family[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2011, 3(1): a004978. |
| 32 | LI Y B, LIU Y Z, LI R H, et al. Collagen-based biomaterials for bone tissue engineering[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 210: 110049. |
| 33 | SIONKOWSKA A, ADAMIAK K, MUSIAŁ K, et al. Collagen based materials in cosmetic applications: a review[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(19): 4217. |
| 34 | BRODSKY B, THIAGARAJAN G, MADHAN B, et al. Triple-helical peptides: an approach to collagen conformation, stability, and self-association[J]. Biopolymers, 2008, 89(5): 345-353. |
| 35 | SILVER F H, FREEMAN J W, SEEHRA G P. Collagen self-assembly and the development of tendon mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2003, 36(10): 1529-1553. |
| 36 | PROCKOP D J, FERTALA A. The collagen fibril: the almost crystalline structure[J]. Journal of Structural Biology, 1998, 122(1/2): 111-118. |
| 37 | SILVER D, MILLER J, HARRISON R, et al. Helical model of nucleation and propagation to account for the growth of type Ⅰ collagen fibrils from symmetrical pointed tips: a special example of self-assembly of rod-like monomers[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(20): 9860-9864. |
| 38 | SUNDARAMOORTHY M, MEIYAPPAN M, TODD P, et al. Crystal structure of NC1 domains: structural basis for type Ⅳ collagen assembly in basement membranes[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(34): 31142-31153. |
| 39 | BOUDKO S P, ENGEL J, BäCHINGER H P. The crucial role of trimerization domains in collagen folding[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2012, 44(1): 21-32. |
| 40 | ORTEGA N, WERB Z. New functional roles for non-collagenous domains of basement membrane collagens[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2002, 115(22): 4201-4214. |
| 41 | FERTALA A. Three decades of research on recombinant collagens: reinventing the wheel or developing new biomedical products?[J]. Bioengineering, 2020, 7(4): 155. |
| 42 | HINTZE V, STEPLEWSKI A, ITO H, et al. Cells expressing partially unfolded R789C/p.R989C type Ⅱ procollagen mutant associated with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia undergo apoptosis[J]. Human Mutation, 2008, 29(6): 841-851. |
| 43 | BACHINGER H P, BRUCKNER P, TIMPL R, et al. Folding mechanism of the triple helix in type-Ⅲ collagen and type-Ⅲ pN-collagen. role of disulfide bridges and peptide bond isomerization[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1980, 106(2): 619-632. |
| 44 | VAN DIJK F S, NESBITT I M, ZWIKSTRA E H, et al. PPIB mutations cause severe osteogenesis imperfecta[J]. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2009, 85(4): 521-527. |
| 45 | PLOTKIN H. Syndromes with congenital brittle bones[J].BMC Pediatrics, 2004, 4(1): 16. |
| 46 | SEVIER C S, KAISER C A. Formation and transfer of disulphide bonds in living cells[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2002, 3(11): 836-847. |
| 47 | SEVIER C S, KAISER C A. Conservation and diversity of the cellular disulfide bond formation pathways[J]. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 2006, 8(5/6): 797-811. |
| 48 | THORPE C, COPPOCK D L. Generating disulfides in multicellular organisms: emerging roles for a new flavoprotein family[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(19): 13929-13933. |
| 49 | HERAS B, KURZ M, SHOULDICE S R, et al. The name's bond……disulfide bond[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2007, 17(6): 691-698. |
| 50 | BRINCKMANN J, NOTBOHM H, MÜLLER P K. Collagen: primer in structure, processing, and assembly[M/OL]. Berlin: Springer, 2005[2023-02-01]. . |
| 51 | GEDDIS A E, PROCKOP D J. Expression of human COL1A1 gene in stably transfected HT1080 cells: the production of a thermostable homotrimer of type Ⅰ collagen in a recombinant system[J]. Matrix, 1993, 13(5): 399-405. |
| 52 | BULLEID N J, JOHN D C A, KADLER K E. Recombinant expression systems for the production of collagen[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2000, 28(4): 350-353. |
| 53 | OLSEN D, YANG C L, BODO M, et al. Recombinant collagen and gelatin for drug delivery[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2003, 55(12): 1547-1567. |
| 54 | BOYDSTON J A, CHEN P, STEICHEN C T, et al. Orientation within the exosporium and structural stability of the collagen-like glycoprotein BclA of Bacillus anthracis [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2005, 187(15): 5310-5317. |
| 55 | RUGGIERO F, KOCH M. Making recombinant extracellular matrix proteins[J]. Methods, 2008, 45(1): 75-85. |
| 56 | WERKMEISTER J A, RAMSHAW J A M. Recombinant protein scaffolds for tissue engineering[J]. Biomedical Materials, 2012, 7(1): 012002. |
| 57 | RAMSHAW J A M, WERKMEISTER J A, DUMSDAY G J. Bioengineered collagens: emerging directions for biomedical materials[J]. Bioengineered, 2014, 5(4): 227-233. |
| 58 | YIN J, LIN J H, LI W T, et al. Evaluation of different promoters and host strains for the high-level expression of collagen-like polymer in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2003, 100(3): 181-191. |
| 59 | 常海燕. 重组大肠杆菌高密度发酵生产类人胶原蛋白Ⅱ工艺研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2009. |
| CHANG H Y. Study on the process of recombinant E . coli high-density fermentation for expressing human-like collagen Ⅱ[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2009. | |
| 60 | 杨晶, 余洁莹, 王蒙, 等. 重组类人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白肽在大肠杆菌中的表达纯化及功能鉴定[J]. 现代食品科技, 2016, 32(2): 60-65. |
| YANG J, YU J Y, WANG M, et al. Expression, purification, and functional characterization of recombinant human-like type Ⅰ collagen peptide in E.coli [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2016, 32(2): 60-65. | |
| 61 | RUTSCHMANN C, BAUMANN S, CABALZAR J, et al. Recombinant expression of hydroxylated human collagen in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(10): 4445-4455. |
| 62 | LIU S, LI Y M, WANG M, et al. Efficient coexpression of recombinant human fusion collagen with prolyl 4-hydroxylase from Bacillus anthracis in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2023, 70(2): 761-772. |
| 63 | VUORELA A. Assembly of human prolyl 4-hydroxylase and type Ⅲ collagen in the yeast Pichia pastoris: formation of a stable enzyme tetramer requires coexpression with collagen and assembly of a stable collagen requires coexpression with prolyl 4-hydroxylase[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1997, 16(22): 6702-6712. |
| 64 | 高力虎. 重复序列类人胶原蛋白表达载体的构建及在毕赤酵母中的分泌表达[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2007. |
| GAO L H. Construction of repetitive human-like collagen expression vector and its secretory expression in Pichia pastoris [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2007. | |
| 65 | WANG L N, FAN D D, HE J, et al. A new strategy for secretory expression and mixed fermentation of recombinant human collagen α1 (Ⅲ) chain in Pichia pastoris [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2014, 19(5): 916-924. |
| 66 | 李伟娜, 尚子方, 段志广, 等. 毕赤酵母高密度发酵产Ⅲ型类人胶原蛋白及其胃粘膜修复功能[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(4): 672-682. |
| LI W N, SHANG Z F, DUAN Z G, et al. Production of gastric-mucosa protective collagen Ⅲ by Pichia pastoris [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(4): 672-682. | |
| 67 | 侯增淼, 李晓颖, 李敏, 等. 重组人源性胶原蛋白的制备及表征[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(2): 319-326. |
| HOU Z M, LI X Y, LI M, et al. Preparation and characterization of recombinant human-source collagen[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(2): 319-326. | |
| 68 | RUGGIERO F, EXPOSITO J Y, BOURNAT P, et al. Triple helix assembly and processing of human collagen produced in transgenic tobacco plants[J]. FEBS Letters, 2000, 469(1): 132-136. |
| 69 | MERLE C, PERRET S, LACOUR T, et al. Hydroxylated human homotrimeric collagen Ⅰ in Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transient expression and in transgenic tobacco plant[J]. FEBS Letters, 2002, 515(1/2/3): 114-118. |
| 70 | STEIN H, WILENSKY M, TSAFRIR Y, et al. Production of bioactive, post-translationally modified, heterotrimeric, human recombinant type-Ⅰ collagen in transgenic tobacco[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10(9): 2640-2645. |
| 71 | XU X, GAN Q L, CLOUGH R C, et al. Hydroxylation of recombinant human collagen type Ⅰ alpha 1 in transgenic maize co-expressed with a recombinant human prolyl 4-hydroxylase[J].BMC Biotechnology, 2011, 11(1): 69. |
| 72 | LAMBERG A, HELAAKOSKI T, MYLLYHARJU J, et al. Characterization of human type Ⅲ collagen expressed in a baculovirus system. Production of a protein with a stable triple helix requires coexpression with the two types of recombinant prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1996, 271(20): 11988-11995. |
| 73 | MYLLYHARJU J, KIVIRIKKO K I. Collagens and collagen-related diseases[J]. Annals of Medicine, 2001, 33(1): 7-21. |
| 74 | TOMITA M, MUNETSUNA H, SATO T, et al. Transgenic silkworms produce recombinant human type Ⅲ procollagen in cocoons[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(1): 52-56. |
| 75 | QI Q, YAO L G, LIANG Z S, et al. Production of human type Ⅱ collagen using an efficient baculovirus-silkworm multigene expression system[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 291(6): 2189-2198. |
| 76 | FRISCHHOLZ S, BEIER F, GIRKONTAITE I, et al. Characterization of human type Ⅹ procollagen and its NC-1 domain expressed as recombinant proteins in HEK293 cells[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273(8): 4547-4555. |
| 77 | TOMAN P D, PIEPER F, SAKAI N M, et al. Production of recombinant human type Ⅰ procollagen homotrimer in the mammary gland of transgenic mice[J]. Transgenic Research, 1999, 8(6): 415-427. |
| 78 | 曾斐鸿. 人胚胎肾细胞HEK293F表达重组胶原蛋白Ⅳ-α1[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2020. |
| ZENG F H. Expression of recombinant collagen Ⅳ-α1 in human embryonic kidney 293 cells[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2020. | |
| 79 | YU Z, AN B, RAMSHAW J A M, et al. Bacterial collagen-like proteins that form triple-helical structures[J]. Journal of Structural Biology, 2014, 186(3): 451-461. |
| 80 | SHI J J, MA X X, GAO Y, et al. Hydroxylation of human type Ⅲ collagen alpha chain by recombinant coexpression with a viral prolyl 4-hydroxylase in Escherichia coli [J]. The Protein Journal, 2017, 36(4): 322-331. |
| 81 | GOFFEAU A, BARRELL B G, BUSSEY H, et al. Life with 6000 genes[J]. Science, 1996, 274(5287): 546-567. |
| 82 | 高云. 真核表达系统的研究进展[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2002, 8(4): 292-294, 298. |
| GAO Y. Advances in eukaryotic expression systems[J]. National Journal of Andrology, 2002, 8(4): 292-294, 298. | |
| 83 | BUYEL J F. Plant molecular farming - integration and exploitation of side streams to achieve sustainable biomanufacturing[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 9: 1893. |
| 84 | CEREGHINO J L, CREGG J M. Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris [J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2000, 24(1): 45-66. |
| 85 | 邹奇, 潘炜松, 邱健, 等. 植物生物反应器优化策略与最新应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2023, 43(1): 71-86. |
| ZOU Q, PAN W S, QIU J, et al. Recent advances in optimization strategies and applications of plant bioreactors[J]. China Biotechnology, 2023, 43(1): 71-86. | |
| 86 | NOKELAINEN M, HELAAKOSKI T, MYLLYHARJU J, et al. Expression and characterization of recombinant human type Ⅱ collagens with low and high contents of hydroxylysine and its glycosylated forms[J]. Matrix Biology, 1998, 16(6): 329-338. |
| 87 | IKONOMOU L, SCHNEIDER J Y, AGATHOS S N. Insect cell culture for industrial production of recombinant proteins[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 62(1): 1-20. |
| 88 | WURM F M. Human therapeutic proteins from silkworms[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(1): 34-35. |
| 89 | MYLLYHARJU J, LAMBERG A, NOTBOHM H, et al. Expression of wild-type and modified proα chains of human type Ⅰ procollagen in insect cells leads to the formation of stable [α1(Ⅰ)]2α2(Ⅰ) collagen heterotrimers and[α1(Ⅰ)]3 homotrimers but not[α2(Ⅰ)]3 homotrimers[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(35): 21824-21830. |
| 90 | WOODLEY D T, KEENE D R, ATHA T, et al. Injection of recombinant human type Ⅶ collagen restores collagen function in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa[J]. Nature Medicine, 2004, 10(7): 693-695. |
| 91 | FICHARD A, TILLET E, DELACOUX F, et al. Human recombinant α1(Ⅴ) collagen chain. Homotrimeric assembly and subsequent processing[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(48): 30083-30087. |
| 92 | JOHN D C A, WATSON R, KIND A J, et al. Expression of an engineered form of recombinant procollagen in mouse milk[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1999, 17(4): 385-389. |
| 93 | 张智武, 夏伟, 胡张捷. 胶原蛋白产业现状及其发展趋势的研究[J]. 中国食品, 2021(18): 126-128. |
| ZHANG Z W, XIA W, HU Z J. Study on the present situation and development trend of collagen industry[J]. China Food, 2021(18): 126-128. | |
| 94 | MYLLYHARJU J, NOKELAINEN M, VUORELA A, et al. Expression of recombinant human type Ⅰ‒Ⅲ collagens in the yeast Pichia pastoris [J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2000, 28(4): 353. |
| 95 | BÁEZ J, OLSEN D, POLAREK J W. Recombinant microbial systems for the production of human collagen and gelatin[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2005, 69(3): 245-252. |
| 96 | HUA C, ZHU Y, XU W, et al. Characterization by high-resolution crystal structure analysis of a triple-helix region of human collagen type Ⅲ with potent cell adhesion activity[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2019, 508(4): 1018-1023. |
| 97 | QUE R A, ARULMOLI J, SILVA N A DA, et al. Recombinant collagen scaffolds as substrates for human neural stem/progenitor cells[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2018, 106(5): 1363-1372. |
| 98 | WOODLEY D T, WANG X Y, AMIR M, et al. Intravenously injected recombinant human type Ⅶ collagen homes to skin wounds and restores skin integrity of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa[J]. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2013, 133(7): 1910-1913. |
| 99 | PODREBARAC J. Development of recombinant human collagen type Ⅰ and type Ⅲ injectable hydrogels for cardiac therapy[EB/OL]. 2017[2023-02-01]. . |
| 100 | FARKASH U, AVISAR E, VOLK I, et al. First clinical experience with a new injectable recombinant human collagen scaffold combined with autologous platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of lateral epicondylar tendinopathy (tennis elbow)[J]. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 2019, 28(3): 503-509. |
| 101 | MIRAZUL ISLAM M, CĖPLA V, HE C L, et al. Functional fabrication of recombinant human collagen-phosphorylcholine hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 12: 70-80. |
| 102 | ZHAO L L, LI X, ZHAO J Q, et al. A novel smart injectable hydrogel prepared by microbial transglutaminase and human-like collagen: Its characterization and biocompatibility[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2016, 68: 317-326. |
| 103 | PAN H, FAN D D, CAO W, et al. Preparation and characterization of breathable hemostatic hydrogel dressings and determination of their effects on full-thickness defects[J]. Polymers, 2017, 9(12): 727. |
| 104 | DONG Y Q, ZHU W D, LEI X X, et al. Treatment of acute wounds with recombinant human-like collagen and recombinant human-like fibronectin in C57BL/6 mice individually or in combination[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 908585. |
| 105 | MCLAUGHLIN S, MCNEILL B, PODREBARAC J, et al. Injectable human recombinant collagen matrices limit adverse remodeling and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4866. |
| 106 | FAGERHOLM P, LAGALI N S, ONG J A, et al. Stable corneal regeneration four years after implantation of a cell-free recombinant human collagen scaffold[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(8): 2420-2427. |
| 107 | FAGERHOLM P, LAGALI N S, MERRETT K, et al. A biosynthetic alternative to human donor tissue for inducing corneal regeneration: 24-month follow-up of a phase 1 clinical study[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2010, 2(46): 46ra61. |
| 108 | SONG X, ZHU C H, FAN D D, et al. A novel human-like collagen hydrogel scaffold with porous structure and sponge-like properties[J]. Polymers, 2017, 9(12): 638. |
| 109 | CHEN Z Y, ZHANG Z, MA X X, et al. Newly designed human-like collagen to maximize sensitive release of BMP-2 for remarkable repairing of bone defects[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(9): 450. |
| 110 | FAN H, HUI J F, DUAN Z G, et al. Novel scaffolds fabricated using oleuropein for bone tissue engineering[J]. BioMed Research International, 2014, 2014: 652432. |
| [1] | 刘晓悦, 王盼娣, 吴刚, 刘芳. 基因工程辅助萝卜硫苷在十字花科作物中的高效生物合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 136-156. |
| [2] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [3] | 刘泽众, 周洁, 朱赟, 陆路, 姜世勃. 基于重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的三聚体抗原疫苗策略在新冠和流感疫苗中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 385-395. |
| [4] | 文志琼, 李煜真, 张金刚, 王菲菲, 马小清, 李福利. 化能驱动的产乙酸菌转化利用CO2研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1178-1190. |
| [5] | 郑涵奇, 吴晴, 李洪军, 顾臻. 合成生物学与纳米生物学的交叉融合及其在生物医药领域的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 279-301. |
| [6] | 刘如欣, 杜磊, 徐晓庆, 丁金鹏, 张伟, 李盛英. 基于紫外诱变与生物合成基因簇倍增的多氧霉素高产菌株构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 609-620. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
