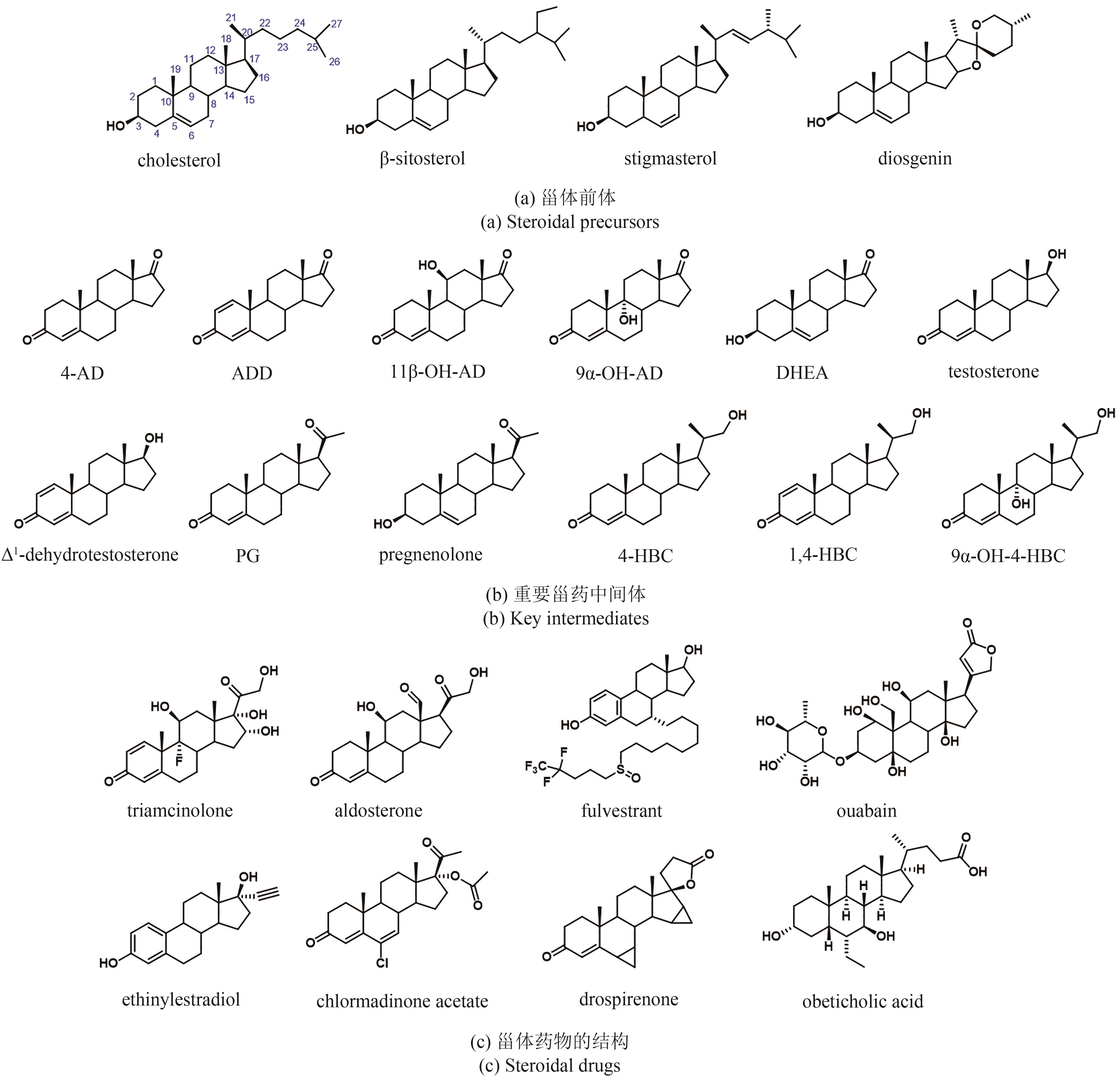
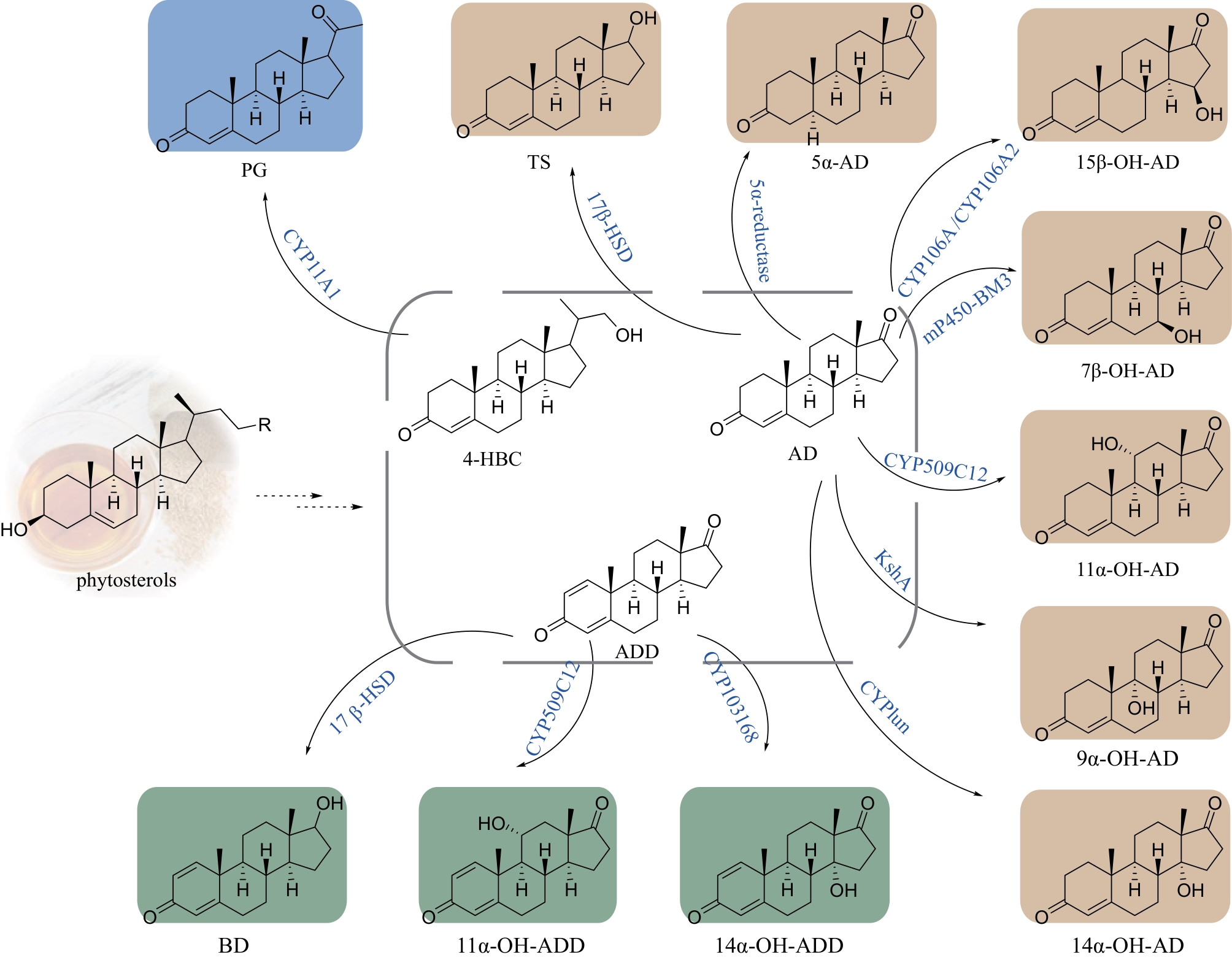
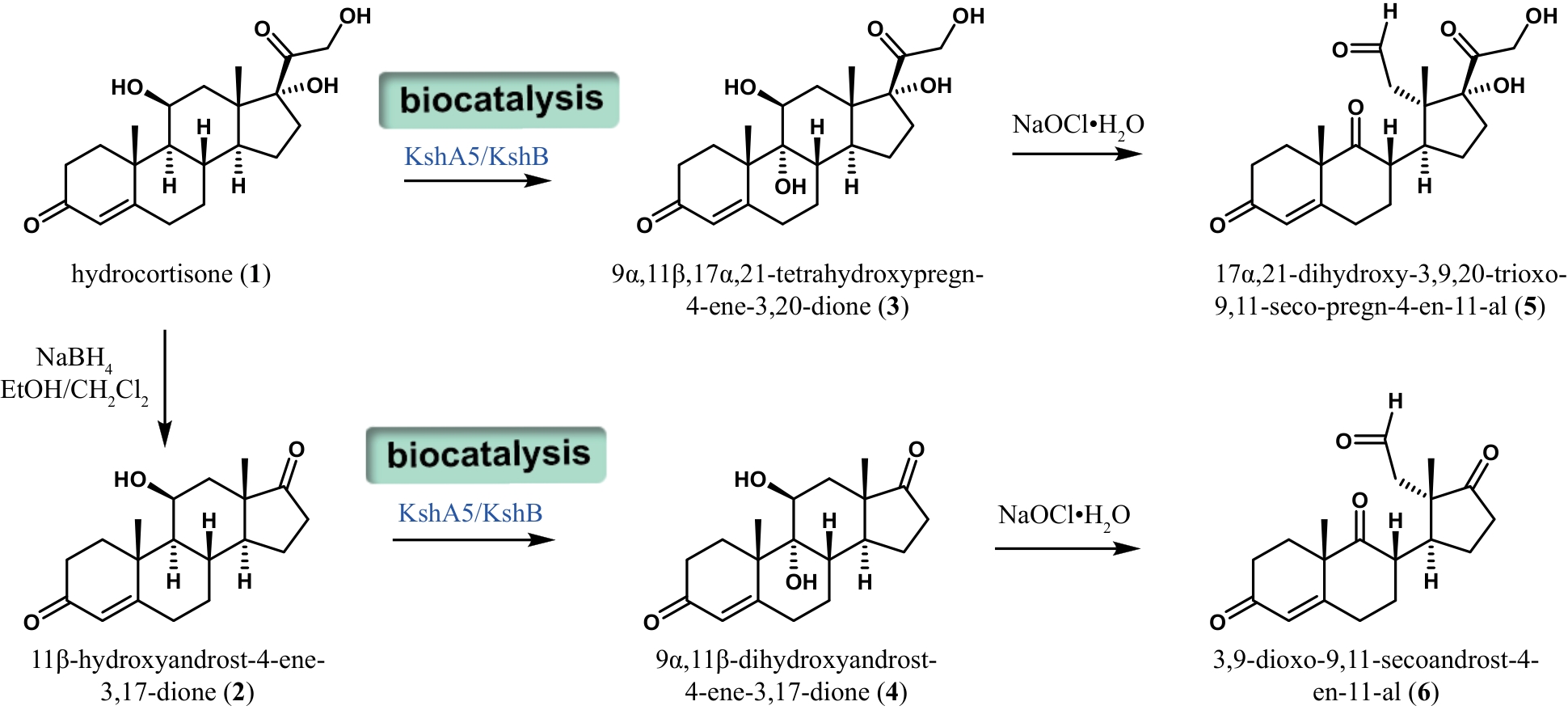
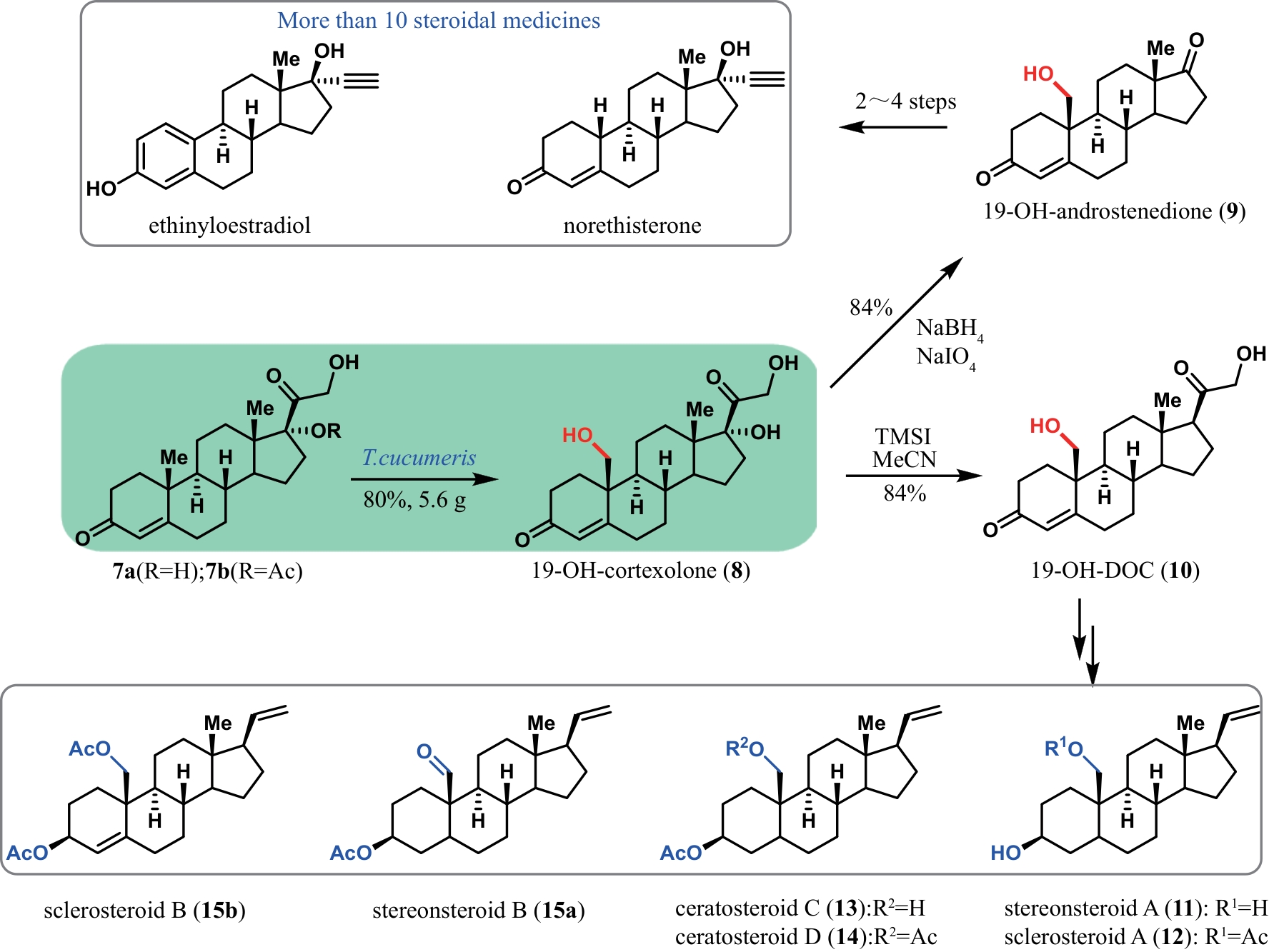
合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (5): 941-959.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-002
重要甾体化合物的化学酶法合成研究进展
郑梦梦1,2, 刘犇犇1,2, 林芝1,2, 瞿旭东1,2
- 1.上海交通大学生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,上海 200240
2.上海交通大学张江高等研究院,上海 201203
-
收稿日期:2024-01-02修回日期:2024-03-20出版日期:2024-10-31发布日期:2024-11-20 -
通讯作者:瞿旭东 -
作者简介:郑梦梦 (1993—),女,博士后。研究方向为天然产物生物合成。 E-mail:sjtu7126164@sjtu.edu.cn瞿旭东 (1980—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为天然骨架的定向生物合成。 E-mail:quxd@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年科学基金(32301216)
Recent advances in chemoenzymatic synthesis of important steroids
ZHENG Mengmeng1,2, LIU Benben1,2, LIN Zhi1,2, QU Xudong1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
2.Zhangjiang Institute for Advanced Study,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 201203,China
-
Received:2024-01-02Revised:2024-03-20Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-20 -
Contact:QU Xudong
摘要:
甾体化合物因其多功能生物活性和理化特性备受生物医药行业的高度重视,被誉为自然界的“生命之钥”。随着植物甾醇代谢途径的不断解析,国内逐渐形成了“植物甾醇原料-甾体药物中间体-甾体药物”的工业合成路线。日益发展的甾药行业需要不断开发新的合成技术推进甾体药物自上而下高效合成。基于生物信息学、合成生物学、代谢工程以及酶工程的快速发展,甾体化合物的合成技术也取得了重大突破。本文对重要甾体化合物的最新合成进展,包括甾体药物中间体的多样化合成、复杂甾体的化学酶法合成和酵母从头合成植物甾醇原料等方面进行了综述,特别强调了近年来P450羟化酶、3-甾酮-Δ1-脱氢酶、还原酶以及酶级联参与的化学酶法在高效简易合成复杂甾体药物中的代表性工作;在此基础上,也从新一代甾药中间体的开发、新型甾体生物催化剂的挖掘、以分枝杆菌为底盘的甾体合成途径的构建等方面对甾体化合物未来的研究机会和挑战进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郑梦梦, 刘犇犇, 林芝, 瞿旭东. 重要甾体化合物的化学酶法合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 941-959.
ZHENG Mengmeng, LIU Benben, LIN Zhi, QU Xudong. Recent advances in chemoenzymatic synthesis of important steroids[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 941-959.
| 1 | WANG F Q, YAO K, WEI D Z. From soybean phytosterols to steroid hormones[M/OL]//Soybean and health. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech(2011-09-12)[2023-12-01]. . |
| 2 | PENG H D, WANG Y Y, JIANG K, et al. A dual role reductase from phytosterols catabolism enables the efficient production of valuable steroid precursors[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(10): 5414-5420. |
| 3 | DONOVA M V, EGOROVA O V. Microbial steroid transformations: current state and prospects[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 94(6): 1423-1447. |
| 4 | TONG W Y, DONG X. Microbial biotransformation: recent developments on steroid drugs[J]. Recent Patents on Biotechnology, 2009, 3(2): 141-153. |
| 5 | FENG J H, WU Q Q, ZHU D M, et al. Biotransformation enables innovations toward green synthesis of steroidal pharmaceuticals[J]. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(9): e202102399. |
| 6 | 熊亮斌, 宋璐, 赵云秋, 等. 甾体化合物绿色生物制造:从生物转化到微生物从头合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. |
| XIONG L B, SONG L, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Green biomanufacturing of steroids: from biotransformation to de novo synthesis by microorganisms[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. | |
| 7 | FERNÁNDEZ-CABEZÓN L, GALÁN B, GARCÍA J L. New insights on steroid biotechnology[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 958. |
| 8 | ZHANG Y, XIAO P Y, PAN D L, et al. New insights into the modification of the non-core metabolic pathway of steroids in Mycolicibacterium and the application of fermentation biotechnology in C-19 steroid production[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(6): 5236. |
| 9 | SONG S K, HE J X, GAO M, et al. Loop pathways are responsible for tuning the accumulation of C19- and C22-sterol intermediates in the mycobacterial phytosterol degradation pathway[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22(1): 19. |
| 10 | FERNÁNDEZ-CABEZÓN L, GALÁN B, GARCÍA J L. Engineering Mycobacterium smegmatis for testosterone production[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2017, 10(1): 151-161. |
| 11 | ZHAO Y Q, SHEN Y B, MA S, et al. Production of 5α-androstene-3,17-dione from phytosterols by co-expression of 5α-reductase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in engineered Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Green Chemistry, 2019, 21(7): 1809-1815. |
| 12 | TANG R, REN X X, XIA M L, et al. Efficient one-step biocatalytic multienzyme cascade strategy for direct conversion of phytosterol to C-17-hydroxylated steroids[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 87(24): e0032121. |
| 13 | FELPETO-SANTERO C, GALÁN B, GARCÍA J L. Production of 11α-hydroxysteroids from sterols in a single fermentation step by Mycolicibacterium smegmatis [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2021, 14(6): 2514-2524. |
| 14 | FELPETO-SANTERO C, GALÁN B, GARCÍA J L. Engineering the steroid hydroxylating system from Cochliobolus lunatus in Mycolicibacterium smegmatis [J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9(7): 1499. |
| 15 | ZHANG C W, SHEN Y B, GAO Y Y, et al. Efficient production of 14α-OH-AD by engineered Mycolicibacterium neoaurum via coupled cofactor and reconstructed electron transport system[J]. Systems Microbiology and Biomanufacturing, 2023, 3(2): 358-369. |
| 16 | LI X, CHEN T, PENG F, et al. Efficient conversion of phytosterols into 4-androstene-3,17-dione and its C1, 2-dehydrogenized and 9α-hydroxylated derivatives by engineered Mycobacteria[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 158. |
| 17 | KARPOV M V, NIKOLAEVA V M, FOKINA V V, et al. Creation and functional analysis of Mycolicibacterium smegmatis recombinant strains carrying the bacillary cytochromes CYP106A1 and CYP106A2 genes[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 2022, 58(9): 947-957. |
| 18 | LIU K, WANG F Q, LIU K, et al. Light-driven progesterone production by InP-(M. neoaurum) biohybrid system[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2022, 9(1): 93. |
| 19 | ZHAO Y Q, LIU Y J, JI W T, et al. One-pot biosynthesis of 7β-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione from phytosterols by cofactor regeneration system in engineered Mycolicibacterium neoaurum [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 59. |
| 20 | ABAS H, BLENCOWE P, BROOKFIELD J, et al. Selective hydroxylation of C(sp3)—H bonds in steroids[J]. Chemistry, 2023, 29(4): e202301066. |
| 21 | RUDROFF F, MIHOVILOVIC M D, GRÖGER H, et al. Opportunities and challenges for combining chemo- and biocatalysis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2018, 1: 12-22. |
| 22 | CHAKRABARTY S, ROMERO E O, PYSER J B, et al. Chemoenzymatic total synthesis of natural products[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2021, 54(6): 1374-1384. |
| 23 | KILLE S, ZILLY F E, ACEVEDO J P, et al. Regio- and stereoselectivity of P450-catalysed hydroxylation of steroids controlled by laboratory evolution[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2011, 3(9): 738-743. |
| 24 | KASPAR F, SCHALLMEY A. Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of natural products and their analogs[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 77: 102759. |
| 25 | LI F Z, DENG H P, RENATA H. Chemoenzymatic approaches for exploring structure-activity relationship studies of bioactive natural products[J]. Nature Synthesis, 2023, 2: 708-718. |
| 26 | LI J, AMATUNI A, RENATA H. Recent advances in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of bioactive natural products[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2020, 55: 111-118. |
| 27 | PAULSEL T Q, WILLIAMS G J. Current state-of-the-art toward chemoenzymatic synthesis of polyketide natural products[J]. ChemBioChem, 2023, 24(21): e202300386. |
| 28 | RODDAN R, CARTER E M, THAIR B, et al. Chemoenzymatic approaches to plant natural product inspired compounds[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2022, 39(7): 1375-1382. |
| 29 | STOUT C N, WASFY N M, CHEN F, et al. Charting the evolution of chemoenzymatic strategies in the syntheses of complex natural products[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(33): 18161-18181. |
| 30 | VANABLE E P, HABGOOD L G, PATRONE J D. Current progress in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of natural products[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(19): 6373. |
| 31 | LATHE R. Steroid and sterol 7-hydroxylation: ancient pathways[J]. Steroids, 2002, 67(12): 967-977. |
| 32 | LI H P, LIU H M, GE W Z, et al. Synthesis of 7α-hydroxy-dehydroepiandrosterone and 7β-hydroxy-dehydroepiandrosterone[J]. Steroids, 2005, 70(14): 970-973. |
| 33 | ZHU R, LIU Y, YANG Y Y, et al. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases catalyse steroid nucleus hydroxylation with regio- and stereo-selectivity[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2022, 364(16): 2701-2719. |
| 34 | SZALENIEC M, WOJTKIEWICZ A M, BERNHARDT R, et al. Bacterial steroid hydroxylases: enzyme classes, their functions and comparison of their catalytic mechanisms[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(19): 8153-8171. |
| 35 | ZHANG X D, PENG Y Q, ZHAO J, et al. Bacterial cytochrome P450-catalyzed regio- and stereoselective steroid hydroxylation enabled by directed evolution and rational design[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2020, 7(1): 2. |
| 36 | WANG L, WU X W, GAO C H, et al. A fungal P450 enzyme from Fusarium graminearum with unique 12β-steroid hydroxylation activity[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2023, 89(3): 22. |
| 37 | FERNANDES P, CRUZ A, ANGELOVA B, et al. Microbial conversion of steroid compounds: recent developments[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2003, 32(6): 688-705. |
| 38 | CAPYK J K, D’ANGELO I, STRYNADKA N C, et al. Characterization of 3-ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylase, a Rieske oxygenase in the cholesterol degradation pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2009, 284(15): 9937-9946. |
| 39 | LIU H H, XU L Q, YAO K, et al. Engineered 3-ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylases in Mycobacterium neoaurum: an efficient platform for production of steroid drugs[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(14): e02777-17. |
| 40 | CHANG Y C, LAI K H, KUMAR S, et al. 1H NMR-based isolation of anti-inflammatory 9,11-secosteroids from the octocoral Sinularia leptoclados [J]. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18(5): 271. |
| 41 | HE Y Q, LEE CAPLAN S, SCESA P, et al. Cyclized 9,11-secosterol enol-ethers from the Gorgonian Pseudopterogorgia americana [J]. Steroids, 2017, 125: 47-53. |
| 42 | KÕLLO M, KASARI M, KASARI V, et al. Designed whole-cell-catalysis-assisted synthesis of 9,11-secosterols[J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 17: 581-588. |
| 43 | RENATA H, ZHOU Q H, DÜNSTL G, et al. Development of a concise synthesis of ouabagenin and hydroxylated corticosteroid analogues[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(3): 1330-1340. |
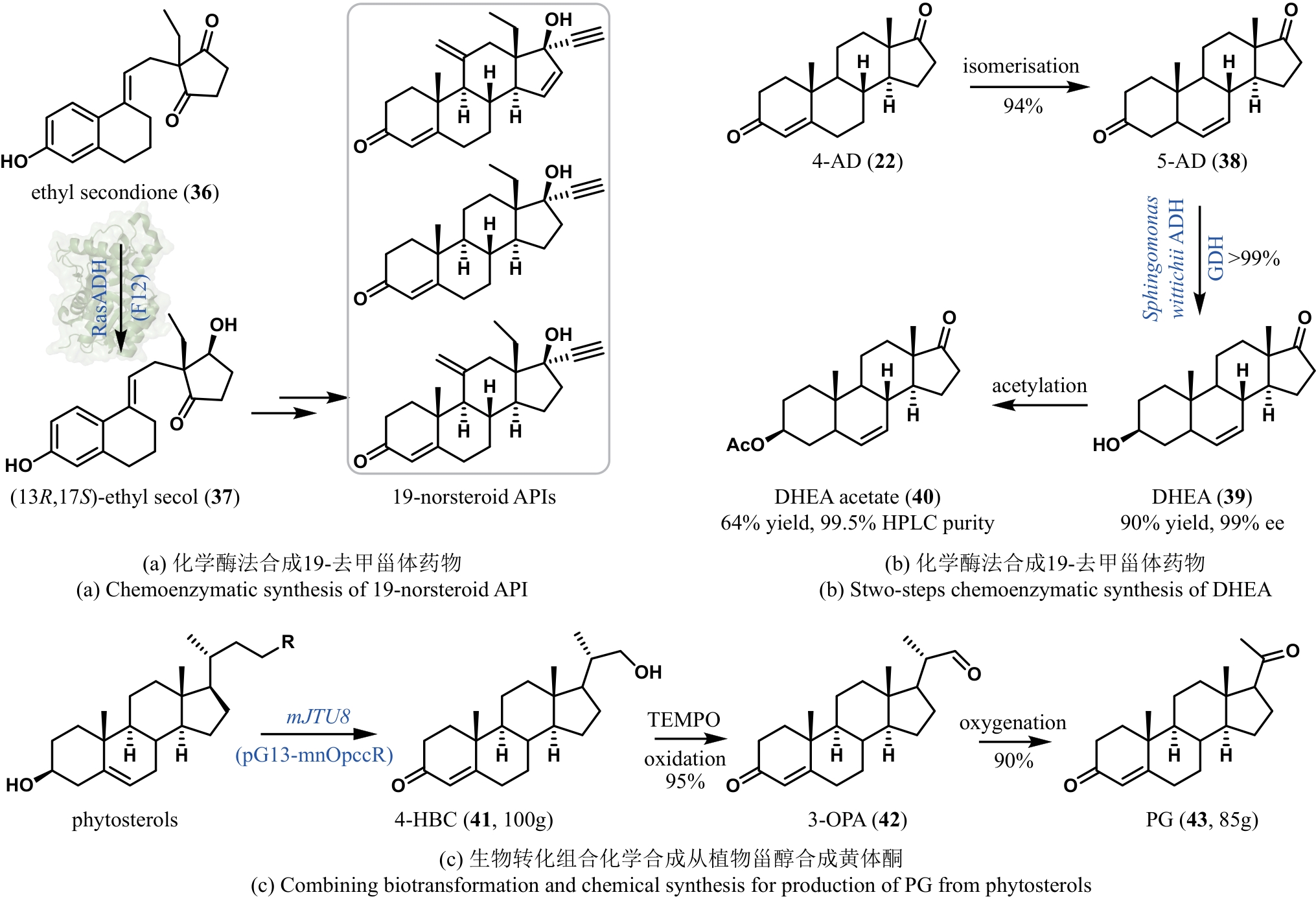
| 44 | KAPLAN W, KHATRI H R, NAGORNY P. Concise enantioselective total synthesis of cardiotonic steroids 19-hydroxysarmentogenin and trewianin aglycone[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(22): 7194-7198. |
| 45 | LU W, CHEN X, FENG J H, et al. A fungal P450 enzyme from Thanatephorus cucumeris with steroid hydroxylation capabilities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(13): e00503-18. |
| 46 | WANG J L, ZHANG Y N, LIU H H, et al. A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3378. |
| 47 | EL-SEEDI H R, KHALIFA S A M, TAHER E A, et al. Cardenolides: insights from chemical structure and pharmacological utility[J]. Pharmacological Research, 2019, 141: 123-175. |
| 48 | ZHONG Y, ZHAO C, WU W Y, et al. Total synthesis, chemical modification and structure-activity relationship of bufadienolides[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 189: 112038. |
| 49 | CHEN J, TANG J L, XI Y Y, et al. Production of 14α-hydroxysteroids by a recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae biocatalyst expressing of a fungal steroid 14α-hydroxylation system[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(20): 8363-8374. |
| 50 | SONG F Z, ZHENG M M, WANG J L, et al. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of C14-functionalized steroids[J]. Nature Synthesis, 2023, 2: 729-739. |
| 51 | ZHAO Y, ZHANG B, SUN Z Q, et al. Biocatalytic C14-hydroxylation on androstenedione enabled modular synthesis of cardiotonic steroids[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(16): 9839-9845. |
| 52 | SAMUEL S, NGUYEN T, CHOI H A. Pharmacologic characteristics of corticosteroids[J]. Journal of Neurocritical Care, 2017, 10(2): 53-59. |
| 53 | ZHANG B, ZHOU D F, LI M J, et al. Progress of 3-ketosteroid Δ1-dehydrogenases for steroid production[J]. Systems Microbiology and Biomanufacturing, 2024, 4(2): 631-660. |
| 54 | PETRUSMA M, VAN DER GEIZE R, DIJKHUIZEN L. 3-Ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylase enzymes: Rieske non-heme monooxygenases essential for bacterial steroid degradation[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2014, 106(1): 157-172. |
| 55 | CHENG H J, SUN Y H, CHANG H W, et al. Compatible solutes adaptive alterations in Arthrobacter simplex during exposure to ethanol, and the effect of trehalose on the stress resistance and biotransformation performance[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 43(5): 895-908. |
| 56 | LUO J M, ZHU W C, CAO S T, et al. Improving biotransformation efficiency of Arthrobacter simplex by enhancement of cell stress tolerance and enzyme activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(2): 704-716. |
| 57 | TANG J, ZENG C L, XIE L Y, et al. Improved synthesis of fluocinolone acetonide and process research of 6α,9α- fluorination[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2018, 47(1): 110-112. |
| 58 | ZHANG R J, XU X X, CAO H J, et al. Purification, characterization, and application of a high activity 3-ketosteroid-Δ1-dehydrogenase from Mycobacterium neoaurum DSM 1381[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(16): 6605-6616. |
| 59 | WÓJCIK P, GLANOWSKI M, WOJTKIEWICZ A M, et al. Universal capability of 3-ketosteroid Δ1-dehydrogenases to catalyze Δ1-dehydrogenation of C17-substituted steroids[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 119. |
| 60 | WU Y, MA J N, SHI J H, et al. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of Arthrobacter simplex in response to cortisone acetate and its mutants with improved Δ1-dehydrogenation efficiency[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(16): 6376-6388. |
| 61 | WANG Y, ZHANG R, FENG J H, et al. A new 3-ketosteroid-Δ1-dehydrogenase with high activity and broad substrate scope for efficient transformation of hydrocortisone at high substrate concentration[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(3): 508. |
| 62 | ZHANG Y J, LIU M J, WANG H J, et al. Focused mutagenesis in non-catalytic cavity for improving catalytic efficiency of 3-ketosteroid-Δ1-dehydrogenase[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2022, 531: 112661. |
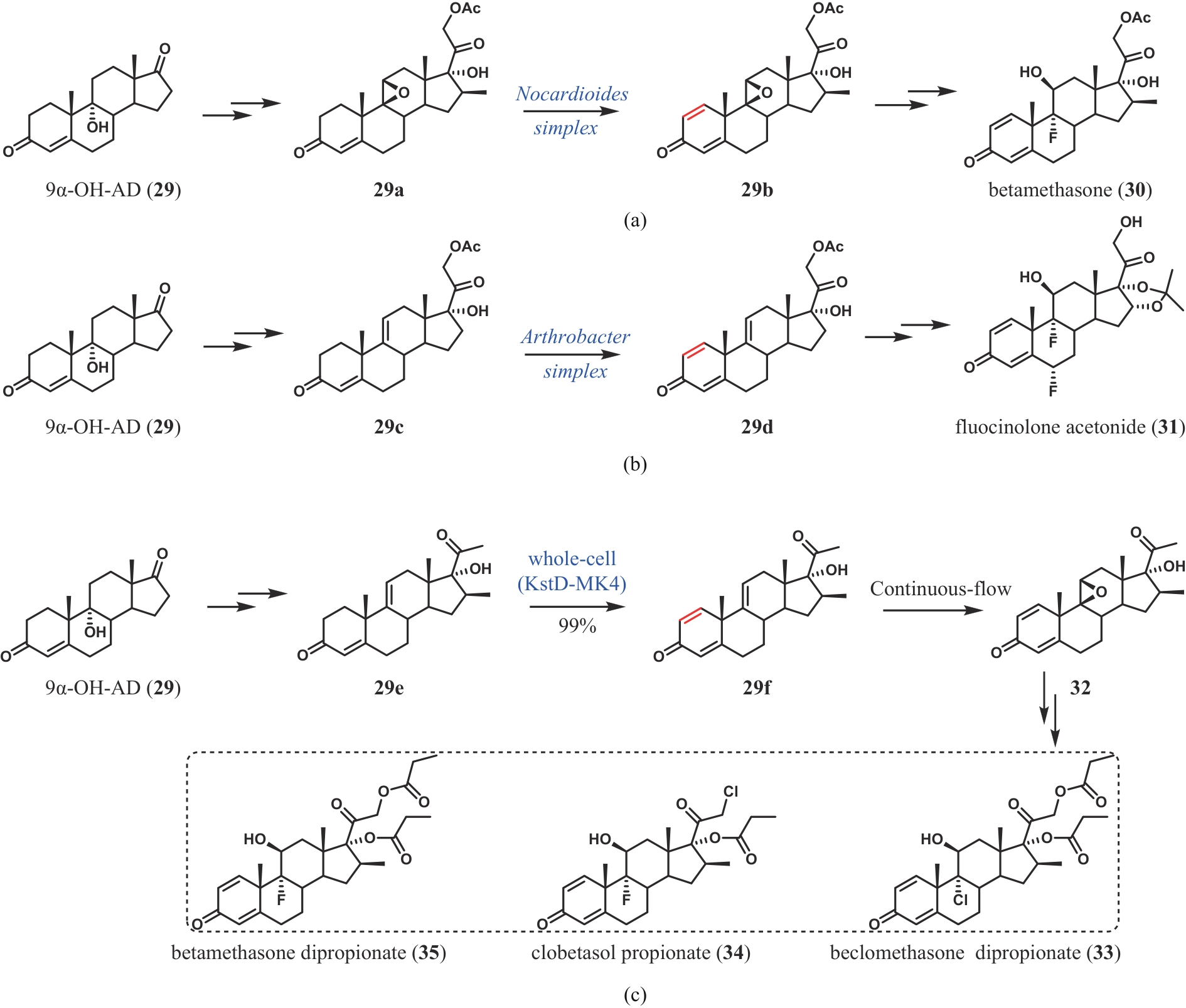
| 63 | WEI J H, ZHANG Y J, LIU M J, et al. Divergent chemo- and biocatalytic route to 16β-methylcorticoids: asymmetric synthesis of betamethasone dipropionate, clobetasol propionate, and beclomethasone dipropionate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(4): e202313952. |
| 64 | CONTENTE M L, MOLINARI F, SERRA I, et al. Stereoselective enzymatic reduction of ethyl secodione: preparation of a key intermediate for the total synthesis of steroids[J]. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2016, 2016(7): 1260-1263. |
| 65 | CHEN X, ZHANG H L, MARIA-SOLANO M A, et al. Efficient reductive desymmetrization of bulky 1,3-cyclodiketones enabled by structure-guided directed evolution of a carbonyl reductase[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2: 931-941. |
| 66 | DING H X, LIU K K C, SAKYA S M, et al. Synthetic approaches to the 2011 new drugs[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2013, 21(11): 2795-2825. |
| 67 | FRYSZKOWSKA A, PETERSON J, DAVIES N L, et al. Development of a chemoenzymatic process for dehydroepiandrosterone acetate synthesis[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2016, 20(8): 1520-1528. |
| 68 | MONTI D, FERRANDI E E, ZANELLATO I, et al. One-pot multienzymatic synthesis of 12-ketoursodeoxycholic acid: subtle cofactor specificities rule the reaction equilibria of five biocatalysts working in a row[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2009, 351(9): 1303-1311. |
| 69 | SUN B Q, KANTZOW C, BRESCH S, et al. Multi-enzymatic one-pot reduction of dehydrocholic acid to 12-keto-ursodeoxycholic acid with whole-cell biocatalysts[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2013, 110(1): 68-77. |
| 70 | TONIN F, ARENDS I W C E. Latest development in the synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA): a critical review[J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2018, 14: 470-483. |
| 71 | LIU L, BRAUN M, GEBHARDT G, et al. One-step synthesis of 12-ketoursodeoxycholic acid from dehydrocholic acid using a multienzymatic system[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(2): 633-639. |
| 72 | SHI S C, YOU Z N, ZHOU K, et al. Efficient synthesis of 12-oxochenodeoxycholic acid using a 12α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Rhodococcus ruber [J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2019, 361(20): 4661-4668. |
| 73 | GROBE S, BADENHORST C P S, BAYER T, et al. Engineering regioselectivity of a P450 monooxygenase enables the synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid via 7β-hydroxylation of lithocholic acid[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(2): 753-757. |
| 74 | YOU Z N, CHEN Q, SHI S C, et al. Switching cofactor dependence of 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase for cost-effective production of ursodeoxycholic acid[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(1): 466-473. |
| 75 | ZHENG M M, WANG R F, LI C X, et al. Two-step enzymatic synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid with a new 7β- hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Ruminococcus torques [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(4): 598-604. |
| 76 | ZHENG M M, CHEN F F, LI H, et al. Continuous production of ursodeoxycholic acid by using two cascade reactors with co-immobilized enzymes[J]. ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(4): 347-353. |
| 77 | LI H P, YOU Z N, LIU Y Y, et al. Continuous-flow microreactor-enhanced clean NAD+ regeneration for biosynthesis of 7-oxo-lithocholic acid[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(1): 456-463. |
| 78 | ZHENG M M, CHEN K C, WANG R F, et al. Engineering 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase for enhanced ursodeoxycholic acid production by multiobjective directed evolution[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(6): 1178-1185. |
| 79 | JI Q Z, TAN J, ZHU L C, et al. Preparing tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) using a double-enzyme-coupled system[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 105: 1-9. |
| 80 | PENG Y Q, GAO C H, ZHANG Z L, et al. A chemoenzymatic strategy for the synthesis of steroid drugs enabled by P450 monooxygenase-mediated steroidal core modification[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(5): 2907-2914. |
| 81 | ZHANG Z L, GAO C H, ZHAO J, et al. A designed chemoenzymatic route for efficient synthesis of 6-dehydronandrolone acetate: a key precursor in the synthesis of C7-functionalized steroidal drugs[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(19): 13111-13116. |
| 82 | ZHANG Y J, LIU M J, YANG Z X, et al. Batch and continuous flow asymmetric synthesis of anabolic-androgenic steroids via a single-cell biocatalytic Δ1-dehydrogenation and C17β- carbonyl reduction cascade[J]. Green Chemistry, 2023, 25(8): 3223-3235. |
| 83 | SZCZEBARA F M, CHANDELIER C, VILLERET C, et al. Total biosynthesis of hydrocortisone from a simple carbon source in yeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(2): 143-149. |
| 84 | BROCARD-MASSON C, BONNIN I, DUMAS B. Process for preparing genetically transformed yeasts capable of producing a molecule of interest at a high titre: US20140186885[P]. 2014-07-03. |
| 85 | GU Y H, JIAO X, YE L D, et al. Metabolic engineering strategies for de novo biosynthesis of sterols and steroids in yeast[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2021, 8(1): 110. |
| 86 | XU S H, LI Y R. Yeast as a promising heterologous host for steroid bioproduction[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47: 829-843. |
| 87 | JIANG Y Q, LIN J P. Recent progress in strategies for steroid production in yeasts[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2022, 38(6): 93. |
| 88 | SU W, XIAO W H, WANG Y, et al. Alleviating redox imbalance enhances 7-dehydrocholesterol production in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0130840. |
| 89 | GUO X J, XIAO W H, WANG Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for 7-dehydrocholesterol overproduction[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 192. |
| 90 | GUO X J, YAO M D, XIAO W H, et al. Compartmentalized reconstitution of post-squalene pathway for 7-dehydrocholesterol overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 663973. |
| 91 | QU L S, XIU X, SUN G Y, et al. Engineered yeast for efficient de novo synthesis of 7-dehydrocholesterol[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2022, 119(5): 1278-1289. |
| 92 | XIU X, SUN Y, WU Y K, et al. Modular remodeling of sterol metabolism for overproduction of 7-dehydrocholesterol in engineered yeast[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 360: 127572. |
| 93 | WEI W Q, GAO S, YI Q, et al. Reengineering of 7-dehydrocholesterol biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using combined pathway and organelle strategies[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 978074. |
| 94 | GU Y H, CHEN S H, JIAO X, et al. Combinatorial metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improved production of 7-dehydrocholesterol[J]. Engineering Microbiology, 2023, 3: 100100. |
| 95 | CHENG J, CHEN J, LIU X N, et al. The origin and evolution of the diosgenin biosynthetic pathway in yam[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(1): 100079. |
| 96 | XU L P, WANG D, CHEN J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for gram-scale diosgenin production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 70: 115-128. |
| 97 | DU H X, XIAO W H, WANG Y, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for campesterol overproduction[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0146773. |
| 98 | ZHANG Y, WANG Y, YAO M D, et al. Improved campesterol production in engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strains[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2017, 39(7): 1033-1039. |
| 99 | XU S H, CHEN C, LI Y R. Engineering of phytosterol-producing yeast platforms for functional reconstitution of downstream biosynthetic pathways[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(11): 3157-3170. |
| 100 | XU S H, TENG X X, LI Y R. Optimization of campesterol-producing yeast strains as a feasible platform for the functional reconstitution of plant membrane-bound enzymes[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(4): 1109-1118. |
| 101 | QIAN Y D, TAN S Y, DONG G R, et al. Increased campesterol synthesis by improving lipid content in engineered Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(16): 7165-7175. |
| 102 | 周武林, 高惠芳, 吴玉玲, 等. 重组酿酒酵母生物合成菜油甾醇[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4314-4324. |
| ZHOU W L, GAO H F, WU Y L, et al. Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biosynthesis of campesterol[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(8): 4314-4324. | |
| 103 | GU L S, ZHANG R X, FAN X Q, et al. Development of CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing tools for polyploid yeast Cyberlindnera jadinii and its application in engineering heterologous steroid-producing strains[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(10): 2947-2960. |
| 104 | DUPORT C, SPAGNOLI R, DEGRYSE E, et al. Self-sufficient biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in engineered yeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1998, 16(2): 186-189. |
| 105 | ZHANG R S, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Pregnenolone overproduction in Yarrowia lipolytica by integrative components pairing of the cytochrome P450scc system[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(12): 2666-2678. |
| 106 | XIONG L B, LIU H H, XU L Q, et al. Role identification and application of SigD in the transformation of soybean phytosterol to 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(3): 626-631. |
| 107 | LIU M, ZHU Z T, TAO X Y, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis for the production of valuable steroid intermediates in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2016, 38(11): 1881-1892. |
| 108 | LIU M, ZHU Z T, TAO X Y, et al. RNA-Seq analysis uncovers non-coding small RNA system of Mycobacterium neoaurum in the metabolism of sterols to accumulate steroid intermediates[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15: 64. |
| 109 | XIONG L B, SUN W J, LIU Y J, et al. Enhancement of 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione production from soybean phytosterols by deficiency of a regulated intramembrane proteolysis metalloprotease in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(48): 10520-10525. |
| 110 | LIU M, XIONG L B, TAO X Y, et al. Integrated transcriptome and proteome studies reveal the underlying mechanisms for sterol catabolism and steroid production in Mycobacterium neoaurum [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(34): 9147-9157. |
| 111 | LIU M, XIONG L B, TAO X Y, et al. Metabolic adaptation of Mycobacterium neoaurum ATCC 25795 in the catabolism of sterols for producing important steroid intermediates[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(45): 12141-12150. |
| [1] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [2] | 杨皓然, 叶发荣, 黄平, 王平. 糖蛋白合成的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1072-1101. |
| [3] | 熊亮斌, 宋璐, 赵云秋, 刘坤, 刘勇军, 王风清, 魏东芝. 甾体化合物绿色生物制造:从生物转化到微生物从头合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. |
| [4] | 吴淑可, 周颐, 王文, 张巍, 高鹏飞, 李智. 从单酶催化到多酶级联催化——从王义翘教授在酶技术领域的贡献说开去[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 543-558. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||