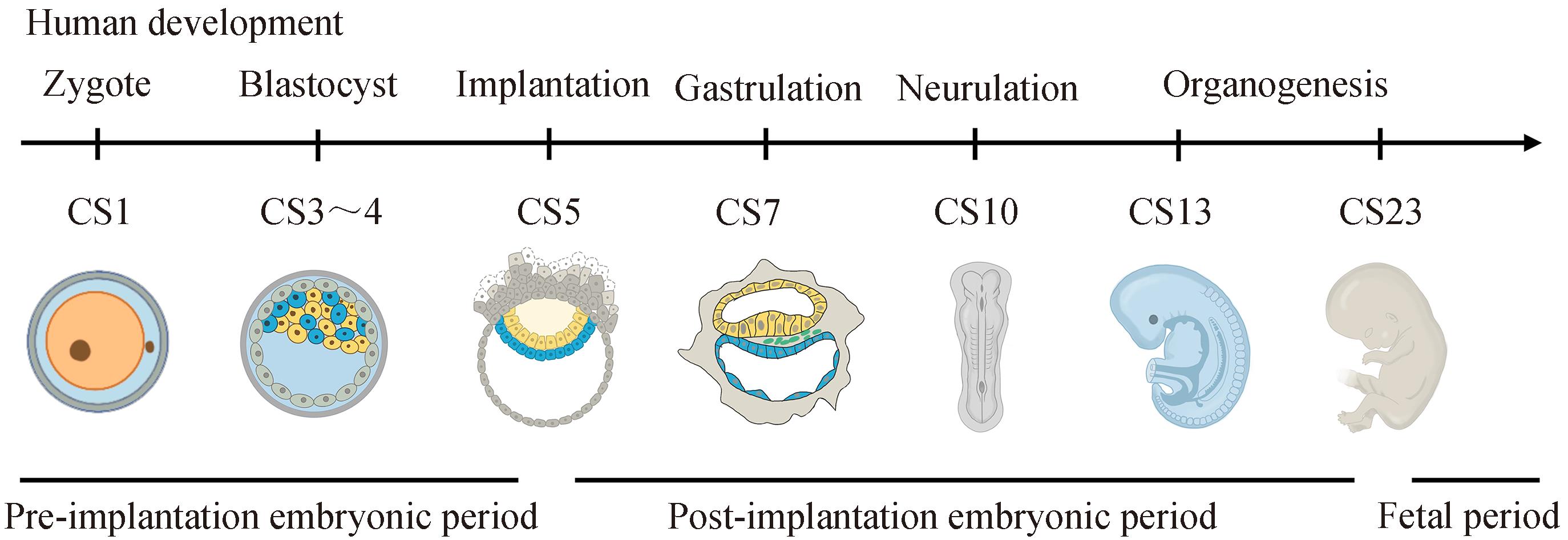
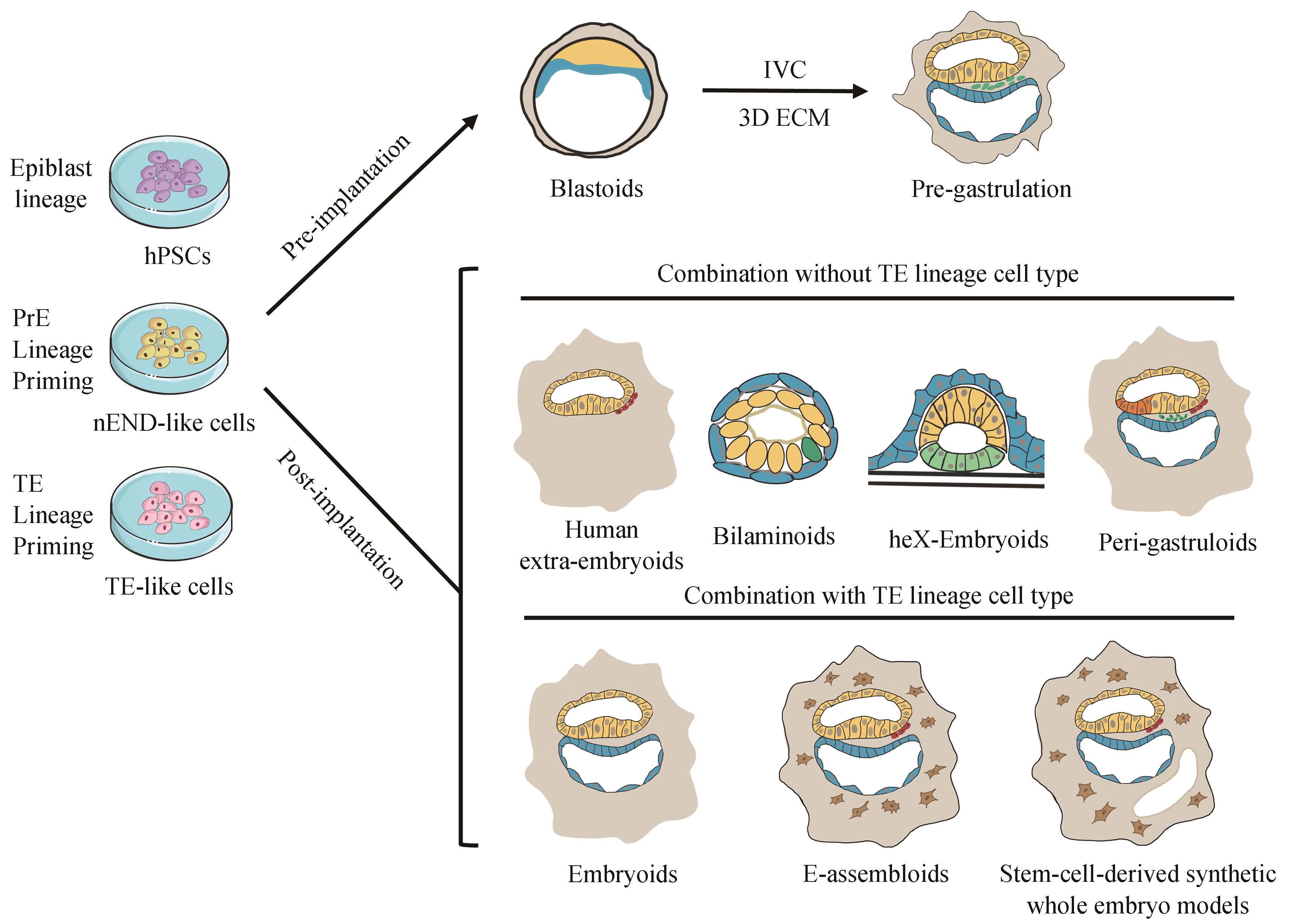
合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (4): 719-733.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-010
人类早期胚胎发育体外模型研究进展
胡博文1,2,3, 陈家斌1,2,3, 刘晓东1,2,3
- 1.西湖大学生命科学学院,西湖生命科学与生物医学实验室,浙江 杭州 310024
2.浙江西湖高等研究院,浙江 杭州 310024
3.西湖大学未来产业研究中心,浙江 杭州 310024
-
收稿日期:2024-01-19修回日期:2024-04-16出版日期:2024-08-31发布日期:2024-09-19 -
通讯作者:刘晓东 -
作者简介:胡博文 (1993—),男,博士后。研究方向为干细胞命运调控,类胚胎构建和应用。E-mail:hubowen@westlake.edu.cn刘晓东 (1988—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为诱导重编程,干细胞命运调控,谱系追踪,类器官和生物材料工程等。E-mail:liuxiaodong@westlake.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(22DAA01467)
Advances in the development of human embryo models
HU Bowen1,2,3, TAN Jiaping1,2,3, LIU Xiaodong1,2,3
- 1.School of Life Sciences,Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310024,Zhejiang,China
2.Westlake Institute for Advanced Study,Hangzhou 310024,Zhejiang,China
3.Research Center for Industries of the Future,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310024,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2024-01-19Revised:2024-04-16Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-19 -
Contact:LIU Xiaodong
摘要:
人类早期胚胎发育阶段对于胎儿的健康出生至关重要。然而,由于伦理和技术的限制,人类早期胚胎发育的具体调控机制仍未完全解密。除了人类胚胎体外培养技术以外,以干细胞为基础模拟人类真实胚胎结构的体外模型被构建出来,被称为“类胚胎/胚胎模型”。通常人类胚胎模型可大致分为两类:非整合型和整合型胚胎模型。整合型胚胎模型通常包含胚内和胚外细胞类型并具有发育成完整胎儿的潜力,而非整合型胚胎模型则不包含任何相关的胚外组织。本文系统总结了人类体外非整合型和整合型胚胎模型的最新研究进展,探讨了有关国际干细胞研究的伦理政策,并简要阐述了人类胚胎模型潜在的应用前景和未来机遇。以期为研究人类早期胚胎发育过程中不同细胞谱系的特化轨迹,以及早期胚胎发育缺陷等重大疾病的临床药物筛选和再生医学提供新的研究思路。
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡博文, 陈家斌, 刘晓东. 人类早期胚胎发育体外模型研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 719-733.
HU Bowen, TAN Jiaping, LIU Xiaodong. Advances in the development of human embryo models[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 719-733.
| 108 | KRENDL C, SHAPOSHNIKOV D, RISHKO V, et al. GATA2/3-TFAP2A/C transcription factor network couples human pluripotent stem cell differentiation to trophectoderm with repression of pluripotency[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(45): E9579-E9588. |
| 109 | WAMAITHA S E, DEL VALLE I, CHO L T, et al. Gata6 potently initiates reprograming of pluripotent and differentiated cells to extraembryonic endoderm stem cells[J]. Genes & Development, 2015, 29(12): 1239-1255. |
| 110 | WEATHERBEE B A T, GANTNER C W, IWAMOTO-STOHL L K, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived model of the post-implantation human embryo[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 584-593. |
| 111 | AI Z Y, NIU B H, YIN Y, et al. Dissecting peri-implantation development using cultured human embryos and embryo-like assembloids[J]. Cell Research, 2023, 33(9): 661-678. |
| 112 | OLDAK B, WILDSCHUTZ E, BONDARENKO V, et al. Complete human day 14 post-implantation embryo models from naive ES cells[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 562-573. |
| 113 | TURCO M Y, GARDNER L, KAY R G, et al. Trophoblast organoids as a model for maternal-fetal interactions during human placentation[J]. Nature, 2018, 564(7735): 263-267. |
| 114 | MANTZIOU V, BAILLIE-BENSON P, JAKLIN M, et al. In vitro teratogenicity testing using a 3D, embryo-like gastruloid system[J]. Reproductive Toxicology, 2021, 105: 72-90. |
| 115 | BLASIMME A, SUGARMAN J. Human stem cell-derived embryo models: toward ethically appropriate regulations and policies[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(8): 1008-1012. |
| 116 | LANDECKER H L, CLARK A T. Human embryo models made from pluripotent stem cells are not synthetic; they aren’t embryos, either[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(10): 1290-1293. |
| 117 | MORIS N. Stem cells used to model a two-week-old human embryo[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 469-470. |
| 118 | ROSSANT J, FU J P. Why researchers should use human embryo models with caution[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 454-456. |
| 119 | RIVRON N C, MARTINEZ-ARIAS A, SERMON K, et al. Changing the public perception of human embryology[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2023, 25(12): 1717-1719. |
| 1 | ROSSANT J, TAM P P L. New insights into early human development: lessons for stem cell derivation and differentiation[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2017, 20(1): 18-28. |
| 2 | GHIMIRE S, MANTZIOU V, MORIS N, et al. Human gastrulation: the embryo and its models[J]. Developmental Biology, 2021, 474: 100-108. |
| 3 | JIRÁSEK J E. Developmental stages of human embryos[J]. Czechoslovak Medicine, 1978, 1(3): 156-161. |
| 4 | O′RAHILLY R, MÜLLER F. Developmental stages in human embryos: revised and new measurements[J]. Cells, Tissues, Organs, 2010, 192(2): 73-84. |
| 5 | KIMBER S J, SNEDDON S F, BLOOR D J, et al. Expression of genes involved in early cell fate decisions in human embryos and their regulation by growth factors[J]. Reproduction, 2008, 135(5): 635-647. |
| 6 | MACKLON N S, GERAEDTS J P M, FAUSER B C J M. Conception to ongoing pregnancy: the ‘black box’ of early pregnancy loss[J]. Human Reproduction Update, 2002, 8(4): 333-343. |
| 7 | ROSSANT J, TAM P P L. Opportunities and challenges with stem cell-based embryo models[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(5): 1031-1038. |
| 8 | THOMSON J A, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO S S, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts[J]. Science, 1998, 282(5391): 1145-1147. |
| 9 | REUBINOFF B E, PERA M F, FONG C Y, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2000, 18(4): 399-404. |
| 10 | TAKAHASHI K, TANABE K, OHNUKI M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors[J]. Cell, 2007, 131(5): 861-872. |
| 11 | PARK I H, ZHAO R, WEST J A, et al. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7175): 141-146. |
| 12 | WERNIG M, MEISSNER A, FOREMAN R, et al. In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state[J]. Nature, 2007, 448(7151): 318-324. |
| 13 | YU J Y, VODYANIK M A, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5858): 1917-1920. |
| 14 | TAKASHIMA Y, GUO G, LOOS R, et al. Resetting transcription factor control circuitry toward ground-state pluripotency in human[J]. Cell, 2015, 162(2): 452-453. |
| 15 | THEUNISSEN T W, POWELL B E, WANG H Y, et al. Systematic identification of culture conditions for induction and maintenance of naive human pluripotency[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 15(4): 524-526. |
| 16 | GUO G, VON MEYENN F, ROSTOVSKAYA M, et al. Epigenetic resetting of human pluripotency[J]. Development, 2017, 144(15): 2748-2763. |
| 17 | MAZID M A, WARD C, LUO Z W, et al. Rolling back human pluripotent stem cells to an eight-cell embryo-like stage[J]. Nature, 2022, 605(7909): 315-324. |
| 18 | BAYERL J, AYYASH M, SHANI T, et al. Principles of signaling pathway modulation for enhancing human naive pluripotency induction[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(9): 1549-1565.e12. |
| 19 | AI Z Y, NIU B H, DUAN K, et al. Modulation of Wnt and Activin/Nodal supports efficient derivation, cloning and suspension expansion of human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 249: 120015. |
| 20 | YANG Y, LIU B, XU J, et al. Derivation of pluripotent stem cells with in vivo embryonic and extraembryonic potency[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(2): 243-257.e25. |
| 21 | YU X, LIANG S Q, CHEN M Q, et al. Recapitulating early human development with 8C-like cells[J]. Cell Reports, 2022, 39(12): 110994. |
| 22 | OKAE H, TOH H, SATO T, et al. Derivation of human trophoblast stem cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 22(1): 50-63.e6. |
| 23 | BAI T, PENG C Y, ANEAS I, et al. Establishment of human induced trophoblast stem-like cells from term villous cytotrophoblasts[J]. Stem Cell Research, 2021, 56: 102507. |
| 24 | LIU X D, OUYANG J F, ROSSELLO F J, et al. Reprogramming roadmap reveals route to human induced trophoblast stem cells[J]. Nature, 2020, 586(7827): 101-107. |
| 25 | IO S, KABATA M, IEMURA Y, et al. Capturing human trophoblast development with naive pluripotent stem cells in vitro [J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(6): 1023-1039.e13. |
| 26 | GUO G, STIRPARO G G, STRAWBRIDGE S E, et al. Human naive epiblast cells possess unrestricted lineage potential[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(6): 1040-1056.e6. |
| 27 | LINNEBERG-AGERHOLM M, WONG Y F, ROMERO HERRERA J A, et al. Naïve human pluripotent stem cells respond to Wnt, Nodal and LIF signalling to produce expandable naïve extra-embryonic endoderm[J]. Development, 2019, 146(24): dev180620. |
| 28 | MACKINLAY K M, WEATHERBEE B A, SOUZA ROSA V, et al. An in vitro stem cell model of human epiblast and yolk sac interaction[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e63930. |
| 29 | SÉGUIN C A, DRAPER J S, NAGY A, et al. Establishment of endoderm progenitors by SOX transcription factor expression in human embryonic stem cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2008, 3(2): 182-195. |
| 30 | GUPTA A, LUTOLF M P, HUGHES A J, et al. Bioengineering in vitro models of embryonic development[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(5): 1104-1116. |
| 31 | XIANG L F, YIN Y, ZHENG Y, et al. A developmental landscape of 3D-cultured human pre-gastrulation embryos[J]. Nature, 2020, 577(7791): 537-542. |
| 32 | ZHOU F, WANG R, YUAN P, et al. Reconstituting the transcriptome and DNA methylome landscapes of human implantation[J]. Nature, 2019, 572(7771): 660-664. |
| 33 | BLAKELEY P, FOGARTY N M, DEL VALLE I, et al. Defining the three cell lineages of the human blastocyst by single-cell RNA-seq[J]. Development, 2015, 142(20): 3613. |
| 34 | MOLÈ M A, COORENS T H H, SHAHBAZI M N, et al. A single cell characterisation of human embryogenesis identifies pluripotency transitions and putative anterior hypoblast centre[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3679. |
| 35 | TYSER R C V, MAHAMMADOV E, NAKANOH S, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic characterization of a gastrulating human embryo[J]. Nature, 2021, 600(7888): 285-289. |
| 36 | BRAUDE P, BOLTON V, MOORE S. Human gene expression first occurs between the four- and eight-cell stages of preimplantation development[J]. Nature, 1988, 332(6163): 459-461. |
| 37 | SCHULZ K N, HARRISON M M. Mechanisms regulating zygotic genome activation[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(4): 221-234. |
| 38 | WILKINSON A L, ZORZAN I, RUGG-GUNN P J. Epigenetic regulation of early human embryo development[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(12): 1569-1584. |
| 39 | YAN L Y, YANG M Y, GUO H S, et al. Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human preimplantation embryos and embryonic stem cells[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2013, 20(9): 1131-1139. |
| 40 | PETROPOULOS S, EDSGÄRD D, REINIUS B, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals lineage and X chromosome dynamics in human preimplantation embryos[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(1):285. |
| 41 | MEISTERMANN D, BRUNEAU A, LOUBERSAC S, et al. Integrated pseudotime analysis of human pre-implantation embryo single-cell transcriptomes reveals the dynamics of lineage specification[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(9): 1625-1640.e6. |
| 42 | ZENG B, LIU Z Y, LU Y F, et al. The single-cell and spatial transcriptional landscape of human gastrulation and early brain development[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(6): 851-866.e7. |
| 43 | XU Y C, ZHANG T J, ZHOU Q, et al. A single-cell transcriptome atlas profiles early organogenesis in human embryos[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2023, 25(4): 604-615. |
| 44 | GOH I, BOTTING R A, ROSE A, et al. Yolk sac cell atlas reveals multiorgan functions during human early development[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6659): eadd7564. |
| 45 | YAO H, SUN N Q, SHAO H L, et al. Ex utero embryogenesis of non-human primate embryos and beyond[J]. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 2023, 82: 102093. |
| 46 | NAKAMURA T, FUJIWARA K, SAITOU M, et al. Non-human primates as a model for human development[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(5): 1093-1103. |
| 47 | ZHAI J L, GUO J, WAN H F, et al. Primate gastrulation and early organogenesis at single-cell resolution[J]. Nature, 2022, 612(7941): 732-738. |
| 48 | SHAHBAZI M N, JEDRUSIK A, VUORISTO S, et al. Self-organization of the human embryo in the absence of maternal tissues[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2016, 18(6): 700-708. |
| 49 | DEGLINCERTI A, CROFT G F, PIETILA L N, et al. Self-organization of the in vitro attached human embryo[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7602): 251-254. |
| 50 | LOVELL-BADGE R, ANTHONY E, BARKER R A, et al. ISSCR guidelines for stem cell research and clinical translation: the 2021 update[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(6): 1398-1408. |
| 51 | MA H X, ZHAI J L, WAN H F, et al. In vitro culture of cynomolgus monkey embryos beyond early gastrulation[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6467): eaax7890. |
| 52 | NIU Y Y, SUN N Q, LI C, et al. Dissecting primate early post-implantation development using long-term in vitro embryo culture[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6467): eaaw5754. |
| 53 | GONG Y D, BAI B, SUN N Q, et al. Ex utero monkey embryogenesis from blastocyst to early organogenesis[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(10): 2092-2110.e23. |
| 54 | ZHAI J L, XU Y H, WAN H F, et al. Neurulation of the cynomolgus monkey embryo achieved from 3D blastocyst culture[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(10): 2078-2091.e18. |
| 55 | CLARK A T, BRIVANLOU A, FU J P, et al. Human embryo research, stem cell-derived embryo models and in vitro gametogenesis: considerations leading to the revised ISSCR guidelines[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(6): 1416-1424. |
| 56 | ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SCHULDINER M, KARSENTI D, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into embryoid bodies compromising the three embryonic germ layers[J]. Molecular Medicine, 2000, 6(2): 88-95. |
| 57 | MURRY C E, KELLER G. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to clinically relevant populations: lessons from embryonic development[J]. Cell, 2008, 132(4): 661-680. |
| 58 | AI Z Y, YIN Y, NIU B H, et al. Deconstructing human peri-implantation embryogenesis based on embryos and embryoids[J]. Biology of Reproduction, 2022, 107(1): 212-225. |
| 59 | TURNER D A, GIRGIN M, ALONSO-CRISOSTOMO L, et al. Anteroposterior polarity and elongation in the absence of extra-embryonic tissues and of spatially localised signalling in gastruloids: mammalian embryonic organoids[J]. Development, 2017, 144(21): 3894-3906. |
| 60 | VAN DEN BRINK S C, BAILLIE-JOHNSON P, BALAYO T, et al. Symmetry breaking, germ layer specification and axial organisation in aggregates of mouse embryonic stem cells[J]. Development, 2014, 141(22): 4231-4242. |
| 61 | BECCARI L, MORIS N, GIRGIN M, et al. Multi-axial self-organization properties of mouse embryonic stem cells into gastruloids[J]. Nature, 2018, 562(7726): 272-276. |
| 62 | GIRGIN M U, BROGUIERE N, MATTOLINI L, et al. Gastruloids generated without exogenous Wnt activation develop anterior neural tissues[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(5): 1143-1155. |
| 63 | VEENVLIET J V, BOLONDI A, KRETZMER H, et al. Mouse embryonic stem cells self-organize into trunk-like structures with neural tube and somites[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6522): eaba4937. |
| 64 | ROSSI G, BROGUIERE N, MIYAMOTO M, et al. Capturing cardiogenesis in gastruloids[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(2): 230-240.e6. |
| 65 | MORIS N, ANLAS K, VAN DEN BRINK S C, et al. An in vitro model of early anteroposterior organization during human development[J]. Nature, 2020, 582(7812): 410-415. |
| 66 | YAMANAKA Y, HAMIDI S, YOSHIOKA-KOBAYASHI K, et al. Reconstituting human somitogenesis in vitro [J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7948): 509-520. |
| 67 | MIAO Y C, DJEFFAL Y, DE SIMONE A, et al. Reconstruction and deconstruction of human somitogenesis in vitro [J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7948): 500-508. |
| 68 | LIBBY A R G, JOY D A, ELDER N H, et al. Axial elongation of caudalized human organoids mimics aspects of neural tube development[J]. Development, 2021, 148(12): dev198275. |
| 69 | OLMSTED Z T, PALUH J L. Co-development of central and peripheral neurons with trunk mesendoderm in human elongating multi-lineage organized gastruloids[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3020. |
| 70 | GRIBAUDO S, ROBERT R, VAN SAMBEEK B, et al. Self-organizing models of human trunk organogenesis recapitulate spinal cord and spine co-morphogenesis[J/OL]. Nature Biotechnology[2023-12-01]. . |
| 71 | WARMFLASH A, SORRE B, ETOC F, et al. A method to recapitulate early embryonic spatial patterning in human embryonic stem cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(8): 847-854. |
| 72 | BRITTON G, HEEMSKERK I, HODGE R, et al. A novel self-organizing embryonic stem cell system reveals signaling logic underlying the patterning of human ectoderm[J]. Development, 2019, 146(20): dev179093. |
| 73 | MARTYN I, KANNO T Y, RUZO A, et al. Self-organization of a human organizer by combined Wnt and Nodal signalling[J]. Nature, 2018, 558(7708): 132-135. |
| 74 | HAREMAKI T, METZGER J J, RITO T, et al. Self-organizing neuruloids model developmental aspects of Huntington’s disease in the ectodermal compartment[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(10): 1198-1208. |
| 75 | XUE X F, SUN Y B, RESTO-IRIZARRY A M, et al. Mechanics-guided embryonic patterning of neuroectoderm tissue from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Materials, 2018, 17(7): 633-641. |
| 76 | MUNCIE J M, AYAD N M E, LAKINS J N, et al. Mechanical tension promotes formation of gastrulation-like nodes and patterns mesoderm specification in human embryonic stem cells[J]. Developmental Cell, 2020, 55(6): 679-694.e11. |
| 77 | CHHABRA S, LIU L Z, GOH R, et al. Dissecting the dynamics of signaling events in the BMP, WNT, and NODAL cascade during self-organized fate patterning in human gastruloids[J]. PLoS Biology, 2019, 17(10): e3000498. |
| 78 | SIMUNOVIC M, METZGER J J, ETOC F, et al. A 3D model of a human epiblast reveals BMP4-driven symmetry breaking[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2019, 21(7): 900-910. |
| 79 | SHAO Y, TANIGUCHI K, GURDZIEL K, et al. Self-organized amniogenesis by human pluripotent stem cells in a biomimetic implantation-like niche[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(4): 419-425. |
| 80 | SHAO Y, TANIGUCHI K, TOWNSHEND R F, et al. A pluripotent stem cell-based model for post-implantation human amniotic sac development[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 208. |
| 81 | ZHENG Y, XUE X F, SHAO Y, et al. Controlled modelling of human epiblast and amnion development using stem cells[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7774): 421-425. |
| 82 | AMADEI G, LAU K Y C, JONGHE J D, et al. Inducible stem-cell-derived embryos capture mouse morphogenetic events in vitro [J]. Developmental Cell, 2021, 56(3): 366-382.e9. |
| 83 | RIVRON N C, FRIAS-ALDEGUER J, VRIJ E J, et al. Blastocyst-like structures generated solely from stem cells[J]. Nature, 2018, 557(7703): 106-111. |
| 84 | HARRISON S E, SOZEN B, CHRISTODOULOU N, et al. Assembly of embryonic and extraembryonic stem cells to mimic embryogenesis in vitro [J]. Science, 2017, 356(6334): eaal1810. |
| 85 | ZHANG S P, CHEN T Z, CHEN N X, et al. Implantation initiation of self-assembled embryo-like structures generated using three types of mouse blastocyst-derived stem cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 496. |
| 86 | SOZEN B, AMADEI G, COX A, et al. Self-assembly of embryonic and two extra-embryonic stem cell types into gastrulating embryo-like structures[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2018, 20(8): 979-989. |
| 87 | SOZEN B, COX A L, JONGHE J D, et al. Self-organization of mouse stem cells into an extended potential blastoid[J]. Developmental Cell, 2019, 51(6): 698-712.e8. |
| 88 | LI R H, ZHONG C Q, YU Y, et al. Generation of blastocyst-like structures from mouse embryonic and adult cell cultures[J]. Cell, 2019, 179(3): 687-702.e18. |
| 89 | YU L Q, WEI Y L, DUAN J L, et al. Blastocyst-like structures generated from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7851): 620-626. |
| 90 | LIU X D, TAN J P, SCHRÖDER J, et al. Modelling human blastocysts by reprogramming fibroblasts into iBlastoids[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7851): 627-632. |
| 91 | KRUITHOF-DE JULIO M, ALVAREZ M J, GALLI A, et al. Regulation of extra-embryonic endoderm stem cell differentiation by Nodal and Cripto signaling[J]. Development, 2011, 138(18): 3885-3895. |
| 92 | NIWA H, TOYOOKA Y, SHIMOSATO D, et al. Interaction between Oct3/4 and Cdx2 determines trophectoderm differentiation[J]. Cell, 2005, 123(5): 917-929. |
| 93 | YANAGIDA A, SPINDLOW D, NICHOLS J, et al. Naive stem cell blastocyst model captures human embryo lineage segregation[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(6): 1016-1022.e4. |
| 94 | KAGAWA H, JAVALI A, KHOEI H H, et al. Human blastoids model blastocyst development and implantation[J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7894): 600-605. |
| 95 | FAN Y, MIN Z Y, ALSOLAMI S, et al. Generation of human blastocyst-like structures from pluripotent stem cells[J]. Cell Discovery, 2021, 7(1): 81. |
| 96 | SOZEN B, JORGENSEN V, WEATHERBEE B A T, et al. Reconstructing aspects of human embryogenesis with pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5550. |
| 97 | TU Z F, BI Y, ZHU X H, et al. Modeling human pregastrulation development by 3D culture of blastoids generated from primed-to-naïve transitioning intermediates[J]. Protein & Cell, 2023, 14(5): 337-349. |
| 98 | YU L Q, LOGSDON D, PINZON-ARTEAGA C A, et al. Large-scale production of human blastoids amenable to modeling blastocyst development and maternal-fetal cross talk[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(9): 1246-1261.e9. |
| 99 | KARVAS R M, ZEMKE J E, ALI S S, et al. 3D-cultured blastoids model human embryogenesis from pre-implantation to early gastrulation stages[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(9): 1148-1165.e7. |
| 100 | LI J, ZHU Q Y, CAO J, et al. Cynomolgus monkey embryo model captures gastrulation and early pregnancy[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(4): 362-377.e7. |
| 101 | LI R H, ZHONG C Q, IZPISUA BELMONTE J C. Time matters: human blastoids resemble the sequence of blastocyst development[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(4): 581-584. |
| 102 | SHAHBAZI M N, WANG T R, TAO X, et al. Developmental potential of aneuploid human embryos cultured beyond implantation[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3987. |
| 120 | AGUILERA-CASTREJON A, OLDAK B, SHANI T, et al. Ex utero mouse embryogenesis from pre-gastrulation to late organogenesis[J]. Nature, 2021, 593(7857): 119-124. |
| 103 | GIULITTI S, PELLEGRINI M, ZORZAN I, et al. Direct generation of human naive induced pluripotent stem cells from somatic cells in microfluidics[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2019, 21(2): 275-286. |
| 104 | PEDROZA M, GASSALOGLU S I, DIAS N, et al. Self-patterning of human stem cells into post-implantation lineages[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 574-583. |
| 105 | LIU L Z, OURA S, MARKHAM Z, et al. Modeling post-implantation stages of human development into early organogenesis with stem-cell-derived peri-gastruloids[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(18): 3776-3792.e16. |
| 106 | HISLOP J, SONG Q, KESHAVARZ F K, et al. Modelling post-implantation human development to yolk sac blood emergence[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(7998): 367-376. |
| 107 | OKUBO T, RIVRON N, KABATA M, et al. Hypoblast from human pluripotent stem cells regulates epiblast development[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(7998): 357-366. |
| [1] | 曹荣凯, 秦建华, 王亚清. 胎盘芯片及其在生殖医学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 831-850. |
| [2] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [3] | 韩宜钊, 郭佳, 邵玥. 干细胞模拟发育:细胞元件、胚胎模型与工程方法[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 734-753. |
| [4] | 李石开, 曾东鳌, 杜方舟, 张京钟, 余爽. 血管化类器官的构建方法及生物材料[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 851-866. |
| [5] | 艾宗勇, 张成庭, 牛宝华, 尹宇, 杨洁, 李天晴. 人胚胎早期发育与干细胞[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 700-718. |
| [6] | 朱骊宇, 赵玉龙, 李伟, 王立宾. 哺乳动物染色体工程研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 394-406. |
| [7] | 张璨, 施李杨, 戴建武. 细胞培养肉用生物材料的设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 676-689. |
| [8] | 宋成治, 孙阳, 曹毅. 力信号在干细胞命运决定过程中的影响[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 781-794. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||