合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 384-398.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-085
DNA信息存储中关键生化方法的研究
郜艳敏, 唐梦童, 刘倩, 乔宏艳, 王桃雪, 齐浩
- 天津大学化工学院,系统生物工程教育部重点实验室,天津 300350
-
收稿日期:2020-11-30修回日期:2021-02-08出版日期:2021-06-30发布日期:2021-07-13 -
通讯作者:齐浩 -
作者简介:郜艳敏 (1990—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为DNA信息存储和核酸检测。E-mail:xiaomingao@tju.edu.cn唐梦童 (1995—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为DNA信息存储。E-mail:tangmengtong126@126.com齐浩 (1978—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学和分子生物学。E-mail:haoq@tju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“变革性技术关键科学问题”重点专项(2020YFA0712104);国家自然科学基金(21778039)
The pivotal biochemical methods in DNA data storage
GAO Yanmin, TANG Mengtong, LIU Qian, QIAO Hongyan, WANG Taoxue, QI Hao
- Key Laboratory of Systems Bioengineering (Ministry of Education),School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300350,China
-
Received:2020-11-30Revised:2021-02-08Online:2021-06-30Published:2021-07-13 -
Contact:QI Hao
摘要:
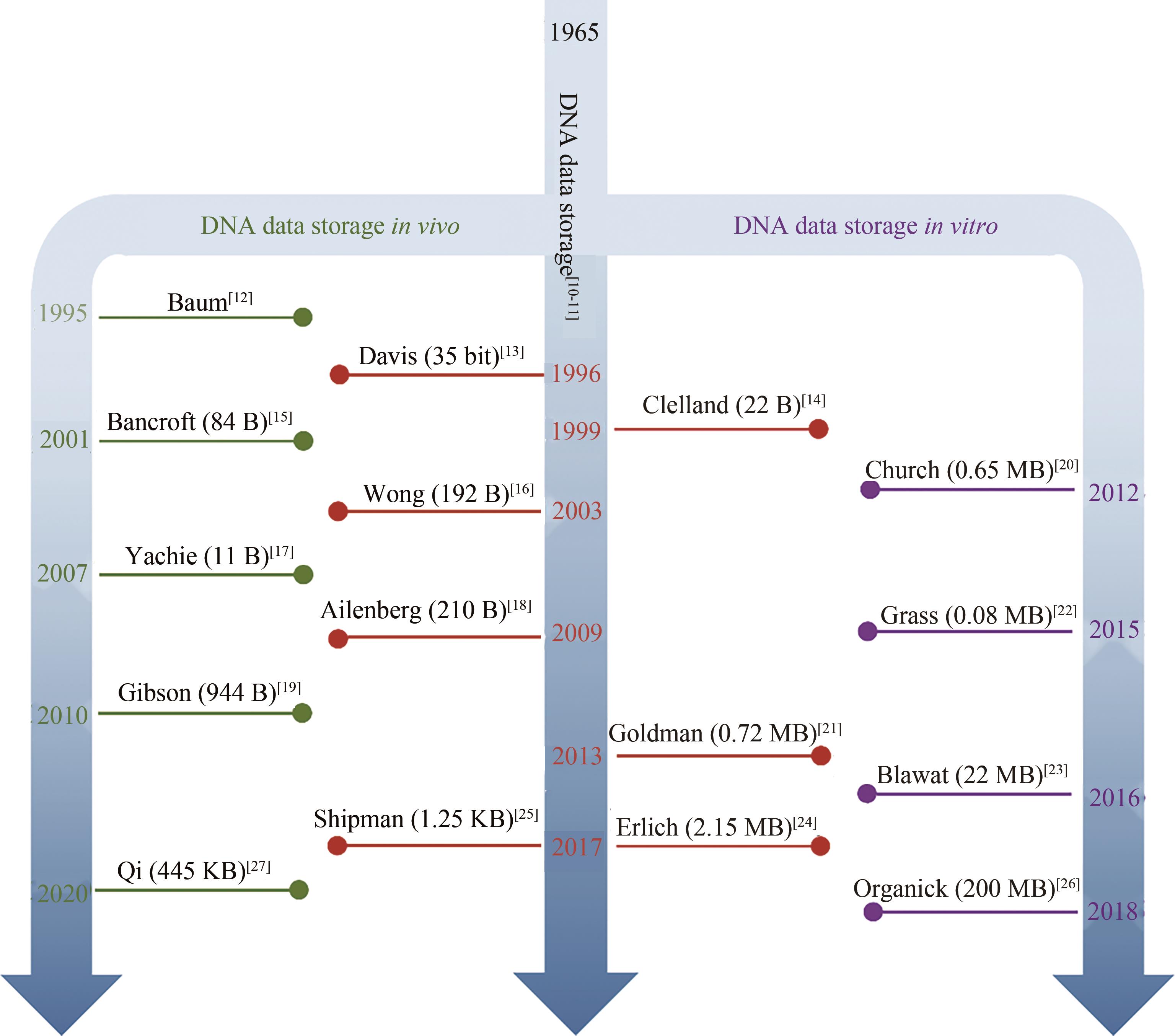
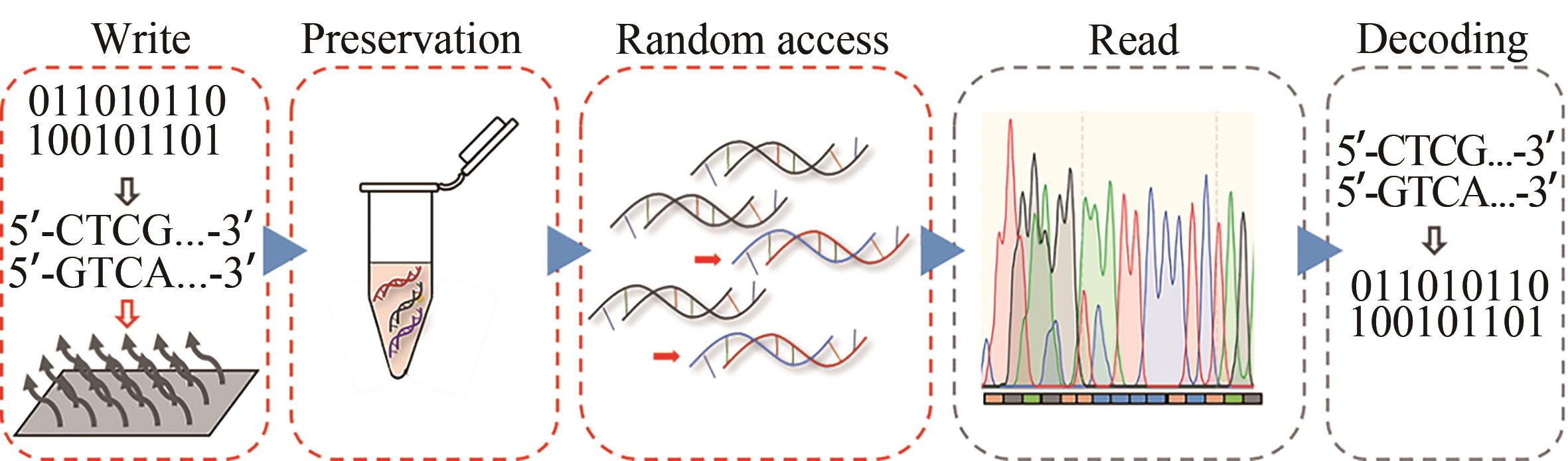
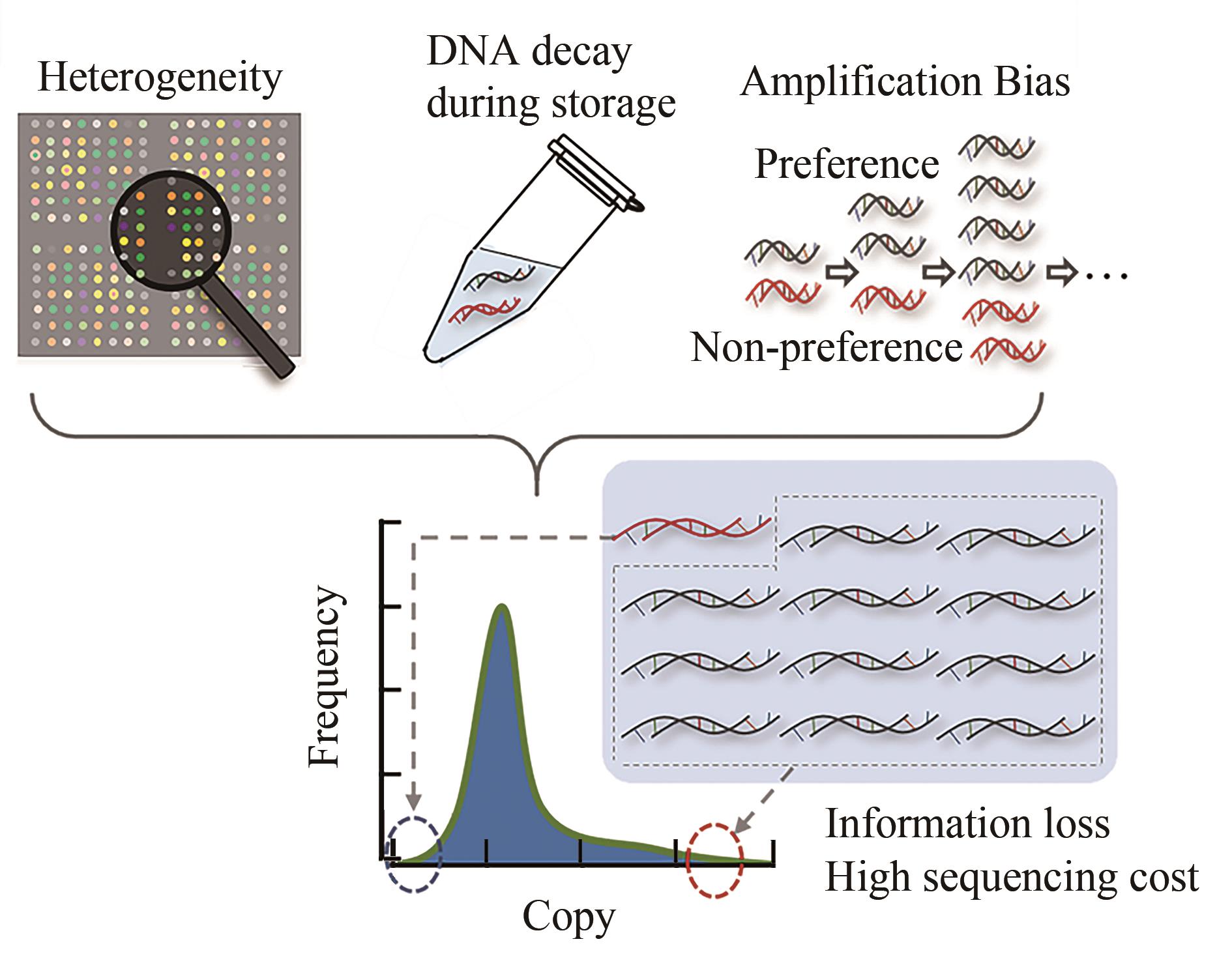
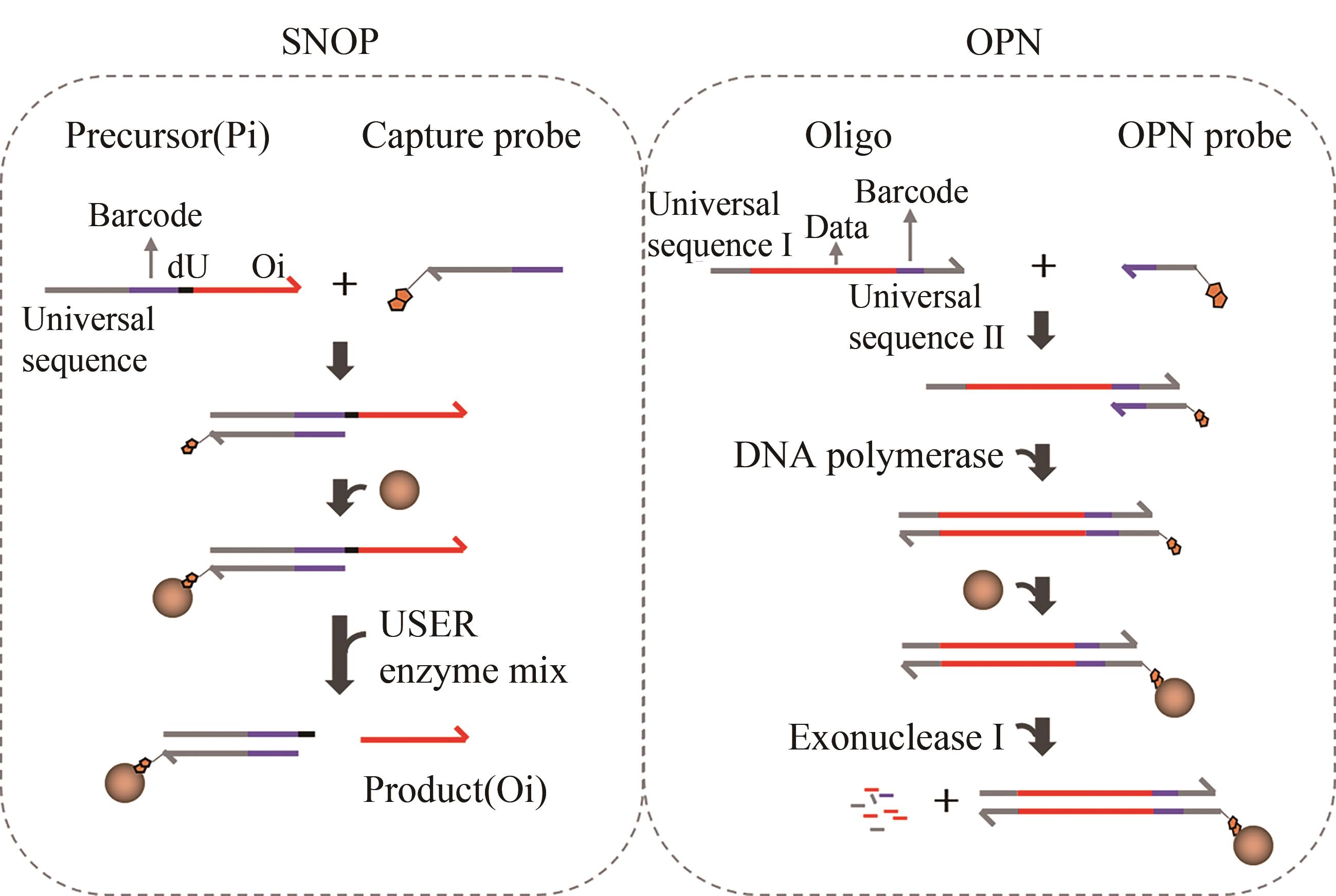
随着生物技术特别是高通量的DNA合成和测序技术的发展,DNA信息存储技术在存储容量、稳定性以及可重复读取等方面都取得了重大成就。但目前携带有数据信息的大规模寡核苷酸文库的生化技术的操纵仍面临着巨大的挑战,比如合成、扩增、保存或测序过程引起的寡核苷酸不均一性、DNA序列丢失、碱基突变、DNA分子的衰减等,这些因素限制了DNA信息存储走向实际工业化应用。本文从操纵大型寡核苷酸文库的生化技术角度出发,归纳总结了造成生化问题的原因以及为解决这些问题所开发的一系列方法,包括合成工艺的改进、寡核苷酸文库的均一化、多种DNA保存方法、变体PCR以及恒温扩增反应,论证了它们在DNA信息存储流程中避免上述生化问题的可行性与有效性,最后分析了现阶段DNA信息存储所面临的合成、长时间保存方法以及扩增等方面的挑战。本文旨在为实现对大型寡核苷酸文库的操纵奠定基础,以期促进DNA信息存储迈向实际应用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郜艳敏, 唐梦童, 刘倩, 乔宏艳, 王桃雪, 齐浩. DNA信息存储中关键生化方法的研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 384-398.
GAO Yanmin, TANG Mengtong, LIU Qian, QIAO Hongyan, WANG Taoxue, QI Hao. The pivotal biochemical methods in DNA data storage[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 384-398.

图5 6种不同DNA保存方法(Dehydrated DNA, unnatural genetic polymer, aqueous solution, encapsulation, DNA in basic salt and DNA in vivo. Stability, handling simplicity, preservation temperature and DNA loading are different in all systems)
Fig. 5 Six different storage methods
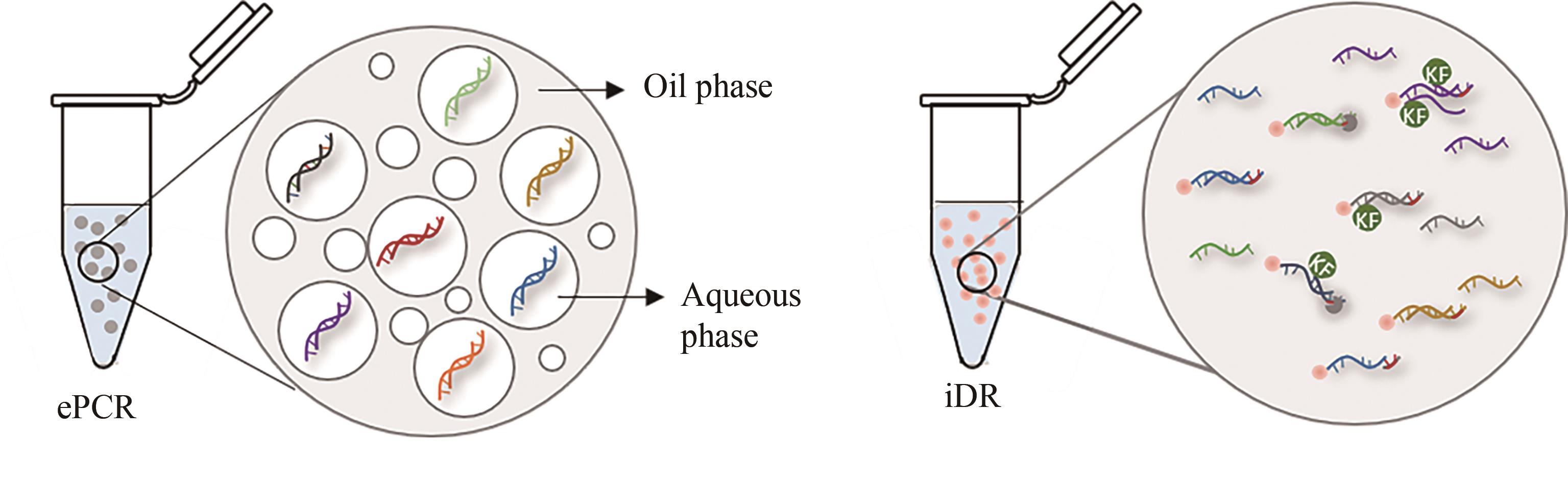
图6 两种大型寡核苷酸文库DNA的扩增方法
Fig. 6 Two different amplification methods of large-scale oligo pool are shown: ePCR (emulsion PCR) and iDR (isothermal DNA reading)
| 1 | EXTANCE A. How DNA could store all the world's data[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7618): 22-24. |
| 2 | CARMEAN D, CEZE L, SEELIG G, et al. DNA data storage and hybrid molecular-electronic computing[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(1): 63-72. |
| 3 | DE SILVA P Y, GANEGODA G U. New trends of digital data storage in DNA[J]. BioMed Research International, 2016, 2016: 8072463. |
| 4 | AKRAM F, HAQ I U, ALI H, et al. Trends to store digital data in DNA: an overview[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2018, 45(5): 1479-1490. |
| 5 | WATERS D L E, SHAPTER F M.The polymerase chain reaction (PCR): general methods[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2014, 1099: 65-75. |
| 6 | TERRANCE W G, FRAISER M S, SCHRAM J L, et al. Strand displacement amplification-an isothermal, in vitro DNA amplification technique[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1992, 20(7): 1691-1696. |
| 7 | MAYBORODA O, KATAKIS I, O'SULLIVAN C K. Multiplexed isothermal nucleic acid amplification[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2018, 545: 20-30. |
| 8 | KOSURI S, CHURCH G M. Large-scale de novo DNA synthesis: technologies and applications[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(5): 499-507. |
| 9 | GOODWIN S, MCPHERSON J D, Richard MCCOMBIE W. Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2016, 17(6): 333-351. |
| 10 | WIENER N. Interview: machines smarter than men? [J]. US News World Report, 1964, 56: 84-86. |
| 11 | NEIMAN M S. On the molecular memory systems and the directed mutations[J]. Radiotekhnika, 1965, 6: 1-8. |
| 12 | BAUM E B. Building an associative memory vastly larger than the brain[J]. Science, 1995, 268(5210): 583-585. |
| 13 | DAVIS J. Microvenus[J]. Art Journal, 1996, 55(1): 70-74. |
| 14 | CLELLAND C T, RISCA V, BANCROFT C. Hiding messages in DNA microdots[J]. Nature, 1999, 399(6736): 533-534. |
| 15 | BANCROFT C, BOWLER T, BLOOM B, et al. Long-term storage of information in DNA[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5536): 1763. |
| 16 | WONG P C, WONG K K, FOOTE H. Organic data memory using the DNA approach[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2003, 46(1): 95-98. |
| 17 | YACHIE N, SEKIYAMA K, SUGAHARA J, et al. Alignment-based approach for durable data storage into living organisms[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2007, 23(2): 501-505. |
| 18 | AILENBERG M, ROTSTEIN O. An improved Huffman coding method for archiving text, images, and music characters in DNA[J]. Biotechniques, 2009, 47(3): 747-754. |
| 19 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 20 | CHURCH G M, GAO Y, KOSURI S. Next-generation digital information storage in DNA[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6102): 1628. |
| 21 | GOLDMAN N, BERTONE P, CHEN S, et al. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7435): 77-80. |
| 22 | GRASS R N, HECKEL R, PUDDU M, et al. Robust chemical preservation of digital information on DNA in silica with error-correcting codes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(8): 2552-2555. |
| 23 | BLAWAT M, GAEDKE K, HVTTER I, et al. Forward error correction for DNA data storage[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 80: 1011-1022. |
| 24 | ERLICH Y, ZIELINSKI D. DNA fountain enables a robust and efficient storage architecture[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 950-954. |
| 25 | SHIPMAN S L, NIVALA J, MACKLIS J D, et al. CRISPR-Cas encoding of a digital movie into the genomes of a population of living bacteria[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7663): 345-349. |
| 26 | ORGANICK L, ANG S D, CHEN Y J, et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 242-248. |
| 27 | HAO Min, QIAO Hongyan, GAO Yanmin, et al. A mixed culture of bacterial cells enables an economic DNA storage on a large scale[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3(1): 416. |
| 28 | BORNHOLT J, LOPEZ R, CARMEAN D M, et al. Toward a DNA-based archival storage system[J]. IEEE Micro, 2017, 37(3): 98-104. |
| 29 | CEZE L, NIVALA J, STRAUSS K. Molecular digital data storage using DNA[J]. Nature Review Genetics, 2019, 20(8): 456-466. |
| 30 | TAKAHASHI C N, NGUYEN B H, STRAUSS K, et al. Demonstration of end-to-end automation of DNA data storage[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 4998. |
| 31 | CHEN Y J, TAKAHASHI C N, ORGANICK L, et al. Quantifying molecular bias in DNA data storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3264. |
| 32 | HECKEL R, MIKUTIS G, GRASS R N. A Characterization of the DNA data storage channel[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 9663. |
| 33 | BHAN N J, STRUTZ J, GLASER J, et al. Recording temporal data onto DNA with minutes resolution[J], 2019. doi:10.1101/634790 |
| 34 | HENDLING M, BARISIC I. In-silico design of DNA oligonucleotides: challenges and approaches[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17: 1056-1065. |
| 35 | TIAN Jingdong, MA K, SAAEM I. Advancing high-throughput gene synthesis technology[J]. Molecular Biosystems, 2009, 5(7): 714-722. |
| 36 | 王霞, 赵鹃, 李炳志, 等. DNA合成技术及应用[J]. 生命科学, 2013, 25(10): 993-999. |
| WANG Xia, ZHAO Juan, LI Bingzhi, et al. DNA synthesis methods and applications [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2013, 25(10):993-999. | |
| 37 | CLORE A. A new route to synthetic DNA[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 593-595. |
| 38 | LEE H H, KALHOR R, GOELA N, et al. Terminator-free template-independent enzymatic DNA synthesis for digital information storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2383. |
| 39 | MURGHA Y E, ROUILLARD J M, GULARI E.Methods for the preparation of large quantities of complex single-stranded oligonucleotide libraries[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e94752. |
| 40 | TIAN Jingdong, GONG Hui, SHENG Nijing, et al. Accurate multiplex gene synthesis from programmable DNA microchips[J]. Nature, 2004, 432(7020): 1050-1054. |
| 41 | KLEIN J C, LAJOIE M J, SCHWARTZ J J, et al. Multiplex pairwise assembly of array-derived DNA oligonucleotides[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(5): e43. |
| 42 | ANTKOWIAK P L, LIETARD J, DARESTANI M Z, et al.Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5345. |
| 43 | TABATABAEI S K, WANG B, ATHREYA N B M, et al. DNA punch cards for storing data on native DNA sequences via enzymatic nicking[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1742. |
| 44 | ELLINGTON A, POLLARD J D. Synthesis and purification of oligonucleotides[J]. Current Protocols Molecular Biology, 2001, 42(1). DOI:10.1002/0471142727.mb0211s42 . |
| 45 | PINTO A, CHEN S X, ZHANG D Y. Simultaneous and stoichiometric purification of hundreds of oligonucleotides[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2467. |
| 46 | GAO Yanmin, CHEN Xin, QIAO Hongyan, et al. Low-bias manipulation of DNA oligo pool for robust data storage[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(12): 3344-3352 |
| 47 | WILLERSLEV E, COOPER A. Ancient DNA[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2005, 272(1558): 3-16. |
| 48 | MITCHELL D, WILLERSLEV E, HANSEN A.Damage and repair of ancient DNA[J]. Mutation Research, 2005, 571(1-2): 265-276. |
| 49 | BONNET J, COLOTTE M, COUDY D, et al. Chain and conformation stability of solid-state DNA: implications for room temperature storage[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(5): 1531-1546. |
| 50 | MIKUTIS G, SCHMID L, STARK W J, et al. Length-dependent DNA degradation kinetic model: decay compensation in DNA tracer concentration measurements[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(1): 40-48. |
| 51 | KNEBELSBERGER T, STOGER I.DNA extraction, preservation, and amplification[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2012, 858: 311-338. |
| 52 | WAN E, AKANA M, PONS J, et al. Green technologies for room temperature nucleic acid storage[J]. Current Issues Molecular Biology, 2010, 12(3): 135-142. |
| 53 | BURGOYNE L A. Solid medium and method for DNA storage: US5985327[P].1996-03-05. |
| 54 | IVANOVA N V, KUZMINA M L. Protocols for dry DNA storage and shipment at room temperature[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2013, 13(5): 890-898. |
| 55 | ALKHAMIS K A. Influence of solid-state acidity on the decomposition of sucrose in amorphous systems [J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2008, 362(1/2): 74-80. |
| 56 | KARNI M, ZIDON D, POLAK P, et al.Thermal degradation of DNA[J]. DNA and Cell Biology, 2013, 32(6): 298-301. |
| 57 | ZHU B, FURUKI T, OKUDA T, et al. Natural DNA mixed with trehalose persists in B-form double-stranding even in the dry state[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111(20): 5542-5544. |
| 58 | ANCHORDOQUY T J, MOLINA M C.Preservation of DNA[J]. Cell Preservation Technology, 2007, 5(4): 180-188. |
| 59 | NEWMAN S, STEPHENSON A P, WILLSEY M, et al. High density DNA data storage library via dehydration with digital microfluidic retrieval[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1706. |
| 60 | HOWLETT S E, CASTILLO H S, GIOENI L J, et al. Evaluation of DNA stable for DNA storage at ambient temperature[J]. Forensic Science International Genetics, 2014, 8(1): 170-178. |
| 61 | ORGANICK L, NGUYEN B H, MCAMIS R, et al. An empirical comparison of preservation methods for synthetic DNA data storage [J]. Small Methods, 2021. DOI:10.1002/smtd 202001094 . |
| 62 | CLERMONT D, SANTONI S, SAKER S, et al. Assessment of DNA encapsulation, a new room-temperature DNA storage method[J]. Biopreservation and Biobanking, 2014, 12(3): 176-183. |
| 63 | PAUNESCU D, FUHRER R, GRASS R N. Protection and deprotection of DNA-high-temperature stability of nucleic acid barcodes for polymer labeling[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(15): 4269-4272. |
| 64 | KOCH J, GANTENBEIN S, MASANIA K, et al. A DNA-of-things storage architecture to create materials with embedded memory[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(1): 39-43. |
| 65 | CHEN W D, KOHLL A X, NGUYEN B H, et al. Combining data longevity with high storage capacity—layer-by-layer DNA encapsulated in magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201901672 . |
| 66 | VALLE L J DEL, BERTRAN O, CHAVES G, et al. DNA adsorbed on hydroxyapatite surfaces[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014, 2(40): 6953-6966. |
| 67 | KOHLL A X, ANTKOWIAK P L, CHEN W D, et al. Stabilizing synthetic DNA for long-term data storage with earth alkaline salts[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(25): 3613-3616. |
| 68 | SCHONING K, SCHOLZ P, GUNTHA S, et al. Chemical etiology of nucleic acid structure: the alpha-threofuranosyl-(3'->2') oligonucleotide system[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5495): 1347-1351. |
| 69 | YANG K, MCCLOSKEY C M, CHAPUT J C. Reading and writing digital information in TNA[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(11): 2936-2942. |
| 70 | DAGHER G G, MACHADO A P, DAVIS E C, et al. Data storage in cellular DNA: contextualizing diverse encoding schemes[J]. Evolutionary Intelligence, 2019. DOI: 10.1007/s12065-019-00202-z . |
| 71 | AKHMETOV A, ELLINGTON A D, MARCOTTE E M. A highly parallel strategy for storage of digital information in living cells[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2018, 18(1): 64. |
| 72 | NGUYEN H, PARK J, PARK S, et al. Long-term stability and integrity of plasmid-based DNA data storage[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(1): 28. |
| 73 | SHIPMAN S L, NIVALA J, MACKLIS J D, et al. Molecular recordings by directed CRISPR spacer acquisition[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6298): aaf1175. |
| 74 | DABNEY J, MEYER M. Length and GC-biases during sequencing library amplification: a comparison of various polymerase-buffer systems with ancient and modern DNA sequencing libraries[J]. BioTechniques, 2012, 52(2): 87-94. |
| 75 | ROUX K H. Optimization and troubleshooting in PCR[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2009, 2009(4): pdb, ip66. |
| 76 | AIRD D, ROSS M G, CHEN W S, et al. Analyzing and minimizing PCR amplification bias in Illumina sequencing libraries[J]. Genome Biology, 2011, 12(2): R18. |
| 77 | BENJAMINI Y, Speed T P. Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high-throughput sequencing[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(10): e72. |
| 78 | CLINE J, BRAMAN J C, HOGREFE H H. PCR fidelity of pfu DNA polymerase and other thermostable DNA polymerases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1996, 24(18): 3546-3551. |
| 79 | CZERNY T. High primer concentration improves PCR amplification from random pools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1996, 24(5): 985-986. |
| 80 | WANG Y, NOOR-A-RAHIM M, ZHANG J, et al. Oligo design with single primer binding site for high capacity DNA-based data storage[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 2020, 17 (6): 2176-2182. |
| 81 | WINSHIP P R. An improved method for directly sequencing PCR-amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1989, 17(3): 1266. |
| 82 | VARADARAJ K, SKINNER D M. Denaturants or cosolvents improve the specificity of PCR amplification of a G+C-rich DNA using genetically engineered DNA polymerases[J]. Gene, 1994, 140(1): 1-5. |
| 83 | HENKE W, HERDEL K, JUNG K, et al. Betaine improves the PCR amplification of GC-rich DNA sequences[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1997, 25(19): 3957-3958. |
| 84 | 王同同,张利平,尹康权. 甜菜碱改善水稻高GC含量DNA序列的PCR扩增[J]. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(3): 80-86. |
| WANG Tongtong, ZHANG Liping, YIN Kangquan. Betaine improves the PCR amplification of rice GC-rich DNA sequence [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018,34(3):80-86. | |
| 85 | FARELL E M, ALEXANDRE G. Bovine serum albumin further enhances the effects of organic solvents on increased yield of polymerase chain reaction of GC-rich templates[J]. BMC Research Notes, 2012, 5: 257. |
| 86 | MCCONLOGUE L, BROW M A D., INNIS Michael A. Structure-independent DNA amplification by PCR using 7-deaza-2'-deoxyguanosine[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1988, 16(20): 9869. |
| 87 | PAN Wenjing, BYRNE-STEELE M, WANG Chunlin, et al. DNA polymerase preference determines PCR priming efficiency[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2014, 14: 10. |
| 88 | DON R H, COX P T, WAINWRIGHT B J, et al. 'Touchdown' PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1991, 19(14): 4008. |
| 89 | HECKER K H, ROUX K H. High and low annealing temperatures increase both specificity and yield in touchdown and stepdown PCR[J]. Biotechniques, 1996, 20(3): 478-485. |
| 90 | FREY U H, BACHMANN H S, PETERS J, et al. PCR-amplification of GC-rich regions: 'slowdown PCR'[J]. Natural Protocols, 2008, 3(8): 1312-1317. |
| 91 | KANAGAL-SHAMANNA R. EMULSION PCR: Techniques and applications[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2016, 1392: 33-42. |
| 92 | VERMA V, GUPTA A, CHAUDHARY V K. Emulsion PCR made easy[J]. BioTechniques, 2020, 69(1): 421-426. |
| 93 | SHAO K, DING Weifeng, WANG Feng, et al. Emulsion PCR: a high efficient way of PCR amplification of random DNA libraries in aptamer selection[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e24910. |
| 94 | POLZ M F, CAVANAUGH C M. Bias in template-to-product ratios in multitemplate PCR[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(10): 3724-3730. |
| 95 | QIAN Cheng, WANG Rui, WU Hui, et al. Nicking enzyme-assisted amplification (NEAA) technology and its applications: a review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1050: 1-15. |
| 96 | ZHAO Yongxi, CHEN Feng, LI Qian, et al. Isothermal amplification of nucleic acids[J]. Chemical Review, 2015, 115(22): 12491-12545. |
| 97 | CHOI Y, BAE H J, LEE A C, et al. DNA micro-disks for the management of DNA-based data storage with index and write-once-read-many (WORM) memory features[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(37): e2001249. |
| 98 | WANG Ting, LIU Yong, SUN Huanhuan, et al. An RNA-guided Cas9 nickase-based method for universal isothermal DNA amplification[J]. Angewandte ChemieInternational Edition, 2019, 58(16): 5382-5386. |
| 99 | ZHOU Wenhua, HU Li, YING Liming, et al. A CRISPR-Cas9-triggered strand displacement amplification method for ultrasensitive DNA detection[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 5012. |
| 100 | WILLSEY M, STRAUSS K, CEZE L, et al. Puddle: a dynamic, error-correcting, full-stack microfluidics platform[C]∥ASPLOS' 19 . New York: ACM, 2019: 183-197. |
| 101 | PRESS W H, HAWKINS J A, JONES S K, et al. HEDGES error-correcting code for DNA storage corrects indels and allows sequence constraints[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(31): 18489-18496. |
| 102 | SONG Wentu, CAI Kui, ZHANG Mu, et al. Codes with run-length and GC-content constraints for DNA-based data storage[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(10): 2004-2007. |
| [1] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [2] | 陈大明, 张学博, 刘晓, 马悦, 熊燕. 从全球专利分析看DNA合成与信息存储技术发展趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 399-411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||