合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (4): 612-634.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-094
大规模哺乳动物细胞培养工程的现状与展望
朱紫瑜, 王冠, 庄英萍
- 华东理工大学生物工程学院,国家生化工程技术研究中心,生物反应器工程国家重点实验室,上海 200237
-
收稿日期:2020-12-31修回日期:2021-03-12出版日期:2021-08-31发布日期:2021-09-10 -
通讯作者:庄英萍 -
作者简介:朱紫瑜 (1996—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为免疫细胞大规模培养。E-mail:852374768@qq.com庄英萍 (1962—),女,博士,教授。研究方向为生物过程优化与放大。E-mail:ypzhuang@ecust.edu.cn -
基金资助:上海研发公共服务平台建设专项(18DZ2290800)
Present situation and prospect for large-scale mammalian cell culture engineering
ZHU Ziyu, WANG Guan, ZHUANG Yingping
- School of Bioengineering,East China University of Science and Technology,National Center of Bio-Engineering &Technology (Shanghai),State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering,Shanghai 200237,China
-
Received:2020-12-31Revised:2021-03-12Online:2021-08-31Published:2021-09-10 -
Contact:ZHUANG Yingping
摘要:
近年来,随着对疫苗和治疗性蛋白类药物等多种生物制品需求量增加以及产品质量要求的提高,细胞大规模培养技术也不断发展。为了增加产量、降低成本,生产更安全有效的药物,大规模细胞培养过程的开发至关重要,而动物细胞的工艺优化和规模放大具有挑战性。提高细胞培养工艺表达量、扩大细胞培养生产规模、保证表达抗体质量稳定成为目前大规模细胞培养过程中亟待解决的问题,迫切需要进一步研究和开发细胞培养工艺。本文围绕以上问题,系统综述了通过优良细胞株的构建、培养基设计与无血清培养基的开发、基于过程分析技术(PAT)培养工艺的优化与放大,建立合适的大规模培养体系,实现细胞的高密度培养和产物的高效表达。与此同时,细胞培养过程中产生的多源异质数据基本依靠低效的人工处理与判断,缺乏深层次的全局因素考虑。为此,未来希望通过人工智能深度挖掘数据之间的关系并指导细胞培养过程工艺优化与放大,实现真正的智能生物制造。
中图分类号:
引用本文
朱紫瑜, 王冠, 庄英萍. 大规模哺乳动物细胞培养工程的现状与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 612-634.
ZHU Ziyu, WANG Guan, ZHUANG Yingping. Present situation and prospect for large-scale mammalian cell culture engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 612-634.
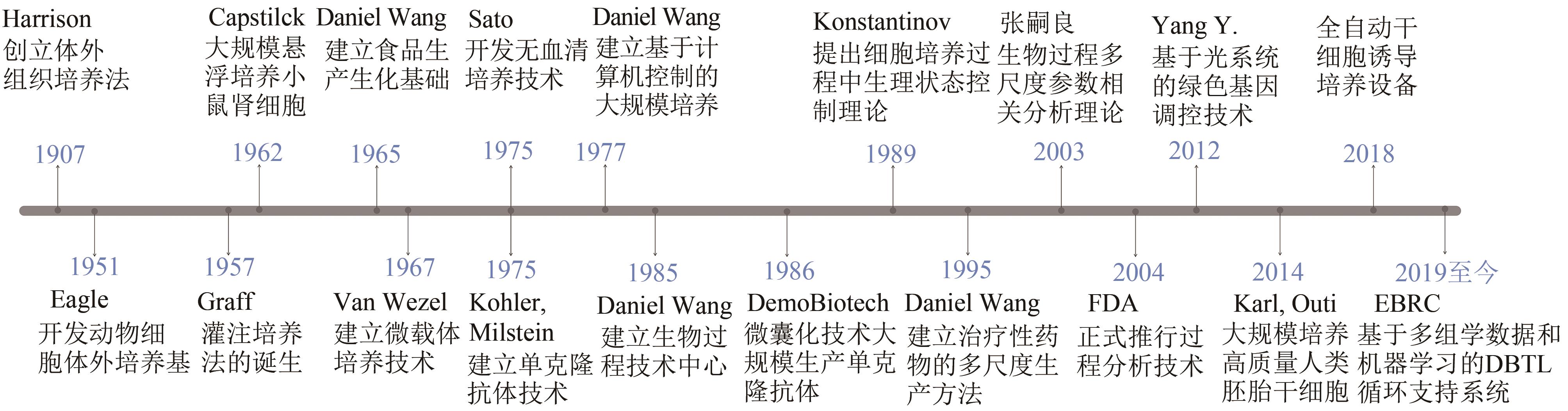
图 1 动物细胞大规模培养技术发展史以及细胞培养技术发展的里程碑事件(从1907年体外组织培养法的建立,发展至今基于多组学数据和机器学习的智能生物制造,列出了动物大规模培养技术的发展过程以及细胞培养技术发展的突破性事件;EBRC—美国工程生物学会联盟)
Fig. 1 History of large-scale animal cell culture technology and milestone events in the development of biotechnology(From the establishment of in vitro tissue culture in 1907 to the development of intelligent biomanufacturing based on multi-omics data and machine learning, the chronological development of large-scale animal culture technology and the breakthrough events in the process are highlighted; EBRC—The Engineering Biology Research Consortium)
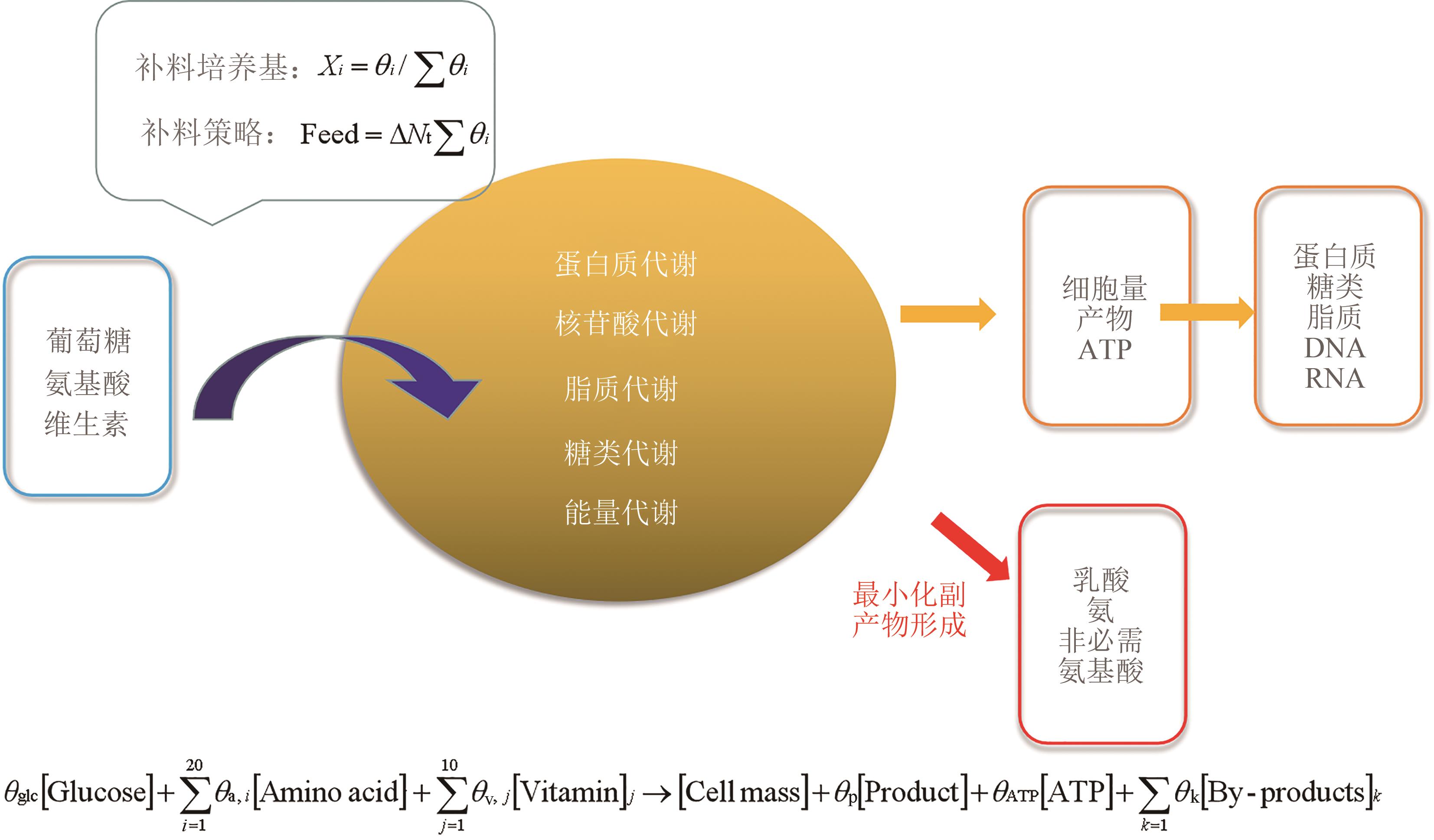
图 2 基于化学计量模型约束的培养基设计[以葡萄糖、20种氨基酸和10种维生素作为反应物,细胞量(包括蛋白质、脂质、DNA、RNA等混合物)、产物和ATP作为反应的产物列出化学计量方程]
Fig. 2 Media design guided by stoichiometric and the constraint-based model(Taking glucose, 20 amino acids and 10 vitamins as reactants, cell mass including the mixtures of protein, lipid, DNA, RNA, etc., products and ATP as reaction products to develop stoichiometric equations)
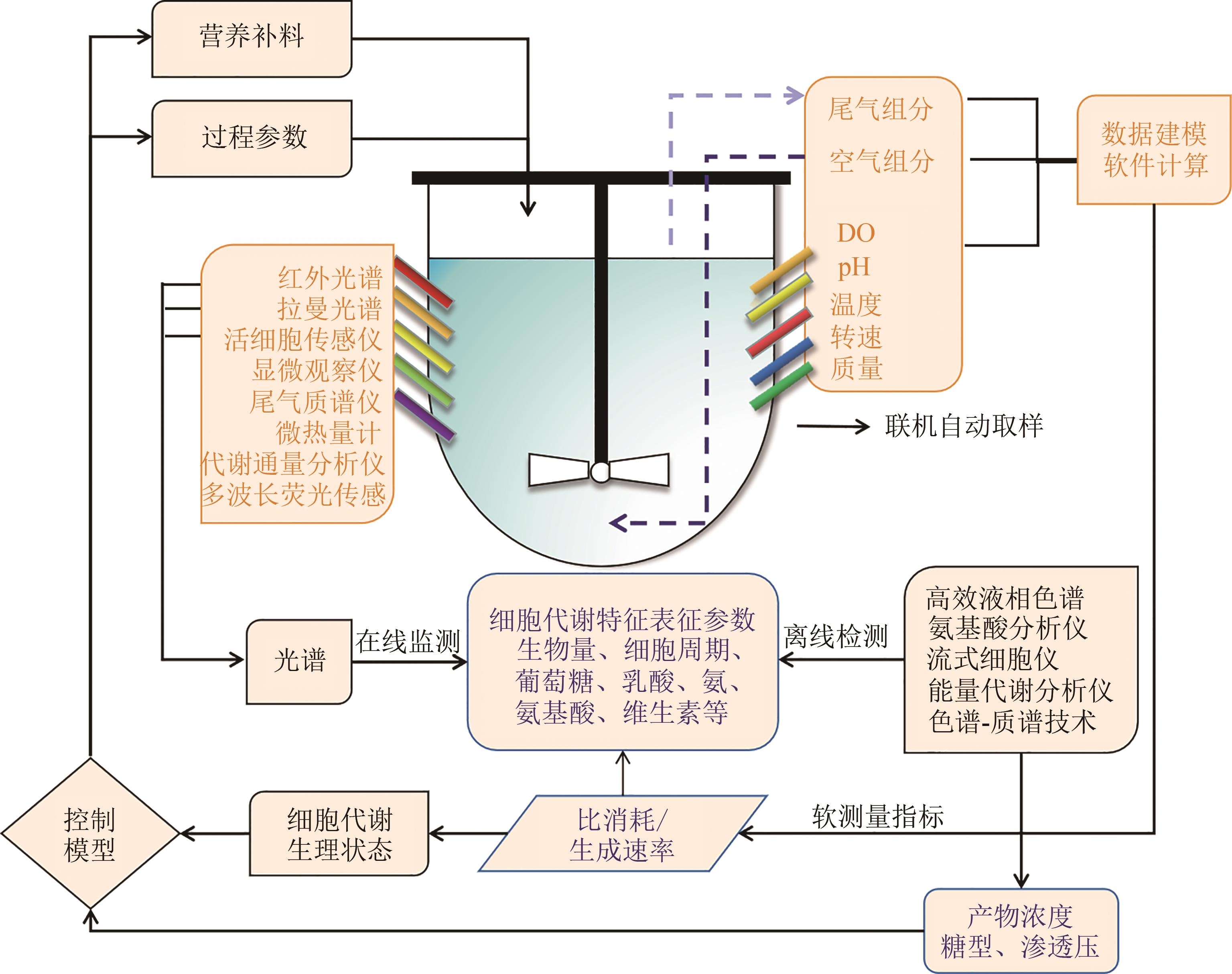
图3 动物细胞培养过程检测技术[69](通过在线检测和离线检测动物细胞培养过程中的变量,并根据数据对系统进行反馈控制;DO—溶解氧)
Fig. 3 Detection technology for animal cell culture processes[69](Through online and offline detection of variables in the process of animal cell culture, and feedback control of the system based on the data; DO—dissolved oxygen)
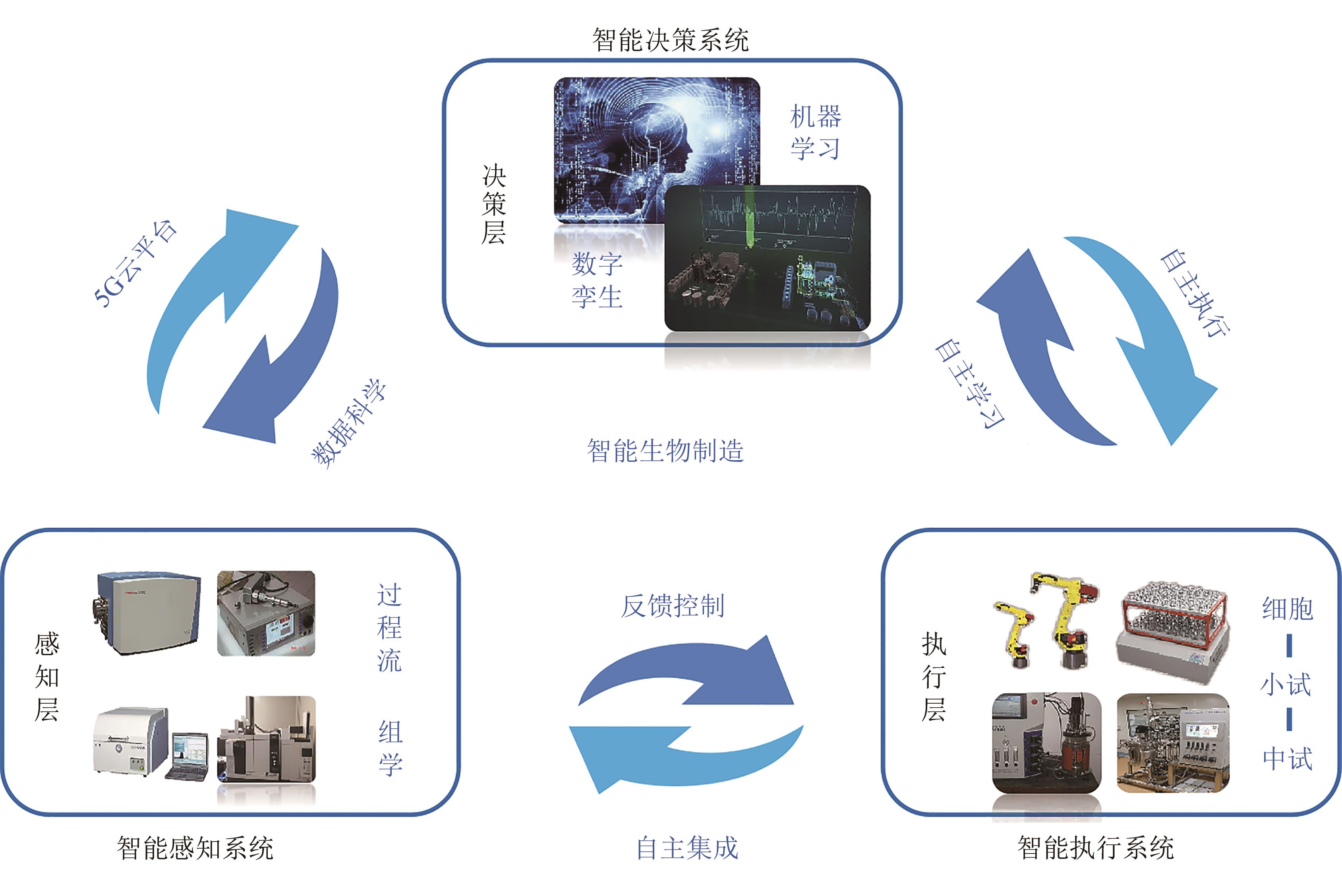
图 4 基于大数据的工业生物过程智能制造系统(通过智能感知系统挖掘大数据,实现对生物培养过程的智能控制,同时利用文献数据、组学数据形成知识图谱并通过机器深度学习,进而指导智能感知系统,实现真正的智能生物制造)
Fig. 4 Intelligent manufacturing systems developed based on big data for industrial processes(Mining big data through the intelligent perception system to realize the intelligent control of the biological training process. On the other hand, using literature and omics data to form a knowledge map for machine deep learning, the intelligent perception system can guide to realize the real intelligent biological manufacturing)
| 1 | 楚品品, 蒋智勇, 勾红潮, 等. 动物细胞规模化培养技术现状[J]. 动物医学进展, 2018, 39(2): 119-123. |
| CHU P P, JIANG Z Y, GOU H C,et al. Overview on large-scale animal cell culture technology[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 39(2): 119-123. | |
| 2 | DELOITTE.2020 Global life sciences outlook[EB/OL]. [2020-2-11]. . |
| 3 | ANTONIO L G, MANTALARIS A. The increasingly human and profitable monoclonal antibody market[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2018, 37 (1): 9-16. |
| 4 | 陈因良, 陈志宏. 细胞培养工程[M]. 上海: 华东化工学院出版社, 1992: 15. |
| CHEN Y L, CHEN Z H. Cell culture engineering[M]. Shanghai:East China Institute of Chemical Technology Press,1992: 15. | |
| 5 | EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture[J]. Science, 1955, 122(3168): 501-504. |
| 6 | HAYASHI I, SATO G H. Replacement of serum by hormones permits growth of cells in a defined medium[J]. Nature, 1976, 259(5539): 132-134. |
| 7 | GRAFF S, MCCARTY K S. Sustained cell culture[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 1957, 13(2): 348-357. |
| 8 | CAPSTICK P B, TELLING R C, CHAPMAN W G, et al. Growth of a cloned strain of hamster kidney cells in suspended cultures and their susceptibility to the virus of foot-and-mouth disease[J]. Nature, 1962, 195(4847): 1163-1164. |
| 9 | WEZEL V. Growth of cell-strains and primary cells on micro-carriers in homogeneous culture[J]. Nature, 1967, 216(5110): 64-65. |
| 10 | KOHLER G, MILSTEIN C. Continuous culture of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity[J]. Nature, 1975, 256(5517): 495-497. |
| 11 | POSILLICO, ELIZABETH G. Microencapsulation technology for large-scale antibody production[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1986, 4(2): 114-117. |
| 12 | KONSTANTINOV K B, ZHOU W, GOLINI F, et al. Expert systems in the control of animal cell culture processes: potentials, functions, and perspectives[J]. Cytotechnology, 1994,14(3): 233-246. |
| 13 | 张嗣良, 储炬. 多尺度微生物过程优化[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2003: 175. |
| ZHANG S L, CHU J. Multi-scale microbial process optimization[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003: 175. | |
| 14 | AURAND E, KEASLING D, FRIEDMAN D, et al. Engineering Biology: a research roadmap for the Next-Generation Bioeconomy[R].Engineering Biology Research Consortium, 2019. |
| 15 | WANG X, CHEN X J, YANG Y. Spatiotemporal control of gene expression by a light-switchable transgene system[J]. Nature Methods, 2012, 9(3): 266-269. |
| 16 | RODIN S, ANTONSSON L, NIAUDET C, et al. Clonal culturing of human embryonic stem cells on laminin-521/E-cadherin matrix in defined and xeno-free environment[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 1145-1147. |
| 17 | 中国科学院广州生物医药与健康研究院. 全自动干细胞诱导培养设备研制[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(1): 86-89. |
| Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health. Development of fully automatic stem cell induction culture equipment[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(1): 86-89. | |
| 18 | LALONDE M E, DUROCHER Y. Therapeutic glycoprotein production in mammalian cells[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 251(4): 128-140. |
| 19 | TRIPATHI N K, SHRIVASTAVA A. Recent developments in bioprocessing of recombinant proteins: expression hosts and process development[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2019, 7(12): 420. |
| 20 | REINHART D. DAMJANOVIC L, KAISERMAYER C,et al. Benchmarking of commercially available CHO cell culture media for antibody production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(11): 4645-4657. |
| 21 | O'FLAHERTY R, BERGIN A, FLAMPOURI E, et al. Mammalian cell culture for production of recombinant proteins: a review of the critical steps in their biomanufacturing[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 43(2): 107552. |
| 22 | ARORA M. Cell culture media: a review[J]. Materials and Methods, 2013, 3(3): 175. |
| 23 | DOUCET C. ERNOU I, ZHANG Y Z,et al. Platelet lysates promote mesenchymal stem cell expansion: a safety substitute for animal serum in cell-based therapy applications[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2005, 205(2): 23-36. |
| 24 | 黄锭. 基于MDCK细胞高密度培养的甲型流感病毒疫苗生产工艺开发与优化[D]. 上海:华东理工大学, 2016. |
| HUANG D. Development and optimization of influenza a virus propagation process based on high density MDCK cell culture system [D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2016. | |
| 25 | STOLFA G, SMONSKEY M T, BONIFACE R, et al. CHO-Omics review: the impact of current and emerging technologies on Chinese hamster ovary based bioproduction[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(3): 227. |
| 26 | CHONG K, YUSUFI K, LEE D Y, et al. Metabolomics-based identification of apoptosis-inducing metabolites in recombinant fed-batch CHO culture media[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2011, 151(2): 218-224. |
| 27 | DOWNEY B J, GRAHAM L J, JEFFREY F B, et al. A novel approach for using dielectric spectroscopy to predict viable cell volume (VCV) in early process development[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2014, 30(2): 479-487. |
| 28 | 李兰. 活细胞传感仪在生物过程优化中的应用研究与开发[D]. 上海:华东理工大学, 2014. |
| LI L. Studies on the application and development of biomass monitor in bioprocess optimization[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2004. | |
| 29 | LI F, VIJAYASANKARAN N, SHEN A, et al. Cell culture processes for monoclonal antibody production[J]. mAbs, 2010, 2(5): 466-479. |
| 30 | 夏建业, 谢明辉, 储炬, 等. 生物反应器流场特性研究及其在生物过程优化与放大中的应用研究[J]. 生物产业技术, 2018(1): 41-48. |
| XIA J Y, XIE M H, CHU J, et al. Study of fluid dynamics in bioreactors and its application in bioprocess optimization and scale-up[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2018(1): 41-48. | |
| 31 | LIU Y, WANG Z J, XIA J Y, et al. Application of Euler-Lagrange CFD for quantitative evaluating the effect of shear force on Carthamus tinctorius L. cell in a stirred tank bioreactor[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 114(6): 209-217. |
| 32 | AFEYAN N B, COONEY C L. Professor Daniel I.C. Wang: a legacy of education, innovation, publication, and leadership[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117: 3615-3627. |
| 33 | HATTON T A. WANG D I C: A tribute to an inspirational leader and colleague[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 95(2):262-269. |
| 34 | 严伟, 信丰学, 董维亮, 等. 合成生物学及其研究进展[J]. 生物学杂志, 2020, 37(5): 1-9. |
| YAN W, XIN F X, DONG W L, et al. Synthetic biology and research progress[J]. Journal of Biology, 2020, 37(5): 1-9. | |
| 35 | 马红武, 陈修来, 袁倩倩, 等. 面向生物合成的代谢工程策略设计[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 44-51. |
| MA H W, CHEN X L, YUAN Q Q, et al. Design of metabolic engineering strategies for biosynthesis of valuable products[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 44-51. | |
| 36 | BO N L. The technology progress of antibody-producing cell line development[J]. China Biotechnology, 2013, 33(6): 111-116. |
| 37 | GREEN A, GLASSEY J. Multivariate analysis of the effect of operating conditions on hybridoma cell metabolism and glycosylation of produced antibody[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2015, 90(2): 303-313. |
| 38 | KUNERT R, REINHART D. Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(8): 3451-3461. |
| 39 | ANGATA, TAKASHI, VARKI, et al. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-Keto acids: an evolutionary perspective[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2002, 102(2): 439-439. |
| 40 | ASHWELL G, HARFORD J. Carbohydrate-specific receptors of the liver[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 1982, 51(1): 531-554. |
| 41 | WONG N S C, YAP M G S, WANG D I C. Enhancing recombinant glycoprotein sialylation through CMP-sialic acid transporter over expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 93(5): 1005-1016. |
| 42 | NGANTUNG F A, MILLER P G, BRUSHETT F R, et al. RNA interference of sialidase improves glycoprotein sialic acid content consistency[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 95(1): 106-119. |
| 43 | ZHANG M, KOSKIE K, ROSS J S, et al. Enhancing glycoprotein sialylation by targeted gene silencing in mammalian cells[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 105(6): 1094-1105. |
| 44 | VOON D C, SUBRATA L S, BALTIC S, et al. Use of mRNA- and protein-destabilizing elements to develop a highly responsive reporter system[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, 33(3): e27. |
| 45 | NG S K, WANG D I C, YAP M G. Application of destabilizing sequences on selection marker for improved recombinant protein productivity in CHO-DG44[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2007, 9(3): 304-316. |
| 46 | CHEN K Q, LIU Q, XIE L Z, et al. Engineering of a mammalian cell line for reduction of lactate formation and high monoclonal antibody production[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2015, 72(1): 55-61. |
| 47 | PENG R W, FUSSENEGGER M. Molecular engineering of exocytic vesicle traffic enhances the productivity of Chinese hamster ovary cells[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2010, 102(4): 1170-1181. |
| 48 | 赵建兵, 易小萍, 张元兴, 等. 过量表达XBP1对于重组CHO细胞中HBsAg分泌的影响[J]. 华东理工大学学报, 2010, 36(1): 42-47. |
| ZHAO J B, YI X P, ZHANG Y X, et al. Effects of XBP1 overexpression on HBsAg secretion in recombinant CHO cells [J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2010, 36(1): 42-47. | |
| 49 | XIE L Z, WANG D I C. Integrated approaches to the design of media and feeding strategies for fed-batch cultures of animal cells[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 1997, 15(3): 109. |
| 50 | XIE L Z, WANG D I C. Stoichiometric analysis of animal cell growth and its application in medium design[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 1994, 43(11): 1164-1174. |
| 51 | XIE L Z, WANG D I C. Applications of improved stoichiometric model in medium design and fed-batch cultivation of animal cells in bioreactor[J]. Cytotechnology, 1994, 15(1): 17-29. |
| 52 | XIE L Z, WANG D I C, et al. High cell density and high monoclonal antibody production through medium design and rational control in a bioreactor[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 1996, 51(6): 591-601. |
| 53 | XIE L Z, NYBERG G, GU X J, et al. Gamma-interferon production and quality in stoichiometric fed-batch cultures of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells under serum-free conditions[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2015, 56(5): 577-582. |
| 54 | GLACKEN M W. Development of mathematical descriptions of mammalian cell culture kinetics for the optimization of fed-batch bioreactors[J]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1987, 66(1): 61-66. |
| 55 | CHANG Y, GRODZINSKY A J, WANG D I C. In-situ removal of ammonium and lactate through electrical means for hybridoma cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1995, 47(3): 308-318. |
| 56 | CHANG Y, GRODZINSKY A J, WANG D I C. Nutrient enrichment and in-situ waste removal through electrical means for hybridoma cultures[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2010, 47(3): 319-326. |
| 57 | 张琼琼, 方明月, 栗军杰, 等. 哺乳动物细胞灌流培养工艺开发与优化[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 258(6): 26-35. |
| ZHANG Q Q, FANG M Y, LI J J, et al. Development and optimization of perfusion process for mammalian cell culture[J].Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 258(6): 26-35. | |
| 58 | HILLER G W, OVALLE A M, GAGNON M P, et al. Cell-controlled hybrid perfusion fed-batch CHO cell process provides significant productivity improvement over conventional fed-batch cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(7): 1438-1447. |
| 59 | LU F, TOH P C, BURNETT L, et al. Automated dynamic fed-batch process and media optimization for high productivity cell culture process development[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2013, 110(1): 191-205. |
| 60 | GSTRAUNTHALER G, LINDL T, VALK J VAN DER, et al. A plea to reduce or replace fetal bovine serum in cell culture media[J]. Cytotechnology, 2013, 65(5): 791-793. |
| 61 | 杨学义, 刘飞, 向双云, 等. 哺乳动物细胞无血清培养基研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展, 2011(2): 69-72. |
| YANG X Y, LIU F, XIANG S Y, et al. Progress on serum-free medium for mammalian cells[J].Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2011(2): 69-72. | |
| 62 | GU X J, XIE L Z, BRYAN J H, et al. Influence of primatone RL supplementation on sialylation of recombinant human interferon- produced by Chinese hamster ovary cell culture using serum-free media[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1997, 56(4):53-60. |
| 63 | CHEN J X, SUN X M, ZHANG L, et al. Mass cultivation of marine fish Chinook salmon embryo cells in bioreactor with low-serum medium[J]. Aquaculture, 2005, 249(1): 35-45. |
| 64 | 张芳, 张立, 易小萍, 等. 表达重组蛋白的CHO-GS细胞的无血清培养[J]. 高技术通讯, 2005, 15(7): 73-78. |
| ZHANG F, ZHANG L, YI X P, et al. Serum-free culture of CHO-GS cells for the production of recombinant protein[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2005, 15(7): 73-78. | |
| 65 | HUANG H, YI X P, ZHANG Y P. Improvement of Vero cell growth in glutamate-based culture by supplementing ammoniagenic compounds[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41(12): 2386-2392. |
| 66 | 滕小诺,易小萍,孙祥明,等. 表达乙型肝炎表面抗原的重组 CHO 细胞无血清培养基的优化及生物反应器培养[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2010, 23(10):1080-1083, 1086. |
| TENG X N, YI X P, SUN X M, et al. Optimization of serum-free medium for recombinant CHO cells expressing HBsAg and culture in bioreactor[J]. Chinese Journal of Biologicals, 2010, 23(10): 1080-1083, 1086. | |
| 67 | 张大鹤, 易小萍, 张元兴, 等. 适于重组CHO细胞培养的无血清培养基的制备[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2011, 24(10): 1152-1156. |
| ZHANG D H, YI X P, ZHANG Y X, et al. Preparation of serum-free medium suitable for culture of CHO cells[J].Chinese Journal of Biologicals, 2011, 24(10):1152-1156. | |
| 68 | MERCIER S M, DIEPENBROEK B, DALM M C F, et al. Multivariate data analysis as a PAT tool for early bioprocess development data[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2013, 167(3): 262-270. |
| 69 | 易小萍. 动物细胞培养过程PAT和在线生物检测技术[J]. 生物产业技术, 2018(1): 33-40. |
| YI X P. PAT and on-line biological detection technology for animal cell culture[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2018(1): 33-40. | |
| 70 | ZHAO L, FU H Y, ZHOU W C, et al. Advances in process monitoring tools for cell culture bioprocesses[J]. Engineering in Life ences, 2015, 15(5): 459-468. |
| 71 | RATHORE A S, WINKLE H. Quality by design for biopharmaceuticals[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 62(5): 380-390. |
| 72 | SOMMEREGGER W, SISSOLAK B, KANDRA K, et al. Quality by control: towards model predictive control of mammalian cell culture bioprocesses[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(7): 35-40. |
| 73 | JUNKER B H, WANG H Y. Bioprocess monitoring and computer control: key roots of the current PAT initiative[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 95(2): 226-261. |
| 74 | GOLD D, MOHAGHEGHI A, COONEY C L, et al. Single-cell protein production from spent sulfite liquor utilizing cell-recycle and computer monitoring[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1981, 23(9): 2105-2116. |
| 75 | 罗燕霞,黄明志,郭元昕,等. 活细胞传感仪在嗜酸乳酸杆菌培养过程中的应用[J].食品工业科技, 2012, 33(21): 152-155+159. |
| LUO Y X, HUANG M Z, GUO Y X, et al. The application of viable cell mass monitoring in Lactobacillus acidophilus cultivation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2012, 33(21): 152-155+159. | |
| 76 | LI J R, WANG Z J, GUO M J, et al. Rapid cryopreservation for iraitia grosvenorii cells based on cells' capacitance detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(5): 817-827. |
| 77 | 化磊召, 易小萍, 储炬, 等. 基于PAT的PCV2VLPs生产过程优化与控制研究[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2018, 38(8): 50-58. |
| HUA L Z, YI X P, CHU J, et al. Process control and optimization of PCV2 production of VLPs based on PAT[J]. China Biotechnology, 2018, 38(8): 50-58. | |
| 78 | SCARFF M, ARNOLD S A, HARVEY L M, et al. Near infrared spectroscopy for bioprocess monitoring and control: current status and future trends[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2006, 26(1): 17-39. |
| 79 | ARNOLD S A, CROWLEY J, WOODS N, et al. In-situ near infrared spectroscopy to monitor key analytes in mammalian cell cultivation[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2003, 84(1): 13-19. |
| 80 | MILLIGAN M, LEWIN N, COLEMAN D, et al. Semisynthetic model calibration for monitoring glucose in mammalian cell culture with in situ near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2014, 111(5): 896-903. |
| 81 | ABU A N, KENTY B M, CUELLAR M E, et al. Real time monitoring of multiple parameters in mammalian cell culture bioreactors using an in-line Raman spectroscopy probe[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2011, 108(5): 1215-1221. |
| 82 | MAES G. Handbook of Raman spectroscopy from the research laboratory to the process line[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Molecular & Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2001, 59(1): 211. |
| 83 | ESMONDE W, KAREN A, CUELLAR M, et al. Raman spectroscopy as a process analytical technology for pharmaceutical manufacturing and bioprocessing[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 409(3): 1-13. |
| 84 | BERRY B, MORETTO J, MATTHEWS T, et al. Cross-scale predictive modeling of CHO cell culture growth and metabolites using Raman spectroscopy and multivariate analysis[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2015, 31(2): 566-577. |
| 85 | EYSTER T, TALWAR S, FERNANDEZ J, et al. Tuning monoclonal antibody galactosylation using Raman spectroscopy-controlled lactic acid feeding[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2020, 45(2): 3085. |
| 86 | SURESH S, SRIVASTAVA V C, MISHRA I M. Techniques for oxygen transfer measurement in bioreactors: a review[J].Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2009, 84(8): 1091-1103. |
| 87 | ZHOU W C, REHM J, HU W S. High viable cell concentration fed-batch cultures of hybridoma cells through on-line nutrient feeding[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 2010, 46(6): 579-587. |
| 88 | PALIWAL S K, NADLER T K, WANG D I C, et al. Automated process monitoring of monoclonal antibody production[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1993, 65(23): 3363. |
| 89 | KURIBAYASHI R, HASHII N, HARAZONO A, et al. Rapid evaluation for heterogeneities in monoclonal antibodies by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with a column-switching system[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biomedical Analysis, 2012, 67(4): 1-9. |
| 90 | HARMON B J, GU X J, WANG D I C. Rapid monitoring of site-specific glycosylation microheterogeneity of recombinant human interferon-γ[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1996, 68(9): 1465-1473. |
| 91 | GU X J, BRYAN J H, WANG D I C. Site- and branch-specific sialylation of recombinant human interferon- in Chinese hamster ovary cell culture[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1997, 55(2): 390. |
| 92 | WALSH G. Biopharmaceutical benchmarks[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(9): 917-924. |
| 93 | LIN J, YI X P, ZHUANG Y P. Medium optimization based on comparative metabolomic analysis of chicken embryo fibroblast DF-1 cells[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(47): 27369-27377. |
| 94 | LIN J, YI X P, ZHUANG Y P. Coupling metabolomics analysis and DOE optimization strategy towards enhanced IBDV production by chicken embryo fibroblast DF-1 cells[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 307(10): 114-124. |
| 95 | XIE L Z, WANG D I C. Energy metabolism and ATP balance in animal cell cultivation using a stoichiometrically based reaction network[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 52(5): 591-601. |
| 96 | FOLLSTAD B D, WANG D I C, STEPHANOPOULOS G. Mitochondrial membrane potential selects hybridomas yielding high viability in fed-batch cultures[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2010, 18(1): 1-5. |
| 97 | FOLLSTAD B D, WANG D I C, STEPHANOPOULOS G. Mitochondrial membrane potential differentiates cells resistant to apoptosis in hybridoma cultures[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2010, 267(22): 6534-6540. |
| 98 | ZHANG F, SUN X M, YI X P, et al. Metabolic characteristics of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing glutamine synthetase in presence and absence of glutamine[J]. Cytotechnology, 2006, 51(1): 21. |
| 99 | 张芳, 易小萍, 孙祥明, 等. 重组CHO-GS细胞降低氨毒副作用的代谢研究[J]. 生物工程学报, 2006, 22(1): 94-100. |
| ZHANG F, YI X P, SUN X M, et al. Metabolism of recombinant CHO-GS cell reducing of toxic effect of ammonia[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2006, 22(1): 94-100. | |
| 100 | MEI J G, ZHUANG X D, ZHANG Y P, et al. Cell culture microcarrier and its application in the field of biomedicine[J]. Biotechnology, 2017, 27(5): 505-510. |
| 101 | LEVINE D W, WONG J S, WANG D I C, et al. Microcarrier cell culture: new methods for research-scale application[J]. Somatic Cell Genetics, 1977, 3(2): 149-155. |
| 102 | SMILEY A L, HU W S, WANG D I C. Production of human immune interferon by recombinant mammalian cells cultivated on microcarriers[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1989, 33(9): 1182-1190. |
| 103 | 贾涵婧, 王逸群, 黄锭, 等. 微载体浓度与细胞接种密度对MDCK细胞生长的影响[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2014, 27(9): 1138-1144. |
| JIA H J, WANG Y Q, HUANG D, et al. Effect of microcarrier concentration and cell density on growth of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Biologicals, 2014, 27(9): 1138-1144. | |
| 104 | HU W S, WANG D I C. Selection of microcarrier diameter for the cultivation of mammalian cells on microcarriers[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering, 1987, 30(4): 548-557. |
| 105 | 陈以恒,陶姝宇,刘旭平,等. 微载体浓度与细胞接种密度对ST细胞生长的影响[J].生物技术通报,2016,32(3):242-250. |
| CHEN Y H, TAO S Y, LIU X P, et al. The effects of microcarrier concentration and cell density on the growth of swine testicle cells[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(3): 242-250. | |
| 106 | CROUGHAN M S, HAMEL J F P, WANG D I C. Effects of microcarrier concentration in animal cell culture[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 32(8): 975-982. |
| 107 | CROUGHAN M S, WANG D I C. Reversible removal and hydrodynamic phenomena in CHO microcarrier cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1990, 36(3): 316-319. |
| 108 | CROUGHAN M S, J-F HAMEL, WANG D I C. Hydrodynamic effects on animal cells grown in microcarrier cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 95(2): 295-305. |
| 109 | CROUGHAN M S, SAYRE E S, WANG D I C. Viscous reduction of turbulent damage in animal cell culture[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1989, 33(7): 862-872. |
| 110 | 谭文松, 陈志宏. 血清和Pouronic F68对悬浮培养杂交瘤细胞的保护作用[J]. 华东理工大学学报, 1996, 22(6): 695-700. |
| TAN W S, CHEN Z H. Protective mechanism of serum and pluronic F68 on hybridoma cells in suspended cultures[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 1996, 22(6): 695-700. | |
| 111 | 夏建业, 田锡炜, 刘娟, 等. 人工智能时代的智能生物制造[J]. 生物加工过程, 2020, 18(1):13-20. |
| XIA J Y, TIAN X W, LIU J, et al. Intelligent biological manufacturing in the age of artificial intelligence[J].Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2020, 18(1): 13-20. | |
| 112 | 张嗣良, 潘杭琳, 黄明志,等. 生物过程大数据分析与智能化[J]. 生物产业技术, 2018(1): 87-94. |
| ZHANG S L, PAN H L, HUANG M Z, et al. Big data and intelligentialized method for industrial bioprocess[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2018(1): 87-94. | |
| 113 | 田锡炜, 王冠, 张嗣良, 等. 工业生物过程智能控制原理和方法进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 2014-2024. |
| TIAN X W, WANG G, ZHANG S L, et al. Progress in intelligent control of industrial bioprocess[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 2014-2024. | |
| 114 | 张嗣良. 大数据时代的生物过程研究与智能生物反应器制造[C]// 宜昌:工业生物过程优化与控制研讨会, 2016: 33-41 |
| ZHANG S L.Biological process research and smart bioreactor manufacturing in the era of big data[C]// Yichang:Industrial Bioprocess Optimization and Control Seminar, 2016: 33-41. | |
| 115 | 龚迪,易小萍,张元兴. MDCK细胞微载体悬浮培养放大工艺研究[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2012, 32(9): 55-60. |
| GONG D, YI X P, ZHANG Y X. A study on scale-up process for microcarrier cultue of MDCK cells using low serum medium[J].China Biotechnology, 2012, 32(9): 55-60. | |
| 116 | 周济. 智能制造——"中国制造2025"的主攻方向[J]. 中国机械工程, 2015, 11(17): 2273-2284. |
| ZHOU J. Intelligent manufacturing-the main direction of "Made in China 2025"[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 11(17): 2273-2284. | |
| 117 | LI M, QIU Y X. A review on current downstream bio-processing technology of vaccine products[J]. Vaccine, 2013, 31(9): 1264-1267. |
| 118 | 王泽建, 王萍, 张琴, 等. 微生物发酵过程生理参数检测传感器技术与过程优化[J]. 生物产业技术, 2018(1): 19-32. |
| WANG Z J, WANG P, ZHANG Q, et al. Principle and application of physiological parameters detection biosensor technology in microbial fermentation process optimization[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2018(1): 19-32. |
| [1] | 吉博涛, 钱志刚, 夏小霞. 无细胞合成策略在生物材料研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 658-675. |
| [2] | 谢良志. 生物药产业蓬勃发展早期的奠基性系统开发——缅怀王义翘教授的开创性研究和成就[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 482-496. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
