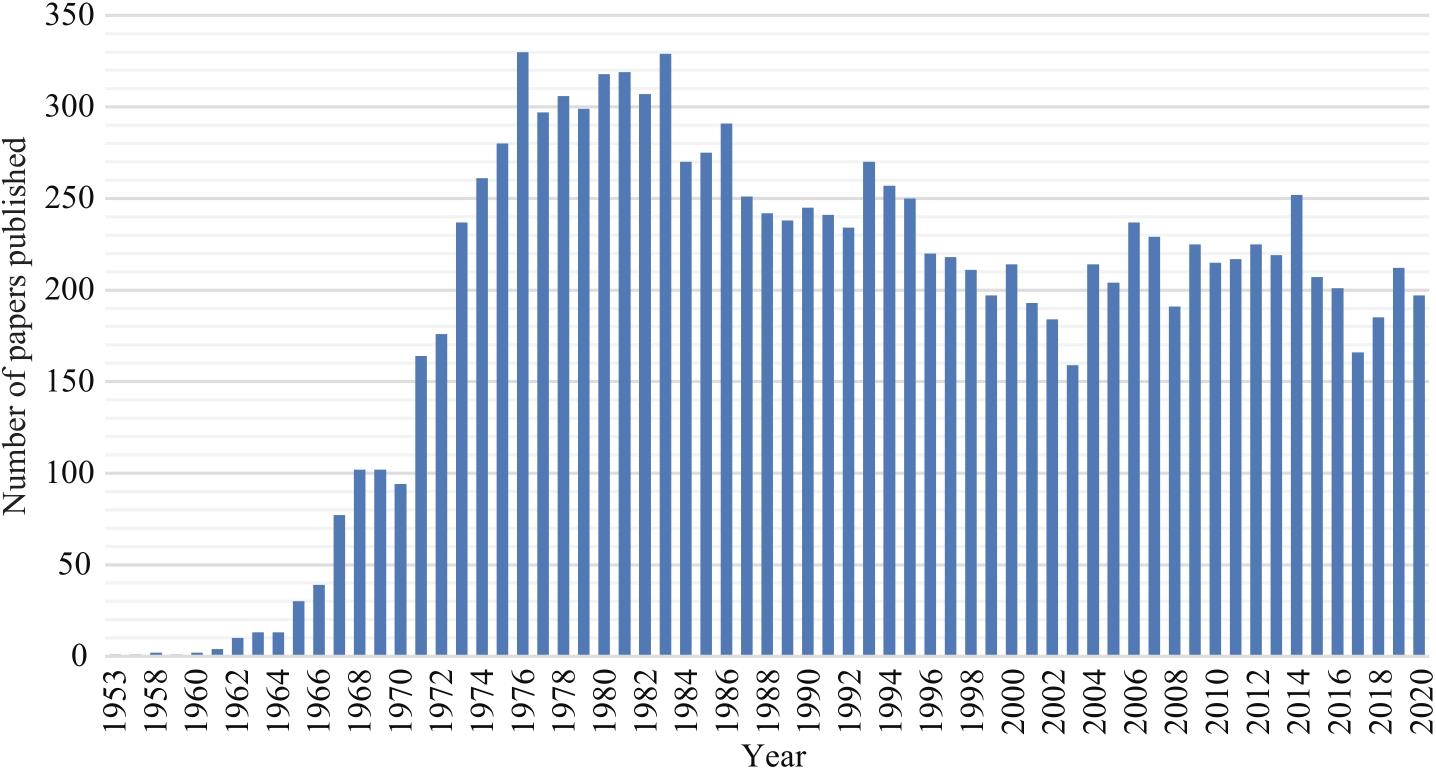
合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (3): 465-486.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-064
无细胞蛋白质合成:从基础研究到工程应用
后佳琦1,2, 姜楠1,2, 马莲菊2, 卢元1
- 1.清华大学化学工程系,北京 100084
2.沈阳师范大学生命科学学院,辽宁 沈阳 110034
-
收稿日期:2021-06-06修回日期:2021-09-21出版日期:2022-06-30发布日期:2022-07-13 -
通讯作者:马莲菊,卢元 -
作者简介:后佳琦 (1994—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为无细胞生物合成。 E-mail:2580070932@qq.com姜楠 (1995—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为无细胞生物合成。 E-mail:1023796982@qq.com马莲菊 (1969—),女,教授,硕士生导师。研究方向为资源与应用微生物学等。 E-mail:malianju@163.com卢元 (1983—),男,副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学、生物大分子工程等。 E-mail:yuanlu@tsinghua.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(21878173);北京市自然科学基金(2192023);国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0901700);清华大学实验室创新基金
Cell-free protein synthesis: from basic research to engineering applications
HOU Jiaqi1,2, JIANG Nan1,2, MA Lianju2, LU Yuan1
- 1.Department of Chemical Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
2.College of Life Sciences,Shenyang Normal University,Shenyang 110034,Liaoning,China
-
Received:2021-06-06Revised:2021-09-21Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-07-13 -
Contact:MA Lianju, LU Yuan
摘要:
无细胞蛋白质合成是无细胞合成生物学的技术核心,亦被称为体外蛋白质翻译,是一种用于补充基于细胞的蛋白质表达的技术。无细胞蛋白质合成系统无需完整的活细胞就可以在体外受控环境中模拟整个细胞的转录和翻译过程,并允许对单个成分和反应网络进行详细深入的研究。因此,无细胞蛋白质合成作为一种平台技术,有望克服当前胞内生产系统中因为细胞膜约束带来的表达局限性,在基础科学研究和应用科学研究中具有广阔的前景。无细胞系统操作简单、便于控制,相对于体内蛋白质表达,其优势还包括其开放特性、消除对活细胞的依赖以及将所有系统物质能量集中在目标蛋白质生产上。本文首先概述了无细胞蛋白质合成系统的组成及基于不同组件类型的无细胞蛋白质合成系统的发展,包括以不同生物提取物为基础的系统以及使用重组元素的蛋白质合成体系。之后介绍了以分批反应、连续交换为代表的无细胞蛋白质合成系统的不同反应模式,阐述了无细胞在基因电路、蛋白质工程和人工“生命体系”构建中的应用和研究进展。其中,基因电路主要概述了无细胞技术在原型设计、生物传感、代谢工程三个方面的最新应用;蛋白质工程依次罗列了无细胞技术在膜蛋白、类病毒颗粒、翻译后修饰、非天然氨基酸嵌入以及蛋白质进化等方面的应用拓展;在人工“生命体系”构建中,噬菌体的合成和人工细胞的构筑开辟了新的前沿领域。最后文章分析了无细胞蛋白质合成系统在未来进一步的科学研究和工业化应用中面临的机遇和挑战。
中图分类号:
引用本文
后佳琦, 姜楠, 马莲菊, 卢元. 无细胞蛋白质合成:从基础研究到工程应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 465-486.
HOU Jiaqi, JIANG Nan, MA Lianju, LU Yuan. Cell-free protein synthesis: from basic research to engineering applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 465-486.
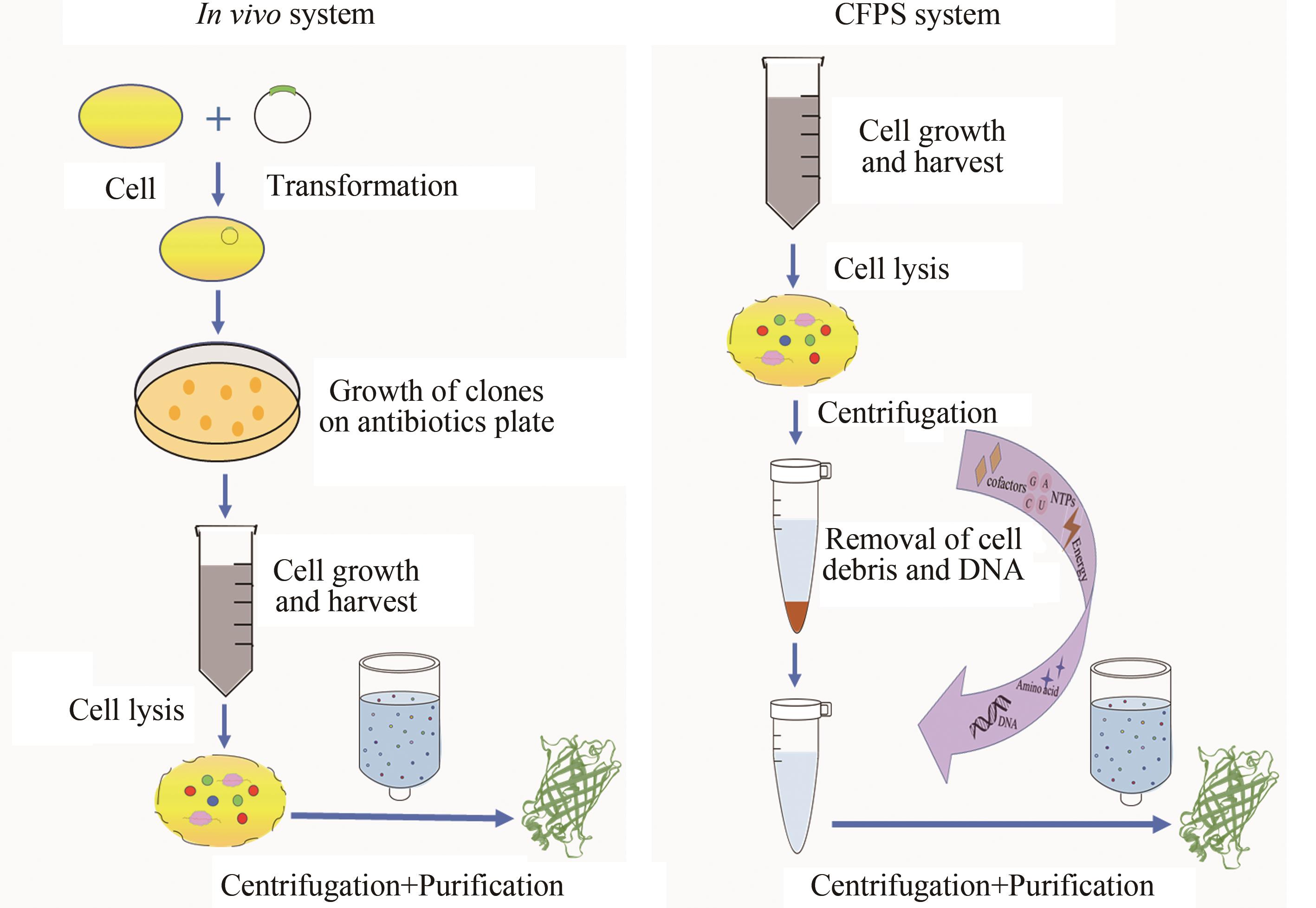
图2 体内细胞和体外无细胞蛋白质合成比较(在体内细胞系统,目的质粒导入细胞,通过培养、裂解和离心纯化获得目的蛋白。在CFPS系统中,通过向细胞提取物中添加DNA模板、氨基酸、NTPs、能量底物等辅助因子,离心纯化后获得目的蛋白)
Fig. 2 Comparison of protein synthesis through in vivo cellular and in vitro cell-free systems(In the in vivo cellular system, the target plasmid is introduced into the cell, and the target protein is obtained through cell culture, lysis, and product purification. In the CFPS system, by adding DNA template, amino acids, NTPs, energy substrates and other cofactors to the cell extract, the target protein is obtained after centrifugation and purification.)
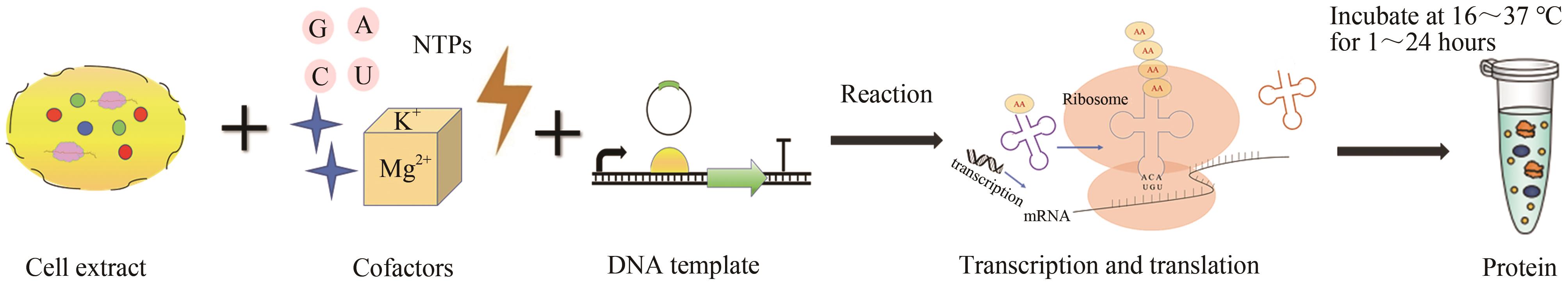
图3 无细胞蛋白质合成过程(无细胞体系的成分包括细胞提取物、辅助因子、DNA模板等,通过细胞提取物中的转录翻译机器,无细胞体系在一定条件下孵育几个小时即可产生目的蛋白)
Fig.3 Cell-free protein synthesis process(The components of the cell-free system include cell extracts, cofactors, DNA templates, etc. Through the transcription and translation machinery in the cell extracts, the cell-free system can produce the target protein after incubating for several hours under designated conditions.)
| 细胞提取物类型 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌细胞 | 生长速度快、易于培养、产量高、成本效益高 | 在翻译后修饰、膜蛋白合成和其他难以合成的蛋白质合成方面存在局限性 |
| 酿酒酵母细胞 | 易于培养、可用于研究真核生物的转录翻译机制 | 蛋白质产量低,未显示充分的翻译后修饰 |
| 小麦胚芽细胞 | 蛋白质可溶性增强、可表达毒性蛋白质、产量高 | 需要去除各种抑制酶,操作流程较繁琐,合成复杂蛋白、进行翻译后修饰具有局限性 |
| 烟草细胞 | 有利于合成翻译后修饰蛋白质,还有助于糖基化和二硫 键形成,相对其他真核平台耗时短 | 蛋白质产量一般,未显示充分的翻译后修饰 |
| 兔网织红细胞 | 具有翻译后修饰功能,可表达膜蛋白、毒性蛋白 | 蛋白质产量低,耗时长 |
| 中国仓鼠卵巢细胞 | 具有翻译后修饰功能,可表达膜蛋白、毒性蛋白 | 蛋白质产量较低 |
| 昆虫细胞 | 具有翻译后修饰功能,可表达膜蛋白、冰结构蛋白 | 蛋白质产量较低,无细胞体系中需要更多的提取物 |
| PURE | 组分纯化后无核酸酶或蛋白酶残留,灵活和模块化 | 成本较高,不能激活内源性代谢 |
表1 不同提取物体系优缺点对比
Tab. 1 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of different extract systems
| 细胞提取物类型 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌细胞 | 生长速度快、易于培养、产量高、成本效益高 | 在翻译后修饰、膜蛋白合成和其他难以合成的蛋白质合成方面存在局限性 |
| 酿酒酵母细胞 | 易于培养、可用于研究真核生物的转录翻译机制 | 蛋白质产量低,未显示充分的翻译后修饰 |
| 小麦胚芽细胞 | 蛋白质可溶性增强、可表达毒性蛋白质、产量高 | 需要去除各种抑制酶,操作流程较繁琐,合成复杂蛋白、进行翻译后修饰具有局限性 |
| 烟草细胞 | 有利于合成翻译后修饰蛋白质,还有助于糖基化和二硫 键形成,相对其他真核平台耗时短 | 蛋白质产量一般,未显示充分的翻译后修饰 |
| 兔网织红细胞 | 具有翻译后修饰功能,可表达膜蛋白、毒性蛋白 | 蛋白质产量低,耗时长 |
| 中国仓鼠卵巢细胞 | 具有翻译后修饰功能,可表达膜蛋白、毒性蛋白 | 蛋白质产量较低 |
| 昆虫细胞 | 具有翻译后修饰功能,可表达膜蛋白、冰结构蛋白 | 蛋白质产量较低,无细胞体系中需要更多的提取物 |
| PURE | 组分纯化后无核酸酶或蛋白酶残留,灵活和模块化 | 成本较高,不能激活内源性代谢 |

图4 CFPS反应模式(a)批式模式。所有反应成分添加到一个管中进行,操作简单、便捷。(b)连续交换。 通过半透膜,营养物质和产生的代谢副产物分隔开,克服了代谢产物对体系的抑制作用。(c)套管。气体通过气泵不断地泵入到内管中,显著提高氧的传递效率,提高产量。(d)数字微流控。数字微流控技术可控制单个液滴的移动、混合、分离等,具有良好的交互性和灵活性
Fig. 4 Modes for CFPS operation(a) Batch mode. All reaction components are added to one tube, which is simple and convenient for operating. (b) Continuous exchange. Through the semi-permeable membrane, nutrients are separated from the metabolic by-products, which overcomes the inhibitory effect of the metabolic products on the reaction. (c) Tube in tube. The gas is continuously pumped into the inner tube through the air pump, which significantly improves the efficiency of oxygen transfer and increases the output. (d) Digital microfluidic technology. It can control the movement, mixing, and separation of a single droplet, with good interactivity and flexibility.

图5 基因电路原型设计(转录单位由单独质粒或线性DNA模板进行编码,可以作为逻辑门的类似物,然后通过无细胞基因表达反应在体外执行分子计算或遗传程序,以预测电路在电路在细胞中的功能)
Fig. 5 Prototype designs for genetic circuits(The transcription unit is encoded by a single plasmid or linear DNA template, which can be used as an analog of a logic gate, and then molecular calculations or genetic programs are performed in vitro through a cell-free gene expression reaction to predict the function of the circuit in the cell.)
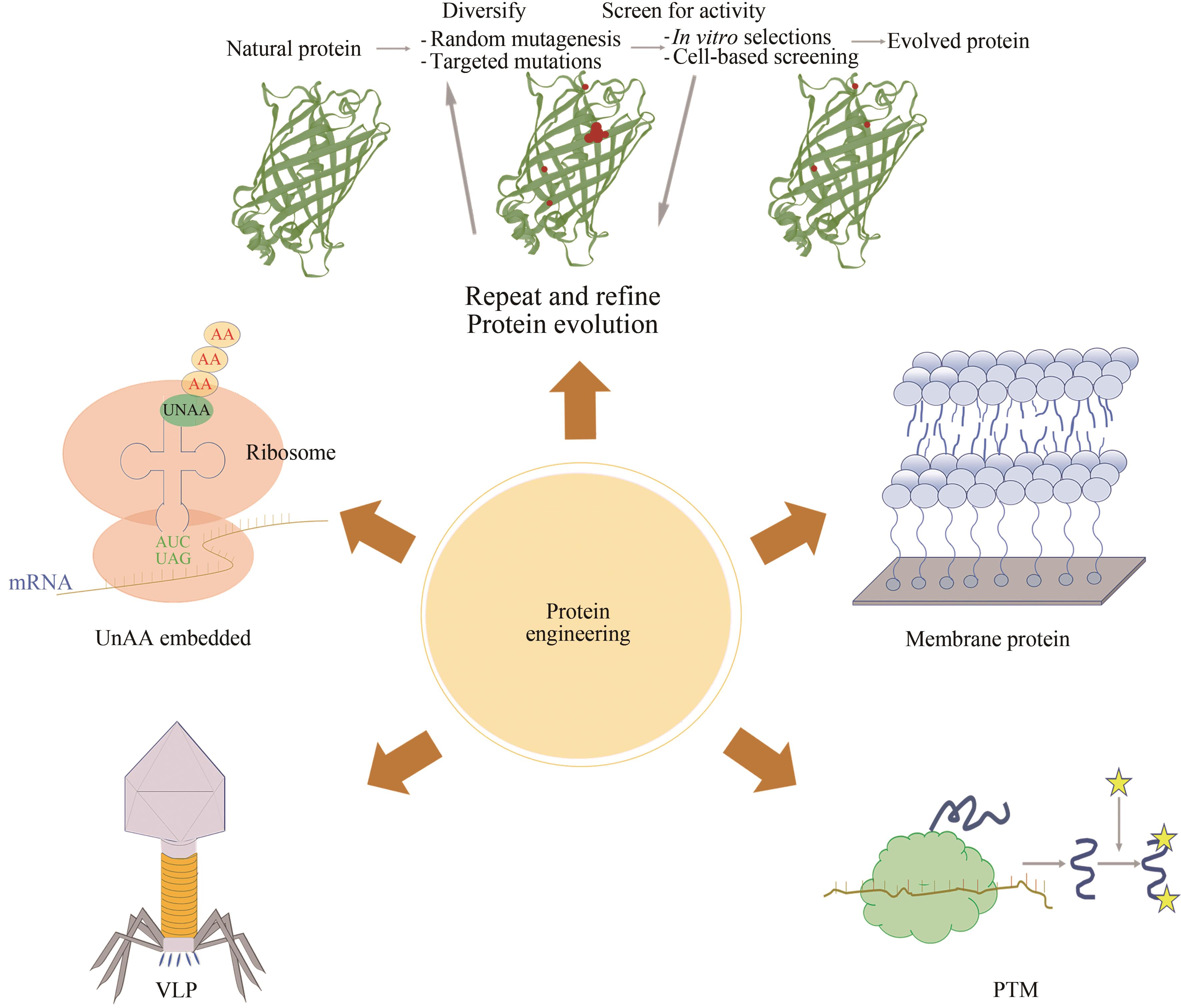
图6 无细胞蛋白质工程的应用(无细胞蛋白质工程的应用主要包括:膜蛋白、类病毒颗粒、翻译后修饰、非天然氨基酸的嵌入和蛋白质进化)
Fig. 6 Applications of cell-free protein engineering(The applications of cell-free protein engineering mainly include membrane proteins, virus-like particles, post-translational modification, unnatural amino acid intercalation, and protein evolution)
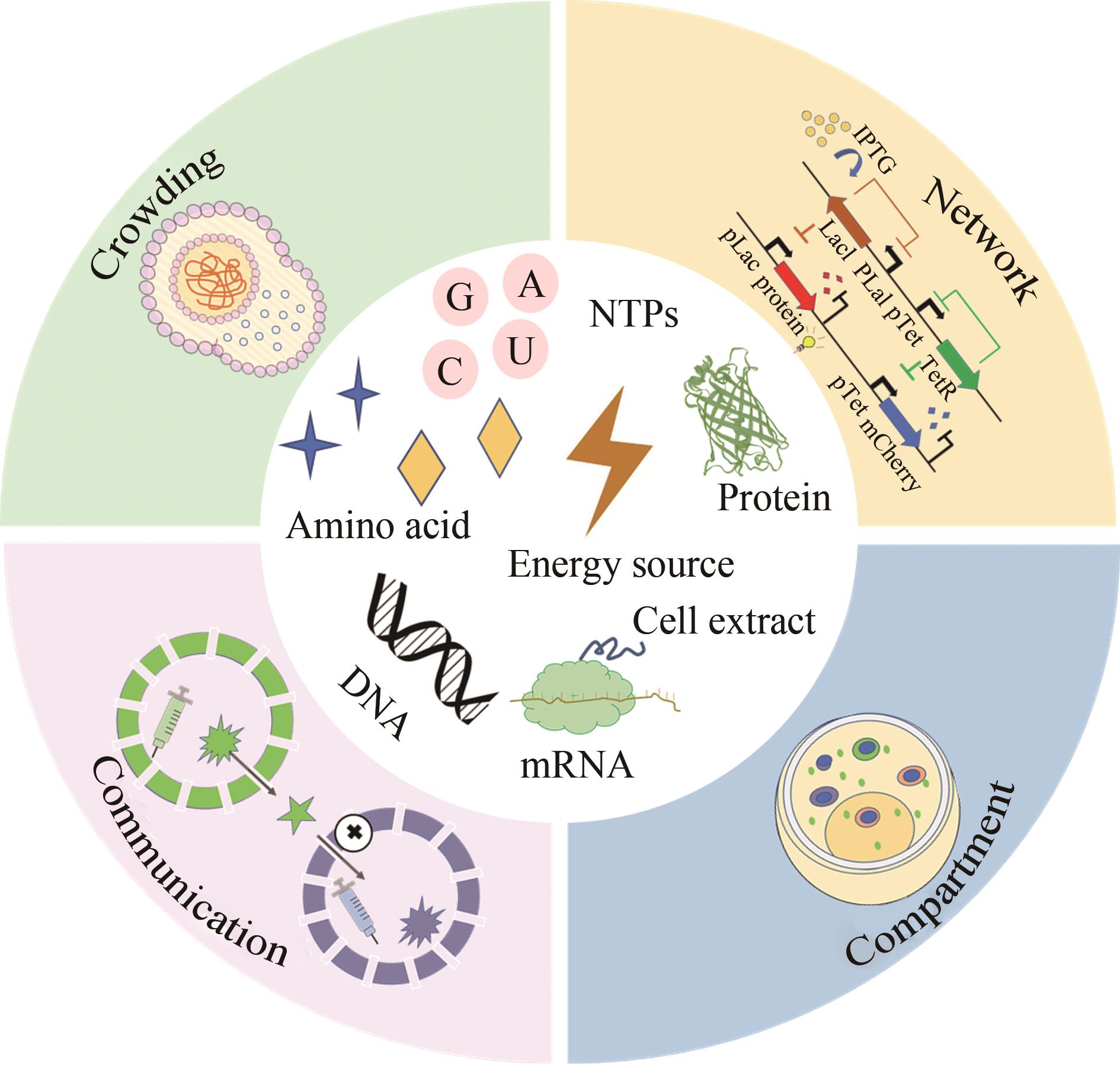
图7 人工细胞的构建(分子拥挤、区室化、基因噪声、网络、动态行为和细胞通讯是维持一个细胞正常生命活动所必须的结构和功能特征,能有效调控操作细胞的正常运行)
Fig. 7 Construction of artificial cells(Molecular crowding, compartmentalization, gene noise, networks, dynamic behaviors and cell communications are the structural and functional characteristics necessary to maintain the normal life activities of a cell, which can effectively regulate and operate the cell)
| 70 | ISKAKOVA M B, SZAFLARSKI W, DREYFUS M, et al. Troubleshooting coupled in vitro transcription-translation system derived from Escherichia coli cells: synthesis of high-yield fully active proteins[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, 34(19): e135. |
| 71 | SMITH M T, BERKHEIMER S D, WERNER C J, et al. Lyophilized Escherichia coli-based cell-free systems for robust, high-density, long-term storage[J]. BioTechniques, 2014, 56(4): 186-193. |
| 72 | HUNT J P, YANG S O, WILDING K M, et al. The growing impact of lyophilized cell-free protein expression systems[J]. Bioengineered, 2017, 8(4): 325-330. |
| 73 | XIA P F, LING H, FOO J L, et al. Synthetic genetic circuits for programmable biological functionalities[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(6): 107393. |
| 74 | GUO S B, YEUNG E, MURRAY R M. Implementation and system identification of a phosphorylation-based insulator in a cell-free transcription-translation system[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, . |
| 75 | WESTBROOK A, TANG X, MARSHALL R, et al. Distinct timescales of RNA regulators enable the construction of a genetic pulse generator[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(5): 1139-1151. |
| 76 | NIEDERHOLTMEYER H, STEPANOVA V, MAERKL S J. Implementation of cell-free biological networks at steady state[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(40): 15985-15990. |
| 77 | NIEDERHOLTMEYER H, SUN Z Z, HORI Y, et al. Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators[J]. eLife, 2015, 4: e09771. |
| 78 | TURNER A P F. Biosensor: sense and sensibility[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(8): 3184-3196. |
| 79 | ZHU C Z, YANG G H, LI H, et al. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(1): 230-249. |
| 80 | LAFLEUR J P, JÖNSSON A, SENKBEIL S, et al. Recent advances in lab-on-a-chip for biosensing applications[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, 76: 213-233. |
| 81 | WEN K Y, CAMERON L, CHAPPELL J, et al. A cell-free biosensor for detecting quorum sensing molecules in P. aeruginosa-infected respiratory samples[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(12): 2293-2301. |
| 1 | 张媛媛, 曾艳, 王钦宏. 合成生物制造进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 145-160. |
| ZHANG Y Y, ZENG Y, WANG Q H. Advances in synthetic biomanufacturing[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 145-160. | |
| 2 | WAY J C, COLLINS J J, KEASLING J D, et al. Integrating biological redesign: where synthetic biology came from and where it needs to go[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(1): 151-161. |
| 3 | CARLSON E D, GAN R, HODGMAN C E, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis: applications come of age[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(5): 1185-1194. |
| 4 | NIRENBERG M W, MATTHAEI J H. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1961, 47(10): 1588-1602. |
| 5 | KATZEN F, CHANG G, KUDLICKI W. The past, present and future of cell-free protein synthesis[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2005, 23(3): 150-156. |
| 6 | RANJI A, WU J C, BUNDY B C, et al. Transforming synthetic biology with cell-free systems[M]//Synthetic Biology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013: 277-301. |
| 7 | SCHINN S M, BROADBENT A, BRADLEY W T, et al. Protein synthesis directly from PCR: progress and applications of cell-free protein synthesis with linear DNA[J]. New Biotechnology, 2016, 33(4): 480-487. |
| 8 | GREGORIO N E, LEVINE M Z, OZA J P. A user's guide to cell-free protein synthesis[J]. Methods and Protocols, 2019, 2(1): 24. |
| 9 | SHIMIZU Y, INOUE A, TOMARI Y, et al. Cell-free translation reconstituted with purified components[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2001, 19(8): 751-755. |
| 10 | MATSUBAYASHI H, UEDA T. Purified cell-free systems as standard parts for synthetic biology[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2014, 22: 158-162. |
| 11 | 张建志, 付立豪, 唐婷, 等. 基于合成生物学策略的酶蛋白元件规模化挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 319-336. |
| 82 | PELLINEN T, HUOVINEN T, KARP M. A cell-free biosensor for the detection of transcriptional inducers using firefly luciferase as a reporter[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2004, 330(1): 52-57. |
| 83 | ZHANG P, YANG J Z, CHO E, et al. Bringing light into cell-free expression[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(8): 2144-2153. |
| 84 | JIANG L, ZHAO J, LIAN J, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis enabled rapid prototyping for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2018, 3(2):90-96. |
| 85 | ZHUANG L, HUANG S H, LIU W Q, et al. Total in vitro biosynthesis of the nonribosomal macrolactone peptide valinomycin[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 60: 37-44. |
| 86 | 张鹏, 林骏, 卢元. 无细胞蛋白质合成的研究进展[J]. 生物加工过程, 2018, 16(1): 59-66. |
| ZHANG P, LIN J, LU Y. Advances in cell-free protein synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2018, 16(1): 59-66. | |
| 87 | JEWETT M C, CALHOUN K A, VOLOSHIN A, et al. An integrated cell-free metabolic platform for protein production and synthetic biology[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4: 220. |
| 88 | CASCHERA F, NOIREAUX V. Synthesis of 2.3 mg/mL of protein with an all Escherichia coli cell-free transcription-translation system[J]. Biochimie, 2014, 99: 162-168. |
| 89 | KARIM A S, JEWETT M C. A cell-free framework for rapid biosynthetic pathway prototyping and enzyme discovery[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 36: 116-126. |
| 90 | SHELBY M L, HE W, DANG A T, et al. Cell-free co-translational approaches for producing mammalian receptors: expanding the cell-free expression toolbox using nanolipoproteins[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2019, 10: 744. |
| 91 | TRIBET C, AUDEBERT R, POPOT J L. Amphipols: polymers that keep membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1996, 93(26): 15047-15050. |
| 92 | RITCHIE T K, GRINKOVA Y V, BAYBURT T H, et al. Chapter 11-Reconstitution of membrane proteins in phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2009, 464: 211-231. |
| 93 | ZEMELLA A, THORING L, HOFFMEISTER C, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis: pros and cons of prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems[J]. Chembiochem: a European Journal of Chemical Biology, 2015, 16(17): 2420-2431. |
| 94 | GAO T J, BLANCHETTE C D, HE W, et al. Characterizing diffusion dynamics of a membrane protein associated with nanolipoproteins using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy[J]. Protein Science, 2011, 20(2): 437-447. |
| 95 | GAO T J, PETRLOVA J, HE W, et al. Characterization of de novo synthesized GPCRs supported in nanolipoprotein discs[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e44911. |
| 96 | QUINN S, SRINIVASAN S, GORDON J B, et al. Single-molecule fluorescence detection of the epidermal growth factor receptor in membrane discs[J]. Biochemistry, 2019, 58(4): 286-294. |
| 97 | LU Y, CHAN W, KO B Y, et al. Assessing sequence plasticity of a virus-like nanoparticle by evolution toward a versatile scaffold for vaccines and drug delivery[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(40): 12360-12365. |
| 98 | PATTENDEN L K, MIDDELBERG A P J, NIEBERT M, et al. Towards the preparative and large-scale precision manufacture of virus-like particles[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2005, 23(10): 523-529. |
| 99 | ROHOVIE M J, NAGASAWA M, SWARTZ J R. Virus-like particles: next-generation nanoparticles for targeted therapeutic delivery[J]. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 2017, 2(1): 43-57. |
| 100 | SMITH M T, HAWES A K, BUNDY B C. Reengineering viruses and virus-like particles through chemical functionalization strategies[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2013, 24(4): 620-626. |
| 101 | LUDGATE L, LIU K C, LUCKENBAUGH L, et al. Cell-free hepatitis B virus capsid assembly dependent on the core protein C-terminal domain and regulated by phosphorylation[J]. Journal of Virology, 2016, 90(12): 5830-5844. |
| 102 | WANG X, LIU J, ZHENG Y, et al. An optimized yeast cell-free system: sufficient for translation of human papillomavirus 58 L1 mRNA and assembly of virus-like particles[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2008, 106(1): 8-15. |
| 103 | SPEARMAN P, RATNER L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid formation in reticulocyte lysates[J]. Journal of Virology, 1996, 70(11): 8187-8194. |
| 104 | RUSTAD M, EASTLUND A, JARDINE P, et al. Cell-free TXTL synthesis of infectious bacteriophage T4 in a single test tube reaction[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2018, 3(1): ysy002. |
| 11 | ZHANG J Z, FU L H, TANG T, et al. Scalable mining of proteins for biocatalysis via synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 319-336. |
| 12 | KWON Y C, JEWETT M C. High-throughput preparation methods of crude extract for robust cell-free protein synthesis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8663. |
| 13 | SITARAMAN K, ESPOSITO D, KLARMANN G, et al. A novel cell-free protein synthesis system[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2004, 110(3): 257-263. |
| 14 | KARIG D K, BESSLING S, THIELEN P, et al. Preservation of protein expression systems at elevated temperatures for portable therapeutic production[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2017, 14(129): 20161039. |
| 15 | PARDEE K. Perspective: Solidifying the impact of cell-free synthetic biology through lyophilization[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 138: 91-97. |
| 16 | CHEN X J, SUN Q, LU Y. Creating a locally crowded environment with nanoclay hydrogels for cell-free biosynthesis[J]. Soft Matter, 2020, 16(22): 5132-5138. |
| 17 | GAO W, BU N, LU Y. Efficient incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins with a robust cell-free system[J]. Methods and Protocols, 2019, 2(1): 16. |
| 18 | JIANG N, DING X W, LU Y. Development of a robust Escherichia coli-based cell-free protein synthesis application platform[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 165: 107830. |
| 19 | 李祎, 林振泉, 刘子鹤. 酿酒酵母适应性实验室进化工具的最新进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 287-301. |
| LI Y, LIN Z Q, LIU Z H. Advances in yeast based adaptive laboratory evolution[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 287-301. | |
| 20 | SISSONS C H. Yeast protein synthesis. Preparation and analysis of a highly active cell-free system[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 1974, 144(1): 131-140. |
| 21 | HARTLEY A D, SANTOS M A, COLTHURST D R, et al. Preparation and use of yeast cell-free translation lysate[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1996, 53: 249-257. |
| 105 | LOTHROP A P, TORRES M P, FUCHS S M. Deciphering post-translational modification codes[J]. FEBS Letters, 2013, 587(8): 1247-1257. |
| 106 | HERSHEWE J, KIGHTLINGER W, JEWETT M C. Cell-free systems for accelerating glycoprotein expression and biomanufacturing[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 47(11): 977-991. |
| 107 | KIGHTLINGER W, DUNCKER K E, RAMESH A, et al. A cell-free biosynthesis platform for modular construction of protein glycosylation pathways[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5404. |
| 108 | MARTIN R W, DES SOYE B J, KWON Y C, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis from genomically recoded bacteria enables multisite incorporation of noncanonical amino acids[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1203. |
| 109 | OZA J P, AERNI H R, PIRMAN N L, et al. Robust production of recombinant phosphoproteins using cell-free protein synthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8168. |
| 110 | PARK H S, HOHN M J, UMEHARA T, et al. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli with phosphoserine[J]. Science, 2011, 333(6046): 1151-1154. |
| 111 | SILVERMAN A D, KARIM A S, JEWETT M C. Cell-free gene expression: an expanded repertoire of applications[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2020, 21(3): 151-170. |
| 112 | DALLEY J A, BULLEID N J. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) translocon can differentiate between hydrophobic sequences allowing signals for glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor addition to be fully translocated into the ER lumen[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(51): 51749-51757. |
| 113 | SUZUKI T, MORIYA K, NAGATOSHI K, et al. Strategy for comprehensive identification of human N-myristoylated proteins using an insect cell-free protein synthesis system[J]. Proteomics, 2010, 10(9): 1780-1793. |
| 114 | SMOLSKAYA S, LOGASHINA Y A, ANDREEV Y A. Escherichia coli extract-based cell-free expression system as an alternative for difficult-to-obtain protein biosynthesis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 928. |
| 115 | YIN G, SWARTZ J R. Enhancing multiple disulfide bonded protein folding in a cell-free system[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2004, 86(2): 188-195. |
| 116 | KIM D M, SWARTZ J R. Efficient production of a bioactive, multiple disulfide-bonded protein using modified extracts of Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2004, 85(2): 122-129. |
| 22 | KAUFMAN R J. Regulation of mRNA translation by protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2004, 29(3): 152-158. |
| 23 | TUITE M F, PLESSET J. mRNA-dependent yeast cell-free translation systems: Theory and practice[J]. Yeast, 1986, 2(1): 35-52. |
| 24 | ANDERSON M J, STARK J C, HODGMAN C E, et al. Energizing eukaryotic cell-free protein synthesis with glucose metabolism[J]. FEBS Letters, 2015, 589(15): 1723-1727. |
| 25 | WANG X, LIU J, ZHENG Y, et al. An optimized yeast cell-free system: Sufficient for translation of human papillomavirus 58 L1 mRNA and assembly of virus-like particles[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2008, 106(1): 8-15. |
| 26 | SULLIVAN C J, PENDLETON E D, SASMOR H H, et al. A cell-free expression and purification process for rapid production of protein biologics[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 11(2): 238-248. |
| 27 | WANG H, LI J, JEWETT M C. Development of a Pseudomonas putida cell-free protein synthesis platform for rapid screening of gene regulatory elements[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2018, 3(1): ysy003. |
| 28 | MOORE S J, MACDONALD J T, WIENECKE S, et al. Rapid acquisition and model-based analysis of cell-free transcription-translation reactions from nonmodel bacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(19): E4340-E4349. |
| 29 | KELWICK R, WEBB A J, MACDONALD J T, et al. Development of a Bacillus subtilis cell-free transcription-translation system for prototyping regulatory elements[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 370-381. |
| 30 | AHMAD M, HIRZ M, PICHLER H, et al. Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(12): 5301-5317. |
| 31 | AW R, POLIZZI K M. Biosensor-assisted engineering of a high-yield Pichia pastoris cell-free protein synthesis platform[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(3): 656-666. |
| 32 | MARCUS A, FEELEY J. Activation of protein synthesis in the imbibition phase of seed germination[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1964, 51(6): 1075-1079. |
| 33 | ROBERTS B E, PATERSON B M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1973, 70(8): 2330-2334. |
| 117 | RYABOVA L A, DESPLANCQ D, SPIRIN A S, et al. Functional antibody production using cell-free translation: effects of protein disulfide isomerase and chaperones[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1997, 15(1): 79-84. |
| 118 | JIANG X P, OOKUBO Y, FUJII I, et al. Expression of Fab fragment of catalytic antibody 6D9 in an Escherichia coli in vitro coupled transcription/translation system[J]. FEBS Letters, 2002, 514(2/3): 290-294. |
| 119 | MURAKAMI S, MATSUMOTO R, KANAMORI T. Constructive approach for synthesis of a functional IgG using a reconstituted cell-free protein synthesis system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 671. |
| 120 | BUNDY B C, SWARTZ J R. Efficient disulfide bond formation in virus-like particles[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2011, 154(4): 230-239. |
| 121 | CHEN H Q, XU Z N, XU N Z, et al. Efficient production of a soluble fusion protein containing human beta-defensin-2 in E. coli cell-free system[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2005, 115(3): 307-315. |
| 122 | GAO W, CHO E, LIU Y Y, et al. Advances and challenges in cell-free incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2019, 10: 611. |
| 123 | 王清, 陈依军. 天然产物成药性的合成生物学改良[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 583-592. |
| WANG Q, CHEN Y J. Synthetic biology approaches to improve druggability of natural products[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 583-592. | |
| 124 | MUKAI T, LAJOIE M J, ENGLERT M, et al. Rewriting the genetic code[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2017, 71: 557-577. |
| 125 | 丁明珠, 李炳志, 王颖, 等. 合成生物学重要研究方向进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| DING M Z, LI B Z, WANG Y, et al. Significant research progress in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. | |
| 126 | HONG S H, KWON Y C, JEWETT M C. Non-standard amino acid incorporation into proteins using Escherichia coli cell-free protein synthesis[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2014, 2: 34. |
| 127 | LU Y. Cell-free synthetic biology: Engineering in an open world[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2(1): 23-27. |
| 128 | CHIN J W. Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code of cells and animals[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2014, 83: 379-408. |
| 129 | NEUMANN H, WANG K H, DAVIS L, et al. Encoding multiple unnatural amino acids via evolution of a quadruplet-decoding ribosome[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7287): 441-444. |
| 130 | ZHANG Y, PTACIN J L, FISCHER E C, et al. A semi-synthetic organism that stores and retrieves increased genetic information[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7682): 644-647. |
| 131 | AXUP J Y, BAJJURI K M, RITLAND M, et al. Synthesis of site-specific antibody-drug conjugates using unnatural amino acids[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(40): 16101-16106. |
| 132 | QUAST R B, BALLION B, STECH M, et al. Cell-free synthesis of functional human epidermal growth factor receptor: Investigation of ligand-independent dimerization in Sf21 microsomal membranes using non-canonical amino acids[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34048. |
| 133 | KATOH T, IWANE Y, SUGA H. Logical engineering of D-arm and T-stem of tRNA that enhances D-amino acid incorporation[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(22): 12601-12610. |
| 134 | KATOH T, TAJIMA K, SUGA H. Consecutive elongation of D-amino acids in translation[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2017, 24(1): 46-54. |
| 135 | LU Y, WELSH J P, SWARTZ J R. Production and stabilization of the trimeric influenza hemagglutinin stem domain for potentially broadly protective influenza vaccines[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(1): 125-130. |
| 136 | BUDISA N, SCHNEIDER T. Expanding the DOPA universe with genetically encoded, mussel-inspired bioadhesives for material sciences and medicine[J]. Chembiochem, 2019, 20(17): 2163-2190. |
| 137 | SAYOUS V, LUBRANO P, LI Y Y, et al. Unbiased libraries in protein directed evolution[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2020, 1868(2): 140321. |
| 138 | COBB R E, CHAO R, ZHAO H M. Directed evolution: Past, present and future[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(5): 1432-1440. |
| 34 | MADIN K, SAWASAKI T, OGASAWARA T, et al. A highly efficient and robust cell-free protein synthesis system prepared from wheat embryos: plants apparently contain a suicide system directed at ribosomes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(2): 559-564. |
| 35 | SAWASAKI T, MORISHITA R, GOUDA M D, et al. Methods for high-throughput materialization of genetic information based on wheat germ cell-free expression system[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2007, 375: 95-106. |
| 36 | GAGOSKI D, POLINKOVSKY M E, MUREEV S, et al. Performance benchmarking of four cell-free protein expression systems[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(2): 292-300. |
| 37 | KHATUN H, YAMAOKA Y, MATSUSHIMA Y, et al. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for major capsid VP1 protein of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus[J]. Microbiology and Immunology, 2018, 62(12): 763-773. |
| 38 | KUDOH A, MIYAKAWA K, MATSUNAGA S, et al. H11/HSPB8 restricts HIV-2 vpx to restore the anti-viral activity of SAMHD1[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 883. |
| 39 | KANOI B N, TAKASHIMA E, MORITA M, et al. Antibody profiles to wheat germ cell-free system synthesized Plasmodium falciparum proteins correlate with protection from symptomatic malaria in Uganda[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(6): 873-881. |
| 40 | SENCHI K, MATSUNAGA S, HASEGAWA H, et al. Development of oligomannose-coated liposome-based nasal vaccine against human parainfluenza virus type 3[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 4: 346. |
| 41 | GOREN M A, FOX B G. Wheat germ cell-free translation, purification, and assembly of a functional human stearoyl-CoA desaturase complex[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2008, 62(2): 171-178. |
| 42 | BUNTRU M, VOGEL S, STOFF K, et al. A versatile coupled cell-free transcription-translation system based on tobacco BY-2 cell lysates[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112(5): 867-878. |
| 43 | GEORGI V, GEORGI L, BLECHERT M, et al. On-chip automation of cell-free protein synthesis: new opportunities due to a novel reaction mode[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(2): 269-281. |
| 44 | ZHU J W. Mammalian cell protein expression for biopharmaceutical production[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(5): 1158-1170. |
| 45 | SCHWEET R, LAMFROM H, ALLEN E. The synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1958, 44(10): 1029-1035. |
| 46 | ANASTASINA M, TERENIN I, BUTCHER S J, et al. A technique to increase protein yield in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate translation system[J]. BioTechniques, 2014, 56(1): 36-39. |
| 47 | PANTHU B, OHLMANN T, PERRIER J, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis enhancement from real-time NMR metabolite kinetics: redirecting energy fluxes in hybrid RRL systems[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 218-226. |
| 48 | CANCEDDA R, SWANSON R, SCHLESINGER M J. Viral proteins formed in a cell-free rabbit reticulocyte system programmed with RNA from a temperature-sensitive mutant of Sindbis virus[J]. Journal of Virology, 1974, 14(3): 664-671. |
| 49 | PENZO M, CARNICELLI D, MONTANARO L, et al. A reconstituted cell-free assay for the evaluation of the intrinsic activity of purified human ribosomes[J]. Nature Protocols, 2016, 11(7): 1309-1325. |
| 50 | BRÖDEL A K, WÜSTENHAGEN D A, KUBICK S. Cell-free protein synthesis systems derived from cultured mammalian cells[M]// OWENS R J. Structural proteomics: high-throughput methods [M]// Methods in Molecular Biology. Springer, 2015, 1261: 129-140. |
| 51 | MATASCI M, HACKER D L, BALDI L, et al. Recombinant therapeutic protein production in cultivated mammalian cells: Current status and future prospects[J]. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, 2008, 5(2/3): e37-e42. |
| 52 | BRÖDEL A K, SONNABEND A, ROBERTS L O, et al. IRES-mediated translation of membrane proteins and glycoproteins in eukaryotic cell-free systems[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e82234. |
| 53 | THORING L, DONDAPATI S K, STECH M, et al. High-yield production of "difficult-to-express" proteins in a continuous exchange cell-free system based on CHO cell lysates[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 11710. |
| 54 | KUNERT R, REINHART D. Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(8): 3451-3461. |
| 55 | MARTIN R W, MAJEWSKA N I, CHEN C X, et al. Development of a CHO-based cell-free platform for synthesis of active monoclonal antibodies[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(7): 1370-1379. |
| 56 | VINAROV D A, LYTLE B L, PETERSON F C, et al. Cell-free protein production and labeling protocol for NMR-based structural proteomics[J]. Nature Methods, 2004, 1(2): 149-153. |
| 57 | SUZUKI T, ITO M, EZURE T, et al. N-Terminal protein modifications in an insect cell-free protein synthesis system and their identification by mass spectrometry[J]. Proteomics, 2006, 6(16): 4486-4495. |
| 139 | MARCHESCHI R J, GRONENBERG L S, LIAO J C. Protein engineering for metabolic engineering: current and next-generation tools[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 8(5): 545-555. |
| 140 | REITINGER S, YU Y, WICKI J, et al. Circular permutation of Bacillus circulans xylanase: a kinetic and structural study[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49(11): 2464-2474. |
| 141 | FUJII S, MATSUURA T, SUNAMI T, et al. In vitro evolution of α-hemolysin using a liposome display[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(42): 16796-16801. |
| 142 | BLOMBERG R, KRIES H, PINKAS D M, et al. Precision is essential for efficient catalysis in an evolved Kemp eliminase[J]. Nature, 2013, 503(7476): 418-421. |
| 143 | CONTRERAS-LLANO L E, TAN C. High-throughput screening of biomolecules using cell-free gene expression systems[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2018, 3(1): ysy012. |
| 144 | SHIN J, JARDINE P, NOIREAUX V. Genome replication, synthesis, and assembly of the bacteriophage T7 in a single cell-free reaction[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(9): 408-413. |
| 145 | YEWDALL N A, MASON A F, VAN HEST J C M. The hallmarks of living systems: Towards creating artificial cells[J]. Interface Focus, 2018, 8(5): 20180023. |
| 146 | JIA H Y, HEYMANN M, BERNHARD F, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis in micro compartments: building a minimal cell from biobricks[J]. New Biotechnology, 2017, 39: 199-205. |
| 147 | ZHU Y, GUO X C, LIU J Q, et al. Emerging advances of cell-free systems toward artificial cells[J]. Small Methods, 2020, 4(10): 2000406. |
| 148 | CHO E, LU Y. Compartmentalizing cell-free systems: toward creating life-like artificial cells and beyond[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(11): 2881-2901. |
| 149 | VECCHIARELLI A G, LI M, MIZUUCHI M, et al. Differential affinities of MinD and MinE to anionic phospholipid influence Min patterning dynamics in vitro [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2014, 93(3): 453-463. |
| 150 | ZHOU P, LIU X M, WU G Y, et al. Programmable modulation of membrane permeability of proteinosome upon multiple stimuli responses[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2016, 5(8): 961-966. |
| 58 | SUZUKI T, EZURE T, ANDO E, et al. Preparation of ubiquitin-conjugated proteins using an insect cell-free protein synthesis system[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 145(1): 73-78. |
| 59 | EZURE T, SUZUKI T, SHIKATA M, et al. Expression of proteins containing disulfide bonds in an insect cell-free system and confirmation of their arrangements by MALDI-TOF MS[J]. Proteomics, 2007, 7(24): 4424-4434. |
| 60 | SUZUKI T, ITO M, EZURE T, et al. Protein prenylation in an insect cell-free protein synthesis system and identification of products by mass spectrometry[J]. Proteomics, 2007, 7(12): 1942-1950. |
| 61 | EZURE T, SUZUKI T, HIGASHIDE S, et al. Cell-free protein synthesis system prepared from insect cells by freeze-thawing[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2006, 22(6): 1570-1577. |
| 62 | QUAST R B, SONNABEND A, STECH M, et al. High-yield cell-free synthesis of human EGFR by IRES-mediated protein translation in a continuous exchange cell-free reaction format[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 30399. |
| 63 | WHITTAKER J W. Cell-free protein synthesis: the state of the art[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2013, 35(2): 143-152. |
| 64 | BOTTE M, DENIAUD A, SCHAFFITZEL C. Cell-free synthesis of macromolecular complexes[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2016, 896: 79-95. |
| 65 | OHASHI H, SHIMIZU Y, YING B W, et al. Efficient protein selection based on ribosome display system with purified components[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2007, 352(1): 270-276. |
| 66 | KANAMORI T, FUJINO Y, UEDA T. PURE ribosome display and its application in antibody technology[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2014, 1844(11): 1925-1932. |
| 67 | LAVICKOVA B, MAERKL S J. A simple, robust, and low-cost method to produce the PURE cell-free system[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(2): 455-462. |
| 68 | KIM T W, KIM D M, CHOI C Y. Rapid production of milligram quantities of proteins in a batch cell-free protein synthesis system[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2006, 124(2): 373-380. |
| 69 | SPIRIN A S, BARANOV V I, RYABOVA L A, et al. A continuous cell-free translation system capable of producing polypeptides in high yield[J]. Science, 1988, 242(4882): 1162-1164. |
| 151 | GOBBO P, PATIL A J, LI M, et al. Programmed assembly of synthetic protocells into thermoresponsive prototissues[J]. Nature Materials, 2018, 17(12): 1145-1153. |
| 152 | Liu J, Tian L, Qiao Y, et al. Hydrogel-immobilized coacervate droplets as modular microreactor assemblies[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(17): 6853-6859. |
| 153 | NOURIAN Z, ROELOFSEN W, DANELON C. Triggered gene expression in fed-vesicle microreactors with a multifunctional membrane[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(13): 3114-3118. |
| 154 | ANDO M, SCHIKULA S, SASAKI Y, et al. Proteoliposome engineering with cell-free membrane protein synthesis: control of membrane protein sorting into liposomes by chaperoning systems[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(10): 1800524. |
| 155 | ELANI Y, TRANTIDOU T, WYLIE D, et al. Constructing vesicle-based artificial cells with embedded living cells as organelle-like modules[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 4564. |
| 156 | TRANTIDOU T, DEKKER L, POLIZZI K, et al. Functionalizing cell-mimetic giant vesicles with encapsulated bacterial biosensors[J]. Interface Focus, 2018, 8(5): 20180024. |
| 157 | LIU Y, YANG D Y. Cell lysates and egg white create homeostatic microenvironment for gene expression in cell-free system[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2018, 3(4): 211-216. |
| 158 | PEREIRA DE SOUZA T, STEINIGER F, STANO P, et al. Spontaneous crowding of ribosomes and proteins inside vesicles: a possible mechanism for the origin of cell metabolism[J]. Chembiochem, 2011, 12(15): 2325-2330. |
| 159 | HANSEN M M K, MEIJER L H H, SPRUIJT E, et al. Macromolecular crowding creates heterogeneous environments of gene expression in picolitre droplets[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2016, 11(2): 191-197. |
| 160 | SHIN J, NOIREAUX V. An E. coli cell-free expression toolbox: Application to synthetic gene circuits and artificial cells[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(1): 29-41. |
| 161 | KARIG D K, IYER S, SIMPSON M L, et al. Expression optimization and synthetic gene networks in cell-free systems[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 40(8): 3763-3774. |
| 162 | GUO S B, MURRAY R M. Construction of incoherent feedforward loop circuits in a cell-free system and in cells[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(3): 606-610. |
| 163 | AUFINGER L, SIMMEL F C. Artificial gel-based organelles for spatial organization of cell-free gene expression reactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(52): 17245-17248. |
| 164 | ADAMALA K P, MARTIN-ALARCON D A, GUTHRIE-HONEA K R, et al. Engineering genetic circuit interactions within and between synthetic minimal cells[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(5): 431-439. |
| 165 | JIA H Y, HEYMANN M, HÄRTEL T, et al. Temperature-sensitive protein expression in protocells[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(45): 6421-6424. |
| 166 | TERASAWA H, NISHIMURA K, SUZUKI H, et al. Coupling of the fusion and budding of giant phospholipid vesicles containing macromolecules[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(16): 5942-5947. |
| 167 | PARDEE K, GREEN A A, FERRANTE T, et al. Paper-based synthetic gene networks[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(4): 940-954. |
| 168 | SHRESTHA P, SMITH M T, BUNDY B C. Cell-free unnatural amino acid incorporation with alternative energy systems and linear expression templates[J]. New Biotechnology, 2014, 31(1): 28-34. |
| [1] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [2] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [3] | 陈志航, 季梦麟, 戚逸飞. 人工智能蛋白质结构设计算法研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 464-487. |
| [4] | 梁丽亚, 刘嵘明. 靶向DNA的Ⅱ类CRISPR/Cas系统的蛋白工程化改造[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| [5] | 祁延萍, 朱晋, 张凯, 刘彤, 王雅婕. 定向进化在蛋白质工程中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. |
| [6] | 涂涛, 罗会颖, 姚斌. 蛋白质工程在饲料用酶研发中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 487-499. |
| [7] | 王汇滨, 车昌丽, 游松. Fe/α-酮戊二酸依赖型卤化酶在绿色卤化反应中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 545-566. |
| [8] | 卞佳豪, 杨广宇. 人工智能辅助的蛋白质工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 429-444. |
| [9] | 万逸尘, 许孔亮, 郑仁朝, 郑裕国. 化学品体外生物合成途径设计、元件组装和应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 886-901. |
| [10] | 刘美霞, 李强子, 孟冬冬, 魏欣蕾, 游淳. 烟酰胺类辅酶依赖型氧化还原酶的辅酶偏好性改造及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 570-582. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||