合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (5): 857-876.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-049
自动化合成生物技术在DNA组装与微生物底盘操作中的应用
- 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,中国科学院定量工程生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2023-07-03修回日期:2023-08-09出版日期:2023-10-31发布日期:2023-11-15 -
通讯作者:司同,张建志 -
作者简介:陈永灿(1988—),男,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为合成生物学。 E-mail: yc.chen@siat.ac.cn陈永灿 (1988—),男,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为合成生物学。 E-mail: yc.chen@siat.ac.cn司同 (1987—),男,博士,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学。 E-mail: tong.si@siat.ac.cn张建志 (1988—),男,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为合成生物学,代谢工程。 E-mail: zhangjz@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFA0910800)
Applications of automated synthetic biotechnology in DNA assembly and microbial chassis manipulation
CHEN Yongcan(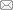 ), SI Tong, ZHANG Jianzhi
), SI Tong, ZHANG Jianzhi
- CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-07-03Revised:2023-08-09Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-15 -
Contact:SI Tong, ZHANG Jianzhi
摘要:
基于绿色生物制造进行物质能量生产,有望减少对天然植被、耕地、石化等资源的依赖,而微生物细胞工厂是绿色生物制造过程的“芯片”。合成生物学为微生物细胞工厂的研究提供了重要的使能技术,但目前仍面临生命系统高度复杂、实验过程需要反复试错、实验通量较低等限制因素。自动化合成生物技术借助高通量、自动化和智能化的软硬件设施平台,基于标准化、模块化的生物元件库和合成生物工艺,可低成本、高通量、快速、多循环地完成海量工程试错性实验,加速特定性能人工细胞工厂的设计和优化,支撑相关研究和应用。本文主要针对细胞工厂“设计-构建-测试-学习”循环中最关键、最耗时的“构建”环节,对DNA组装和底盘细胞操作自动化工艺和设施平台进行了总结,对自动化合成生物技术应用于生物合成基因簇挖掘、代谢通路优化和底盘细胞优化的最新进展进行了介绍。最后展望了微生物细胞工厂自动化构建面临的挑战和未来发展,讨论了包括非模式微生物在内的全流程自动化的发展趋势,而自动化装备的国产化自主研发将为此做出重要贡献。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈永灿, 司同, 张建志. 自动化合成生物技术在DNA组装与微生物底盘操作中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 857-876.
CHEN Yongcan, SI Tong, ZHANG Jianzhi. Applications of automated synthetic biotechnology in DNA assembly and microbial chassis manipulation[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 857-876.

图1 Golden Gate和Gibson组装自动化 [ 33](蓝色折线图表示试剂成本,绿色柱状图表示组装效率)
Fig. 1 Automated DNA assembly methods [ 33][Principles of (a) Golden Gate and (b) Gibson DNA assembly. Cost and efficiency of microscale DNA assembly based on (c) Golden Gate and (d) Gibson assembly methods.]

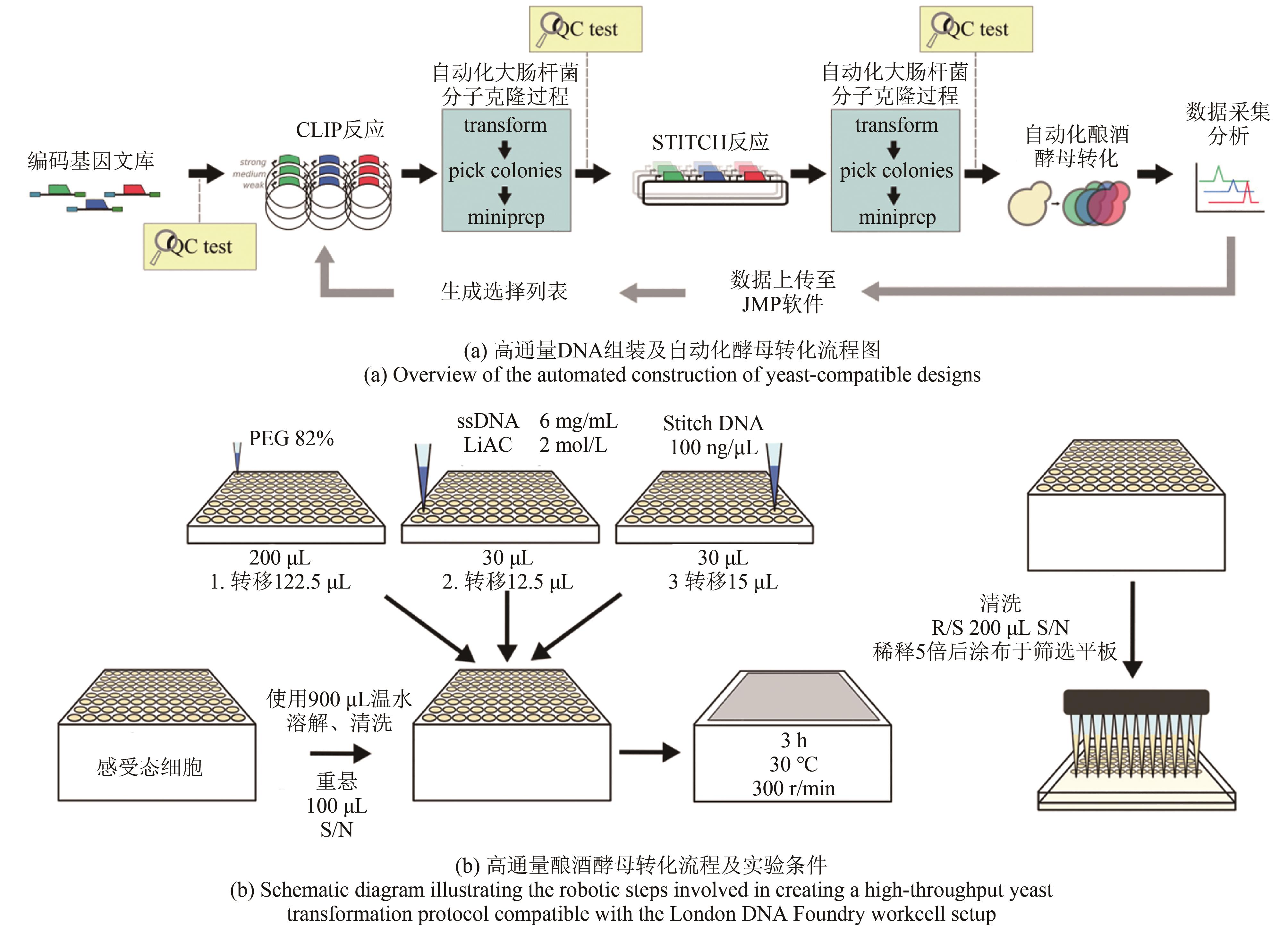
图2 BASIC DNA组装及DNA-BOT自动化工作流程 [ 34](a) BASIC DNA组装流程包括剪接反应、纯化、组装和转化四个步骤;(b) DNA-BOT程序读取元件、接头存储信息和构建设计信息的csv文件,输出四个OT-2脚本以及元信息文件,每个脚本以微孔板的形式运行对应的BASIC组装步骤。虚线表示信息流,实线表示物理过程
Fig. 2 Automated workflow of DNA-BOT based on the BASIC DNA assembly method [ 34](a) Principle of BASIC DNA assembly; (b) Processes of DNA-BOT
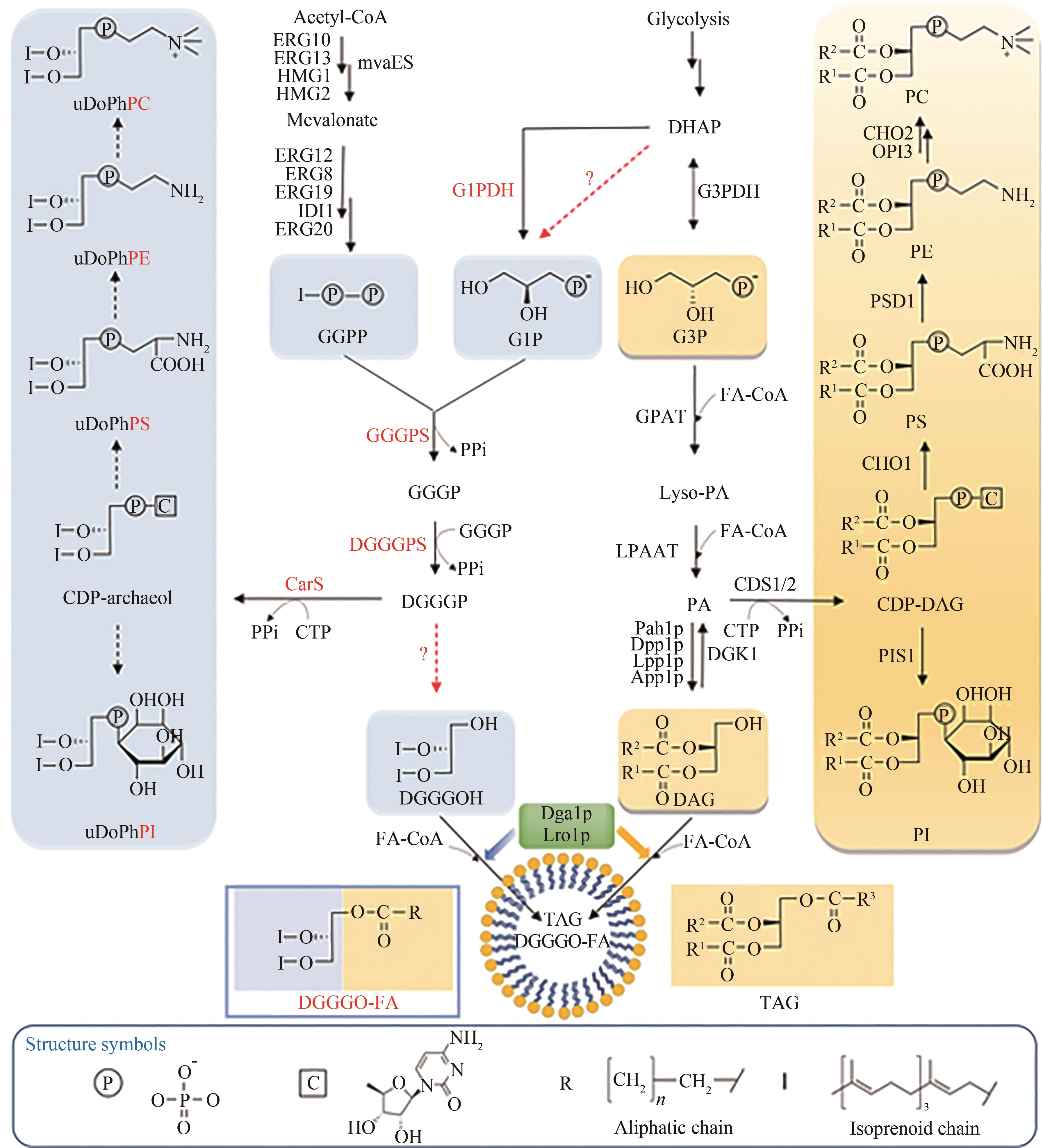
图7 重组酿酒酵母中古菌特征脂类合成途径(蓝色背景)及酵母内源脂类合成途径(黄色背景) [ 57](The metabolites naturally present in archaeal and eukaryotic hosts are labeled with blue and yellow shading, respectively.)
Fig. 7 Biosynthetic pathways of archaeal phospholipids, hybrid neutral lipids (DGGGO-FAs) and triacylglycerol (TAG) in engineered S. cerevisiae[ 57]
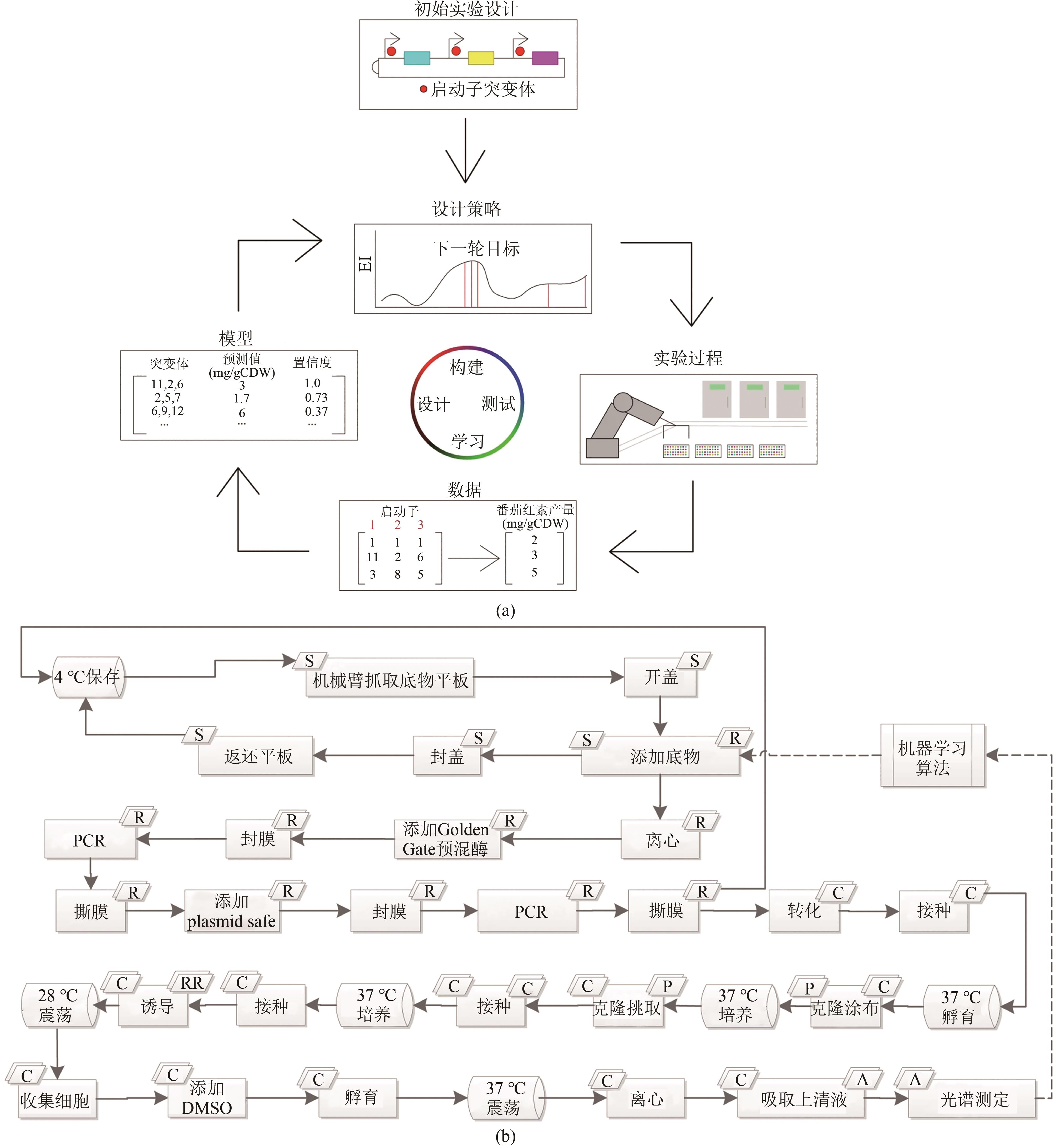
图8 基于iBioFAB平台开发的机器学习算法驱动的生物系统设计优化平台BioAutomata在大肠杆菌细胞底盘进行番茄红素代谢途径组合优化构建、番茄红素合成和筛选 [ 10](a) BioAutomata平台整体流程图:初始参数设定之后,对实验变量(例如代谢途径组合文库中具有不同强度的启动子等)进行设计,并预设目标功能。BioAutomata平台软件对具有预期功能的组合进行筛选并输出命令、执行实验操作、收集实验数据,并将实验数据反馈给机器学习模型进行分析,从而进行迭代实验。(b) 单元操作流程拆解
Fig. 8 The application of an integrated robotic system coupled with machine learning algorithms to fully automate the DBTL process for biosystems design [ 10](a) The overall workflow of BioAutomata; (b)the corresponding automated processes
图10 酿酒酵母自动化多重基因组进化技术 [ 61](a)酿酒酵母多重基因组突变方法,其中基因调控元件侧翼为同源δ序列,用于迭代和多重整合到基因组重复序列;(b) 基于全长双链cDNA文库构建全基因组规模调控元件文库,有义和反义构型分别实现目标基因的过表达或敲低;(c)基于iBioFAB的全基因组水平酿酒酵母定向进化自动化单元操作流程
Fig. 10 Scheme of automated RNAi-assisted genome evolution in S. cerevisiae[ 61](a) Method to create multiplex genomic mutations in S. cerevisiae; (b) Construction of genome-scale modulation part libraries; (c) Workflow of automated RNAi-assisted genome evolution
| 1 | DAVY A M, KILDEGAARD H F, ANDERSEN M R. Cell factory engineering[J]. Cell Systems, 2017, 4( 3): 262- 275. |
| 2 | BACHHAV B, DE ROSSI J, LLANOS C D, et al. Cell factory engineering: challenges and opportunities for synthetic biology applications[J/OL]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023[ 2023-07-01]. . |
| 3 | 袁姚梦, 邢新会, 张翀. 微生物细胞工厂的设计构建: 从诱变育种到全基因组定制化创制[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1( 6): 656- 673. |
| YUAN Y M, XING X H, ZHANG C. Progress and prospective of engineering microbial cell factories: from random mutagenesis to customized design in genome scale[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1( 6): 656- 673. | |
| 4 | YAN W L, CAO Z B, DING M Z, et al. Design and construction of microbial cell factories based on systems biology[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2023, 8( 1): 176- 185. |
| 5 | LIU H, QI Y L, ZHOU P, et al. Microbial physiological engineering increases the efficiency of microbial cell factories[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2021, 41( 3): 339- 354. |
| 6 | 张亭, 冷梦甜, 金帆, 等. 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施概述[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3( 1): 184- 194. |
| ZHANG T, LENG M T, JIN F, et al. Overview on platform for synthetic biology research at Shenzhen[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3( 1): 184- 194. | |
| 7 | HILLSON N, CADDICK M, CAI Y Z, et al. Building a global alliance of biofoundries[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2040. |
| 8 | 唐婷, 付立豪, 郭二鹏, 等. 自动化合成生物技术与工程化设施平台[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66( 3): 300- 309. |
| TANG T, FU L H, GUO E P, et al. Automation in synthetic biology using biological foundries[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66( 3): 300- 309. | |
| 9 | CHAO R, MISHRA S, SI T, et al. Engineering biological systems using automated biofoundries[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 98- 108. |
| 10 | HAMEDIRAD M, CHAO R, WEISBERG S, et al. Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5150. |
| 11 | CHAO R, LIANG J, TASAN I, et al. Fully automated one-step synthesis of single-transcript TALEN pairs using a biological foundry[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6( 4): 678- 685. |
| 12 | ZHANG J Z, CHEN Y C, FU L H, et al. Accelerating strain engineering in biofuel research via build and test automation of synthetic biology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2021, 67: 88- 98. |
| 13 | CARBONELL P, JERVIS A J, ROBINSON C J, et al. An automated Design-Build-Test-Learn pipeline for enhanced microbial production of fine chemicals[J]. Communications Biology, 2018, 1: 66. |
| 14 | THUROW K, JUNGINGER S. Devices and systems for laboratory automation[M/OL]. Weinheim: Wiley, 2022[ 2023-07-01]. . |
| 15 | HOLOWKO M B, FROW E K, REID J C, et al. Building a biofoundry[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2021, 6( 1): ysaa026. |
| 16 | TELLECHEA-LUZARDO J, OTERO-MURAS I, GOÑI-MORENO A, et al. Fast biofoundries: coping with the challenges of biomanufacturing[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40( 7): 831- 842. |
| 17 | 卢挥, 张芳丽, 黄磊. 合成生物学自动化装置 iBioFoundry 的构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4( 5): 877- 891. |
| LU H, ZHANG F L, HUANG L. Establishment of iBioFoundry for synthetic biology applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4( 5): 877- 891. | |
| 18 | 孟娇, 刘丁玉, 黄灿, 等. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑系统在原核微生物细胞工厂构建中的开发与应用[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46( 10): 2730- 2742. |
| MENG J, LIU D Y, HUANG C, et al. Development and application of CRISPR/Cas genome editing system in the construction of prokaryotic microbial cell factories[J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46( 10): 2730- 2742. | |
| 19 | WU Y K, LIU Y F, LV X Q, et al. Applications of CRISPR in a microbial cell factory: from genome reconstruction to metabolic network reprogramming[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9( 9): 2228- 2238. |
| 20 | 李洋, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 等. CRISPR基因编辑技术在微生物合成生物学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2( 1): 106- 120. |
| LI Y, SHEN X L, SUN X X, et al. Advances of CRISPR gene editing in microbial synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2( 1): 106- 120. | |
| 21 | 涂然, 毛雨丰, 刘叶, 等. 工程菌种自动化高通量编辑与筛选研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38( 11): 4162- 4179. |
| TU R, MAO Y F, LIU Y, et al. Advances in automated high-throughput editing and screening of engineered strains[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38( 11): 4162- 4179. | |
| 22 | APPLETON E, DENSMORE D, MADSEN C, et al. Needs and opportunities in bio-design automation: four areas for focus[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 40: 111- 118. |
| 23 | FU L H, ZHANG J Z, SI T. Recent advances in high-throughput mass spectrometry that accelerates enzyme engineering for biofuel research[J]. BMC Energy, 2020, 2( 1): 1- 9. |
| 24 | CAMACHO D M, COLLINS K M, POWERS R K, et al. Next-generation machine learning for biological networks[J]. Cell, 2018, 173( 7): 1581- 1592. |
| 25 | KIM G B, KIM W J, KIM H U, et al. Machine learning applications in systems metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 64: 1- 9. |
| 26 | 晁然, 原永波, 赵惠民. 构建合成生物学制造厂[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2015, 45( 10): 976- 984. |
| CHAO R, YUAN Y B, ZHAO H M. Building biological foundries for next generation synthetic biology[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2015, 58: 658- 665. | |
| 27 | LU G Q, MORIYAMA E N. Vector NTI, a balanced all-in-one sequence analysis suite[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2004, 5( 4): 378- 388. |
| 28 | HILLSON N J, ROSENGARTEN R D, KEASLING J D. j5 DNA assembly design automation software[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1( 1): 14- 21. |
| 29 | APPLETON E, TAO J, HADDOCK T, et al. Interactive assembly algorithms for molecular cloning[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11( 6): 657- 662. |
| 30 | HAMEDIRAD M, WEISBERG S, CHAO R, et al. Highly efficient single-pot scarless golden gate assembly[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8( 5): 1047- 1054. |
| 31 | ENGHIAD B, XUE P, SINGH N, et al. PlasmidMaker is a versatile, automated, and high throughput end-to-end platform for plasmid construction[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2697. |
| 32 | 张建志, 付立豪, 唐婷, 等. 基于合成生物学策略的酶蛋白元件规模化挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1( 3): 319- 336. |
| ZHANG J Z, FU L H, TANG T, et al. Scalable mining of proteins for biocatalysis via synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1( 3): 319- 336. | |
| 33 | KANIGOWSKA P, SHEN Y, ZHENG Y J, et al. Smart DNA fabrication using sound waves: applying acoustic dispensing technologies to synthetic biology[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2016, 21( 1): 49- 56. |
| 34 | STORCH M, HAINES M C, BALDWIN G S. DNA-BOT: a low-cost, automated DNA assembly platform for synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2020, 5( 1): ysaa010. |
| 35 | LIU Y F, SU A Q, LI J H, et al. Towards next-generation model microorganism chassis for biomanufacturing[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104( 21): 9095- 9108. |
| 36 | KAVŠČEK M, STRAŽAR M, CURK T, et al. Yeast as a cell factory: current state and perspectives[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 94. |
| 37 | GUO E P, FU L H, FANG X T, et al. Robotic construction and screening of lanthipeptide variant libraries in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11( 12): 3900- 3911. |
| 38 | FATMA Z, SCHULTZ J C, ZHAO H M. Recent advances in domesticating non-model microorganisms[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2020, 36( 5): e3008. |
| 39 | GURDO N, VOLKE D C, NIKEL P I. Merging automation and fundamental discovery into the design-build-test-learn cycle of nontraditional microbes[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40( 10): 1148- 1159. |
| 40 | 杨永富, 耿碧男, 宋皓月, 等. 合成生物学时代基于非模式细菌的工业底盘细胞研究现状与展望[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37( 3): 874- 910. |
| YANG Y F, GENG B N, SONG H Y, et al. Progress and perspective on development of non-model industrial bacteria as chassis cells for biochemical production in the synthetic biology era[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37( 3): 874- 910. | |
| 41 | MOFFAT A D, ELLISTON A, PATRON N J, et al. A biofoundry workflow for the identification of genetic determinants of microbial growth inhibition[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2021, 6( 1): ysab004. |
| 42 | 郭肖杰, 王立言, 张翀, 等. 高通量自动化微生物微液滴进化培养与筛选技术及其装备化[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37( 3): 991- 1003. |
| GUO X J, WANG L Y, ZHANG C, et al. Technology development and instrumentation of a high-throughput and automated microbial microdroplet culture system for microbial evolution and screening[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37( 3): 991- 1003. | |
| 43 | TU R, ZHANG Y, HUA E B, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput screening of Streptomyces[J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4: 647. |
| 44 | JIAN X J, GUO X J, WANG J, et al. Automated microbial cultivation and adaptive evolution using microbial microdroplet culture system (MMC)[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2022( 180): e62800. |
| 45 | MARTELLA A, MATJUSAITIS M, AUXILLOS J, et al. EMMA: an extensible mammalian modular assembly toolkit for the rapid design and production of diverse expression vectors[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6( 7): 1380- 1392. |
| 46 | RAJAKUMAR P D, GOWERS G O F, SUCKLING L, et al. Rapid prototyping platform for Saccharomyces cerevisiae using computer-aided genetic design enabled by parallel software and workcell platform development[J]. SLAS Technology: Translating Life Sciences Innovation, 2019, 24( 3): 291- 297. |
| 47 | ROBINSON C J, DUNSTAN M S, SWAINSTON N, et al. Multifragment DNA assembly of biochemical pathways via automated ligase cycling reaction[M/OL]// Methods in enzymology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018, 608: 369- 392 [2023-07-01]. . |
| 48 | WANG Y, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. MACBETH: multiplex automated Corynebacterium glutamicum base editing method[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 200- 210. |
| 49 | KOO B M, KRITIKOS G, FARELLI J D, et al. Construction and analysis of two genome-scale deletion libraries for Bacillus subtilis [J]. Cell Systems, 2017, 4( 3): 291- 305.e7. |
| 50 | BRUNO K S, WESTFALL P, SZEWCZYK E, et al. Method to build fungal production strains using automated steps for genetic manipulation and strain purification: US20190323036[P]. 2019-10-24. |
| 51 | MADISON A C, ROYAL M W, VIGNEAULT F, et al. Scalable device for automated microbial electroporation in a digital microfluidic platform[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6( 9): 1701- 1709. |
| 52 | IM D J, JEONG S N, YOO B S, et al. Digital microfluidic approach for efficient electroporation with high productivity: transgene expression of microalgae without cell wall removal[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87( 13): 6592- 6599. |
| 53 | KUIVANEN J, KORJA V, HOLMSTRÖM S, et al. Development of microtiter plate scale CRISPR/Cas9 transformation method for Aspergillus niger based on in vitro assembled ribonucleoprotein complexes[J]. Fungal Biology and Biotechnology, 2019, 6: 3. |
| 54 | YUAN Y J, CHENG S, BIAN G K, et al. Efficient exploration of terpenoid biosynthetic gene clusters in filamentous fungi[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5( 4): 277- 287. |
| 55 | AYIKPOE R S, SHI C Y, BATTISTE A J, et al. A scalable platform to discover antimicrobials of ribosomal origin[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 6135. |
| 56 | ZHANG S Y, ZHU J, FAN S, et al. Directed evolution of a cyclodipeptide synthase with new activities via label-free mass spectrometric screening[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13( 25): 7581- 7586. |
| 57 | ZHANG J Z, LI T, HONG Z L, et al. Biosynthesis of hybrid neutral lipids with archaeal and eukaryotic characteristics in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62( 4): e202214344. |
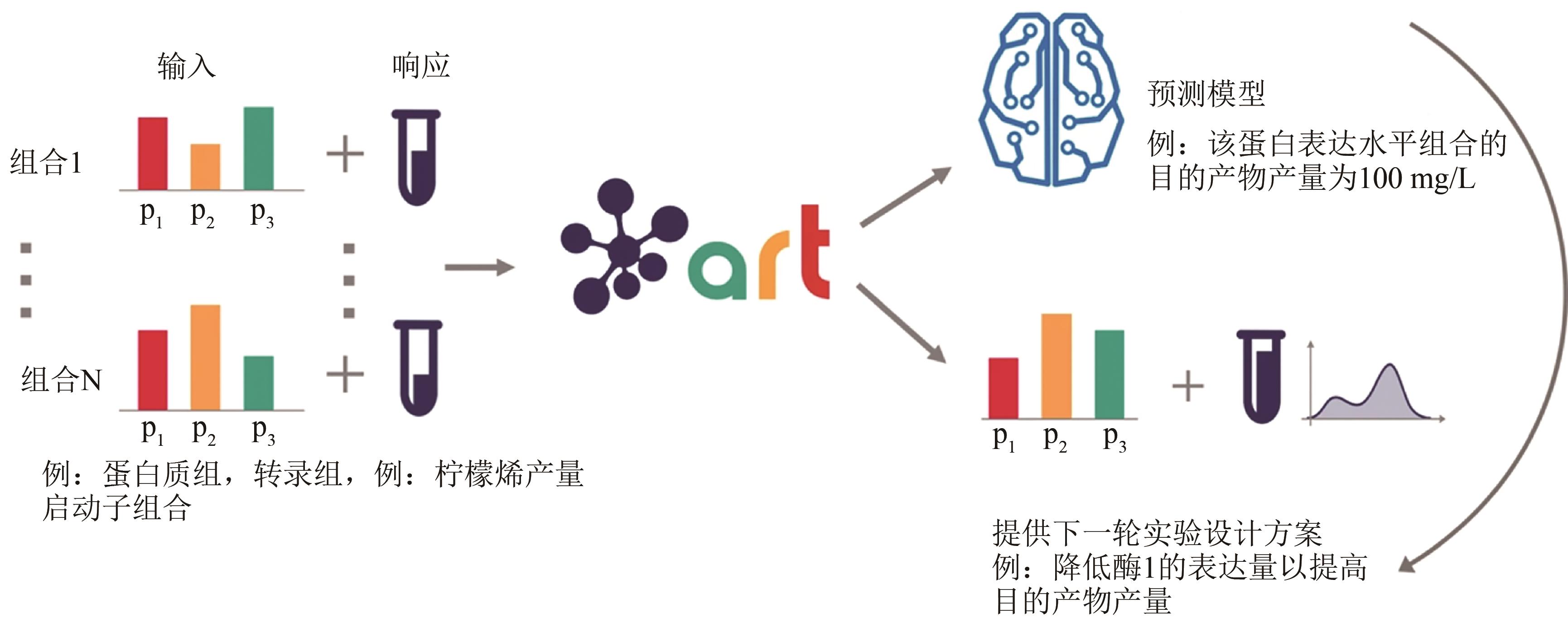
| 58 | ZHANG J, PETERSEN S D, RADIVOJEVIC T, et al. Combining mechanistic and machine learning models for predictive engineering and optimization of tryptophan metabolism[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4880. |
| 59 | RADIVOJEVIĆ T, COSTELLO Z, WORKMAN K, et al. A machine learning Automated Recommendation Tool for synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4879. |
| 60 | WANG H H, ISAACS F J, CARR P A, et al. Programming cells by multiplex genome engineering and accelerated evolution[J]. Nature, 2009, 460( 7257): 894- 898. |
| 61 | SI T, CHAO R, MIN Y H, et al. Automated multiplex genome-scale engineering in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15187. |
| [1] | 杨毅, 毛雨丰, 杨春贺, 王猛, 廖小平, 马红武. 面向微生物遗传操作的编辑序列设计工具的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 30-46. |
| [2] | 姜婵娟, 崔天琦, 孙洪娈, 焦念志, 符军, 张友明, 王海龙. ExoCET-BAC策略高效抓取和组装高AT含量基因组大片段[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 238-251. |
| [3] | 彭凯, 逯晓云, 程健, 刘莹, 江会锋, 郭晓贤. DNA合成、组装与纠错技术研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 697-708. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||