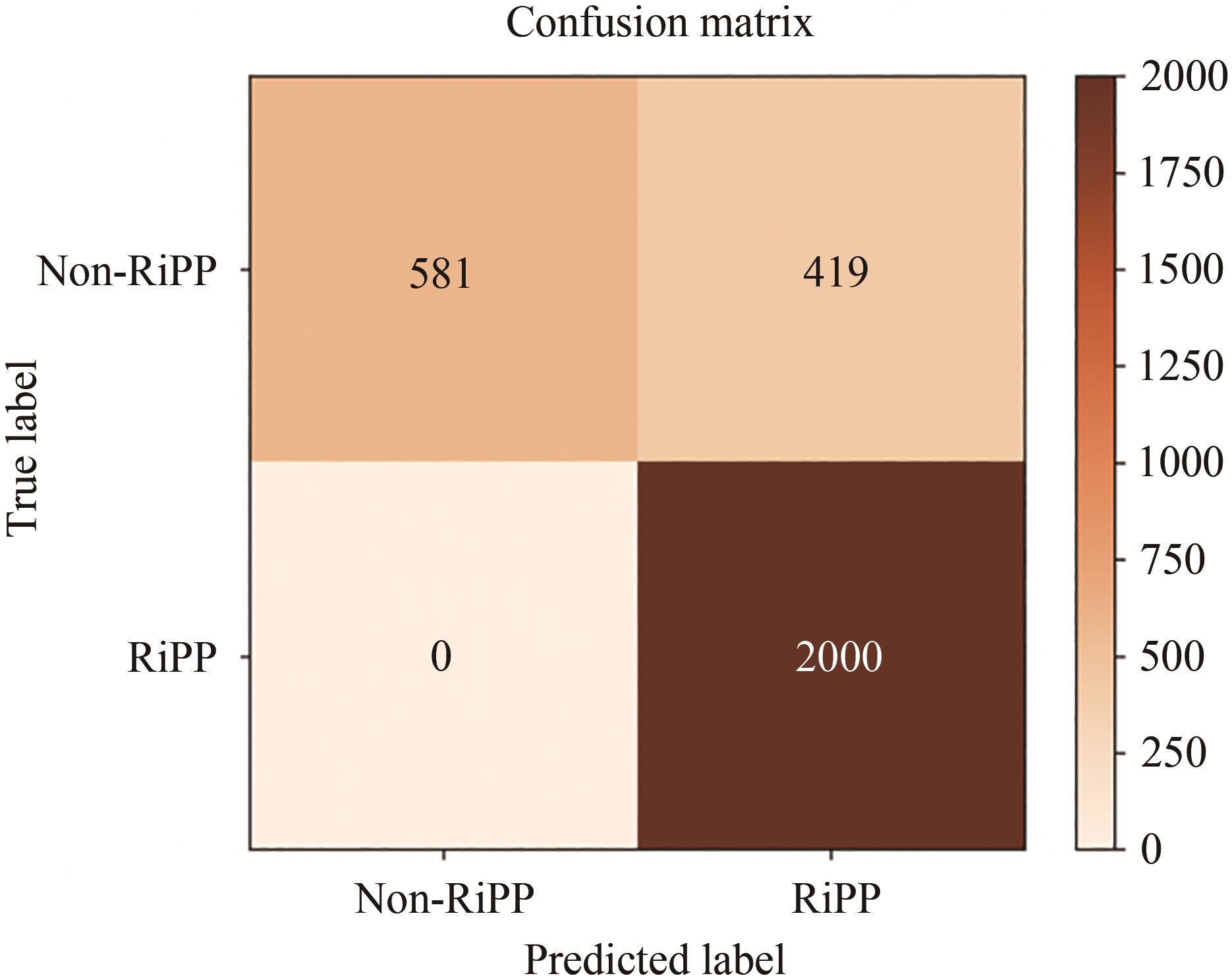
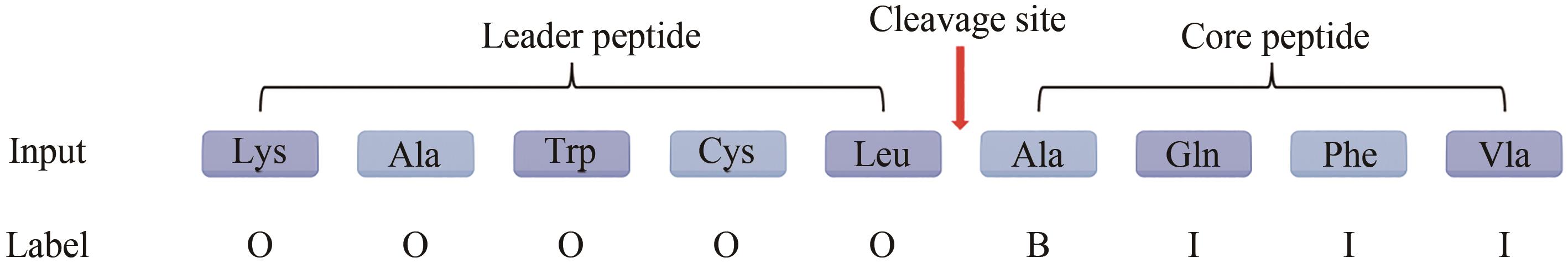
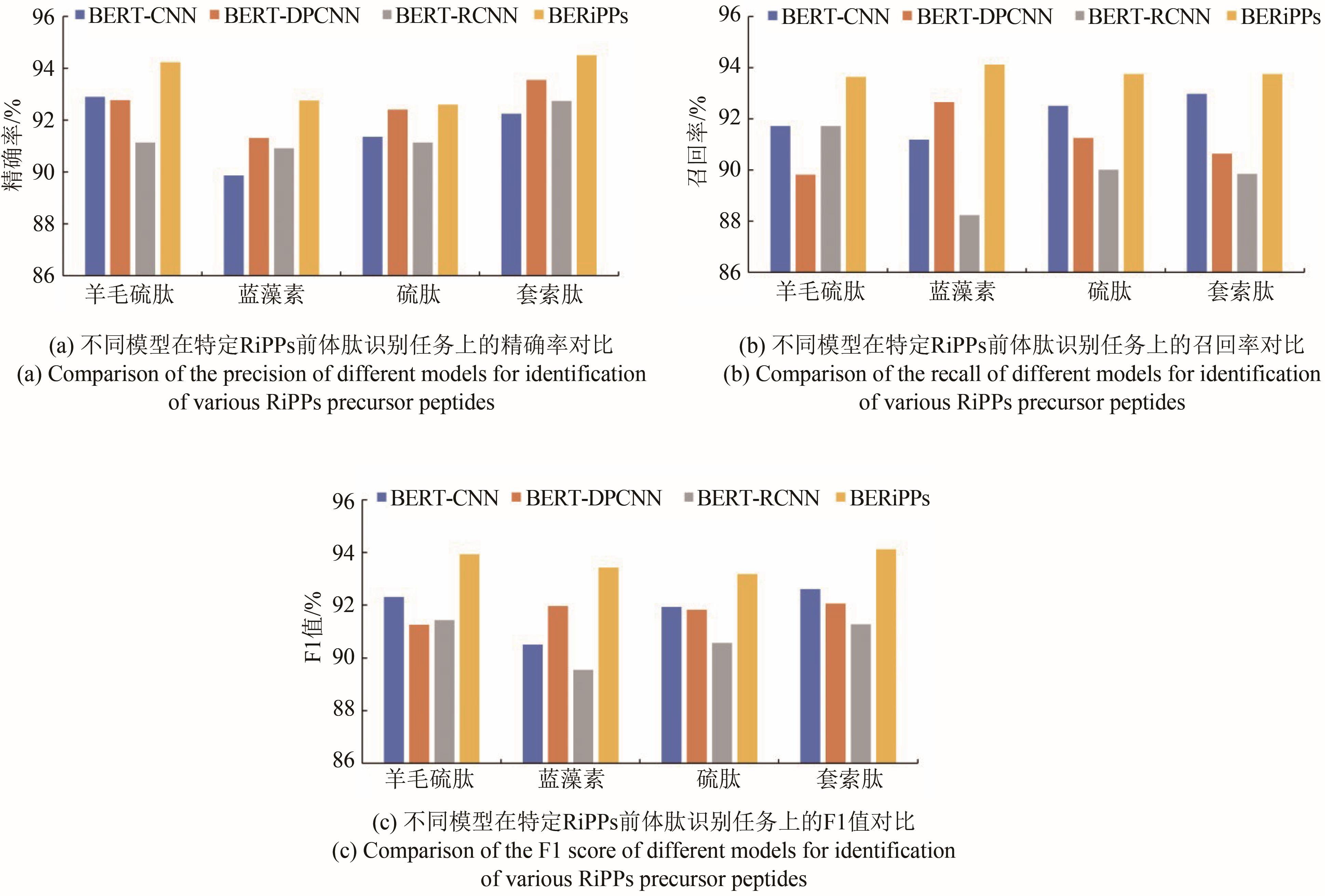
| 1 |
MARTENS E, DEMAIN A L. The antibiotic resistance crisis, with a focus on the United States[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2017, 70(5): 520-526.
|
| 2 |
HUTCHINGS M I, TRUMAN A W, WILKINSON B. Antibiotics: past, present and future[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2019, 51: 72-80.
|
| 3 |
HUDSON G A, MITCHELL D A. RiPP antibiotics: Biosynthesis and engineering potential[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2018, 45: 61-69.
|
| 4 |
WANG F T, WEI W Q, ZHAO J F, et al. Genome mining and biosynthesis study of a type B linaridin reveals a highly versatile α-N-methyltransferase[J]. CCS Chemistry, 2021, 3(3): 1049-1057.
|
| 5 |
SKINNIDER M A, JOHNSTON C W, EDGAR R E, et al. Genomic charting of ribosomally synthesized natural product chemical space facilitates targeted mining[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(42): E6343-E6351.
|
| 6 |
ARNISON P G, BIBB M J, BIERBAUM G, et al. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2013, 30(1): 108-160.
|
| 7 |
YU Y, ZHANG Q, VAN DER DONK W A. Insights into the evolution of lanthipeptide biosynthesis[J]. Protein Science, 2013, 22(11): 1478-1489.
|
| 8 |
ZHONG Z, HE B B, LI J, et al. Challenges and advances in genome mining of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs)[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2020, 5(3): 155-172.
|
| 9 |
BLIN K, SHAW S, STEINKE K, et al. antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(W1): W81-W87.
|
| 10 |
HETRICK K J, VAN DER DONK W A. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural product discovery in the genomic era[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 38: 36-44.
|
| 11 |
HYATT D, CHEN G L, LOCASCIO P F, et al. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2010, 11: 119.
|
| 12 |
DELCHER A L, BRATKE K A, POWERS E C, et al. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(6): 673-679.
|
| 13 |
VAN HEEL A J, DE JONG A, MONTALBÁN-LÓPEZ M, et al. BAGEL3: automated identification of genes encoding bacteriocins and (non-) bactericidal posttranslationally modified peptides[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(W1): W448-W453.
|
| 14 |
TIETZ J I, SCHWALEN C J, PATEL P S, et al. A new genome-mining tool redefines the lasso peptide biosynthetic landscape[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(5): 470-478.
|
| 15 |
MERWIN N J, MOUSA W K, DEJONG C A, et al. DeepRiPP integrates multiomics data to automate discovery of novel ribosomally synthesized natural products[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(1): 371-380.
|
| 16 |
AGRAWAL P, KHATER S, GUPTA M, et al. RiPPMiner: a bioinformatics resource for deciphering chemical structures of RiPPs based on prediction of cleavage and cross-links[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W80-W88.
|
| 17 |
DE LOS SANTOS E L C. NeuRiPP: Neural network identification of RiPP precursor peptides[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 13406.
|
| 18 |
SHIN H C, ROTH H R, GAO M C, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1285-1298.
|
| 19 |
SUNDERMEYER M, SCHLÜTER R, NEY H. LSTM neural networks for language modeling[C]// 13th Annual conference of the International Speech Communication Association 2012 (INTERSPEECH 2012). Portland, OR, USA: International Speech Communications Association, 2012:194-197.
|
| 20 |
DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[C]//Proceedings of NAACL-HLT. 2019: 4171-4186.
|
| 21 |
TENNEY I, DAS D, PAVLICK E. BERT rediscovers the classical NLP pipeline[C]//Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Florence, Italy. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019: 4593-4601.
|
| 22 |
CHO K, VAN MERRIENBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). Doha, Qatar. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 1724-1734.
|
| 23 |
Bahdanau D, Cho K H, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[C]//3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015. 2015.
|
| 24 |
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017: 5998-6008.
|
| 25 |
SHERSTINSKY A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (RNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) network[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 2020, 404: 132306.
|
| 26 |
WANG Q, LI B, XIAO T, et al. Learning deep transformer models for machine translation[C]//Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Florence, Italy. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019: 1810-1822.
|
| 27 |
SÖDING J. Protein homology detection by HMM-HMM comparison[J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(7): 951-960.
|
| 28 |
LIU L Y, REN X, SHANG J B, et al. Efficient contextualized representation: Language model pruning for sequence labeling[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Brussels, Belgium. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018: 1215-1225.
|
| 29 |
Huang Z, Xu W, Yu K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging[EB/OL]. arXiv preprint: 2015, arXiv:1508.01991.
|
| 30 |
ZHAO H S, JIA J Y, KOLTUN V. Exploring self-attention for image recognition[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle: IEEE, 2020, 10073-10082.
|
| 31 |
Dodge J, Ilharco G, Schwartz R, et al. Fine-tuning pretrained language models: Weight initializations, data orders, and early stopping[EB/OL]. arXiv preprint: 2020, arXiv:2002.06305.
|
| 32 |
YADAV S, SHUKLA S. Analysis of k-fold cross-validation over hold-out validation on colossal datasets for quality classification[C]//2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing. Bhimavaram, India: IEEE, 2016: 78-83.
|
| 33 |
ZHANG Z L, SABUNCU M. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels[J]. Montréal: NeurIPS, 2018, 31.
|
| 34 |
LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice: IEEE, 2017: 2999-3007.
|
| 35 |
LI B, SHER D, KELLY L, et al. Catalytic promiscuity in the biosynthesis of cyclic peptide secondary metabolites in planktonic marine cyanobacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(23): 10430-10435.
|
| 36 |
JUMPER J, EVANS R, PRITZEL A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 583-589.
|
| 37 |
XIE Q Z, LUONG M T, HOVY E, et al. Self-training with noisy student improves ImageNet classification[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle: IEEE,2020 : 10684-10695.
|