合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (2): 310-320.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-072
“国际公共卫生紧急事件”下的mRNA疫苗研发
叶青, 秦成峰
- 军事科学院军事医学研究院微生物流行病研究所,病原微生物生物安全全国重点实验室,北京 100071
-
收稿日期:2023-10-07修回日期:2024-01-29出版日期:2024-04-30发布日期:2024-04-28 -
通讯作者:秦成峰 -
作者简介:叶青 (1988—),女,副研究员。研究方向为RNA病毒疫苗设计。E-mail:yy.0526@163.com秦成峰 (1979—),男,研究员,博士生导师,国家杰出青年基金获得者。研究方向为病毒的防控基础与疫苗研究。E-mail:qincf@bmi.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2302400);国家自然科学基金(82241069)
Development of mRNA vaccines in response to the Public Health Emergency of International Concern
YE Qing, QIN Chengfeng
- State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Biosecurity,Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology,Academy of Military Medical Sciences,Academy of Military Sciences,Beijing 100071,China
-
Received:2023-10-07Revised:2024-01-29Online:2024-04-30Published:2024-04-28 -
Contact:QIN Chengfeng
摘要:
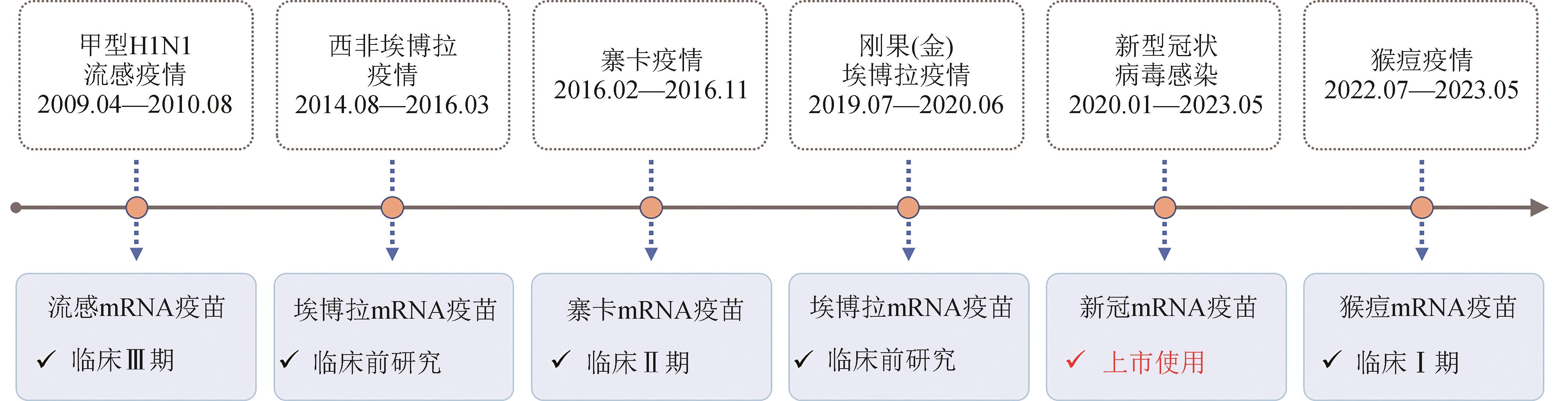
“国际公共卫生紧急事件”(简称PHEIC)是指疾病的国际传播对其他国家构成公共卫生风险,需要采取协调一致的国际应对措施的不同寻常事件。迄今为止,世界卫生组织(WHO)一共宣布了7次PHEIC,包括甲型H1N1流感、埃博拉、脊髓灰质炎、寨卡、新型冠状病毒感染和猴痘疫情。疫苗是应对传染病疫情的有力武器,合成生物学的发展突破了传统疫苗存在的难点问题和技术瓶颈,为病毒性传染病防控提供了全新的思路,尤其是mRNA疫苗作为下一代疫苗研发的平台技术,具有安全性强、有效性良好、研发周期短、易规模化生产、易扩大产能等特点,在应对新突发传染病疫情方面具有明显的优势。目前,新冠mRNA疫苗已正式获批上市,针对流感、寨卡和猴痘病毒的多款mRNA疫苗已进入临床研究阶段,埃博拉mRNA疫苗处于临床前研究阶段,而针对脊髓灰质炎病毒尚无mRNA疫苗研究的报道。本文就历次PHEIC应对中mRNA疫苗的研发进展进行了详细梳理和评述,同时对mRNA疫苗应对PHEIC的未来发展趋势和挑战进行了展望和讨论。结合合成生物学、生物化学和人工智能等多学科技术对mRNA分子设计、高效递送以及疫苗生产和储存运输等进行优化,有望进一步提高mRNA疫苗的有效性和可及性。综上,尽管尚无法预知下一次PHEIC何时会出现,但当下一次PHEIC出现时,mRNA疫苗技术一定会成为人类防范PHEIC的有力武器。
中图分类号:
引用本文
叶青, 秦成峰. “国际公共卫生紧急事件”下的mRNA疫苗研发[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 310-320.
YE Qing, QIN Chengfeng. Development of mRNA vaccines in response to the Public Health Emergency of International Concern[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(2): 310-320.
| 1 | KHAN K, ARINO J, HU W, et al. Spread of a novel influenza A (H1N1) virus via global airline transportation[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2009, 361(2): 212-214. |
| 2 | GOSTIN L O, FRIEDMAN E A. Ebola: a crisis in global health leadership[J]. The Lancet, 2014, 384(9951): 1323-1325. |
| 3 | SOGHAIER M A, SAEED K M I, ZAMAN K K. Public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) has declared twice in 2014; Polio and Ebola at the top[J]. AIMS Public Health, 2015, 2(2): 218-222. |
| 4 | PETERSEN L R, JAMIESON D J, POWERS A M, et al. Zika virus[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2016, 374(16): 1552-1563. |
| 5 | Eurosurveillance Editorial Team. Ebola public health emergency of international concern, democratic republic of the Congo, 2019[J]. Eurosurveillance, 2019, 24(29): 190718e. |
| 6 | WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard[EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. . |
| 7 | MITJÀ O, OGOINA D, TITANJI B K, et al. Monkeypox[J]. The Lancet, 2023, 401(10370): 60-74. |
| 8 | WILDER-SMITH A, OSMAN S. Public health emergencies of international concern: a historic overview[J]. Journal of Travel Medicine, 2020, 27(8): taaa227. |
| 9 | MASCOLA J R, FAUCI A S. Novel vaccine technologies for the 21st century[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2020, 20(2): 87-88. |
| 10 | CHAUDHARY N, WEISSMAN D, WHITEHEAD K A. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: principles, delivery and clinical translation[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(11): 817-838. |
| 11 | PARDI N, HOGAN M J, WEISSMAN D. Recent advances in mRNA vaccine technology[J]. Current Opinion in Immunology, 2020, 65: 14-20. |
| 12 | WOLFF J A, MALONE R W, WILLIAMS P, et al. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo [J]. Science, 1990, 247(4949 Pt 1): 1465-1468. |
| 13 | KARIKÓ K, BUCKSTEIN M, NI H P, et al. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA[J]. Immunity, 2005, 23(2): 165-175. |
| 14 | SIMONSEN L, SPREEUWENBERG P, LUSTIG R, et al. Global mortality estimates for the 2009 Influenza Pandemic from the GLaMOR project: a modeling study[J]. PLoS Medicine, 2013, 10(11): e1001558. |
| 15 | DAWOOD F S, IULIANO A D, REED C, et al. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: a modelling study[J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2012, 12(9): 687-695. |
| 16 | PAPPAS C, AGUILAR P V, BASLER C F, et al. Single gene reassortants identify a critical role for PB1, HA, and NA in the high virulence of the 1918 pandemic influenza virus[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(8): 3064-3069. |
| 17 | WATANABE T, TISONCIK-GO J, TCHITCHEK N, et al. 1918 Influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) and the viral RNA polymerase complex enhance viral pathogenicity, but only HA induces aberrant host responses in mice[J]. Journal of Virology, 2013, 87(9): 5239-5254. |
| 18 | NACHBAGAUER R, KRAMMER F. Universal influenza virus vaccines and therapeutic antibodies[J]. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 2017, 23(4): 222-228. |
| 19 | FREYN A W, RAMOS DA SILVA J, ROSADO V C, et al. A multi-targeting, nucleoside-modified mRNA influenza virus vaccine provides broad protection in mice[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2020, 28(7): 1569-1584. |
| 20 | BAHL K, SENN J J, YUZHAKOV O, et al. Preclinical and clinical demonstration of immunogenicity by mRNA vaccines against H10N8 and H7N9 influenza viruses[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2017, 25(6): 1316-1327. |
| 21 | FELDMAN R A, FUHR R, SMOLENOV I, et al. mRNA vaccines against H10N8 and H7N9 influenza viruses of pandemic potential are immunogenic and well tolerated in healthy adults in phase 1 randomized clinical trials[J]. Vaccine, 2019, 37(25): 3326-3334. |
| 22 | Moderna Announces Positive Interim Phase 1 Data for mRNA Flu Vaccine and Provides Program Update[EB/OL]. (2021-12-10)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 23 | Moderna Announces First Participants Dosed in Phase 3 Study of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Candidate(mRNA-1010)[Eb/OL]. 2022-06-07[2023-10-01]. . |
| 24 | Moderna Announces First Participants Dosed in Phase 1/2 Study with mRNA-1020 and mRNA-1030 Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Candidates[EB/OL]. (2022-04-11)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 25 | AREVALO C P, BOLTON M J, LE SAGE V, et al. A multivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine against all known influenza virus subtypes[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6622): 899-904. |
| 26 | JACOB S T, CROZIER I, FISCHER W A, et al. Ebola virus disease[J]. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2020, 6(1): 13. |
| 27 | WHO. Ebola outbreak 2014-2016-West Africa[EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. . |
| 28 | CDC. 2014-2016 Ebola Outbreak in West Africa[EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. . |
| 29 | WHO. Ebola virus disease Democratic Republic of Congo: external situation report 98/ 2020[EB/OL]. (2020-06-24)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 30 | GHOSH S, SAHA A, SAMANTA S, et al. Genome structure and genetic diversity in the Ebola virus[J]. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 2021, 60: 83-90. |
| 31 | HENAO-RESTREPO A M, CAMACHO A, LONGINI I M, et al. Efficacy and effectiveness of an rVSV-vectored vaccine in preventing Ebola virus disease: final results from the Guinea ring vaccination, open-label, cluster-randomised trial (Ebola Ça Suffit!)[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10068): 505-518. |
| 32 | MILLIGAN I D, GIBANI M M, SEWELL R, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of novel adenovirus type 26- and modified vaccinia ankara-vectored Ebola vaccines: a randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(15): 1610-1623. |
| 33 | ZHU F C, WURIE A H, HOU L H, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant adenovirus type-5 vector-based Ebola vaccine in healthy adults in Sierra Leone: a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10069): 621-628. |
| 34 | MALIK S, KISHORE S, NAG S, et al. Ebola virus disease vaccines: development, current perspectives & challenges[J]. Vaccines, 2023, 11(2): 268. |
| 35 | CHAHAL J S, KHAN O F, COOPER C L, et al. Dendrimer-RNA nanoparticles generate protective immunity against lethal Ebola, H1N1 influenza, and Toxoplasma gondii challenges with a single dose[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(29): E4133-E4142. |
| 36 | MEYER M, HUANG E, YUZHAKOV O, et al. Modified mRNA-based vaccines elicit robust immune responses and protect guinea pigs from Ebola virus disease[J]. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2018, 217(3): 451-455. |
| 37 | KRÄHLING V, ERBAR S, KUPKE A, et al. Self-amplifying RNA vaccine protects mice against lethal Ebola virus infection[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2023, 31(2): 374-386. |
| 38 | PLATT L R, ESTÍVARIZ C F, SUTTER R W. Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis: a review of the epidemiology and estimation of the global burden[J]. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2014, 210(): S380-S389. |
| 39 | WHO. Poliomyelitis[EB/OL]. [2023-10-25]. . |
| 40 | MBANI C J, NEKOUA M P, MOUKASSA D, et al. The fight against poliovirus is not over[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(5): 1323. |
| 41 | CUGOLA F R, FERNANDES I R, RUSSO F B, et al. The Brazilian Zika virus strain causes birth defects in experimental models[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7606): 267-271. |
| 42 | IKEJEZIE J, SHAPIRO C N, KIM J, et al. Zika virus transmission-region of the americas, May 15, 2015—December 15, 2016[J]. MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 2017, 66(12): 329-334. |
| 43 | LINDENBACH B D, RICE C M. Molecular biology of flaviviruses[J]. Advances in Virus Research, 2003, 59: 23-61. |
| 44 | DAI L P, SONG J, LU X S, et al. Structures of the Zika virus envelope protein and its complex with a flavivirus broadly protective antibody[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2016, 19(5): 696-704. |
| 45 | KIM S Y, ZHAO J, LIU X Y, et al. Interaction of Zika virus envelope protein with glycosaminoglycans[J]. Biochemistry, 2017, 56(8): 1151-1162. |
| 46 | HASAN S S, MILLER A, SAPPARAPU G, et al. A human antibody against Zika virus crosslinks the E protein to prevent infection[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14722. |
| 47 | LIN H H, YIP B S, HUANG L M, et al. Zika virus structural biology and progress in vaccine development[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(1): 47-53. |
| 48 | RICHNER J M, HIMANSU S, DOWD K A, et al. Modified mRNA vaccines protect against Zika virus infection[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(1): 176. |
| 49 | PARDI N, HOGAN M J, PELC R S, et al. Zika virus protection by a single low-dose nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccination[J]. Nature, 2017, 543(7644): 248-251. |
| 50 | BOLLMAN B, NUNNA N, BAHL K, et al. An optimized messenger RNA vaccine candidate protects non-human Primates from Zika virus infection[J]. NPJ Vaccines, 2023, 8(1): 58. |
| 51 | HUANG C L, WANG Y M, LI X W, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China[J]. The Lancet, 2020, 395(10223): 497-506. |
| 52 | PULLIAM J R C, VAN SCHALKWYK C, GOVENDER N, et al. Increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection associated with emergence of Omicron in South Africa[J]. Science, 2022, 376(6593): eabn4947. |
| 53 | LIPSITCH M, KRAMMER F, REGEV-YOCHAY G, et al. SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals: measurement, causes and impact[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2022, 22(1): 57-65. |
| 54 | HU B, GUO H, ZHOU P, et al. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 19(3): 141-154. |
| 55 | SHANG J, YE G, SHI K, et al. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2[J]. Nature, 2020, 581(7807): 221-224. |
| 56 | OU X Y, LIU Y, LEI X B, et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1620. |
| 57 | HOFFMANN M, KLEINE-WEBER H, SCHROEDER S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(2): 271-280.e8. |
| 58 | LETKO M, MARZI A, MUNSTER V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2020, 5(4): 562-569. |
| 59 | WALLS A C, PARK Y J, TORTORICI M A, et al. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(2): 281-292.e6. |
| 60 | WANG K, JIA Z J, BAO L, et al. Memory B cell repertoire from triple vaccinees against diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants[J]. Nature, 2022, 603(7903): 919-925. |
| 61 | PICCOLI L, PARK Y J, TORTORICI M A, et al. Mapping neutralizing and immunodominant sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain by structure-guided high-resolution serology[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(4): 1024-1042.e21. |
| 62 | GREANEY A J, LOES A N, GENTLES L E, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine elicits more RBD-focused neutralization, but with broader antibody binding within the RBD[EB/OL]. bioRxiv 2021: 2021.04.14.439844(2021-04-14)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 63 | JU B, ZHANG Q, GE J W, et al. Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection[J]. Nature, 2020, 584(7819): 115-119. |
| 64 | PINTO D, PARK Y J, BELTRAMELLO M, et al. Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody[J]. Nature, 2020, 583(7815): 290-295. |
| 65 | RAPPAZZO C G, TSE L V, KAKU C I, et al. Broad and potent activity against SARS-like viruses by an engineered human monoclonal antibody[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6531): 823-829. |
| 66 | ZHOU Y J, LIU Z Z, LI S B, et al. Enhancement versus neutralization by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from a convalescent donor associates with distinct epitopes on the RBD[J]. Cell Reports, 2021, 34(5): 108699. |
| 67 | WHO. COVID-19 vaccines with WHO emergency use listing[EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. . |
| 68 | JACKSON L A, ANDERSON E J, ROUPHAEL N G, et al. An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 - preliminary report[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2020, 383(20): 1920-1931. |
| 69 | BADEN L R, SAHLY H M EL, ESSINK B, et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2021, 384(5): 403-416. |
| 70 | FRENCK R W JR, KLEIN N P, KITCHIN N, et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2021, 385(3): 239-250. |
| 71 | POLACK F P, THOMAS S J, KITCHIN N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2020, 383(27): 2603-2615. |
| 72 | WANG Q, IKETANI S, LI Z T, et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(2): 279-286.e8. |
| 73 | ZHANG N N, LI X F, DENG Y Q, et al. A thermostable mRNA vaccine against COVID-19[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(5): 1271-1283.e16. |
| 74 | CHEN G L, LI X F, DAI X H, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 ARCoV mRNA vaccine in Chinese adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial[J]. The Lancet Microbe, 2022, 3(3): e193-e202. |
| 75 | LUM F M, TORRES-RUESTA A, TAY M Z, et al. Monkeypox: disease epidemiology, host immunity and clinical interventions[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2022, 22(10): 597-613. |
| 76 | EBIoMEDICINE. Monkeypox virus outbreak: can evolution guide us to new treatments or vaccines?[J]. EBioMedicine, 2022, 82: 104221. |
| 77 | WHO. Multi-country monkeypox outbreak in non-endemic countries[EB/OL]. (2022-05-21)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 78 | ZUMLA A, VALDOLEIROS S R, HAIDER N, et al. Monkeypox outbreaks outside endemic regions: scientific and social priorities[J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2022, 22(7): 929-931. |
| 79 | DUQUE M P, RIBEIRO S, MARTINS J V, et al. Ongoing monkeypox virus outbreak, Portugal, 29 April to 23 May 2022[J]. Eurosurveillance, 2022, 27(22): 2200424. |
| 80 | VIVANCOS R, ANDERSON C, BLOMQUIST P, et al. Community transmission of monkeypox in the United Kingdom, April to May 2022[J]. Eurosurveillance, 2022, 27(22): 2200422. |
| 81 | WHO. 2022-23 Mpox (Monkeypox) outbreak:global trends[EB/OL]. [2024-01-26]. . |
| 82 | TARÍN-VICENTE E J, ALEMANY A, AGUD-DIOS M, et al. Clinical presentation and virological assessment of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in Spain: a prospective observational cohort study[J]. The Lancet, 2022, 400(10353): 661-669. |
| 83 | PAULI G, BLÜMEL J, BURGER R, et al. Orthopox viruses: infections in humans[J]. Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy, 2010, 37(6): 351-364. |
| 84 | ROBERTS K L, SMITH G L. Vaccinia virus morphogenesis and dissemination[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2008, 16(10): 472-479. |
| 85 | HOOPER J W, CUSTER D M, THOMPSON E. Four-gene-combination DNA vaccine protects mice against a lethal vaccinia virus challenge and elicits appropriate antibody responses in nonhuman Primates[J]. Virology, 2003, 306(1): 181-195. |
| 86 | MUCKER E M, GOLDEN J W, HAMMERBECK C D, et al. A nucleic acid-based orthopoxvirus vaccine targeting the vaccinia virus L1, A27, B5, and A33 proteins protects rabbits against lethal rabbitpox virus aerosol challenge[J]. Journal of Virology, 2022, 96(3): e0150421. |
| 87 | HOOPER J W, GOLDEN J W, FERRO A M, et al. Smallpox DNA vaccine delivered by novel skin electroporation device protects mice against intranasal poxvirus challenge[J]. Vaccine, 2007, 25(10): 1814-1823. |
| 88 | HIRAO L A, DRAGHIA-AKLI R, PRIGGE J T, et al. Multivalent smallpox DNA vaccine delivered by intradermal electroporation drives protective immunity in nonhuman primates against lethal monkeypox challenge[J]. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2011, 203(1): 95-102. |
| 89 | SAKHATSKYY P, WANG S X, CHOU T H W, et al. Immunogenicity and protection efficacy of monovalent and polyvalent poxvirus vaccines that include the D8 antigen[J]. Virology, 2006, 355(2): 164-174. |
| 90 | FDA. FDA approves first live, non-replicating vaccine to prevent smallpox and monkeypox[EB/OL]. (2019-09-24)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 91 | FDA. Key facts about vaccines to prevent monkeypox disease[EB/OL]. (2022-08-18)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 92 | ZAECK L M, LAMERS M M, VERSTREPEN B E, et al. Low levels of monkeypox virus-neutralizing antibodies after MVA-BN vaccination in healthy individuals[J]. Nature Medicine, 2023, 29(1): 270-278. |
| 93 | FREYN A W, ATYEO C, EARL P, et al. A monkeypox mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine targeting virus binding, entry, and transmission drives protection against lethal orthopoxviral challenge[EB/OL]. bioRxiv(2022-12-19)[2023-10-01]. . |
| 94 | FANG Z H, MONTEIRO V S, RENAUER P A, et al. Polyvalent mRNA vaccination elicited potent immune response to monkeypox virus surface antigens[J]. Cell Research, 2023, 33(5): 407-410. |
| 95 | HOU F J, ZHANG Y T, LIU X H, et al. mRNA vaccines encoding fusion proteins of monkeypox virus antigens protect mice from vaccinia virus challenge[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 5925. |
| 96 | ZHANG R R, WANG Z J, ZHU Y L, et al. Rational development of multicomponent mRNA vaccine candidates against mpox[J]. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 2023, 12(1): 2192815. |
| 97 | SANG Y, ZHANG Z, LIU F, et al. Monkeypox virus quadrivalent mRNA vaccine induces immune response and protects against vaccinia virus[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2023, 8(1): 172. |
| 98 | ZENG J W, LI Y, JIANG L R, et al. Mpox multi-antigen mRNA vaccine candidates by a simplified manufacturing strategy afford efficient protection against lethal orthopoxvirus challenge[J]. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 2023, 12(1): 2204151. |
| [1] | 刘泽众, 周洁, 朱赟, 陆路, 姜世勃. 基于重组人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的三聚体抗原疫苗策略在新冠和流感疫苗中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 385-395. |
| [2] | 郭茜亚, 陈积, 董铭心. 流感病毒改造新策略及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 267-280. |
| [3] | 万里川, 王学军, 王升启. 新型冠状病毒复制子人工合成和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 174-190. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||