合成生物学 ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (1): 213-227.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-046
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
大肠杆菌中终止子对下游转录单元基因表达的影响
任家卫1,2, 张金鹏1,2, 徐国强1,2, 张晓梅3, 许正宏4, 张晓娟1,2
- 1.江南大学生物工程学院工业生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
2.江南大学粮食发酵与食品生物制造国家工程研究中心,江苏 无锡 214122
3.江南大学生命科学与健康工程学院,江苏 无锡 214122
4.四川大学轻工科学与工程学院,四川 成都 610065
-
收稿日期:2024-06-17修回日期:2024-08-22出版日期:2025-02-28发布日期:2025-03-12 -
通讯作者:张晓娟 -
作者简介:任家卫 (1999—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为终止子调控元件开发。E-mail:297887816@qq.com张晓娟 (1982—),女,教授。研究方向为酿造食品微生物开发与应用、新型工业菌株的基因表达调控元件开发。E-mail:zhangxj@jiangnan.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32171421)
Effect of terminators on the downstream transcript unit with gene expression in Escherichiacoli
REN Jiawei1,2, ZHANG Jinpeng1,2, XU Guoqiang1,2, ZHANG Xiaomei3, XU Zhenghong4, ZHANG Xiaojuan1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology of Ministry of Education,School of Biotechnology,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
2.National Engineering Research Center for Cereal Fermentation and Food Biomanufacturing,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
3.School of Life Science and Health Engineering,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
4.College of Light Industry Science and Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,Sichuan,China
-
Received:2024-06-17Revised:2024-08-22Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-12 -
Contact:ZHANG Xiaojuan
摘要:
在基因转录过程中,RNA聚合酶通过识别启动子序列启动转录过程,而当其识别到位于3′-UTR的终止子序列后,转录复合物解离,转录过程终止。因此,转录单元内的启动子和终止子分别发挥启动和终止转录的作用。然而,对于下游的转录单元,终止子除了终止转录本通读这一直接作用以外,其与RNA聚合酶之间的解离可能会影响后续转录单元中启动子与RNA聚合酶的结合,从而间接改变下游转录单元的表达。这种跨转录单元的终止子和启动子之间的互作关系目前尚缺少研究,因此,明确终止子对下游转录单元的转录反应强度的影响对于精准调控基因表达、开发高效终止子具有重要的意义。本研究通过one-pot技术将9种终止子、5种间隔序列和9种启动子进行组合构建了一个包含405种不同组合元件(终止子-间隔序列-启动子)的组装文库,基于FlowSeq技术对文库中所有组合进行测序和荧光强度分析,进而建立组合序列-下游基因表达之间的相关性。结果表明弱终止子、短间隔以及强启动子的组合更有利于提高下游基因的表达。通过对转录本的定量分析发现弱终止子不仅提高下游的渗漏转录(提高21~70倍),同时也促进了下游启动子重新招募RNA聚合酶进行重启转录(提高2~3倍)。本研究解析了终止子对下游转录单元基因表达的调控效果和机制,为利用终止子构建基因回路提供设计依据。
中图分类号:
引用本文
任家卫, 张金鹏, 徐国强, 张晓梅, 许正宏, 张晓娟. 大肠杆菌中终止子对下游转录单元基因表达的影响[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 213-227.
REN Jiawei, ZHANG Jinpeng, XU Guoqiang, ZHANG Xiaomei, XU Zhenghong, ZHANG Xiaojuan. Effect of terminators on the downstream transcript unit with gene expression in Escherichiacoli[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 213-227.
| Name | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichiacoli JM109 | EUROSCARF | |
| Escherichiacoli BL21 | EUROSCARF | |
| PTK | Dual Fluorescent Probe Plasmid,Kanr, T7 promoter, EGFP, mRFP1, T7 terminator | this study |
| PTK-pot | PTK derivatives carrying one-pot assembly libraries | this study |
| PTK-pheA-13-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-13, and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-pheA-13-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-13, and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| PTK-pheA-40-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-40, and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-pheA-40-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-40, and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| PTK-recA-13-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-13 and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-recA-13-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-13 and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| PTK-recA-40-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-40 and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-recA-40-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-40 and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
表1 本研究所涉及的菌株和质粒信息
Table 1 Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Name | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichiacoli JM109 | EUROSCARF | |
| Escherichiacoli BL21 | EUROSCARF | |
| PTK | Dual Fluorescent Probe Plasmid,Kanr, T7 promoter, EGFP, mRFP1, T7 terminator | this study |
| PTK-pot | PTK derivatives carrying one-pot assembly libraries | this study |
| PTK-pheA-13-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-13, and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-pheA-13-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-13, and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| PTK-pheA-40-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-40, and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-pheA-40-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator pheA, the spacer sequence sp-40, and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| PTK-recA-13-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-13 and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-recA-13-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-13 and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| PTK-recA-40-e | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-40 and the promoter dap-e | this study |
| PTK-recA-40-e12 | PTK derivatives carrying the terminator recA, the spacer sequence sp-40 and the promoter dap-e12 | this study |
| Primer | Description |
|---|---|
| pheA-F | TAGCAACAATAAGGCCTCCCAAATCGGGGGGCCTTTTTTATTGAT |
| pheA-R | TTAGATCAATAAAAAAGGCCCCCCGATTTGGGAGGCCTTATTGTT |
| thrL-F | TAGCTCAAAAAAGCCCGCACCTGACAGTGCGGGCTTTTTTTTTACT |
| thrL-R | TTAGAGTAAAAAAAAAGCCCGCACTGTCAGGTGCGGGCTTTTTTGA |
| rpsO-F | TAGCCAGAAAAGGGGGCCTGAGTGGCCCCTTTTTTCAAGCT |
| rpsO-R | TTAGAGCTTGAAAAAAGGGGCCACTCAGGCCCCCTTTTCTG |
| arcA-F | TAGCAATAAAAACGGCGCTAAAAAGCGCCGTTTTTTTTGACG |
| arcA-R | TTAGCGTCAAAAAAAACGGCGCTTTTTAGCGCCGTTTTTATT |
| fhuE-F | TAGCGTAAAAAAGGCAGCCATCTGGCTGCCTTAGTCTCCCCA |
| fhuE-R | TTAGTGGGGAGACTAAGGCAGCCAGATGGCTGCCTTTTTTAC |
| hisI-F | TAGCCCCTGCCCTTTTTCTTTAAAACCGAAAAGATTACTTCGCGT |
| hisI-R | TTAGACGCGAAGTAATCTTTTCGGTTTTAAAGAAAAAGGGCAGGG |
| recA-F | TAGCAAGCAAAAGGGCCGCAGATGCGACCCTTGTGTATCAAC |
| recA-R | TTAGGTTGATACACAAGGGTCGCATCTGCGGCCCTTTTGCTT |
| T7-MOD-F | TAGCAAACAGATAGGCCCTCttcgGAGGGCCtatctgttTTTTTTT |
| T7-MOD-R | TTAGAAAAAAAaacagataGGCCCTCcgaaGAGGGCCTATCTGTTT |
| SP-TE-F | TAGCCCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SP-TE-R | TTAGGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAACATTGG |
| SPACE-5-F | CTAACTATC |
| SPACE-5-R | TTATGATAG |
| SPACE-13-F | CTAAAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-13-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTT |
| SPACE-20-F | CTAAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-20-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGAC |
| SPACE-28-F | CTAACATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-28-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATG |
| SPACE-35-F | CTAAGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-35-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAAC |
| SPACE-40-F | CTAACCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-40-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAACATTGG |
| dap-A16-F | ATAATTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAAGAAGGTATAATTGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dap-A16-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCAATTATACCTTCTTCCCTCATTTGGGGGTTAAACAA |
| dap-e-F | ATAATTGTTTAGCCACCAAATGAGGGAAAGAGGCACAATGGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dap-e-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCCATTGTGCCTCTTTCCCTCATTTGGTGGCTAAACAA |
| dapA-e10-F | ATAATTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e10-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCAATTATACCACATTCCCTCATTTGGTGTCAAAACAA |
| dapA-e11-F | ATAATTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGCTATAATGGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e11-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCCATTATAGCACATTCCCTCATTTGGTGTCAAAACAA |
| dapA-e12-F | ATAATTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTAGAGTGGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e12-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCCACTCTACCACATTCCCTCATTTGGTGTCAAAACAA |
| dapA-e10-35-F | ATAATTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e10-35-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCAATTATACCACATTCCCTCATTTGGGGGTTAAACAA |
| J1-F | ATAATTGACAATTTTCTTAAATTGTGTTACAATGGGTTTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| J1-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAAACCCATTGTAACACAATTTAAGAAAATTGTCAA |
| J2-F | ATAATTGACATTTTTTTAGTTTTGAGTTACAATGGTTGTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| J2-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGACAACCATTGTAACTCAAAACTAAAAAAATGTCAA |
| SP-PRO-F | ATAAGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| SP-TRO-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAAC |
| T7-CG-F | AATTCCGGCCGCGGGGCCCGCTTCGGCGGGCCCCGCGGCCGTTTTTTTAAACTGAACTATCG |
| T7-CG-R | GATCCGATAGTTCAGTTTAAAAAAACGGCCGCGGGGCCCGCCGAAGCGGGCCCCGCGGCCGG |
| WEAK-F | AATTCAGCCCCTCAGTATAGGGGCGTATTTTCTCAAACTGAACTATCG |
| WEAK-R | GATCCGATAGTTCAGTTTGAGAAAATACGCCCCTATACTGAGGGGCTG |
表2 本实验所用的引物
Table 2 Primers used in this study
| Primer | Description |
|---|---|
| pheA-F | TAGCAACAATAAGGCCTCCCAAATCGGGGGGCCTTTTTTATTGAT |
| pheA-R | TTAGATCAATAAAAAAGGCCCCCCGATTTGGGAGGCCTTATTGTT |
| thrL-F | TAGCTCAAAAAAGCCCGCACCTGACAGTGCGGGCTTTTTTTTTACT |
| thrL-R | TTAGAGTAAAAAAAAAGCCCGCACTGTCAGGTGCGGGCTTTTTTGA |
| rpsO-F | TAGCCAGAAAAGGGGGCCTGAGTGGCCCCTTTTTTCAAGCT |
| rpsO-R | TTAGAGCTTGAAAAAAGGGGCCACTCAGGCCCCCTTTTCTG |
| arcA-F | TAGCAATAAAAACGGCGCTAAAAAGCGCCGTTTTTTTTGACG |
| arcA-R | TTAGCGTCAAAAAAAACGGCGCTTTTTAGCGCCGTTTTTATT |
| fhuE-F | TAGCGTAAAAAAGGCAGCCATCTGGCTGCCTTAGTCTCCCCA |
| fhuE-R | TTAGTGGGGAGACTAAGGCAGCCAGATGGCTGCCTTTTTTAC |
| hisI-F | TAGCCCCTGCCCTTTTTCTTTAAAACCGAAAAGATTACTTCGCGT |
| hisI-R | TTAGACGCGAAGTAATCTTTTCGGTTTTAAAGAAAAAGGGCAGGG |
| recA-F | TAGCAAGCAAAAGGGCCGCAGATGCGACCCTTGTGTATCAAC |
| recA-R | TTAGGTTGATACACAAGGGTCGCATCTGCGGCCCTTTTGCTT |
| T7-MOD-F | TAGCAAACAGATAGGCCCTCttcgGAGGGCCtatctgttTTTTTTT |
| T7-MOD-R | TTAGAAAAAAAaacagataGGCCCTCcgaaGAGGGCCTATCTGTTT |
| SP-TE-F | TAGCCCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SP-TE-R | TTAGGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAACATTGG |
| SPACE-5-F | CTAACTATC |
| SPACE-5-R | TTATGATAG |
| SPACE-13-F | CTAAAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-13-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTT |
| SPACE-20-F | CTAAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-20-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGAC |
| SPACE-28-F | CTAACATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-28-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATG |
| SPACE-35-F | CTAAGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-35-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAAC |
| SPACE-40-F | CTAACCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC |
| SPACE-40-R | TTATGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAACATTGG |
| dap-A16-F | ATAATTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAAGAAGGTATAATTGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dap-A16-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCAATTATACCTTCTTCCCTCATTTGGGGGTTAAACAA |
| dap-e-F | ATAATTGTTTAGCCACCAAATGAGGGAAAGAGGCACAATGGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dap-e-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCCATTGTGCCTCTTTCCCTCATTTGGTGGCTAAACAA |
| dapA-e10-F | ATAATTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e10-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCAATTATACCACATTCCCTCATTTGGTGTCAAAACAA |
| dapA-e11-F | ATAATTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGCTATAATGGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e11-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCCATTATAGCACATTCCCTCATTTGGTGTCAAAACAA |
| dapA-e12-F | ATAATTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTAGAGTGGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e12-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCCACTCTACCACATTCCCTCATTTGGTGTCAAAACAA |
| dapA-e10-35-F | ATAATTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| dapA-e10-35-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGAGTTCAATTATACCACATTCCCTCATTTGGGGGTTAAACAA |
| J1-F | ATAATTGACAATTTTCTTAAATTGTGTTACAATGGGTTTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| J1-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAAACCCATTGTAACACAATTTAAGAAAATTGTCAA |
| J2-F | ATAATTGACATTTTTTTAGTTTTGAGTTACAATGGTTGTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| J2-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGACAACCATTGTAACTCAAAACTAAAAAAATGTCAA |
| SP-PRO-F | ATAAGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATCTCGCTCAAGGCGCAAGGAGCACACACA |
| SP-TRO-R | TCATTGTGTGTGCTCCTTGCGCCTTGAGCGAGATAGTTCAGTTTCTGTGACTGGATATGAGTAAAC |
| T7-CG-F | AATTCCGGCCGCGGGGCCCGCTTCGGCGGGCCCCGCGGCCGTTTTTTTAAACTGAACTATCG |
| T7-CG-R | GATCCGATAGTTCAGTTTAAAAAAACGGCCGCGGGGCCCGCCGAAGCGGGCCCCGCGGCCGG |
| WEAK-F | AATTCAGCCCCTCAGTATAGGGGCGTATTTTCTCAAACTGAACTATCG |
| WEAK-R | GATCCGATAGTTCAGTTTGAGAAAATACGCCCCTATACTGAGGGGCTG |
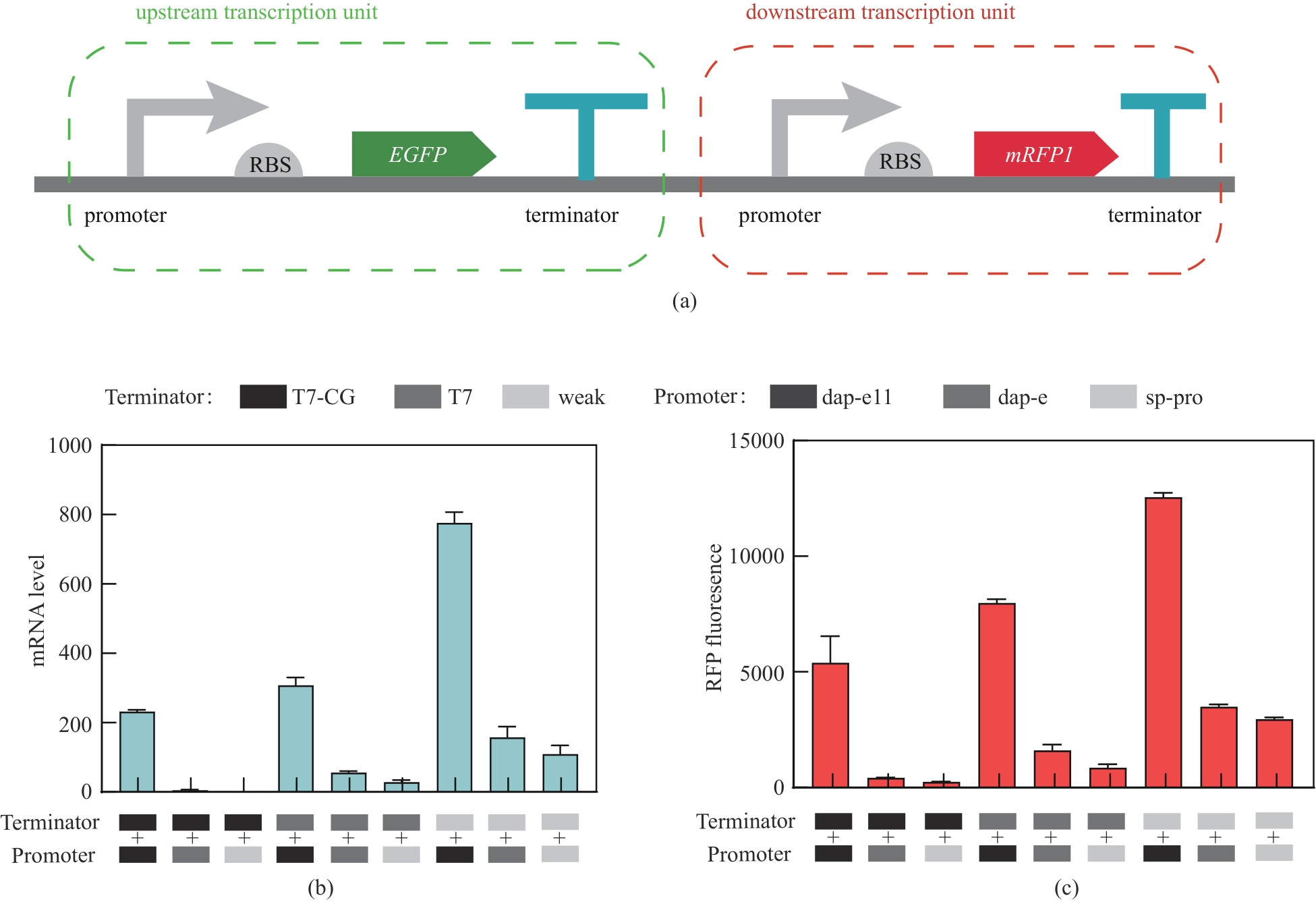
图1 不同强度终止子和启动子组合调控效果质粒中上游和下游转录单元结构示意图(a)以及9种突变质粒中下游转录单元红色荧光转录水平(b)和表达水平(c)
Fig. 1 Analysis of the regulatory effect of the combination of terminators and promoters with different strengthsSchematic structure of upstream and downstream transcriptional units in the plasmid (a), red fluorescent transcript levels (b), and expression levels (c) of downstream transcriptional units in the nine mutant plasmids
| Assembly | Part Name | Activity | Sequence(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terminator | pheA | Strong ↓ weak | AATCATAAGGCCTGACAAATCGGGGGGGATTTTTTCTTGA |
| thrL | TCCAAAAAGCCCCGACCTGACAGTGACGGCTTTTTTATTAC | ||
| T7-MOD | AAACAGATAGGCCCTCTTCGGAGGGCCTATCTGTTTTTTTTT | ||
| arcA | AATATAAACGGCGCTAAAACGCGCGGTTTTTTTTGCC | ||
| rpsO | CAGCAAAGGGTGCCTGAGTGCTCCCTTTTTGCAAGC | ||
| fhuE | GTAAAAAAGGCAGCCATCTGGCTGCCTTAGTCTCCCCA | ||
| hisI | CCCTGCCCTTTTTCTTTAAAACCGAAAAGATTACTTCGCGT | ||
| recA | AAGCAAAAGGGCCGCAGATGCGACCCTTGTGTATCAAC | ||
| SP-TE | CCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| Spacer | SP-13 | Short ↓ Long | AAACTGAACTATC |
| SP-20 | GTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| SP-28 | CATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| SP-35 | GTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| SP-40 | CCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| Promoter | dapA-e12 | Strong ↓ weak | TTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTAGAGTGGAACTC |
| dapA-e11 | TTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGCTATAATGGAACTC | ||
| dapA-e10 | TTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTC | ||
| dap-A16 | TAGGTTTTTTGCGGGGTTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAAGAAGGTATAATTGAACTC | ||
| J2 | TTGACATTTTTTTAGTTTTGAGTTACAATGGTTG | ||
| dapA-e10-35 | TTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTC | ||
| J1 | TTGACAATTTTCTTAAATTGTGTTACAATGGGTT | ||
| dap-e | TTGTTTAGCCACCAAATGAGGGAAAGAGGCACAATGGAACTC | ||
| SP-PRO | GTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAAC |
表3 文库中包含的组件
Table 3 Parts in the library
| Assembly | Part Name | Activity | Sequence(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terminator | pheA | Strong ↓ weak | AATCATAAGGCCTGACAAATCGGGGGGGATTTTTTCTTGA |
| thrL | TCCAAAAAGCCCCGACCTGACAGTGACGGCTTTTTTATTAC | ||
| T7-MOD | AAACAGATAGGCCCTCTTCGGAGGGCCTATCTGTTTTTTTTT | ||
| arcA | AATATAAACGGCGCTAAAACGCGCGGTTTTTTTTGCC | ||
| rpsO | CAGCAAAGGGTGCCTGAGTGCTCCCTTTTTGCAAGC | ||
| fhuE | GTAAAAAAGGCAGCCATCTGGCTGCCTTAGTCTCCCCA | ||
| hisI | CCCTGCCCTTTTTCTTTAAAACCGAAAAGATTACTTCGCGT | ||
| recA | AAGCAAAAGGGCCGCAGATGCGACCCTTGTGTATCAAC | ||
| SP-TE | CCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| Spacer | SP-13 | Short ↓ Long | AAACTGAACTATC |
| SP-20 | GTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| SP-28 | CATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| SP-35 | GTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| SP-40 | CCAATGTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAACTATC | ||
| Promoter | dapA-e12 | Strong ↓ weak | TTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTAGAGTGGAACTC |
| dapA-e11 | TTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGCTATAATGGAACTC | ||
| dapA-e10 | TTGTTTTGACACCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTC | ||
| dap-A16 | TAGGTTTTTTGCGGGGTTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAAGAAGGTATAATTGAACTC | ||
| J2 | TTGACATTTTTTTAGTTTTGAGTTACAATGGTTG | ||
| dapA-e10-35 | TTGTTTAACCCCCAAATGAGGGAATGTGGTATAATTGAACTC | ||
| J1 | TTGACAATTTTCTTAAATTGTGTTACAATGGGTT | ||
| dap-e | TTGTTTAGCCACCAAATGAGGGAAAGAGGCACAATGGAACTC | ||
| SP-PRO | GTTTACTCATATCCAGTCACAGAAACTGAAC |
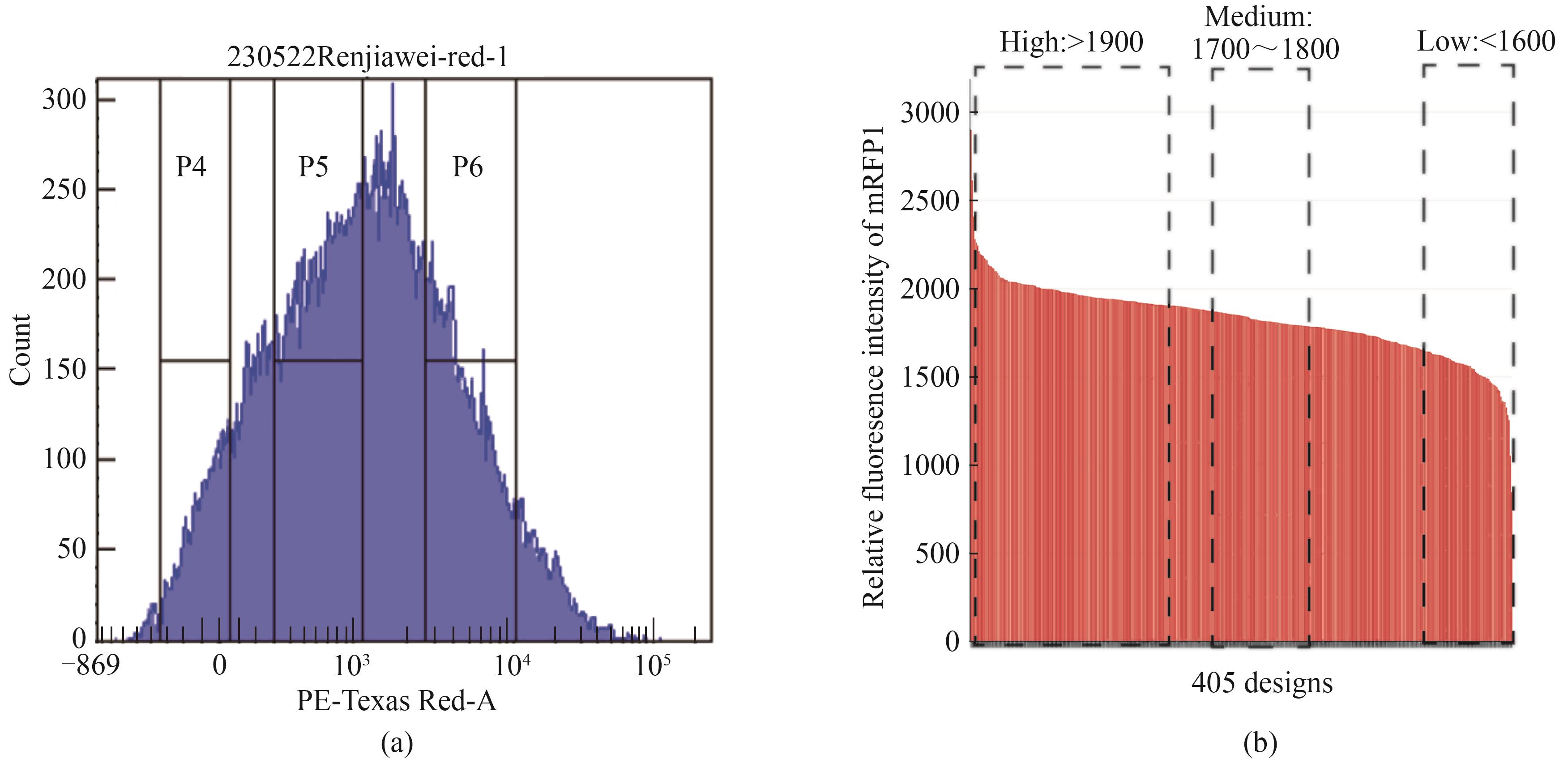
图2 组合调控元件(终止子-间隔-启动子)调控的下游基因表达强度(a)根据下游红色荧光表达水平对包含组合元件的细胞进行流式筛选;(b)根据下游相对荧光加权强度对组合元件进行高表达、中表达、低表达分组
Fig. 2 Expression of downstream genes regulated by the assemblies of terminator-spacer-promoter(a) Screening of combinatorial elements by flow cytometry based on the red fluorescence for the expression of targeted genes; (b) Grouping of the assemblies of terminator-spacer-promoter into High, Medium, and Low expression groups based on the relative fluorescence intensity of mRFP1 associated with the expression of targeted genes
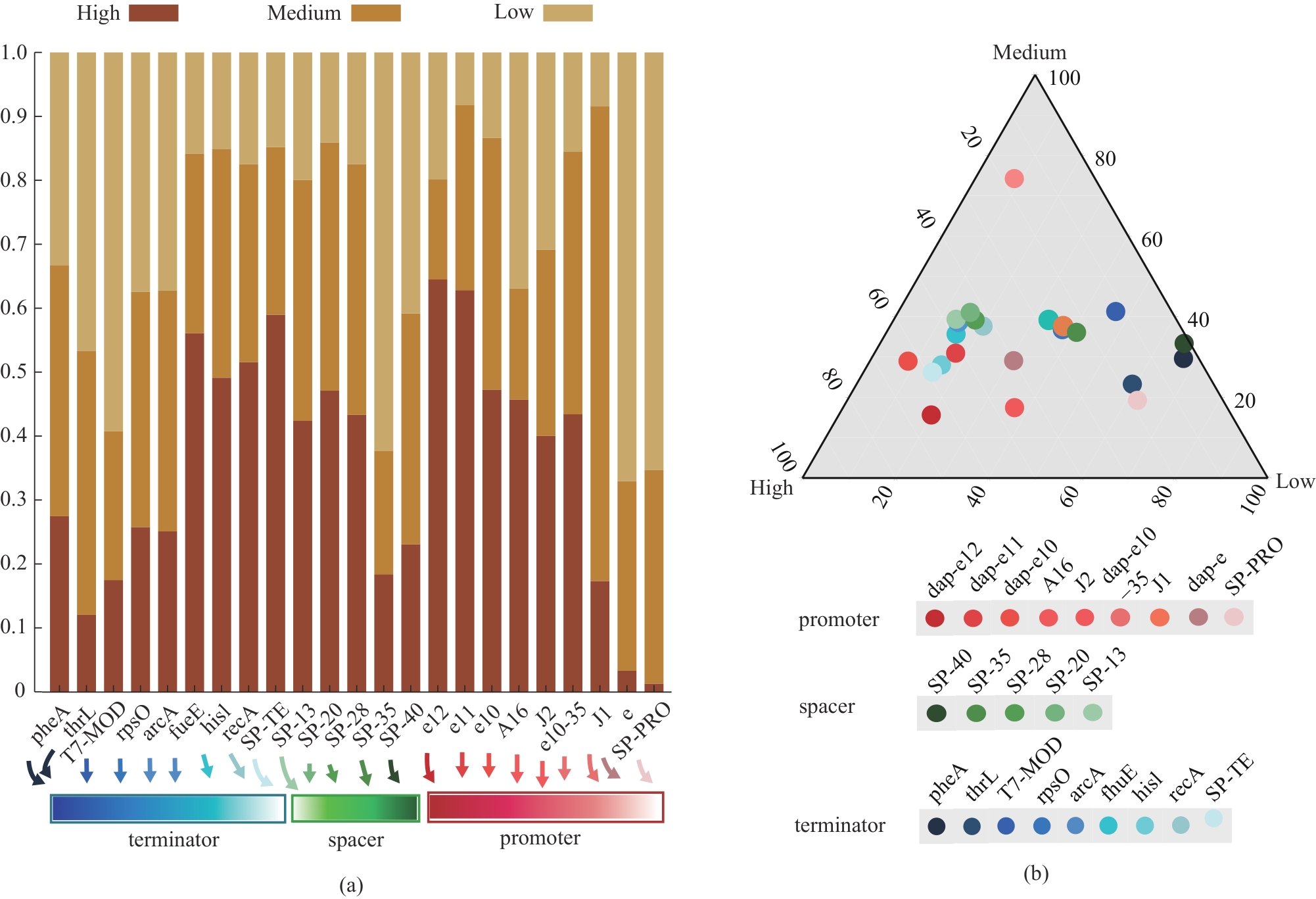
图3 组件中的各元件在高、中和低表达组的出现频率(a)高、中和低表达组中不同元件出现频率的叠加;(b)高、中和低表达组中不同元件出现频率的三元图
Fig. 3 Frequency of each part used in the assemblies at the “High”, “Medium”, and “Low” groups(a) Stacked histograms of the occurrence frequency of different components in the “High”, “Medium”, and “Low” groups; (b) Ternary results of the occurrence frequency of different components in the “High”, “Medium”, and “Low” groups
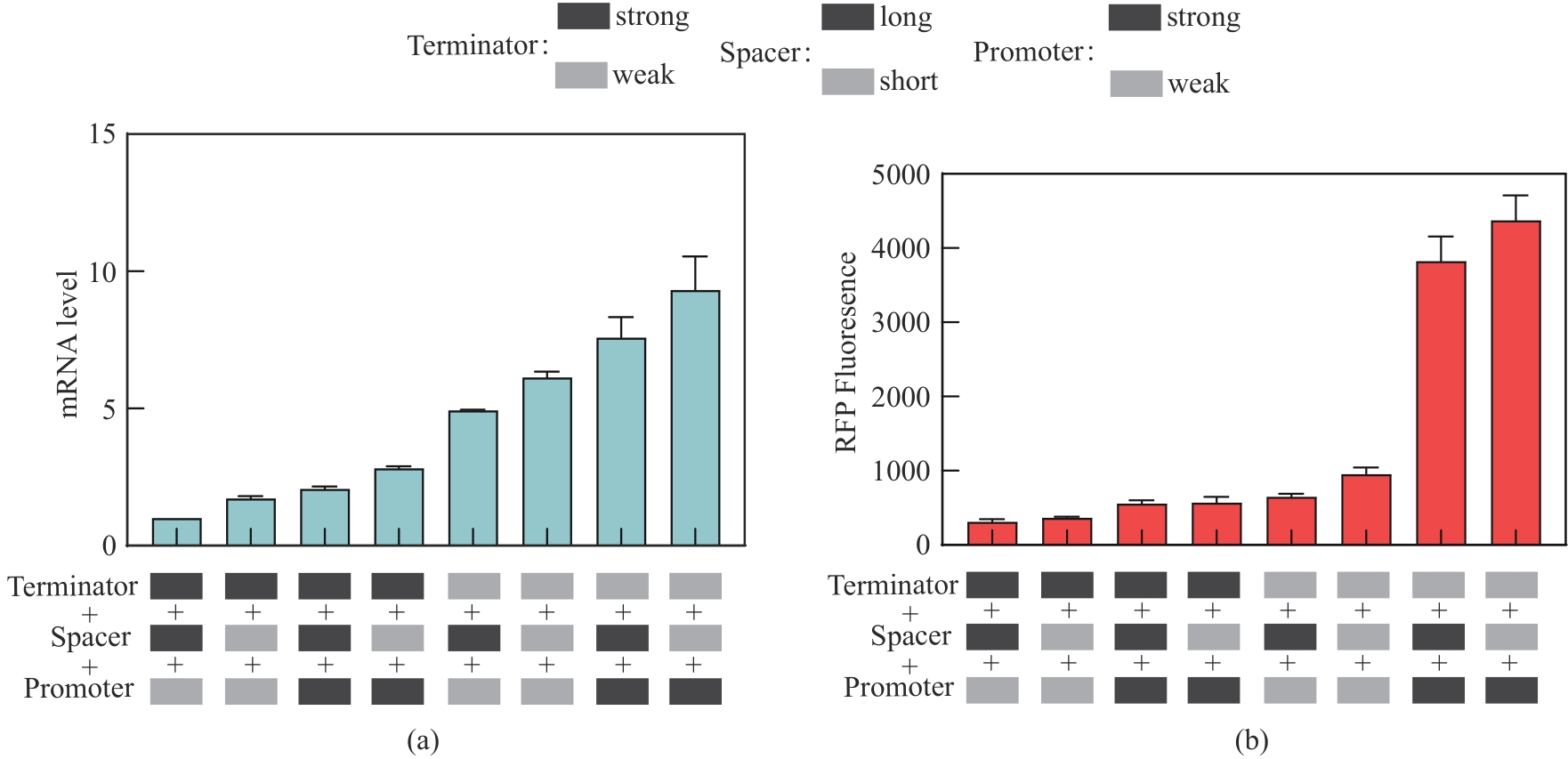
图4 典型组合元件调控的下游基因mRNA水平(a)和红色荧光蛋白表达水平(b)(强弱启动子分别为dap-e11和dap-e,强弱终止子分别为pheA和recA,长短间隔序列分别为sp-40和sp-13)
Fig. 4 Expression levels of mRNA and red fluorescent protein with the downstream transcription unit regulated by typical assemblies selected from the one-pot assembly library(The strong and weak promoters were dap-e11 and dap-e, the strong and weak terminators were pheA and recA, and the long and short interval sequences were sp-40 and sp-13, respectively.)
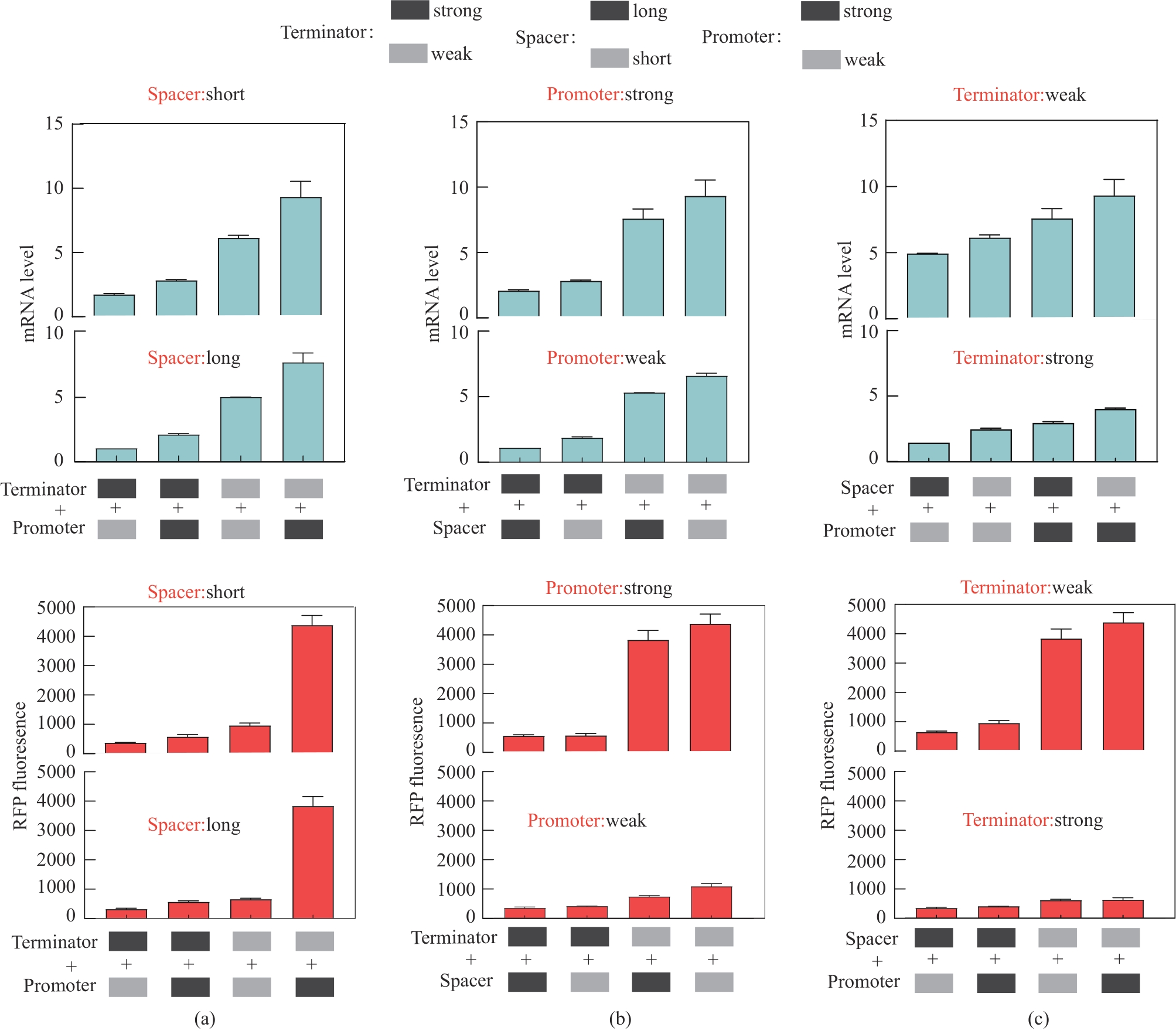
图5 不同强度启动子和终止子组合对下游转录单元mRNA水平和荧光蛋白的影响(a)固定间隔序列的情况下不同终止子和启动子组合对基因表达的影响;(b)固定启动子的情况下不同间隔序列和终止子组合对基因表达的影响;(c)固定终止子的情况下不同启动子和启动子组合对基因表达的影响;强弱启动子分别为dap-e11和dap-e,强弱终止子分别为pheA和recA,长短间隔序列分别为sp-40和sp-13
Fig. 5 Influence of the combination of promoters and terminators on expression of the mRNA and fluorescence protein(a) Effect of different terminator and promoter combinations on gene expression with fixed interval sequences; (b) Effect of different spacer sequences and terminator combinations on gene expression with fixed promoters; (c) Effects of different promoters and combinations of promoters on gene expression with fixed terminators. The strong and weak promoters were dap-e11 and dap-e, the strong and weak terminators were pheA and recA, and the long and short interval sequences were sp-40 and sp-13, respectively.
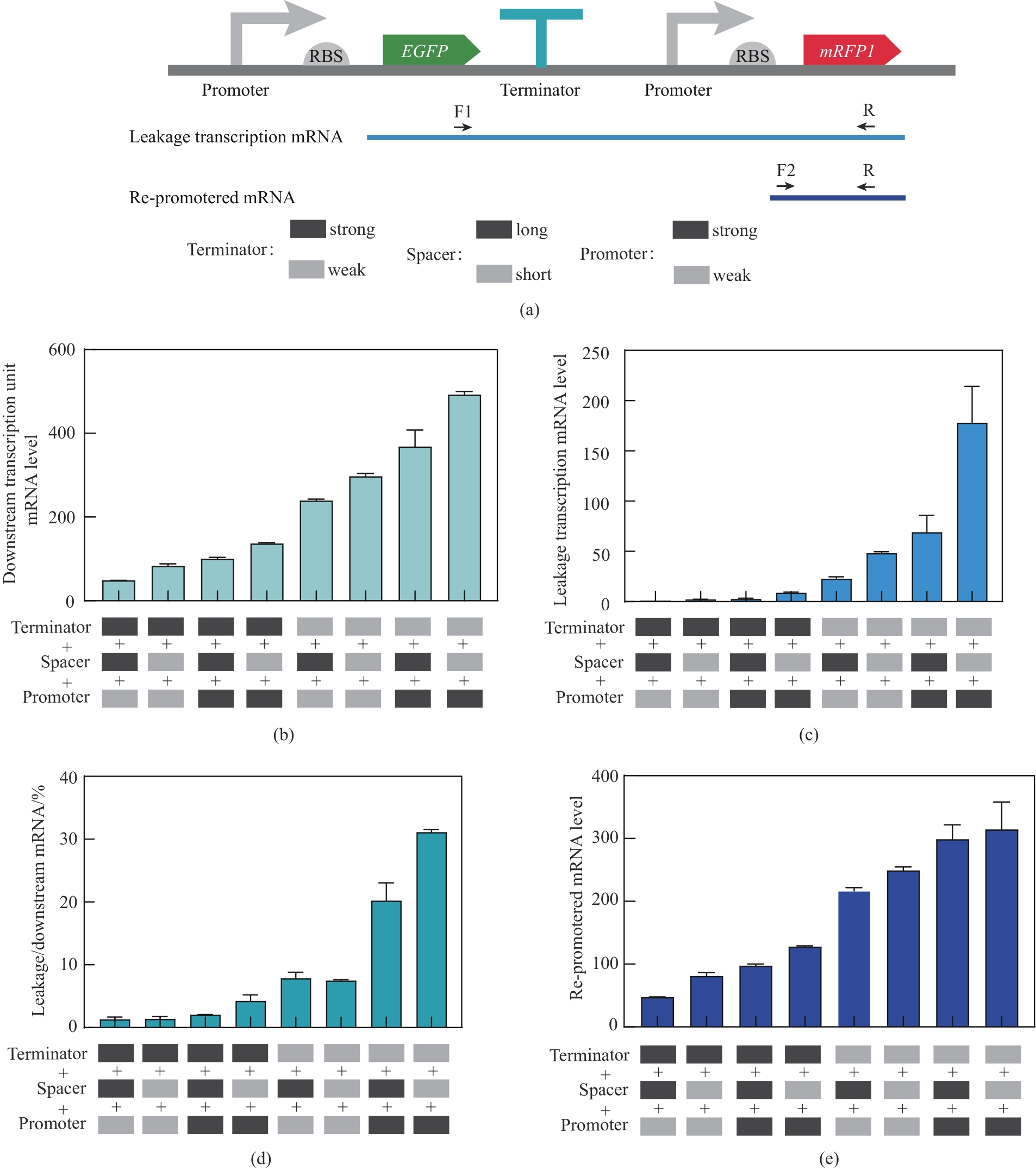
图6 不同组合元件调控下的下游整体mRNA、渗漏转录mRNA以及重启mRNA水平分析(a)通过不同引物的qPCR获得渗漏转录mRNA和重启转录mRNA示意图;(b)不同组合元件调控下的下游mRNA水平;(c)不同组合元件调控下的渗漏转录mRNA水平;(d)渗漏转录mRNA在下游mRNA中的占比;(e)不同组合元件调控下的重启转录的mRNA水平;强弱启动子分别为dap-e11和dap-e,强弱终止子分别为pheA和recA,长短间隔序列分别为sp-40和sp-13
Fig. 6 Schematic representation of downstream mRNA, leakage transcription mRNA, and re-promoted mRNA levels under the regulation of different combinatorial elements.(a) Schematic representation of leakage transcription mRNA and re-promoted mRNA; (b) Downstream mRNA levels under the regulation of different combinatorial elements; (c) Leakage transcription mRNA levels under the regulation of different combinatorial elements; (d) Percentage of Leakage transcription mRNA in downstream mRNA; (e) Re-promoted mRNA levels under the regulation of different combinatorial elements; The strong and weak promoters were dap-e11 and dap-e, the strong and weak terminators were pheA and recA, and the long and short interval sequences were sp-40 and sp-13, respectively.
| 1 | LAURSEN B S, SØRENSEN H P, MORTENSEN K K, et al. Initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2005, 69(1): 101-123. |
| 2 | MORENO J M, SØRENSEN H P, MORTENSEN K K, et al. Macromolecular mimicry in translation initiation: a model for the initiation factor IF2 on the ribosome[J]. IUBMB Life, 2000, 50(6): 347-354. |
| 3 | RAMAKRISHNAN V. Ribosome structure and the mechanism of translation[J]. Cell, 2002, 108(4): 557-572. |
| 4 | ZHOU S H, DU G C, KANG Z, et al. The application of powerful promoters to enhance gene expression in industrial microorganisms[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 33(2): 23. |
| 5 | XU N, WEI L, LIU J. Recent advances in the applications of promoter engineering for the optimization of metabolite biosynthesis[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 35(2): 33. |
| 6 | ZALATAN F, PLATT T. Effects of decreased cytosine content on rho interaction with the rho-dependent Terminator trp t′ in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267(27): 19082-19088. |
| 7 | HENKIN T M, YANOFSKY C. Regulation by transcription attenuation in bacteria: how RNA provides instructions for transcription termination/antitermination decisions[J]. BioEssays, 2002, 24(8): 700-707. |
| 8 | ABE H, ABO T, AIBA H. Regulation of intrinsic Terminator by translation in Escherichia coli: transcription termination at a distance downstream[J]. Genes to Cells, 1999, 4(2): 87-97. |
| 9 | RAY-SONI A, BELLECOURT M J, LANDICK R. Mechanisms of bacterial transcription termination: all good things must end[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2016, 85: 319-347. |
| 10 | LEE D N, PHUNG L, STEWART J, et al. Transcription pausing by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase is modulated by downstream DNA sequences[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1990, 265(25): 15145-15153. |
| 11 | KIREEVA M L, KASHLEV M. Mechanism of sequence-specific pausing of bacterial RNA polymerase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(22): 8900-8905. |
| 12 | CHAN C L, WANG D G, LANDICK R. Multiple interactions stabilize a single paused transcription intermediate in which hairpin to 3΄ end spacing distinguishes pause and termination pathways [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1997, 268(1): 54-68. |
| 13 | MAIRHOFER J, WITTWER A, CSERJAN-PUSCHMANN M, et al. Preventing T7 RNA polymerase read-through transcription-a synthetic termination signal capable of improving bioprocess stability[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(3): 265-273. |
| 14 | ZHANG B, YU M, ZHOU Y, et al. Improvement of L-ornithine production by attenuation of argF in engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114[J]. AMB Express, 2018, 8(1): 26. |
| 15 | JU X W, LI D Y, LIU S X. Full-length RNA profiling reveals pervasive bidirectional transcription terminators in bacteria[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(11): 1907-1918. |
| 16 | AHN J H, KANG T J, KIM D M. Tuning the expression level of recombinant proteins by modulating mRNA stability in a cell-free protein synthesis system[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 101(2): 422-427. |
| 17 | CHEN Y J, LIU P, NIELSEN A A K, et al. Characterization of 582 natural and synthetic terminators and quantification of their design constraints[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(7): 659-664. |
| 18 | CUI W J, LIN Q, HU R C, et al. Data-driven and in silico-assisted design of broad host-range minimal intrinsic terminators adapted for bacteria[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(6): 1438-1450. |
| 19 | ZHAI W J, DUAN Y T, ZHANG X M, et al. Sequence and thermodynamic characteristics of terminators revealed by FlowSeq and the discrimination of terminators strength[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2022, 7(4): 1046-1055. |
| 20 | 翟伟绩. 大肠杆菌终止子文库构建及构效关系分析[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2022. |
| ZHAI W J. The construction of the terminator library and analysis of the structure-activity relationship[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022. | |
| 21 | DU L P, GAO R, FORSTER A C. Engineering multigene expression in vitro and in vivo with small terminators for T7 RNA polymerase[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2009, 104(6): 1189-1196. |
| 22 | TARNOWSKI M J, GOROCHOWSKI T E. Massively parallel characterization of engineered transcript isoforms using direct RNA sequencing[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 434. |
| 23 | LI R, ZHANG Q, LI J B, et al. Effects of cooperation between translating ribosome and RNA polymerase on termination efficiency of the rho-independent terminator[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(6): 2554-2563. |
| 24 | LALANNE J B, TAGGART J C, GUO M S, et al. Evolutionary convergence of pathway-specific enzyme expression stoichiometry[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(3): 749-761.e38. |
| 25 | GOROCHOWSKI T E, ESPAH BORUJENI A, PARK Y, et al. Genetic circuit characterization and debugging using RNA-seq[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2017, 13(11): 952. |
| 26 | KOSURI S, GOODMAN D B, CAMBRAY G, et al. Composability of regulatory sequences controlling transcription and translation in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(34): 14024-14029. |
| 27 | CAMBRAY G, GUIMARAES J C, ARKIN A P. Evaluation of 244,000 synthetic sequences reveals design principles to optimize translation in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36: 1005-1015. |
| 28 | EVFRATOV S A, OSTERMAN I A, KOMAROVA E S, et al. Application of sorting and next generation sequencing to study 5′-UTR influence on translation efficiency in Escherichia coli [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(6): 3487-3502. |
| 29 | YOON B J. Hidden Markov models and their applications in biological sequence analysis[J]. Current Genomics, 2009, 10(6): 402-415. |
| 30 | KUO S T, JAHN R L, CHENG Y J, et al. Global fitness landscapes of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence[J]. Genome Research, 2020, 30(5): 711-723. |
| 31 | OSTERMAN I A, CHERVONTSEVA Z S, EVFRATOV S A, et al. Translation at first sight: the influence of leading codons[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(12): 6931-6942. |
| 32 | VERMA M, CHOI J, COTTRELL K A, et al. A short translational ramp determines the efficiency of protein synthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5774. |
| 33 | GAO R, YU K, NIE J K, et al. Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mRNA recruitment during translation initiation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 30170. |
| 34 | LESNIK E A, SAMPATH R, LEVENE H B, et al. Prediction of rho-independent transcriptional terminators in Escherichia coli [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29(17): 3583-3594. |
| 35 | DUAN Y T, ZHAI W J, LIU W J, et al. Fine-tuning multi-gene clusters via well-characterized gene expression regulatory elements: case study of the arginine synthesis pathway in C. glutamicum [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(1): 38-48. |
| 36 | HUDSON A J, WIEDEN H J. Rapid generation of sequence-diverse terminator libraries and their parameterization using quantitative Term-Seq[J]. Synthetic Biology, 2019, 4(1): ysz026. |
| [1] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [2] | 于慧敏, 郑煜堃, 杜岩, 王苗苗, 梁有向. 合成生物学研究中的微生物启动子工程策略[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 598-611. |
| [3] | 盛月, 张根林. 酵母终止子工程:从机理探索到人工设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 709-721. |
| [4] | 曹中正, 张心怡, 徐艺源, 周卓, 魏文胜. 基因组编辑技术及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 413-426. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
