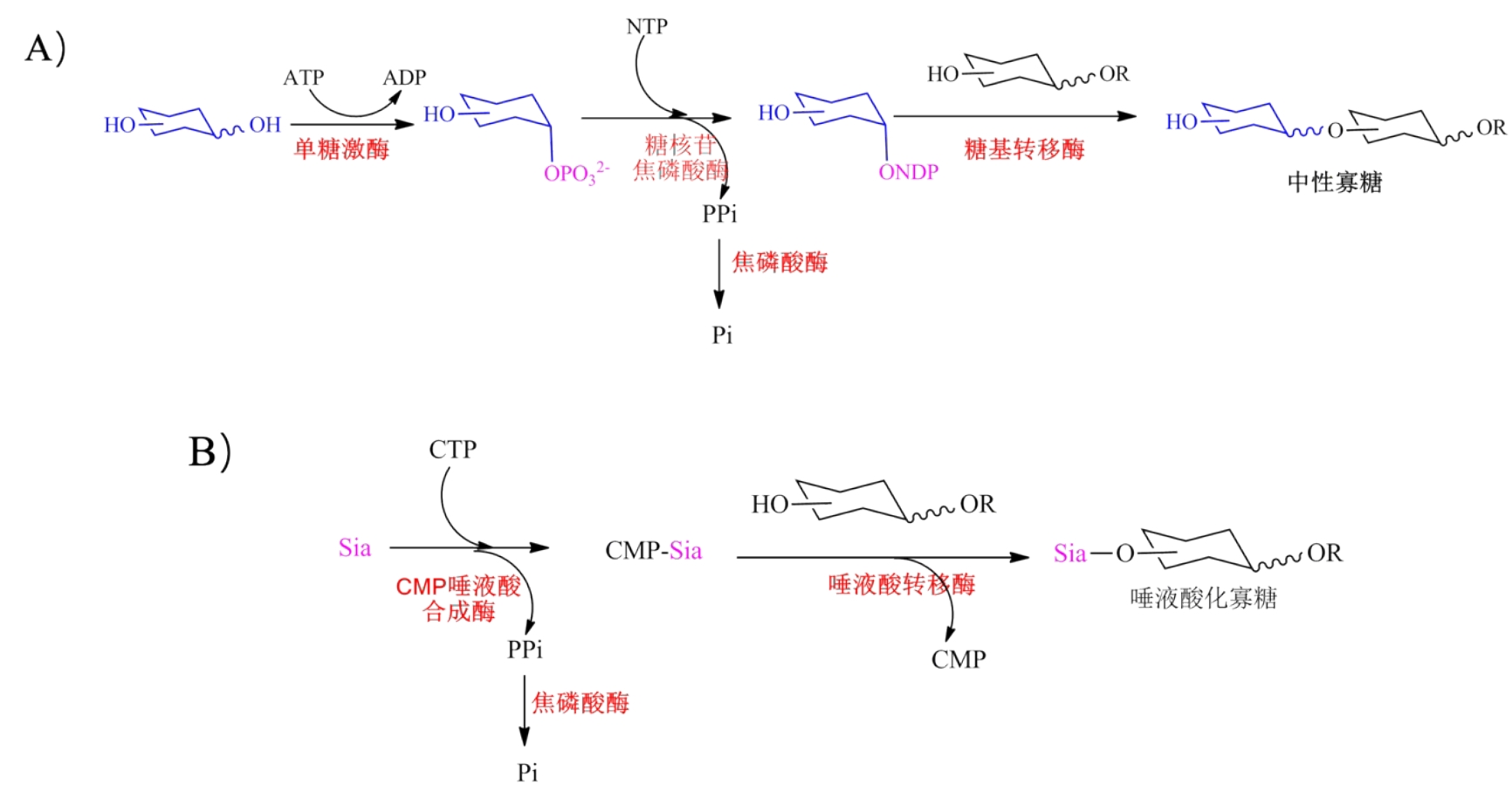
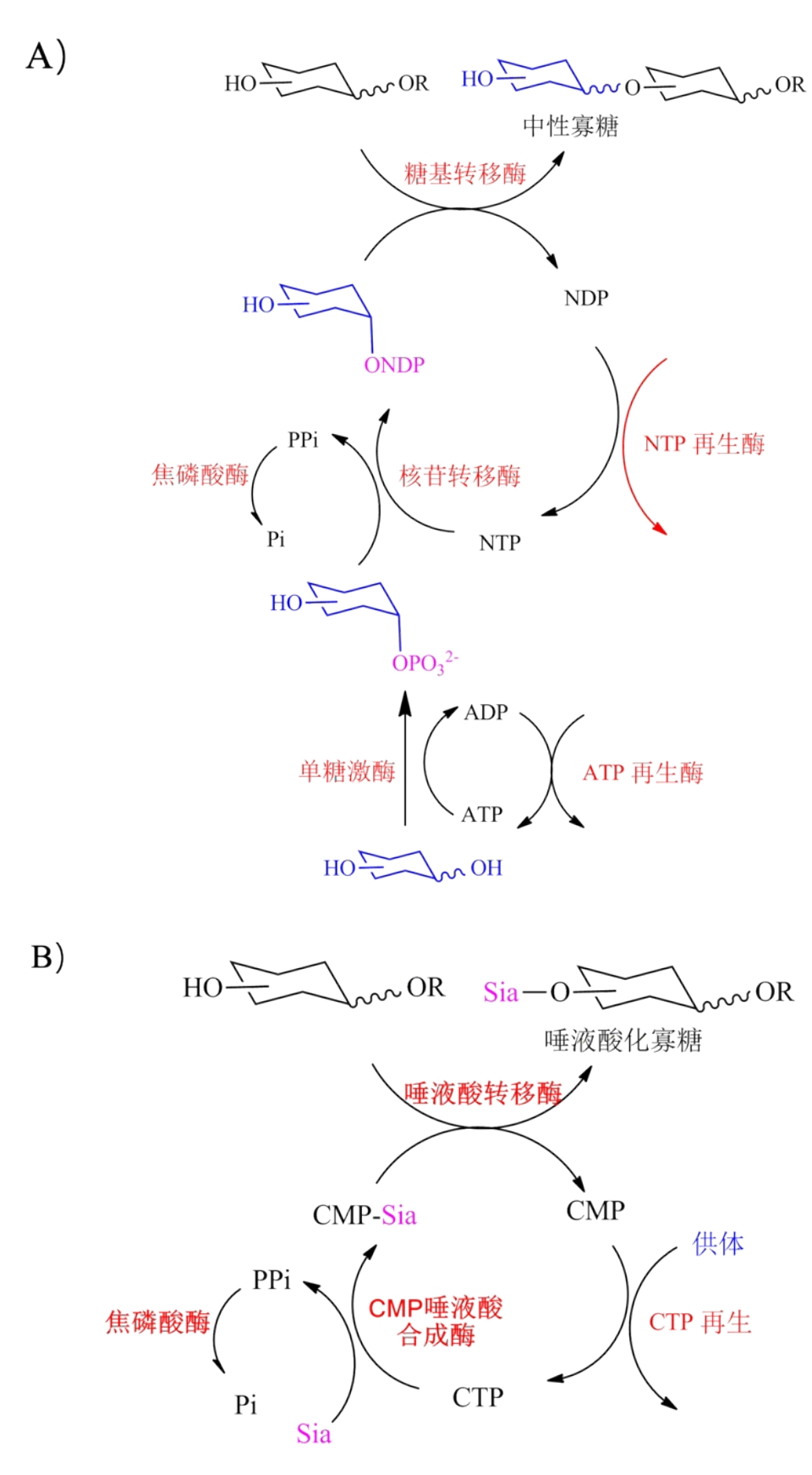
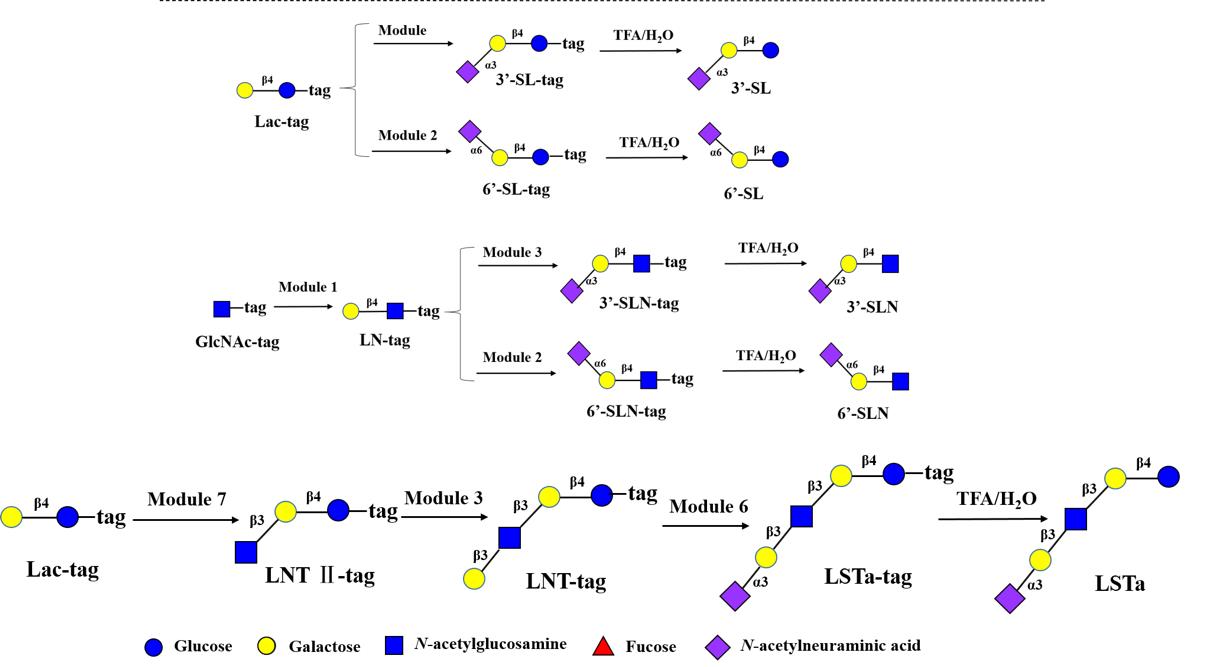
• 特约评述 •
糖质ivBT生物合成的核心元件及关键技术
裴彩霞1,2, 李建军1,2, 杜昱光1,2
- 1.中国科学院过程工程研究所,生物药制备与递送全国重点实验室,北京 100190
2.中国科学院过程工程研究所,国家生化工程技术研究中心(北京),北京 100190
-
收稿日期:2025-06-23修回日期:2025-08-10出版日期:2025-08-13 -
通讯作者:李建军,杜昱光 -
作者简介:裴彩霞 (1994—),女,博士,博士后,研究方向为功能寡糖的酶催化合成等研究。E-mail:peicaixia@ipe.ac.cn李建军 (1970—),男,博士,副研究员,硕士生导师,研究方向为蛋白质工程、功能寡糖的酶催化合成等研究。E-mail:jjli@ipe.ac.cn杜昱光 (1963—),男,硕士,研究员,博士生导师,研究方向为功能寡糖的制备、活性评估与产业化等研究。E-mail:ygdu@ipe.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(21877114)
Core Elements and Key Technologies of ivBT-based Glycan Synthesis
PEI Caixia1,2, LI Jianjun1,2, DU Yuguang1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Biopharmaceutical Preparation and Delivery,Institute of Process Engineering,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China
2.National Engineering Research Center for Biotechnology (Beijing),Institute of Process Engineering,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China
-
Received:2025-06-23Revised:2025-08-10Online:2025-08-13 -
Contact:LI Jianjun, DU Yuguang
摘要:
糖质(glycans)是构成生命的基本生物分子,在生物过程中发挥重要作用,与人类健康和疾病密切相关。由于糖质结构的复杂性,糖质所携带的密码信息大大超过核酸及蛋白质等任何其它生物大分子。为了破译糖质携带的密码信息,就需要获得一定量的、结构明确的糖质。合成仍然是获得糖质的最佳方式。体外生物转化(in vitro biotransformation, ivBT)是一个基于体外多酶催化的新型工业生物制造技术,由酶、辅酶等元件体外重构生化反应途径,实现目标产物的高效合成,正逐渐发展成为合成糖质的一种重要技术。本文综述了ivBT在糖质合成中的应用、ivBT糖质合成相关的糖核苷合成、糖基转移、NTP再生等核心元件及酶的固定化、微流控、酶促自动化合成、动力学模拟、离子液体等关键技术,展望了糖质ivBT合成相关的酶的协同性、特殊重组酶生产成本的降低、仿生辅酶的循环再生、多酶复合体的应用、硫酸化糖质的合成、AI辅助的反应条件优化等发展方向,旨在为糖质ivBT合成的未来发展提供指导。
中图分类号:
引用本文
裴彩霞, 李建军, 杜昱光. 糖质ivBT生物合成的核心元件及关键技术[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-064.
PEI Caixia, LI Jianjun, DU Yuguang. Core Elements and Key Technologies of ivBT-based Glycan Synthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-064.
| 化学法 | 酶法 | 细胞工厂法 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 专一性 | 低 | 最高 | 高 |
| 选择性(区域、立体选择性) | 低 | 最高 | 高 |
| 反应过程 | 繁琐(涉及到保护、脱保护以及活化单糖的过程)、反应时间长 | 反应过程简单、反应时间短 | 反应过程简单、反应时间短 |
| 反应条件 | 某些反应需要剧烈或特殊的条件(如高温、低温、高压等) | 温和(37 ℃左右、pH 接近中性等) | 温和(37 ℃左右、pH接近中性等) |
| 环境 | 不友好(使用有机溶剂及重金属催化剂等) | 友好(水溶液中反应、不用重金属催化剂) | 友好(水溶液中反应、不用重金属催化剂 |
| 设备 | 某些反应需要特殊的设备(高压、低温等) | 传统设备(发酵罐、反应罐) | 传统设备(发酵罐) |
| 转化率 | 低 | 高 | 低 |
| 产量 | 低 | 高 | 低 |
| 规模化生产 | 不适合 | 可以 | 可以 |
表1 三种糖质合成方法的比较
Table 1 Comparison of three methods for glycan synthesis
| 化学法 | 酶法 | 细胞工厂法 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 专一性 | 低 | 最高 | 高 |
| 选择性(区域、立体选择性) | 低 | 最高 | 高 |
| 反应过程 | 繁琐(涉及到保护、脱保护以及活化单糖的过程)、反应时间长 | 反应过程简单、反应时间短 | 反应过程简单、反应时间短 |
| 反应条件 | 某些反应需要剧烈或特殊的条件(如高温、低温、高压等) | 温和(37 ℃左右、pH 接近中性等) | 温和(37 ℃左右、pH接近中性等) |
| 环境 | 不友好(使用有机溶剂及重金属催化剂等) | 友好(水溶液中反应、不用重金属催化剂) | 友好(水溶液中反应、不用重金属催化剂 |
| 设备 | 某些反应需要特殊的设备(高压、低温等) | 传统设备(发酵罐、反应罐) | 传统设备(发酵罐) |
| 转化率 | 低 | 高 | 低 |
| 产量 | 低 | 高 | 低 |
| 规模化生产 | 不适合 | 可以 | 可以 |
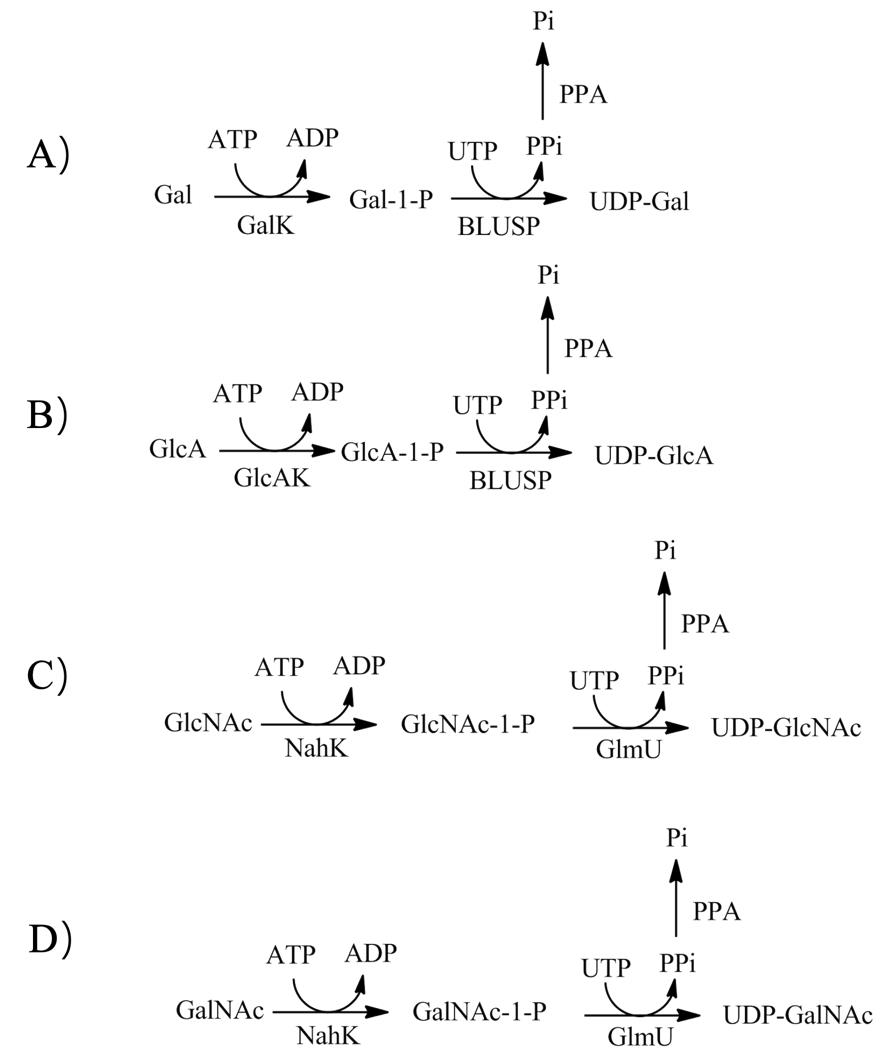
图3 UDP-Gal(A)、UDP-GlcA(B)、UDP-GlcNAcA(C)、UDP-GalNAcA(D)的ivBT合成GalK:半乳糖激酶;BLUSP:UDP-糖焦磷酸化酶;PPA:焦磷酸酶;GlcAK:葡萄糖醛酸激酶;NahK:N-乙酰己糖胺1-激酶;GlmU:N-乙酰葡萄糖胺-1磷酸尿苷酰转移酶或UDP-GlcNAc焦磷酸化酶
Fig. 3 ivBT synthesis of UDP-Gal(A)、UDP-GlcA(B)、UDP-GlcNAcA(C)、UDP-GalNAcA(D)GalK: galactokinase; BLUSP: UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase; PPA: pyrophosphatase; GlcAK: glucuronokinase; NahK: N-acetylhexosamine 1-kinase; GlmU: UDP-GlcNAc pyrophosphorylase or N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphateuridyltransferase
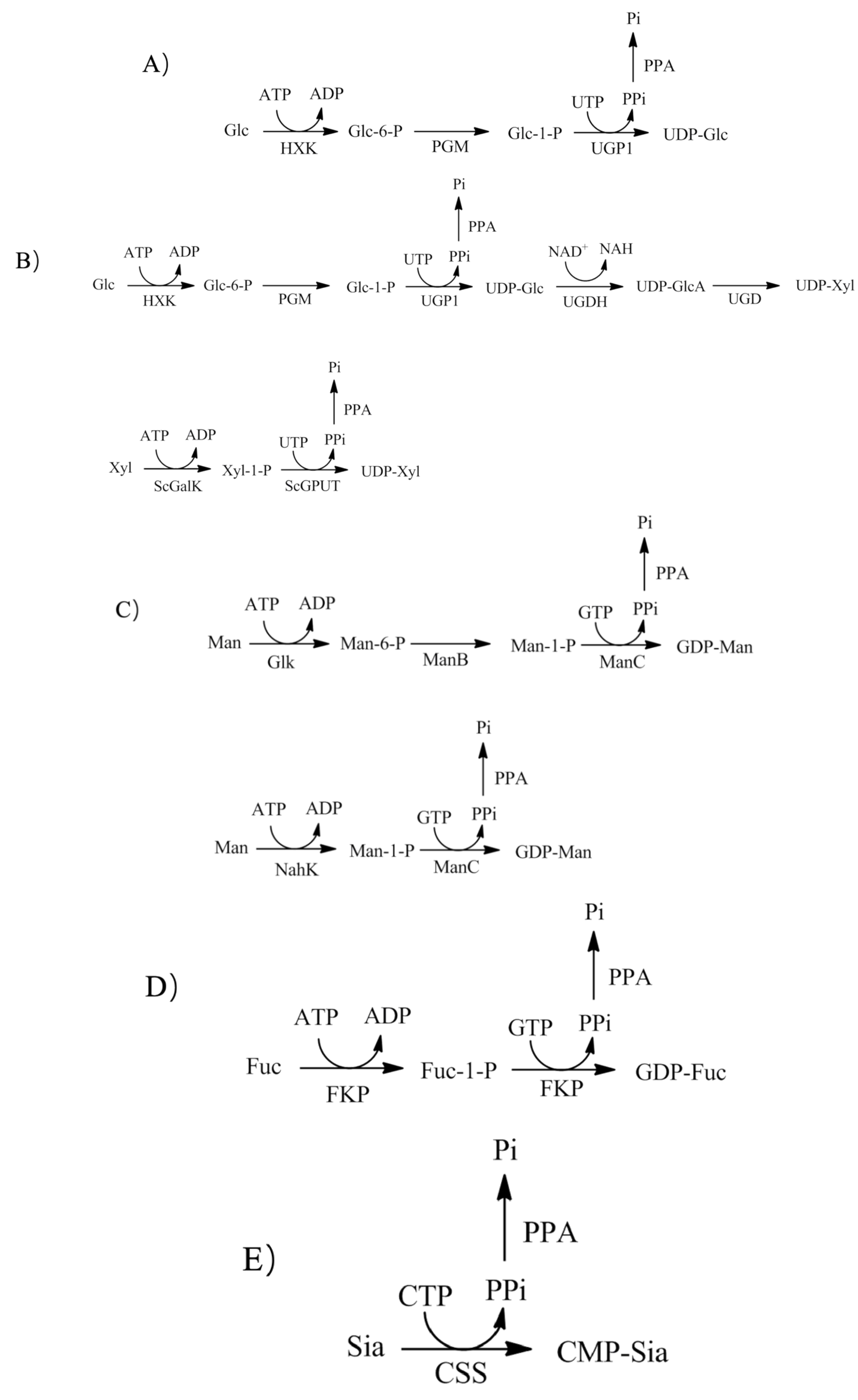
图4 UDP-Glc(A)、UDP-Xyl(B)、GDP-Man(C)、GDP-Fuc(D) 、CMP-Sia(E)的ivBT合成HXK:己糖激酶; PGM:磷酸葡萄糖变位酶;UGP1:葡萄糖-1磷酸尿苷酰转移酶或UDP-葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶;UGHD:UDP-葡萄糖6-脱氢酶;UGD:UDP-葡萄糖醛酸脱羧酶;ScGalK:来源于沼泽红假单胞菌的半乳糖激酶;ScGPUT:来源于沼泽红假单胞菌的葡萄糖-1-磷酸尿苷酰转移酶或UDP-葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶;Glk:葡萄糖激酶;ManB:磷酸甘露糖变位酶;ManC:甘露糖-1-磷酸鸟嘌呤转移酶或GDP-甘露糖焦磷酸化酶;FKP:岩藻糖激酶/GDP-岩藻糖焦磷酸化酶或岩藻糖-1-(双功能酶);CSS:CMP-唾液酸合成酶
Fig. 4 ivBT synthesis of UDP-Glc(A)、UDP-Xyl(B)、GDP-Man(C)、GDP-Fuc(D) 、CMP-Sia(E)HXK: hexokinase; PGM: phosphoglucomutase; UGP1: glucose-1-phosphateuridyltransferase or UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; UGHD: UDP-glucose-6-dehydrogenase; UGD: UDP-glucuronate decarboxylase; ScGalK: galactokinase from Solitalea canadensis; ScGPUT: glucose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase or UDP-Glc pyrophosphorylase from Solitalea canadensis; Glk: glucokinase; ManB: phosphomannomutase; ManC: mannose-1-phosphate-guanyltransferase or GDP-Man pyrophosphorylase; FKP: fucokinase/GDP-Fuc pyrophosphorylase or fucose-1-phosphateguanyltransferase; CSS: CMP-sialic acid synthetase
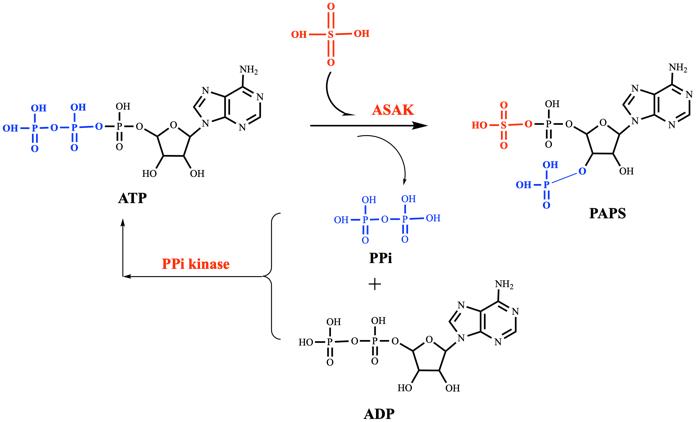
图6 PAPS的再生[104]ASAK:双功能酶,ATP硫酸化酶 + 3′-磷酸腺苷-5′-磷酰硫酸激酶
Fig. 6 Regeneration of PAPSASAK: bifunctional enzyme, ATP sulfurylase + 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate kinase
表2 ivBT和细胞工厂的优劣势比较
Table 2 Comparison of pros and cons of ivBT and cell factory
| [1] | VARKI A, CUMMINGS R D, ESKO J D, et al. Essentials of Glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor (NY). 2022. |
| [2] | Transforming Glycoscience: A Roadmap for the Future. Washington (DC). 2012. |
| [3] | SEEBERGER P H. The logic of automated glycan assembly [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2015, 48(5): 1450-1463. |
| [4] | BOLTJE T J, BUSKAS T, BOONS G J. Opportunities and challenges in synthetic oligosaccharide and glycoconjugate research [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2009, 1(8): 611-622. |
| [5] | HSU C H, HUNG S C, WU C Y, et al. Toward automated oligosaccharide synthesis [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(50): 11872-11923. |
| [6] | YU H, CHRN X. One-pot multienzyme (OPME) systems for chemoenzymatic synthesis of carbohydrates [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry,, 2016, 14(10): 2809-2818. |
| [7] | MUTHANA S, CAO H, CHEN X. Recent progress in chemical and chemoenzymatic synthesis of carbohydrates [J]. Current Opinions in Chemical Biology, 2009, 13(5-6): 573-581. |
| [8] | ZHANG Y H P, MYUNGy S, YOU C, et al. Toward low-cost biomanufacturing through in vitro synthetic biology: bottom-up design [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(47): 18877-18886. |
| [9] | LOPEZ-GALLEGO F, SCHMIDT-DANNERT C. Multi-enzymatic synthesis [J]. Current Opinions in Chemical Biology, 2010, 14(2): 174-183. |
| [10] | VASIC-RACKI D, FINDRIK Z, PRESCKI A V. Modelling as a tool of enzyme reaction engineering for enzyme reactor development [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 91(4): 845-856. |
| [11] | VILKHOVOY M, ADHIKARI A, VADHIN S, et al. The Evolution of Cell Free Biomanufacturing [J]. Processes, 2020, 8(6): 675. |
| [12] | JAROENTOMEECHAI T, TAW M N, Li M, et al. Cell-Free Synthetic Glycobiology: Designing and Engineering Glycomolecules Outside of Living Cells [J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020, 8: 645. |
| [13] | LUO S, LIN P P, L-Y NIEH, et al. A cell-free self-replenishing CO2-fixing system [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5(2): 154-162. |
| [14] | ZHANG Y H. Production of biocommodities and bioelectricity by cell-free synthetic enzymatic pathway biotransformations: challenges and opportunities [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 105(4): 663-677. |
| [15] | ZHANG Y H P J, ZHU Z, YOU C, al at. In Vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): Definitions, Opportunities, and Challenges [J]. Synthtic Biology and Engineering, 2023, 1(2): 10013 |
| [16] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 等,体外生物转化(ivBT) :生物制造的新前沿[J],合成生物学,2024,5(6):1437-1460 |
| SHI T, SONG Z, SONG S, et al. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of. industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024,5(6):1437-1460 | |
| [17] | BHOSALE S H, RAO M B, DESHPANDE V V. Molecular and industrial aspects of glucose isomerase [J]. Microbiological reviews, 1996, 60(2): 280-300. |
| [18] | DEMAIN A L. Pickles, pectin, and penicillin [J]. Annual Review Microbiology, 2004, 58: 1-42. |
| [19] | TAHERZADEH M J, KARIMI K J B. Enzyme-based hydrolysis processes for ethanol from lignocellulosic materials: A review [J]. BioResources, 2007, 2(4): 707-738. |
| [20] | WICHMANN R, VASIC-RACKI D. Cofactor regeneration at the lab scale [J]. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 2005, 92: 225-260. |
| [21] | KOELLER K M, WONG C H. Synthesis of complex carbohydrates and glycoconjugates: enzyme-based and programmable one-pot strategies [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2000, 100(12): 4465-4494. |
| [22] | THIBODEAUX C J, MELANCON C E, LIU H W. Unusual sugar biosynthesis and natural product glycodiversification [J]. Nature, 2007, 446(7139): 1008-1016. |
| [23] | THIBODEAUX C J, MELANÇON C E, LIU H W. Natural‐Product Sugar Biosynthesis and Enzymatic Glycodiversification [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(51): 9814-9859. |
| [24] | YOU C, CHENh H, MYUNG S, et al. Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(18): 7182-7187. |
| [25] | V-R DURDA. History of industrial biotransformations-dreamand realities[M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, KGaA, 2006. |
| [26] | FRANCE S P, HEPWORTH L J, TURNER N J, et al. Constructing Biocatalytic Cascades: In Vitro and in Vivo Approaches to de Novo Multi-Enzyme Pathways [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(1): 710-724. |
| [27] | DING Q B, OU L. NTP Regeneration and its Application in the Biosynthesis of Nucleotides and their Derivatives [J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2017, 23(45): 6936–6947. |
| [28] | YANG J, ZHANG T, TIAN C, et al. Multi-enzyme systems and recombinant cells for synthesis of valuable saccharides: Advances and perspectives [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(7): 107406. |
| [29] | YE J, LIU X PENG P, et al. Diversity-Oriented Enzymatic Modular Assembly of ABO Histo-blood Group Antigens [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(12): 8140-8144. |
| [30] | WANG S, ZHANG Q, CHEN C, et al. Facile Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of O-Mannosyl Glycans [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(30): 9268-9273. |
| [31] | MENG C, SASMAL A, ZHANG Y, et al. Chemoenzymatic Assembly of Mammalian O-Mannose Glycans [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(29): 9003-9007. |
| [32] | LI Y, LI Y, GUO Y, et al. Enzymatic modular synthesis of asymmetrically branched human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 333: 121908. |
| [33] | BAI Y, AGRAHARI A K, ZHANG L, et al. EASyMap-Guided Stepwise One-Pot Multienzyme (StOPMe) Synthesis and Multiplex Assays Identify Functional Tetraose-Core-Human Milk Oligosaccharides [J]. JACS Au, 2025, 5(2): 822-837. |
| [34] | TSAI T I, LEE H Y, CHANG S H, et al. Effective sugar nucleotide regeneration for the large-scale enzymatic synthesis of Globo H and SSEA4 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(39): 14831-14839. |
| [35] | TSENG H W, TSENG H K, OOI K E, et al. Controllable Enzymatic Synthesis of Natural Asymmetric Human Milk Oligosaccharides [J]. JACS Au, 2024, 4(11): 4496-4506. |
| [36] | REXER T F T, SCHILDBACH A, KLAPPROTH J, et al. One pot synthesis of GDP-mannose by a multi-enzyme cascade for enzymatic assembly of lipid-linked oligosaccharides [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(1): 192-205. |
| [37] | DU Z, LIU Z, TAN Y, et al. Lacto-N-biose synthesis via a modular enzymatic cascade with ATP regeneration [J]. iScience, 2021, 24(3): 102236. |
| [38] | JIAO R, ZHANG L, YOU R, et al. Efficient and Cost-Effective Synthesis of N-Acetyllactosamine by Sequential Modular Enzymatic Cascade Reactions Involving NTP Regeneration [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(50): 28060-28071. |
| [39] | JIAO R, PENG X, WANG B, DU Y, QIAN E W, LI J. Highly Efficient and Economical One-Pot Two-Step Multienzymatic Synthesis of 6′/3′-Sialyllactosamine from In Situ-Produced N-Acetyllactosamine [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(23): 14444-14452. |
| [40] | FENG Y, YAO M, WANG Y, et al. Advances in engineering UDP-sugar supply for recombinant biosynthesis of glycosides in microbes [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 41: 107538. |
| [41] | ZHUANG J D, SHI J M, HONG C C, et al. Engineering Bifunctional Galactokinase/Uridyltransferase Chimera for Enhanced UDP-d-Xylose Production [J]. JACS Au, 2024, 4(7): 2557-2563. |
| [42] | SHI J, WU T, ZHOU H, et al. Substrate promiscuities of a bacterial galactokinase and a glucose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase enable xylose salvaging [J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(9): 3717-3722. |
| [43] | WEIJERS C A, FRANSSEN M C, VISSER G M. Glycosyltransferase-catalyzed synthesis of bioactive oligosaccharides [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2008, 26(5): 436-456. |
| [44] | LAIRSON L L, HENRISSAT B, DAVIES G J, et al. Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms [J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2008, 77: 521-555. |
| [45] | SCHMALTZ R M, HANSON S R, WONG C H. Enzymes in the Synthesis of Glycoconjugates [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2011, 111(7): 4259-4307. |
| [46] | REXER T, LAAF D, GOTTSCHALK J, et al. Enzymatic Synthesis of Glycans and Glycoconjugates [J]. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 2021, 175: 231-280. |
| [47] | CHANG L, CUI H, LIU W, et al. Electrodriven ATP Synthesis via a Reconstructed Thylakoid Membrane [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(6): e202421120. |
| [48] | LUO S S, ADAM D, GIAVERI S, et al. ATP production from electricity with a new-to-nature electrobiological module [J]. Joule, 2023, 7(8): 1745-1758. |
| [49] | RUCCOLO S, BRITO G, CHRISTENSEN M, et al. Electrochemical Recycling of Adenosine Triphosphate in Biocatalytic Reaction Cascades [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 144(49): 22582-22588. |
| [50] | LEE J H, CHUNG S W, LEE H J, et al. Optimization of the enzymatic one pot reaction for the synthesis of uridine 5'-diphosphogalactose [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2010, 33(1): 71-78. |
| [51] | LEE S G, LEE J O, YI J K, et al. Production of cytidine 5′-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid using recombinant as a biocatalyst [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2002, 80(5): 516-524. |
| [52] | ANDEXER J N, RICHTER M. Emerging enzymes for ATP regeneration in biocatalytic processes [J]. Chembiochem, 2015, 16(3): 380-386. |
| [53] | NAHALKA J, PATOPRSTY V. Enzymatic synthesis of sialylation substrates powered by a novel polyphosphate kinase (PPK3) [J] Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2009, 7(9): 1778-1780. |
| [54] | Cai T, Sun H, Qiao J, et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide [J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1523-1527. |
| [55] | LIU Z, ZHANG J, CHEN X, et al. Combined biosynthetic pathway for de novo production of UDP-galactose: catalysis with multiple enzymes immobilized on agarose beads [J]. Chembiochem, 2002, 3(4): 348-355. |
| [56] | ZHANG J, WU B, ZHANG Y, et al. Creatine phosphate--creatine kinase in enzymatic synthesis of glycoconjugates [J]. Organic Letters, 2003, 5(15): 2583-2586. |
| [57] | WOHLGEMUTH R. Biocatalysis-key to sustainable industrial chemistry [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2010, 21(6): 713-724. |
| [58] | STEPANKOVA V, BIDMANOVA S, KOUDELAKOVA T, et al. Strategies for Stabilization of Enzymes in Organic Solvents [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(12): 2823-2836. |
| [59] | HANEFELD U, GARDOSSI L, MAGNER E. Understanding enzyme immobilisation[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(2): 453-468. |
| [60] | MATEO C, PALOMO J M, FERNANDEZ-LORENTE G, et al. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2007, 40(6): 1451-1463. |
| [61] | BARBOSA O, ORTIZ C, BERENGUER-MURCIA A, et al. Strategies for the one-step immobilization-purification of enzymes as industrial biocatalysts [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2015, 33(5): 435-456. |
| [62] | JI Q, WANG B, TAN J, et al. Immobilized multienzymatic systems for catalysis of cascade reactions [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2016, 51(9): 1193-1203. |
| [63] | CHEN X, FANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Sugar nucleotide regeneration beads (superbeads): a versatile tool for the practical synthesis of oligosaccharides [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(9): 2081-2082. |
| [64] | LI Z, LIU X, NAKANISHI H, et al. Encapsulation of Mannose-6-phosphate Isomerase in Yeast Spores and Its Application in l-Ribose Production [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(25): 6892-6899. |
| [65] | LI Z, LI Y, DUAN S, et al. Bioconversion of D-glucose to D-psicose with immobilized D-xylose isomerase and D-psicose 3-epimerase on Saccharomyces cerevisiae spores [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 42(8): 1117-1128. |
| [66] | CHAO Q, LI T L, JIA J X, et al. Spore-Encapsulating Glycosyltransferase Catalysis Tandem Reactions: Facile Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Complex Human Glycans [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(5): 3181-3188. |
| [67] | LIANG W, WIED P, CARRARO F, et al. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Enzyme Biocomposites [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(3): 1077-1129. |
| [68] | BAILEY J B, ZHANG L, CHIONG J A, et al. Synthetic Modularity of Protein-Metal-Organic Frameworks [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(24): 8160-8166. |
| [69] | PATIL P D, GARGATE N, TIWARI M S, et al. Designable metal-organic frameworks for enzyme immobilization: The reality of controlled architecture [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 508, 160994. |
| [70] | SHA F R, WANG X L, KIRLIKOVALI K O, et al. Enhancing Biocatalysis: Metal-Organic Frameworks as Multifunctional Enzyme Hosts [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2024, 57(24): 3500-3511. |
| [71] | ZHENG J, XU H, LI B, et al. Spatially Segregated MOF Bioreactor Enables Versatile Modular Glycoenzyme Assembly for Hierarchical Glycan Library Construction [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(16): 19807-19816. |
| [72] | PENG X, PEI C, QIAN E W, et al. Co-immobilization of a bi-enzymatic cascade into hierarchically porous MIL-53 for efficient 6'-sialyllactose production [J]. Nanoscale, 2024, 16(31): 14932-14939. |
| [73] | Han P, Wang X, Li Y, et al. Synthesis of a Healthy Sweetener d-Tagatose from Starch Catalyzed by Semiartificial Cell Factories [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(8): 3813-3820. |
| [74] | 林炳承. 微纳流控芯片实验室 [M]. 2013. |
| [75] | MARTIN J G, GUPTA M, XU Y, et al. Toward an artificial Golgi: redesigning the biological activities of heparan sulfate on a digital microfluidic chip [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(31): 11041-11048. |
| [76] | GONG M, LI T, WU L, et al. Liquid-Phase and Ultrahigh-Frequency-Acoustofluidics-Based Solid-Phase Synthesis of Biotin-Tagged 6′/3′-Sialyl-N-Acetylglucosamine by Sequential One-Pot Multienzyme System [J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10(11): 1347. |
| [77] | SUN Y, WU Y, MA D, et al. Digital microfluidics-engaged automated enzymatic degradation and synthesis of oligosaccharides [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11: 1201300. |
| [78] | WU Y, SUN Y, PEI C, et al. Automated chemoenzymatic modular synthesis of human milk oligosaccharides on a digital microfluidic platform [J]. RSC Advances, 2024, 14(25): 17397-17405. |
| [79] | WEN L, EDMUNDS G, GIBBONS C, et al. Toward Automated Enzymatic Synthesis of Oligosaccharides [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(17): 8151-8187. |
| [80] | PLANTE O J, PALMACCI E R, SEEBERGER P H. Automated solid-phase synthesis of oligosaccharides [J]. Science, 2001, 291(5508): 1523-1527. |
| [81] | YAO W, XIONG D, YANG Y, et al. Automated solution-phase multiplicative synthesis of complex glycans up to a 1,080-mer [J]. Nature Synthesis, 2022, 1: 854-863. |
| [82] | SCHUSTER M, WANG P, PAULSON J C, et al. Solid-Phase Chemical-Enzymatic Synthesis of Glycopeptides and Oligosaccharides [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1994, 116(3): 1135-1136. |
| [83] | HALCOMB R L, HUANG H, C-H WONG. Solution- and Solid-Phase Synthesis of Inhibitors of H. pylori Attachment and E-Selectin-Mediated Leukocyte Adhesion [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1994, 116(25): 11315-11322. |
| [84] | MATSUSHITA T, NAGASHIMA I, FUMOTO M, et al. Artificial Golgi apparatus: globular protein-like dendrimer facilitates fully automated enzymatic glycan synthesis [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(46): 16651-16656. |
| [85] | ZHANG J, CHEN C, GADI M R, et al. Machine-Driven Enzymatic Oligosaccharide Synthesis by Using a Peptide Synthesizer [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(51): 16638-16642. |
| [86] | ZHANG J, LIU D, SAIKAM V, et al. Machine-Driven Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Glycopeptide [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(45): 19825-19829. |
| [87] | LI T, LIU L, WEI N, et al. An automated platform for the enzyme-mediated assembly of complex oligosaccharides [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(3): 229-236. |
| [88] | MAHOUR R, KLAPPROTH J, REXER T F T, et al. Establishment of a five-enzyme cell-free cascade for the synthesis of uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 283: 120-129. |
| [89] | SCHELCH S, EIBINGER M, GROSS Belduma S, et al. Engineering analysis of multienzyme cascade reactions for 3'-sialyllactose synthesis [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(11): 4290-4304. |
| [90] | DONG K, LIU X, DONG H, et al. Multiscale Studies on Ionic Liquids [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(10): 6636-6695. |
| [91] | ANGELL C A, ANSARI Y, ZHAO Z. Ionic liquids: past, present and future [J]. Faraday Discussions, 2012, 154: 9-27. |
| [92] | ITOH T. Ionic Liquids as Tool to Improve Enzymatic Organic Synthesis [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(15): 10567-10607. |
| [93] | LI Z, HAN Q, WANG K, et al. Ionic liquids as a tunable solvent and modifier for biocatalysis [J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2024, 66(2): 484-530. |
| [94] | JI X L, XUE Y J, LI Z, et al. Ionozyme: ionic liquids as solvent and stabilizer for efficient bioactivation of CO2 [J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(18): 6990-7000. |
| [95] | LI Z, WANG K, XUE Y J, et al. Ionozymes for Efficient Synthesis of Cadaverine: Offering a Sustainable Way for Bio-nylon 5X Production [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(10): 4197-4208. |
| [96] | LANG M, KAMRAT T, NIDETZKY B. Influence of ionic liquid cosolvent on transgalactosylation reactions catalyzed by thermostable β-glycosylhydrolase celB from [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 95(6): 1093-1100. |
| [97] | SANDOVAL M, CORTÉS A, CIVERA C, et al. Efficient and selective enzymatic synthesis of N-acetyl-lactosamine in ionic liquid: a rational explanation [J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(15): 6306-6314. |
| [98] | BAYÓN C, CORTÉS A, BERENGUER J, et al. Highly efficient enzymatic synthesis of Galβ-(1→3)-GalNAc and Galβ-(1→3)-GlcNAc in ionic liquids [J]. Tetrahedron, 2013, 69(24): 4973-4978. |
| [99] | PATEL M S, NEMERIA N S, FUREY W, et al. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes: structure-based function and regulation [J]. The Journal of biological chemistry, 2014, 289(24): 16615-16623. |
| [100] | PAPAGEORGIOU A C. Structural Characterization of Multienzyme Assemblies: An Overview [J]. Methods in molecular biology, 2022, 2487: 51-72. |
| [101] | QU J, CAO S, WEI Q, et al. Synthetic Multienzyme Complexes, Catalytic Nanomachineries for Cascade Biosynthesis In Vivo [J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9): 9895-9906. |
| [102] | OVADI J, SRERE P A. Metabolic consequences of enzyme interactions [J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 1996, 14(4): 249-258. |
| [103] | HWANG E T, LEE S. Multienzymatic Cascade Reactions via Enzyme Complex by Immobilization [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(5): 4402-4425. |
| [104] | XU R R, WANG Y, HUANG H, et al. Closed-Loop System Driven by ADP Phosphorylation from Pyrophosphate Affords Equimolar Transformation of ATP to 3′-Phosphoadenosine-5′- phosphosulfate [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(16): 10405-10415. |
| [1] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||