合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (6): 1109-1125.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-029
哺乳动物细胞的趋化迁移及人工控制
郭伟, 付禹豪, 范盈盈, 周佳铃, 李鑫, 魏平
- 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,细胞与基因线路设计中心,中国科学院定量工程生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2022-05-23修回日期:2022-09-05出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2023-01-17 -
通讯作者:魏平 -
作者简介:郭伟 (1987—),男,博士后。研究方向为基于合成生物学的蛋白质工程、免疫细胞趋化线路的设计与开发。E-mail:wei.guo@siat.ac.cn魏平 (1980—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为生物网络的人工设计合成,基于合成生物学的细胞信息处理机制研究,以及免疫细胞工程化设计等。E-mail:ping.wei@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902800);国家自然科学基金(31622022)
Artificial control of mammalian cell chemotaxis and motility
GUO Wei, FU Yuhao, FAN Yingying, ZHOU Jialing, LI Xin, WEI Ping
- CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology,Cell and Gene Circuit Design Center,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Science,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-05-23Revised:2022-09-05Online:2022-12-31Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:WEI Ping
摘要:
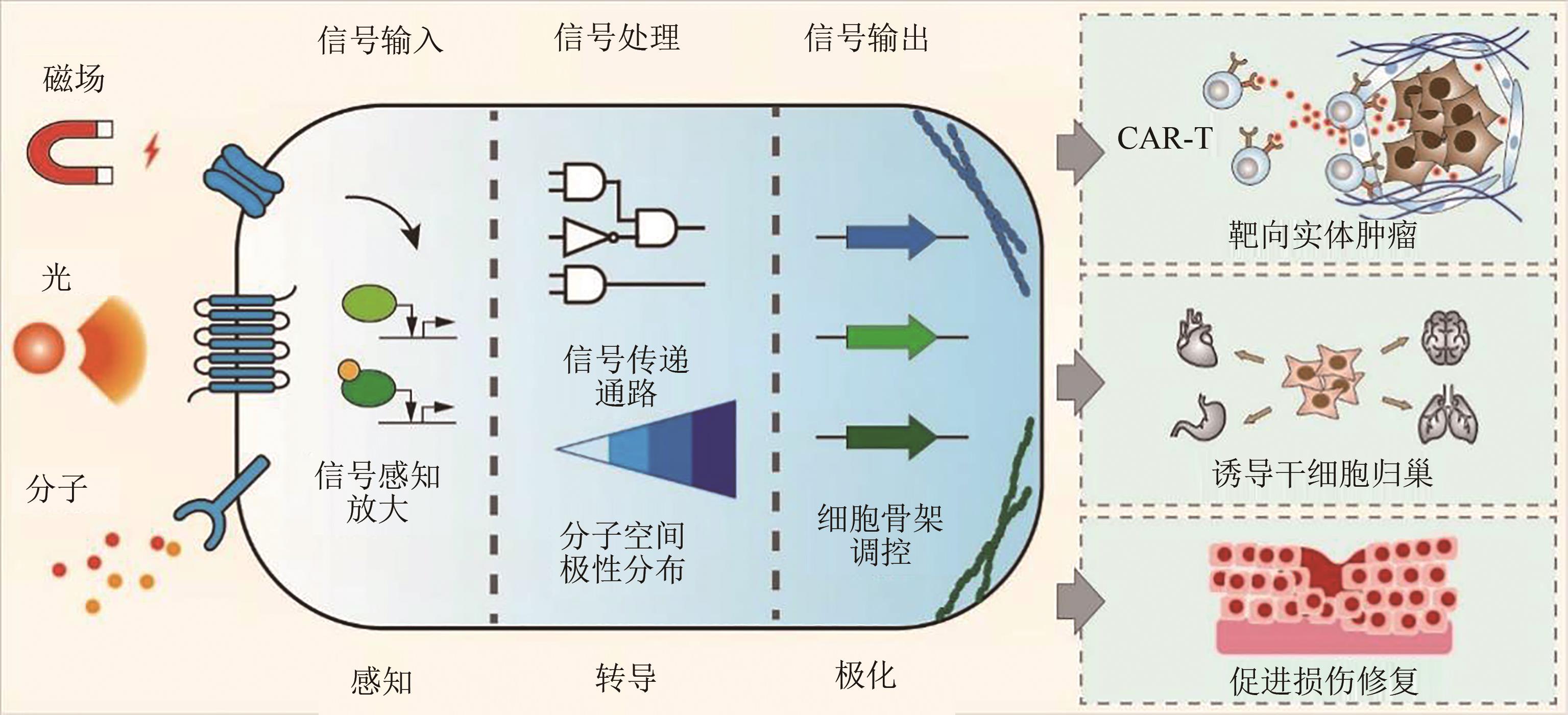
哺乳动物细胞的趋化与迁移对于生命过程重要。许多关键生理过程依赖于细胞迁移,从胚胎发育到骨和血管生成,细胞迁移在组织修复、炎症、免疫应答和癌症转移中起关键作用。在人体内,细胞必须能够感知所在环境中的各种线索,并趋向或远离这些线索,以便在发育过程中执行形态发生程序,面对病原体产生免疫以及修复受损组织。这些过程的失控会给生命带来严重的不良后果,细胞如果不能以适当的方式进行迁移,就会导致发育和免疫的缺陷、慢性伤口的无法愈合以及癌症侵袭性转移、自身免疫和纤维化等疾病。细胞迁移的机制是通过表面受体和机械感知分子将环境中的化学、物理线索传递给细胞内信号网络,通过在细胞内建立不对称的分子空间梯度,激活下游细胞骨架调控因子使细胞发生持续的极化现象。整个过程涉到将线索传递到胞内的膜受体、胞内第二信使、细胞骨架调节因子、肌动蛋白组装等一系列组分和步骤。因此系统性理解细胞趋化过程对于发展哺乳动物细胞合成生物学理性设计与改造能力具有重要意义。工程化改造细胞趋化迁移能力来实现对细胞迁移的人工控制,将是哺乳动物细胞工程的重要方向。这能帮助人们进一步探索发育机制,提升免疫治疗效果,治愈由细胞趋化紊乱造成的疾病,加快组织损伤的修复。本综述将从细胞趋化的迁移方式、环境线索、分子机制、工程改造、临床应用几个方面对哺乳动物细胞的趋化迁移进行综述介绍。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭伟, 付禹豪, 范盈盈, 周佳铃, 李鑫, 魏平. 哺乳动物细胞的趋化迁移及人工控制[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1109-1125.
GUO Wei, FU Yuhao, FAN Yingying, ZHOU Jialing, LI Xin, WEI Ping. Artificial control of mammalian cell chemotaxis and motility[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1109-1125.

图2 细胞趋化迁移机制(a)细胞的两种主要迁移模式(间充质迁移,变形虫迁移)及其转换;(b)细胞迁移环境(化学线索趋化、趋触,物理线索的硬度、拓扑结构、电场);(c)细胞迁移分子调控网络(外部线索感知,兴奋信号转导,肌动蛋白组装)
Fig. 2 Cellular chemotactic mechanisms

图3 细胞趋化迁移的工程化调控(a)利用化学小分子对细胞趋化迁移进行调控,仅由合成配体激活的受体(RASSL)能响应正交小分子如氯氮平-N-氧化物(clozapine-N-oxide,CNO)诱导迁移,化学诱导二聚化(CID)是一种灵活的方法,可招募蛋白质到细胞的特定位置。(b)利用光刺激调控细胞迁移,PA-CXCR4在505 nm光响应下传输细胞内CXCR信号,PA-CXCR4的局部激活可诱导T细胞极化和定向迁移。PA-Rac1利用蓝光诱导蛋白二聚化,实现Rac1膜定位介导细胞迁移。BcLOV4利用动态膜结合蛋白与GTPase融合,实现单个蛋白的光控诱导迁移系统。(c)利用磁场对细胞迁移进行调控, TF-CaRQ利用嵌合瞬时受体电位香草素1 (TRPV1)和嵌合RhoA蛋白,通过磁控引起Ca2+内流,Ca2+激活RhoA,从而允许磁场开启细胞迁移, MNP-GTPase通过将GTPase与磁纳米颗粒融合,在磁场作用下改变GTPase膜定位诱导迁移
Fig. 3 Engineering regulation of cell chemotaxis
| 1 | SENGUPTA S, PARENT C A, BEAR J E. The principles of directed cell migration[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021, 22(8): 529-547. |
| 2 | LI D, SUN F F, YANG Y H, et al. Gradients of PI(4, 5)P2 and PI(3, 5)P2 jointly participate in shaping the back state of dictyostelium cells[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2022, 10: 835185. |
| 3 | MUYLAERT D E, FLEDDERUS J O, BOUTEN C V, et al. Combining tissue repair and tissue engineering; bioactivating implantable cell-free vascular scaffolds[J]. Heart, 2014, 100(23): 1825-1830. |
| 4 | MARTINEZ M, MOON E K. CAR T cells for solid tumors: New strategies for finding, infiltrating, and surviving in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2019, 10: 128. |
| 5 | HUANG C H, TANG M, SHI C J, et al. An excitable signal integrator couples to an idling cytoskeletal oscillator to drive cell migration[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2013, 15(11): 1307-1316. |
| 6 | CARLIER M F, LE CLAINCHE C, WIESNER S, et al. Actin-based motility: from molecules to movement[J]. BioEssays: News and Reviews in Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology, 2003, 25(4): 336-345. |
| 7 | BORRELL V. Recent advances in understanding neocortical development[J]. F1000Research, 2019, 8(F1000FacultyRev-F1000Faculty): 1791. |
| 8 | LOCASCIO A, NIETO M A. Cell movements during vertebrate development: integrated tissue behaviour versus individual cell migration[J]. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 2001, 11(4): 464-469. |
| 9 | FRANZE K. The mechanical control of nervous system development[J]. Development 2013, 140(15): 3069-3077. |
| 10 | SCARPA E, MAYOR R. Collective cell migration in development[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 2016, 212(2): 143-155. |
| 11 | JANSSEN E, GEHA R S. Primary immunodeficiencies caused by mutations in actin regulatory proteins[J]. Immunological Reviews, 2019, 287(1): 121-134. |
| 12 | MRASS P, WENINGER W. Immune cell migration as a means to control immune privilege: lessons from the CNS and tumors[J]. Immunological Reviews, 2006, 213(1): 195-212. |
| 13 | Migration GUNZER M., cell–cell interaction and adhesion in the immune system[C]// Baier G, Schraven B, Zügel U, von Bonin A ed. Sparking Signals. Ernst Schering Foundation Symposium Proceedings. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2007, 3(3): 97-137. |
| 14 | LI L, JIANG J X. Regulatory factors of mesenchymal stem cell migration into injured tissues and their signal transduction mechanisms[J]. Frontiers of Medicine, 2011, 5(1): 33-39. |
| 15 | ZHAO M. Electrical fields in wound healing—an overriding signal that directs cell migration[J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2009, 20(6): 674-682. |
| 16 | ABREU-BLANCO M T, WATTS J J, VERBOON J M, et al. Cytoskeleton responses in wound repair[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2012, 69(15): 2469-2483. |
| 17 | GARCÍA-CUESTA E M, SANTIAGO C A, VALLEJO-DÍAZ J, et al. The role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/ACKR3 axis in autoimmune diseases[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2019, 10: 585. |
| 18 | GRIFFITH J W, LUSTER A D. Targeting cells in motion: migrating toward improved therapies[J]. European Journal of Immunology, 2013, 43(6): 1430-1435. |
| 19 | ZERNECKE A, WEBER C. Chemokines in the vascular inflammatory response of atherosclerosis[J]. Cardiovascular Research, 2010, 86(2): 192-201. |
| 20 | NOVIKOV N M, ZOLOTARYOVA S Y, GAUTREAU A M, et al. Mutational drivers of cancer cell migration and invasion[J]. British Journal of Cancer, 2021, 124(1): 102-114. |
| 21 | WELLS A, GRAHOVAC J, WHEELER S, et al. Targeting tumor cell motility as a strategy against invasion and metastasis[J]. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2013, 34(5): 283-289. |
| 22 | POLACHECK W J, ZERVANTONAKIS I K, KAMM R D. Tumor cell migration in complex microenvironments[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2013, 70(8): 1335-1356. |
| 23 | SHELLARD A, MAYOR R. All roads lead to directional cell migration[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 2020, 30(11): 852-868. |
| 24 | LADOUX B, MÈGE R M. Mechanobiology of collective cell behaviours[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2017, 18(12): 743-757. |
| 25 | ARMSTRONG J P K, STEVENS M M. Using remote fields for complex tissue engineering[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(3): 254-263. |
| 26 | STRÖMBLAD S. Cancer biology: hypoxia-induced talin tail-docking Sparks cancer metastasis[J]. Current Biology: CB, 2022, 32(2): R79-R81. |
| 27 | GRAZIANI V, RODRIGUEZ-HERNANDEZ I, MAIQUES O, et al. The amoeboid state as part of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition programme[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 2022, 32(3): 228-242. |
| 28 | AOUN L, FARUTIN A, GARCIA-SEYDA N, et al. Amoeboid swimming is propelled by molecular paddling in lymphocytes[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2020, 119(6): 1157-1177. |
| 29 | LIU Y J, LE BERRE M, LAUTENSCHLAEGER F, et al. Confinement and low adhesion induce fast amoeboid migration of slow mesenchymal cells[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(4): 659-672. |
| 30 | OAKES P W. Balancing forces in migration[J]. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 2018, 54: 43-49. |
| 31 | BOEKHORST V TE, PREZIOSI L, FRIEDL P. Plasticity of cell migration in vivo and in silico[J]. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 2016, 32: 491-526. |
| 32 | SCHUMANN K, LÄMMERMANN T, BRUCKNER M, et al. Immobilized chemokine fields and soluble chemokine gradients cooperatively shape migration patterns of dendritic cells[J]. Immunity, 2010, 32(5): 703-713. |
| 33 | YAMADA K M, SIXT M. Mechanisms of 3D cell migration[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2019, 20(12): 738-752. |
| 34 | JIAO H F, JIANG D, HU X Y, et al. Mitocytosis, a migrasome-mediated mitochondrial quality-control process[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(11): 2896-2910.e13. |
| 35 | GRAY A L, PUN N, RIDLEY A J L, et al. Role of extracellular matrix proteoglycans in immune cell recruitment[J]. International Journal of Experimental Pathology, 2022, 103(2): 34-43. |
| 36 | SCHWARTZ M A. Integrins and extracellular matrix in mechanotransduction[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2010, 2(12): a005066. |
| 37 | ESPINA J A, MARCHANT C L, BARRIGA E H. Durotaxis: the mechanical control of directed cell migration[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2022, 289(10): 2736-2754. |
| 38 | SEETHARAMAN S, ETIENNE-MANNEVILLE S. Integrin diversity brings specificity in mechanotransduction[J]. Biology of the Cell, 2018, 110(3): 49-64. |
| 39 | LOU H Y, ZHAO W T, ZENG Y P, et al. The role of membrane curvature in nanoscale topography-induced intracellular signaling[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(5): 1046-1053. |
| 40 | HOTARY K B, ROBINSON K R. Endogenous electrical currents and voltage gradients in Xenopus embryos and the consequences of their disruption[J]. Developmental Biology, 1994, 166(2): 789-800. |
| 41 | SONG B, GU Y, JIANG W K, et al. Electric signals counterbalanced posterior vs anterior PTEN signaling in directed migration of Dictyostelium[J]. Cell & Bioscience, 2021, 11(1): 111. |
| 42 | PAL D S, LI X G, BANERJEE T, et al. The excitable signal transduction networks: movers and shapers of eukaryotic cell migration[J]. The International Journal of Developmental Biology, 2019, 63(8/9): 407-416. |
| 43 | RIDLEY A J, SCHWARTZ M A, BURRIDGE K, et al. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back[J]. Science, 2003, 302(5651): 1704-1709. |
| 44 | FRITZ R D, PERTZ O. The dynamics of spatio-temporal Rho GTPase signaling: formation of signaling patterns[J]. F1000Research, 2016, 5(F1000FacultyRev): 749. |
| 45 | BEMENT W M, MILLER A L, VON DASSOW G. Rho GTPase activity zones and transient contractile arrays[J]. BioEssays, 2006, 28(10): 983-993. |
| 46 | MAÑES S, GÓMEZ-MOUTÓN C, LACALLE R A, et al. Mastering time and space: Immune cell polarization and chemotaxis[J]. Seminars in Immunology, 2005, 17(1): 77-86. |
| 47 | WANG Y Q, KU C J, ZHANG E R, et al. Identifying network motifs that buffer front-to-back signaling in polarized neutrophils[J]. Cell Reports, 2013, 3(5): 1607-1616. |
| 48 | BISHOP A L, HALL A. Rho GTPases and their effector proteins[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2000, 348(Pt 2): 241-255. |
| 49 | MENG X T, AROCENA M, PENNINGER J, et al. PI3K mediated electrotaxis of embryonic and adult neural progenitor cells in the presence of growth factors[J]. Experimental Neurology, 2011, 227(1): 210-217. |
| 50 | MIAO Y C, BHATTACHARYA S, EDWARDS M, et al. Altering the threshold of an excitable signal transduction network changes cell migratory modes[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2017, 19(4): 329-340. |
| 51 | KUROKAWA K, NAKAMURA T, AOKI K, et al. Mechanism and role of localized activation of Rho-family GTPases in growth factor-stimulated fibroblasts and neuronal cells[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2005, 33(Pt 4): 631-634. |
| 52 | BOS J L, REHMANN H, WITTINGHOFER A. GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins[J]. Cell, 2007, 129(5): 865-877. |
| 53 | GERMENA G, HIRSCH E. PI3Ks and small GTPases in neutrophil migration: Two sides of the same coin[J]. Molecular Immunology, 2013, 55(1): 83-86. |
| 54 | VICKER M G. F-actin assembly in Dictyostelium cell locomotion and shape oscillations propagates as a self-organized reaction-diffusion wave[J]. FEBS Letters, 2002, 510(1/2): 5-9. |
| 55 | VAN HAASTERT P J, KEIZER-GUNNINK I, KORTHOLT A. Coupled excitable Ras and F-actin activation mediates spontaneous pseudopod formation and directed cell movement[J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2017, 28(7): 922-934. |
| 56 | WEINER O D, MARGANSKI W A, WU L F, et al. An actin-based wave generator organizes cell motility[J]. PLoS Biology, 2007, 5(9): e221. |
| 57 | TANG M, WANG M J, SHI C J, et al. Evolutionarily conserved coupling of adaptive and excitable networks mediates eukaryotic chemotaxis[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5175. |
| 58 | MIAO Y C, BHATTACHARYA S, BANERJEE T, et al. Wave patterns organize cellular protrusions and control cortical dynamics[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2019, 15(3): e8585. |
| 59 | KAMIMURA Y, XIONG Y, IGLESIAS P A, et al. PIP3-independent activation of TorC2 and PKB at the cell's leading edge mediates chemotaxis[J]. Current Biology, 2008, 18(14): 1034-1043. |
| 60 | FETS L, NICHOLS J M E, KAY R R. A PIP5 kinase essential for efficient chemotactic signaling[J]. Current Biology, 2014, 24(4): 415-421. |
| 61 | CHAREST P G, SHEN Z X, LAKODUK A, et al. A ras signaling complex controls the RasC-TORC2 pathway and directed cell migration[J]. Developmental Cell, 2010, 18(5): 737-749. |
| 62 | PIPATHSOUK A, BRUNETTI R M, TOWN J P, et al. WAVE complex self-organization templates lamellipodial formation[J]. bioRxiv, 2019, DOI:10.1101/836585 . |
| 63 | BRUNETTI R M, KOCKELKOREN G, RAGHAVAN P, et al. WASP integrates substrate topology and cell polarity to guide neutrophil migration[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 2022, 221(2): e202104046. |
| 64 | GRAZIANO B R, GONG D, ANDERSON K E, et al. A module for Rac temporal signal integration revealed with optogenetics[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 2017, 216(8): 2515-2531. |
| 65 | ALLEN T M, CULLIS P R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2013, 65(1): 36-48. |
| 66 | PAUL C D, HUNG W C, WIRTZ D, et al. Engineered models of confined cell migration[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 18: 159-180. |
| 67 | ULLAH M, LIU D D, THAKOR A S. Mesenchymal stromal cell homing: Mechanisms and strategies for improvement[J]. iScience, 2019, 15: 421-438. |
| 68 | WON Y W, PATEL A N, BULL D A. Cell surface engineering to enhance mesenchymal stem cell migration toward an SDF-1 gradient[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(21): 5627-5635. |
| 69 | SASAKI T, FUKAZAWA R, OGAWA S, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α improves infarcted heart function through angiogenesis in mice[J]. Pediatrics International, 2007, 49(6): 966-971. |
| 70 | SEGERS V F M, REVIN V, WU W T, et al. Protease-resistant stromal cell-derived factor-1 for the treatment of experimental peripheral artery disease[J]. Circulation, 2011, 123(12): 1306-1315. |
| 71 | FUJII H, LI S H, WU J, et al. Repeated and targeted transfer of angiogenic plasmids into the infarcted rat heart via ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction enhances cardiac repair[J]. European Heart Journal, 2010, 32(16): 2075-2084. |
| 72 | KIMURA Y, TABATA Y. Controlled release of stromal-cell-derived factor-1 from gelatin hydrogels enhances angiogenesis[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition, 2010, 21(1): 37-51. |
| 73 | CONKLIN B R, HSIAO E C, CLAEYSEN S, et al. Engineering GPCR signaling pathways with RASSLs[J]. Nature Methods, 2008, 5(8): 673-678. |
| 74 | PARK J S, RHAU B, HERMANN A, et al. Synthetic control of mammalian-cell motility by engineering chemotaxis to an orthogonal bioinert chemical signal[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(16): 5896-5901. |
| 75 | XU Y, HYUN Y M, LIM K, et al. Optogenetic control of chemokine receptor signal and T-cell migration[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(17): 6371-6376. |
| 76 | WU Y I, FREY D, LUNGU O I, et al. A genetically encoded photoactivatable Rac controls the motility of living cells[J]. Nature, 2009, 461(7260): 104-108. |
| 77 | DAGLIYAN O, DOKHOLYAN N V, HAHN K M. Engineering proteins for allosteric control by light or ligands[J]. Nature Protocols, 2019, 14(6): 1863-1883. |
| 78 | O'NEILL P R, GAUTAM N. Subcellular optogenetic inhibition of G proteins generates signaling gradients and cell migration[J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2014, 25(15): 2305-2314. |
| 79 | KARUNARATHNE W K A, GIRI L, PATEL A K, et al. Optical control demonstrates switch-like PIP3 dynamics underlying the initiation of immune cell migration[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(17): E1575-E1583. |
| 80 | BERLEW E E, KUZNETSOV I A, YAMADA K, et al. Single-component optogenetic tools for inducible RhoA GTPase signaling[J]. Advanced Biology, 2021, 5(9): e2100810. |
| 81 | BERLEW E E, KUZNETSOV I A, YAMADA K, et al. Optogenetic Rac1 engineered from membrane lipid-binding RGS-LOV for inducible lamellipodia formation[J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2020, 19(3): 353-361. |
| 82 | HANNANTA-ANAN P, GLANTZ S T, CHOW B Y. Optically inducible membrane recruitment and signaling systems[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2019, 57: 84-92. |
| 83 | ARBAB A S, JORDAN E K, WILSON L B, et al. In vivo trafficking and targeted delivery of magnetically labeled stem cells[J]. Human Gene Therapy, 2004, 15(4): 351-360. |
| 84 | KOBAYASHI T, OCHI M, YANADA S, et al. Augmentation of degenerated human cartilage in vitro using magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells and an external magnetic device[J]. Arthroscopy: the Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery, 2009, 25(12): 1435-1441. |
| 85 | YUN W S, CHOI J S, JU H M, et al. Enhanced homing technique of mesenchymal stem cells using iron oxide nanoparticles by magnetic attraction in olfactory-injured mouse models[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(5): 1376. |
| 86 | SONG Y S, KU J H. Monitoring transplanted human mesenchymal stem cells in rat and rabbit bladders using molecular magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Neurourology and Urodynamics, 2007, 26(4): 584-593. |
| 87 | FENG Q, LEE S S, KORNMANN B. A toolbox for organelle mechanobiology research-current needs and challenges[J]. Micromachines, 2019, 10(8): 538. |
| 88 | ETOC F, LISSE D, BELLAICHE Y, et al. Subcellular control of Rac-GTPase signalling by magnetogenetic manipulation inside living cells[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8(3): 193-198. |
| 89 | MOSABBIR A A, TRUONG K. Genetically encoded circuit for remote regulation of cell migration by magnetic fields[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(2): 718-726. |
| 90 | MILLS E, TRUONG K. Engineering Ca2+/calmodulin-mediated modulation of protein translocation by overlapping binding and signaling peptide sequences[J]. Cell Calcium, 2010, 47(4): 369-377. |
| 91 | SENGUPTA S, PARENT C A, BEAR J E. The principles of directed cell migration[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021, 22(8): 529-547. |
| 92 | SCHULTZ G S, WYSOCKI A. Interactions between extracellular matrix and growth factors in wound healing[J]. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 2009, 17(2): 153-162. |
| 93 | MOSABBIR A A, TRUONG K. Light directed migration of a cluster of cells in the centimeter scale[J]. Small GTPases, 2020, 11(4): 301-307. |
| 94 | WEI F Y, LEUNG K S, LI G, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound enhanced mesenchymal stem cell recruitment through stromal derived factor-1 signaling in fracture healing[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(9): e106722. |
| 95 | XIA P, SHI Y, WANG X J, et al. Advances in the application of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound to mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 2022, 13(1): 214. |
| 96 | CHEN J L, JIANG J W, WANG W, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the migration of bone marrow- derived mesenchymal stem cells via activating FAK-ERK1/2 signalling pathway[J]. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 2019, 47(1): 3603-3613. |
| 97 | CHEN C, BAI X, DING Y H, et al. Electrical stimulation as a novel tool for regulating cell behavior in tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials Research, 2019, 23: 25. |
| 98 | ROYBAL K T, LIM W A. Synthetic immunology: hacking immune cells to expand their therapeutic capabilities[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 2017, 35: 229-253. |
| 99 | JIN L Y, CAO L, ZHU Y J, et al. Enhance anti-lung tumor efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor-T cells by ectopic expression of C-C motif chemokine receptor 6[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(8): 803-812. |
| 100 | MOON E K, CARPENITO C, SUN J, et al. Expression of a functional CCR2 receptor enhances tumor localization and tumor eradication by retargeted human T cells expressing a mesothelin-specific chimeric antibody receptor[J]. Clinical Cancer Research: an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 2011, 17(14): 4719-4730. |
| 101 | DI STASI A, DE ANGELIS B, ROONEY C M, et al. T lymphocytes coexpressing CCR4 and a chimeric antigen receptor targeting CD30 have improved homing and antitumor activity in a Hodgkin tumor model[J]. Blood, 2009, 113(25): 6392-6402. |
| 102 | SANTORELLI M, LAM C, MORSUT L. Synthetic development: Building mammalian multicellular structures with artificial genetic programs[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 59: 130-140. |
| 103 | TODA S, BRUNGER J M, LIM W A. Synthetic development: Learning to program multicellular self-organization[J]. Current Opinion in Systems Biology, 2019, 14: 41-49. |
| 104 | GEERING B, FUSSENEGGER M. Synthetic immunology: modulating the human immune system[J]. Trends in biotechnology, 2015, 33(2): 65-79. |
| [1] | 柳柯, 林桂虹, 刘坤, 周伟, 王风清, 魏东芝. CRISPR/Cas系统的挖掘、改造与功能拓展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 47-66. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||