合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (1): 47-66.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-022
CRISPR/Cas系统的挖掘、改造与功能拓展
柳柯, 林桂虹, 刘坤, 周伟, 王风清, 魏东芝
- 华东理工大学生物反应器工程国家重点实验室,鲁华生物技术研究所,上海 200237
-
收稿日期:2021-02-08修回日期:2021-04-28出版日期:2023-02-28发布日期:2023-03-07 -
通讯作者:王风清,魏东芝 -
作者简介:柳柯 (1995—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为基因组编辑技术的开发与应用等。E-mail:y12190016@mail.ecust.edu.cn王风清 (1977—),男,副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为利用代谢工程和合成生物学的原理和方法,致力于微生物细胞工厂的研究和开发等。E-mail:fqwang@ecust.edu.cn魏东芝 (1963—),男,二级教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物元器件的发现、改造与应用研究, 致力于发现和改进具有工业应用价值的微生物和生物催化剂,开拓生物转化新反应等。E-mail:dzhwei@ecust.edu.cn
第一联系人:柳柯(1995—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为基因组编辑技术的开发与应用等。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(21978084)
Mining, engineering and functional expansion of CRISPR/Cas systems
LIU Ke, LIN Guihong, LIU Kun, ZHOU Wei, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi
- State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering,Newworld Institute of Biotechnology,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
-
Received:2021-02-08Revised:2021-04-28Online:2023-02-28Published:2023-03-07 -
Contact:WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi
摘要:
规律成簇间隔短回文重复序列及其相关蛋白(CRISPR/Cas)是一种微生物获得性免疫系统,自从证实其可用于基因编辑之后,迅速增强了我们编辑、操纵、注释、检测甚至成像生物体DNA和RNA的能力,为基础生命科学、医学和生物工程等领域的创新发展注入了强劲动力,快速推动了合成生物学等学科的兴盛发展。然而,CRISPR/Cas系统也有一些固有的问题,例如脱靶效应、原间隔序列邻近基序(PAM)对靶目标的约束性以及基因编辑活性的可控性等,严重制约了该系统在基因精准可控编辑等方面的长足发展,阻碍了其新功能和新应用的拓展。为了突破这些限制,“蛋白质工程修饰Cas蛋白”与“基于生物信息学的新型CRISPR/Cas系统的挖掘”就成为完善发展CRISPR/Cas系统以及扩充CRISPR工具箱的两种重要策略。本文主要针对当前应用最为广泛的Ⅱ类CRISPR/Cas系统,重点介绍了CRISPR/Cas9、CRISPR/Cas12a和CRISPR/Cas13a这三种代表性系统的基本结构和作用机制,及其在结构改造和功能拓展等方面的新进展,同时也对一些新近发掘的具有重要特色和潜在应用价值的CRISPR/Cas系统进行了综述,例如CRISPR/CasФ 和 CRISPR/Cas12k。这些改造和发掘工作显著改善了CRISPR/Cas系统的固有问题,有力地拓展了其功能和适用性,势必会进一步快速推动CRISPR/Cas系统在诸多领域的创新发展。
中图分类号:
引用本文
柳柯, 林桂虹, 刘坤, 周伟, 王风清, 魏东芝. CRISPR/Cas系统的挖掘、改造与功能拓展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 47-66.
LIU Ke, LIN Guihong, LIU Kun, ZHOU Wei, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Mining, engineering and functional expansion of CRISPR/Cas systems[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 47-66.
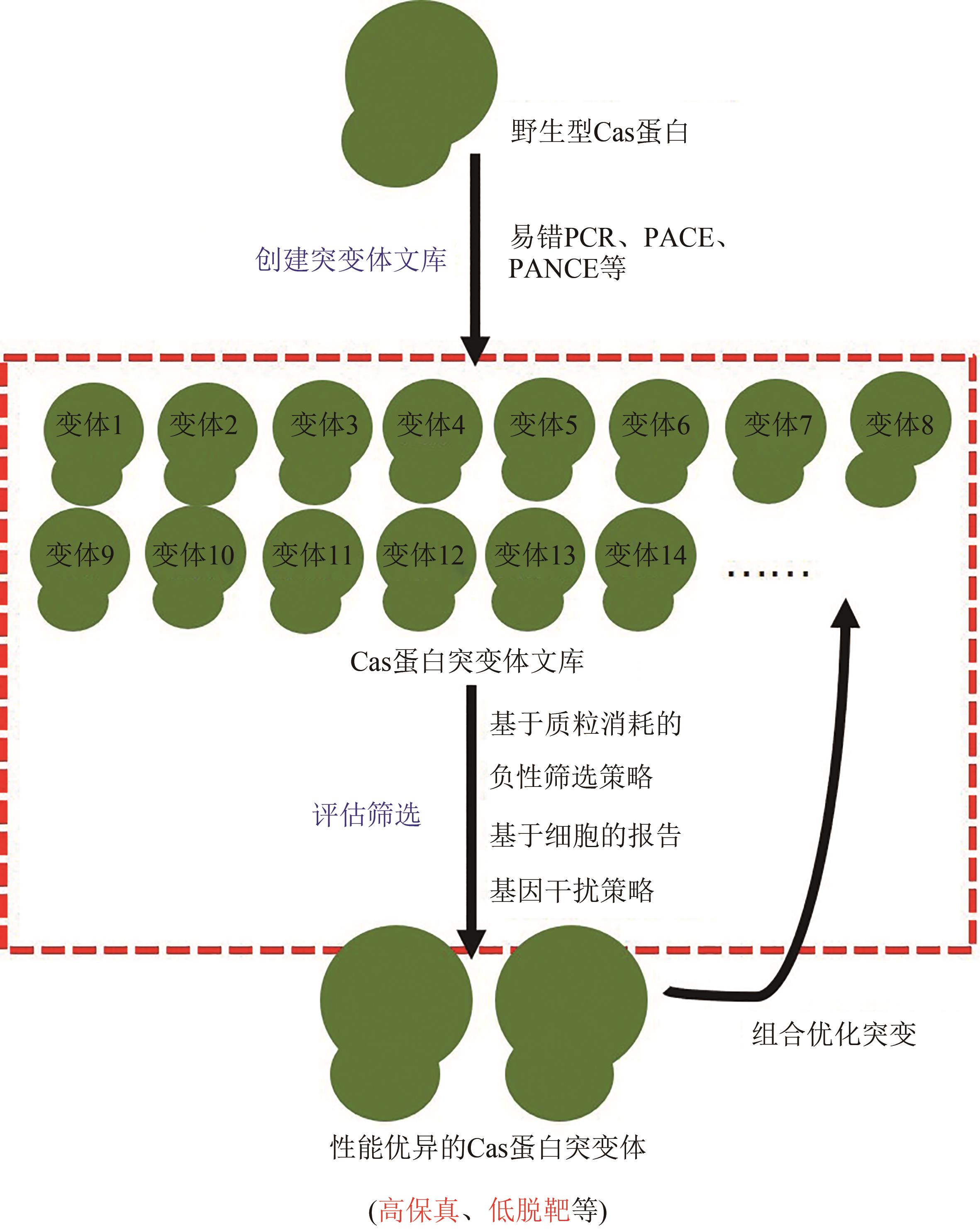
图2 基于非理性进化的Cas蛋白改造策略示意图(The random modification strategy for Cas proteins contains following steps: Firstly, random mutagenesis, such as Error-prone PCR, PACE, PANCE, etc, are employed to generate variant libraries of Cas proteins. Secondly, effective assessments, such as plasmid interference-based depletion screening, human cell-based EGFP reporter assay, and so on, are applied to screen positive mutations. Finally, the positive mutations are combined for mutagenesis to develop more significant Cas variants.)
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram for random modifications of Cas proteins
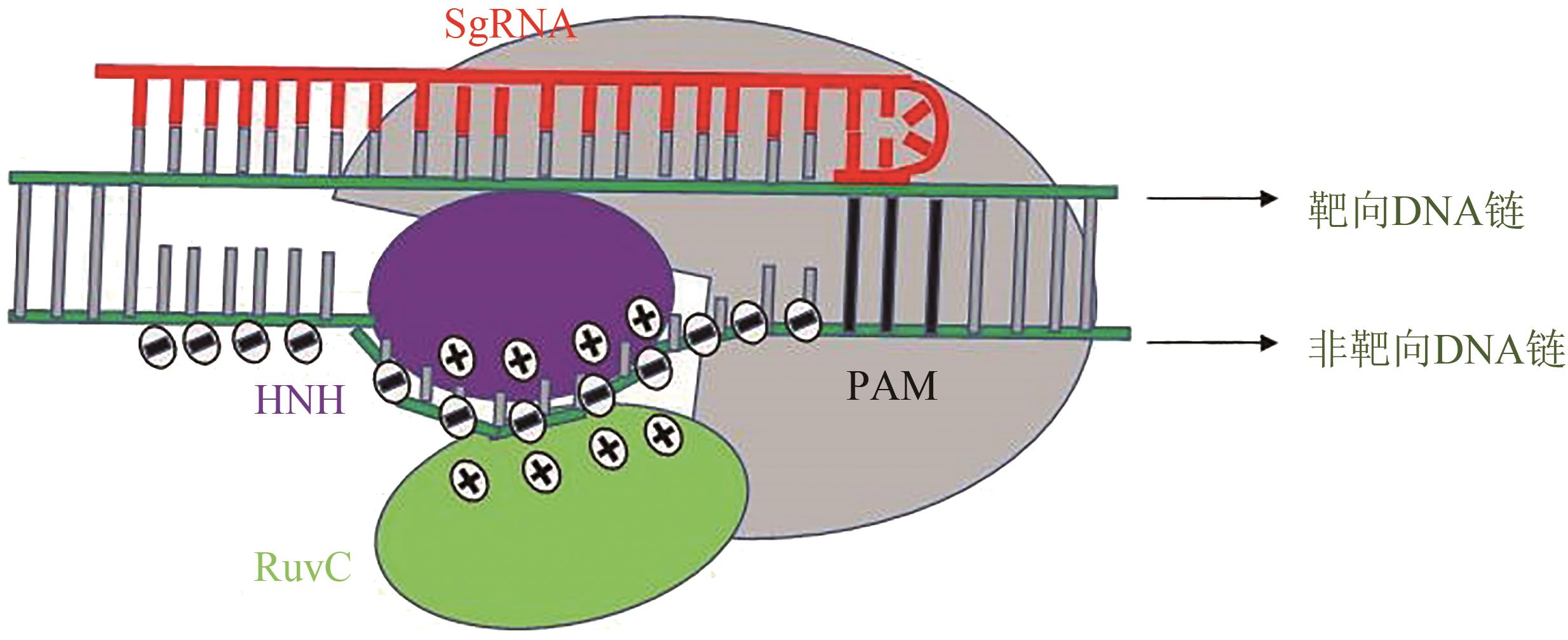
图3 SpCas9解开靶DNA链双螺旋结构后DNA链与非靶向DNA链凹槽的电荷分布模型图[35](Positively charged grooves among the HNH (purple), RuvC (green), and PI domains (gray) in SpCas9 play a key role in stabilizing the non-target strand of the target DNA by DNA interactions. Then, the SpCas9 complex can readily target paired DNA strands through complementation to drive DNA unwinding and prevent re-hybridization of DNA double strands.)
Fig. 3 Model for charge distribution on DNA and the nt-groove after SpCas9 unwinds the double helix structure of targeted DNA strands[35]
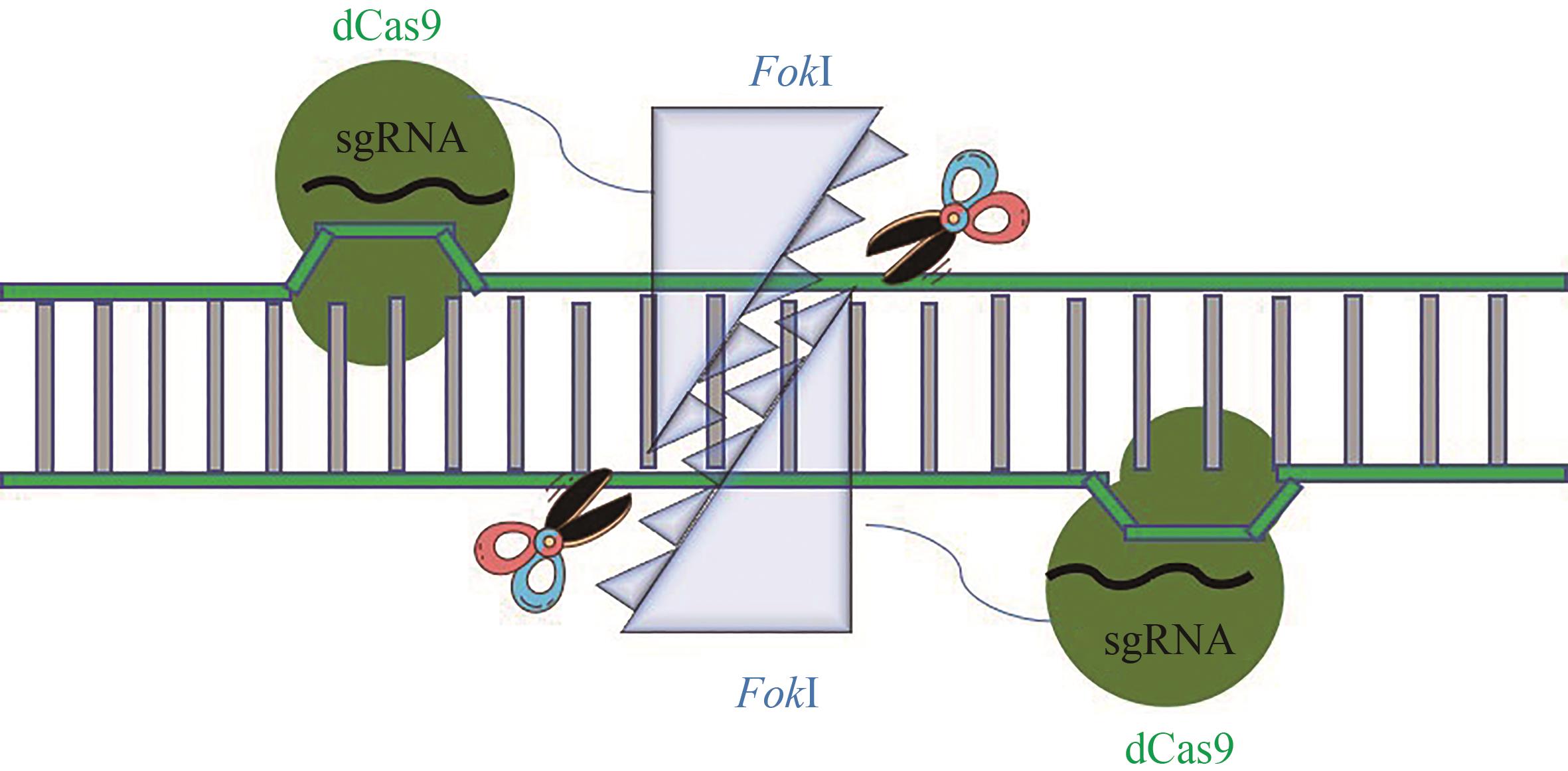
图4 FokI-dCas9融合蛋白变体的结构及功能示意图[64](Two distinct FokI nuclease (blue grey)-dCas9 (green) complexes with sgRNA (black) bind to adjacent target sites with particular spacing constraints, and dsDNA cleavage can be triggered only when the two FokI-dCas9 complexes assemble a dimeric active FokI nuclease.)
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram for the structure and function of FokI-dCas9 fusion protein variants[64]

图5 ShCAST所介导的DNA转座模型[50](The ShCAST consists of a Tn7-like transposase (blue) and a Cas12k protein (green), which catalyzes sgRNA-guided DNA transposition. The cargo gene between transposon LE and RE sequences can be inserted into DNA at 60~66 bp downstream of PAM.)
Fig. 5 Model for ShCAST-mediated DNA transposition[50]
| Cas蛋白变体 | 突变点 | PAM序列 | 保真性 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KKH SaCas9 | E782K/N968K/R1015H | NNNRRT | — | [ |
| RRAsCas12a | S542R/K607R | TYCV | — | [ |
| RVRAsCas12a | S542R/K548V/N552R | TATV | — | [ |
| xCas9-3.7 | A262T/R324L/S409I/E480K/E543D/M694I/E1219V | NG/NNG/GAA/GAT/CAA | 提高 | [ |
| SpCas9-NRRH/NRTH/NRCH | — | NRNH | 提高 | [ |
| HypaCas9 | N692A/M694A/Q695A/H698A | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| eSpCas9(1.0) | K810A/K1003A/R1060A | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| SpCas9-HF1 | N497A/R661A/Q695AQ926A | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| SpG | D1135L/S1136W/G1218K/E1219Q/R1335Q/T1337R | NGN | — | [ |
| SpRY | SpG突变点+L1111R/A1322R/R1333P/A61R/N1317R | NYN/NRN | — | [ |
| enAsCas12a-HF1 | E174R/S542R/K548R/N282A | TTYN/VTTV/TRTV | 提高 | [ |
| LbCas12a-RVRR | G532R/K538V/Y542R/K595R | TNTN/TACV/TTCV/CTCV/CCCV | — | [ |
| Blackjack SpCas9 | — | NGG | 提高 | [ |
表1 工程化改造的Cas蛋白变体
Table 1 Engineered Cas protein variants
| Cas蛋白变体 | 突变点 | PAM序列 | 保真性 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KKH SaCas9 | E782K/N968K/R1015H | NNNRRT | — | [ |
| RRAsCas12a | S542R/K607R | TYCV | — | [ |
| RVRAsCas12a | S542R/K548V/N552R | TATV | — | [ |
| xCas9-3.7 | A262T/R324L/S409I/E480K/E543D/M694I/E1219V | NG/NNG/GAA/GAT/CAA | 提高 | [ |
| SpCas9-NRRH/NRTH/NRCH | — | NRNH | 提高 | [ |
| HypaCas9 | N692A/M694A/Q695A/H698A | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| eSpCas9(1.0) | K810A/K1003A/R1060A | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| SpCas9-HF1 | N497A/R661A/Q695AQ926A | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| SpG | D1135L/S1136W/G1218K/E1219Q/R1335Q/T1337R | NGN | — | [ |
| SpRY | SpG突变点+L1111R/A1322R/R1333P/A61R/N1317R | NYN/NRN | — | [ |
| enAsCas12a-HF1 | E174R/S542R/K548R/N282A | TTYN/VTTV/TRTV | 提高 | [ |
| LbCas12a-RVRR | G532R/K538V/Y542R/K595R | TNTN/TACV/TTCV/CTCV/CCCV | — | [ |
| Blackjack SpCas9 | — | NGG | 提高 | [ |
| Cas蛋白 | 靶向核酸类型 | CRISPR阵列加工 | PAM/PFS | 切割后的DNA末端 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas12b | dsDNA | 无 | 富含T的PAM | 黏性末端 | [ |
| Cas12c | dsDNA | 无 | — | — | [ |
| Cas12d | dsDNA | 无 | 富含T的PAM | — | [ |
| Cas12e | dsDNA | 无 | 富含T的PAM | — | [ |
| CasФ | dsDNA | 无 | TBN | 黏性末端 | [ |
| Cas12k | dsDNA | 无 | GTN | 仅靶向不切割 | [ |
| Cas13b | ssRNA | 是 | 5′D PFS 3′NAN/NNA | ssRNA以及邻近的RNA | [ |
| Cas13c | ssRNA | 无 | — | — | [ |
表2 新型的Cas蛋白
Table 2 Novel Cas proteins
| Cas蛋白 | 靶向核酸类型 | CRISPR阵列加工 | PAM/PFS | 切割后的DNA末端 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas12b | dsDNA | 无 | 富含T的PAM | 黏性末端 | [ |
| Cas12c | dsDNA | 无 | — | — | [ |
| Cas12d | dsDNA | 无 | 富含T的PAM | — | [ |
| Cas12e | dsDNA | 无 | 富含T的PAM | — | [ |
| CasФ | dsDNA | 无 | TBN | 黏性末端 | [ |
| Cas12k | dsDNA | 无 | GTN | 仅靶向不切割 | [ |
| Cas13b | ssRNA | 是 | 5′D PFS 3′NAN/NNA | ssRNA以及邻近的RNA | [ |
| Cas13c | ssRNA | 无 | — | — | [ |
| 1 | MARRAFFINI L A. CRISPR-Cas immunity in prokaryotes[J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7571): 55-61. |
| 2 | GARNEAU J E, M-È DUPUIS, VILLION M, et al. The CRISPR/Cas bacterial immune system cleaves bacteriophage and plasmid DNA[J]. Nature, 2010, 468(7320): 67-71. |
| 3 | TERNS M P, TERNS R M. CRISPR-based adaptive immune systems[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2011, 14(3): 321-327. |
| 4 | AMITAI G, SOREK R. CRISPR-Cas adaptation: Insights into the mechanism of action[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(2): 67-76. |
| 5 | CHARPENTIER E, RICHTER H, VAN DER OOST J, et al. Biogenesis pathways of RNA guides in archaeal and bacterial CRISPR-Cas adaptive immunity[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2015, 39(3): 428-441. |
| 6 | PLAGENS A, RICHTER H, CHARPENTIER E, et al. DNA and RNA interference mechanisms by CRISPR-Cas surveillance complexes[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2015, 39(3): 442-463. |
| 7 | NISHIMASU H, NUREKI O. Structures and mechanisms of CRISPR RNA-guided effector nucleases[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2017, 43: 68-78. |
| 8 | MILLER J C, HOLMES M C, WANG J B, et al. An improved zinc-finger nuclease architecture for highly specific genome editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(7): 778-785. |
| 9 | CERMAK T, DOYLE E L, CHRISTIAN M, et al. Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(12): e82. |
| 10 | SANTOS-MORENO J, TASIUDI E, STELLING J, et al. Multistable and dynamic CRISPRi-based synthetic circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2746. |
| 11 | LIU Y, WAN X Y, WANG B J. Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 3693. |
| 12 | LIAN J Z, HAMEDIRAD M, HU S M, et al. Combinatorial metabolic engineering using an orthogonal tri-functional CRISPR system[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1688. |
| 13 | KANG J G, PARK J S, KO J H, et al. Regulation of gene expression by altered promoter methylation using a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated epigenetic editing system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 11960. |
| 14 | THAKORE P I, BLACK J B, HILTON I B, et al. Editing the epigenome: technologies for programmable transcription and epigenetic modulation[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(2): 127-137. |
| 15 | HILTON I B, D′IPPOLITO A M, VOCKLEY C M, et al. Epigenome editing by a CRISPR-Cas9-based acetyltransferase activates genes from promoters and enhancers[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(5): 510-517. |
| 16 | KOMOR A C, KIM Y B, PACKER M S, et al. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 420-424. |
| 17 | NISHIDA K, ARAZOE T, YACHIE N, et al. Targeted nucleotide editing using hybrid prokaryotic and vertebrate adaptive immune systems[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6305): aaf8729. |
| 18 | DREISSIG S, SCHIML S, SCHINDELE P, et al. Live-cell CRISPR imaging in plants reveals dynamic telomere movements[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2017, 91(4):565-573. |
| 19 | ROUET R, THUMA B A, ROY M D, et al. Receptor-mediated delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 endonuclease for cell-type-specific gene editing[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(21): 6596-6603. |
| 20 | ZHOU Y X, WANG P, TIAN F, et al. Painting a specific chromosome with CRISPR/Cas9 for live-cell imaging[J]. Cell Research, 2017, 27(2): 298-301. |
| 21 | JIANG W, BIKARD D, COX D, et al. RNA-guided editing of bacterial genomes using CRISPR-Cas systems [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(3): 233-239. |
| 22 | BAO Z H, XIAO H, LIANG J, et al. Homology-integrated CRISPR-Cas (HI-CRISPR) system for one-step multigene disruption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(5): 585-594. |
| 23 | XIE K B, YANG Y N. RNA-guided genome editing in plants using a CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(6): 1975-1983. |
| 24 | GUAN L H, HAN Y W, ZHU S Y, et al. Application of CRISPR-Cas system in gene therapy: pre-clinical progress in animal model[J]. DNA Repair, 2016, 46: 1-8. |
| 25 | MODARAI S R, KANDA S, BLOH K, et al. Precise and error-prone CRISPR-directed gene editing activity in human CD34+ cells varies widely among patient samples[J]. Gene Therapy, 2021, 28(1/2): 105-113. |
| 26 | MARX V. Guide RNAs: It's good to be choosy[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(12): 1179-1182. |
| 27 | FU Y F, FODEN J A, KHAYTER C, et al. High-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR-Cas nucleases in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(9): 822-826. |
| 28 | TASAN I, ZHAO H M. Targeting specificity of the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(9): 1609-1613. |
| 29 | WANG Y, WANG M R, ZHENG T, et al. Specificity profiling of CRISPR system reveals greatly enhanced off-target gene editing [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 2269. |
| 30 | KLEINSTIVER B P, SOUSA A A, WALTON R T, et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas12a variants with increased activities and improved targeting ranges for gene, epigenetic and base editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(3): 276-282. |
| 31 | WALTON R T, CHRISTIE K A, WHITTAKER M N, et al. Unconstrained genome targeting with near-PAMless engineered CRISPR-Cas9 variants[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6488): 290-296. |
| 32 | GILBERT L A, HORLBECK M A, ADAMSON B, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(3): 647-661. |
| 33 | CHO S W, KIM S, KIM Y, et al. Analysis of off-target effects of CRISPR/Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases and nickases[J]. Genome Research, 2014, 24(1): 132-141. |
| 34 | ZETSCHE B, VOLZ S E, ZHANG F. A split-Cas9 architecture for inducible genome editing and transcription modulation[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(2): 139-142. |
| 35 | SLAYMAKER I M, GAO L Y, ZETSCHE B, et al. Rationally engineered Cas9 nucleases with improved specificity[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 84-88. |
| 36 | GAO Z L, HERRERA-CARRILLO E, BERKHOUT B. A single H1 promoter can drive both guide RNA and endonuclease expression in the CRISPR-Cas9 system[J]. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids, 2019, 14: 32-40. |
| 37 | KULCSÁR P I, TÁLAS A, TÓTH E, et al. Blackjack mutations improve the on-target activities of increased fidelity variants of SpCas9 with 5′G-extended sgRNAs[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1223. |
| 38 | TÓTH E, VARGA É, KULCSÁR P I, et al. Improved LbCas12a variants with altered PAM specificities further broaden the genome targeting range of Cas12a nucleases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(7):3722-3733. |
| 39 | HIRANO S, NISHIMASU H, ISHITANI R, et al. Structural basis for the altered PAM specificities of engineered CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Molecular Cell, 2016, 61(6): 886-894. |
| 40 | CASINI A, OLIVIERI M, PETRIS G, et al. A highly specific SpCas9 variant is identified by in vivo screening inyeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 265-271. |
| 41 | VAKULSKAS C A, DEVER D P, RETTIG G R, et al. A high-fidelity Cas9 mutant delivered as a ribonucleoprotein complex enables efficient gene editing in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells[J]. Nature Medicine, 2018, 24(8): 1216-1224. |
| 42 | CHOI G C G, ZHOU P, YUEN C T L, et al. Combinatorial mutagenesis en masse optimizes the genome editing activities of SpCas9[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(8): 722-730. |
| 43 | LIU R M, LIANG L L, FREED E, et al. Synthetic chimeric nucleases function for efficient genome editing[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5524. |
| 44 | KLEINSTIVER B P, PATTANAYAK V, PREW M S, et al. High-fidelity CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with no detectable genome-wide off-target effects[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 490-495. |
| 45 | HIRANO H, GOOTENBERG J S, HORII T, et al. Structure and engineering of francisella novicida Cas9[J]. Cell, 2016, 164(5): 950-961. |
| 46 | SHMAKOV S, ABUDAYYEH O O, MAKAROVA K S, et al. Discovery and functional characterization of diverse class 2 CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Molecular Cell, 2015, 60(3): 385-397. |
| 47 | SHMAKOV S, SMARGON A, SCOTT D, et al. Diversity and evolution of class 2 CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2017, 15(3): 169-182. |
| 48 | PAUSCH P, AL-SHAYEB B, BISOM-RAPP E, et al. CRISPR-CasΦ from huge phages is a hypercompact genome editor[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6501): 333-337. |
| 49 | MOHANRAJU P, MAKAROVA K S, ZETSCHE B, et al. Diverse evolutionary roots and mechanistic variations of the CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6299): aad5147. |
| 50 | STRECKER J, LADHA A, GARDNER Z, et al. RNA-guided DNA insertion with CRISPR-associated transposases[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6448): 48-53. |
| 51 | LIU L, CHEN P, WANG M, et al. C2c1-sgRNA complex structure reveals RNA-guided DNA cleavage mechanism[J]. Molecular Cell, 2017, 65(2): 310-322. |
| 52 | HARRINGTON L B, MA E B, CHEN J S, et al. A scoutRNA is required for some type V CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Molecular Cell, 2020, 79(3): 416-424.e5. |
| 53 | BARRANGOU R, GERSBACH C A. Expanding the CRISPR toolbox: targeting RNA with Cas13b[J]. Molecular Cell, 2017, 65(4): 582-584. |
| 54 | BURSTEIN D, HARRINGTON L B, STRUTT S C, et al. New CRISPR-Cas systems from uncultivated microbes[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7640): 237-241. |
| 55 | MAKAROVA K S, WOLF Y I, ALKHNBASHI O S, et al. An updated evolutionary classification of CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2015, 13(11): 722-736. |
| 56 | MAKAROVA K S, KOONIN E V. Annotation and classification of CRISPR-Cas systems[M]//LUNDGREN M, CHARPENTIER E, FINERAN P.CRISPR. Methods in Molecular Biology. New York: Humana Press, 2015, 1311: 47-75. |
| 57 | HOCHSTRASSER M L, TAYLOR D W, BHAT P, et al. CasA mediates Cas3-catalyzed target degradation during CRISPR RNA-guided interference[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(18): 6618-6623. |
| 58 | BROUNS S J J, JORE M M, LUNDGREN M, et al. Small CRISPR RNAs guide antiviral defense in prokaryotes[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5891): 960-964. |
| 59 | JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6096): 816-821. |
| 60 | CONG L, RAN F A, COX D, et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819-823. |
| 61 | JIANG F G, DOUDNA J A. CRISPR-Cas9 structures and mechanisms[J]. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2017, 46: 505-529. |
| 62 | STERNBERG S H, LAFRANCE B, KAPLAN M, et al. Conformational control of DNA target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Nature, 2015, 527(7576): 110-113. |
| 63 | ANDERS C, NIEWOEHNER O, DUERST A, et al. Structural basis of PAM-dependent target DNA recognition by the Cas9 endonuclease[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 569-573. |
| 64 | GUILINGER J P, THOMPSON D B, LIU D R. Fusion of catalytically inactive Cas9 to FokI nuclease improves the specificity of genome modification[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(6): 577-582. |
| 65 | JASIN M, HABER J E. The democratization of gene editing: insights from site-specific cleavage and double-strand break repair[J]. DNA Repair, 2016, 44: 6-16. |
| 66 | BÉTERMIER M, BERTRAND P, LOPEZ B S. Is non-homologous end-joining really an inherently error-prone process? [J]. PLoS genetics, 2014, 10(1): e1004086. |
| 67 | NAKADE S, TSUBOTA T, SAKANE Y, et al. Microhomology-mediated end-joining-dependent integration of donor DNA in cells and animals using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5560. |
| 68 | SUZUKI K, TSUNEKAWA Y, HERNANDEZ-BENITEZ R, et al. In vivo genome editing via CRISPR/Cas9 mediated homology-independent targeted integration[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7631): 144-149. |
| 69 | HSU P D, LANDER E S, ZHANG F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(6): 1262-1278. |
| 70 | CHAMBERLAIN K, RIYAD J M, WEBER T. Expressing transgenes that exceed the packaging capacity of adeno-associated virus capsids[J]. Human Gene Therapy Methods, 2016, 27(1): 1-12. |
| 71 | YANG S, LI S H, LI X J. Shortening the half-life of Cas9 maintains its gene editing ability and reduces neuronal toxicity[J]. Cell Reports, 2018, 25(10): 2653-2659. |
| 72 | LIU R M, LIANG L Y, FREED E F, et al. Directed evolution of CRISPR/Cas systems for precise gene editing[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(3): 262-273. |
| 73 | LIANG M D, LI Z L, WANG W S, et al. A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensing platform for the highly sensitive detection of diverse small molecules[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 3672. |
| 74 | GIER R A, BUDINICH K A, EVITT N H, et al. High-performance CRISPR-Cas12a genome editing for combinatorial genetic screening[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 3455. |
| 75 | YAN M Y, YAN H Q, REN G X, et al. CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted recombineering in bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(17): e00947-17. |
| 76 | TANG X, LOWDER L G, ZHANG T, et al. A CRISPR-Cpf1 system for efficient genome editing and transcriptional repression in plants[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3(3): 17018. |
| 77 | VERWAAL R, BUITING-WIESSENHAAN N, DALHUIJSEN S, et al. CRISPR/Cpf1 enables fast and simple genome editing of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Yeast, 2018, 35(2): 201-211. |
| 78 | ZETSCHE B, GOOTENBERG J S, ABUDAYYEH O O, et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Cell, 2015, 163(3): 759-771. |
| 79 | STELLA S, ALCÓN P, MONTOYA G. Structure of the Cpf1 endonuclease R-loop complex after target DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7659): 559-563. |
| 80 | SWARTS D C, VAN DER OOST J, JINEK M. Structural basis for guide RNA processing and seed-dependent DNA targeting by CRISPR-Cas12a [J]. Molecular Cell, 2017, 66(2): 221-233.e4. |
| 81 | ABUDAYYEH O O, GOOTENBERG J S, ESSLETZBICHLER P, et al. RNA targeting with CRISPR-Cas13[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7675): 280-284. |
| 82 | KNOTT G J, EAST-SELETSKY A, COFSKY J C, et al. Guide-bound structures of an RNA-targeting A-cleaving CRISPR-Cas13a enzyme[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2017, 24(10): 825-833. |
| 83 | ABUDAYYEH O O, GOOTENBERG J S, KONERMANN S, et al. C2c2 is a single-component programmable RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6299): aaf5573. |
| 84 | LIU L, LI X Y, MA J, et al. The molecular architecture for RNA-guided RNA cleavage by Cas13a[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(4): 714-726.e10. |
| 85 | GOOTENBERG J S, ABUDAYYEH O O, LEE J W, et al. Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6336): 438-442. |
| 86 | FOZOUNI P, SON S M, DE LEÓN DERBY M D, et al. Amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR-Cas13a and mobile phone microscopy[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(2): 323-333.e9. |
| 87 | PYZOCHA N K, CHEN S D. Diverse class 2 CRISPR-Cas effector proteins for genome engineering applications[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2018, 13(2): 347-356. |
| 88 | KIM D, KIM J, HUR J K, et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals specificities of Cpf1 endonucleases in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(8): 863-868. |
| 89 | GAO L Y, COX D B T, YAN W X, et al. Engineered Cpf1 variants with altered PAM specificities[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(8): 789-792. |
| 90 | KLEINSTIVER B P, PREW M S, TSAI S Q, et al. Broadening the targeting range of Staphylococcus aureus CRISPR-Cas9 by modifying PAM recognition[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(12): 1293-1298. |
| 91 | KLEINSTIVER B P, PREW M S, TSAI S Q, et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with altered PAM specificities[J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7561): 481-485. |
| 92 | HU J H, MILLER S M, GEURTS M H, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 57-63. |
| 93 | MILLER S M, WANG T N, RANDOLPH P B, et al. Continuous evolution of SpCas9 variants compatible with non-G PAMs[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(4): 471-481. |
| 94 | CHEN J S, DAGDAS Y S, KLEINSTIVER B P, et al. Enhanced proofreading governs CRISPR-Cas9 targeting accuracy[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 407-410. |
| 95 | KLEINSTIVER B P, PATTANAYAK V, PREW M S, et al. High-fidelity CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with no detectable genome-wide off-target effects[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 490-495. |
| 96 | KIM N, KIM H K, LEE S, et al. Prediction of the sequence-specific cleavage activity of Cas9 variants[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(11):1328-1336. |
| 97 | ZHOU X X, ZOU X Z, CHUNG H K, et al. A single-chain photoswitchable CRISPR-Cas9 architecture for light-inducible gene editing and transcription[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2018, 13(2): 443-448. |
| 98 | WANG Y, CHENG H J, LIU Y, et al. In-situ generation of large numbers of genetic combinations for metabolic reprogramming via CRISPR-guided base editing[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 678. |
| 99 | ZHAO D D, LI J, LI S W, et al. Glycosylase base editors enable C-to-A and C-to-G base changes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(1): 35-40. |
| 100 | GE R Q, MAI G Q, WANG P, et al. CRISPRdigger: detecting CRISPRs with better direct repeat annotations[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32942. |
| 101 | GRISSA I, VERGNAUD G, POURCEL C. CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, 35(): W52-W57. |
| 102 | BLAND C, RAMSEY T L, SABREE F, et al. CRISPR recognition tool (CRT): a tool for automatic detection of clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2007, 8: 209. |
| 103 | ABBY S S, NÉRON B, MÉNAGER H, et al. MacSyfinder: a program to mine genomes for molecular systems with an application to CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e110726. |
| 104 | CHAI G S, YU M, JIANG L X, et al. HMMCAS: a web tool for the identification and domain annotations of Cas proteins[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2019, 16(4): 1313-1315. |
| 105 | COUVIN D, BERNHEIM A, TOFFANO-NIOCHE C, et al. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(W1): W246-W251. |
| 106 | SUNG K, PARK J, KIM Y, et al. Target specificity of Cas9 nuclease via DNA rearrangement regulated by the REC2 domain[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(25): 7778-7781. |
| 107 | CUI Y, TANG Y C, LIANG M, et al. Direct observation of the formation of CRISPR-Cas12a R-loop complex at the single-molecule level[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(14):2123-2126. |
| 108 | KLOMPE S E, VO P L H, HALPIN-HEALY T S, et al. Transposon-encoded CRISPR-Cas systems direct RNA-guided DNA integration[J]. Nature, 2019, 571(7764): 219-225. |
| 109 | YANG H, GAO P, RAJASHANKAR K R, et al. PAM-dependent target DNA recognition and cleavage by C2c1 CRISPR-Cas endonuclease[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(7): 1814-1828.e12. |
| 110 | SHIN J, OH J W. Development of CRISPR/Cas9 system for targeted DNA modifications and recent improvements in modification efficiency and specificity[J]. BMB Reports, 2020, 53(7): 341-348. |
| 111 | ZHENG T, HOU Y Z, ZHANG P J, et al. Profiling single-guide RNA specificity reveals a mismatch sensitive core sequence[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40638. |
| 112 | KIGA K, TAN X E, IBARRA-CHÁVEZ R, et al. Development of CRISPR-Cas13a-based antimicrobials capable of sequence-specific killing of target bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2934. |
| [1] | 陈盈盈, 刘扬, 史俊杰, 马俊英, 鞠建华. CRISPR/Cas基因编辑及其新兴技术在丝状真菌研究中的系统应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 672-693. |
| [2] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [3] | 许志锰, 谢震. 引导编辑研究进展及其应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 1-15. |
| [4] | 陈雅如, 曹英秀, 宋浩. 电活性微生物基因编辑与转录调控技术进展与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [5] | 林继聪, 邹根, 刘宏民, 魏勇军. CRISPR/Cas基因组编辑技术在丝状真菌次级代谢产物合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. |
| [6] | 滕小龙, 史硕博. CRISPR/Cas9系统在基因组编辑中的优化与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 67-85. |
| [7] | 梁丽亚, 刘嵘明. 靶向DNA的Ⅱ类CRISPR/Cas系统的蛋白工程化改造[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| [8] | 刘佳昕, 程驰, 李欣启, 汪超俊, 张颖, 薛闯. 梭菌分子遗传改造工具研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1201-1217. |
| [9] | 龚仕涛, 王宇, 陈宇庭. CRISPR/Cas9及其衍生编辑器在衰老研究中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 66-77. |
| [10] | 毕嘉成, 田志刚. 合成免疫学与未来NK细胞免疫治疗[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 22-34. |
| [11] | 汪庆卓, 宋萍, 黄和. 合成生物技术驱动天然的真核油脂细胞工厂开发[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 920-941. |
| [12] | 肖晗, 刘宜欣. CRISPR-Cas系统编辑丝状真菌的进展与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 274-286. |
| [13] | 李洋, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 袁其朋, 闫亚军, 王佳. CRISPR基因编辑技术在微生物合成生物学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 106-120. |
| [14] | 杨永富, 耿碧男, 宋皓月, 何桥宁, 何明雄, 鲍杰, 白凤武, 杨世辉. 运动发酵单胞菌底盘细胞研究现状及展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 59-90. |
| [15] | 曹中正, 张心怡, 徐艺源, 周卓, 魏文胜. 基因组编辑技术及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 413-426. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

