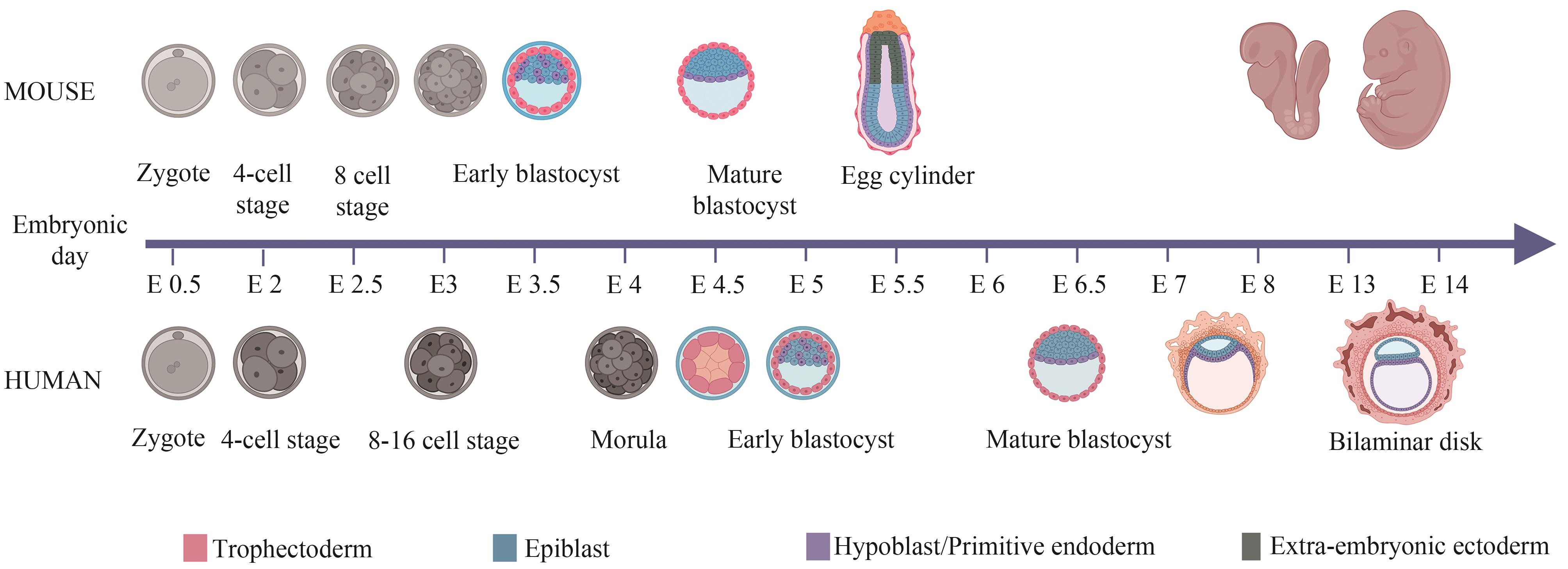
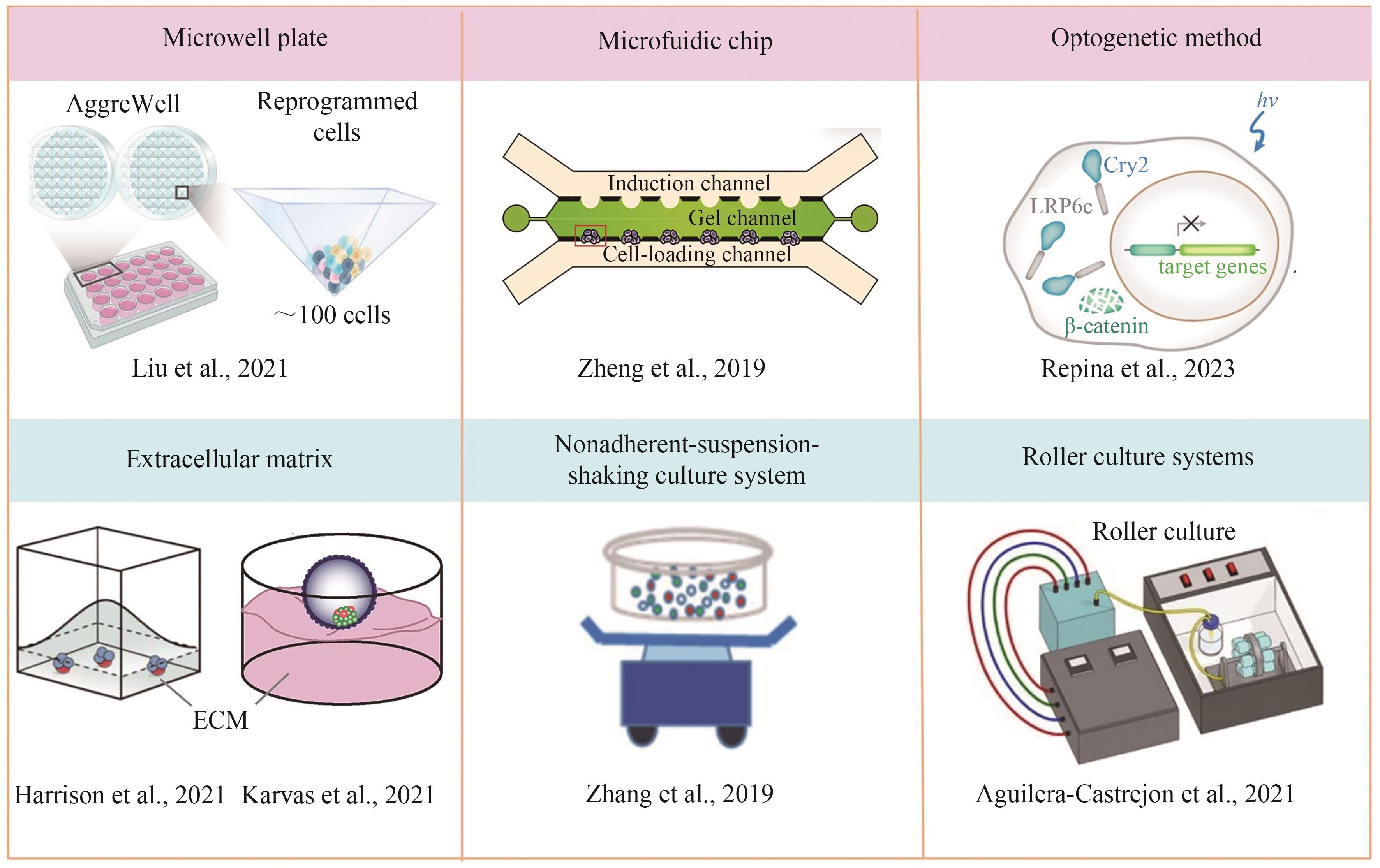
合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (4): 734-753.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-100
干细胞模拟发育:细胞元件、胚胎模型与工程方法
韩宜钊, 郭佳, 邵玥
- 清华大学航天航空学院工程力学系,生物力学与医学工程研究所,北京 100084
-
收稿日期:2023-12-01修回日期:2024-03-04出版日期:2024-08-31发布日期:2024-09-19 -
通讯作者:邵玥 -
作者简介:韩宜钊 (1997—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为基于生物工程的干细胞发育生物学。E-mail:hanyz22@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn邵玥 (1986—),男,副教授,博士生导师,“国家海外高层次青年人才引进计划”获得者。研究方向包括生物力学、器官修复、生殖健康、合成胚胎学等。E-mail:yshao@tsinghua.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12102229)
Stem cell-based synthetic development: cellular components, embryonic models, and engineering approaches
HAN Yizhao, GUO Jia, SHAO Yue
- Institute of Biomechanics and Medical Engineering,Department of Engineering Mechanics,School of Aerospace Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
-
Received:2023-12-01Revised:2024-03-04Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-19 -
Contact:SHAO Yue
摘要:
近百年来,胚胎发育的理论基础主要源于对模式动物的研究,珍稀哺乳动物的发育研究一直受到种间差异、伦理及技术手段等条件的制约。随着干细胞技术的迅猛发展,研究者们利用干细胞构建体外胚胎模型突破传统发育研究的局限性。目前,胚胎模型是否能够完全模拟真实胚胎的发育过程尚待验证,但这无疑为发育生物学研究带来新的可能性。本文以小鼠和人为主要讨论模型,总结用于构建胚胎模型的干细胞种类,阐释不同干细胞在模拟发育过程中的作用和重要性。文章系统呈现了胚胎在不同发育阶段的关键事件和时空动态过程,全面阐述胚胎模型取得的显著成果,详细探讨如何评估胚胎模型的仿生度,以及生物工程学方法在胚胎模型开发中的关键作用,为胚胎模型的进一步优化和发展提供参考。通过对胚胎模型领域的深入研究,有助于更全面细致地了解胚胎发育过程,并为早期发育研究、疾病研究、药物筛选、生殖医学及毒性评估等领域提供更为精确的理论依据和应用工具,进而为未来生命科学的发展开辟新的途径。
中图分类号:
引用本文
韩宜钊, 郭佳, 邵玥. 干细胞模拟发育:细胞元件、胚胎模型与工程方法[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 734-753.
HAN Yizhao, GUO Jia, SHAO Yue. Stem cell-based synthetic development: cellular components, embryonic models, and engineering approaches[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 734-753.
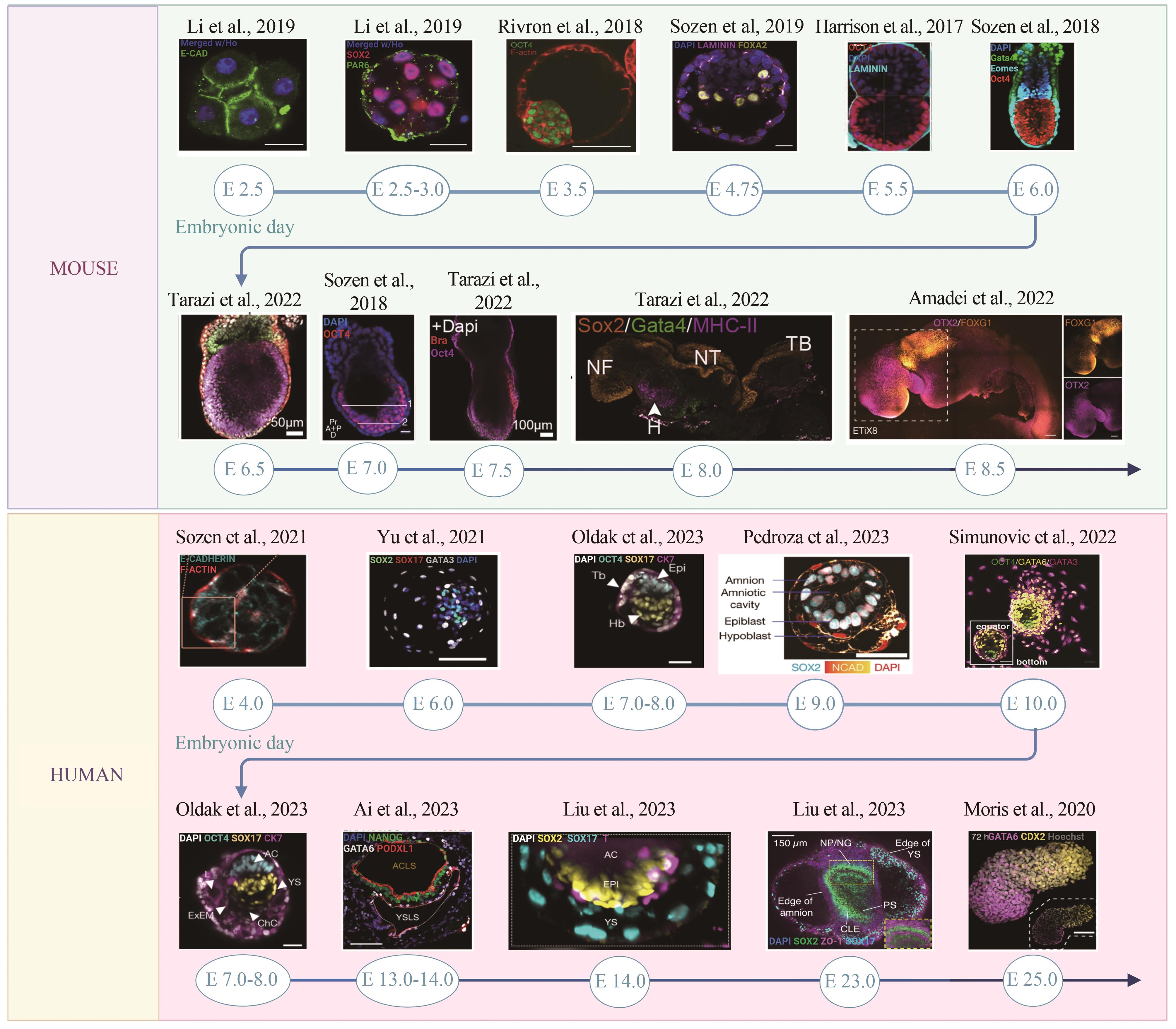
图2 基于干细胞的小鼠和人的胚胎模型研究成果展示(本图已由BioRender.com授权)
Fig. 2 Presentation of research achievements in stem cell-based mouse and human embryonic models (Created with BioRender.com)
| 1 | MALL F P. On the frequency of localized anomalies in human embryos and infants at birth[J]. American Journal of Anatomy, 1917, 22(1): 49-72. |
| 2 | KIM J, KOO B K, KNOBLICH J A. Human organoids: model systems for human biology and medicine[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2020, 21(10): 571-584. |
| 3 | MA H, MARTI-GUTIERREZ N, PARK S W, et al. Correction of a pathogenic gene mutation in human embryos[J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7668): 413-419. |
| 4 | DENNIS S J, THOMAS M A, WILLIAMS D B, et al. Embryo morphology score on day 3 is predictive of implantation and live birth rates[J]. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, 2006, 23(4): 171-175. |
| 5 | SHAHBAZI M N, JEDRUSIK A, VUORISTO S, et al. Self-organization of the human embryo in the absence of maternal tissues[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2016, 18(6): 700-708. |
| 6 | PERLMAN R L. Mouse models of human disease: an evolutionary perspective[J]. Evolution, Medicine, and Public Health, 2016, 2016(1): 170-176. |
| 7 | DAVIS N A. Interests and sentience: life before birth: the moral and legal status of embryos and fetuses by bonnie steinbock[J]. The Hastings Center Report, 1994, 24(6): 36-37. |
| 8 | THOMSON J A, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO S S, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts[J]. Science, 1998, 282(5391): 1145-1147. |
| 9 | TAKAHASHI K, TANABE K, OHNUKI M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors[J]. Cell, 2007, 131(5): 861-872. |
| 10 | LIN F, LI X, SUN S Y, et al. Mechanically enhanced biogenesis of gut spheroids with instability-driven morphomechanics[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 6016. |
| 11 | CLEVERS H. Modeling development and disease with organoids[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(7): 1586-1597. |
| 12 | MARTIN G R, EVANS M J. Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1975, 72(4): 1441-1445. |
| 13 | RIVRON N C, FRIAS-ALDEGUER J, VRIJ E J, et al. Blastocyst-like structures generated solely from stem cells[J]. Nature, 2018, 557(7703): 106-111. |
| 14 | RIVRON N C, MARTINEZ ARIAS A, PERA M F, et al. An ethical framework for human embryology with embryo models[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(17): 3548-3557. |
| 15 | CLARK A T, BRIVANLOU A, FU J P, et al. Human embryo research, stem cell-derived embryo models and in vitro gametogenesis: considerations leading to the revised ISSCR guidelines[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2021, 16(6): 1416-1424. |
| 16 | SHAO Y, FU J P. Engineering multiscale structural orders for high-fidelity embryoids and organoids[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(5): 722-743. |
| 17 | STEVENS L C, LITTLE C C. Spontaneous testicular teratomas in an inbred strain of mice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1954, 40(11): 1080-1087. |
| 18 | EVANS M J. The isolation and properties of a clonal tissue culture strain of pluripotent mouse teratoma cells[J]. Journal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology, 1972, 28(1): 163-176. |
| 19 | EVANS M J, KAUFMAN M H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos[J]. Nature, 1981, 292(5819): 154-156. |
| 20 | NICHOLS J, SMITH A. Naive and primed pluripotent states[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2009, 4(6): 487-492. |
| 21 | HANNA J, MARKOULAKI S, MITALIPOVA M, et al. Metastable pluripotent states in NOD-mouse-derived ESCs[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2009, 4(6): 513-524. |
| 22 | TESAR P J, CHENOWETH J G, BROOK F A, et al. New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells[J]. Nature, 2007, 448(7150): 196-199. |
| 23 | KOJIMA Y, KAUFMAN-FRANCIS K, STUDDERT J B, et al. The transcriptional and functional properties of mouse epiblast stem cells resemble the anterior primitive streak[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 14(1): 107-120. |
| 24 | BERNEMANN C, GREBER B, KO K, et al. Distinct developmental ground states of epiblast stem cell lines determine different pluripotency features[J]. Stem Cells, 2011, 29(10): 1496-1503. |
| 25 | TANAKA S, KUNATH T, HADJANTONAKIS A K, et al. Promotion of trophoblast stem cell proliferation by FGF4[J]. Science, 1998, 282(5396): 2072-2075. |
| 26 | SEONG J, FRIAS-ALDEGUER J, HOLZMANN V, et al. Epiblast inducers capture mouse trophectoderm stem cells in vitro and pattern blastoids for implantation in utero [J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(7): 1102-1118. |
| 27 | NIAKAN K K, SCHRODE N, CHO L T, et al. Derivation of extraembryonic endoderm stem (XEN) cells from mouse embryos and embryonic stem cells[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(6): 1028-1041. |
| 28 | ANDERSON K G V, HAMILTON W B, ROSKE F V, et al. Insulin fine-tunes self-renewal pathways governing naive pluripotency and extra-embryonic endoderm[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2017, 19(10): 1164-1177. |
| 29 | OHINATA Y, ENDO T A, SUGISHITA H, et al. Establishment of mouse stem cells that can recapitulate the developmental potential of primitive endoderm[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6580): 574-578. |
| 30 | YANG Y, LIU B, XU J, et al. Derivation of pluripotent stem cells with in vivo embryonic and extraembryonic potency[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(2): 243-257. e25. |
| 31 | YANG J, RYAN D J, WANG W, et al. Establishment of mouse expanded potential stem cells[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 393-397. |
| 32 | POSFAI E, SCHELL J P, JANISZEWSKI A, et al. Evaluating totipotency using criteria of increasing stringency[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2021, 23(1): 49-60. |
| 33 | WANG X X, XIANG Y L, YU Y, et al. Formative pluripotent stem cells show features of epiblast cells poised for gastrulation[J]. Cell Research, 2021, 31(5): 526-541. |
| 34 | SHEN H, YANG M, LI S Y, et al. Mouse totipotent stem cells captured and maintained through spliceosomal repression[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(11): 2843-2859. e20. |
| 35 | HU Y Y, YANG Y Y, TAN P C, et al. Induction of mouse totipotent stem cells by a defined chemical cocktail[J]. Nature, 2023, 617(7962): 792-797. |
| 36 | YANG M Z, YU H W, YU X, et al. Chemical-induced chromatin remodeling reprograms mouse ESCs to totipotent-like stem cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(3): 400-418. e13. |
| 37 | XU Y X, ZHAO J R, REN Y X, et al. Derivation of totipotent-like stem cells with blastocyst-like structure forming potential[J]. Cell Research, 2022, 32(6): 513-529. |
| 38 | WU J, GREELY H T, JAENISCH R, et al. Stem cells and interspecies chimaeras[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7631): 51-59. |
| 39 | GUO H S, ZHU P, YAN L Y, et al. The DNA methylation landscape of human early embryos[J]. Nature, 2014, 511(7511): 606-610. |
| 40 | YAN L Y, YANG M Y, GUO H S, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq profiling of human preimplantation embryos and embryonic stem cells[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2013, 20(9): 1131-1139. |
| 41 | O′LEARY T, HEINDRYCKX B, LIERMAN S, et al. Tracking the progression of the human inner cell mass during embryonic stem cell derivation[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(3): 278-282. |
| 42 | CHEN G K, GULBRANSON D R, HOU Z G, et al. Chemically defined conditions for human iPSC derivation and culture[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(5): 424-429. |
| 43 | LUDWIG T E, LEVENSTEIN M E, JONES J M, et al. Derivation of human embryonic stem cells in defined conditions[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006, 24: 185-187. |
| 44 | OKUBO T, RIVRON N, KABATA M, et al. Hypoblast from human pluripotent stem cells regulates epiblast development[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(7998): 357-366. |
| 45 | GUO G, VON MEYENN F, SANTOS F, et al. Naive pluripotent stem cells derived directly from isolated cells of the human inner cell mass[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2016, 6(4): 437-446. |
| 46 | LIU X D, NEFZGER C M, ROSSELLO F J, et al. Comprehensive characterization of distinct states of human naive pluripotency generated by reprogramming[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(11): 1055-1062. |
| 47 | GIULITTI S, PELLEGRINI M, ZORZAN I, et al. Direct generation of human naive induced pluripotent stem cells from somatic cells in microfluidics[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2019, 21(2): 275-286. |
| 48 | KILENS S, MEISTERMANN D, MORENO D, et al. Parallel derivation of isogenic human primed and naive induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 360. |
| 49 | BAYERL J, AYYASH M, SHANI T, et al. Principles of signaling pathway modulation for enhancing human naive pluripotency induction[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(9): 1549-1565. e12. |
| 50 | THEUNISSEN T W, POWELL B E, WANG H Y, et al. Systematic identification of culture conditions for induction and maintenance of naive human pluripotency[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 15(4): 471-487. |
| 51 | CHAN Y S, GÖKE J, NG J H, et al. Induction of a human pluripotent state with distinct regulatory circuitry that resembles preimplantation epiblast[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2013, 13(6): 663-675. |
| 52 | GAFNI O, WEINBERGER L, MANSOUR A A, et al. Derivation of novel human ground state naive pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7479): 282-286. |
| 53 | TAKASHIMA Y, GUO G, LOOS R, et al. Resetting transcription factor control circuitry toward ground-state pluripotency in human[J]. Cell, 2014, 158(6): 1254-1269. |
| 54 | THEUNISSEN T W, FRIEDLI M, HE Y P, et al. Molecular criteria for defining the naive human pluripotent state[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2016, 19(4): 502-515. |
| 55 | BREDENKAMP N, STIRPARO G G, NICHOLS J, et al. The cell-surface marker sushi containing domain 2 facilitates establishment of human naive pluripotent stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2019, 12(6): 1212-1222. |
| 56 | ZIMMERLIN L, PARK T S, HUO J S, et al. Tankyrase inhibition promotes a stable human naïve pluripotent state with improved functionality[J]. Development, 2016, 143(23): 4368-4380. |
| 57 | OKAE H, TOH H, SATO T, et al. Derivation of human trophoblast stem cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 22(1): 50-63. e6. |
| 58 | GUO G, STIRPARO G G, STRAWBRIDGE S E, et al. Human naive epiblast cells possess unrestricted lineage potential[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(6): 1040-1056. e6. |
| 59 | CASTEL G, MEISTERMANN D, BRETIN B, et al. Induction of human trophoblast stem cells from somatic cells and pluripotent stem cells[J]. Cell Reports, 2020, 33(8): 108419. |
| 60 | LIU X D, OUYANG J F, ROSSELLO F J, et al. Reprogramming roadmap reveals route to human induced trophoblast stem cells[J]. Nature, 2020, 586(7827): 101-107. |
| 61 | MAZID M A, WARD C, LUO Z W, et al. Rolling back human pluripotent stem cells to an eight-cell embryo-like stage[J]. Nature, 2022, 605(7909): 315-324. |
| 62 | MOLÈ M A, WEBERLING A, ZERNICKA-GOETZ M. Comparative analysis of human and mouse development: from zygote to pre-gastrulation[J]. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 2020, 136: 113-138. |
| 63 | VAN DEN BRINK S C, VAN OUDENAARDEN A. 3D gastruloids: a novel frontier in stem cell-based in vitro modeling of mammalian gastrulation[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 2021, 31(9): 747-759. |
| 64 | SHAHBAZI M N, ZERNICKA-GOETZ M. Deconstructing and reconstructing the mouse and human early embryo[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2018, 20(8): 878-887. |
| 65 | KIME C, KIYONARI H, OHTSUKA S, et al. Induced 2C expression and implantation-competent blastocyst-like cysts from primed pluripotent stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2019, 13(3): 485-498. |
| 66 | SOZEN B, COX A L, DE JONGHE J, et al. Self-organization of mouse stem cells into an extended potential blastoid[J]. Developmental Cell, 2019, 51(6): 698-712. e8. |
| 67 | LI R H, ZHONG C Q, YU Y, et al. Generation of blastocyst-like structures from mouse embryonic and adult cell cultures[J]. Cell, 2019, 179(3): 687-702. e18. |
| 68 | JANA D, SINGH P, SAILASREE P, et al. Efficient self-organization of blastoids solely from mouse ESCs is facilitated by transient reactivation of 2C gene network[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2023: 2023.04.12.536583. (2023-04-13)[2023-12-01]. . |
| 69 | ZHANG P F, ZHAI X Z, HUANG B Y, et al. Highly efficient generation of blastocyst-like structures from spliceosomes-repressed mouse totipotent blastomere-like cells[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2023, 66(3): 423-435. |
| 70 | VAN DEN BRINK S C, BAILLIE-JOHNSON P, BALAYO T, et al. Symmetry breaking, germ layer specification and axial organisation in aggregates of mouse embryonic stem cells[J]. Development, 2014, 141(22): 4231-4242. |
| 71 | HARRISON S E, SOZEN B, CHRISTODOULOU N, et al. Assembly of embryonic and extraembryonic stem cells to mimic embryogenesis in vitro [J]. Science, 2017, 356(6334): eaal1810. |
| 72 | SOZEN B, AMADEI G, COX A, et al. Self-assembly of embryonic and two extra-embryonic stem cell types into gastrulating embryo-like structures[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2018, 20(8): 979-989. |
| 73 | ZHANG S P, CHEN T Z, CHEN N X, et al. Implantation initiation of self-assembled embryo-like structures generated using three types of mouse blastocyst-derived stem cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 496. |
| 74 | GIRGIN M U, BROGUIERE N, HOEHNEL S, et al. Bioengineered embryoids mimic post-implantation development in vitro [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5140. |
| 75 | XU P F, BORGES R M, FILLATRE J, et al. Construction of a mammalian embryo model from stem cells organized by a morphogen signalling centre[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3277. |
| 76 | AMADEI G, LAU K Y C, DE JONGHE J, et al. Inducible stem-cell-derived embryos capture mouse morphogenetic events in vitro [J]. Developmental Cell, 2021, 56(3): 366-382. e9. |
| 77 | AMADEI G, HANDFORD C E, QIU C X, et al. Embryo model completes gastrulation to neurulation and organogenesis[J]. Nature, 2022, 610(7930): 143-153. |
| 78 | TARAZI S, AGUILERA-CASTREJON A, JOUBRAN C, et al. Post-gastrulation synthetic embryos generated ex utero from mouse naive ESCs[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(18): 3290-3306. e25. |
| 79 | LAU K Y C, RUBINSTEIN H, GANTNER C W, et al. Mouse embryo model derived exclusively from embryonic stem cells undergoes neurulation and heart development[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(10): 1445-1458. e8. |
| 80 | YU L Q, WEI Y L, DUAN J L, et al. Blastocyst-like structures generated from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7851): 620-626. |
| 81 | YANAGIDA A, SPINDLOW D, NICHOLS J, et al. Naive stem cell blastocyst model captures human embryo lineage segregation[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(6): 1016-1022. e4. |
| 82 | LIU X D, TAN J P, SCHRÖDER J, et al. Modelling human blastocysts by reprogramming fibroblasts into iBlastoids[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7851): 627-632. |
| 83 | SOZEN B, JORGENSEN V, WEATHERBEE B A T, et al. Reconstructing aspects of human embryogenesis with pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5550. |
| 84 | FAN Y, MIN Z Y, ALSOLAMI S, et al. Generation of human blastocyst-like structures from pluripotent stem cells[J]. Cell Discovery, 2021, 7(1): 81. |
| 85 | YU L Q, LOGSDON D, PINZON-ARTEAGA C A, et al. Large-scale production of human blastoids amenable to modeling blastocyst development and maternal-fetal cross talk[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(9): 1246-1261. e9. |
| 86 | KAGAWA H, JAVALI A, KHOEI H H, et al. Human blastoids model blastocyst development and implantation[J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7894): 600-605. |
| 87 | DE SANTIS R, RICE E, CROFT G, et al. The emergence of human gastrulation upon in vitro attachment[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2024, 19(1): 41-53. |
| 88 | KARVAS R M, ZEMKE J E, ALI S S, et al. 3D-cultured blastoids model human embryogenesis from pre-implantation to early gastrulation stages[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(9): 1148-1165. e7. |
| 89 | SHAO Y, TANIGUCHI K, GURDZIEL K, et al. Self-organized amniogenesis by human pluripotent stem cells in a biomimetic implantation-like niche[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(4): 419-425. |
| 90 | SHAO Y, TANIGUCHI K, TOWNSHEND R F, et al. A pluripotent stem cell-based model for post-implantation human amniotic sac development[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 208. |
| 91 | ZHENG Y, XUE X F, SHAO Y, et al. Controlled modelling of human epiblast and amnion development using stem cells[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7774): 421-425. |
| 92 | ROSTOVSKAYA M, ANDREWS S, REIK W, et al. Amniogenesis occurs in two independent waves in primates[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(5): 744-759. e6. |
| 93 | WARMFLASH A, SORRE B, ETOC F, et al. A method to recapitulate early embryonic spatial patterning in human embryonic stem cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(8): 847-854. |
| 94 | MORIS N, ANLAS K, VAN DEN BRINK S C, et al. An in vitro model of early anteroposterior organization during human development[J]. Nature, 2020, 582(7812): 410-415. |
| 95 | SIMUNOVIC M, SIGGIA E D, BRIVANLOU A H. In vitro attachment and symmetry breaking of a human embryo model assembled from primed embryonic stem cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(6): 962-972. |
| 96 | AI Z Y, NIU B H, YIN Y, et al. Dissecting peri-implantation development using cultured human embryos and embryo-like assembloids[J]. Cell Research, 2023, 33(9): 661-678. |
| 97 | XIANG L F, YIN Y, ZHENG Y, et al. A developmental landscape of 3D-cultured human pre-gastrulation embryos[J]. Nature, 2020, 577(7791): 537-542. |
| 98 | WEATHERBEE B A T, GANTNER C W, IWAMOTO-STOHL L K, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived model of the post-implantation human embryo[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 584-593. |
| 99 | PEDROZA M, GASSALOGLU S I, DIAS N, et al. Self-patterning of human stem cells into post-implantation lineages[J]. Nature, 2023, 622: 574-583. |
| 100 | YING Q L, WRAY J, NICHOLS J, et al. The ground state of embryonic stem cell self-renewal[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7194): 519-523. |
| 101 | LIU L Z, OURA S, MARKHAM Z, et al. Modeling post-implantation stages of human development into early organogenesis with stem-cell-derived peri-gastruloids[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(18): 3776-3792. |
| 102 | OLDAK B, WILDSCHUTZ E, BONDARENKO V, et al. Complete human day 14 post-implantation embryo models from naive ES cells[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7983): 562-573. |
| 103 | KARSENTI E. Self-organization in cell biology: a brief history[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2008, 9(3): 255-262. |
| 104 | CHEN Q, SHI J C, TAO Y, et al. Tracing the origin of heterogeneity and symmetry breaking in the early mammalian embryo[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1819. |
| 105 | IMUTA Y, KOYAMA H, SHI D B, et al. Mechanical control of notochord morphogenesis by extra-embryonic tissues in mouse embryos[J]. Mechanisms of Development, 2014, 132: 44-58. |
| 106 | CAMPÀS O. A toolbox to explore the mechanics of living embryonic tissues[J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2016, 55: 119-130. |
| 107 | CHAN C J, COSTANZO M, RUIZ-HERRERO T, et al. Hydraulic control of mammalian embryo size and cell fate[J]. Nature, 2019, 571(7763): 112-116. |
| 108 | HIRAMATSU R, MATSUOKA T, KIMURA-YOSHIDA C, et al. External mechanical cues trigger the establishment of the anterior-posterior axis in early mouse embryos[J]. Developmental Cell, 2013, 27(2): 131-144. |
| 109 | SAMAL P, MAURER P, VAN BLITTERSWIJK C, et al. A new microengineered platform for 4D tracking of single cells in a stem-cell-based in vitro morphogenesis model[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(24): e1907966. |
| 110 | CHUNG K, KIM Y, KANODIA J S, et al. A microfluidic array for large-scale ordering and orientation of embryos[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(2): 171-176. |
| 111 | SONNEN K F, LAUSCHKE V M, URAJI J, et al. Modulation of phase shift between Wnt and Notch signaling oscillations controls mesoderm segmentation[J]. Cell, 2018, 172(5): 1079-1090. e12. |
| 112 | GOVINDASAMY N, LONG H Y, JEONG H W, et al. 3D biomimetic platform reveals the first interactions of the embryo and the maternal blood vessels[J]. Developmental Cell, 2021, 56(23): 3276-3287. |
| 113 | SAMAL P, VAN BLITTERSWIJK C, TRUCKENMÜLLER R, et al. Grow with the flow: when morphogenesis meets microfluidics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(17): e1805764. |
| 114 | REPINA N A, JOHNSON H J, BAO X P, et al. Optogenetic control of Wnt signaling models cell-intrinsic embryogenic patterning using 2D human pluripotent stem cell culture[J]. Development, 2023, 150(14): dev201386. |
| 115 | IZQUIERDO E, QUINKLER T, DE RENZIS S. Guided morphogenesis through optogenetic activation of Rho signalling during early Drosophila embryogenesis [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2366. |
| 116 | VEENVLIET J V, BOLONDI A, KRETZMER H, et al. Mouse embryonic stem cells self-organize into trunk-like structures with neural tube and somites[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6522): eaba4937. |
| 117 | BONDARENKO V, NIKOLAEV M, KROMM D, et al. Embryo-uterine interaction coordinates mouse embryogenesis during implantation[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2023, 42(17): e113280. |
| 118 | AGUILERA-CASTREJON A, OLDAK B, SHANI T, et al. Ex utero mouse embryogenesis from pre-gastrulation to late organogenesis[J]. Nature, 2021, 593(7857): 119-124. |
| 119 | PINZÓN-ARTEAGA C A, WANG Y J, WEI Y L, et al. Bovine blastocyst-like structures derived from stem cell cultures[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(5): 611-616. e7. |
| 120 | NIETHAMMER M, BURGDORF T, WISTORF E, et al. In vitro models of human development and their potential application in developmental toxicity testing[J]. Development, 2022, 149(20): dev200933. |
| 121 | DE BAKKER B S, DE JONG K H, HAGOORT J, et al. An interactive three-dimensional digital atlas and quantitative database of human development[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6315): aag0053. |
| 122 | HERTIG A T, ROCK J, ADAMS E C. A description of 34 human ova within the first 17 days of development[J]. The American Journal of Anatomy, 1956, 98(3): 435-493. |
| 123 | FUJIMOTO T. Nishimura's collection of human embryos and related publications[J]. Congenital Anomalies, 2001, 41(1): 67-71. |
| [1] | 艾宗勇, 张成庭, 牛宝华, 尹宇, 杨洁, 李天晴. 人胚胎早期发育与干细胞[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 700-718. |
| [2] | 曹荣凯, 秦建华, 王亚清. 胎盘芯片及其在生殖医学领域的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 831-850. |
| [3] | 胡博文, 陈家斌, 刘晓东. 人类早期胚胎发育体外模型研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 719-733. |
| [4] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [5] | 张博航, 祁晓萱, 袁艳. 睾丸类器官在体外精子发生中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 770-781. |
| [6] | 李石开, 曾东鳌, 杜方舟, 张京钟, 余爽. 血管化类器官的构建方法及生物材料[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 851-866. |
| [7] | 谭子斌, 梁康, 陈有海. 合成生物学在基于微生物载体肿瘤疫苗设计中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 221-238. |
| [8] | 朱骊宇, 赵玉龙, 李伟, 王立宾. 哺乳动物染色体工程研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 394-406. |
| [9] | 宋成治, 孙阳, 曹毅. 力信号在干细胞命运决定过程中的影响[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 781-794. |
| [10] | 张璨, 施李杨, 戴建武. 细胞培养肉用生物材料的设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 676-689. |
| [11] | 魏岱旭, 龚海伦, 张旭维. 抗菌肽的生物合成及医学应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 709-727. |
| [12] | 翟婷婷, 顾宏周, 樊春海. 蛋白质组装体辅助的酶固定:精准构建有机相高效生物催化剂[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 256-259. |
| [13] | 冯银刚, 刘亚君, 崔球. 纤维小体在合成生物学中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 138-154. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||