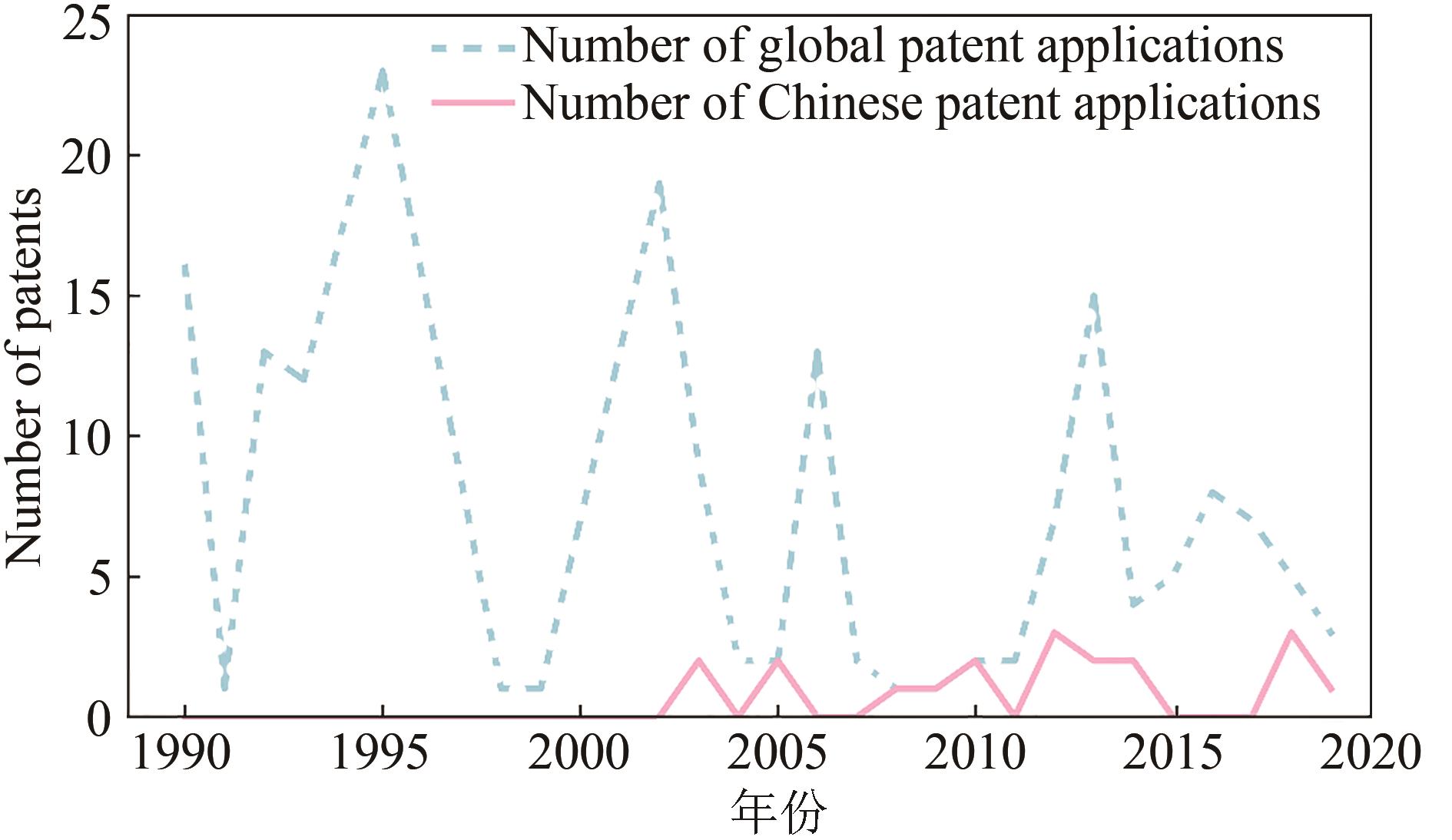
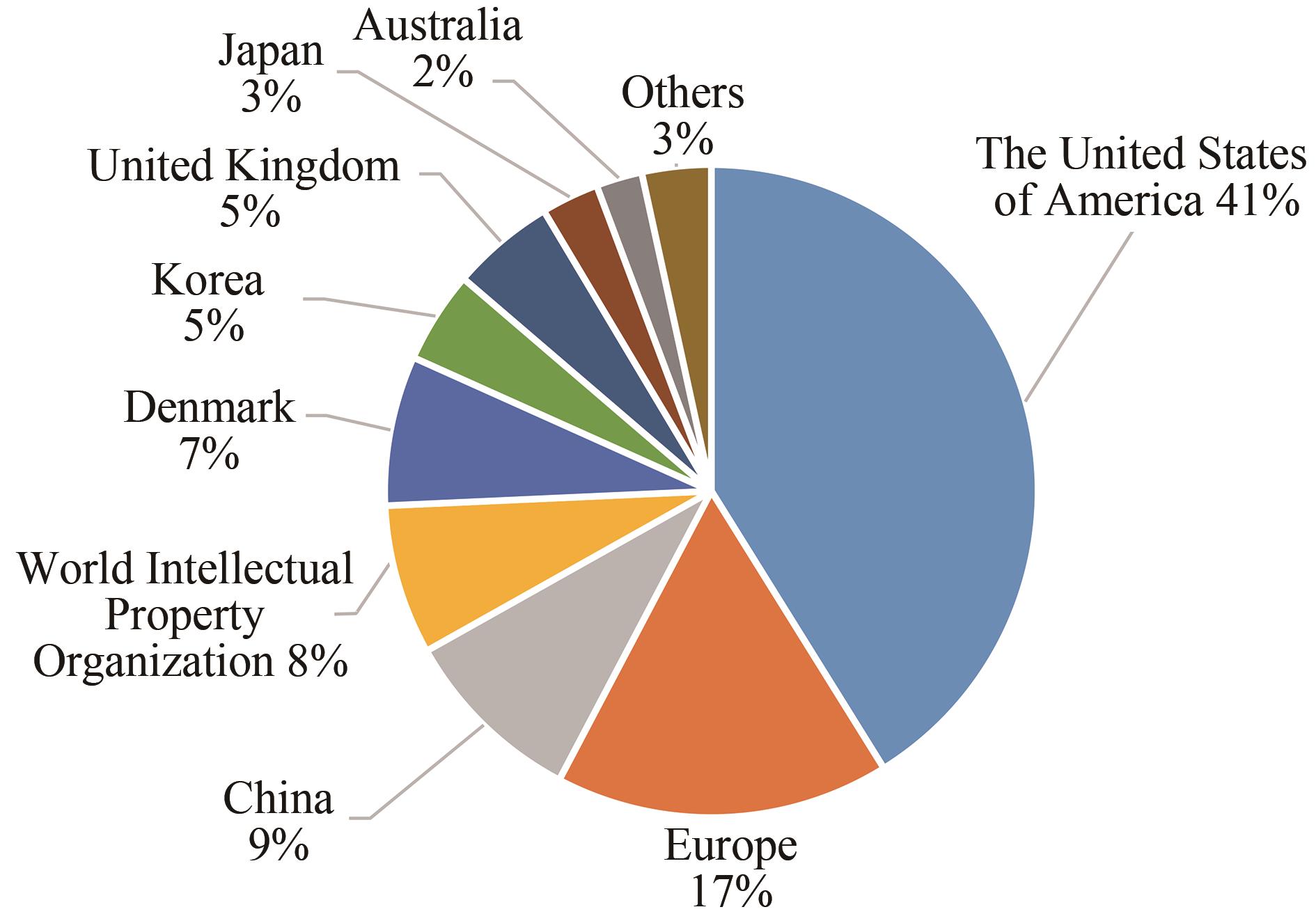
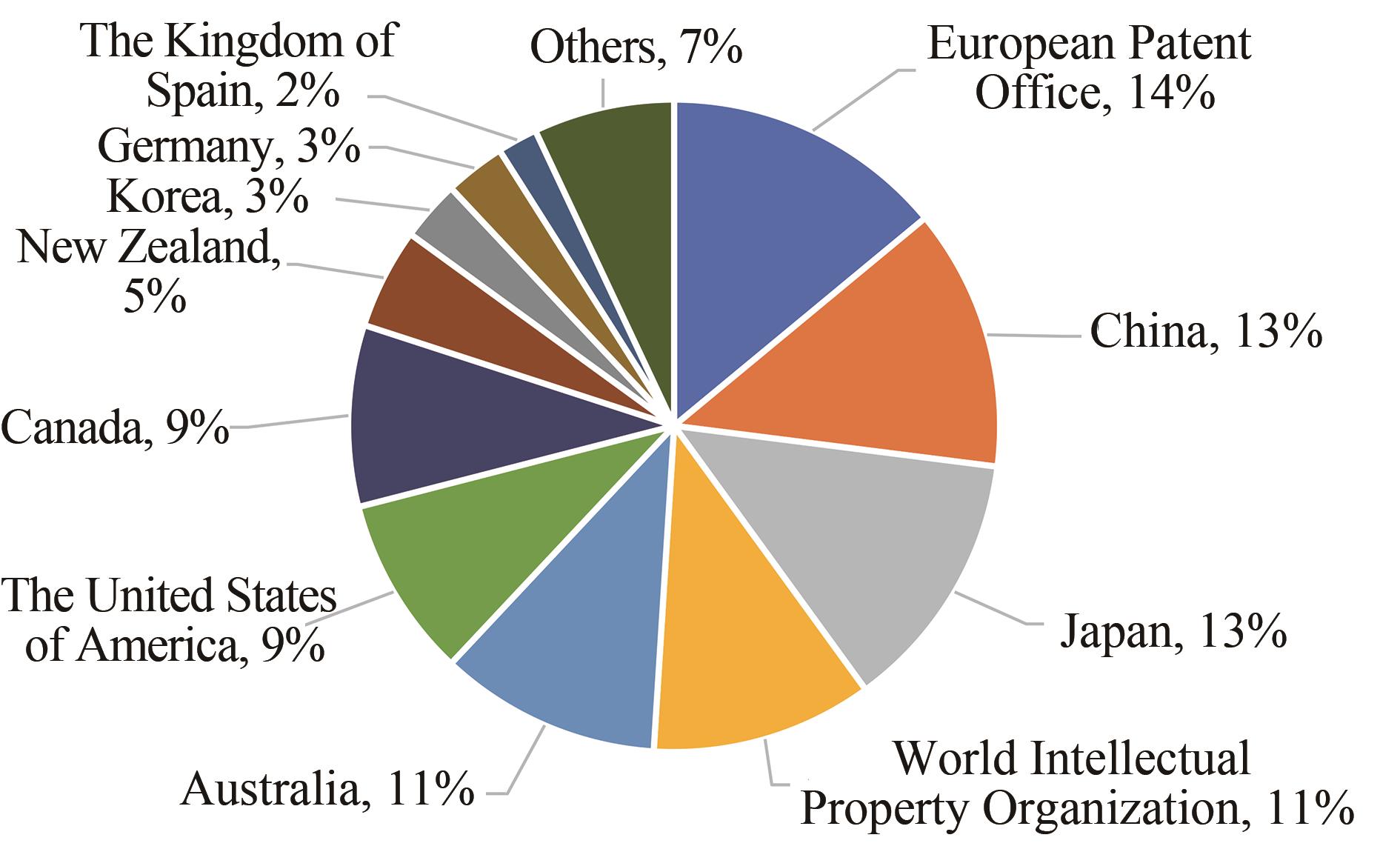
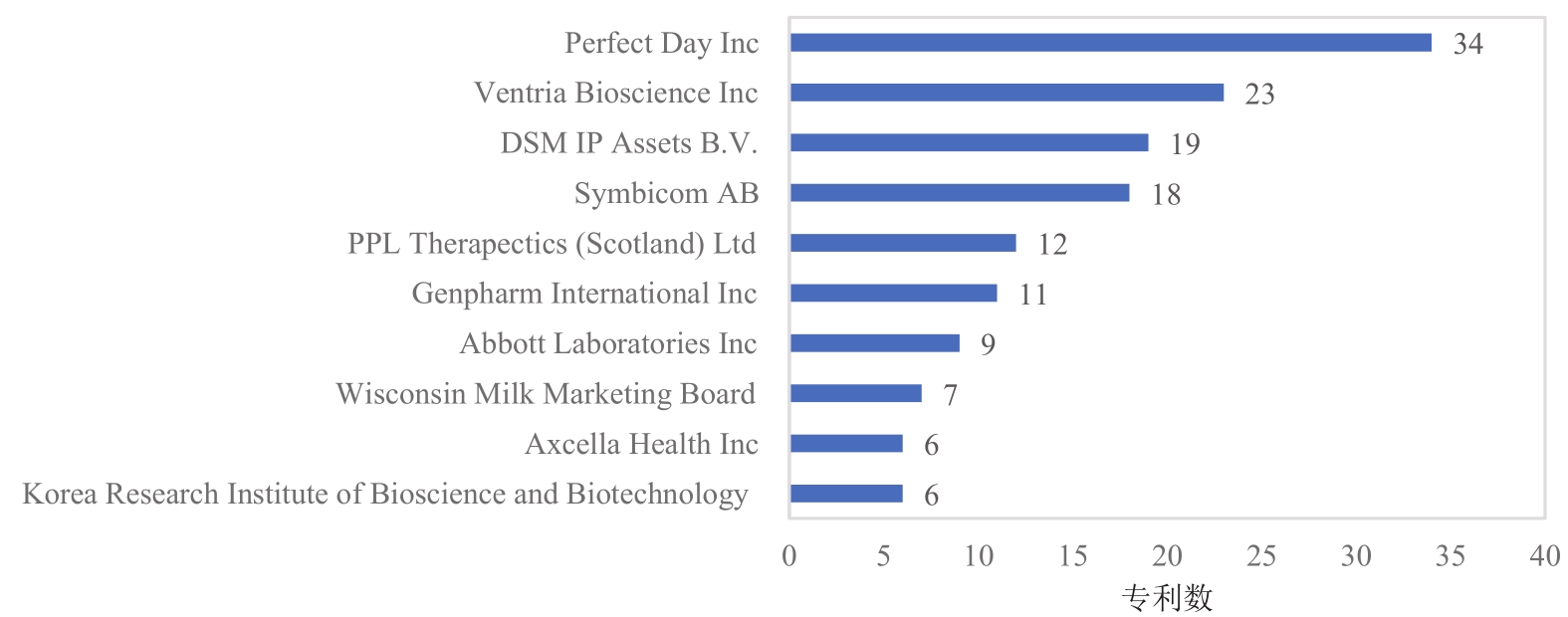
| 1 |
张超. 中国保持乳制品进口大国地位[N]. 中国食品报, 2019-09-17(4).
|
|
ZHANG Chao. China maintains its position as a major importer of dairy products[N]. China Food Newspaper, 2019-09-17(4).
|
| 2 |
LUCEY J A, OTTER D, HORNE D S. A 100-Year Review: Progress on the chemistry of milk and its components[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2017, 100(12): 9916-9932.
|
| 3 |
AUGUSTIN M A, UDABAGE P. Influence of processing on functionality of milk and dairy proteins[J]. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 2007, 53: 1-38.
|
| 4 |
SOPHIA T, KOSTAS D, KOSTAS N P. Cow's milk[J]. Allergenicity, 2014, 14(1):16-26.
|
| 5 |
顾梅琪, 那立欣, 王力强. 国内外乳及乳制品食品安全问题及监督管理现状[J]. 管理观察, 2020(21): 92-94.
|
|
GU Meiqi, NA Lixin, WANG Liqiang. Domestic and foreign milk and dairy products food safety issues and supervision status[J]. Management Observer, 2020(21):92-94
|
| 6 |
SALTER A M. Improving the sustainability of global meat and milk production[J]. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 2016, 76(1): 22-27.
|
| 7 |
沈金荣, 史梦珂, 邓泽元, 等. 大豆复合植物蛋白饮料配方优化及其理化性质[J]. 食品工业科技, 2018, 39(2): 175-181.
|
|
SHEN J R, SHI M K, DEND Z Y, et al. Formulation optimization and physicochemical properties of soybean compound plant protein beverage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(2): 175-181.
|
| 8 |
THOMPSON P, KAPLAN D. Encyclopedia of food and agricultural ethics[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2018.
|
| 9 |
陈坚. 中国食品科技:从2020到2035[J].中国食品学报, 2019, 19(12): 1-5.
|
|
CHEN Jian. Food science and technology in China: from 2020 to 2035[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2019, 19(12): 1-5.
|
| 10 |
BELTRÁN-BARRIENTOS L M, HERNÁNDEZ-MENDOZA A, TORRES-LLANEZ M J, et al. Fermented milk as antihypertensive functional food[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2016, 99: 4099-4110.
|
| 11 |
人造牛奶有望在未来问世[J].中国乳业, 2014(7): 74.
|
|
Artificial milk is expected to be introduced in the future[J]. China Dairy, 2014(7): 74
|
| 12 |
FARRELL H M, MALIN E L, BROWN E M, et al. Casein micelle structure: what can be learned from milk synthesis and structural biology?[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2006, 11(2/3): 135-147.
|
| 13 |
KORHONEN H J. Bioactive components in bovine milk[M]. Wiley‐Blackwell, 2009.
|
| 14 |
IMAFIDON G I, FARKYE N Y, SPANIER A M. Isolation, purification, and alteration of some functional groups of major milk proteins: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1997, 37(7): 663-689.
|
| 15 |
BAUMAN D E, MATHER I H, WALL R J, et al. Major advances associated with the biosynthesis of milk[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2006, 89(4): 1235-1243.
|
| 16 |
HANSSON L, BERGSTRÖM S, HERNELL O, et al. Expression of human milk beta-casein in Escherichia coli: comparison of recombinant protein with native isoforms[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 1993, 4(5): 373-381.
|
| 17 |
LÖNNERDAL B, RIGO J, ZIEGLER E E. Recombinant human milk proteins[J]. Nestlé Nutrition Workshop, 2006, 58(58): 207.
|
| 18 |
IDIRIS A, TOHDA H, KUMAGAI H, et al. Engineering of protein secretion in yeast: strategies and impact on protein production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 86(2): 403-417.
|
| 19 |
GODA S K, AQEL Y W ABU, AL-ASWAD M R, et al. Production of synthetic methionine-free and synthetic methionine-limited alpha casein: protein foodstuff for patients with homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency[J]. The Protein Journal, 2010, 29(1): 44-49.
|
| 20 |
PARK Y W. Rheological characteristics of goat and sheep milk[J]. Small Ruminant Research, 2007, 68(1/2): 73-87.
|
| 21 |
张健, 刘晓军, 李柱刚, 等. 一种利用基因工程技术改良植物营养品质的方法: CN1544641A[P]. 2004-11-10.
|
|
ZHANG Jian, LIU Xiaojun, LI Zhugang, et al. A method for improving the nutritional quality of plants using genetic engineering technology: CN1544641A[P]. 2004-11-10.
|
| 22 |
WITTE B, OBLOJ P, KOKTENTURK S, et al. Food for thought: the protein transformation[R]. Boston Consulting Group. 2021-03-24. https://web-assets.bcg.com/a0/28/4295860343c6a2a5b9f4e3436114/bcg-food-for-thought-the-protein-transformation-mar-2021.pdf
|
| 23 |
农业农村部市场预警专家委员会. 中国农业展望报告(2021—2030)[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2021.
|
|
Professional Committee of Market Early Warning, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,PRC. China agriculture outlook report (2021—2030)[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2021.
|
| 24 |
林敏, 周正富, 燕永亮, 等. 一种高效降解羽毛并合成人工血红素蛋白的基因模块及应用: CN112501164A[P]. 2021-03-16.
|
|
LIN Min, ZHOU Zhengfu, YAN Yongliang, et al. A gene module for efficient degradation of feathers and synthesis of artificial heme protein and the uses thereof: CN112501164A[P]. 2021-03-16.
|
| 25 |
张齐, 崔金明, 蒙海林, 等. 7种牛奶蛋白基因在大肠杆菌中的异源表达[J]. 集成技术, 2016, 5(6): 79-84.
|
|
ZHANG Q, CUI J M, MENG H L, et al. Synthesis of seven milk proteins in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Integration Technology, 2016, 5(6): 79-84.
|
| 26 |
林敏, 周正富, 燕永亮, 等. 提高重组牛奶蛋白异源表达效率的氨基酸序列: CN112481286A[P]. 2021-03-12.
|
|
LIN Min, ZHOU Zhengfu, YAN Yongliang, et al. Amino acid sequences to improve the efficiency of heterologous expression of recombinant milk proteins: CN112481286A[P]. 2021-03-12.
|
| 27 |
PANDYA R, GANDHI P, JI S W, et al. Compositions comprising a casein and methods of producing the same: US10595545[P]. 2020-03-24.
|
| 28 |
GEISTLINGER T, JHALA R, KRUEGER K P, et al. Food products comprising milk proteins and non-animal proteins, and methods of producing the same: US20190216106[P]. 2019-07-18.
|
| 29 |
GEISTLINGER T. Recombinant components and compositions for use in food products: WO2020081789A9[P]. 2019-10-1.
|
| 30 |
MÅNSSON H L. Fatty acids in bovine milk fat[J]. Food & Nutrition Research, 2008, 52: 1821.
|
| 31 |
VALENTIN W, LIZ S. Cellular agriculture: an extension of common production methods for food[R]. The Good Food Institute, 2018-03-6. https://www.gfi.org/images/uploads/2018/03/Cellular-Agriculture-for-Animal-Protein.pdf.
|
| 32 |
VOIGT C A. Synthetic biology 2020-2030: six commercially-available products that are changing our world[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 6379.
|
| 33 |
DESHPANDE N, WILKINS M R, PACKER N, et al. Protein glycosylation pathways in filamentous fungi[J]. Glycobiology, 2008, 18(8): 626-637.
|
| 34 |
VILLA C, COSTA J, OLIVEIRA M B P P, et al. Bovine milk allergens: a comprehensive review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2018, 17(1): 137-164.
|
| 35 |
LEHRER S B, BANNON G A. Risks of allergic reactions to biotech proteins in foods: perception and reality[J]. Allergy, 2015, 60(5):559-564.
|
| 36 |
郭明璋, 许文涛, 罗云波, 等. 中国食物过敏原数据库的建立与应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2014, 5(9): 2951-2955.
|
|
GUO M Z, XU W T, LUO Y B, et al. Establishment and application of Chinese food allergen database[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2014, 5(9): 2951-2955.
|
| 37 |
KANEKANIAN A. The health benefits of bioactive compounds from milk and dairy products[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2014.
|
| 38 |
ROELL M S, ZURBRIGGEN M D. The impact of synthetic biology for future agriculture and nutrition[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 61: 102-109.
|
| 39 |
SUN L C, XIN F J, ALPER H S. Bio-synthesis of food additives and colorants-a growing trend in future food[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 47: 107694.
|
| 40 |
TRUMP B D. Synthetic biology regulation and governance: Lessons from TAPIC for the United States, European Union, and Singapore[J]. Health Policy, 2017, 121(11): 1139-1146.
|
| 41 |
TRUMP B D, GALAITSI S E, APPLETON E, et al. Building biosecurity for synthetic biology[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2020, 16(7): e9723.
|
| 42 |
杜立, 王萌. 合成生物学技术制造食品的商业化法律规范[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 593-608.
|
|
DU L, WANG M. The legal issues about commercialization of food products employing synthetic biology strategies[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 593-608.
|
| 43 |
European Food Safety Authority. Outcome of the public consultation on the draft scientific opinion on the evaluation of existing guidelines for their adequacy for the microbial characterisation and environmental risk assessment of micro-organisms obtained through synthetic biology[R]. EFSA Supporting publication 2020:EN- 1934. doi:10.2903/sp.efsa.2020.EN-1934.
|
| 44 |
李德茂, 曾艳, 周桔, 等. 生物制造食品原料市场准入政策比较及对我国的建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(8): 1041-1052.
|
|
LI D M, ZENG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Regulation and guidance for marketing of food ingredients from biomanufacturing and policy suggestions for China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(8): 1041-1052.
|
| 45 |
刘晓, 熊燕, 王方, 等. 合成生物学伦理、法律与社会问题探讨[J]. 生命科学, 2012, 24(11): 1334-1338.
|
|
LIU Xiao, XIONG Yan, WANG Fang, et al. Ethical, legal and social issues (ELSI) of synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2012, 24(11): 1334-1338.
|
| 46 |
KAEBNICK G E, GUSMANO M K, MURRAY T H. The ethics of synthetic biology: next steps and prior questions[J]. Hastings Center Report, 2014, 44(S5): S4.
|
| 47 |
欧亚昆, 雷瑞鹏. 合成生物学自我管治的伦理探析[J]. 伦理学研究, 2018(2): 53-58.
|
|
Yakun OU, LEI Ruipeng. An ethical exploration of self-governance in synthetic biology[J]. Studies in Ethics, 2018(2): 53-58.
|
| 48 |
张先恩. 中国合成生物学发展回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019, 49(12): 1543-1572.
|
|
ZHANG X-E. Synthetic biology in China: Review and prospects[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Vitae, 2019, 49(12): 1543-1572.
|
| 49 |
MOUAT M J, PRINCE R. Cultured meat and cowless milk: on making markets for animal-free food[J]. Journal of Cultural Economy, 2018, 11(4): 315-329.
|
| 50 |
STEPHENS D N, DUNSFORD I, SILVIO L D, et al. Bringing cultured meat to market: Technical, socio-political, and regulatory challenges in cellular agriculture[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2018, 78(8): 155-166.
|
| 51 |
林敏. 转基因技术[M].北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社. 2020
|
|
LIN Min. Transgenic technology[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2020
|
| 52 |
STEPHENS N, ELLIS M. Cellular agriculture in the UK: a review[J]. Wellcome Open Research, 2020, 5:12.
|
| 53 |
RISCHER H, SZILVAY G R, OKSMAN-CALDENTEY K M. Cellular agriculture-industrial biotechnology for food and materials[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 61: 128-134.
|
| 54 |
MATTICK C S. Cellular agriculture: the coming revolution in food production[J]. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, 2018, 74(1): 32-35.
|
| 55 |
SEXTON A E, GARNETT T, LORIMER J. Framing the future of food: the contested promises of alternative proteins[J]. Environment and Planning E, Nature and Space, 2019, 2(1): 47-72.
|
| 56 |
SPRINGMANN M, CLARK M, MASON-D'CROZ D, et al. Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits[J]. Nature, 2018, 562: 519-525
|
| 57 |
LÜ X Q, WU Y K, GONG M Y, et al. Synthetic biology for future food: research progress and future directions[J]. Future Foods, 2021, 3: 100025.
|