合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (5): 751-763.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-068
植物天然农药除虫菊酯的生物合成和应用研究进展
王凤姣1,2, 徐海洋3, 闫建斌1, 李伟1
- 1.中国农业科学院深圳农业基因组研究所,深圳市农业合成生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518120
2.华中农业大学植物科学技术学院,湖北 武汉 430071
3.重庆大学生命科学学院,重庆 400044
-
收稿日期:2021-06-21修回日期:2021-08-17出版日期:2021-10-31发布日期:2021-11-19 -
通讯作者:闫建斌,李伟 -
作者简介:王凤姣 (1995—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为药用植物代谢。E-mail:fjwang@webmail.hzau.edu.cn闫建斌 (1979—), 男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为植物分子生物学与合成生物学。E-mail:jianbinlab@caas.cn李伟 (1985—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为植物天然产物代谢。E-mail:liwei11@caas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2020YFA0907900);中国农业科学院科技创新工程;中国农业科学院青年英才计划
Biosynthesis and application of pyrethrins: a natural pesticide from plants
WANG Fengjiao1,2, XU Haiyang3, YAN Jianbin1, LI Wei1
- 1.Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Agricultural Synthetic Biology,Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Shenzhen 518120,Guangdong,China
2.College of Plant Science & Technology,Huazhong Agricultural University,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China
3.School of Life Sciences,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
-
Received:2021-06-21Revised:2021-08-17Online:2021-10-31Published:2021-11-19 -
Contact:YAN Jianbin, LI Wei
摘要:
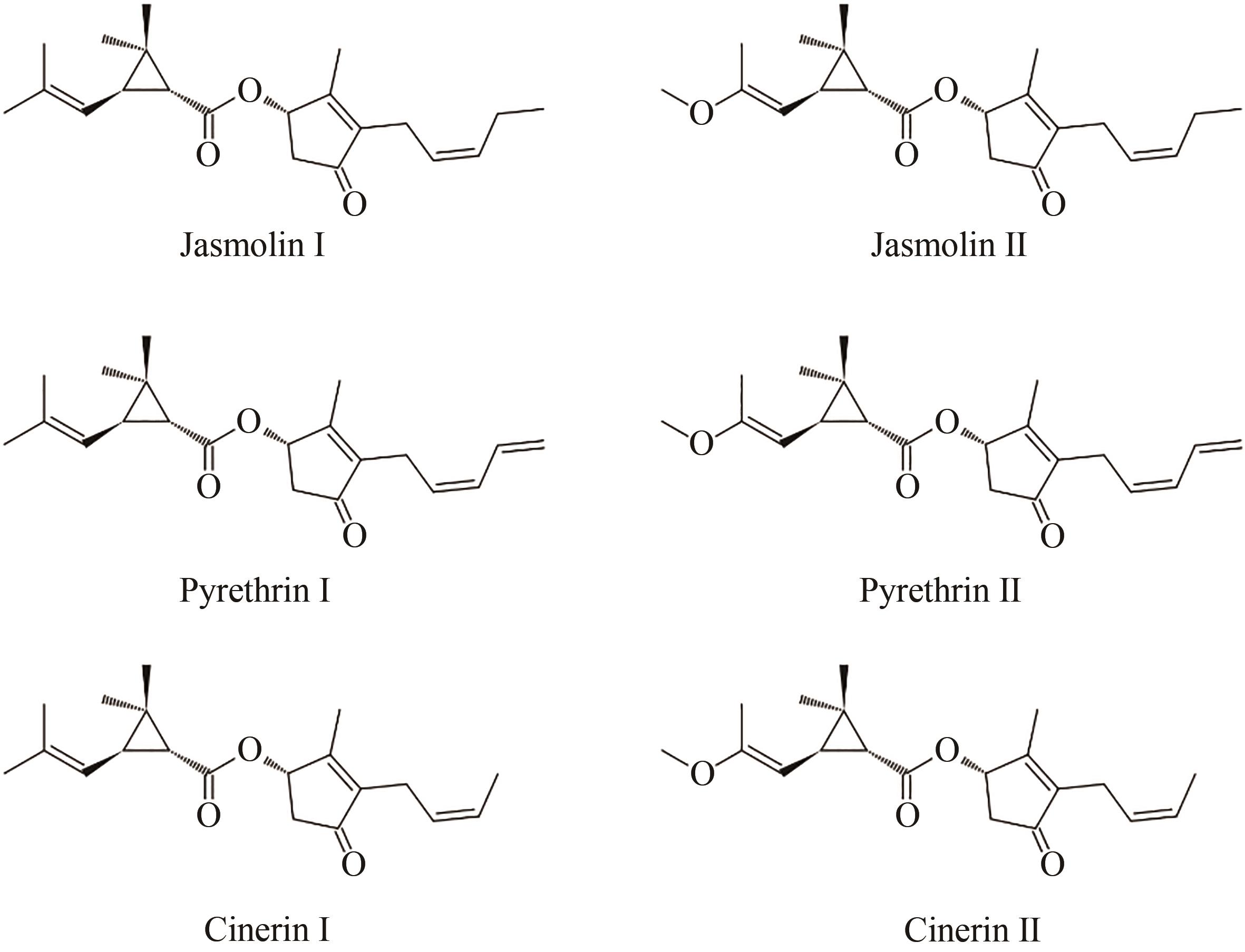
利用生物底盘进行生物农药的绿色低耗能生产是合成生物学未来发展的重要方向。除虫菊酯是一种源自菊科植物除虫菊的天然高效杀虫剂,具有广谱和强力的杀虫和驱虫作用,相较于化学合成的类似物(拟除虫菊酯),对哺乳动物毒性小,无环境危害,是生物农药的最优选择之一,具有广阔的应用前景。天然除虫菊酯含有六种主要成分,由两种异型萜类酸配体和茉莉酸合成途径来源的三种醇配体缩合而成。本文总结了除虫菊酯的研究历程,重点介绍了其生物合成途径解析与生物制造等方面的进展,综述了近期解析的细胞色素P450等相关生物合成酶,并讨论除虫菊酯生产中涉及的调控、转运和底盘适配等尚待解决的问题。随着合成生物学技术的发展,利用已解析的代谢合成途径在微生物等底盘表达体系规模化生产除虫菊酯,能够为合成生物学生产绿色生物农药的科学理论与应用实践提供重要范例。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王凤姣, 徐海洋, 闫建斌, 李伟. 植物天然农药除虫菊酯的生物合成和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 751-763.
WANG Fengjiao, XU Haiyang, YAN Jianbin, LI Wei. Biosynthesis and application of pyrethrins: a natural pesticide from plants[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 751-763.
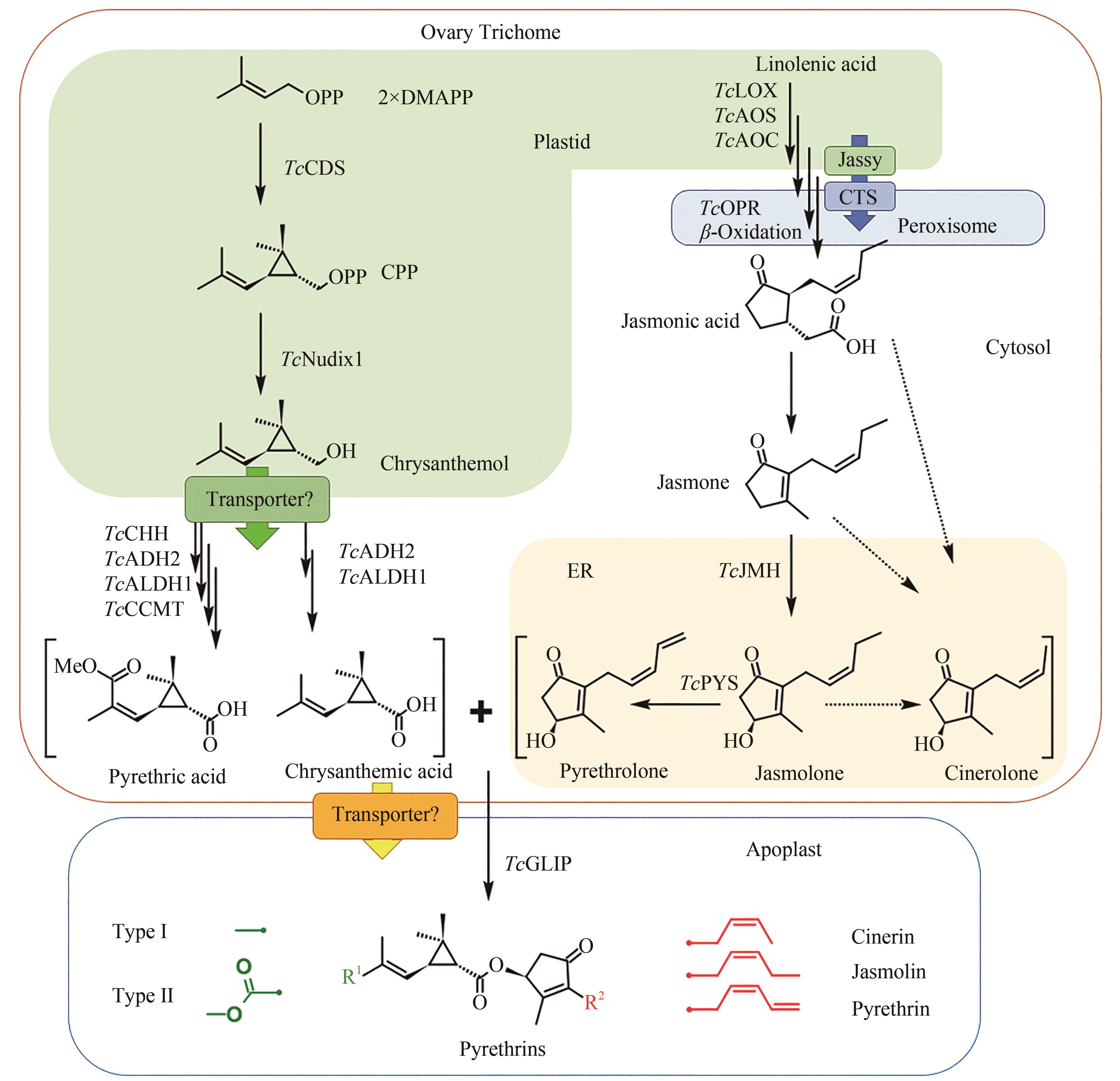
图3 除虫菊酯生物合成途径(除虫菊酯的配体合成起始于在除虫菊花器官的子房外壁腺体腺毛中,TcCDS催化2分子的DMAPP生成菊醇二磷酸,并在磷酸水解酶TcNudix1、脱氢酶TcADH2和TcALDH1的作用下生成菊酸,以及另外的氧化酶TcCHH和甲基转移酶TcCCMT的参与下形成第二菊酸;醇配体的前体茉莉酮通过茉莉酸的合成途径生成,而下游醇配体的合成由细胞色素P450酶TcJMH和TcPYS催化形成茉莉酮醇和除虫酮醇,瓜菊酮醇的合成途径尚不清楚;两种醇配体和三种酸配体在TcGLIP酶的催化下形成六种化合物。酸配体合成前期在质体中进行,后进入细胞质中进行进一步的氧化;茉莉酸的合成前体在质体中,后进入过氧化物酶体进行进一步反应,参与醇配体合成的细胞色素P450定位于内质网。分别定位于质体膜和过氧化物酶体膜的转运蛋白Jassy和CTS参与茉莉酸的合成,菊醇从质体中运出到细胞质和各配体从腺体腺毛运送到胞间是否需要转运蛋白还需要进一步验证)
Fig. 3 Pyrethrin biosynthesis pathway(Synthesis of pyrethrin moieties are originated in the ovary trichome, TcCDS catalyzes 2 DMAPP to generate chrysanthemyl diphosphate, which is further catalyzed by phosphatase TcNudix1, dehydrogenases TcADH2 and TcALDH1 to generate chrysanthemic acid, and two additional enzymes oxidase TcCHH and methyltransferase TcCCMT participate the reaction to form pyrethric acid. Alcohol moieties are generated from the jasmonic acid biosynthesis pathway, and the downstream biosynthesis are catalyzed by cytochrome P450 TcJMH and TcPYS for the biosynthesis of jasmolone and pyrethrolone, but the reactions for cinerolone biosynthesis are still unknown. One of two acid moieties and one of three alcohol moieties are condensed by the catalysis of TcGLIP to produce six different pyrethrins. Upstream steps of the acid moiety pathway are located within plastid, and then the intermediates are transferred to cytosol for further oxidation. The biosynthesis of jasmonic acid is in the plastid and peroxisome under the catalysis of the cytochrome P450s localized at endoplasmic reticulum. Two transporter proteins Jassy and CTS involved in the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid are localized at the membrane of plastid and peroxisome, respectively, and more transporters may exist for transferring chrysanthemol from plastid to cytosol and also for transferring moieties from trichome to apoplast, which need further validation)
| 基因 | 英文名称 | 中文名称 | 功能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TcAOS | allene oxide synthase | 丙二烯氧化物合酶 | 13-HPOT 12、13位C的氧化 | [ |
| TcAOC | allene oxide cyclase | 丙二烯氧化物环化酶 | 13-EOT生成OPDA(12-氧-植物二烯酸) | [ |
| TcOPR | 3-oxo-2-(2-pentenyl)-cyclopentane-1- octanoic acid reductase 3 | 12-氧-植物二烯酸还原酶 | OPDA 10、11位C还原 | [ |
| TcJMH | jasmone hydroxylase | 茉莉酮羟化酶 | 茉莉酮4位C羟基化反应 | [ |
| TcPYS | pyrethrolone synthase | 除虫酮醇合成酶 | 茉莉酮醇戊烯基侧链去饱和 | [ |
| TcCDS | chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase | 菊醇二磷酸合酶 | 酸配体骨架合成 | [ |
| TcNudix1 | nudix-family phosphatase | Nudix磷酸水解酶 | CPP去磷酸化 | [ |
| TcADH2 | alcohol dehydrogenase 2 | 醇脱氢酶 | 酸配体侧链氧化 | [ |
| TcALDH1 | aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 | 醛脱氢酶 | 酸配体侧链氧化 | [ |
| TcCHH | chrysanthemol 10-hydroxylase | 菊醇羟化酶 | 酸配体侧链羟化 | [ |
| TcCCMT | 10-carboxychrysanthemic acid 10- methyltransferase | 10-羧菊酸-10-甲基转移酶 | 10-羧基的甲基化 | [ |
| TcGLIP | GDSL lipase-like protein | GDSL脂肪酶 | 酸配体和醇配体缩合反应 | [ |
| TcLOX1 | lipoxygenase1 | 脂氧合酶 | 亚麻酸13位C的氧化 | [ |
表1 参与除虫菊酯生物合成途径的基因
Tab. 1 Genes involved in the pyrethrin biosynthesis pathway
| 基因 | 英文名称 | 中文名称 | 功能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TcAOS | allene oxide synthase | 丙二烯氧化物合酶 | 13-HPOT 12、13位C的氧化 | [ |
| TcAOC | allene oxide cyclase | 丙二烯氧化物环化酶 | 13-EOT生成OPDA(12-氧-植物二烯酸) | [ |
| TcOPR | 3-oxo-2-(2-pentenyl)-cyclopentane-1- octanoic acid reductase 3 | 12-氧-植物二烯酸还原酶 | OPDA 10、11位C还原 | [ |
| TcJMH | jasmone hydroxylase | 茉莉酮羟化酶 | 茉莉酮4位C羟基化反应 | [ |
| TcPYS | pyrethrolone synthase | 除虫酮醇合成酶 | 茉莉酮醇戊烯基侧链去饱和 | [ |
| TcCDS | chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase | 菊醇二磷酸合酶 | 酸配体骨架合成 | [ |
| TcNudix1 | nudix-family phosphatase | Nudix磷酸水解酶 | CPP去磷酸化 | [ |
| TcADH2 | alcohol dehydrogenase 2 | 醇脱氢酶 | 酸配体侧链氧化 | [ |
| TcALDH1 | aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 | 醛脱氢酶 | 酸配体侧链氧化 | [ |
| TcCHH | chrysanthemol 10-hydroxylase | 菊醇羟化酶 | 酸配体侧链羟化 | [ |
| TcCCMT | 10-carboxychrysanthemic acid 10- methyltransferase | 10-羧菊酸-10-甲基转移酶 | 10-羧基的甲基化 | [ |
| TcGLIP | GDSL lipase-like protein | GDSL脂肪酶 | 酸配体和醇配体缩合反应 | [ |
| TcLOX1 | lipoxygenase1 | 脂氧合酶 | 亚麻酸13位C的氧化 | [ |
| 1 | ÖZKARA A, AKYIL D, Pesticides KONUK M., pollution environmental, and health[M]//LARRAMENDY ML, SOLONESKI S. Enviromental health risk—Hazardous factors to living species. In Tech, 2016: 1-26. |
| 2 | NICOLOPOULOU-STAMATI P, MAIPAS S, KOTAMPASI C, et al. Chemical pesticides and human health: the urgent need for a new concept in agriculture[J]. Frontiers in Public Health, 2016, 4: 148. |
| 3 | CARVALHO P F. Pesticides, environment, and food safety[J]. Food & Energy Security, 2017, 6(2): 48-60. |
| 4 | COSTA J A V, FREITAS B C B, CRUZ C G, et al. Potential of microalgae as biopesticides to contribute to sustainable agriculture and environmental development[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 2019, 54(5): 366-375. |
| 5 | SCHUSTER C, KONSTANTINIDOU-DOLTSINIS S, SCHMITT A. Glycyrrhiza glabra extract protects plants against important phytopathogenic fungi[J]. Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences, 2010, 75(4): 531-540. |
| 6 | BARDIN M, AJOUZ S, COMBY M, et al. Is the efficacy of biological control against plant diseases likely to be more durable than that of chemical pesticides[J]? Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 566. |
| 7 | LAHLOU M. Methods to study the phytochemistry and bioactivity of essential oils[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2004, 18(6): 435-448. |
| 8 | CASIDA J E, QUISTAD G B. Pyrethrum flowers: production, chemistry, toxicology, and uses[M]. Oxford University Press, 1995: 1-25. |
| 9 | ISMAN M B. Botanical insecticides in the twenty-first century-fulfilling their promise[J]? Annual Review of Entomology, 2020, 65: 233-249. |
| 10 | LYBRAND D B, XU H, LAST R L, et al. How plants synthesize pyrethrins: safe and biodegradable insecticides[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 25(12): 1240-1251. |
| 11 | XU H Y, MOGHE G D, WIEGERT-RININGER K, et al. Coexpression analysis identifies two oxidoreductases involved in the biosynthesis of the monoterpene acid moiety of natural pyrethrin insecticides in Tanacetum cinerariifolium [J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176(1): 524-537. |
| 12 | LI W, LYBRAND D B, ZHOU F, et al. Pyrethrin biosynthesis: the cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase CYP82Q3 converts jasmolone to pyrethrolone[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 181(3): 934-944. |
| 13 | LI W, ZHOU F, PICHERSKY E. Jasmone hydroxylase, a key enzyme in the synthesis of the alcohol moiety of pyrethrin insecticides[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 177(4): 1498-1509. |
| 14 | BAN D, BARBARA S, MARINA L, et al. Comparison of pyrethrins eextraction methods efficiencies[J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 9 (18), 2702-2708. |
| 15 | XU H, LI W, SCHILMILLER A L, et al. Pyrethric acid of natural pyrethrin insecticide: complete pathway elucidation and reconstitution in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. The New Phytologist, 2019, 223(2): 751-765. |
| 16 | XU H, LYBRAND D, BENNEWITZ S, et al. Production of trans-chrysanthemic acid, the monoterpene acid moiety of natural pyrethrin insecticides, in tomato fruit[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 271-278. |
| 17 | HU H, LI J, DELATTE T, et al. Modification of chrysanthemum odour and taste with chrysanthemol synthase induces strong dual resistance against cotton aphids[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2018,16(8):1434-1445. |
| 18 | CLARK J F. Bugs in the system: insects, agricultural science, and professional aspirations in Britain, 1890-1920[J]. Agricultural History, 2001, 75(1): 83-114. |
| 19 | GRUNGE W H. Japan's pyrethrum position threatened[J]. Far Eastern Survey, 1939, 8(9): 109-110. |
| 20 | JERAN N, GRDIŠA M, VARGA F, et al. Pyrethrin from Dalmatian pyrethrum (Tanacetum cinerariifolium/Trevir./Sch. Bip.): Biosynthesis, biological activity, methods of extraction and determination[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2020. doi: 10.1007/s/1101-020-09724-2 . |
| 21 | YANG T, STOOPEN G, WIEGERS G, et al. Pyrethrins protect pyrethrum leaves against attack by western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis [J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2012, 38(4): 370-377. |
| 22 | RAMIREZ A M, STOOPEN G, MENZEL T R, et al. Bidirectional secretions from glandular trichomes of pyrethrum enable immunization of seedlings[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(10): 4252-4265. |
| 23 | BLOOMQUIST J R. Chloride channels as tools for developing selective insecticides[J]. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 2003, 54(4): 145-156. |
| 24 | DAVIES T G, FIELD L M, USHERWOOD P N, et al. DDT, pyrethrins, pyrethroids and insect sodium channels[J]. IUBMB Life, 2007, 59(3): 151-162. |
| 25 | CASIDA J E. Pyrethrum, the natural insecticide[M]. Pittsburgh: Academic Press, 1973: 101-120. |
| 26 | ISMAN M B. Botanical insecticides: for richer, for poorer[J]. Pest Management Science, 2008, 64(1): 8-11. |
| 27 | KALINOVIĆ I, KORUNIĆ Z, ROZMAN V, et al. Effectiveness of pure diatomaceous earth and different mixtures of diatomaceous earth with pyrethrins[J]. Poljoprivreda, 2011, 17(2): 13-17. |
| 28 | AKHTAR Y, YEOUNG Y R, ISMAN M B. Comparative bioactivity of selected extracts from Meliaceae and some commercial botanical insecticides against two noctuid caterpillars, Trichoplusia ni and Pseudaletia unipuncta [J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2008, 7(1): 77-88. |
| 29 | JOFFE T, GUNNING R V, ALLEN G R, et al. Investigating the potential of selected natural compounds to increase the potency of pyrethrum against houseflies Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) [J]. Pest Management Science, 2012, 68(2): 178-184. |
| 30 | KALAITZAKI A, PAPANIKOLAOU N E, KARAMAOUNA F, et al. Biocompatible colloidal dispersions as potential formulations of natural pyrethrins: a structural and efficacy study[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(21): 5722-5730. |
| 31 | PAL R. Use of pyrethrum in vector control[J]. Bulletin of the World Health Organisation, 1960, 22: 595-599. |
| 32 | PAJNIK J, STAMENIĆ M, RADETIĆ M, et al. Impregnation of cotton fabric with pyrethrum extract in supercritical carbon dioxide[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2017, 128: 66-72. |
| 33 | BOYCE W M, LAWLER S P, SCHULTZ J M, et al. Nontarget effects of the mosquito adulticide pyrethrin applied aerially during a West Nile virus outbreak in an urban California environment[J]. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 2007, 23(3): 335-339. |
| 34 | SCHLEIER Ⅲ J J, PETERSON R K D. Pyrethrins and pyrethroid insecticides[M]//LOPEZ O, FerNANDER-BOLANOS J. Green trends in insect control. The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2011: 94-131. |
| 35 | FENG X X, PAN L X, WANG C, et al. Residue analysis and risk assessment of pyrethrins in open field and greenhouse turnips[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(1): 877-886. |
| 36 | PAN L X, FENG X X, ZHANG H Y. Dissipation and residues of pyrethrins in leaf lettuce under greenhouse and open field conditions[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(7): 822. |
| 37 | ANTONIOUS G F, BYERS M E, KERST W C. Residue levels of pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide in soil and runoff water[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 1997, 32(5): 621-644. |
| 38 | ANTONIOUS G F. Residues and half-lives of pyrethrins on field-grown pepper and tomato[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 2004, 39(4): 491-503. |
| 39 | ANGIONI A, DEDOLA F, MINELLI E V, et al. Residues and half-life times of pyrethrins on peaches after field treatments[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005, 53(10): 4059-4063. |
| 40 | CHENG X, UMINA P A, LEE S F, et al. Pyrethroid resistance in the pest mite, Halotydeus destructor: dominance patterns and a new method for resistance screening[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2019, 159: 9-16. |
| 41 | MAESTRE‐SERRANO R, PAREJA‐LOAIZA P, GOMEZ C D, et al. Co‐occurrence of V1016I and F1534C mutations in the voltage‐gated sodium channel and resistance to pyrethroids in Aedes aegypti (L.) from the Colombian Caribbean region[J]. Pest Management Science, 2019, 75(6): 1681-1688. |
| 42 | LI H, CHENG F, WEI Y, et al. Global occurrence of pyrethroid insecticides in sediment and the associated toxicological effects on benthic invertebrates: an overview[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 258-271. |
| 43 | STEHLE S, SCHULZ R. Agricultural insecticides threaten surface waters at the global scale[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(18): 5750-5755. |
| 44 | KGOROEBUTSWE T K, RAMATLHO P, REEDER S, et al. Distribution of Anopheles mosquito species, their vectorial role and profiling of knock-down resistance mutations in Botswana[J]. Parasitology Research, 2020, 119(4): 1201-1208. |
| 45 | MATSUO N. Discovery and development of pyrethroid insecticides[J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B, Physical and Biological Sciences, 2019, 95(7): 378-400. |
| 46 | STAUDINGER H, RUZICKA L, INSEKTENTÖTENDE STOFFE Ⅰ. Über Isolierung und Konstitution des wirksamen Teiles des dalmatinischen Insektenpulvers[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1924, 7(1): 177-201. |
| 47 | LAFORGE F B, BARTHEL W F. Constituents of pyrethrum flowers; the partial synthesis of pyrethrins and cinerins and their relative toxicities[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1947, 12(1): 199-202. |
| 48 | INOUYE Y, TAKESHIYA Y, OHNO M. Studies on synthetic pyrethroids. Part V. synthesis of geometrical isomers of chrysanthemum dicarboxylic acid[J]. Scientific Pest Control, 2008, 19(3): 193-199. |
| 49 | KATSUDA Y, CHIKAMOTO T, INOUYE Y. The absolute configuration of naturally derived pyrethrolone and cinerolone[J]. Bulletin of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 1958, 22(6): 427-428. |
| 50 | GODIN P J, SLEEMAN R J, SNAREY M, et al. The jasmolins, new insecticidally active constituents of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium VIS[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society C: Organic, 1966(0): 332-334. |
| 51 | KIKUTA Y, UEDA H, TAKAHASHI M, et al. Identification and characterization of a GDSL lipase-like protein that catalyzes the ester-forming reaction for pyrethrin biosynthesis in Tanacetum cinerariifolium-a new target for plant protection[J]. Plant Journal, 2012, 71(2): 183-193. |
| 52 | KAWAMOTO M, MORIYAMA M, ASHIDA Y, et al. Total syntheses of all six chiral natural pyrethrins: Accurate determination of the physical properties, their insecticidal activities, and evaluation of synthetic methods[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 85(5): 2984-2999. |
| 53 | KATSUDA Y. Progress and future of pyrethroids[J]. Topics in Current Chemistry, 2011, 314: 1-30. |
| 54 | DUCHON S, BONNET J, MARCOMBE S, et al. Pyrethrum: a mixture of natural pyrethrins has potential for malaria vector control[J]. Journal of Medical Entomology, 2009, 46(3): 516-522. |
| 55 | KAZUHIKO M. Pyrethrin biosynthesis and its regulation in Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium [J]. Topics in Current Chemistry, 2011, 314(1): 73. |
| 56 | RIVERA S B, SWEDLUND B D, KING G J, et al. Chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase: isolation of the gene and characterization of the recombinant non-head-to-tail monoterpene synthase from Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(8): 4373-4378. |
| 57 | LI W, LYBRAND D B, XU H, et al. A trichome-specific, plastid-localized Tanacetum cinerariifolium nudix protein hydrolyzes the natural pyrethrin pesticide biosynthetic intermediate trans-chrysanthemyl diphosphate[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 482. |
| 58 | MATSUDA K, KIKUTA Y, HABA A, et al. Biosynthesis of pyrethrin I in seedlings of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium [J]. Phytochemistry, 2005, 66(13): 1529-1535. |
| 59 | SCHALLER A, STINTZI A. Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis—structure, function, regulation[J]. Phytochemistry, 2009, 70(13/14): 1532-1538. |
| 60 | MATSUI R, AMANO N, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Elucidation of the biosynthetic pathway of cis-jasmone in Lasiodiplodia theobromae [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 6688. |
| 61 | UEDA H, KIKUTA Y, MATSUDA K. Plant communication: Mediated by individual or blended VOCs[J]? Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(2): 222-226. |
| 62 | ZDYB A, SALGADO M G, DEMCHENKO K N, et al. Allene oxide synthase, allene oxide cyclase and jasmonic acid levels in Lotus japonicus nodules[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1): e0190884. |
| 63 | PENG Q, ZHOU Y, LIAO Y, et al. Functional characterization of an allene oxide synthase involved in biosynthesis of jasmonic acid and its influence on metabolite profiles and ethylene formation in tea (Camellia sinensis) flowers[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(8): 2440. |
| 64 | CHINI A, MONTE I, ZAMARREÑO A M, et al. An OPR3-independent pathway uses 4,5-didehydrojasmonate for jasmonate synthesis[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(2): 171-178. |
| 65 | DABIRI M, MAJDI M, BAHRAMNEJAD B. Partial sequence isolation of DXS and AOS genes and gene expression analysis of terpenoids and pyrethrin biosynthetic pathway of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium under abiotic elicitation[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2020, 42(3): 1-15. |
| 66 | KIKUTA Y, UEDA H, NAKAYAMA K, et al. Specific regulation of pyrethrin biosynthesis in Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium by a blend of volatiles emitted from artificially damaged conspecific plants[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2011, 52(3): 588-596. |
| 67 | YAMASHIRO T, SHIRAISHI A, SATAKE H, et al. Draft genome of Tanacetum cinerariifolium, the natural source of mosquito coil[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 18249. |
| 68 | PAN W H, CHANG C C, SU T T, et al. Preparative supercritical fluid extraction of pyrethrin I and II from pyrethrum flower[J]. Talanta, 1995, 42(11): 1745-1749. |
| 69 | KASAJ D, RIEDER A, KRENN L, et al. Separation and quantitative analysis of natural pyrethrins by high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chromatographia, 1999, 50(9/10): 607-610. |
| 70 | REVERCHON E, MARCO I D. Supercritical fluid extraction and fractionation of natural matter[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2006, 38(2): 146-166. |
| 71 | NAZARI F, KAMBARANI M. Extraction and determination of pyrethrins from pyrethrum cultivated in Iran[J]. Journal of Medicinal Plants. 2008, 7(25): 79-84, 119. |
| 72 | NAGAR A, CHATTERJEE A, REHMAN L U, et al. Comparative extraction and enrichment techniques for pyrethrins from flowers of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium [J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2015, 76: 955-960. |
| 73 | KIRIAMITI H K, CAMY S, GOURDON C, et al. Pyrethrin exraction from pyrethrum flowers using carbon dioxide[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2003, 26(3): 193-200. |
| 74 | BABIC S, GRDIA M, PERIA M, al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of pyrethrins from pyrethrum flowers[J]. Agrochimica-Pisa-, 2012, 56(4/5): 193-206. |
| 75 | MARTÍN L, MARQUÉS J L, GONZÁLEZ-COLOMA A, et al. Supercritical methodologies applied to the production of biopesticides: a review[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2012, 11(4): 413-431. |
| 76 | LEVY L W. A large-scale application of tissue culture: the mass propagation of pyrethrum clones in ecuador[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 1981, 21(3/4): 389-395. |
| 77 | ZITO S W, TIO C D. Constituents of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium in leaves, regenerated plantlets and callus[J]. Phytochemistry, 1990, 29(8): 2533-2534. |
| 78 | HITMI A, COUDRET A, BARTHOMEUF C. The production of pyrethrins by plant cell and tissue cultures of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium and tagetes species[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2000, 19(1): 69-89. |
| 79 | KHAN S A, VERMA P, PARASHARAMI V A, et al. In vitro manipulations for value addition in potent herbal insecticidal activities of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium [M]//KUMAR N. Biotechnological approaches for medicinal and aromatic plants. Singapore: Springer, 2018: 395-416. |
| 80 | JEANMART S. Trends in chrysanthemic acid chemistry: a survey of recent pyrethrum syntheses[J]. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 2003, 56(6): 559-566. |
| 81 | BRAMWELL A F, CROMBIE L, HEMESLEY P, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of the natural pyrethrins and related compounds[J]. Tetrahedron, 1969, 25(8): 1727-1741. |
| 82 | KUMAR M, SUN Y, RATHOUR R, et al. Algae as potential feedstock for the production of biofuels and value-added products: opportunities and challenges[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 716: 137116. |
| 83 | GALANIE S, THODEY K, TRENCHARD I J, et al. Complete biosynthesis of opioids in yeast[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6252): 1095-1100. |
| 84 | 闻志强,孙小曼,汪庆卓 等. 梭菌正丁醇代谢工程研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021,2(2):194-221. |
| WEN Z Q, SUN X M, WANG Q Z, et al. Recent advances in metabolic engineering of clostridia for n-butanol production[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2):194-221. | |
| 85 | RO D K, PARADISE E M, OUELLET M, et al. Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7086): 940-943. |
| 86 | MCCARTY N S, LEDESMA-AMARO R. Synthetic biology tools to engineer microbial communities for biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(2): 181-197. |
| 87 | ZHU Q, YU S, ZENG D, et al. Development of “purple endosperm rice” by engineering anthocyanin biosynthesis in the endosperm with a high-efficiency transgene stacking system[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(7): 918-929. |
| 88 | FU R, ZHANG P, JIN G, et al. Versatility in acyltransferase activity completes chicoric acid biosynthesis in purple coneflower[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1563. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||