合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (6): 863-875.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-015
基于合成生物技术构建高效生物制造系统的研究进展
张晓龙1,2,3, 王晨芸1,2,3, 刘延峰1,2,3, 李江华2,3, 刘龙1,2,3, 堵国成1,2,3
- 1.江南大学糖化学与生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
2.江南大学未来食品科学中心,江苏 无锡 214122
3.江南大学工业生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
-
收稿日期:2021-02-02修回日期:2021-08-09出版日期:2021-12-31发布日期:2022-01-21 -
通讯作者:堵国成 -
作者简介:张晓龙 (1988—),男,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为发酵工程。E-mail:qingshuang0302@163.com堵国成 (1965—),男,博士,教授。研究方向为发酵工程与酶工程。E-mail:gcdu@jiangnan.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0900300);国家自然科学基金(31972854)
Research progress of constructing efficient biomanufacturing system based on synthetic biotechnology
ZHANG Xiaolong1,2,3, WANG Chenyun1,2,3, LIU Yanfeng1,2,3, LI Jianghua2,3, LIU Long1,2,3, DU Guocheng1,2,3
- 1.Key Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biotechnology,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
2.Science Center for Future Foods,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
3.Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology,Ministry of Education,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2021-02-02Revised:2021-08-09Online:2021-12-31Published:2022-01-21 -
Contact:DU Guocheng
摘要:
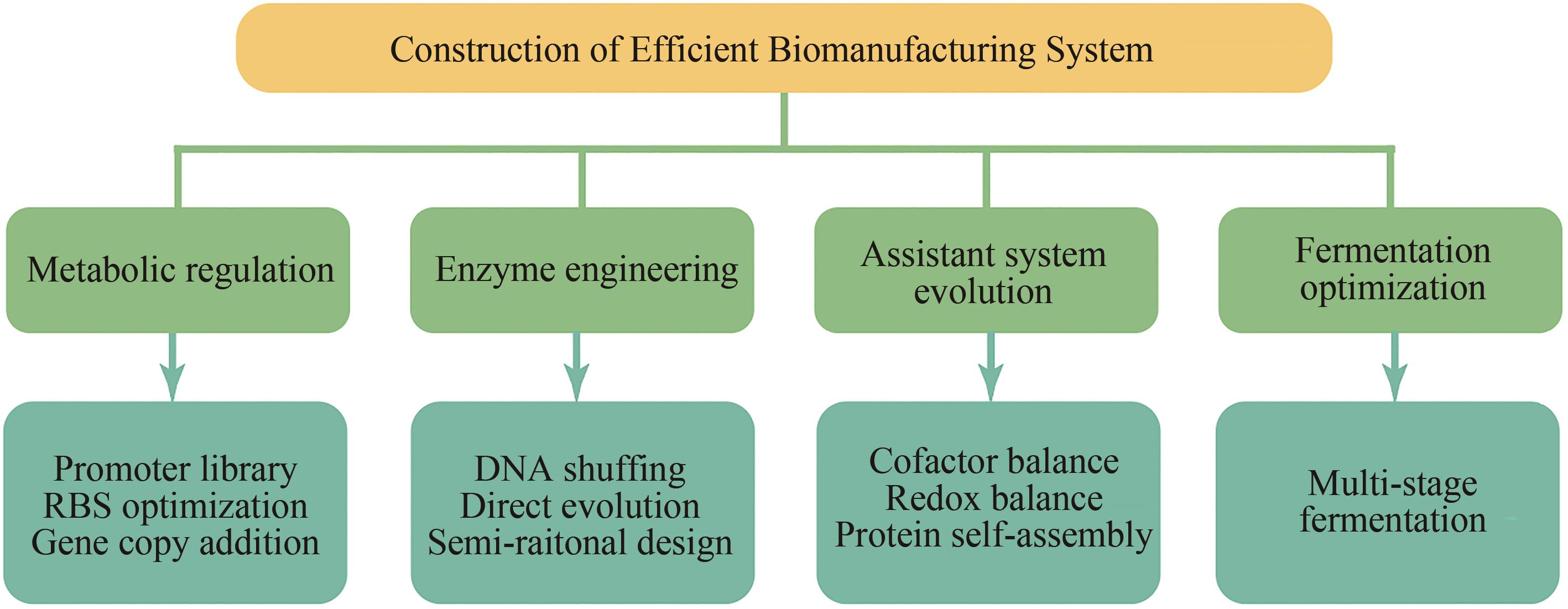
基于合成生物技术构建绿色高效的生物制造系统是实现可持续化发展的重要途径,该技术的发展应用有望为食品、能源、医药、化工以及畜牧养殖等行业带来革命性的技术变革。本文针对基于合成生物技术构建高效生物制造系统进行系统性的总结与讨论。首先概述了代谢工程、酶工程、辅助系统优化以及发酵过程控制等技术的研究进展;其次,着重对比总结了大肠杆菌、芽孢杆菌属、谷氨棒酸杆菌以及酵母属等典型模式宿主的代谢特性,探究了各微生物制造系统的适用范围。最后,对合成生物技术在构建高效生物制造系统领域中的应用前景进行了展望。精细多元的代谢工程技术、高效简便的酶工程策略以及数字化的微生物系统将是促进高效生物制造系统构建的新引擎与新动力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张晓龙, 王晨芸, 刘延峰, 李江华, 刘龙, 堵国成. 基于合成生物技术构建高效生物制造系统的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 863-875.
ZHANG Xiaolong, WANG Chenyun, LIU Yanfeng, LI Jianghua, LIU Long, DU Guocheng. Research progress of constructing efficient biomanufacturing system based on synthetic biotechnology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 863-875.
| 典型模式微生物 | 优缺点 | 适用范围 | 产品应用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 发酵周期短,遗传背景清晰,具有成熟的基因编辑工具以及多元化的代谢调控策略;但不适于表达需要翻译后修饰的蛋白及膜蛋白 | 非糖基化重组蛋白表达系统 | 类胡萝卜素、紫杉醇、青蒿酸、丹参素、1,3-丙二醇、1,4-丁二醇以及1,3-丁二醇 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 | 出色的蛋白质分泌系统;同时具有典型的芽孢形成能力、细胞分裂以及生物膜系统;但极易形成不溶性包涵体,潜在的脂多糖和内毒素风险 | 碱性丝氨酸蛋白酶与中温淀粉酶制备生产;为微生物机理研究的首选微生物之一 | 核苷酸、维生素、表面活性剂、维生素B2复合物、D-(-)-2,3-丁二醇、透明质酸[ |
| 地衣芽孢杆菌 | 清晰的遗传背景,出色的蛋白质分泌系统,在高温培养环境中拥有极佳的液化和糊化特性;但极易形成不溶性包涵体,潜在的脂多糖和内毒素风险 | 高温淀粉酶的工业化生产 | 耐热碱性蛋白酶、银纳米颗粒、生物絮凝剂、聚γ-谷氨酸、2,3-丁二醇 |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 | 出色的蛋白质分泌系统;但极易形成不溶性包涵体,潜在的脂多糖和内毒素风险 | 中性或碱性蛋白酶的工业化生产 | 表面活性、果聚糖、S-腺苷甲硫氨酸、银纳米颗粒 |
| 谷氨酸棒杆菌 | 耗糖迅速,易于高密度发酵,无碳源分解代谢阻遏效应,且对有毒醇和芳香族化合物有较高耐受性;但遗传背景清晰,有成熟的调控工具 | 芳香族化合物的工业化生产 | L-谷氨酸、L-赖氨酸以及透明质酸 |
| 酿酒酵母 | 遗传背景清晰,胞内代谢机制高度解析,拥有内质网、线粒体等细胞器,且有较好的pH与渗透压耐受性;但其糖基化过高,较低的蛋白表达能力限制其工业化生产 | 适合生产生物能源、蛋白质、萜类、脂肪酸和脂肪醇、芳香族化合物等生物制品 | 乙酰辅酶A、香叶醇、柠檬烯、白藜芦醇、柚皮素、胰岛素等 |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母 | 极佳的蛋白分泌能力,优异的翻译后修饰(糖基化与二硫键),并且胞外内源性蛋白极少 | 适合异源蛋白表达 | 人促红细胞生成素、磷脂酶C、人超氧化物歧化酶、胰蛋白酶、人血清白蛋白、胶原蛋白和人单克隆抗体3H6 Fab片段 |
表1 典型模式宿主系统及适用范围总结
Tab. 1 Summary of various typical model organism system and their scope of application
| 典型模式微生物 | 优缺点 | 适用范围 | 产品应用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 发酵周期短,遗传背景清晰,具有成熟的基因编辑工具以及多元化的代谢调控策略;但不适于表达需要翻译后修饰的蛋白及膜蛋白 | 非糖基化重组蛋白表达系统 | 类胡萝卜素、紫杉醇、青蒿酸、丹参素、1,3-丙二醇、1,4-丁二醇以及1,3-丁二醇 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 | 出色的蛋白质分泌系统;同时具有典型的芽孢形成能力、细胞分裂以及生物膜系统;但极易形成不溶性包涵体,潜在的脂多糖和内毒素风险 | 碱性丝氨酸蛋白酶与中温淀粉酶制备生产;为微生物机理研究的首选微生物之一 | 核苷酸、维生素、表面活性剂、维生素B2复合物、D-(-)-2,3-丁二醇、透明质酸[ |
| 地衣芽孢杆菌 | 清晰的遗传背景,出色的蛋白质分泌系统,在高温培养环境中拥有极佳的液化和糊化特性;但极易形成不溶性包涵体,潜在的脂多糖和内毒素风险 | 高温淀粉酶的工业化生产 | 耐热碱性蛋白酶、银纳米颗粒、生物絮凝剂、聚γ-谷氨酸、2,3-丁二醇 |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 | 出色的蛋白质分泌系统;但极易形成不溶性包涵体,潜在的脂多糖和内毒素风险 | 中性或碱性蛋白酶的工业化生产 | 表面活性、果聚糖、S-腺苷甲硫氨酸、银纳米颗粒 |
| 谷氨酸棒杆菌 | 耗糖迅速,易于高密度发酵,无碳源分解代谢阻遏效应,且对有毒醇和芳香族化合物有较高耐受性;但遗传背景清晰,有成熟的调控工具 | 芳香族化合物的工业化生产 | L-谷氨酸、L-赖氨酸以及透明质酸 |
| 酿酒酵母 | 遗传背景清晰,胞内代谢机制高度解析,拥有内质网、线粒体等细胞器,且有较好的pH与渗透压耐受性;但其糖基化过高,较低的蛋白表达能力限制其工业化生产 | 适合生产生物能源、蛋白质、萜类、脂肪酸和脂肪醇、芳香族化合物等生物制品 | 乙酰辅酶A、香叶醇、柠檬烯、白藜芦醇、柚皮素、胰岛素等 |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母 | 极佳的蛋白分泌能力,优异的翻译后修饰(糖基化与二硫键),并且胞外内源性蛋白极少 | 适合异源蛋白表达 | 人促红细胞生成素、磷脂酶C、人超氧化物歧化酶、胰蛋白酶、人血清白蛋白、胶原蛋白和人单克隆抗体3H6 Fab片段 |
| 1 | SHEN X L, WANG J, LI C Y, et al. Dynamic gene expression engineering as a tool in pathway engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 59: 122-129. |
| 2 | WU Y K, CHEN T C, LIU Y F, et al. Design of a programmable biosensor-CRISPRi genetic circuits for dynamic and autonomous dual-control of metabolic flux in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(2): 996-1009. |
| 3 | SANDER T, FARKE N, DIEHL C, et al. Allosteric feedback inhibition enables robust amino acid biosynthesis in E. coli by enforcing enzyme overabundance[J]. Cell Systems, 2019, 8(1): 66-75.e8. |
| 4 | 陈修来, 刘佳, 罗秋玲, 等. 微生物辅因子平衡的代谢调控[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 16-26. |
| CHEN X L, LIU J, LUO Q L, et al. Manipulation of cofactor balance in microorganisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(1): 16-26. | |
| 5 | GU Y, LÜ X Q, LIU Y F, et al. Synthetic redesign of central carbon and redox metabolism for high yield production of N-acetylglucosamine in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 51: 59-69. |
| 6 | KIM Y E, HIPP M S, BRACHER A, et al. Molecular chaperone functions in protein folding and proteostasis[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2013, 82: 323-355. |
| 7 | LIANG C N, ZHANG X X, WU J Y, et al. Dynamic control of toxic natural product biosynthesis by an artificial regulatory circuit[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 57: 239-246. |
| 8 | POLKA J K, HAYS S G, SILVER P A. Building spatial synthetic biology with compartments, scaffolds, and communities[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2016, 8(8): a024018. |
| 9 | WANG Y, HU L T, HUANG H, et al. Eliminating the capsule-like layer to promote glucose uptake for hyaluronan production by engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3120. |
| 10 | 陈坚, 刘立明, 堵国成. 发酵过程优化原理与技术[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2009: 5-14. |
| CHEN J, LIU L M, DU G C. Principle and technology of fermentation optimization[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009: 5-14. | |
| 11 | GOPAL G J, KUMAR A. Strategies for the production of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli [J]. The Protein Journal, 2013, 32(6): 419-425. |
| 12 | TERPE K. Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72(2): 211-222. |
| 13 | TERPE K. Overview of tag protein fusions: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 60(5): 523-533. |
| 14 | ROSANO G L, CECCARELLI E A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2014, 5:172. |
| 15 | SCHLEIF R. AraC protein, regulation of the L-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli, and the light switch mechanism of AraC action[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2010, 34(5): 779-796. |
| 16 | QING G L, MA L C, KHORCHID A, et al. Cold-shock induced high-yield protein production in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(7): 877-882. |
| 17 | WANG X, HAN J N, ZHANG X, et al. Reversible thermal regulation for bifunctional dynamic control of gene expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1411. |
| 18 | COSTA S J, ALMEIDA A, CASTRO A, et al. The novel Fh8 and H fusion partners for soluble protein expression in Escherichia coli: a comparison with the traditional gene fusion technology[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(15): 6779-6791. |
| 19 | BANKI M R, FENG L, WOOD D W. Simple bioseparations using self-cleaving elastin-like polypeptide tags[J]. Nature Methods, 2005, 2(9): 659-661. |
| 20 | KAPUST R B, TÖZSÉR J, COPELAND T D, et al. The P1′ specificity of tobacco etch virus protease[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2002, 294(5): 949-955. |
| 21 | CHOI J H, LEE S Y. Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004, 64(5):625-635. |
| 22 | SCHIERLE C F, BERKMEN M, HUBER D, et al. The DsbA signal sequence directs efficient, cotranslational export of passenger proteins to the Escherichia coli periplasm via the signal recognition particle pathway[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2003, 185(19): 5706-5713. |
| 23 | SOARES C R J, GOMIDE F I C, UEDA E K M, et al. Periplasmic expression of human growth hormone via plasmid vectors containing the λPL promoter: use of HPLC for product quantification[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2003, 16(12): 1131-1138. |
| 24 | MESSENS J, COLLET J F. Pathways of disulfide bond formation in Escherichia coli [J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2006, 38(7): 1050-1062. |
| 25 | NISHIHARA K, KANEMORI M, YANAGI H, et al. Overexpression of trigger factor prevents aggregation of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(3): 884-889. |
| 26 | FERRER M, LÜNSDORF H, CHERNIKOVA T N, et al. Functional consequences of single: double ring transitions in chaperonins: life in the cold[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2004, 53(1): 167-182. |
| 27 | LUEKING A, HOLZ C, GOTTHOLD C, et al. A system for dual protein expression in Pichia pastoris and Escherichia coli [J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2000, 20(3): 372-378. |
| 28 | STEWART E J, ÅSLUND F, BECKWITH J. Disulfide bond formation in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm: an in vivo role reversal for the thioredoxins[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1998, 17(19):5543-5550. |
| 29 | KIM K, CHOE D, LEE D-H, et al. Engineering biology to construct microbial chassis for the production of difficult-to-express proteins[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 990. |
| 30 | FAULKNER M J, VEERAVALLI K, GON S, et al. Functional plasticity of a peroxidase allows evolution of diverse disulfide-reducing pathways[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(18): 6735-6740. |
| 31 | ZELIĆ B, GOSTOVIĆ S, VUORILEHTO K, et al. Process strategies to enhance pyruvate production with recombinant Escherichia coli: from repetitive fed-batch to in situ product recovery with fully integrated electrodialysis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2004, 85(6): 638-646. |
| 32 | YANG M H, ZHANG X. Construction of pyruvate producing strain with intact pyruvate dehydrogenase and genome-wide transcription analysis[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 59. |
| 33 | MATSUMOTO T, TANAKA T, KONDO A. Engineering metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli for constructing a "microbial chassis" for biochemical production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 1362-1368. |
| 34 | KRIVORUCHKO A, ZHANG Y M, SIEWERS V, et al. Microbial acetyl-CoA metabolism and metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 28: 28-42. |
| 35 | HUANG J F, LIU Z Q, JIN L Q, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial production of L-methionine[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(4): 843-851. |
| 36 | YANG P, WANG J, PANG Q X, et al. Pathway optimization and key enzyme evolution of N-acetylneuraminate biosynthesis using an in vivo aptazyme-based biosensor[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 43(A): 21-28. |
| 37 | YE L J, ZHANG C Z, BI C H, et al. Combinatory optimization of chromosomal integrated mevalonate pathway for β-carotene production in Escherichia coli [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 202. |
| 38 | ALONSO-GUTIERREZ J, CHAN R, BATTH T S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for limonene and perillyl alcohol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 19: 33-41. |
| 39 | ZHOU L, DING Q, JIANG G Z, et al. Chromosome engineering of Escherichia coli for constitutive production of salvianic acid A[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 84. |
| 40 | SCHALLMEY M, SINGH A, WARD O P. Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2004, 50(1): 1-17. |
| 41 | PETSCH D, ANSPACH F B. Endotoxin removal from protein solutions[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2000, 76(2/3): 97-119. |
| 42 | SHI T, WANG Y C, WANG Z W, et al. Deregulation of purine pathway in Bacillus subtilis and its use in riboflavin biosynthesis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2014, 13(1): 101. |
| 43 | JIN P, KANG Z, YUAN P H, et al. Production of specific-molecular-weight hyaluronan by metabolically engineered Bacillus subtilis 168[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 35: 21-30. |
| 44 | GU Y, XU X H, WU Y K, et al. Advances and prospects of Bacillus subtilis cellular factories: from rational design to industrial applications[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 50: 109-121. |
| 45 | SAITO N. A thermophilic extracellular α-amylase from Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1973, 155(2): 290-298. |
| 46 | MACHIUS M, DECLERCK N, HUBER R, et al. Kinetic stabilization of Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase through introduction of hydrophobic residues at the surface[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(13): 11546-11553. |
| 47 | SELLAMI-KAMOUN A, HADDAR A, E-H ALI N, et al. Stability of thermostable alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis RP1 in commercial solid laundry detergent formulations[J]. Microbiological Research, 2008, 163(3): 299-306. |
| 48 | KALIMUTHU K, BABU R S, VENKATARAMAN D, et al. Biosynthesis of silver nanocrystals by Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2008, 65(1): 150-153. |
| 49 | KALISHWARALAL K, DEEPAK V, RAMKUMARPANDIAN S, et al. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by the culture supernatant of Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(29): 4411-4413. |
| 50 | SHIH I L, VAN Y T, YEH L C, et al. Production of a biopolymer flocculant from Bacillus licheniformis and its flocculation properties [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2001, 78(3): 267-272. |
| 51 | CAO M F, FENG J, SIRISANSANEEYAKUL S, et al. Genetic and metabolic engineering for microbial production of poly-γ-glutamic acid[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(5):1424-1433. |
| 52 | QIU Y M, ZHANG J Y, LI L, et al. Engineering Bacillus licheniformis for the production of meso-2,3-butanediol[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2016, 9(1): 117. |
| 53 | QI G F, KANG Y F, LI L, et al. Deletion of meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase gene budC for enhanced D-2,3-butanediol production in Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2014, 7(1): 16. |
| 54 | VEITH B, HERZBERG C, STECKEL S, et al. The complete genome sequence of Bacillus licheniformis DSM13, an organism with great industrial potential[J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004, 7(4): 204-211. |
| 55 | ZHOU C X, LIU H, YUAN F Y, et al. Development and application of a CRISPR/Cas9 system for Bacillus licheniformis genome editing[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 122: 329-337. |
| 56 | ZHAN Y Y, XU Y, ZHENG P L, et al. Establishment and application of multiplexed CRISPR interference system in Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(1): 391-403. |
| 57 | WANG H, YANG L, PING Y H, et al. Engineering of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain with high neutral protease producing capacity and optimization of its fermentation conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0146373. |
| 58 | SHA Y Y, HUANG Y Y, ZHU Y F, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of low-molecular-weight poly-γ-glutamic acid based on stereochemistry regulation in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(6): 1395-1405. |
| 59 | ZHANG F, HUO K Y, SONG X Y, et al. Engineering of a genome-reduced strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for enhancing surfactin production[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 223. |
| 60 | YANG N, WU Q, XU Y. Fe nanoparticles enhanced surfactin production in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(12): 6321-6329. |
| 61 | GU Y Y, ZHENG J Y, FENG J, et al. Improvement of levan production in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens through metabolic optimization of regulatory elements[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(10): 4163-4174. |
| 62 | JIANG C, RUAN L Y, WEI X T, et al. Enhancement of S-adenosylmethionine production by deleting thrB gene and overexpressing SAM2 gene in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2020, 42(11): 2293-2298. |
| 63 | SAMUEL M S, JOSE S, SELVARAJAN E, et al. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Application for cytotoxicity effect on A549 cell line and photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 2020, 202: 111642. |
| 64 | INUI M, KAWAGUCHI H, MURAKAMI S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for fuel ethanol production under oxygen-deprivation conditions[J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004, 8(4): 243-254. |
| 65 | SASAKI M, JOJIMA T, KAWAGUCHI H, et al. Engineering of pentose transport in Corynebacterium glutamicum to improve simultaneous utilization of mixed sugars[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2009, 85(1): 105-115. |
| 66 | KITADE Y, HASHIMOTO R, SUDA M, et al. Production of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid by an aerobic growth-arrested bioprocess using metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(6). |
| 67 | KUBOTA T, WATANABE A, SUDA M, et al. Production of para-aminobenzoate by genetically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum and non-biological formation of an N-glucosyl byproduct[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 322-330. |
| 68 | CHOI J W, JEON E J, JEONG K J. Recent advances in engineering Corynebacterium glutamicum for utilization of hemicellulosic biomass[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 57: 17-24. |
| 69 | JORGE J M P, PÉREZ-GARCÍA F, WENDISCH V F. A new metabolic route for the fermentative production of 5-aminovalerate from glucose and alternative carbon sources[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245(B): 1701-1709. |
| 70 | BARITUGO K A, KIM H T, DAVID Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for fermentative production of chemicals in biorefinery[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(9):3915-3937. |
| 71 | SCHÄFER A, TAUCH A, JÄGER W, et al. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Gene, 1994, 145(1): 69-73. |
| 72 | SUZUKI N, NONAKA H, TSUGE Y, et al. New multiple-deletion method for the Corynebacterium glutamicum genome, using a mutant lox sequence[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(12): 8472-8480. |
| 73 | WANG Y, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. MACBETH: Multiplex automated Corynebacterium glutamicum base editing method[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 200-210. |
| 74 | HEIDER S A E, WENDISCH V F. Engineering microbial cell factories: metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum with a focus on non-natural products[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 10(8): 1170-1184. |
| 75 | BELL S P, LABIB K. Chromosome duplication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Genetics, 2016, 203(3): 1027-1067. |
| 76 | ZHANG W P, DU G C, ZHOU J W, et al. Regulation of sensing, transportation, and catabolism of nitrogen sources in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2018, 82(1): e00040-17. |
| 77 | LAUN P, PICHOVA A, MADEO F, et al. Aged mother cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae show markers of oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2001, 39(5): 1166-1173. |
| 78 | HO Y, GRUHLER A, HEILBUT A, et al. Systematic identification of protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mass spectrometry[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6868): 180-183. |
| 79 | UETZ P, GIOT L, CAGNEY G, et al. A comprehensive analysis of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6770): 623-627. |
| 80 | KROGAN N J, CAGNEY G, YU H Y, et al. Global landscape of protein complexes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7084): 637-643. |
| 81 | NEIMAN A M. Ascospore formation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2005, 69(4): 565-584. |
| 82 | LEVIN D E. Cell wall integrity signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2005, 69(2): 262-291. |
| 83 | YAMANISHI M, ITO Y, KINTAKA R, et al. A genome-wide activity assessment of terminator regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provides a ''terminatome'' toolbox[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(6): 337-347. |
| 84 | TEIXEIRA M C, MONTEIRO P T, PALMA M, et al. YEASTRACT: an upgraded database for the analysis of transcription regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(D1): D348-D353. |
| 85 | BALAKRISHNAN R, PARK J, KARRA K, et al. YeastMine—an integrated data warehouse for Saccharomyces cerevisiae data as a multipurpose tool-kit[J]. Database, 2012, 2012: bar062. |
| 86 | SHAO Z Y, ZHAO H, ZHAO H M. DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(2): e16-e16. |
| 87 | KUIJPERS N G, SOLIS-ESCALANTE D, BOSMAN L, et al. A versatile, efficient strategy for assembly of multi-fragment expression vectors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using 60 bp synthetic recombination sequences[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2013, 12: 47. |
| 88 | HONG K K, NIELSEN J. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a key cell factory platform for future biorefineries[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2012, 69(16): 2671-2690. |
| 89 | KAYIKCI Ö, NIELSEN J. Glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2015, 15(6): fov068. |
| 90 | HOU J, QIU C X, SHEN Y, et al. Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the efficient co-utilization of glucose and xylose[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2017, 17(4): fox034. |
| 91 | KOZAK B U, ROSSUM H M VAN, LUTTIK M A H, et al. Engineering acetyl coenzyme A supply: functional expression of a bacterial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the cytosol of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. mBio, 2014, 5(5): e01696-e01614. |
| 92 | JIANG G Z, YAO M D, WANG Y, et al. Manipulation of GES and ERG20 for geraniol overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 41: 57-66. |
| 93 | CHENG S, LIU X, JIANG G Z, et al. Orthogonal engineering of biosynthetic pathway for efficient production of limonene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(5): 968-975. |
| 94 | DAI Z B, LIU Y, ZHANG X N, et al. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of ginsenosides[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 20: 146-156. |
| 95 | PADDON C J, WESTFALL P J, PITERA D J, et al. High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 528-532. |
| 96 | LUO X, REITER M A, D'ESPAUX L, et al. Complete biosynthesis of cannabinoids and their unnatural analogues in yeast[J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7746): 123-126. |
| 97 | GOTTARDI M, REIFENRATH M, BOLES E, et al. Pathway engineering for the production of heterologous aromatic chemicals and their derivatives in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: bioconversion from glucose[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2017, 17(4): fox035. |
| 98 | KRIVORUCHKO A, NIELSEN J. Production of natural products through metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 35: 7-15. |
| 99 | LUTTIK M AH, VURALHAN Z, SUIR E, et al. Alleviation of feedback inhibition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae aromatic amino acid biosynthesis: quantification of metabolic impact[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2008, 10(3/4): 141-153. |
| 100 | DEVER T E, KINZY T G, PAVITT G D. Mechanism and regulation of protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Genetics, 2016, 203(1):65-107. |
| 101 | RASALA B A, MAYFIELD S P. Photosynthetic biomanufacturing in green algae; production of recombinant proteins for industrial, nutritional, and medical uses[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2015, 123(3):227-239. |
| 102 | DE SCHUTTER K, LIN Y C, TIELS P, et al. Genome sequence of the recombinant protein production host Pichia pastoris [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(6): 561-566. |
| 103 | SCHWARZHANS J P, LUTTERMANN T, GEIER M, et al. Towards systems metabolic engineering in Pichia pastoris [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(6): 681-710. |
| 104 | 韩明哲, 陈为刚, 宋理富, 等. DNA信息存储: 生命系统与信息系统的桥梁[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 309-322. |
| HAN M Z, CHEN W G, SONG L F, et al. DNA information storage: bridging biological and digital world[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 309-322. | |
| 105 | 张媛媛, 曾艳, 王钦宏. 合成生物制造进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 145-160. |
| ZHANG Y Y, ZENG Y, WANG Q H. Advances in synthetic biomanufacturing[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 145-160. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [3] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [4] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [5] | 禹伟, 高教琪, 周雍进. 一碳生物转化合成有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| [6] | 陈锡玮, 张华然, 邹懿. 真菌源非核糖体肽类药物生物合成及代谢工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [7] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [8] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [9] | 赵静宇, 张健, 祁庆生, 王倩. 基于细菌双组分系统的生物传感器的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 38-52. |
| [10] | 孙绘梨, 崔金玉, 栾国栋, 吕雪峰. 面向高效光驱固碳产醇的蓝细菌合成生物技术研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1161-1177. |
| [11] | 晏雄鹰, 王振, 娄吉芸, 张皓瑜, 黄星宇, 王霞, 杨世辉. 生物燃料高效生产微生物细胞工厂构建研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(6): 1082-1121. |
| [12] | 陈永灿, 司同, 张建志. 自动化合成生物技术在DNA组装与微生物底盘操作中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 857-876. |
| [13] | 程真真, 张健, 高聪, 刘立明, 陈修来. 代谢工程改造微生物利用甲酸研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 756-778. |
| [14] | 刘家宇, 杨智晗, 杨蕾, 朱丽英, 朱政明, 江凌. 合成生物技术驱动酪丁酸梭菌细胞工厂开发的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1174-1200. |
| [15] | 郭姝媛, 吴良焕, 刘香健, 王博, 于涛. 微生物中一碳代谢网络构建的进展与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 116-137. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||