The design and delivery of RNA vaccines
YANG Lu1, ZHANG Jingming2, XUShan 1, TONG Yigang1
- 1.BAICSM,State Key Laboratory of Green Biomanufacturing,College of Life Science and Technology,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,Beijing 100029,China
2.Advanced Medicine and Regenerative Medicine Institute,Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center for Health,Hefei 230601,Anhui,China
-
Received:2025-08-15Revised:2025-09-28Published:2025-09-30 -
Contact:XUShan , TONG Yigang
RNA疫苗的设计与递送
杨璐1, 张镜明2, 徐杉1, 童贻刚1
- 1.北京化工大学,生命科学与技术学院,绿色生物制造国家重点实验室,中国 北京 100029
2.合肥市综合性国家中心大健康研究院,先进医药与再生医学研究所,安徽 合肥 230601
-
通讯作者:徐杉,童贻刚 -
作者简介:杨璐 (1997—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为mRNA疫苗、噬菌体载体疫苗。E-mail:1359526291@qq.com徐杉 (1992—),女,博士,副教授,硕士生导师。研究方向为流感病毒等复制机制及利用高通量测序技术发现未知病原体。徐杉 ,北京协和医学院生物化学与分子生物学博士,浙江大学博士后,青年优秀后备人才,主要研究流感病毒等复制机制及利用高通量测序技术发现未知病原体,在病毒分子机制与生物技术应用方面具有丰富研究经验,以第一/通讯作者在Nucleic Acids Research、Virus Research、Science Bulletin等期刊发表多篇重要论文,主持国家自然科学基金青年项目、博士后特别资助和博士后面上项目等科研课题。 E-mail:shanxu@buct.edu.cn童贻刚 (1966—),男,博士,教授。研究方向为病毒学、抗病毒药物、疫苗、噬菌体学、生物信息学。从事新发病原体、生物安全、生物信息学、高通量测序、噬菌体学等领域研究。先后在Nature、Cell、PNAS、Lancet等刊物发表中英文论文500余篇,其中SCI论文370余篇。教育部微生物病毒学知识领域首席专家,教育部重点领域微生物病毒学课程虚拟教研室负责人,中国生物工程学会噬菌体技术专业委员会主任委员;世界卫生组织新冠肺炎病毒溯源联合团队动物与环境组中方组长,国家科技部新型冠状病毒溯源专班工作组咨询专家,中国援非抗击埃博拉疫情医疗队首席科学家,国家传染病重大专项项目、“合成生物学”与“前沿生物技术”国家重点专项项目首席专家。 E-mail:tongyigang@mail.buct.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(92369201)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Lu, ZHANG Jingming, XUShan , TONG Yigang. The design and delivery of RNA vaccines[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-085.
杨璐, 张镜明, 徐杉, 童贻刚. RNA疫苗的设计与递送[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-085.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-085
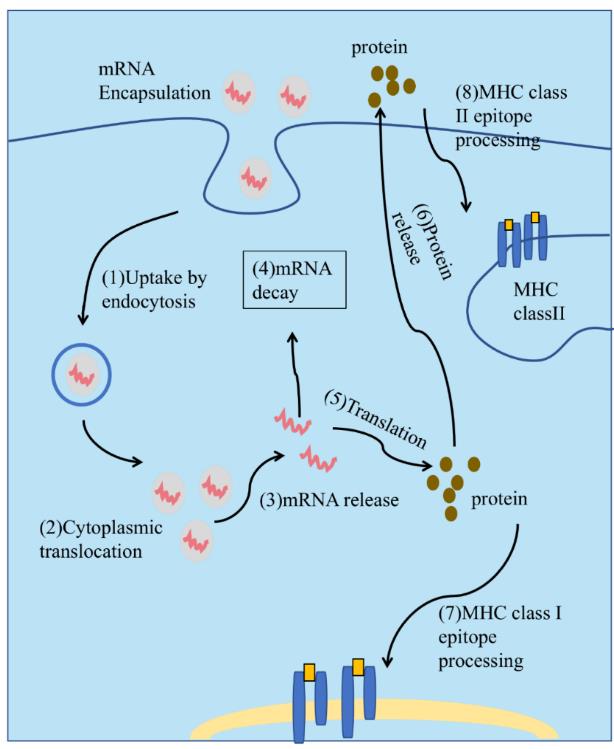
Fig. 2 Principle of mRNA Delivery(1) The encapsulated mRNA is taken up by cells via endocytosis and enters the endosomal pathway.(2) The encapsulated mRNA is released into the cytoplasm.(3) The mRNA is released from the delivery vehicle.(4) Translation termination is accompanied by mRNA degradation, catalyzed by exonucleases.(5) The mRNA is translated into protein.(6) The protein is secreted extracellularly via autocrine, paracrine, or endocrine mechanisms to exert its function.(7) The protein product needs to be degraded into antigenic peptide epitopes. These epitopes are loaded onto Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules and presented on the cell surface for recognition by immune effector cells. (8) In Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs), to obtain T cell help for enhanced persistence of the immune response, the protein product needs to be directed to the MHC class II loading compartment.
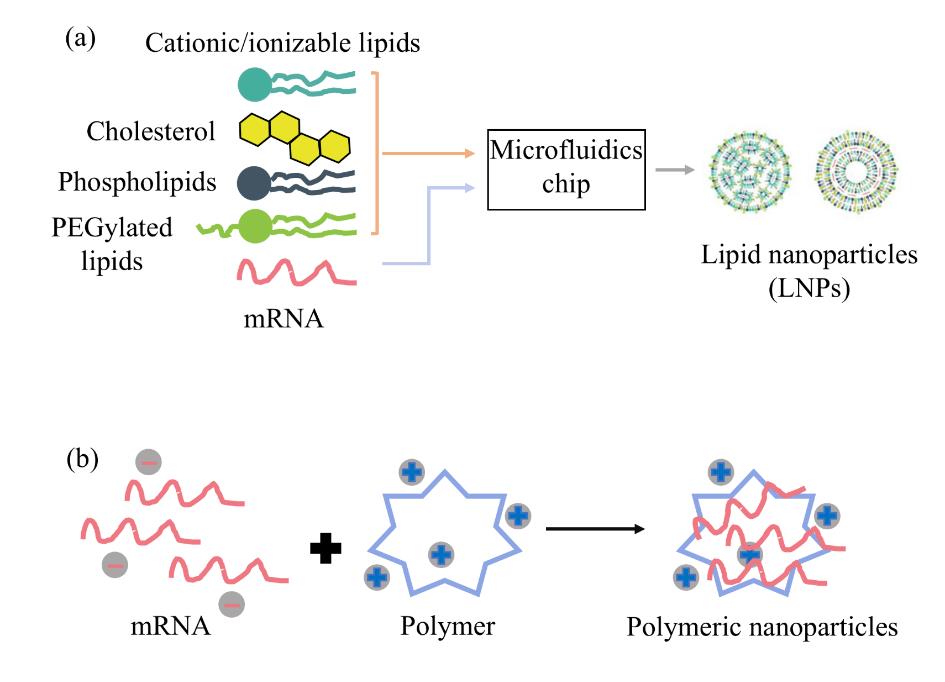
Fig. 3 The common structures of delivery systems are as follows:(a) Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs): Typically prepared via microfluidic technology, their components include conventional (cationic or ionizable) lipids, functionalized lipids, cholesterol, and helper lipids.(b) Polymer-based carriers: These include polyethylenimine (PEI), ionizable amphiphilic Janus dendrimers (IAJD), chitosan, etc. They can form stable nanoparticles encapsulating mRNA through simple mixing.
| [1] | NIU D, WU Y, LIAN J. Circular RNA vaccine in disease prevention and treatment [J]. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 2023, 8(1): 341. |
| [2] | TEO S P. Review of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 [J]. Journal of pharmacy practice, 2022, 35(6): 947-51. |
| [3] | VIZCARRA P, HAEMMERLE J, VELASCO H, et al. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine Reactogenicity: The key role of immunity [J]. Vaccine, 2021, 39(51): 7367-74. |
| [4] | BADEN L R, SAHLY H M EL, ESSINK B, et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine [J]. The New England journal of medicine, 2021, 384(5): 403-16. |
| [5] | KON E, ELIA U, PEER D. Principles for designing an optimal mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine [J]. Current opinion in biotechnology, 2022, 73: 329-36. |
| [6] | RICHNER J M, HIMANSU S, DOWD K A, et al. Modified mRNA Vaccines Protect against Zika Virus Infection [J]. Cell, 2017, 168(6): 1114-25.e10. |
| [7] | PARDI N, KRAMMER F. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases - advances, challenges and opportunities [J]. Nature reviews Drug discovery, 2024, 23(11): 838-61. |
| [8] | CAI Z, WURI Q, SONG Y, et al. CircRNA-loaded DC vaccine in combination with low-dose gemcitabine induced potent anti-tumor immunity in pancreatic cancer model [J]. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, 2025, 74(2): 68. |
| [9] | WEI H Y, FAN X J, MAO M W. A Review on Circular RNA Translation and Its Implications in Disease [J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ), 2025, 2883: 109-37. |
| [10] | WAYNE C J, BLAKNEY A K. Self-amplifying RNA COVID-19 vaccine [J]. Cell, 2024, 187(8): 1822-.e1. |
| [11] | SAHIN U, KARIKó K, TüRECI Ö. mRNA-based therapeutics--developing a new class of drugs [J]. Nature reviews Drug discovery, 2014, 13(10): 759-80. |
| [12] | ESTAPé SENTI M, GARCíA DEL VALLE L, SCHIFFELERS R M. mRNA delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy: Lipid nanoparticles and beyond [J]. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 2024, 206: 115190. |
| [13] | VERMA A, AWASTHI A. Innovative Strategies to Enhance mRNA Vaccine Delivery and Effectiveness: Mechanisms and Future Outlook [J]. Current pharmaceutical design, 2024, 30(14): 1049-59. |
| [14] | GUPTA R, ARORA K, MEHROTRA ARORA N, et al. Significance of VLPs in Vlp-circRNA vaccines: a vaccine candidate or delivery vehicle? [J]. RNA biology, 2024, 21(1): 17-28. |
| [15] | SU J, ZHANG J, FENG X, et al. A universal viral capsid protein based one step RNA synthesis and packaging system for rapid and efficient mRNA vaccine development [J]. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 2025, 33(4): 1720-34. |
| [16] | BACHMANN M F, JENNINGS G T. Vaccine delivery: a matter of size, geometry, kinetics and molecular patterns [J]. Nature reviews Immunology, 2010, 10(11): 787-96. |
| [17] | MOCHIDA Y, UCHIDA S. mRNA vaccine designs for optimal adjuvanticity and delivery [J]. RNA biology, 2024, 21(1): 1-27. |
| [18] | WOLFF J A, MALONE R W, WILLIAMS P, et al. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo [J]. Science (New York, NY), 1990, 247(4949 Pt 1): 1465-8. |
| [19] | PARDI N, HOGAN M J, PORTER F W, et al. mRNA vaccines-a new era in vaccinology [J]. Nature reviews Drug discovery, 2018, 17(4): 261-79. |
| [20] | PARDI N, MURAMATSU H, WEISSMAN D, et al. In vitro transcription of long RNA containing modified nucleosides [J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ), 2013, 969: 29-42. |
| [21] | KARIKó K, KUO A, BARNATHAN E. Overexpression of urokinase receptor in mammalian cells following administration of the in vitro transcribed encoding mRNA [J]. Gene therapy, 1999, 6(6): 1092-100. |
| [22] | KALLEN K J, THEß A. A development that may evolve into a revolution in medicine: mRNA as the basis for novel, nucleotide-based vaccines and drugs [J]. Therapeutic advances in vaccines, 2014, 2(1): 10-31. |
| [23] | SHANMUGASUNDARAM M, SENTHILVELAN A, KORE A R. Recent Advances in Modified Cap Analogs: Synthesis, Biochemical Properties, and mRNA Based Vaccines [J]. Chemical record (New York, NY), 2022, 22(8): e202200005. |
| [24] | PASQUINELLI A E, DAHLBERG J E, LUND E. Reverse 5′ caps in RNAs made in vitro by phage RNA polymerases [J]. RNA (New York, NY), 1995, 1(9): 957-67. |
| [25] | JEMIELITY J, FOWLER T, ZUBEREK J, et al. Novel "anti-reverse" cap analogs with superior translational properties [J]. RNA (New York, NY), 2003, 9(9): 1108-22. |
| [26] | MOCKEY M, GONçALVES C, DUPUY F P, et al. mRNA transfection of dendritic cells: synergistic effect of ARCA mRNA capping with Poly(A) chains in cis and in trans for a high protein expression level [J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2006, 340(4): 1062-8. |
| [27] | RAMANATHAN A, ROBB G B, CHAN S H. mRNA capping: biological functions and applications [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2016, 44(16): 7511-26. |
| [28] | DAFFIS S, SZRETTER K J, SCHRIEWER J, et al. 2′-O methylation of the viral mRNA cap evades host restriction by IFIT family members [J]. Nature, 2010, 468(7322): 452-6. |
| [29] | MUHLRAD D, DECKER C J, PARKER R. Turnover mechanisms of the stable yeast PGK1 mRNA [J]. Molecular and cellular biology, 1995, 15(4): 2145-56. |
| [30] | HSU C L, STEVENS A. Yeast cells lacking 5′-->3′ exoribonuclease 1 contain mRNA species that are poly(A) deficient and partially lack the 5′ cap structure [J]. Molecular and cellular biology, 1993, 13(8): 4826-35. |
| [31] | MUKHERJEE D, GAO M, O′CONNOR J P, et al. The mammalian exosome mediates the efficient degradation of mRNAs that contain AU-rich elements [J]. The EMBO journal, 2002, 21(1-2): 165-74. |
| [32] | LIU H, RODGERS N D, JIAO X, et al. The scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme DcpS is a member of the HIT family of pyrophosphatases [J]. The EMBO journal, 2002, 21(17): 4699-708. |
| [33] | MIGNONE F, GISSI C, LIUNI S, et al. Untranslated regions of mRNAs [J]. Genome biology, 2002, 3(3): Reviews0004. |
| [34] | GEBAUER F, HENTZE M W. Molecular mechanisms of translational control [J]. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology, 2004, 5(10): 827-35. |
| [35] | LEPPEK K, DAS R, BARNA M. Functional 5′ UTR mRNA structures in eukaryotic translation regulation and how to find them [J]. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology, 2018, 19(3): 158-74. |
| [36] | PELLETIER J, SONENBERG N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5′ noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency [J]. Cell, 1985, 40(3): 515-26. |
| [37] | LIU T, LIANG Y, HUANG L. Development and Delivery Systems of mRNA Vaccines [J]. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology, 2021, 9: 718753. |
| [38] | KIM S C, SEKHON S S, SHIN W R, et al. Modifications of mRNA vaccine structural elements for improving mRNA stability and translation efficiency [J]. Molecular & cellular toxicology, 2022, 18(1): 1-8. |
| [39] | JIA L, MAO Y, JI Q, et al. Decoding mRNA translatability and stability from the 5′ UTR [J]. Nature structural & molecular biology, 2020, 27(9): 814-21. |
| [40] | HOLCIK M, LIEBHABER S A. Four highly stable eukaryotic mRNAs assemble 3′ untranslated region RNA-protein complexes sharing cis and trans components [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1997, 94(6): 2410-4. |
| [41] | PASCOLO S. Vaccination with messenger RNA (mRNA) [J]. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, 2008, (183): 221-35. |
| [42] | ROSS J, SULLIVAN T D. Half-lives of beta and gamma globin messenger RNAs and of protein synthetic capacity in cultured human reticulocytes [J]. Blood, 1985, 66(5): 1149-54. |
| [43] | HOLTKAMP S, KREITER S, SELMI A, et al. Modification of antigen-encoding RNA increases stability, translational efficacy, and T-cell stimulatory capacity of dendritic cells [J]. Blood, 2006, 108(13): 4009-17. |
| [44] | CHEN C Y, SHYU A B. AU-rich elements: characterization and importance in mRNA degradation [J]. Trends in biochemical sciences, 1995, 20(11): 465-70. |
| [45] | KOZAK M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? [J]. Cell, 1978, 15(4): 1109-23. |
| [46] | GUSTAFSSON C, GOVINDARAJAN S, MINSHULL J. Codon bias and heterologous protein expression [J]. Trends in biotechnology, 2004, 22(7): 346-53. |
| [47] | CANNAROZZI G, SCHRAUDOLPH N N, FATY M, et al. A role for codon order in translation dynamics [J]. Cell, 2010, 141(2): 355-67. |
| [48] | BOSSI L, ROTH J R. The influence of codon context on genetic code translation [J]. Nature, 1980, 286(5769): 123-7. |
| [49] | ZHAO Y, FAN B, SONG X, et al. PEDV-spike-protein-expressing mRNA vaccine protects piglets against PEDV challenge [J]. mBio, 2024, 15(2): e0295823. |
| [50] | WANG Z, TIAN C, ZHU J, et al. Avian influenza mRNA vaccine encoding hemagglutinin provides complete protection against divergent H5N1 viruses in specific-pathogen-free chickens [J]. Journal of nanobiotechnology, 2025, 23(1): 55. |
| [51] | RAUCH S, ROTH N, SCHWENDT K, et al. mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate CVnCoV induces high levels of virus-neutralising antibodies and mediates protection in rodents [J]. NPJ vaccines, 2021, 6(1): 57. |
| [52] | ROTH N, SCHöN J, HOFFMANN D, et al. Optimised Non-Coding Regions of mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine CV2CoV Improves Homologous and Heterologous Neutralising Antibody Responses [J]. Vaccines, 2022, 10(8). |
| [53] | ROTH N, GERGEN J, KOVACIKOVA K, et al. Assessment of Immunogenicity and Efficacy of CV0501 mRNA-Based Omicron COVID-19 Vaccination in Small Animal Models [J]. Vaccines, 2023, 11(2). |
| [54] | MAUGER D M, CABRAL B J, PRESNYAK V, et al. mRNA structure regulates protein expression through changes in functional half-life [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(48): 24075-83. |
| [55] | ZHANG H, ZHANG L, LIN A, et al. Algorithm for optimized mRNA design improves stability and immunogenicity [J]. Nature, 2023, 621(7978): 396-403. |
| [56] | KIMCHI-SARFATY C, OH J M, KIM I W, et al. A "silent" polymorphism in the MDR1 gene changes substrate specificity [J]. Science (New York, NY), 2007, 315(5811): 525-8. |
| [57] | MALARKANNAN S, HORNG T, SHIH P P, et al. Presentation of out-of-frame peptide/MHC class I complexes by a novel translation initiation mechanism [J]. Immunity, 1999, 10(6): 681-90. |
| [58] | SAULQUIN X, SCOTET E, TRAUTMANN L, et al. +1 Frameshifting as a novel mechanism to generate a cryptic cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope derived from human interleukin 10 [J]. The Journal of experimental medicine, 2002, 195(3): 353-8. |
| [59] | SCHWAB S R, LI K C, KANG C, et al. Constitutive display of cryptic translation products by MHC class I molecules [J]. Science (New York, NY), 2003, 301(5638): 1367-71. |
| [60] | GALLIE D R. The cap and poly(A) tail function synergistically to regulate mRNA translational efficiency [J]. Genes & development, 1991, 5(11): 2108-16. |
| [61] | SACHS A B, DAVIS R W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation [J]. Cell, 1989, 58(5): 857-67. |
| [62] | KAREKAR N, REID CAHN A, MORLA-FOLCH J, et al. Protocol for the development of mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccines and analysis of immunization efficiency in mice [J]. STAR protocols, 2024, 5(2): 103087. |
| [63] | POURSEIF M M, MASOUDI-SOBHANZADEH Y, AZARI E, et al. Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines: Mode of action, design, development and optimization [J]. Drug discovery today, 2022, 27(11): 103341. |
| [64] | MARUGGI G, MALLETT C P, WESTERBECK J W, et al. A self-amplifying mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate induces safe and robust protective immunity in preclinical models [J]. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 2022, 30(5): 1897-912. |
| [65] | BRITO L A, KOMMAREDDY S, MAIONE D, et al. Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines [J]. Advances in genetics, 2015, 89: 179-233. |
| [66] | VALLET T, VIGNUZZI M. Self-Amplifying RNA: Advantages and Challenges of a Versatile Platform for Vaccine Development [J]. Viruses, 2025, 17(4). |
| [67] | SILVA-PILIPICH N, BELOKI U, SALABERRY L, et al. Self-Amplifying RNA: A Second Revolution of mRNA Vaccines against COVID-19 [J]. Vaccines, 2024, 12(3). |
| [68] | BLAKNEY A K, IP S, GEALL A J. An Update on Self-Amplifying mRNA Vaccine Development [J]. Vaccines, 2021, 9(2). |
| [69] | VOGEL A B, LAMBERT L, KINNEAR E, et al. Self-Amplifying RNA Vaccines Give Equivalent Protection against Influenza to mRNA Vaccines but at Much Lower Doses [J]. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 2018, 26(2): 446-55. |
| [70] | MCKAY P F, HU K, BLAKNEY A K, et al. Self-amplifying RNA SARS-CoV-2 lipid nanoparticle vaccine candidate induces high neutralizing antibody titers in mice [J]. Nature communications, 2020, 11(1): 3523. |
| [71] | AKAHATA W, SEKIDA T, NOGIMORI T, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 self-amplifying RNA vaccine expressing an anchored RBD: A randomized, observer-blind phase 1 study [J]. Cell reports Medicine, 2023, 4(8): 101134. |
| [72] | BEISSERT T, PERKOVIC M, VOGEL A, et al. A Trans-amplifying RNA Vaccine Strategy for Induction of Potent Protective Immunity [J]. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 2020, 28(1): 119-28. |
| [73] | SPUUL P, BALISTRERI G, HELLSTRöM K, et al. Assembly of alphavirus replication complexes from RNA and protein components in a novel trans-replication system in mammalian cells [J]. Journal of virology, 2011, 85(10): 4739-51. |
| [74] | BLAKNEY A K, MCKAY P F, SHATTOCK R J. Structural Components for Amplification of Positive and Negative Strand VEEV Splitzicons [J]. Frontiers in molecular biosciences, 2018, 5: 71. |
| [75] | SCHMIDT C, HAEFNER E, GERBETH J, et al. A taRNA vaccine candidate induces a specific immune response that protects mice against Chikungunya virus infections [J]. Molecular therapy Nucleic acids, 2022, 28: 743-54. |
| [76] | SCHMIDT C, HASTERT F D, GERBETH J, et al. A Bivalent Trans-Amplifying RNA Vaccine Candidate Induces Potent Chikungunya and Ross River Virus Specific Immune Responses [J]. Vaccines, 2022, 10(9). |
| [77] | ALDON Y, MCKAY P F, MORENO HERRERO J, et al. Immunogenicity of stabilized HIV-1 Env trimers delivered by self-amplifying mRNA [J]. Molecular therapy Nucleic acids, 2021, 25: 483-93. |
| [78] | HICK T A H, GEERTSEMA C, NGUYEN W, et al. Safety concern of recombination between self-amplifying mRNA vaccines and viruses is mitigated in vivo [J]. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 2024, 32(8): 2519-34. |
| [79] | ALLISON A B, STALLKNECHT D E, HOLMES E C. Evolutionary genetics and vector adaptation of recombinant viruses of the western equine encephalitis antigenic complex provides new insights into alphavirus diversity and host switching [J]. Virology, 2015, 474: 154-62. |
| [80] | PUTTARAJU M, BEEN M D. Group I permuted intron-exon (PIE) sequences self-splice to produce circular exons [J]. Nucleic acids research, 1992, 20(20): 5357-64. |
| [81] | FORD E, ARES M, JR. Synthesis of circular RNA in bacteria and yeast using RNA cyclase ribozymes derived from a group I intron of phage T4 [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(8): 3117-21. |
| [82] | CHEN Y G, KIM M V, CHEN X, et al. Sensing Self and Foreign Circular RNAs by Intron Identity [J]. Molecular cell, 2017, 67(2): 228-38.e5. |
| [83] | WESSELHOEFT R A, KOWALSKI P S, ANDERSON D G. Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells [J]. Nature communications, 2018, 9(1): 2629. |
| [84] | QU L, YI Z, SHEN Y, et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants [J]. Cell, 2022, 185(10): 1728-44.e16. |
| [85] | UNTI M J, JAFFREY S R. Highly efficient cellular expression of circular mRNA enables prolonged protein expression [J]. Cell chemical biology, 2024, 31(1): 163-76.e5. |
| [86] | GONG Z, HU W, ZHOU C, et al. Recent advances and perspectives on the development of circular RNA cancer vaccines [J]. NPJ vaccines, 2025, 10(1): 41. |
| [87] | SOKOLOVA N I, ASHIRBEKOVA D T, DOLINNAYA N G, et al. Chemical reactions within DNA duplexes. Cyanogen bromide as an effective oligodeoxyribonucleotide coupling agent [J]. FEBS letters, 1988, 232(1): 153-5. |
| [88] | DOLINNAYA N G, BLUMENFELD M, MERENKOVA I N, et al. Oligonucleotide circularization by template-directed chemical ligation [J]. Nucleic acids research, 1993, 21(23): 5403-7. |
| [89] | WANG S, KOOL E T. Circular RNA oligonucleotides. Synthesis, nucleic acid binding properties, and a comparison with circular DNAs [J]. Nucleic acids research, 1994, 22(12): 2326-33. |
| [90] | MICURA R J C-A E J. Cyclic Oligoribonucleotides (RNA) by Solid‐Phase Synthesis [J]. 1999, 5. |
| [91] | SILBER R, MALATHI V G, HURWITZ J. Purification and properties of bacteriophage T4-induced RNA ligase [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1972, 69(10): 3009-13. |
| [92] | PETKOVIC S, MüLLER S. RNA circularization strategies in vivo and in vitro [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2015, 43(4): 2454-65. |
| [93] | KAUFMANN G, KLEIN T, LITTAUER U Z. T4 RNA ligase: substrate chain length requirements [J]. FEBS letters, 1974, 46(1): 271-5. |
| [94] | SUGINO A, SNOPER T J, COZZARELLI N R. Bacteriophage T4 RNA ligase. Reaction intermediates and interaction of substrates [J]. The Journal of biological chemistry, 1977, 252(5): 1732-8. |
| [95] | ENGLAND T E, UHLENBECK O C. Enzymatic oligoribonucleotide synthesis with T4 RNA ligase [J]. Biochemistry, 1978, 17(11): 2069-76. |
| [96] | ROMANIUK E, MCLAUGHLIN L W, NEILSON T, et al. The effect of acceptor oligoribonucleotide sequence on the T4 RNA ligase reaction [J]. European journal of biochemistry, 1982, 125(3): 639-43. |
| [97] | WANG L, RUFFNER D E. Oligoribonucleotide circularization by ′template-mediated′ ligation with T4 RNA ligase: synthesis of circular hammerhead ribozymes [J]. Nucleic acids research, 1998, 26(10): 2502-4. |
| [98] | FROMMER J, HIERONYMUS R, SELVI ARUNACHALAM T, et al. Preparation of modified long-mer RNAs and analysis of FMN binding to the ypaA aptamer from B. subtilis [J]. RNA biology, 2014, 11(5): 609-23. |
| [99] | BEAUDRY D, PERREAULT J P. An efficient strategy for the synthesis of circular RNA molecules [J]. Nucleic acids research, 1995, 23(15): 3064-6. |
| [100] | HO C K, SHUMAN S. Bacteriophage T4 RNA ligase 2 (gp24.1) exemplifies a family of RNA ligases found in all phylogenetic domains [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(20): 12709-14. |
| [101] | BULLARD D R, BOWATER R P. Direct comparison of nick-joining activity of the nucleic acid ligases from bacteriophage T4 [J]. The Biochemical journal, 2006, 398(1): 135-44. |
| [102] | PETKOVIC S, MüLLER S. RNA self-processing: formation of cyclic species and concatemers from a small engineered RNA [J]. FEBS letters, 2013, 587(15): 2435-40. |
| [103] | YIN S, KIONG HO C, MILLER E S, et al. Characterization of bacteriophage KVP40 and T4 RNA ligase 2 [J]. Virology, 2004, 319(1): 141-51. |
| [104] | LIAO K C, ESHAGHI M, HONG Z, et al. Characterization of group I introns in generating circular RNAs as vaccines [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2025, 53(4). |
| [105] | FENG Z, ZHANG X, ZHOU J, et al. An in vitro-transcribed circular RNA targets the mitochondrial inner membrane cardiolipin to ablate EIF4G2(+)/PTBP1(+) pan-adenocarcinoma [J]. Nature cancer, 2024, 5(1): 30-46. |
| [106] | LIU Y, CUI H, WANG W, et al. Construction of circular miRNA sponges targeting miR-21 or miR-221 and demonstration of their excellent anticancer effects on malignant melanoma cells [J]. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 2013, 45(11): 2643-50. |
| [107] | LIU X, LI Z, LI X, et al. A single-dose circular RNA vaccine prevents Zika virus infection without enhancing dengue severity in mice [J]. Nature communications, 2024, 15(1): 8932. |
| [108] | YUE X, ZHONG C, CAO R, et al. CircRNA based multivalent neuraminidase vaccine induces broad protection against influenza viruses in mice [J]. NPJ vaccines, 2024, 9(1): 170. |
| [109] | MIKHEEVA S, HAKIM-ZARGAR M, CARLSON D, et al. Use of an engineered ribozyme to produce a circular human exon [J]. Nucleic acids research, 1997, 25(24): 5085-94. |
| [110] | SUN Z, LU L, LIU L, et al. Group IIC self-splicing intron-derived novel circular RNA vaccine elicits superior immune response against RSV [J]. Frontiers in immunology, 2025, 16: 1574568. |
| [111] | ZHANG Z, FU Y, JU X, et al. Advances in Engineering Circular RNA Vaccines [J]. Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland), 2024, 13(8). |
| [112] | VINCENT H A, DEUTSCHER M P. Substrate recognition and catalysis by the exoribonuclease RNase R [J]. The Journal of biological chemistry, 2006, 281(40): 29769-75. |
| [113] | XIAO M S, WILUSZ J E. An improved method for circular RNA purification using RNase R that efficiently removes linear RNAs containing G-quadruplexes or structured 3′ ends [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2019, 47(16): 8755-69. |
| [114] | ZHANG Y, YANG L, CHEN L L. Characterization of Circular RNAs [J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ), 2016, 1402: 215-27. |
| [115] | YANG Y, LI H, LI Z, et al. Size-exclusion HPLC provides a simple, rapid, and versatile alternative method for quality control of vaccines by characterizing the assembly of antigens [J]. Vaccine, 2015, 33(9): 1143-50. |
| [116] | WESSELHOEFT R A, KOWALSKI P S, PARKER-HALE F C, et al. RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration In Vivo [J]. Molecular cell, 2019, 74(3): 508-20.e4. |
| [117] | CHEN N, XIA P, LI S, et al. RNA sensors of the innate immune system and their detection of pathogens [J]. IUBMB life, 2017, 69(5): 297-304. |
| [118] | KARIKó K, MURAMATSU H, LUDWIG J, et al. Generating the optimal mRNA for therapy: HPLC purification eliminates immune activation and improves translation of nucleoside-modified, protein-encoding mRNA [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2011, 39(21): e142. |
| [119] | DE HARO C, MéNDEZ R, SANTOYO J. The eIF-2alpha kinases and the control of protein synthesis [J]. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 1996, 10(12): 1378-87. |
| [120] | LIANG S L, QUIRK D, ZHOU A. RNase L: its biological roles and regulation [J]. IUBMB life, 2006, 58(9): 508-14. |
| [121] | ZHANG Z, OHTO U, SHIBATA T, et al. Structural Analysis Reveals that Toll-like Receptor 7 Is a Dual Receptor for Guanosine and Single-Stranded RNA [J]. Immunity, 2016, 45(4): 737-48. |
| [122] | TANJI H, OHTO U, SHIBATA T, et al. Toll-like receptor 8 senses degradation products of single-stranded RNA [J]. Nature structural & molecular biology, 2015, 22(2): 109-15. |
| [123] | ISAACS A, COX R A, ROTEM Z. Foreign nucleic acids as the stimulus to make interferon [J]. Lancet (London, England), 1963, 2(7299): 113-6. |
| [124] | KARIKó K, MURAMATSU H, WELSH F A, et al. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability [J]. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 2008, 16(11): 1833-40. |
| [125] | ANDRIES O, CAFFERTY S MC, DE SMEDT S C, et al. N(1)-methylpseudouridine-incorporated mRNA outperforms pseudouridine-incorporated mRNA by providing enhanced protein expression and reduced immunogenicity in mammalian cell lines and mice [J]. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 2015, 217: 337-44. |
| [126] | ANDERSON B R, MURAMATSU H, NALLAGATLA S R, et al. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2010, 38(17): 5884-92. |
| [127] | ANDERSON B R, MURAMATSU H, JHA B K, et al. Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2011, 39(21): 9329-38. |
| [128] | KARIKó K, BUCKSTEIN M, NI H, et al. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA [J]. Immunity, 2005, 23(2): 165-75. |
| [129] | POLACK F P, THOMAS S J, KITCHIN N, et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine [J]. The New England journal of medicine, 2020, 383(27): 2603-15. |
| [130] | KREMSNER P G, AHUAD GUERRERO R A, ARANA-ARRI E, et al. Efficacy and safety of the CVnCoV SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine candidate in ten countries in Europe and Latin America (HERALD): a randomised, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial [J]. The Lancet Infectious diseases, 2022, 22(3): 329-40. |
| [131] | LORENZ C, FOTIN-MLECZEK M, ROTH G, et al. Protein expression from exogenous mRNA: uptake by receptor-mediated endocytosis and trafficking via the lysosomal pathway [J]. RNA biology, 2011, 8(4): 627-36. |
| [132] | VALADI H, EKSTRöM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells [J]. Nature cell biology, 2007, 9(6): 654-9. |
| [133] | DIKEN M, KREITER S, SELMI A, et al. Selective uptake of naked vaccine RNA by dendritic cells is driven by macropinocytosis and abrogated upon DC maturation [J]. Gene therapy, 2011, 18(7): 702-8. |
| [134] | BENTEYN D, HEIRMAN C, BONEHILL A, et al. mRNA-based dendritic cell vaccines [J]. Expert review of vaccines, 2015, 14(2): 161-76. |
| [135] | DAS R, GE X, FEI F, et al. Lipid Nanoparticle-mRNA Engineered Dendritic Cell Based Adoptive Cell Therapy Enhances Cancer Immune Response [J]. Small methods, 2025, 9(1): e2400633. |
| [136] | WYKES M, POMBO A, JENKINS C, et al. Dendritic cells interact directly with naive B lymphocytes to transfer antigen and initiate class switching in a primary T-dependent response [J]. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950), 1998, 161(3): 1313-9. |
| [137] | SELMI A, VASCOTTO F, KAUTZ-NEU K, et al. Uptake of synthetic naked RNA by skin-resident dendritic cells via macropinocytosis allows antigen expression and induction of T-cell responses in mice [J]. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, 2016, 65(9): 1075-83. |
| [138] | BERNEMAN Z N, DE LAERE M, GERMONPRé P, et al. WT1-mRNA dendritic cell vaccination of patients with glioblastoma multiforme, malignant pleural mesothelioma, metastatic breast cancer, and other solid tumors: type 1 T-lymphocyte responses are associated with clinical outcome [J]. Journal of hematology & oncology, 2025, 18(1): 9. |
| [139] | GóMEZ-AGUADO I, RODRíGUEZ-CASTEJóN J, VICENTE-PASCUAL M, et al. Nanomedicines to Deliver mRNA: State of the Art and Future Perspectives [J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 10(2). |
| [140] | MALONE R W, FELGNER P L, VERMA I M. Cationic liposome-mediated RNA transfection [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1989, 86(16): 6077-81. |
| [141] | ZOHRA F T, CHOWDHURY E H, TADA S, et al. Effective delivery with enhanced translational activity synergistically accelerates mRNA-based transfection [J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2007, 358(1): 373-8. |
| [142] | LU D, BENJAMIN R, KIM M, et al. Optimization of methods to achieve mRNA-mediated transfection of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo employing cationic liposome vectors [J]. Cancer gene therapy, 1994, 1(4): 245-52. |
| [143] | ZOHRA F T, CHOWDHURY E H, NAGAOKA M, et al. Drastic effect of nanoapatite particles on liposome-mediated mRNA delivery to mammalian cells [J]. Analytical biochemistry, 2005, 345(1): 164-6. |
| [144] | ZOHRA F T, MAITANI Y, AKAIKE T. mRNA delivery through fibronectin associated liposome-apatite particles: a new approach for enhanced mRNA transfection to mammalian cell [J]. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin, 2012, 35(1): 111-5. |
| [145] | KAUFFMAN K J, DORKIN J R, YANG J H, et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for mRNA Delivery in Vivo with Fractional Factorial and Definitive Screening Designs [J]. Nano letters, 2015, 15(11): 7300-6. |
| [146] | DEL POZO-RODRíGUEZ A, SOLINíS M, RODRíGUEZ-GASCóN A. Applications of lipid nanoparticles in gene therapy [J]. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik eV, 2016, 109: 184-93. |
| [147] | BOGERS W M, OOSTERMEIJER H, MOOIJ P, et al. Potent immune responses in rhesus macaques induced by nonviral delivery of a self-amplifying RNA vaccine expressing HIV type 1 envelope with a cationic nanoemulsion [J]. The Journal of infectious diseases, 2015, 211(6): 947-55. |
| [148] | LUISI K, MORABITO K M, BURGOMASTER K E, et al. Development of a potent Zika virus vaccine using self-amplifying messenger RNA [J]. Science advances, 2020, 6(32): eaba5068. |
| [149] | KAUFFMAN K J, WEBBER M J, ANDERSON D G. Materials for non-viral intracellular delivery of messenger RNA therapeutics [J]. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 2016, 240: 227-34. |
| [150] | HE X, LI G, HUANG L, et al. Nonviral targeted mRNA delivery: principles, progresses, and challenges [J]. MedComm, 2025, 6(1): e70035. |
| [151] | TILSTRA G, COUTURE-SENéCAL J, LAU Y M A, et al. Iterative Design of Ionizable Lipids for Intramuscular mRNA Delivery [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(4): 2294-304. |
| [152] | OYAMA R, ISHIGAME H, TANAKA H, et al. An Ionizable Lipid Material with a Vitamin E Scaffold as an mRNA Vaccine Platform for Efficient Cytotoxic T Cell Responses [J]. ACS nano, 2023, 17(19): 18758-74. |
| [153] | TANG Q, LIU J, JIANG Y, et al. Cell-Selective Messenger RNA Delivery and CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing by Modulating the Interface of Phenylboronic Acid-Derived Lipid Nanoparticles and Cellular Surface Sialic Acid [J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2019, 11(50): 46585-90. |
| [154] | BAE S H, YOO S, LEE J, et al. A lipid nanoparticle platform incorporating trehalose glycolipid for exceptional mRNA vaccine safety [J]. Bioactive materials, 2024, 38: 486-98. |
| [155] | AI L, LI Y, ZHOU L, et al. Lyophilized mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccines with long-term stability and high antigenicity against SARS-CoV-2 [J]. Cell discovery, 2023, 9(1): 9. |
| [156] | GUAN S, ROSENECKER J. Nanotechnologies in delivery of mRNA therapeutics using nonviral vector-based delivery systems [J]. Gene therapy, 2017, 24(3): 133-43. |
| [157] | AKINC A, THOMAS M, KLIBANOV A M, et al. Exploring polyethylenimine-mediated DNA transfection and the proton sponge hypothesis [J]. The journal of gene medicine, 2005, 7(5): 657-63. |
| [158] | KUNATH K, VON HARPE A, FISCHER D, et al. Low-molecular-weight polyethylenimine as a non-viral vector for DNA delivery: comparison of physicochemical properties, transfection efficiency and in vivo distribution with high-molecular-weight polyethylenimine [J]. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 2003, 89(1): 113-25. |
| [159] | GUO X, YANG Z, GUO Z, et al. A Polymeric mRNA Vaccine Featuring Enhanced Site-Specific mRNA Delivery and Inherent STING-Stimulating Performance for Tumor Immunotherapy [J]. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2025, 37(17): e2410998. |
| [160] | CHEN Q, CHANG Y, HE X, et al. Targeted Delivery of mRNA with Polymer-Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Base Editing [J]. ACS nano, 2025, 19(8): 7835-50. |
| [161] | TANG Z, YOU X, XIAO Y, et al. Inhaled mRNA nanoparticles dual-targeting cancer cells and macrophages in the lung for effective transfection [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(44): e2304966120. |
| [162] | MCCARTHY H O, MCCAFFREY J, MCCRUDDEN C M, et al. Development and characterization of self-assembling nanoparticles using a bio-inspired amphipathic peptide for gene delivery [J]. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 2014, 189: 141-9. |
| [163] | QIU Y, MAN R C H, LIAO Q, et al. Effective mRNA pulmonary delivery by dry powder formulation of PEGylated synthetic KL4 peptide [J]. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society, 2019, 314: 102-15. |
| [164] | JARZEBSKA N T, MELLETT M, FREI J, et al. Protamine-Based Strategies for RNA Transfection [J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(6). |
| [165] | KALLEN K J, HEIDENREICH R, SCHNEE M, et al. A novel, disruptive vaccination technology: self-adjuvanted RNActive(®) vaccines [J]. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics, 2013, 9(10): 2263-76. |
| [166] | PAPACHRISTOFILOU A, HIPP M M, KLINKHARDT U, et al. Phase Ib evaluation of a self-adjuvanted protamine formulated mRNA-based active cancer immunotherapy, BI1361849 (CV9202), combined with local radiation treatment in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Journal for immunotherapy of cancer, 2019, 7(1): 38. |
| [167] | ALBERER M, GNAD-VOGT U, HONG H S, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a mRNA rabies vaccine in healthy adults: an open-label, non-randomised, prospective, first-in-human phase 1 clinical trial [J]. Lancet (London, England), 2017, 390(10101): 1511-20. |
| [168] | SEBASTIAN M, SCHRöDER A, SCHEEL B, et al. A phase I/IIa study of the mRNA-based cancer immunotherapy CV9201 in patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, 2019, 68(5): 799-812. |
| [169] | ZHAN S, LI J, XU R, et al. Armored long RNA controls or standards for branched DNA assay for detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 [J]. Journal of clinical microbiology, 2009, 47(8): 2571-6. |
| [170] | CALDEIRA J C, PEABODY D S. Thermal stability of RNA phage virus-like particles displaying foreign peptides [J]. Journal of nanobiotechnology, 2011, 9: 22. |
| [171] | LI J, SUN Y, JIA T, et al. Messenger RNA vaccine based on recombinant MS2 virus-like particles against prostate cancer [J]. International journal of cancer, 2014, 134(7): 1683-94. |
| [172] | WANG G, JIA T, XU X, et al. Novel miR-122 delivery system based on MS2 virus like particle surface displaying cell-penetrating peptide TAT for hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(37): 59402-16. |
| [173] | BIDDLECOME A, HABTE H H, MCGRATH K M, et al. Delivery of self-amplifying RNA vaccines in in vitro reconstituted virus-like particles [J]. PloS one, 2019, 14(6): e0215031. |
| [174] | ABOSHI M, MATSUDA K, KAWAKAMI D, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of VLPCOV-02, a SARS-CoV-2 self-amplifying RNA vaccine with a modified base, 5-methylcytosine [J]. iScience, 2024, 27(2): 108964. |
| [175] | ZHANG P, FALCONE S, TSYBOVSKY Y, et al. Increased neutralization potency and breadth elicited by a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine forming virus-like particles [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(29): e2305896120. |
| [176] | SOMINSKAYA I, SKRASTINA D, PETROVSKIS I, et al. A VLP library of C-terminally truncated Hepatitis B core proteins: correlation of RNA encapsidation with a Th1/Th2 switch in the immune responses of mice [J]. PloS one, 2013, 8(9): e75938. |
| [177] | ZHANG P, NARAYANAN E, LIU Q, et al. A multiclade env-gag VLP mRNA vaccine elicits tier-2 HIV-1-neutralizing antibodies and reduces the risk of heterologous SHIV infection in macaques [J]. Nature medicine, 2021, 27(12): 2234-45. |
| [178] | MADIGAN V, ZHANG Y, RAGHAVAN R, et al. Human paraneoplastic antigen Ma2 (PNMA2) forms icosahedral capsids that can be engineered for mRNA delivery [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(11): e2307812120. |
| [1] | YE Qing, QIN Chengfeng. Development of mRNA vaccines in response to the Public Health Emergency of International Concern [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(2): 310-320. |
| [2] | LIU Zezhong, ZHOU Jie, ZHU Yun, LU Lu, JIANG Shibo. Applications of the recombinant human collagen type Ⅲ-based trimerization motif in the design of vaccines to fight against SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(2): 385-395. |
| [3] | LIN Sisi, PAN Chao, ZHANG Yifan, LIU Jinyao. Coated probiotic-based drug carriers for oral delivery of tumor antigens [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 810-820. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||