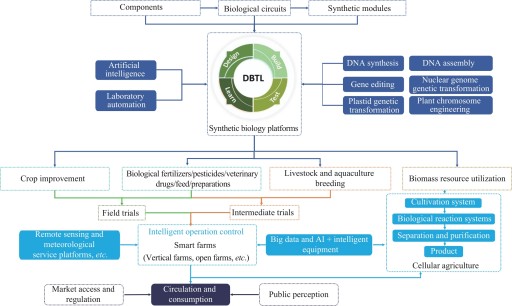
Agricultural synthetic biology, an emerging interdisciplinary field, synergistically integrates fundamental principles from biology, engineering and computer science, and is dedicated to advancing agricultural production towards greater efficiency and sustainability by innovatively designing and engineering of biological systems. In recent years, governments worldwide have accelerated the development of this field through the combined efforts of policy initiatives and technological innovation. Countries and regions including the United States, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and Australia have introduced policies to explicitly support the research and application of key technologies, such as gene editing and metabolic engineering, in the agricultural field. These supportive frameworks have greatly advanced the global development of agricultural synthetic biology. In China, active efforts are being made to construct an integrated innovation ecosystem connecting industry, academia, and research institutions, with the goal of accelerating the industrialization of agricultural synthetic biology technologies. Currently, several technologies have achieved initial commercial applications in areas such as breeding, food and feed production, and biological pesticides. In crop breeding, precise genome editing enables the development of varieties with enhanced yield, improved nutritional quality, and greater resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. In the field of food and feed, genetic engineering is employed to modify microorganisms to produce enzyme preparations that improve feed digestibility and nutritional value, as well as to develop microbial-based biopreservatives to replace chemical preservatives, or natural-source coatings that extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables. Additionally, biological pesticides derived from natural microorganisms, plant extracts or insect pheromones can effectively reduce the impact on soil, water sources and ecosystems, while reducing the risk of residues. These products are increasingly applied in crop protection, and offer sustainable alternatives for reducing environmental pollution while safeguarding food safety. Several innovative enterprises worldwide have provided valuable experience and insights into the development and application of agricultural microbial products. These companies not only demonstrate effective pathways for translating laboratory research into practical products, but also offer business models that serve as valuable references for the broader industry. Simultaneously, a number of Chinese enterprises are actively exploring the application of synthetic biology to improve crop breeding, enhance crop resistance to stress and diseases, and develop biopesticides, biofertilizers, and new bio-based materials. Some are employing synthetic biology approaches to improve crop performance under adverse environmental conditions or to enhance soil health by optimizing microbial community structures. Despite recent breakthroughs, the continued development of agricultural synthetic biology still faces numerous challenges, including limited market acceptance, underdeveloped regulatory frameworks, insufficient capital investments, and persistent technological bottlenecks. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted, multi-faceted approach that integrates policy guidance, technological innovation, and industrial upgrading. It is essential to foster synergistic development across key domains, including the engineering of non-food crops, the expansion of photoautotrophic microbial platforms, and the advancement of carbon capture and utilization technologies. At the same time, interdisciplinary collaboration should be strengthened to encourage more research institutions and enterprises to engage in this field. Through the combined forces of supportive policies and increased capital investment, barriers such as ecological risk assessment can be effectively addressed, thereby accelerating the commercialization of new products. Governments must act promptly to establish clear, science-based regulatory pathways that ensure the safety and efficacy of emerging agricultural biotechnologies, at the same time investors should recognize the transformative potential of this field and provide financial support for startups and research initiatives. Ultimately, the goal is to catalyze a global agricultural transformation that ensures food security for a growing population, mitigates the impacts of climate change, and promotes ecological conservation and restoration. Through collaborative efforts among all stakeholders, agricultural synthetic biology has the potential to become a driving force for advancing modern agriculture and building a greener, healthier, and more sustainable future for humanity.