Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (5): 1025-1040.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-094
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Strategies and prospects of synthetic biology in crop photosynthesis
SUN Yang, CHEN Lichao, SHI Yanyun, WANG Ke, LV Dandan, XU Xiumei, ZHANG Lixin
- State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Adaptation and Improvement,Henan Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology and Biomanufacturing,School of Life Sciences,Henan University,Kaifeng 475004,Henan,China
-
Received:2024-12-17Revised:2025-03-12Online:2025-11-05Published:2025-10-31 -
Contact:ZHANG Lixin
作物光合作用合成生物学的策略与展望
孙扬, 陈立超, 石艳云, 王珂, 吕丹丹, 徐秀美, 张立新
- 河南大学生命科学学院,省部共建作物逆境适应与改良国家重点实验室,河南省合成生物与生物制造重点实验室,河南 开封 475004
-
通讯作者:张立新 -
作者简介:孙扬 (1993—),男,讲师,硕士生导师。研究方向为逆境下光合作用调控机制以及光合作用合成生物学。E-mail:sunyy@henu.edu.cn张立新 (1970—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为光合作用功能调控机理,包括叶绿体基因表达调控、光合膜复合物组装、叶绿体信号转导、光合作用环境调节等。 E-mail:zhanglixin@henu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2020YFA0907600);国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2023YFA0914601);河南省中原学者项目(234000510005)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SUN Yang, CHEN Lichao, SHI Yanyun, WANG Ke, LV Dandan, XU Xiumei, ZHANG Lixin. Strategies and prospects of synthetic biology in crop photosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1025-1040.
孙扬, 陈立超, 石艳云, 王珂, 吕丹丹, 徐秀美, 张立新. 作物光合作用合成生物学的策略与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1025-1040.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-094
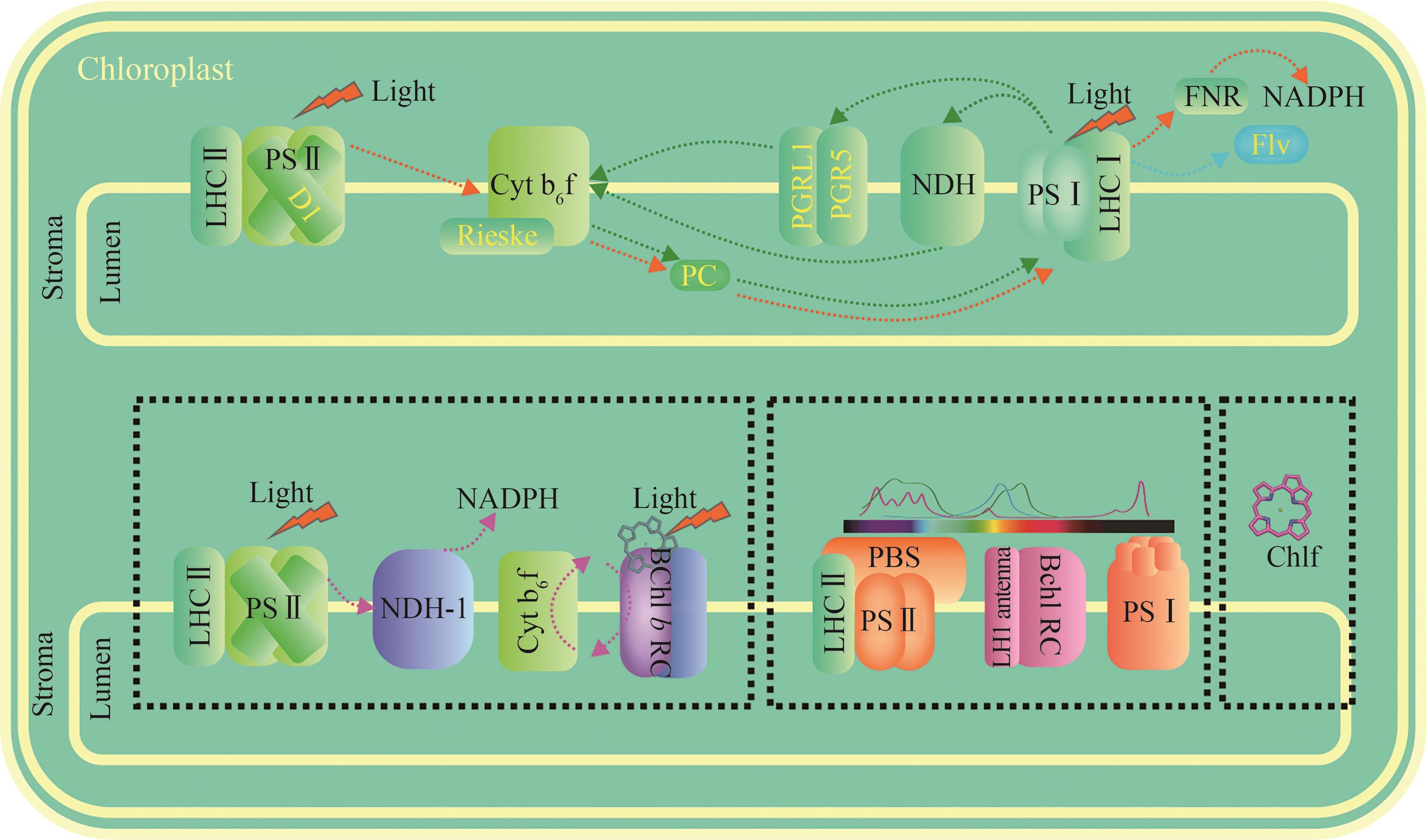
Fig. 1 Engineering of photosynthetic electron transport and design of novel light-energy conversion models[The upper section illustrates modifications of electron transport on the existing photosynthetic membrane system, with target proteins experimentally modified being highlighted in yellow. Linear and cyclic electron transport are indicated by orange and green dashed arrows, respectively. The lower section, enclosed within a black dashed box, depicts novel light energy conversion models/projects currently under design (awaiting experimental validation). From left to right, these include: (1) the new photosynthetic reaction center and electron transfer model designed by Ort et al. [13], (2) the novel light-harvesting model proposed by Leister [11], and (3) the introduction of chlorophyll f into the photosystems of higher plants [14]. Purple dashed arrows indicate potential electron transport pathways.]
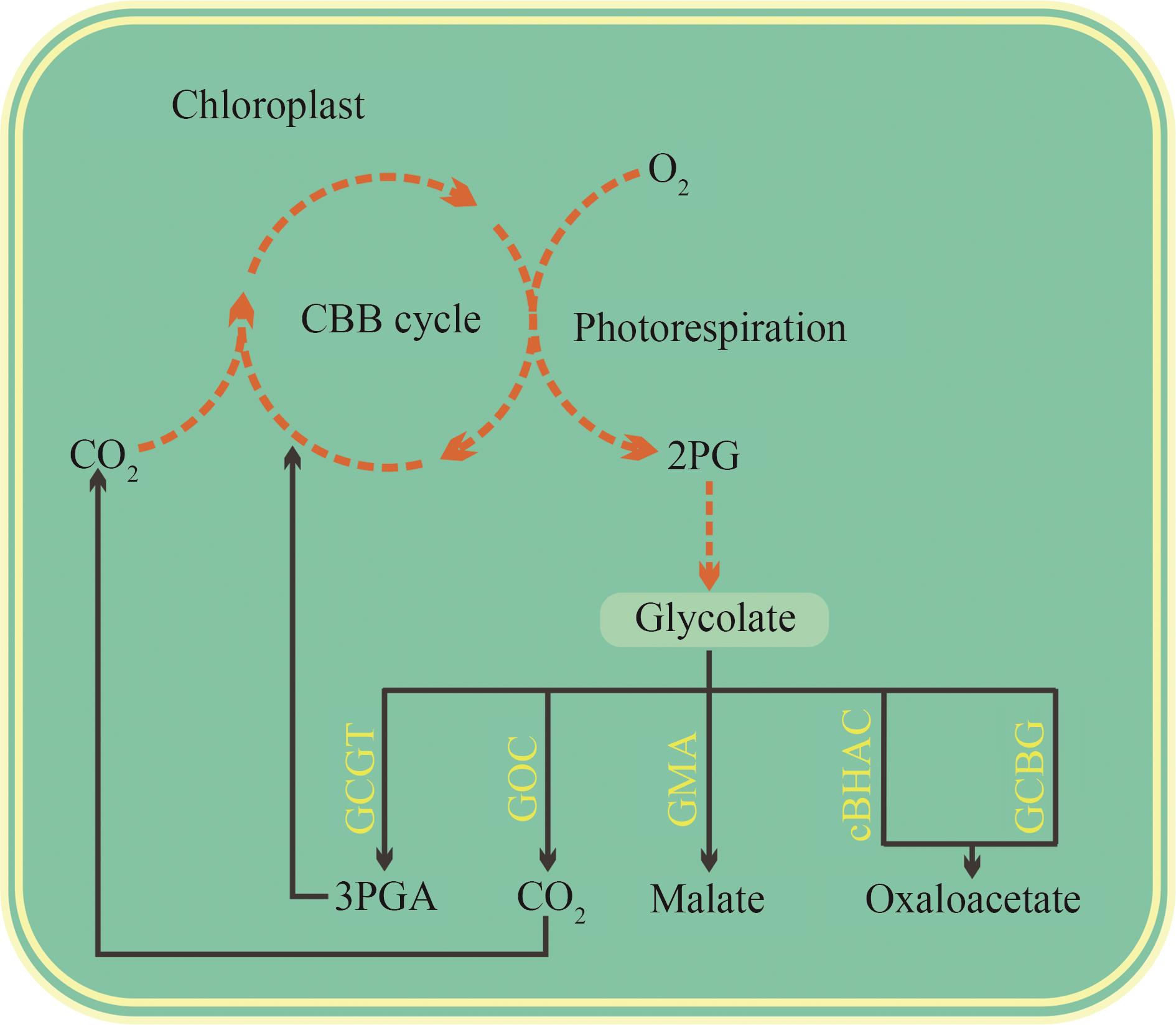
Fig. 3 Current photorespiratory bypasses constructed in rice.[The photorespiratory bypasses engineered in rice (highlighted in yellow) directly metabolize glycolate within chloroplasts (indicated by black solid arrows), aiming to reduce carbon loss associated with photorespiration and thereby enhance the carbon fixation efficiency of the CBB cycle.]
| [74] | SAGE R F, CHRISTIN P A, EDWARDS E J. The C4 plant lineages of planet Earth[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(9): 3155-3169. |
| [75] | SAGE R F, SAGE T L, KOCACINAR F. Photorespiration and the evolution of C4 photosynthesis[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63: 19-47. |
| [76] | YAMORI W, HIKOSAKA K, WAY D A. Temperature response of photosynthesis in C3, C4, and CAM plants: temperature acclimation and temperature adaptation[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2014, 119(1): 101-117. |
| [77] | LONG B M, HEE W Y, SHARWOOD R E, et al. Carboxysome encapsulation of the CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3570. |
| [78] | RAE B D, LONG B M, FÖRSTER B, et al. Progress and challenges of engineering a biophysical CO2-concentrating mechanism into higher plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(14): 3717-3737. |
| [79] | HE S, CRANS V L, JONIKAS M C. The pyrenoid: the eukaryotic CO2-concentrating organelle[J]. The Plant Cell, 2023, 35(9): 3236-3259. |
| [80] | LONG B M, RAE B D, ROLLAND V, et al. Cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating mechanism components: function and prospects for plant metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2016, 31: 1-8. |
| [81] | HIBBERD J M, QUICK W P. Characteristics of C4 photosynthesis in stems and petioles of C3 flowering plants[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6870): 451-454. |
| [82] | SCHULER M L, MANTEGAZZA O, WEBER A P M. Engineering C4 photosynthesis into C3 chassis in the synthetic biology age[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 87(1): 51-65. |
| [83] | CHEN T Y, HOJKA M, DAVEY P, et al. Engineering α-carboxysomes into plant chloroplasts to support autotrophic photosynthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 2118. |
| [84] | QIN K Z, YE X Y, LUO S S, et al. Engineering carbon assimilation in plants[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2025, 67(4): 926-948. |
| [85] | FEI C Y, WILSON A T, MANGAN N M, et al. Modelling the pyrenoid-based CO2-concentrating mechanism provides insights into its operating principles and a roadmap for its engineering into crops[J]. Nature Plants, 2022, 8(5): 583-595. |
| [86] | ATKINSON N, MAO Y W, CHAN K X, et al. Condensation of Rubisco into a proto-pyrenoid in higher plant chloroplasts[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 6303. |
| [87] | 凌丽俐, 林宏辉, 焦德茂. 转PEPC基因水稻种质的稳定光合生理特性[J]. 作物学报, 2006, 32(4): 527-531. |
| LING L L, LIN H H, JIAO D M. The stable photosynthetic characteristics of a PEPC transgenic rice germplasm[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006, 32(4): 527-531. | |
| [88] | ERMAKOVA M, ARRIVAULT S, GIULIANI R, et al. Installation of C4 photosynthetic pathway enzymes in rice using a single construct[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(3): 575-588. |
| [89] | SWIFT J, LUGINBUEHL L H, HUA L, et al. Exaptation of ancestral cell-identity networks enables C4 photosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2024, 636(8041): 143-150. |
| [90] | SEDELNIKOVA O V, HUGHES T E, LANGDALE J A. Understanding the genetic basis of C4 Kranz anatomy with a view to engineering C3 crops[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2018, 52: 249-270. |
| [91] | BAUWE H. Photorespiration-Rubisco’s repair crew[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2023, 280: 153899. |
| [92] | SOUTH P F, CAVANAGH A P, LIU H W, et al. Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6422): eaat9077. |
| [93] | ROELL M S, SCHADA VON BORZYKOWSKI L, WESTHOFF P, et al. A synthetic C4 shuttle via the β-hydroxyaspartate cycle in C3 plants[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(21): e2022307118. |
| [94] | SHEN B R, WANG L M, LIN X L, et al. Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(2): 199-214. |
| [95] | WANG L M, SHEN B R, LI B D, et al. A synthetic photorespiratory shortcut enhances photosynthesis to boost biomass and grain yield in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(12): 1802-1815. |
| [96] | XU H W, WANG H H, ZHANG Y W, et al. A synthetic light-inducible photorespiratory bypass enhances photosynthesis to improve rice growth and grain yield[J]. Plant Communications, 2023, 4(6): 100641. |
| [97] | CHEN G X, LI Y N, JIN K N, et al. Synthetic photorespiratory bypass improves rice productivity by enhancing photosynthesis and nitrogen uptake[J]. The Plant Cell, 2025, 37(1): koaf015. |
| [98] | ERB T J. Photosynthesis 2.0: realizing new-to-nature CO2-fixation to overcome the limits of natural metabolism[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2024, 16(2): a041669. |
| [99] | SCHEFFEN M, MARCHAL D G, BENEYTON T, et al. A new-to-nature carboxylation module to improve natural and synthetic CO2 fixation[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(2): 105-115. |
| [100] | CHI W, SUN X W, ZHANG L X. The roles of chloroplast proteases in the biogenesis and maintenance of photosystem Ⅱ[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2012, 1817(1): 239-246. |
| [101] | MU X H, CHEN Q W, CHEN F J, et al. Within-leaf nitrogen allocation in adaptation to low nitrogen supply in maize during grain-filling stage[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 699. |
| [102] | SHARMA A, KUMAR V, SINGH R, et al. Effect of seed pre-soaking with 24-epibrassinolide on growth and photosynthetic parameters of Brassica juncea L. in imidacloprid soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 133: 195-201. |
| [103] | SHARMA A, SHAHZAD B, KUMAR V, et al. Phytohormones regulate accumulation of osmolytes under abiotic stress[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(7): 285. |
| [104] | KAUR R, YADAV P, SHARMA A, et al. Castasterone and citric acid treatment restores photosynthetic attributes in Brassica juncea L. under Cd(Ⅱ) toxicity[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 145: 466-475. |
| [105] | DEMMIG-ADAMS B, STEWART J J, BAKER C R, et al. Optimization of photosynthetic productivity in contrasting environments by regulons controlling plant form and function[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(3): 872. |
| [106] | KOHLI S K, HANDA N, SHARMA A, et al. Interaction of 24-epibrassinolide and salicylic acid regulates pigment contents, antioxidative defense responses, and gene expression in Brassica juncea L. seedlings under Pb stress[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(15): 15159-15173. |
| [107] | PAUNOV M, KOLEVA L, VASSILEV A, et al. Effects of different metals on photosynthesis: cadmium and zinc affect chlorophyll fluorescence in durum wheat[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(3): 787. |
| [108] | SOARES C, BRANCO-NEVES S, DE SOUSA A, et al. SiO2 nanomaterial as a tool to improve Hordeum vulgare L. tolerance to nano-NiO stress[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622-623: 517-525. |
| [109] | YADAV P, KAUR R, KANWAR M K, et al. Castasterone confers copper stress tolerance by regulating antioxidant enzyme responses, antioxidants, and amino acid balance in B. juncea seedlings[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 147: 725-734. |
| [110] | XIA X J, HUANG Y Y, WANG L, et al. Pesticides-induced depression of photosynthesis was alleviated by 24-epibrassinolide pretreatment in Cucumis sativus L[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2006, 86(1): 42-48. |
| [111] | KALAJI H M, JAJOO A, OUKARROUM A, et al. Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(4): 102. |
| [112] | SHARMA A, THAKUR S, KUMAR V, et al. Pre-sowing seed treatment with 24-epibrassinolide ameliorates pesticide stress in Brassica juncea L. through the modulation of stress markers[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1569. |
| [113] | GURURANI M A, VENKATESH J, TRAN L S P. Regulation of photosynthesis during abiotic stress-induced photoinhibition[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(9): 1304-1320. |
| [114] | CHAVES M M, FLEXAS J, PINHEIRO C. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell[J]. Annals of Botany, 2009, 103(4): 551-560. |
| [115] | ZHANG X F, ZHANG X H, GAO B, et al. Effect of cadmium on growth, photosynthesis, mineral nutrition and metal accumulation of an energy crop, king grass (Pennisetum americanum × P. purpureum)[J]. Biomass & Bioenergy, 2014, 67: 179-187. |
| [116] | KOHLI S K, HANDA N, SHARMA A, et al. Synergistic effect of 24-epibrassinolide and salicylic acid on photosynthetic efficiency and gene expression in Brassica juncea L. under Pb stress[J]. Turkish Journal of Biology, 2017, 41(6): 943-953. |
| [117] | MUHAMMAD I, SHALMANI A, ALI M, et al. Mechanisms regulating the dynamics of photosynthesis under abiotic stresses[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 11: 615942. |
| [118] | RUBAN A V. Nonphotochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching: mechanism and effectiveness in protecting plants from photodamage[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(4): 1903-1916. |
| [119] | CAZZANIGA S, DALL′OSTO L, KONG S G, et al. Interaction between avoidance of photon absorption, excess energy dissipation and Zeaxanthin synthesis against photooxidative stress in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 76(4): 568-579. |
| [120] | ZHU X G, ORT D R, WHITMARSH J, et al. The slow reversibility of photosystem Ⅱ thermal energy dissipation on transfer from high to low light may cause large losses in carbon gain by crop canopies: a theoretical analysis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(400): 1167-1175. |
| [121] | HUANG W, HU H, ZHANG S B. Photorespiration plays an important role in the regulation of photosynthetic electron flow under fluctuating light in tobacco plants grown under full sunlight[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 621. |
| [122] | LAUREAU C, DE PAEPE R, LATOUCHE G, et al. Plastid terminal oxidase (PTOX) has the potential to act as a safety valve for excess excitation energy in the alpine plant species Ranunculus glacialis L.[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2013, 36(7): 1296-1310. |
| [1] | LEISTER D. Genetic engineering, synthetic biology and the light reactions of photosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 179(3): 778-793. |
| [2] | LONG S P, AINSWORTH E A, LEAKEY A D B, et al. Global food insecurity. Treatment of major food crops with elevated carbon dioxide or ozone under large-scale fully open-air conditions suggests recent models may have overestimated future yields[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2005, 360(1463): 2011-2020. |
| [3] | 张立新, 卢从明, 彭连伟, 等. 利用合成生物学原理提高光合作用效率的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 486-493. |
| ZHANG L X, LU C M, PENG L W, et al. Progress in improving photosynthetic efficiency by synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 486-493. | |
| [4] | 朱新广, 熊燕, 阮梅花, 等. 光合作用合成生物学研究现状及未来发展策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1239-1248. |
| ZHU X G, XIONG Y, RUAN M H, et al. Research status and future development strategies of synthetic biology in photosynthesis[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1239-1248. | |
| [5] | DRUBIN D A, WAY J C, SILVER P A. Designing biological systems[J]. Genes & Development, 2007, 21(3): 242-254. |
| [6] | ZHAO Y, COELHO C, HUGHES A L, et al. Debugging and consolidating multiple synthetic chromosomes reveals combinatorial genetic interactions[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(24): 5220-5236.e16. |
| [7] | SCHINDLER D, WALKER R S K, JIANG S Y, et al. Design, construction, and functional characterization of a tRNA neochromosome in yeast[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(24): 5237-5253.e22. |
| [8] | ZHANG W M, LAZAR-STEFANITA L, YAMASHITA H, et al. Manipulating the 3D organization of the largest synthetic yeast chromosome[J]. Molecular Cell, 2023, 83(23): 4424-4437.e5. |
| [9] | HANANIA U, ARIEL T, TEKOAH Y, et al. Establishment of a tobacco BY2 cell line devoid of plant-specific xylose and fucose as a platform for the production of biotherapeutic proteins[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(9): 1120-1129. |
| [10] | ČERMÁK T, CURTIN S J, GIL-HUMANES J, et al. A multipurpose toolkit to enable advanced genome engineering in plants[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(6): 1196-1217. |
| [11] | LEISTER D. Enhancing the light reactions of photosynthesis: strategies, controversies, and perspectives[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(1): 4-22. |
| [12] | BAG P, CHUKHUTSINA V, ZHANG Z S, et al. Direct energy transfer from photosystem Ⅱ to photosystem Ⅰ confers winter sustainability in Scots pine[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 6388. |
| [13] | ORT D R, MERCHANT S S, ALRIC J, et al. Redesigning photosynthesis to sustainably meet global food and bioenergy demand[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(28): 8529-8536. |
| [14] | CHEN M, BLANKENSHIP R E. Expanding the solar spectrum used by photosynthesis[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2011, 16(8): 427-431. |
| [15] | ROCHAIX J D. Regulation and dynamics of the light-harvesting system[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2014, 65: 287-309. |
| [16] | NÜRNBERG D J, MORTON J, SANTABARBARA S, et al. Photochemistry beyond the red limit in chlorophyll f-containing photosystems[J]. Science,2018, 360(6394): 1210-1213. |
| [17] | CHEN M, SCHLIEP M, WILLOWS R D, et al. A red-shifted chlorophyll[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5997): 1318-1319. |
| [18] | KATO K, SHINODA T, NAGAO R, et al. Structural basis for the adaptation and function of chlorophyll f in photosystem Ⅰ[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 238. |
| [19] | BLANKENSHIP R E, TIEDE D M, BARBER J, et al. Comparing photosynthetic and photovoltaic efficiencies and recognizing the potential for improvement[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6031): 805-809. |
| [20] | ORT D R, ZHU X G, MELIS A. Optimizing antenna size to maximize photosynthetic efficiency[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 155(1): 79-85. |
| [21] | TIAN J G, WANG C L, CHEN F Y, et al. Maize smart-canopy architecture enhances yield at high densities[J]. Nature, 2024, 632(8025): 576-584. |
| [22] | YAMAMOTO H, TAKAHASHI S, BADGER M R, et al. Artificial remodelling of alternative electron flow by flavodiiron proteins in Arabidopsis [J]. Nature Plants, 2016, 2: 16012. |
| [23] | DANN M, LEISTER D. Evidence that cyanobacterial Sll1217 functions analogously to PGRL1 in enhancing PGR5-dependent cyclic electron flow[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5299. |
| [24] | PESARESI P, SCHARFENBERG M, WEIGEL M, et al. Mutants, overexpressors, and interactors of Arabidopsis plastocyanin isoforms: revised roles of plastocyanin in photosynthetic electron flow and thylakoid redox state[J]. Molecular Plant, 2009, 2(2): 236-248. |
| [25] | SIMKIN A J, MCAUSLAND L, LAWSON T, et al. Overexpression of the RieskeFeS protein increases electron transport rates and biomass yield[J]. Plant Physiology, 2017, 175(1): 134-145. |
| [26] | ERMAKOVA M, LOPEZ-CALCAGNO P E, RAINES C A, et al. Overexpression of the Rieske FeS protein of the cytochrome b6f complex increases C4 photosynthesis in Setaria viridis [J]. Communications Biology, 2019, 2: 314. |
| [27] | HEYNO E, ERMAKOVA M, LOPEZ-CALCAGNO P E, et al. Rieske FeS overexpression in tobacco provides increased abundance and activity of cytochrome b6f[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2022, 174(6): e13803. |
| [28] | CHEN J H, CHEN S T, HE N Y, et al. Nuclear-encoded synthesis of the D1 subunit of photosystem Ⅱ increases photosynthetic efficiency and crop yield[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(5): 570-580. |
| [29] | GIMPEL J A, NOUR-ELDIN H H, SCRANTON M A, et al. Refactoring the six-gene photosystem Ⅱ core in the chloroplast of the green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(7): 589-596. |
| [30] | SHEN L L, TANG K L, WANG W D, et al. Architecture of the chloroplast PSⅠ-NDH super complex in Hordeum vulgare [J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7894): 649-654. |
| [31] | WU J H, CHEN S, WANG C, et al. Regulatory dynamics of the higher-plant PSⅠ-LHCⅠ super complex during state transitions[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(12): 1937-1950. |
| [32] | IWAI M, TAKIZAWA K, TOKUTSU R, et al. Isolation of the elusive super complex that drives cyclic electron flow in photosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7292): 1210-1213. |
| [33] | SHAN J Y, NIEDZWIEDZKI D M, TOMAR R S, et al. Architecture and functional regulation of a plant PSⅡ-LHCⅡ mega complex[J]. Science Advances, 2024, 10(50): eadq9967. |
| [34] | STIRBET A, LAZÁR D, GUO Y, et al. Photosynthesis: basics, history and modelling[J]. Annals of Botany, 2020, 126(4): 511-537. |
| [35] | PORTIS A R JR. Rubisco activase-Rubisco’s catalytic chaperone[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2003, 75(1): 11-27. |
| [36] | SHARKEY T D, BADGER M R, VON CAEMMERER S, et al. Increased heat sensitivity of photosynthesis in tobacco plants with reduced Rubisco activase[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2001, 67(1-2): 147-156. |
| [37] | WAHEEDA K, KITCHEL H, WANG Q, et al. Molecular mechanism of Rubisco activase: dynamic assembly and Rubisco remodeling[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 2023, 10: 1125922. |
| [38] | QU Y C, SAKODA K, FUKAYAMA H, et al. Overexpression of both Rubisco and Rubisco activase rescues rice photosynthesis and biomass under heat stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2021, 44(7): 2308-2320. |
| [39] | BHAT J Y, THIEULIN-PARDO G, HARTL F U, et al. Rubisco activases: AAA+ chaperones adapted to enzyme repair[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 2017, 4: 20. |
| [40] | MORENO J, GARCÍA-MURRIA M J, MARÍN-NAVARRO J. Redox modulation of Rubisco conformation and activity through its cysteine residues[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1605-1614. |
| [41] | SUDHANI H P K, MORENO J. Control of the ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity by the chloroplastic glutathione pool[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2015, 567: 30-34. |
| [42] | CARMO-SILVA E, SHARWOOD R E. Rubisco and its regulation: major advances to improve carbon assimilation and productivity[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2023, 74(2): 507-509. |
| [43] | BAR-ON Y M, MILO R. The global mass and average rate of Rubisco[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(10): 4738-4743. |
| [44] | JENSEN R G. Activation of Rubisco regulates photosynthesis at high temperature and CO2 [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(24): 12937-12938. |
| [45] | BRACHER A, WHITNEY S M, HARTL F U, et al. Biogenesis and metabolic maintenance of Rubisco[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2017, 68: 29-60. |
| [46] | SPREITZER R J, SALVUCCI M E. Rubisco: structure, regulatory interactions, and possibilities for a better enzyme[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2002, 53: 449-475. |
| [47] | ELLIS R J. The most abundant protein in the world[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1979, 4(11): 241-244. |
| [48] | KU M S B, SCHMITT M R, EDWARDS G E. Quantitative determination of RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase protein in leaves of several C3 and C4 plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1979, 30(1): 89-98. |
| [49] | PARIKH M R, GREENE D N, WOODS K K, et al. Directed evolution of RuBisCO hypermorphs through genetic selection in engineered E.coli [J]. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 2006, 19(3): 113-119. |
| [50] | MUELLER-CAJAR O, MORELL M, WHITNEY S M. Directed evolution of rubisco in Escherichia coli reveals a specificity-determining hydrogen bond in the form Ⅱ enzyme[J]. Biochemistry, 2007, 46(49): 14067-14074. |
| [51] | DURÃO P, AIGNER H, NAGY P, et al. Opposing effects of folding and assembly chaperones on evolvability of Rubisco[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(2): 148-155. |
| [52] | CAI Z, LIU G X, ZHANG J L, et al. Development of an activity-directed selection system enabled significant improvement of the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco[J]. Protein & Cell, 2014, 5(7): 552-562. |
| [53] | WILSON R H, ALONSO H, WHITNEY S M. Evolving Methanococcoides burtonii archaeal Rubisco for improved photosynthesis and plant growth[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 22284. |
| [54] | PRYWES N, PHILLIPS N R, OLTROGGE L M, et al. A map of the Rubisco biochemical landscape[J]. Nature, 2025, 638(8051): 823-828. |
| [55] | LIN M T, STONE W D, CHAUDHARI V, et al. Small subunits can determine enzyme kinetics of tobacco Rubisco expressed in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(10): 1289-1299. |
| [56] | AIGNER H, WILSON R H, BRACHER A, et al. Plant RuBisCo assembly in E. coli with five chloroplast chaperones including BSD2[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6368): 1272-1278. |
| [57] | BUCK S, RHODES T, GIONFRIDDO M, et al. Escherichia coli expressing chloroplast chaperones as a proxy to test heterologous Rubisco production in leaves[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2023, 74(2): 664-676. |
| [58] | IQBAL W A, LISITSA A, KAPRALOV M V. Predicting plant Rubisco kinetics from RbcL sequence data using machine learning[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2023, 74(2): 638-650. |
| [59] | GIONFRIDDO M, RHODES T, WHITNEY S M. Perspectives on improving crop Rubisco by directed evolution[J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2024, 155: 37-47. |
| [60] | ZHU X G, LONG S P, ORT D R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 235-261. |
| [61] | CHAO M N, HU G H, DONG J, et al. Sequence characteristics and expression analysis of the gene encoding sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase, an important Calvin cycle enzyme in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(7): 6648. |
| [62] | WANG M L, BI H G, LIU P P, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the gene encoding sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase from Cucumis sativus [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2011, 129(3): 414-420. |
| [63] | LEFEBVRE S, LAWSON T, ZAKHLENIUK O V, et al. Increased sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase activity in transgenic tobacco plants stimulates photosynthesis and growth from an early stage in development[J]. Plant Physiology, 2005, 138(2): 1174-1174. |
| [64] | LIU X L, YU H D, GUAN Y, et al. Carbonylation and loss-of-function analyses of SBPase reveal its metabolic interface role in oxidative stress, carbon assimilation, and multiple aspects of growth and development in Arabidopsis [J]. Molecular Plant, 2012, 5(5): 1082-1099. |
| [65] | SCHURMANN P, JACQUOT J P. Plant thioredoxin systems revisited[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 2000, 51: 371-400. |
| [66] | THIEULIN-PARDO G, REMY T, LIGNON S, et al. Phosphoribulokinase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: a Benson-Calvin cycle enzyme enslaved to its cysteine residues[J]. Molecular BioSystems, 2015, 11(4): 1134-1145. |
| [67] | MARRI L, ZAFFAGNINI M, COLLIN V, et al. Prompt and easy activation by specific thioredoxins of Calvin cycle enzymes of Arabidopsis thaliana associated in the GAPDH/CP12/PRK supramolecular complex[J]. Molecular Plant, 2009, 2(2): 259-269. |
| [68] | ZHU X G, DE STURLER E, LONG S P. Optimizing the distribution of resources between enzymes of carbon metabolism can dramatically increase photosynthetic rate: a numerical simulation using an evolutionary algorithm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 145(2): 513-526. |
| [69] | SIMKIN A J, LOPEZ-CALCAGNO P E, DAVEY P A, et al. Simultaneous stimulation of sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase, fructose 1,6-bisphophate aldolase and the photorespiratory glycine decarboxylase-H protein increases CO2 assimilation, vegetative biomass and seed yield in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(7): 805-816. |
| [70] | SIMKIN A J, MCAUSLAND L, HEADLAND L R, et al. Multigene manipulation of photosynthetic carbon assimilation increases CO2 fixation and biomass yield in tobacco[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(13): 4075-4090. |
| [71] | DING F, WANG M L, ZHANG S X, et al. Changes in SBPase activity influence photosynthetic capacity, growth, and tolerance to chilling stress in transgenic tomato plants[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32741. |
| [72] | DRIEVER S M, SIMKIN A J, ALOTAIBI S, et al. Increased SBPase activity improves photosynthesis and grain yield in wheat grown in greenhouse conditions[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2017, 372(1730): 20160384. |
| [73] | ZHAO H L, TANG Q M, CHANG T G, et al. Why an increase in activity of an enzyme in the Calvin-Benson cycle does not always lead to an increased photosynthetic CO2 uptake rate?—a theoretical analysis[J]. In Silico Plants, 2021, 3(1): diaa009. |
| [123] | DE SOUZA A P, BURGESS S J, DORAN L, et al. Soybean photosynthesis and crop yield are improved by accelerating recovery from photoprotection[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6608): 851-854. |
| [124] | KROMDIJK J, GŁOWACKA K, LEONELLI L, et al. Improving photosynthesis and crop productivity by accelerating recovery from photoprotection[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 857-861. |
| [125] | CUI L L, LU Y S, LI Y, et al. Overexpression of glycolate oxidase confers improved photosynthesis under high light and high temperature in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1165. |
| [126] | SCAFARO A P, ATWELL B J, MUYLAERT S, et al. A thermotolerant variant of Rubisco activase from a wild relative improves growth and seed yield in rice under heat stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1663. |
| [127] | LEISTER D. How can the light reactions of photosynthesis be improved in plants?[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012, 3: 199. |
| [128] | BATISTA-SILVA W, FONSECA-PEREIRA P DA, MARTINS A O, et al. Engineering improved photosynthesis in the era of synthetic biology[J]. Plant Communications, 2020, 1(2): 100032. |
| [129] | KUBIS A, BAR-EVEN A. Synthetic biology approaches for improving photosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(5): 1425-1433. |
| [130] | CROCE R, CARMO-SILVA E, CHO Y B, et al. Perspectives on improving photosynthesis to increase crop yield[J]. The Plant Cell, 2024, 36(10): 3944-3973. |
| [131] | LI B D, HUANG A Y, WANG L M, et al. Increased sugar content impairs pollen fertility and reduces seed-setting in high-photosynthetic-efficiency rice[J]. The Crop Journal, 2024, 12(6): 1547-1558. |
| [132] | ERMAKOVA M, DANILA F R, FURBANK R T, et al. On the road to C4 rice: advances and perspectives[J]. The Plant Journal, 2020, 101(4): 940-950. |
| [1] | SONG Kainan, ZHANG Liwen, WANG Chao, TIAN Pingfang, LI Guangyue, PAN Guohui, XU Yuquan. Advances in small-molecule biopesticides and their biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1203-1223. |
| [2] | YU Wenwen, LV Xueqin, LI Zhaofeng, LIU Long. Plant synthetic biology and bioproduction of human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 992-997. |
| [3] | YAN Zhaotao, ZHOU Pengfei, WANG Yangzhong, ZHANG Xin, XIE Wenyan, TIAN Chenfei, WANG Yong. Plant synthetic biology: new opportunities for large-scale culture of plant cells [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1107-1125. |
| [4] | ZHAO Xinyu, SHENG Qi, LIU Kaifang, LIU Jia, LIU Liming. Construction of microbial cell factories for aspartate-family feed amino acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1184-1202. |
| [5] | HE Yangyu, YANG Kai, WANG Weilin, HUANG Qian, QIU Ziying, SONG Tao, HE Liushang, YAO Jinxin, GAN Lu, HE Yuchi. Design and practice of plant synthetic biology theme in the International Genetically Engineered Machine Competition [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1243-1254. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xuebo, ZHU Chengshu, CHEN Ruiyun, JIN Qingzi, LIU Xiao, XIONG Yan, CHEN Daming. Policy planning and industrial development of agricultural synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1224-1242. |
| [7] | LIU Jie, GAO Yu, MA Yongshuo, SHANG Yi. Progress and challenges of synthetic biology in agriculture [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 998-1024. |
| [8] | ZHENG Lei, ZHENG Qiteng, ZHANG Tianjiao, DUAN Kun, ZHANG Ruifu. Engineering rhizosphere synthetic microbial communities to enhance crop nutrient use efficiency [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1058-1071. |
| [9] | LI Chao, ZHANG Huan, YANG Jun, WANG Ertao. Research advances in nitrogen fixation synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1041-1057. |
| [10] | WEI Jiaxiu, JI Peiyun, JIE Qingyu, HUANG Qiuyan, YE Hao, DAI Junbiao. Construction and application of plant artificial chromosomes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1093-1106. |
| [11] | FANG Xinyi, SUN Lichao, HUO Yixin, WANG Ying, YUE Haitao. Trends and challenges in microbial synthesis of higher alcohols [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 873-898. |
| [12] | WU Xiaoyan, SONG Qi, XU Rui, DING Chenjun, CHEN Fang, GUO Qing, ZHANG Bo. A comparative analysis of global research and development competition in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 940-955. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jiankang, WANG Wenjun, GUO Hongju, BAI Beichen, ZHANG Yafei, YUAN Zheng, LI Yanhui, LI Hang. Development and application of a high-throughput microbial clone picking workstation based on machine vision [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 956-971. |
| [14] | LI Quanfei, CHEN Qian, LIU Hao, HE Kundong, PAN Liang, LEI Peng, GU Yi’an, SUN Liang, LI Sha, QIU Yibin, WANG Rui, XU Hong. Synthetic biology and applications of high-adhesion protein materials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 806-828. |
| [15] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||