Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (5): 1255-1273.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-060
• Invited Review • Previous Articles
Research on market access and regulation of global bio-manufactured feed protein materials and additives
CHEN Wuxi1,2, MA Longxue1,2, YANG Yang1,2, ZHU Zhen1,2, ZHAI Yida1, DUAN Yu1, CHEN Limei1,2, LI Demao1,2
- 1.Tianjin Key Laboratory for Industrial Biological Systems and Bioprocessing Engineering,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
2.National Center of Technology Innovation for Synthetic Biology,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2025-06-13Revised:2025-08-21Online:2025-11-05Published:2025-10-31 -
Contact:LI Demao
全球生物制造饲料蛋白原料及添加剂市场准入与监管研究
陈吴西1,2, 马龙雪1,2, 杨洋1,2, 朱振1,2, 翟艺达1, 段玉1, 陈利梅1,2, 李德茂1,2
- 1.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,天津市工业生物系统与过程工程重点实验室,天津 300308
2.国家合成生物技术创新中心,天津 300308
-
通讯作者:李德茂 -
作者简介:陈吴西 (1984—),女,高级工程师。研究方向为微生物蛋白的生物制造。E-mail:chen_wx@tib.cas.cn李德茂 (1978—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为以发酵工程、化工过程控制与模拟、代谢工程等为技术手段,重点解决生物制造系统中的高效底物(农林废弃物、城市有机废弃物和C1气体等)利用、代谢途径的重塑与优化、过程模拟与放大等关键问题,实现替代蛋白/油脂的低碳生物制造。E-mail:li_dm@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:中国科学院关键核心技术攻坚先导专项(C类先导专项) “蛋白合成的生产菌种创制”(XDC0110300)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Wuxi, MA Longxue, YANG Yang, ZHU Zhen, ZHAI Yida, DUAN Yu, CHEN Limei, LI Demao. Research on market access and regulation of global bio-manufactured feed protein materials and additives[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1255-1273.
陈吴西, 马龙雪, 杨洋, 朱振, 翟艺达, 段玉, 陈利梅, 李德茂. 全球生物制造饲料蛋白原料及添加剂市场准入与监管研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1255-1273.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-060
| 原料 | 菌种 | 企业 | 国家/地区 | 用途 | 工业化生产时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 小球藻 | 台湾绿藻制造股份有限公司 Taiwan Chiorella Manufacturer Co., Ltd. | 中国台湾 | 食用 | 1964年[ |
| 螺旋藻 | 索萨・特斯科科股份有限公司 Sosa Texcoco, S.A. | 西班牙 | 食用 | 1972年[ | |
| 甲醇 | 甲基营养嗜甲基菌 | 英国帝国化学工业公司 Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) | 英国 | 饲料 | 1979年[ |
| 甲基单胞菌 | 挪威水电公司与马拉博公司 Norsk Hydro and AB Marabou “Norprotein” | 瑞典 | 食用和饲料 | 1974年开发工艺,工业化时间未知[ | |
| 乙醇 | 产朊假丝酵母 | 哈金森公司 Pure Culture Products, Hutchinson | 美国 | 食用 | 20世纪60—70年代[ |
| 假丝酵母 | 三菱石化公司 Mitsubishi Petro-Chemical Co. | 日本 | 食用和饲料 | 1979年[ |
Table 1 Early global industrialization of single-cell protein technologies
| 原料 | 菌种 | 企业 | 国家/地区 | 用途 | 工业化生产时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 小球藻 | 台湾绿藻制造股份有限公司 Taiwan Chiorella Manufacturer Co., Ltd. | 中国台湾 | 食用 | 1964年[ |
| 螺旋藻 | 索萨・特斯科科股份有限公司 Sosa Texcoco, S.A. | 西班牙 | 食用 | 1972年[ | |
| 甲醇 | 甲基营养嗜甲基菌 | 英国帝国化学工业公司 Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) | 英国 | 饲料 | 1979年[ |
| 甲基单胞菌 | 挪威水电公司与马拉博公司 Norsk Hydro and AB Marabou “Norprotein” | 瑞典 | 食用和饲料 | 1974年开发工艺,工业化时间未知[ | |
| 乙醇 | 产朊假丝酵母 | 哈金森公司 Pure Culture Products, Hutchinson | 美国 | 食用 | 20世纪60—70年代[ |
| 假丝酵母 | 三菱石化公司 Mitsubishi Petro-Chemical Co. | 日本 | 食用和饲料 | 1979年[ |
| 类别 | 定义 | 典型案例 | 准入时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ类 | 化学成分明确的纯化化合物及其混合物,GMM和新引入的基因均已去除(例如氨基酸、维生素) | 大肠杆菌NITEBP-02917生产的浓缩液态L-赖氨酸[ | 2022年 |
| Ⅱ类 | 不含有GMM和新引入基因的复杂产品(例如细胞提取物、大多数酶制剂) | Paenibacillus lentus DSM 33618 生产的endo-1,4-β-甘露聚糖酶[ | 2023年 |
| Ⅲ类 | 源自遗传改造物质的产品,其中不存在能够增殖或转移基因的遗传改造物质,但仍存在新引入的基因(例如热失活的发酵剂培养物) | 基因改造后的PT73(TM)经过干燥热灭活细菌生物质[ | 2017年 |
| Ⅳ类 | 含有或含有能够繁殖或转移基因的遗传改造物质的产品(例如发酵食品和饲料的活发酵剂培养物) | — | — |
Table 2 EFSA’s classification of genetically modified microorganisms with typical cases for feeding
| 类别 | 定义 | 典型案例 | 准入时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ类 | 化学成分明确的纯化化合物及其混合物,GMM和新引入的基因均已去除(例如氨基酸、维生素) | 大肠杆菌NITEBP-02917生产的浓缩液态L-赖氨酸[ | 2022年 |
| Ⅱ类 | 不含有GMM和新引入基因的复杂产品(例如细胞提取物、大多数酶制剂) | Paenibacillus lentus DSM 33618 生产的endo-1,4-β-甘露聚糖酶[ | 2023年 |
| Ⅲ类 | 源自遗传改造物质的产品,其中不存在能够增殖或转移基因的遗传改造物质,但仍存在新引入的基因(例如热失活的发酵剂培养物) | 基因改造后的PT73(TM)经过干燥热灭活细菌生物质[ | 2017年 |
| Ⅳ类 | 含有或含有能够繁殖或转移基因的遗传改造物质的产品(例如发酵食品和饲料的活发酵剂培养物) | — | — |
| 年份 | 文件名称 | 主要内容 |
|---|---|---|
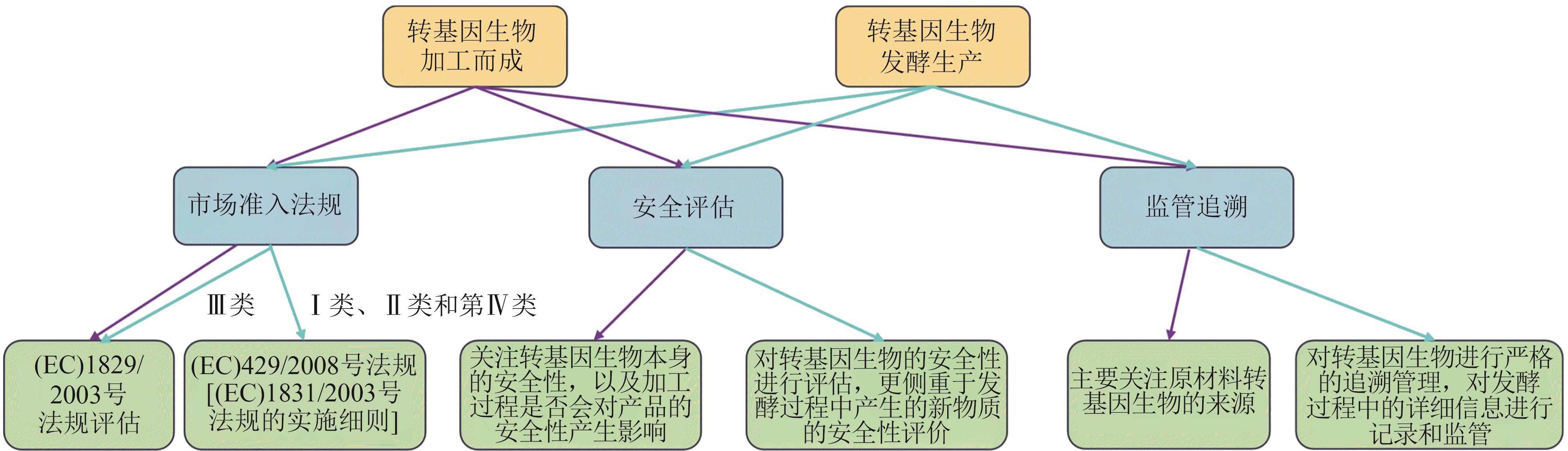
| 2003 | (EC) No 1829/2003 | 这是欧盟关于转基因生物授权和监管的重要法规,规定了转基因生物包括转基因微生物的授权程序、风险评估要求以及转基因食品和饲料的标签等内容,旨在确保转基因产品在欧盟市场的安全使用和消费者的知情权 |
| 2011 | 《转基因微生物及其用于食品和饲料产品的风险评估》 | 为评估转基因微生物及其产品在食品和饲料中的安全性提供了指导,包括对转基因微生物的特性、潜在风险以及风险评估方法等方面的阐述,确保转基因微生物在食品和饲料领域的安全应用[ |
| 2012 | 《转基因动物食品和饲料以及动物健康和福利方面的风险评估》 | 对转基因动物制成的食品和饲料的安全性以及对动物健康和福利的影响进行了评估指导,包括对转基因动物的遗传修饰、生理特性、食用安全性等方面的考虑,保障转基因动物产品的安全和可持续发展[ |
| 2014 | 《关于 EFSA 科学委员会在啮齿动物中进行全食物/饲料重复剂量 90 天经口毒性研究指南对 GMO 风险评估适用性的解释说明》 | 阐述了 90 天喂养研究在转基因食品风险评估中的应用,包括研究设计、实施和结果解读等方面的指导,帮助评估转基因食品对动物健康的长期影响[ |
| 2015 | 《根据(EC)1829/2003 法规授权的转基因食品和饲料续期申请指南》 | 明确了转基因食品和饲料在续期申请时需要提供的信息和数据要求,指导企业和申请人准备续期申请材料,确保转基因食品和饲料在市场上的持续安全供应[ |
| 2018 | 《用作饲料添加剂或生产生物的微生物特征描述指南》 | 规范了用作饲料添加剂或生产生物的转基因微生物的特征描述要求,有助于准确评估其安全性和有效性[ |
| 2022 | 《转基因植物来源饲料风险评估中的动物膳食暴露》 | 关注转基因植物来源饲料在动物饲养中的安全性,指导评估动物在食用转基因饲料时的膳食暴露情况,以及对动物健康和生产性能的影响[ |
Table 3 EFSA’s key regulations and guidance documents on feed and additive access for GMMs
| 年份 | 文件名称 | 主要内容 |
|---|---|---|
| 2003 | (EC) No 1829/2003 | 这是欧盟关于转基因生物授权和监管的重要法规,规定了转基因生物包括转基因微生物的授权程序、风险评估要求以及转基因食品和饲料的标签等内容,旨在确保转基因产品在欧盟市场的安全使用和消费者的知情权 |
| 2011 | 《转基因微生物及其用于食品和饲料产品的风险评估》 | 为评估转基因微生物及其产品在食品和饲料中的安全性提供了指导,包括对转基因微生物的特性、潜在风险以及风险评估方法等方面的阐述,确保转基因微生物在食品和饲料领域的安全应用[ |
| 2012 | 《转基因动物食品和饲料以及动物健康和福利方面的风险评估》 | 对转基因动物制成的食品和饲料的安全性以及对动物健康和福利的影响进行了评估指导,包括对转基因动物的遗传修饰、生理特性、食用安全性等方面的考虑,保障转基因动物产品的安全和可持续发展[ |
| 2014 | 《关于 EFSA 科学委员会在啮齿动物中进行全食物/饲料重复剂量 90 天经口毒性研究指南对 GMO 风险评估适用性的解释说明》 | 阐述了 90 天喂养研究在转基因食品风险评估中的应用,包括研究设计、实施和结果解读等方面的指导,帮助评估转基因食品对动物健康的长期影响[ |
| 2015 | 《根据(EC)1829/2003 法规授权的转基因食品和饲料续期申请指南》 | 明确了转基因食品和饲料在续期申请时需要提供的信息和数据要求,指导企业和申请人准备续期申请材料,确保转基因食品和饲料在市场上的持续安全供应[ |
| 2018 | 《用作饲料添加剂或生产生物的微生物特征描述指南》 | 规范了用作饲料添加剂或生产生物的转基因微生物的特征描述要求,有助于准确评估其安全性和有效性[ |
| 2022 | 《转基因植物来源饲料风险评估中的动物膳食暴露》 | 关注转基因植物来源饲料在动物饲养中的安全性,指导评估动物在食用转基因饲料时的膳食暴露情况,以及对动物健康和生产性能的影响[ |
| 批准时间 | 名称 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 长期使用的传统蛋白 | 豆粕、菜籽粕、马铃薯蛋白、鱼粉等 | 用于饲料蛋白原料 |
| 20世纪70—80年代初 | 利用甲基营养型细菌(Methylophilus methylotrophus)以甲醇为碳源生产高蛋白饲料Pruteen | 用于家禽和猪饲料[ |
| 2016年 | Methylococcus capsulatus以甲烷为碳源生产蛋白饲料 | 用于水产饲料[ |
| 2017年 | 黑水虻蛋白 | 用于禽类和水产养殖[ |
| 2021年 | 家蝇幼虫蛋白 | 用于家禽和猪的饲料[ |
| 2014年 | 酿酒酵母 NCYCR404 | 用于奶牛饲料添加剂[ |
| 2019年 | 解脂耶氏酵母生物质 | 用于饲料蛋白来源 |
| 2021年 | 地衣芽孢杆菌DSM 19670生产的丝氨酸蛋白酶 | 育肥鸡饲料添加剂[ |
| 2024年 | 地衣芽孢杆菌DSM 33099蛋白酶 | 育肥家禽和饲养用于产蛋/繁殖家禽的饲料添加剂[ |
| 2024年 | 缬氨酸(谷氨酸棒状菌CGMCC 18932) | 所有动物氨基酸类营养添加剂 |
| 2024年 | 大肠杆菌NITEBP-02917生产的浓缩液态L-赖氨酸 | 营养添加剂[ |
Table 4 Protein materials or additives approved for feeding in the EU
| 批准时间 | 名称 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 长期使用的传统蛋白 | 豆粕、菜籽粕、马铃薯蛋白、鱼粉等 | 用于饲料蛋白原料 |
| 20世纪70—80年代初 | 利用甲基营养型细菌(Methylophilus methylotrophus)以甲醇为碳源生产高蛋白饲料Pruteen | 用于家禽和猪饲料[ |
| 2016年 | Methylococcus capsulatus以甲烷为碳源生产蛋白饲料 | 用于水产饲料[ |
| 2017年 | 黑水虻蛋白 | 用于禽类和水产养殖[ |
| 2021年 | 家蝇幼虫蛋白 | 用于家禽和猪的饲料[ |
| 2014年 | 酿酒酵母 NCYCR404 | 用于奶牛饲料添加剂[ |
| 2019年 | 解脂耶氏酵母生物质 | 用于饲料蛋白来源 |
| 2021年 | 地衣芽孢杆菌DSM 19670生产的丝氨酸蛋白酶 | 育肥鸡饲料添加剂[ |
| 2024年 | 地衣芽孢杆菌DSM 33099蛋白酶 | 育肥家禽和饲养用于产蛋/繁殖家禽的饲料添加剂[ |
| 2024年 | 缬氨酸(谷氨酸棒状菌CGMCC 18932) | 所有动物氨基酸类营养添加剂 |
| 2024年 | 大肠杆菌NITEBP-02917生产的浓缩液态L-赖氨酸 | 营养添加剂[ |
| 序号 | 制品名称 | 生产手段或特性 | 用 途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 浓缩、提取的谷氨酸发酵产物 | 将提取谷氨酸后剩余的液体,与用于生产谷氨酸的谷氨酸棒状杆菌(Corynebacterium glutamicum)混合而成 | 用作牛和家禽饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 02 | 浓缩的氨化发酵乳清 | 乳清经德氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus delbrueckii)在加氨情况下发酵而成 | 用作牛饲料的蛋白质和非蛋白质氮的来源 |
| 03 | γ-亚麻酸红花粉 | 异源表达异丝水霉(Saprolegnia diclina)delta-6-去饱和酶基因的红花(Carthamus tinctorius)种子,经去油后的粉状物 | 用作牛和家禽饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 04 | 干燥的毕赤酵母 | 不具有活性的干燥后酵母(Komagataella pastoris) | 用作鸡饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 05 | 干燥的产朊假丝酵母 | 产朊假丝酵母(Candida utilis)经培养基分离后的干燥菌体,蛋白质含量不少于40% | 用作饲料中蛋白质的来源 |
| 06 | 干燥的甲基杆菌 | 甲基杆菌(Methylobacterium extorquens)经发酵、离心、干燥得到的菌体蛋白 | 用作甲壳类、有鳍鱼类饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 07 | 干燥的荚膜甲基球菌 | 在12周的连续发酵过程中每天收集荚膜甲基球菌(Methylococcus capsulatus)发酵液,经热处理及干燥等步骤所得菌体蛋白 | 用作鲑鱼饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 08 | 干燥的黑曲霉 | 黑曲霉(Aspergillus niger)经发酵、干燥得到的菌体蛋白 | 用作饲料中蛋白质的来源 |
| 09 | 干燥的米曲霉 | 米曲霉(Aspergillus oryzae)经发酵、干燥得到的菌体蛋白 | 用作饲料中蛋白质的来源 |
Table 5 Typical cases of protein-related feeding additives in the United States
| 序号 | 制品名称 | 生产手段或特性 | 用 途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 浓缩、提取的谷氨酸发酵产物 | 将提取谷氨酸后剩余的液体,与用于生产谷氨酸的谷氨酸棒状杆菌(Corynebacterium glutamicum)混合而成 | 用作牛和家禽饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 02 | 浓缩的氨化发酵乳清 | 乳清经德氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus delbrueckii)在加氨情况下发酵而成 | 用作牛饲料的蛋白质和非蛋白质氮的来源 |
| 03 | γ-亚麻酸红花粉 | 异源表达异丝水霉(Saprolegnia diclina)delta-6-去饱和酶基因的红花(Carthamus tinctorius)种子,经去油后的粉状物 | 用作牛和家禽饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 04 | 干燥的毕赤酵母 | 不具有活性的干燥后酵母(Komagataella pastoris) | 用作鸡饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 05 | 干燥的产朊假丝酵母 | 产朊假丝酵母(Candida utilis)经培养基分离后的干燥菌体,蛋白质含量不少于40% | 用作饲料中蛋白质的来源 |
| 06 | 干燥的甲基杆菌 | 甲基杆菌(Methylobacterium extorquens)经发酵、离心、干燥得到的菌体蛋白 | 用作甲壳类、有鳍鱼类饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 07 | 干燥的荚膜甲基球菌 | 在12周的连续发酵过程中每天收集荚膜甲基球菌(Methylococcus capsulatus)发酵液,经热处理及干燥等步骤所得菌体蛋白 | 用作鲑鱼饲料的蛋白质来源 |
| 08 | 干燥的黑曲霉 | 黑曲霉(Aspergillus niger)经发酵、干燥得到的菌体蛋白 | 用作饲料中蛋白质的来源 |
| 09 | 干燥的米曲霉 | 米曲霉(Aspergillus oryzae)经发酵、干燥得到的菌体蛋白 | 用作饲料中蛋白质的来源 |
| 分类 | 名称 |
|---|---|
| 植物性蛋白饲料 | 大豆粉、豌豆蛋白、马铃薯蛋白等 |
| 动物性蛋白饲料 | 虾粉、鱼粉、肉骨粉、酶处理鱼蛋白、浓缩乳清蛋白等 |
| 微生物蛋白饲料 | 谷氨酸发酵副产物、小球藻、饲料酵母 (torula yeast)等 |
| 饲料添加剂(19种) | 甘氨酸、DL-丙氨酸、L-精氨酸、L-异亮氨酸、L-组氨酸盐酸一水合物、L-赖氨酸盐酸盐、左旋肉碱、胍基乙酸、L-谷氨酸钠、牛磺酸、2-脱氨基-2-羟基-甲硫氨酸、2-脱氨基-2-羟基-甲硫氨酸异丙酯、DL-色氨酸、L-色氨酸、L-苏氨酸、L-缬氨酸、DL-蛋氨酸、L-蛋氨酸、L-赖氨酸硫酸盐 |
Table 6 List of protein raw materials or additives for feeding in Japan[83]
| 分类 | 名称 |
|---|---|
| 植物性蛋白饲料 | 大豆粉、豌豆蛋白、马铃薯蛋白等 |
| 动物性蛋白饲料 | 虾粉、鱼粉、肉骨粉、酶处理鱼蛋白、浓缩乳清蛋白等 |
| 微生物蛋白饲料 | 谷氨酸发酵副产物、小球藻、饲料酵母 (torula yeast)等 |
| 饲料添加剂(19种) | 甘氨酸、DL-丙氨酸、L-精氨酸、L-异亮氨酸、L-组氨酸盐酸一水合物、L-赖氨酸盐酸盐、左旋肉碱、胍基乙酸、L-谷氨酸钠、牛磺酸、2-脱氨基-2-羟基-甲硫氨酸、2-脱氨基-2-羟基-甲硫氨酸异丙酯、DL-色氨酸、L-色氨酸、L-苏氨酸、L-缬氨酸、DL-蛋氨酸、L-蛋氨酸、L-赖氨酸硫酸盐 |
| 时间 | 名称 | 过程特征 | 申报类别 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025年公告921号 | 解脂耶氏酵母蛋白 | 以煤化工或天然气化工产生的CO2和H2为主要原料,通过热醋穆尔氏菌(Moorella thermoacetica CGMCC 28818)发酵得到含乙酸的发酵液,解脂耶氏酵母(Yarrowia lipolytica CGMCC 25047)利用乙酸进行发酵,收集解脂耶氏酵母菌体细胞,经分离、灭活、干燥等工艺制得 | 饲料原料[ |
| 2024年公告862号 | 红色无定形态单质硒 | 以枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis CGMCC11741)为菌种,经液体发酵,对培养基中的亚硒酸钠进行还原,再经离心分离、添加载体、喷雾干燥和辐照灭菌等工艺制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2024年 公告809号 | 吡咯并喹啉醌二钠 | 以脱氮生丝微菌(Hyphomicrobium denitrificans FJNU-R8)为生产菌种,经液体发酵、分离、纯化制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2023年 公告744号 | 荚膜甲基球菌蛋白 | 以荚膜甲基球菌(Methylococcus capsulatus CICC11106s)为主要生产菌株,以(Cupriavidus cauae CICC11107s)、丹麦解硫胺素芽孢杆菌(Aneurinibacillus danicu CICC11108s)和土壤短芽孢杆菌(Brevibacillus agri CICC11109s)为辅助菌株,以天然气中的甲烷为主要原料,经液体连续发酵、固液分离和干燥等工艺制得。终产品不含生产菌株活细胞 | 饲料原料[ |
| 2023年 公告692号 | 马克斯克鲁维酵母 | 以马克斯克鲁维酵母(Kluyveromyces marxianus CGMCC 10621)为生产菌种,经液体发酵、过滤浓缩、制粒、干燥等工艺制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2022年公告614号 | 枯草三十七肽 | 以枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis CGMCC15404)为生产菌种,经液体发酵、膜分离、浓缩、干燥等工艺制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2022年 公告614号 | 腺苷七肽 | 以约氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus johnsoni CGMCC19858)为菌种,经液体发酵、提取、添加载体进行喷雾干燥,再添加稀释剂制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2021年公告 465号 | 乙醇梭菌蛋白 | 以乙醇梭菌(Clostridium autoethanogenum CICC11088s)为发酵菌种,以钢铁工业转炉气中的 CO 为主要原料,采用液体发酵,生产乙醇后的剩余物,经分离、喷雾干燥等工艺制得。终产品不含生产菌株活细胞 | 饲料原料[ |
Table 7 Bio-manufactured feed raw materials or additives approved between 2012 and 2025
| 时间 | 名称 | 过程特征 | 申报类别 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025年公告921号 | 解脂耶氏酵母蛋白 | 以煤化工或天然气化工产生的CO2和H2为主要原料,通过热醋穆尔氏菌(Moorella thermoacetica CGMCC 28818)发酵得到含乙酸的发酵液,解脂耶氏酵母(Yarrowia lipolytica CGMCC 25047)利用乙酸进行发酵,收集解脂耶氏酵母菌体细胞,经分离、灭活、干燥等工艺制得 | 饲料原料[ |
| 2024年公告862号 | 红色无定形态单质硒 | 以枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis CGMCC11741)为菌种,经液体发酵,对培养基中的亚硒酸钠进行还原,再经离心分离、添加载体、喷雾干燥和辐照灭菌等工艺制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2024年 公告809号 | 吡咯并喹啉醌二钠 | 以脱氮生丝微菌(Hyphomicrobium denitrificans FJNU-R8)为生产菌种,经液体发酵、分离、纯化制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2023年 公告744号 | 荚膜甲基球菌蛋白 | 以荚膜甲基球菌(Methylococcus capsulatus CICC11106s)为主要生产菌株,以(Cupriavidus cauae CICC11107s)、丹麦解硫胺素芽孢杆菌(Aneurinibacillus danicu CICC11108s)和土壤短芽孢杆菌(Brevibacillus agri CICC11109s)为辅助菌株,以天然气中的甲烷为主要原料,经液体连续发酵、固液分离和干燥等工艺制得。终产品不含生产菌株活细胞 | 饲料原料[ |
| 2023年 公告692号 | 马克斯克鲁维酵母 | 以马克斯克鲁维酵母(Kluyveromyces marxianus CGMCC 10621)为生产菌种,经液体发酵、过滤浓缩、制粒、干燥等工艺制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2022年公告614号 | 枯草三十七肽 | 以枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis CGMCC15404)为生产菌种,经液体发酵、膜分离、浓缩、干燥等工艺制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2022年 公告614号 | 腺苷七肽 | 以约氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus johnsoni CGMCC19858)为菌种,经液体发酵、提取、添加载体进行喷雾干燥,再添加稀释剂制得 | 饲料添加剂[ |
| 2021年公告 465号 | 乙醇梭菌蛋白 | 以乙醇梭菌(Clostridium autoethanogenum CICC11088s)为发酵菌种,以钢铁工业转炉气中的 CO 为主要原料,采用液体发酵,生产乙醇后的剩余物,经分离、喷雾干燥等工艺制得。终产品不含生产菌株活细胞 | 饲料原料[ |
| 评价内容 | 直接饲喂微生物 | 发酵制品生产菌株 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 | 酵母和丝状真菌 | 细菌 | 酵母和丝状真菌 | |
| 微生物鉴定 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 产毒能力和致病性 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 抗菌药物敏感性 | √ | √ | ||
| 抗菌药物产生 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 生产菌株的遗传修饰 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 |
| 发酵制品中无生产菌株活细胞评价 | √ | √ | ||
| 发酵制品中生产菌株DNA检测 | 必要时 | 必要时 | ||
Table 8 Basic requirements for strain identification and safety evaluation
| 评价内容 | 直接饲喂微生物 | 发酵制品生产菌株 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 | 酵母和丝状真菌 | 细菌 | 酵母和丝状真菌 | |
| 微生物鉴定 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 产毒能力和致病性 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 抗菌药物敏感性 | √ | √ | ||
| 抗菌药物产生 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 生产菌株的遗传修饰 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 | 仅适用于转基因微生物 |
| 发酵制品中无生产菌株活细胞评价 | √ | √ | ||
| 发酵制品中生产菌株DNA检测 | 必要时 | 必要时 | ||
| 年份 | 项目内容 | 应用类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 重组地衣芽孢杆菌 S10-34zEK4表达的角蛋白酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 |
| 重组地衣芽孢杆菌 SJ10402表达的α-淀粉酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组米曲霉 JaL339表达的木聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组李氏木霉 Morph-Y5#2表达的木聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组李氏木霉 MorphΔE8BP174c表达的植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-AppaT75)表达的高温植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-BGL739)表达的 β-葡萄糖苷酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-XynNA)表达的木聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组地衣芽孢杆菌BML612-LATori1CAP75表达的 α-淀粉酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9K-LYC7)表达的溶菌酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组大肠杆菌K12(PT06)表达的D-泛酸钙生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 2023 | 重组毕赤酵母 GS115(pPIC9-agaF75)表达的α-半乳糖苷酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 |
| 重组毕赤酵母 GS115(pPIC9-MAN1)表达的β-甘露聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组米曲霉COls741表达的植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组地衣芽孢杆菌NZJs-AHN表达的蛋白酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-godA)表达的葡萄糖氧化酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-pgA)表达的果胶酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-phyP)表达的植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母PichiapastorisX-33/pPICZαA-NZ2114表达的生泰素生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组枯草芽孢杆菌168(pWB980-CBP21)表达的几丁质氧化水解酶 CBP21 生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-Chi92)表达的几丁质酶 Chi92 生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 |
Table 9 List of approved agricultural GMO safety certificates (Feed Applications) for 2023—2024
| 年份 | 项目内容 | 应用类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 重组地衣芽孢杆菌 S10-34zEK4表达的角蛋白酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 |
| 重组地衣芽孢杆菌 SJ10402表达的α-淀粉酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组米曲霉 JaL339表达的木聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组李氏木霉 Morph-Y5#2表达的木聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组李氏木霉 MorphΔE8BP174c表达的植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-AppaT75)表达的高温植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-BGL739)表达的 β-葡萄糖苷酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-XynNA)表达的木聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组地衣芽孢杆菌BML612-LATori1CAP75表达的 α-淀粉酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9K-LYC7)表达的溶菌酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组大肠杆菌K12(PT06)表达的D-泛酸钙生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 2023 | 重组毕赤酵母 GS115(pPIC9-agaF75)表达的α-半乳糖苷酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 |
| 重组毕赤酵母 GS115(pPIC9-MAN1)表达的β-甘露聚糖酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组米曲霉COls741表达的植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组地衣芽孢杆菌NZJs-AHN表达的蛋白酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-godA)表达的葡萄糖氧化酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-pgA)表达的果胶酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-phyP)表达的植酸酶生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母PichiapastorisX-33/pPICZαA-NZ2114表达的生泰素生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组枯草芽孢杆菌168(pWB980-CBP21)表达的几丁质氧化水解酶 CBP21 生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 | |
| 重组毕赤酵母GS115(pPIC9-Chi92)表达的几丁质酶 Chi92 生产应用 | 饲料添加剂 |
| [1] | WANG G K, WU X, YIN Y L. Synthetic biology-driven customization of functional feed resources[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(7): 777-780. |
| [2] | NYYSSÖLÄ A, SUHONEN A, RITALA A, et al. The role of single cell protein in cellular agriculture[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 75: 102686. |
| [3] | JEAN A B, BROWN R C. Techno-economic analysis of gas fermentation for the production of single cell protein[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2024, 58(8): 3823-3829. |
| [4] | RITALA A, HÄKKINEN S T, TOIVARI M, et al. Single cell protein: state-of-the-art, industrial landscape and patents 2001-2016[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2009. |
| [5] | SALAZAR-LÓPEZ N J, BARCO-MENDOZA G A, ZUÑIGA-MARTÍNEZ B S, et al. Single-cell protein production as a strategy to reincorporate food waste and agro by-products back into the processing chain[J]. Bioengineering, 2022, 9(11): 623. |
| [6] | KHAN S, REHMAN A, SHAH H, et al. Fish protein and its derivatives: the novel applications, bioactivities, and their functional significance in food products[J]. Food Reviews International, 2022, 38(8): 1607-1634. |
| [7] | RAJA K, SURESH K, ANBALAGAN S, et al. Investigating the nutritional viability of marine-derived protein for sustainable future development[J]. Food Chemistry, 2024, 448: 139087. |
| [8] | VIANA D F, ZAMBORAIN-MASON J, GAINES S D, et al. Nutrient supply from marine small-scale fisheries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13: 11357. |
| [9] | COTTRELL R S, BLANCHARD J L, HALPERN B S, et al. Global adoption of novel aquaculture feeds could substantially reduce forage fish demand by 2030[J]. Nature Food, 2020, 1(5): 301-308. |
| [10] | AMARA A A, EL-BAKY N A. Fungi as a source of edible proteins and animal feed[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2023, 9(1): 73. |
| [11] | 赵天宇, 杨绪磊, 王孟磊, 等. 大豆CMS恢复基因Rf2功能性分子标记开发及恢复系新种质创制[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2025, 26(9): 1788-1795. |
| ZHAO T Y, YANG X L, WANG M L, et al. Development of functional molecular markers for soybean CMS Restorer-of-fertility gene Rf2 and creation of new germplasm for restorer lines[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2025, 26(9): 1788-1795. | |
| [12] | GREGORY G J, BENNETT R K, PAPOUTSAKIS E T. Recent advances toward the bioconversion of methane and methanol in synthetic methylotrophs[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 71: 99-116. |
| [13] | RAMÍREZ ROJAS A A, SWIDAH R, SCHINDLER D. Microbes of traditional fermentation processes as synthetic biology chassis to tackle future food challenges[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 982975. |
| [14] | XU J, WANG J, MA C L, et al. Embracing a low-carbon future by the production and marketing of C1 gas protein[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2023, 63: 108096. |
| [15] | SHELEF G, SOEDER C J. Algae biomass: production and use[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, 1980: 852. |
| [16] | CLEMENT G. Producing spirulina with CO2 [C]//Single Cell Protein Ⅱ, International Conference on Single Cell Protein, 1975. |
| [17] | GOW J, LITTLEHAILES J, SMITH S, et al. SCP production from methanol: Bacteria[C]//Single-Cell Protein Ⅱ, International Conference on Single Cell Protein, 1975. |
| [18] | MOGREN H. SCP from methanol the Norprotein process [J]. Process Biochemistry, 1979, 14(3): 2-7. |
| [19] | EBBINGHAUS L, ERICSSON M, LINDBLOM M. Production of single cell protein from methanol by bacteria[J]. Advances in Biotechnology, 1981: 413-418. |
| [20] | RIDGWAY J, LAPPIN A J, et al. Single-cell protein materials from ethanol: US3865691A [P]. 1975-02-11. |
| [21] | SOLOMONS G L, LITCHFIELD J H. Single cell protein[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 1983, 1(1): 21-58. |
| [22] | BUD R. The uses of life: a history of biotechnology[M].Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1994. |
| [23] | KHAN F A. Environmental biotechnology[M]//Biotechnology fundamentals. New York: CRC Press. 2018: 316-354. |
| [24] | WESTLAKE R. Large-scale continuous production of single cell protein[J]. Chemie Ingenieur Technik, 1986, 58(12): 934-937. |
| [25] | GAO Y R, LI D P, LIU Y. Production of single cell protein from soy molasses using Candida tropicalis [J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2012, 62(3): 1165-1172. |
| [26] | JACOB-LOPES E, ZEPKA L Q, QUEIROZ M I, et al. Caracterização da fração protéica da cianobactéria Aphanothece Microscopica Nägeli cultivada no efluente da parboilização do arroz[J]. Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, 2006, 26(2): 482-488. |
| JACOB-LOPES E, ZEPKA L Q, QUEIROZ M I, et al. Protein characterisation of the Aphanothece Microscopica Nägeli cyanobacterium cultivated in parboiled rice effluent [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2006, 26(2): 482-488. | |
| [27] | YI Y Y, LI J B, ZHOU P, et al. Production of single cell protein rich in potassium by Nectaromyces rattus using biogas slurry and molasses[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 350: 119627. |
| [28] | BERTASINI D, BINATI R L, BOLZONELLA D, et al. Single cell proteins production from food processing effluents and digestate[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 296: 134076. |
| [29] | GODLEY A. Green entrepreneurship in UK foods and the emergence of the alternative meat sector: Quorn 1965—2006[J]. Business History, 2024: 1-27. |
| [30] | PEREIRA A A, YAVERINO-GUTIERREZ M A, MONTEIRO M C, et al. Precision fermentation in the realm of microbial protein production: state-of-the-art and future insights[J]. Food Research International, 2025, 200: 115527. |
| [31] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 等. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| ZHAO L, LI Z S, FU L P, et al. Progress in biomanufacturing of lipids and single cell protein from one-carbon compounds[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. | |
| [32] | 郭亮, 高聪, 柳亚迪, 等. 大肠杆菌生产饲用氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 964-981. |
| GUO L, GAO C, LIU Y D, et al. Advances in bioproduction of feed amino acid by Escherichia coli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 964-981. | |
| [33] | FREUND F, SOISONTES S, LAQUAI V, et al. Global land-use implications of preference shifts towards regional feed and sustainable diets in Germany and the European Union[J]. Ecological Economics, 2025, 228: 108455. |
| [34] | HAKME E, HERRMANN S S, POULSEN M E. European Union Proficiency Tests for pesticide residues in cereals and feedstuff, from 2007 to 2022- data collection experience[J]. Food Control, 2023, 152: 109867. |
| [35] | SPORCHIA F, KEBREAB E, CARO D. Assessing the multiple resource use associated with pig feed consumption in the European Union[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 759: 144306. |
| [36] | 李德茂, 曾艳, 周桔, 等. 生物制造食品原料市场准入政策比较及对我国的建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(8): 1041-1052. |
| LI D M, ZENG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Regulation and guidance for marketing of food ingredients from biomanufacturing and policy suggestions for China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(8): 1041-1052. | |
| [37] | EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards BIOHAZ). Scientific opinion on an update on the present knowledge on the occurrence and control of foodborne viruses[J]. EFSA Journal, 2011, 9(7): 2190. |
| [38] | Regulation (EC) No 767/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 July 2009 on the placing on the market and use of feed, amending European Parliament and Council Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003 and repealing Council Directive 79/373/EEC, DirectiveCommission 80/511/EEC, DirectivesCouncil 82/471/EEC, 83/228/EEC, 93/74/EEC, 93/113/EC and 96/25/EC and Commission Decision 2004/217 /EC (Text with EEA relevance) [EB/OL]. [2025-09-23]. |
| [39] | Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 on additives for use in animal nutrition (Text with EEA relevance) [EB/OL]. [2025-09-23]. |
| [40] | VON HOLST C, ROBOUCH P, BELLORINI S, et al. The work of the European Union Reference Laboratory for Food Additives (EURL) and its support for the authorisation process of feed additives in the European Union: a review[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 2016, 33(1): 66-77. |
| [41] | Commission Regulation (EC) No 429/2008 of 25 April 2008 on detailed rules for the implementation of Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the preparation and the presentation of applications and the assessment and the authorisation of feed additives (Text with EEA relevance) [EB/OL]. [2025-09-23]. |
| [42] | EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards BIOHAZ). Update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 4: suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2016[J]. EFSA Journal, 2016, 14(7): e04522. |
| [43] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP), RYCHEN G, AQUILINA G, et al. Guidance on the characterisation of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms[J]. EFSA Journal, 2018, 16(3): e05206. |
| [44] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP), BAMPIDIS V, AZIMONTI G, et al. Safety and efficacy of a feed additive consisting of endo-1,4-β-D-mannanase produced by Paenibacillus lentus DSM 33618 (Hemicell® HT/HT-L) for chickens and turkeys for fattening, chickens reared for laying, turkeys reared for breeding, minor poultry species to point of lay, pigs for fattening, weaned piglets and minor porcine species (Elanco GmbH)[J]. EFSA Journal, 2023, 21(2): e07878. |
| [45] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP), RYCHEN G, AQUILINA G, et al. Safety and nutritional value of a dried killed bacterial biomass from Escherichia coli (FERM BP-10942) (PT73 (TM)) as a feed material for pigs, ruminants and salmonids[J]. EFSA Journal, 2017, 15(8): e04936. |
| [46] | EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms GMO). Guidance on the risk assessment of genetically modified microorganisms and their products intended for food and feed use[J]. EFSA Journal, 2011, 9(6): 2193. |
| [47] | EFSA Panels on Genetically Modified Organisms and Animal Health and Welfare AHAW). Guidance on the risk assessment of food and feed from genetically modified animals and on animal health and welfare aspects[J]. EFSA Journal, 2012, 10(1): 2501. |
| [48] | European Food Safety Authority. Explanatory statement for the applicability of the Guidance of the EFSA Scientific Committee on conducting repeated-dose 90-day oral toxicity study in rodents on whole food/feed for GMO risk assessment [J]. EFSA Journal, 2014, 12(10): 3871. |
| [49] | EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms GMO). Guidance for renewal applications of genetically modified food and feed authorised under Regulation (EC) No 1829/2003[J]. EFSA Journal, 2015, 13(6): 4129.. |
| [50] | EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms GMO), MULLINS E, BRESSON J L, et al. Animal dietary exposure in the risk assessment of feed derived from genetically modified plants[J]. EFSA Journal, 2023, 21(1): e07732. |
| [51] | WESSELER J, KLETER G, MEULENBROEK M, et al. EU regulation of genetically modified microorganisms in light of new policy developments: possible implications for EU bioeconomy investments[J]. Applied Economic Perspectives and Policy, 2023, 45(2): 839-859. |
| [52] | EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards BIOHAZ), KOUTSOUMANIS K, ALLENDE A, et al. Scientific Opinion on the update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA (2017—2019)[J]. EFSA Journal, 2020, 18(2): e05966. |
| [53] | European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). EFSA statement on the requirements for whole genome sequence analysis of microorganisms intentionally used in the food chain[J]. EFSA Journal, 2024, 22(8): e8912. |
| [54] | BRUETSCHY C. The EU regulatory framework on genetically modified organisms (GMOs)[J]. Transgenic Research, 2019, 28(2): 169-174. |
| [55] | RAUW W M, GÓMEZ IZQUIERDO E, TORRES O, et al. Future farming: protein production for livestock feed in the EU[J]. Sustainable Earth Reviews, 2023, 6(1): 3. |
| [56] | WATERWORTH D G, HEATH M E. Pruteen in the diet of breeding pigs: reproductive performance[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 1981, 6(3): 297-307. |
| [57] | XU B Y, LIU Y C, CHEN K, et al. Evaluation of methanotroph (Methylococcus capsulatus, Bath) bacteria meal (FeedKind®) as an alternative protein source for juvenile black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii [J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2021, 8: 778301. |
| [58] | SILVA B C R, LEHNEN C R, MARCATO S M. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as a protein ingredient in poultry feed[J]. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 2024, 80(4): 1123-1154. |
| [59] | SANTORI D, GELLI A, MENEGUZ M, et al. Microbiological stability of Hermetia illucens meal subjected to two different heat treatments[J]. Journal of Stored Products Research, 2024, 109: 102440. |
| [60] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP). Scientific Opinion on the safety and efficacy of MycoCell (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a feed additive for dairy cows[J]. EFSA Journal, 2014, 12(9): 3830. |
| [61] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP), BAMPIDIS V, AZIMONTI G,, et al. Safety and efficacy of a feed additive consisting of serine protease produced by Bacillus licheniformis DSM 19670 (Ronozyme® ProAct) for chickens for fattening (DSM Nutritional Products Ltd.)[J]. EFSA Journal, 2021, 19(3): e06448. |
| [62] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP), BAMPIDIS V, AZIMONTI G, et al. Safety and efficacy of the feed additive consisting of protease produced by Bacillus licheniformis DSM 33099 (ProAct 360) for use in poultry species for fattening or reared for laying/breeding (DSM Nutritional Products Ltd)[J]. EFSA Journal, 2023, 21(8): e08163. |
| [63] | EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed FEEDAP), BAMPIDIS V, AZIMONTI G, et al. Safety and efficacy of a feed additive consisting of concentrated liquid L-lysine, L-lysine monohydrochloride and concentrated liquid L-lysine monohydrochloride produced by Escherichia coli NITE BP-02917 for all animal species (Metex NoovistaGo)[J]. EFSA Journal, 2022, 20(10): e07612. |
| [64] | RODRÍGUEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, SÁNCHEZ-MUROS M J, DEL CARMEN VARGAS-GARCÍA M, et al. Evaluation of in vitro protein hydrolysis in seven insects approved by the EU for use as a protein alternative in aquaculture[J]. Animals, 2024, 14(1): 96. |
| [65] | 李虓峰, 李会, 尚晓帆. 浅析食品相关产品现状 构建安全监管长效机制[J]. 中国标准化, 2023(13): 227-233. |
| LI X F, LI H, SHANG X F. A brief analysis on the status quo of food related products to build a long-term safety supervision mechanism[J]. China Standardization, 2023(13): 227-233. | |
| [66] | LYON J. Regulating personal care products[J]. JAMA, 2016, 316(18): 1859. |
| [67] | American Feed Industry Association. Timeline of the significant feed regulatory changes over the years [EB/OL]. [2024-12-25]. . |
| [68] | U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Food additive petitions for animal food [EB/OL].(2024-01-31) [2024-12-25]. . |
| [69] | U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) notification program [EB/OL].(2024-01-31) [2024-12-25]. . |
| [70] | U.S. Food and Drug Administration. CVM GFI #293 - FDA enforcement policy for AAFCO-defined animal feed ingredients[EB/OL]. (2024-10-23)[2024-12-25]. . |
| [71] | 魏笑莲, 钱智玲, 陈巧巧, 等. 遗传改造微生物制造食品和饲料的监管要求及欧盟授权案例分析[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(1): 121-133. |
| WEI X L, QIAN Z L, CHEN Q Q, et al. Regulatory requirements for food and feed produced with genetically modified microorganisms and case studies for EU authorization[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(1): 121-133. | |
| [72] | PRICE W D, UNDERHILL L. Application of laws, policies, and guidance from the United States and Canada to the regulation of food and feed derived from genetically modified crops: interpretation of composition data[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(35): 8349-8355. |
| [73] | Coordinated Framework for the Regulation of Biotechnology. Regulation under the coordinated framework [EB/OL]. [2024-12-06]. . |
| [74] | U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA’s regulation of plant and animal biotechnology products[EB/OL]. [2024-12-14]. . |
| [75] | United States Department of Agriculture. Biotechnology regulatory services[EB/OL]. [2025-01-23]. . |
| [76] | United States Environmental Protection Agency. Regulation of biotechnology under TSCA and FIFRA[EB/OL]. [2025-01-23]. . |
| [77] | Code of Federal Regulations. Title 21 Food and Drugs. Part 573—Food additives permitted in feed and drinking water of animals[EB/OL]. [2025-02-06]. . |
| [78] | Code of Federal Regulations. Title 21 Food and Drugs. Part 582—Substances generally recognized as safe[EB/OL]. [2025-06-02]. . |
| [79] | Code of Federal Regulations. Title 21 Food and Drugs. Part 584—Food substances affirmed as generally recognized as safe in feed and drinking water of animals[EB/OL]. [2024-12-23]. . |
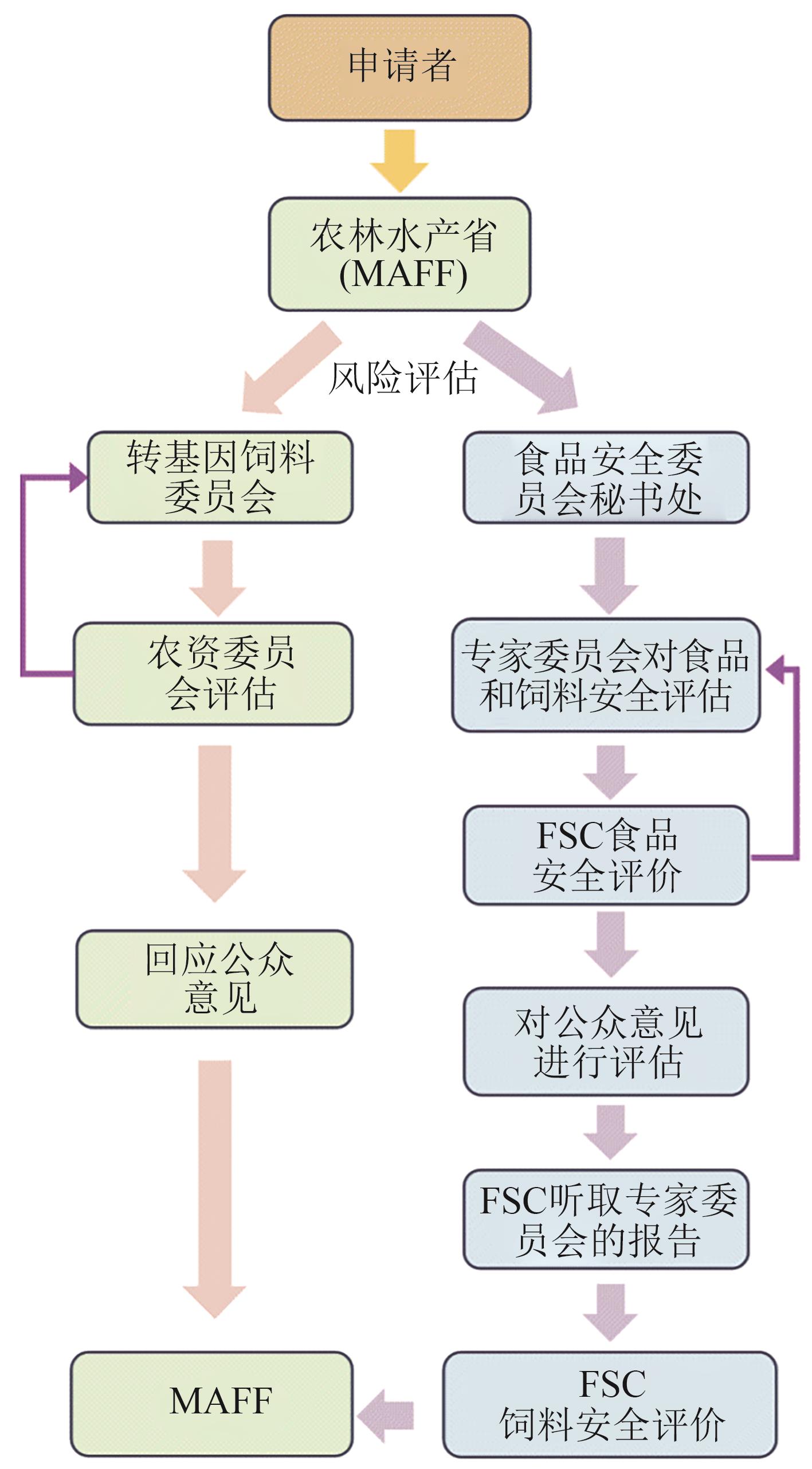
| [80] | Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center(FAMIC). Regulatory frameworks to ensure feeds safety in Japan [EB/OL]. [2025-07-06]. . |
| [81] | 農林水産省. 遺伝子組換え飼料等として安全性が確認された品目一覧[EB/OL]. (2025-07-28)[2025-07-28]. . |
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. The list of items recognized as safe for genetically modified feeds [EB/OL]. (2025-07-28)[2025-07-28]. . | |
| [82] | KONDO K, TAGUCHI C. Japanese regulatory framework and approach for genome-edited foods based on latest scientific findings[J]. Food Safety, 2022, 10(4): 113-128. |
| [83] | Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center(FAMIC). List of feed additives[EB/OL]. (2025-05-01)[2025-06-20]. . |
| [84] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第921号[EB/OL]. (2025-06-20)[2025-06-20]. . |
| Announcement No. 921 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China [EB/OL]. (2025-06-20)[2025-06-20]. . | |
| [85] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第 862 号[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2025(3): 64-140. |
| No Announcement. 862 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2025(3): 64-140. | |
| [86] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第 809 号[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2024(8): 50-117. |
| No Announcement. 809 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2024(8): 50-117. | |
| [87] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第 744 号[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2024(2): 88-89 |
| No Announcement. 744 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2024(2): 88-89 | |
| [88] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第 692 号[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2023(9): 123-125. |
| No Announcement. 692 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2023(9): 123-125. | |
| [89] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第 614 号[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2022(12): 63-69. |
| No Announcement. 614 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2022(12): 63-69. | |
| [90] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告 第 465 号[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2021(10): 79. |
| No Announcement. 465 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2021(10): 79. | |
| [91] | JIN Y, DRABIK D, HEERINK N, et al. Getting an imported GM crop approved in China[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(6): 566-569. |
| [92] | HUANG J K, WANG X B, DANG H. Impacts of and attitudes toward GM technology in China: challenges, policy and research implications[J]. China Agricultural Economic Review, 2017, 9(3): 334-339. |
| [93] | 中华人民共和国农业部公告 第2045号[EB/OL]. (2013-12-30)[2025-07-30]. . |
| Announcement No. 2045 of the ministry of agriculture and rural affairs of the People’s Republic of China[EB/OL]. (2013-12-30)[2025-07-30]. . | |
| [94] | 农业转基因生物安全管理条例(2017年10月7日修订版)[EB/OL]. (2018-01-08)[2025-07-30]. . |
| Regulations on the safety management of agricultural genetically modified organisms (Revised on October 7, 2017). [EB/OL]. (2018-01-08)[2025-07-30]. . | |
| [95] | WU Y, TIAN S J, YUAN J, et al. Effects of Clostridium autoethanogenum protein as substitute for dietary fishmeal on the growth, feed utilization, intestinal health and muscle quality of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea [J]. Aquaculture, 2022, 561: 738591. |
| [96] | ZHU S J, GAO W H, WEN Z Y, et al. Partial substitution of fish meal by Clostridium autoethanogenum protein in the diets of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides)[J]. Aquaculture Reports, 2022, 22: 100938. |
| [97] | DAI J H, LUO H, LIU Z P, et al. Evaluation of fish meal replacement by Methylcoccus capsulatus protein in diets for juvenile Chinese softshell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis)[J]. Aquaculture, 2024, 587: 740857. |
| [98] | DÍAZ-VERGARA L, PEREYRA C M, MONTENEGRO M, et al. Encapsulated whey-native yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus as a feed additive for animal production[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 2017, 34(5): 750-759. |
| [99] | 农业农村部办公厅关于印发《直接饲喂微生物和发酵制品生产菌株鉴定及其安全性评价指南》的通知(农办牧[2021]43号)[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2021(11): 97-111. |
| Circular of the general office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs on printing and distributing the guidelines on identification and safety evaluation of direct-fed microbials and fermented-food-derived bacterial strains[J]. Gazette of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2021(11): 97-111. | |
| [100] | 侯安会, 吴立新, 薛敏, 等. 乙醇梭菌蛋白的创制过程及在饲料中的应用进展[J]. 中国水产, 2024(4): 105-107. |
| HOU A H, WU L X, XUE M, et al. Creation progress and feed application of Clostridium autoethanogenum protein[J]. China Fisheries, 2024(4): 105-107. | |
| [101] | 丁健, 杨正楠, 陆健, 等. 美国饲料原料和饲料添加剂行业准入管理及启示[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2022, 58(11): 307-310. |
| DING J, YANG Z N, LU J, et al. Access management of feed raw materials and feed additives in the United States and its enlightenment[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2022, 58(11): 307-310. | |
| [102] | European Food Safety Authority(EFSA). EFSA statement on the requirements for whole genome sequence analysis of microorganisms intentionally used in the food chain[J]. EFSA Journal, 2021, 19(7): e06506. |
| [103] | 赖锴. 我国饲料行业管理法规体系的规范化探析[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2019, 39(4): 65-69. |
| LAI K. Analysis on standardization of management laws and regulations system of feed industry in China[J]. China Herbivore Science, 2019, 39(4): 65-69. |
| [1] | HAN Lin, GUO Yuman, LI Yan, CAO Hengheng, LI Jiajing, YANG Minghao, WANG Mengmeng, LI Jinping, LV Yongqin. Advances in electro-microbial synergistic systems for value-added conversion of carbon dioxide [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-30. |
| [2] | LIU Jiakun, YOU Di, XIANYU Yunlei, QU Qiang. Multi-party collaborative secured DNA data storage and access: toward a hybrid dna-silicon storage facility [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-11. |
| [3] | ZHONG Naicai, CHEN Yuan, PAN Wenfeng, SU Xiaofeng, LIAO Jingwen, ZHAI Yinglei, ZHONG Jinyi. Application of plasma microbial breeding technology in biofabrication [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 789-805. |
| [4] | WANG Kunkun, CHEN Hongyu, ZHANG Andong, LU Xiaoyun, TAN Dan. A preliminary study on the regulation and analysis of indole mediated bidirectional chemotaxis behavior of Escherichia coli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-22. |
| [5] | LI Yongzhu, CHEN Yu. Advances and prospects in genome-scale models of yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 585-602. |
| [6] | ZHU Siyu, ZHAO Xuanye, YU Wenjing, CAO Jingtian, LIU Sihui, QIAN Wenda, JIA Haiyang. Advances in Biological Recovery of Key Battery Metals [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-18. |
| [7] | KUANG Jiaqi, ZHANG Suxiu, JIANG Han, WEI Tao. Research on live biotherapeutic products in metabolic diseases [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-17. |
| [8] | HUANG Shuhan, MA He, LUO Yunzi. Research progress in the biosynthesis of salidroside [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 391-407. |
| [9] | LU Jinchang, WU Yaokang, LV Xueqin, LIU Long, CHEN Jian, LIU Yanfeng. Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 422-444. |
| [10] | ZHOU Yujie, YI Xiao. Engineering an in vivo directed evolution system for developing genetic switches [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-13. |
| [11] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [12] | REN Jiawei, ZHANG Jinpeng, XU Guoqiang, ZHANG Xiaomei, XU Zhenghong, ZHANG Xiaojuan. Effect of terminators on the downstream transcript unit with gene expression in Escherichiacoli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 213-227. |
| [13] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [14] | LIU Kuanqing, ZHANG Yi-Heng P.Job. Biological degradation and utilization of lignin [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1264-1278. |
| [15] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||