Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 789-805.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-005
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of plasma microbial breeding technology in biofabrication
ZHONG Naicai1,2, CHEN Yuan1, PAN Wenfeng1, SU Xiaofeng1, LIAO Jingwen1, ZHAI Yinglei2, ZHONG Jinyi1,3
- 1.Guangzhou Institute of Advanced Technology,Guangzhou 511458,Guangdong,China
2.Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 117004,Liaoning,China
3.National Innovation Center for Bio-Manufacturing Industry,Shenzhen 518107,Guangodng,China
-
Received:2025-01-20Revised:2025-03-05Online:2025-09-03Published:2025-08-31 -
Contact:ZHONG Jinyi
等离子体微生物育种技术在生物制造中的应用进展
钟奶才1,2, 陈缘1, 潘文锋1, 苏小凤1, 廖景文1, 翟英雷2, 钟近艺1,3
- 1.广州先进技术研究所,广东 广州 511458
2.沈阳药科大学,辽宁 沈阳 117004
3.国家生物制造产业创新中心,广东 深圳 518107
-
通讯作者:钟近艺 -
作者简介:钟奶才 (1999—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为等离子体微生物育种。 E-mail:kylian66@163.com钟近艺 (1975—),女,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为核生化防护技术。E-mail:jy.zhong@giat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFC2604700)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHONG Naicai, CHEN Yuan, PAN Wenfeng, SU Xiaofeng, LIAO Jingwen, ZHAI Yinglei, ZHONG Jinyi. Application of plasma microbial breeding technology in biofabrication[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 789-805.
钟奶才, 陈缘, 潘文锋, 苏小凤, 廖景文, 翟英雷, 钟近艺. 等离子体微生物育种技术在生物制造中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 789-805.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-005
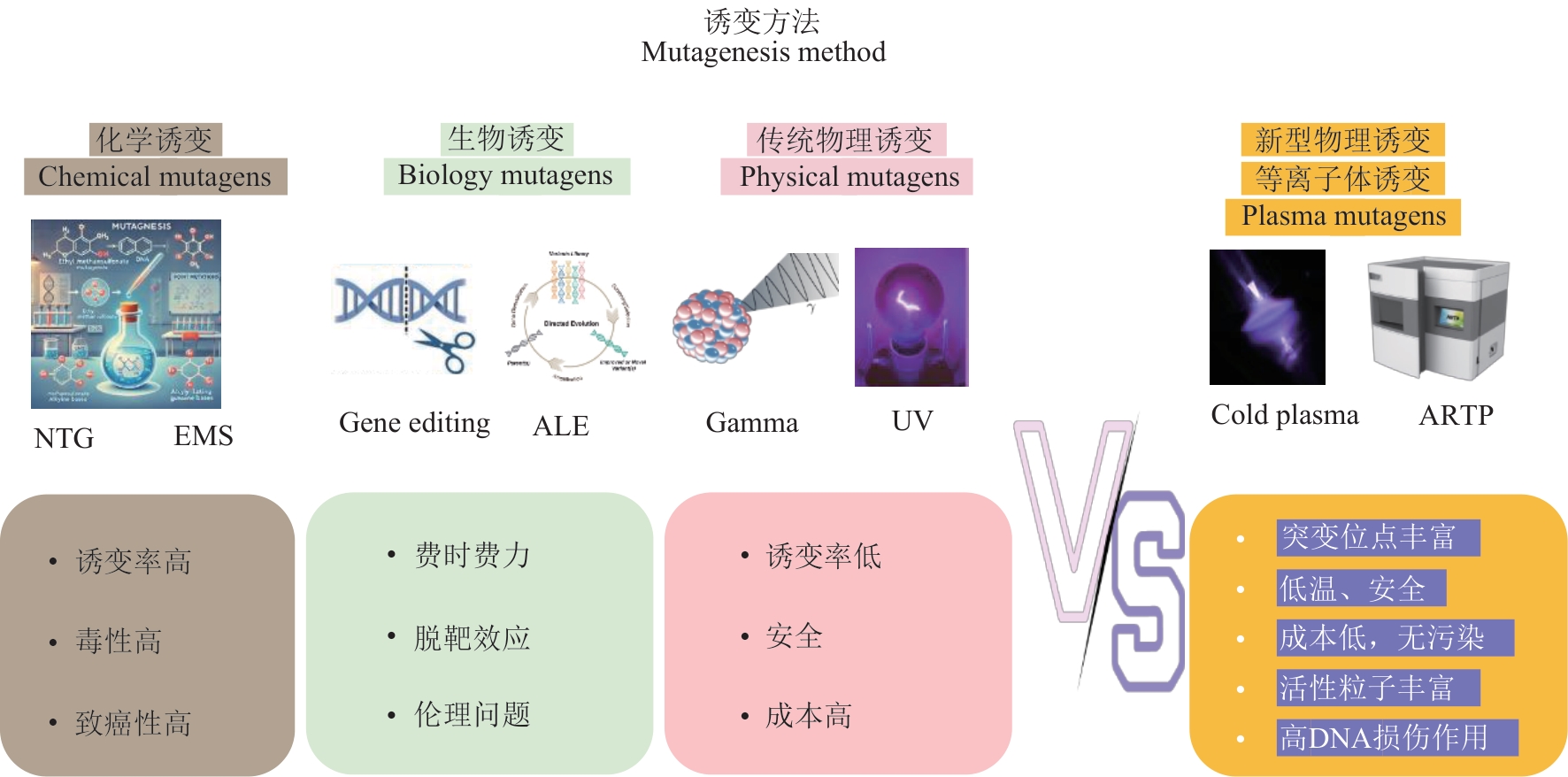
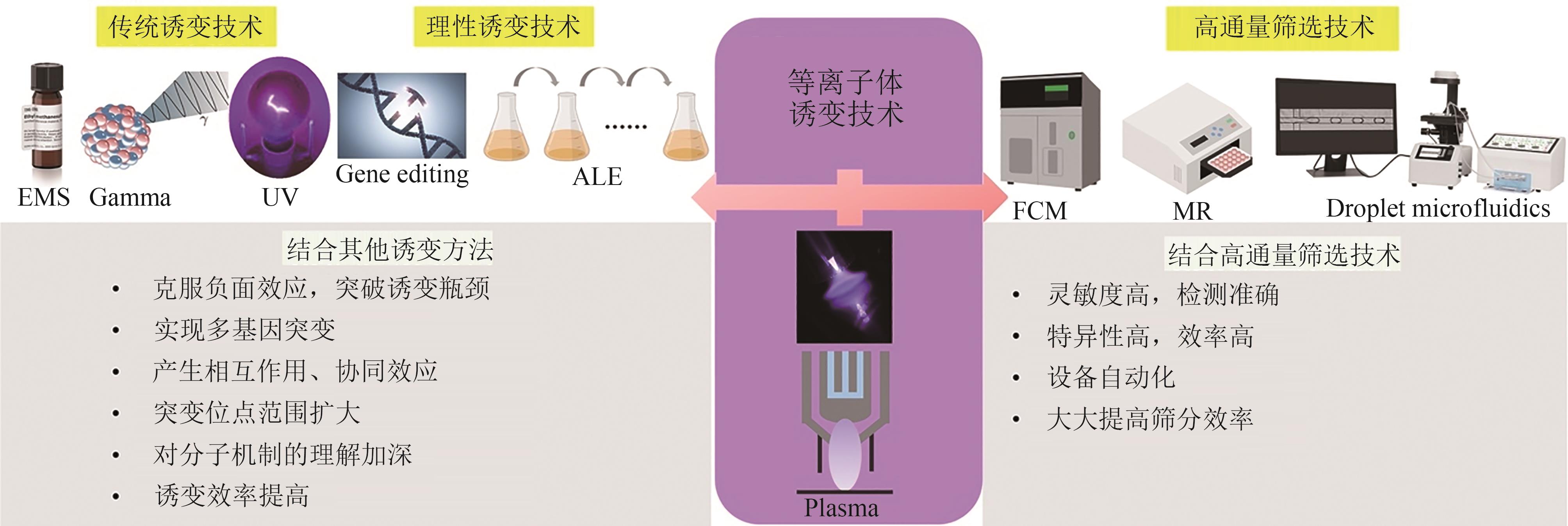
| 等离子体联用技术 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 高通量筛选技术 | 筛选效率高,筛选范围广通量高 | 设备成本要求高,操作复杂 |
| 传统诱变方法 | 互补性强突变位点广,突破单一方法局限 | 操作烦琐,遗传稳定性差 |
| 理性突变方法 | 精准性高,突变效果明显 | 技术要求高,成本较高,伦理限制 |
Table 1 Advantages and disadvantages of plasma coupling technology
| 等离子体联用技术 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 高通量筛选技术 | 筛选效率高,筛选范围广通量高 | 设备成本要求高,操作复杂 |
| 传统诱变方法 | 互补性强突变位点广,突破单一方法局限 | 操作烦琐,遗传稳定性差 |
| 理性突变方法 | 精准性高,突变效果明显 | 技术要求高,成本较高,伦理限制 |
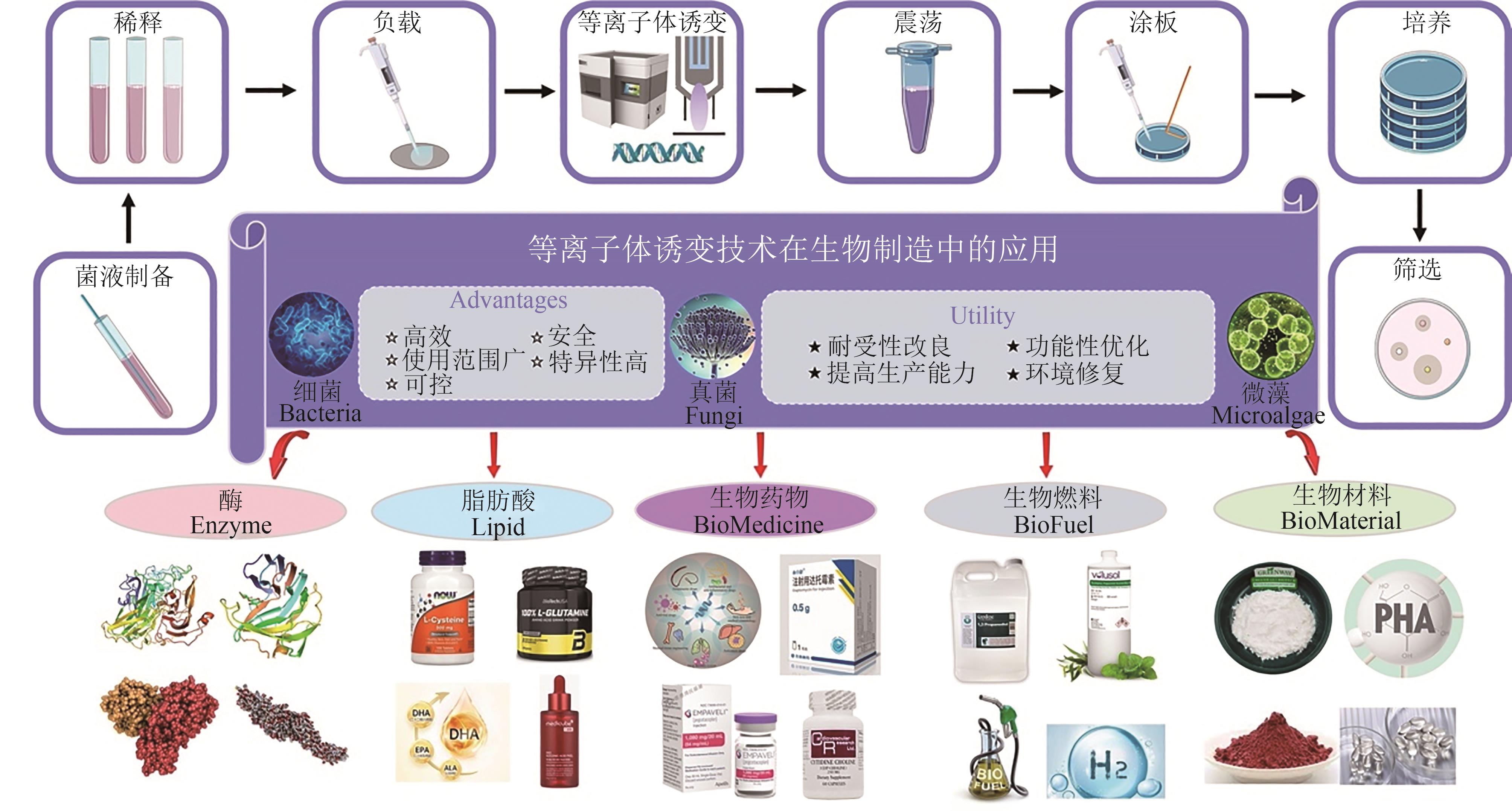
应用 领域 | 诱变菌株 | 诱变目的 | 评价参数 | 实验结果 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酶 | 红平菇 | 漆酶 | 酶活 | 酶活提高86.36%,遗传稳定 | [ |
| 莫巴拉链霉菌 | 谷氨酰胺转氨酶 | 比活性 | TGase提高35.6倍和2.9倍 | [ | |
| 米曲霉 | 蛋白酶 | 酶活 | 酶活及相关关键基因表达提高 | [ | |
| 黑曲霉 | 单宁酶 | 酶活 | 酶活提高2.27倍,具良好遗传稳定性 | [ | |
| 高山被孢霉 | 花生四烯酸(ARA) | 花生四烯酸产量 | ARA总脂肪酸占比及总产量分别提高75.40%和232.21% | [ | |
| 脂肪酸 | 大肠杆菌 | L-半胱氨酸 | 滴度 | L-半胱氨酸滴度增加了2.2倍 | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | 谷氨酸 | 耐高糖和丙二酸 | 合成关键基因表达提高 | [ | |
| 酿酒酵母 | 酪氨酸 | 前体香豆酸p-CA滴度 | p-CA产量提高7.6倍 | [ | |
| 裂殖壶菌 | 二十二碳六烯酸(DHA) | 关键酶表达及DHA产量 | DHA产量提高14.3% | [ | |
| 琥珀酸放线杆菌 | 琥珀酸 | 抗逆性、产量 | 琥珀酸环境抗逆性提高2倍,产量增加113% | [ | |
生物 药物 | 马杜拉放线菌 | 喷司他丁 | 喷司他丁产量 | 喷司他丁产量增加33.79% | [ |
| 短孢杆菌SPR20 | 抗菌肽 | MIC值 | MIC值达到250~500 μg/mL和500 μg/mL | [ | |
| 玫瑰链霉菌 | 达托霉素 | 达托霉素产量 | 达托霉素产量提高58.33% | [ | |
| 大肠杆菌E. coli NXBG-13 | 胞苷 | 胞苷滴度、产量、生产率 | 胞苷的效价、产量和生产率达到15.7 g/L, 0.164 g/g和0.327 g/(L·h) | [ | |
| 桑黄多孔菌 | 胞内多糖 | 多糖产量 | 多糖产量提高1.5倍 | [ | |
生物 燃料 | 丁酸梭菌 | 1,3-丙二醇 (1,3-PD) | 1,3-PD滴度 | 1,3-PD滴度提高4.88倍 | [ |
| 嗜热毁丝霉 | 木聚糖酶 | 酶活、耐酸性 | 木聚糖酶活性提高21.71%,酸性(pH 4.0~7.0)适应性提高 | [ | |
| 酿酒酵母 | 乙醇 | 乙醇及前体产量 | 乙酸乙酯和乙酸异戊酯浓度提高2.8倍和3.3倍 | [ | |
| 卷枝毛霉 | 生物柴油 | 甲醇耐受性、生物柴油产率 | 甲醇耐受性提高,柴油产率达到91% | [ | |
| 热带念珠菌 | 脂质 | 脂质产量 | 脂质产量增强16.8% | [ | |
| 莱茵衣藻 | 氢气 | 氢气产量 | 氢气产量增加1.8~5.2倍和2.7~3.1倍 | [ | |
| 凯斯小球藻 | 生物柴油、脂质 | 生物柴油、脂质产量 | 生物量和脂质生产力提高75%和44% | [ | |
生物 材料 | 嗜盐单胞菌 | 聚羟基脂肪酸酯 | 盐胁迫条件 | 生产盐度降低,PHA生产成本降低33% | [ |
| 出芽短梗霉 | 普鲁兰多糖 | 普鲁兰多糖产量 | 普鲁兰多糖产量提高17.6% | [ | |
| 蜡样芽孢杆菌 | 壳聚糖酶 | 酶活 | 壳聚糖酶活性提高2.49倍 | [ | |
| 紫红曲霉 | 色素 | 橙色素、橘霉素含量 | 橙色素产量提高66.7%,橘霉素降低69% | [ | |
| 克雷伯氏菌 | 苯二甲酸丙二醇酯单体1,3-丙二醇 | 1,3-丙二醇产量,甘油转化率 | 1,3-丙二醇产量达到118 g/L,甘油转化率为42% | [ |
Table 2 Application of plasma mutagenesis breeding technology in biofabrication
应用 领域 | 诱变菌株 | 诱变目的 | 评价参数 | 实验结果 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酶 | 红平菇 | 漆酶 | 酶活 | 酶活提高86.36%,遗传稳定 | [ |
| 莫巴拉链霉菌 | 谷氨酰胺转氨酶 | 比活性 | TGase提高35.6倍和2.9倍 | [ | |
| 米曲霉 | 蛋白酶 | 酶活 | 酶活及相关关键基因表达提高 | [ | |
| 黑曲霉 | 单宁酶 | 酶活 | 酶活提高2.27倍,具良好遗传稳定性 | [ | |
| 高山被孢霉 | 花生四烯酸(ARA) | 花生四烯酸产量 | ARA总脂肪酸占比及总产量分别提高75.40%和232.21% | [ | |
| 脂肪酸 | 大肠杆菌 | L-半胱氨酸 | 滴度 | L-半胱氨酸滴度增加了2.2倍 | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | 谷氨酸 | 耐高糖和丙二酸 | 合成关键基因表达提高 | [ | |
| 酿酒酵母 | 酪氨酸 | 前体香豆酸p-CA滴度 | p-CA产量提高7.6倍 | [ | |
| 裂殖壶菌 | 二十二碳六烯酸(DHA) | 关键酶表达及DHA产量 | DHA产量提高14.3% | [ | |
| 琥珀酸放线杆菌 | 琥珀酸 | 抗逆性、产量 | 琥珀酸环境抗逆性提高2倍,产量增加113% | [ | |
生物 药物 | 马杜拉放线菌 | 喷司他丁 | 喷司他丁产量 | 喷司他丁产量增加33.79% | [ |
| 短孢杆菌SPR20 | 抗菌肽 | MIC值 | MIC值达到250~500 μg/mL和500 μg/mL | [ | |
| 玫瑰链霉菌 | 达托霉素 | 达托霉素产量 | 达托霉素产量提高58.33% | [ | |
| 大肠杆菌E. coli NXBG-13 | 胞苷 | 胞苷滴度、产量、生产率 | 胞苷的效价、产量和生产率达到15.7 g/L, 0.164 g/g和0.327 g/(L·h) | [ | |
| 桑黄多孔菌 | 胞内多糖 | 多糖产量 | 多糖产量提高1.5倍 | [ | |
生物 燃料 | 丁酸梭菌 | 1,3-丙二醇 (1,3-PD) | 1,3-PD滴度 | 1,3-PD滴度提高4.88倍 | [ |
| 嗜热毁丝霉 | 木聚糖酶 | 酶活、耐酸性 | 木聚糖酶活性提高21.71%,酸性(pH 4.0~7.0)适应性提高 | [ | |
| 酿酒酵母 | 乙醇 | 乙醇及前体产量 | 乙酸乙酯和乙酸异戊酯浓度提高2.8倍和3.3倍 | [ | |
| 卷枝毛霉 | 生物柴油 | 甲醇耐受性、生物柴油产率 | 甲醇耐受性提高,柴油产率达到91% | [ | |
| 热带念珠菌 | 脂质 | 脂质产量 | 脂质产量增强16.8% | [ | |
| 莱茵衣藻 | 氢气 | 氢气产量 | 氢气产量增加1.8~5.2倍和2.7~3.1倍 | [ | |
| 凯斯小球藻 | 生物柴油、脂质 | 生物柴油、脂质产量 | 生物量和脂质生产力提高75%和44% | [ | |
生物 材料 | 嗜盐单胞菌 | 聚羟基脂肪酸酯 | 盐胁迫条件 | 生产盐度降低,PHA生产成本降低33% | [ |
| 出芽短梗霉 | 普鲁兰多糖 | 普鲁兰多糖产量 | 普鲁兰多糖产量提高17.6% | [ | |
| 蜡样芽孢杆菌 | 壳聚糖酶 | 酶活 | 壳聚糖酶活性提高2.49倍 | [ | |
| 紫红曲霉 | 色素 | 橙色素、橘霉素含量 | 橙色素产量提高66.7%,橘霉素降低69% | [ | |
| 克雷伯氏菌 | 苯二甲酸丙二醇酯单体1,3-丙二醇 | 1,3-丙二醇产量,甘油转化率 | 1,3-丙二醇产量达到118 g/L,甘油转化率为42% | [ |
| [29] | YARANGSEE P, KHACHA-ANANDA S, PITCHAKARN P, et al. A nonclinical safety evaluation of cold atmospheric plasma for medical applications: the role of genotoxicity and mutagenicity studies[J]. Life, 2024, 14(6): 759. |
| [30] | PATENALL B L, HATHAWAY H J, LAABEI M, et al. Assessment of mutations induced by cold atmospheric plasma jet treatment relative to known mutagens in Escherichia coli [J]. Mutagenesis, 2021, 36(5): 380-387. |
| [31] | LI G, LI H P, WANG L Y, et al. Genetic effects of radio-frequency, atmospheric-pressure glow discharges with helium[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(22): 221504. |
| [32] | KHLYUSTOVA A, LABAY C, MACHALA Z, et al. Important parameters in plasma jets for the production of RONS in liquids for plasma medicine: a brief review[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2019, 13(2): 238-252. |
| [33] | CHEN H X, BAI F W, XIU Z L. Oxidative stress induced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae exposed to dielectric barrier discharge plasma in air at atmospheric pressure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(8): 1885-1891. |
| [34] | SREEDEVI P R, SURESH K. Cold atmospheric plasma mediated cell membrane permeation and gene delivery-empirical interventions and pertinence[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 320: 102989. |
| [35] | NIEDŹWIEDŹ I, WAŚKO A, PAWŁAT J, et al. The state of research on antimicrobial activity of cold plasma[J]. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 68(2): 153-164. |
| [36] | ZHANG A D, MA Y D, DENG Y, et al. Enhancing protease and amylase activities in Bacillus licheniformis XS-4 for traditional soy sauce fermentation using ARTP mutagenesis[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(12): 2381. |
| [37] | JIANG P X, WANG L Y, HUANG Z L, et al. Studies on the mutation breeding mechanism of Streptomyces avermitilis by a novel atmospheric-pressure, low-temperature discharge plasma[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2008, 136: S22. |
| [38] | LIEW K J, ZHANG X H, CAI X H, et al. The biological responses of Staphylococcus aureus to cold plasma treatment[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(4): 1188. |
| [39] | GAUR N, KURITA H, OH J S, et al. On cold atmospheric-pressure plasma jet induced DNA damage in cells[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2021, 54(3): 035203. |
| [40] | ADHIKARI E R, PTASINSKA S. Correlation between helium atmospheric pressure plasma jet (APPJ) variables and plasma induced DNA damage[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2016, 70(9): 180. |
| [41] | LI M T, GAO S H, YANG P C, et al. Improvement of ribonucleic acid production in Cyberlindnera jadinii and optimization of fermentation medium[J]. AMB Express, 2024, 14(1): 24. |
| [42] | HUANG Y T, WANG L Y, ZHANG X, et al. Quantitative evaluation of DNA damage caused by atmospheric and room-temperature plasma (ARTP) and other mutagenesis methods using a rapid umu-microplate test protocol for microbial mutation breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 39: 205-210. |
| [43] | ZHANG H, YANG L F, YU Z L, et al. Inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa by DC glow discharge plasma: impacts on cell integrity, pigment contents and microcystins degradation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 268: 33-42. |
| [44] | FAN X G, WU H Y, LI G L, et al. Improvement of uridine production of Bacillus subtilis by atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis and high-throughput screening[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0176545. |
| [45] | YU F, ZHANG M, SUN J F, et al. Improved neomycin sulfate potency in Streptomyces fradiae using atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis and fermentation medium optimization[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(1): 94. |
| [46] | 祝金山, 吴烨飞, 陆建卫. 常压室温等离子体诱变选育核黄素高产突变株[J]. 发酵科技通讯, 2020, 49(1): 58-62. |
| ZHU J S, WU Y F, LU J W. Mutagenesis of Bacillus subtilis using the atmospheric and room temperature plasma technology for improved riboflavin production[J]. Bulletin of Fermentation Science and Technology, 2020, 49(1): 58-62. | |
| [47] | YUAN H L, TU R, TONG X W, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput screening of industrial enzyme-producing strains by droplet-based microfluidic system[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 49(3): kuac007. |
| [48] | HU W, LI W, CHEN J. Recent advances of microbial breeding via heavy-ion mutagenesis at IMP[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2017, 65(4): 274-280. |
| [49] | QIU L, NIE S X, HU S J, et al. Screening of Beauveria bassiana with high biocontrol potential based on ARTP mutagenesis and high-throughput FACS[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2021, 171: 104732. |
| [50] | DING R R, HUANG R L, SU H, et al. Screening of astaxanthin-overproducing Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous strains via iterative ARTP mutagenesis and cell sorting by flow cytometry[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2024, 135(2): lxae020. |
| [51] | 袁姚梦, 邢新会, 张翀. 微生物细胞工厂的设计构建: 从诱变育种到全基因组定制化创制[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 656-673. |
| YUAN Y M, XING X H, ZHANG C. Progress and prospective of engineering microbial cell factories: from random mutagenesis to customized design in genome scale[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 656-673. | |
| [52] | 梁英, 闫译允, 赖秋璇, 等. 微藻诱变育种研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(6): 19-32. |
| [1] | YU Q H, LI Y C, WU B, et al. Novel mutagenesis and screening technologies for food microorganisms: advances and prospects[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(4): 1517-1531. |
| [2] | MAGOCHA T A, ZABED H, YANG M M, et al. Improvement of industrially important microbial strains by genome shuffling: current status and future prospects[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 257: 281-289. |
| [3] | WU Y N, JAMEEL A, XING X H, et al. Advanced strategies and tools to facilitate and streamline microbial adaptive laboratory evolution[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(1): 38-59. |
| [4] | CABAHUG R A M, HA M K T T, LIM K B, et al. LD50 determination and phenotypic evaluation of three Echeveria varieties induced by chemical mutagens[J]. Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences, 2020, 12(1): 1-9. |
| [5] | KODYM A, AFZA R. Physical and chemical mutagenesis[M/OL]//Plant functional genomics. New Jersey: Humana Press, 2003: 189-203 [2025-01-01]. . |
| [6] | OTTENHEIM C, NAWRATH M, WU J C. Microbial mutagenesis by atmospheric and room-temperature plasma (ARTP): the latest development[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2018, 5(1): 12. |
| [7] | LIU T, HUANG Z Y, GUI X, et al. Multi-omics comparative analysis of Streptomyces mutants obtained by iterative atmosphere and room-temperature plasma mutagenesis[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 11: 630309. |
| [8] | ACHEAMPONG A, BONDZIE-QUAYE P, FETISOA M R, et al. Applications of low-temperature plasma technology in microalgae cultivation and mutant breeding: a comprehensive review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2025, 419: 132019. |
| [9] | FOOLADI S, RABIEE N, IRAVANI S. Genetically engineered bacteria: a new frontier in targeted drug delivery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2023, 11(42): 10072-10087. |
| [10] | VADIKKEETTIL Y, SUBRAMANIAM Y, MURUGAN R, et al. Plasma assisted decomposition and reforming of greenhouse gases: a review of current status and emerging trends[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 161: 112343. |
| [11] | JIA Y K, LI T H, ZHANG R, et al. Different bactericidal abilities of plasma-activated saline with various reactive species prepared by surface plasma-activated air and plasma jet combinations[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2024, 26(1): 015502. |
| [12] | WANG L Y, ZHAO H X, HE D, et al. Insights into the molecular-level effects of atmospheric and room-temperature plasma on mononucleotides and single-stranded homo- and hetero-oligonucleotides[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 14298. |
| [13] | ZHU Z R, DING X Z, RANG J, et al. Application and research progress of ARTP mutagenesis in actinomycetes breeding[J]. Gene, 2024, 929: 148837. |
| [52] | LIANG Y, YAN Y Y, LAI Q X, et al. Researching advances in microalgal mutation breeding[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2020, 50(6): 19-32. |
| [53] | WAN Z J, HU H B, LIU K, et al. Engineering industrial yeast for improved tolerance and robustness[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2024, 44(8): 1461-1477. |
| [54] | MA Y H, SUN X, SUN Y R, et al. Synchronous enhancement of astaxanthin and lipid accumulation in Haematococcus lacustris through co-mutation of ethanol and atmospheric and room temperature plasma: exploration of characteristics and underlying mechanisms[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 394: 130305. |
| [55] | WANG L J, LYU Y B, MIAO X, et al. Enhanced protein glutaminase production from Chryseobacterium proteolyticum combining physico-chemical mutagenesis and resistance screening and its application to soybean protein isolates[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2023, 103(9): 4562-4572. |
| [56] | SUN J J, ZHANG Z, LIU J S, et al. UV-ARTP combined mutagenesis selection of lignin-degrading strain and enzymatic characterization of the resultant organisms[J]. Food Bioscience, 2024, 60: 104478. |
| [57] | XIA X K, ZHANG Y E, LEI S J, et al. Identification and iterative combinatorial mutagenesis of a new naringinase-producing strain, Aspergillus tubingensis MN589840[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2021, 72(2): 141-148. |
| [58] | PAN J, ZHANG J, WEI H F, et al. Optimizing mycelial protein yield in Pleurotus djamor via ARTP mutagenesis and hybridization strategies[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 386: 64-71. |
| [59] | 张萍, 石彦鹏, 牛春, 等. 霉酚酸高产菌株短密青霉菌SA-2的选育[J]. 生物资源, 2022, 44(4): 411-416. |
| ZHANG P, SHI Y P, NIU C, et al. Screening of Penicillium brevicompactum SA-2 with high yield of mycophenolic acid[J]. Biotic Resources, 2022, 44(4): 411-416. | |
| [60] | ZHANG X J, LIU L, MA C, et al. Improving the level of the cytidine biosynthesis in E. coli through atmospheric room temperature plasma mutagenesis and metabolic engineering[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2024, 135(6): lxae133. |
| [61] | Belinda Amanda Nyabako. 基于常压室温等离子体诱变(ARTP)结合适应性进化(ALE)提高嗜酸乳杆菌的耐酸性能[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2020. |
| NYABAKO B A. Enhancing acid tolerance of Lactobacilus acidophilus atomospheric and room temperature plasma(ARTP) with adaptive laboratory evolution (ALE) [D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2020. | |
| [14] | SETSUHARA Y. Low-temperature atmospheric-pressure plasma sources for plasma medicine[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2016, 605: 3-10. |
| [15] | BRANDENBURG R. Dielectric barrier discharges: progress on plasma sources and on the understanding of regimes and single filaments[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2017, 26(5): 053001. |
| [16] | VO P H N, KIM M, KUZHIUMPARAMBIL U, et al. Random mutagenesis using cold atmospheric plasma to produce mutant microalgae for hyper-recovery of rare earth elements from mining materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 503: 158512. |
| [17] | KOH H G, KIM J, RAO C V, et al. Construction of a compact array of Microplasma jet devices and its application for random mutagenesis of Rhodosporidium toruloides [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(11): 3406-3413. |
| [18] | ZHANG X, ZHANG X F, LI H P, et al. Atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) as a new powerful mutagenesis tool[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(12): 5387-5396. |
| [19] | UMAIR M, JABBAR S, AYUB Z, et al. Recent advances in plasma technology: influence of atmospheric cold plasma on spore inactivation[J]. Food Reviews International, 2022, 38(S1): 789-811. |
| [20] | WEI Q Y, YUAN Y, ZHANG J H, et al. Fungicidal efficiency of DBD cold plasma against Aspergillus niger on dried jujube[J]. Food Microbiology, 2024, 121: 104523. |
| [21] | MA C L, NIKIFOROV A, DE GEYTER N, et al. Plasma for biomedical decontamination: from plasma-engineered to plasma-active antimicrobial surfaces[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2022, 36: 100764. |
| [22] | 徐欢欢, 张红兵, 李会宣, 等. 常压室温等离子体技术在微生物诱变中的应用进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2020, 10(4): 358-362. |
| XU H H, ZHANG H B, LI H X, et al. Application progress of atmospheric and room temperature plasma technology in microbial mutagenesis[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2020, 10(4): 358-362. | |
| [23] | WANG L Y, HUANG Z L, LI G, et al. Novel mutation breeding method for Streptomyces avermitilis using an atmospheric pressure glow discharge plasma[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2010, 108(3): 851-858. |
| [24] | LIU J H, CHEN J, CHEN Z, et al. Isolation and characterization of astaxanthin-hyperproducing mutants of Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae) produced by dielectric barrier discharge plasma[J]. Phycologia, 2016, 55(6): 650-658. |
| [25] | GUAN Y X, TANG S Y, WANG S Q, et al. Degradation of toluene with negative DC Corona plasma enhanced by microdischarge[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2022, 50(1): 61-68. |
| [62] | REN Y, YANG X W, DING L T, et al. Adaptive evolutionary strategy coupled with an optimized biosynthesis process for the efficient production of pyrroloquinoline quinone from methanol[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 2023, 16(1): 11. |
| [63] | ZHOU K, YU C, LIANG N, et al. Adaptive evolution and metabolic engineering boost lycopene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via enhanced precursors supply and utilization[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(8): 3821-3831. |
| [64] | ZHANG Z C, SHAH A M, MOHAMED H, et al. Improved laccase production in Pleurotus djamor RP by atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis[J]. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 58: 1-9. |
| [65] | YE J C, YANG P H, ZHOU J W, et al. Efficient production of a thermostable mutant of transglutaminase by Streptomyces mobaraensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(8): 4207-4216. |
| [66] | GAO X L, LIU E M, YIN Y Y, et al. Enhancing activities of salt-tolerant proteases secreted by Aspergillus oryzae using atmospheric and room-temperature plasma mutagenesis[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(9): 2757-2764. |
| [67] | 马东旭, 李忠辉, 张子恒, 等. 高产单宁酶黑曲霉菌株的常温常压等离子体诱变选育及发酵工艺研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2025, 51(12): 115-122. |
| MA D X, LI Z H, ZHANG Z H, et al. Atmospheric room temperature plasma mutagenesis breeding and fermentation optimization of Aspergillus niger with high yield of tannase[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2025, 51(12): 115-122. | |
| [68] | 张鑫, 凤元邦, 冯雪, 等. 紫外-LiCl联合ARTP诱变选育高产花生四烯酸的高山被孢霉突变株[J]. 中国油脂, 2025, 50(4): 82-87, 110. |
| ZHANG X, FENG Y B, FENG X, et al. Breeding of Mortierella alpina mutants with high yield of arachidonic acid by UV-LiCl combined with ARTP mutagenesis[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2025, 50(4): 82-87, 110. | |
| [69] | YANG H, ZHANG B, WU Z D, et al. Synergistic application of atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis and adaptive laboratory evolution improves the tolerance of Escherichia coli to L-cysteine[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 19(2): 2300648. |
| [70] | SHANGGUAN L L, ZHANG H Y, LIU Z X, et al. Improved glutamic acid production capacity of Corynebacterium glutamicum by the ARTP mutagenesis method[J]. Fermentation, 2023, 9(7): 599. |
| [71] | CAI M, WU Y Z, QI H, et al. Improving the level of the tyrosine biosynthesis pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through HTZ1 knockout and atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(1): 49-62. |
| [26] | MAGUREANU M, PIROI D, GHERENDI F, et al. Decomposition of methylene blue in water by Corona discharges[J]. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2008, 28(6): 677-688. |
| [27] | WANG R R, BIAN W, HU Z R, et al. Mutation of Bacillus velezensis using Corona discharge[J]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(1): 166. |
| [28] | XU Y Y, BASSI A. Non-thermal plasma decontamination of microbes: a state of the art[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2025, 41(2): e3511. |
| [72] | WANG Q, JIN W B, ZHOU X, et al. Enhancing docosahexaenoic acid production in Aurantiochytrium species using atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis and comprehensive multi-omics analysis[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2024, 912: 169217. |
| [73] | WU J, LI Y L, YIN J B, et al. Mutation breeding of high-stress resistant strains for succinic acid production from corn straw[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2024, 108(1): 278. |
| [74] | ZHANG H Y, ZHANG D G, LIU R, et al. Enhanced pentostatin production in Actinomadura sp. by combining ARTP mutagenesis, ribosome engineering and subsequent fermentation optimization[J]. Fermentation, 2023, 9(4): 398. |
| [75] | SONGNAKA N, LERTCANAWANICHAKUL M, HUTAPEA A M, et al. Atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis improved the anti-MRSA activity of Brevibacillus sp. SPR20[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(15): 12016. |
| [76] | ZHU C Y, ZHAO X Y, LYU Z Y, et al. Daptomycin production enhancement by ARTP mutagenesis and fermentation optimization in Streptomyces roseosporus[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2023, 134(10): lxad230. |
| [77] | LI T T, CHEN L J, WU D, et al. The structural characteristics and biological activities of intracellular polysaccharide derived from mutagenic Sanghuangporous sanghuang strain[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(16): 3693. |
| [78] | YUN J H, ZABED H M, ZHANG Y F, et al. Improving tolerance and 1,3-propanediol production of Clostridium butyricum using physical mutagenesis, adaptive evolution and genome shuffling[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 363: 127967. |
| [79] | ZHANG N, JIANG Y, SUN Y J, et al. Breeding of a thermostable xylanase-producing strain of Myceliophthora thermophila by atmospheric room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 10: 1095323. |
| [80] | HONG K Q, FU X M, LEI F F, et al. Selection of salt-tolerance and ester-producing mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae to improve flavour formation of soy sauce during co-fermentation with Torulopsis globosa [J]. Foods, 2023, 12(18): 3449. |
| [81] | JI S L, XIE X Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Atmospheric and room temperature plasma treatment to improve methanol tolerance and catalytic activity of Mucor circinelloides for one-step biodiesel production[J]. Fuel, 2025, 387: 134343. |
| [82] | LUO H, ZHAO Z J, HUANG R, et al. High-temperature fermentation of corn stover for biodiesel production using Candida tropicalis with enhanced lipid accumulation: a new strategy for breeding thermotolerant biodiesel-production strains[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2023, 206: 117542. |
| [83] | BAN S D, LIN W T, LUO Z W, et al. Improving hydrogen production of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by reducing chlorophyll content via atmospheric and room temperature plasma[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 275: 425-429. |
| [84] | ELSHOBARY M E, ZABED H M, QI X H, et al. Enhancing biomass and lipid productivity of a green microalga Parachlorella kessleri for biodiesel production using rapid mutation of atmospheric and room temperature plasma[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 2022, 15(1): 122. |
| [85] | ZHANG L Z, LIN Y N, YI X Q, et al. Engineering low-salt growth Halomonas bluephagenesis for cost-effective bioproduction combined with adaptive evolution[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2023, 79: 146-158. |
| [86] | BAI R X, CHEN J L, HAO Y Q, et al. ARTP mutagenesis of Aureobasidium pullulans RM1603 for high pullulan production and transcriptome analysis of mutants[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2024, 206(9): 375. |
| [87] | ZHANG C Z, LI Y, ZHANG T S, et al. Increasing chitosanase production in Bacillus cereus by a novel mutagenesis and screen method[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1): 266-277. |
| [88] | ZHANG C, SUN Q, YANG L, et al. Mutation breeding of Monascus to produce a high yield of orange pigment and low citrinin content using the ARTP method[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2024, 10(8): 553. |
| [89] | 张少伦, 高聪, 李晓敏, 等. 代谢工程改造克雷伯氏菌生产1,3-丙二醇[J]. 生物工程学报, 2024, 40(8): 2386-2402. |
| ZHANG S L, GAO C, LI X M, et al. Metabolic engineering of Klebsiella pneumoniae for 1,3-propanediol production[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2024, 40(8): 2386-2402. | |
| [90] | HASSAN F S, EL-FAKHARANY E M, EL-MARADNY Y A, et al. Comprehensive insight into exploring the potential of microbial enzymes in cancer therapy: progress, challenges, and opportunities: a review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 277: 134535. |
| [91] | KUDDUS M, ROOHI, BANO N, et al. Cold-active microbial enzymes and their biotechnological applications[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2024, 17(4): e14467. |
| [92] | THAPA S, LI H, OHAIR J, et al. Biochemical characteristics of microbial enzymes and their significance from industrial perspectives[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2019, 61(8): 579-601. |
| [93] | JIANG N, ZHANG A, MIRUKA A C, et al. Synergistic effects and mechanisms of plasma coupled with peracetic acid in enhancing short-chain fatty acid production from sludge: motivation of reactive species and metabolic tuning of microbial communities[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 387: 129618. |
| [94] | LI D A, SHEN J, DING Q, et al. Recent progress of atmospheric and room-temperature plasma as a new and promising mutagenesis technology[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 2024, 42(3): e3991. |
| [95] | ABDEL-RAZEK A S, EL-NAGGAR M E, ALLAM A, et al. Microbial natural products in drug discovery[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(4): 470. |
| [96] | ZHANG J, HANSEN L G, GUDICH O, et al. A microbial supply chain for production of the anti-cancer drug vinblastine[J]. Nature, 2022, 609(7926): 341-347. |
| [97] | MEDEMA M H, BREITLING R, BOVENBERG R, et al. Exploiting plug-and-play synthetic biology for drug discovery and production in microorganisms[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2011, 9(2): 131-137. |
| [98] | LOVE J. Microbial pathways for advanced biofuel production[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2022, 50(2): 987-1001. |
| [99] | CHEN G Y, ZHAO K G, LI W Q, et al. A review on bioenergy production from duckweed[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2022, 161: 106468. |
| [100] | KEASLING J, GARCIA MARTIN H, LEE T S, et al. Microbial production of advanced biofuels[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 19(11): 701-715. |
| [101] | JIANG Y J, DONG W L, XIN F X, et al. Designing synthetic microbial consortia for biofuel production[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 828-831. |
| [1] | WANG Hong, LU Kongyong, ZHENG Yangyang, CHEN Tao, WANG Zhiwen. Construction and advances in the applications of transcription factor-based biosensors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 829-845. |
| [2] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [3] | HONG Yuan, LIU Yan. Research progress of brain organoids in regenerative medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 754-769. |
| [4] | YU Xuchang, WU Hui, LI Lei. Library construction and targeted BGC screening for more efficient discovery of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| [5] | MENG Qian, YIN Cong, HUANG Weiren. Tumor organoids and their research progress in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 191-201. |
| [6] | GUO Xiaojie, JIAN Xingjin, WANG Liyan, ZHANG Chong, XING Xinhui. Progress in bioreactors and instruments for phenotype testing with synthetic biology research [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 16-37. |
| [7] | ZHANG Chenyue, MA Yingqun, WANG Xing, FU Rongzhan, HUANG Jiwei, HUA Xiufu, FAN Daidi, FEI Qiang. Progress in the bioconversion of biogas into sustainable aviation fuel [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1246-1258. |
| [8] | LIU Huan, CUI Qiu. Advances and applications of ambient ionization mass spectrometry in screening of microbial strains [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 980-999. |
| [9] | WU Yujie, LIU Xinxin, LIU Jianhui, Yang Kaiguang, SUI Zhigang, ZHANG Lihua, ZHANG Yukui. Research progress of strain screening and quantitative analysis of key molecules based on high-throughput liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 1000-1019. |
| [10] | QIN Weitong, YANG Guangyu. Research and application progress of microdroplets high throughput screening methods [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 966-979. |
| [11] | ZHAO Guomiao, YANG Xin, ZHANG Yuan, WANG Jing, TAN Jian, WEI Chao, ZHOU Nana, LI Fan, WANG Xiaoyan. Biofoundry and its industrial application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 892-903. |
| [12] | MA Mengdan, SHANG Mengyu, LIU Yuchen. Application and prospect of CRISPR-Cas9 system in tumor biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 703-719. |
| [13] | TU Ran, LI Shixin, LI Haoni, WANG Meng. Advances and applications of droplet-based microfluidics in evolution and screening of engineered microbial strains [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 165-184. |
| [14] | ZHU Runtao, ZHONG Chao, DAI Zhuojun. Biofilm matrixes-from soft matters to engineered materials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 626-637. |
| [15] | WANG Junting, GUO Xiaojia, LI Qing, WAN Li, ZHAO Zongbao. Creation of non-natural cofactor-dependent methanol dehydrogenase [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 651-661. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||