Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (2): 422-444.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-059
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids
LU Jinchang1,2, WU Yaokang1,2, LV Xueqin1,2, LIU Long1,2, CHEN Jian1,2, LIU Yanfeng1,2
- 1.School of Biotechnology,Key Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biotechnology,Ministry of Education,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
2.Science Center for Future Foods,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2024-08-01Revised:2024-10-11Online:2025-05-20Published:2025-04-30 -
Contact:LIU Yanfeng
神经酰胺类鞘脂的绿色生物制造
鲁锦畅1,2, 武耀康1,2, 吕雪芹1,2, 刘龙1,2, 陈坚1,2, 刘延峰1,2
- 1.江南大学生物工程学院,糖化学与生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214112
2.江南大学未来食品科学中心,江苏 无锡 214112
-
通讯作者:刘延峰 -
作者简介:鲁锦畅 (1999—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为微生物代谢工程。E-mail:7230201010@stu.jiangnan.edu.cn刘延峰 (1987—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为微生物代谢工程。E-mail:yanfengliu@jiangnan.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32222069)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LU Jinchang, WU Yaokang, LV Xueqin, LIU Long, CHEN Jian, LIU Yanfeng. Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 422-444.
鲁锦畅, 武耀康, 吕雪芹, 刘龙, 陈坚, 刘延峰. 神经酰胺类鞘脂的绿色生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 422-444.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-059
| 出发底物 | 产物 | 总收率 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鞘氨醇碱从头合成 | 2-叠氮-4-硝基苯基磺酸衍生物 | 鞘氨醇;植物鞘氨醇 | 58% | [ |
| 立体选择性的环氧化物 | 鞘氨醇 | 51% | [ | |
| D-葡萄糖衍生物 | D-赤式鞘氨醇; D-苏式鞘氨醇 | 52% | [ | |
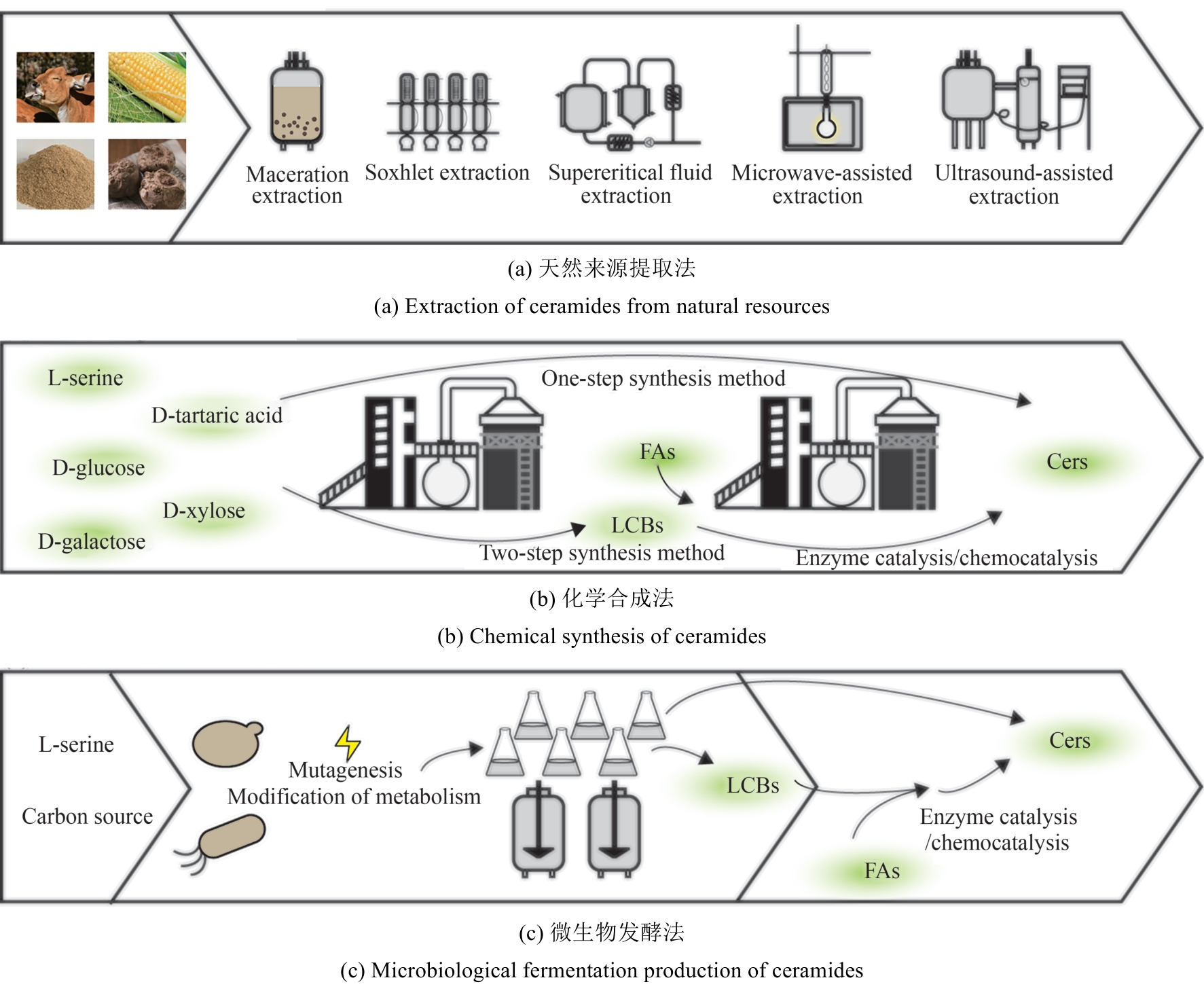
| L-丝氨酸 | 鞘氨醇;鞘磷脂;1-磷酸鞘氨醇;鞘氨醇衍生物 | 37% | [ | |
| N-Boc-L-丝氨酸 | 鞘氨醇 | 71% | [ | |
| 神经酰胺从头合成 | 三羟甲基氨基甲烷;脂肪酸羟基取代物 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 33%~65% | [ |
| (2S)-2-氨基苯乙醇(苯甘氨醇);(1R,2R)2-氨基-1-苯基-1,3-丙二醇;(S)-2-氨基(-4-甲氧基)苯乙醇 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 63.5% | [ | |
| 羟化脂肪酸;环氧甘油基醚 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 60%~75% | [ | |
| N-十六烷基-2-氨基乙醇;环己烷;丙二酸二甲酯 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 69% | [ | |
| C16-烷基烯二聚体;二乙醇胺/N-甲基-2,3,4,5,6-五羟基己胺/D-氨基葡萄糖/3-氨基-1,2-丙二醇/N-(1,3-二羟基异丙基)胺/N-(2,3,4,5,6-五羟基己基)胺等 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 20%~90% | [ | |
| 脂肪酸与鞘碱化学法合成神经酰胺 | 神经鞘氨醇;不同碳链长度有机酸 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 51%~96% | [ |
| 共轭羧酸与N‑羟基琥珀酰亚胺;鞘氨醇 | 含共轭羧酸的神经酰胺 | 50%~70% | [ | |
| 羧酸;植物鞘氨醇 | 神经酰胺Ⅲ | 84% | [ | |
| 脂肪酸与鞘碱生物酶法法合成神经酰胺 | 二氢鞘氨醇;脂肪酸;Novozym 435 | 神经酰胺NG | 70%~98% | [ |
| 活化的羧酸衍生物;植物鞘氨醇/二氢鞘氨醇;Novozym 435 | 神经酰胺 | 98%~99.7% | [ | |
| 植物鞘氨酸;脂肪酸;Novozym 435 | 神经酰胺Ⅲ | 94% | [ |
Table 1 Chemical synthesis of ceramides and their precursor sphingosine base
| 出发底物 | 产物 | 总收率 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鞘氨醇碱从头合成 | 2-叠氮-4-硝基苯基磺酸衍生物 | 鞘氨醇;植物鞘氨醇 | 58% | [ |
| 立体选择性的环氧化物 | 鞘氨醇 | 51% | [ | |
| D-葡萄糖衍生物 | D-赤式鞘氨醇; D-苏式鞘氨醇 | 52% | [ | |
| L-丝氨酸 | 鞘氨醇;鞘磷脂;1-磷酸鞘氨醇;鞘氨醇衍生物 | 37% | [ | |
| N-Boc-L-丝氨酸 | 鞘氨醇 | 71% | [ | |
| 神经酰胺从头合成 | 三羟甲基氨基甲烷;脂肪酸羟基取代物 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 33%~65% | [ |
| (2S)-2-氨基苯乙醇(苯甘氨醇);(1R,2R)2-氨基-1-苯基-1,3-丙二醇;(S)-2-氨基(-4-甲氧基)苯乙醇 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 63.5% | [ | |
| 羟化脂肪酸;环氧甘油基醚 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 60%~75% | [ | |
| N-十六烷基-2-氨基乙醇;环己烷;丙二酸二甲酯 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 69% | [ | |
| C16-烷基烯二聚体;二乙醇胺/N-甲基-2,3,4,5,6-五羟基己胺/D-氨基葡萄糖/3-氨基-1,2-丙二醇/N-(1,3-二羟基异丙基)胺/N-(2,3,4,5,6-五羟基己基)胺等 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 20%~90% | [ | |
| 脂肪酸与鞘碱化学法合成神经酰胺 | 神经鞘氨醇;不同碳链长度有机酸 | 神经酰胺类似物 | 51%~96% | [ |
| 共轭羧酸与N‑羟基琥珀酰亚胺;鞘氨醇 | 含共轭羧酸的神经酰胺 | 50%~70% | [ | |
| 羧酸;植物鞘氨醇 | 神经酰胺Ⅲ | 84% | [ | |
| 脂肪酸与鞘碱生物酶法法合成神经酰胺 | 二氢鞘氨醇;脂肪酸;Novozym 435 | 神经酰胺NG | 70%~98% | [ |
| 活化的羧酸衍生物;植物鞘氨醇/二氢鞘氨醇;Novozym 435 | 神经酰胺 | 98%~99.7% | [ | |
| 植物鞘氨酸;脂肪酸;Novozym 435 | 神经酰胺Ⅲ | 94% | [ |
| 宿主 | 产物 | 底物碳源 | 策略 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 | 三乙酰鞘氨醇 | 葡萄糖 | 异源表达棉桃阿舒来源laf1和des1;突变SYR、DES | 33.45 mg/g DCW (500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母(P.ciferrii lig4D strain CS.PCDPro2) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | 阻断shm1、shm2;缺失cha1;删除lcb4;过表达lcb1、lcb2;敲除orm1、orm2;过表达sur2 | 199 mg/g DCW;2 g/L (摇瓶培养) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母(NRRL Y1031) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | — | (291.2±63.7) mg/L (120 mL/500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 NRRL Y-1031(M40) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 30 g/L葡萄糖 30g /L糖蜜 | EMS诱变;BODIPY 505/515染色;荧光激活细胞分选(FACS) | 2.895 g/L (5.6 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 酿酒酵母K26 | 二乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | 质粒表达异源基因sli1、atf2 | (4.3±0.8) mg/L (120 mL/500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 酿酒酵母K26 | 三乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | 质粒表达异源基因sli1、atf2 | (1.2±0.1) mg/L (120 mL/500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 解脂耶氏酵母PO1g(MatA, leu2-270, ura3-302::URA3, xpr2-332. axp-2) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 200 g/L甘油 橄榄油 | 异源表达sli1、atf2;删除lcb4基因;有性杂交;发酵优化 | (650±24) mg/L (5 L生物反应器) | [ |
威克汉姆西弗酵母 F-60-10A NRRL1031 诱变后菌株:Mutant736 | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 5 g/L丝氨酸; 50 g/L甘油; 补加甘油 | γ射线诱变 | 17.7 g/L (3 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 50 g/L甘油; 5 g/L L‑丝氨酸 | ARTP诱变 | 30.47 g/L (5 L生物反应器) | [ |
威克汉姆西弗酵母DSCC 7-25 (KCCM-10131) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 25~35 g/L甘油 | 从NRRL Y-1031单倍体分离 | 14 g/L (500 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母CGMCC19562 | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 6.0 g/L L‑丝氨酸; 42.0 g/L甘油 | 单倍体分离 | 22.14 g/L (生物反应器) | [ |
酿酒酵母 CEN.PK2‑1D | 植物鞘氨醇 | 500 g/L葡萄糖 | 敲除lcb4、shm2、cha1;orm2:: tsc10;elo3::sur2;shm1::lcb1,lcb2; delta 22::hac1 | 2817 mg/L;150.54 mg/g干重 (5 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 酿酒酵母NCYC 3608(MATalpha gal2 ho::HygMX ura3::KanMX) | 植物鞘氨醇 | 20 g/L葡萄糖 | 缺失his3、leu2、ura3、cha1、cha2、lcb4、lcb5、orm2;质粒过表达ARS/CEN/URA/ScTSC10/ScSUR2、ARS/CEN/HIS/ScLCB1/ScLCB2、ARS/CEN/LEU | 2169 mg/L | [ |
| 酿酒酵母KCCM50515 | 神经酰胺 | 20 g/L葡萄糖 | 发酵优化 | 1.46 mg/L | [ |
酿酒酵母 KCCM 50515(Matα ura3-52 lys2-801 ade2-101 trp1-∆63 his3-∆200 leu2-∆1) | 神经酰胺 | 20 g/L葡萄糖 | 过表达tscl0 | 9.8 mg/g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 神经酰胺 | 葡萄糖;半乳糖 | 过表达tsc10 | 10.52 mg/g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 SCEL2,1 | 神经酰胺 | 葡萄糖;半乳糖 | 过表达lcb1、lcb2 | 10.08 mg /g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 SCEG1C1 | 神经酰胺 | 葡萄糖;半乳糖 | 过表达lag1、lac1 | 9.88 mg/g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 神经酰胺NS | 葡萄糖 | 敲除sur2和scs7;引入人类鞘脂去饱和酶基因des1;失活ydc1;过表达isc1;des1基因产物的内质网定位 | 未定量 | [ |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母GS115 | 神经酰胺(d18:0) | 10 g/L甘油 | 敲除Ku70同源的基因 PAS_chr3_0329;敲除orm1、orm2 同系物同源基因 PAS_chr4_0427 | 90.22 mg/L | [ |
Table 2 Biosynthesis of ceramides and their precursor derivatives
| 宿主 | 产物 | 底物碳源 | 策略 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 | 三乙酰鞘氨醇 | 葡萄糖 | 异源表达棉桃阿舒来源laf1和des1;突变SYR、DES | 33.45 mg/g DCW (500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母(P.ciferrii lig4D strain CS.PCDPro2) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | 阻断shm1、shm2;缺失cha1;删除lcb4;过表达lcb1、lcb2;敲除orm1、orm2;过表达sur2 | 199 mg/g DCW;2 g/L (摇瓶培养) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母(NRRL Y1031) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | — | (291.2±63.7) mg/L (120 mL/500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 NRRL Y-1031(M40) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 30 g/L葡萄糖 30g /L糖蜜 | EMS诱变;BODIPY 505/515染色;荧光激活细胞分选(FACS) | 2.895 g/L (5.6 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 酿酒酵母K26 | 二乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | 质粒表达异源基因sli1、atf2 | (4.3±0.8) mg/L (120 mL/500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 酿酒酵母K26 | 三乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 33 g/L葡萄糖 | 质粒表达异源基因sli1、atf2 | (1.2±0.1) mg/L (120 mL/500 mL挡板摇瓶) | [ |
| 解脂耶氏酵母PO1g(MatA, leu2-270, ura3-302::URA3, xpr2-332. axp-2) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 200 g/L甘油 橄榄油 | 异源表达sli1、atf2;删除lcb4基因;有性杂交;发酵优化 | (650±24) mg/L (5 L生物反应器) | [ |
威克汉姆西弗酵母 F-60-10A NRRL1031 诱变后菌株:Mutant736 | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 5 g/L丝氨酸; 50 g/L甘油; 补加甘油 | γ射线诱变 | 17.7 g/L (3 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 50 g/L甘油; 5 g/L L‑丝氨酸 | ARTP诱变 | 30.47 g/L (5 L生物反应器) | [ |
威克汉姆西弗酵母DSCC 7-25 (KCCM-10131) | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 25~35 g/L甘油 | 从NRRL Y-1031单倍体分离 | 14 g/L (500 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母CGMCC19562 | 四乙酰植物鞘氨醇 | 6.0 g/L L‑丝氨酸; 42.0 g/L甘油 | 单倍体分离 | 22.14 g/L (生物反应器) | [ |
酿酒酵母 CEN.PK2‑1D | 植物鞘氨醇 | 500 g/L葡萄糖 | 敲除lcb4、shm2、cha1;orm2:: tsc10;elo3::sur2;shm1::lcb1,lcb2; delta 22::hac1 | 2817 mg/L;150.54 mg/g干重 (5 L生物反应器) | [ |
| 酿酒酵母NCYC 3608(MATalpha gal2 ho::HygMX ura3::KanMX) | 植物鞘氨醇 | 20 g/L葡萄糖 | 缺失his3、leu2、ura3、cha1、cha2、lcb4、lcb5、orm2;质粒过表达ARS/CEN/URA/ScTSC10/ScSUR2、ARS/CEN/HIS/ScLCB1/ScLCB2、ARS/CEN/LEU | 2169 mg/L | [ |
| 酿酒酵母KCCM50515 | 神经酰胺 | 20 g/L葡萄糖 | 发酵优化 | 1.46 mg/L | [ |
酿酒酵母 KCCM 50515(Matα ura3-52 lys2-801 ade2-101 trp1-∆63 his3-∆200 leu2-∆1) | 神经酰胺 | 20 g/L葡萄糖 | 过表达tscl0 | 9.8 mg/g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 神经酰胺 | 葡萄糖;半乳糖 | 过表达tsc10 | 10.52 mg/g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 SCEL2,1 | 神经酰胺 | 葡萄糖;半乳糖 | 过表达lcb1、lcb2 | 10.08 mg /g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 SCEG1C1 | 神经酰胺 | 葡萄糖;半乳糖 | 过表达lag1、lac1 | 9.88 mg/g cell | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 神经酰胺NS | 葡萄糖 | 敲除sur2和scs7;引入人类鞘脂去饱和酶基因des1;失活ydc1;过表达isc1;des1基因产物的内质网定位 | 未定量 | [ |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母GS115 | 神经酰胺(d18:0) | 10 g/L甘油 | 敲除Ku70同源的基因 PAS_chr3_0329;敲除orm1、orm2 同系物同源基因 PAS_chr4_0427 | 90.22 mg/L | [ |
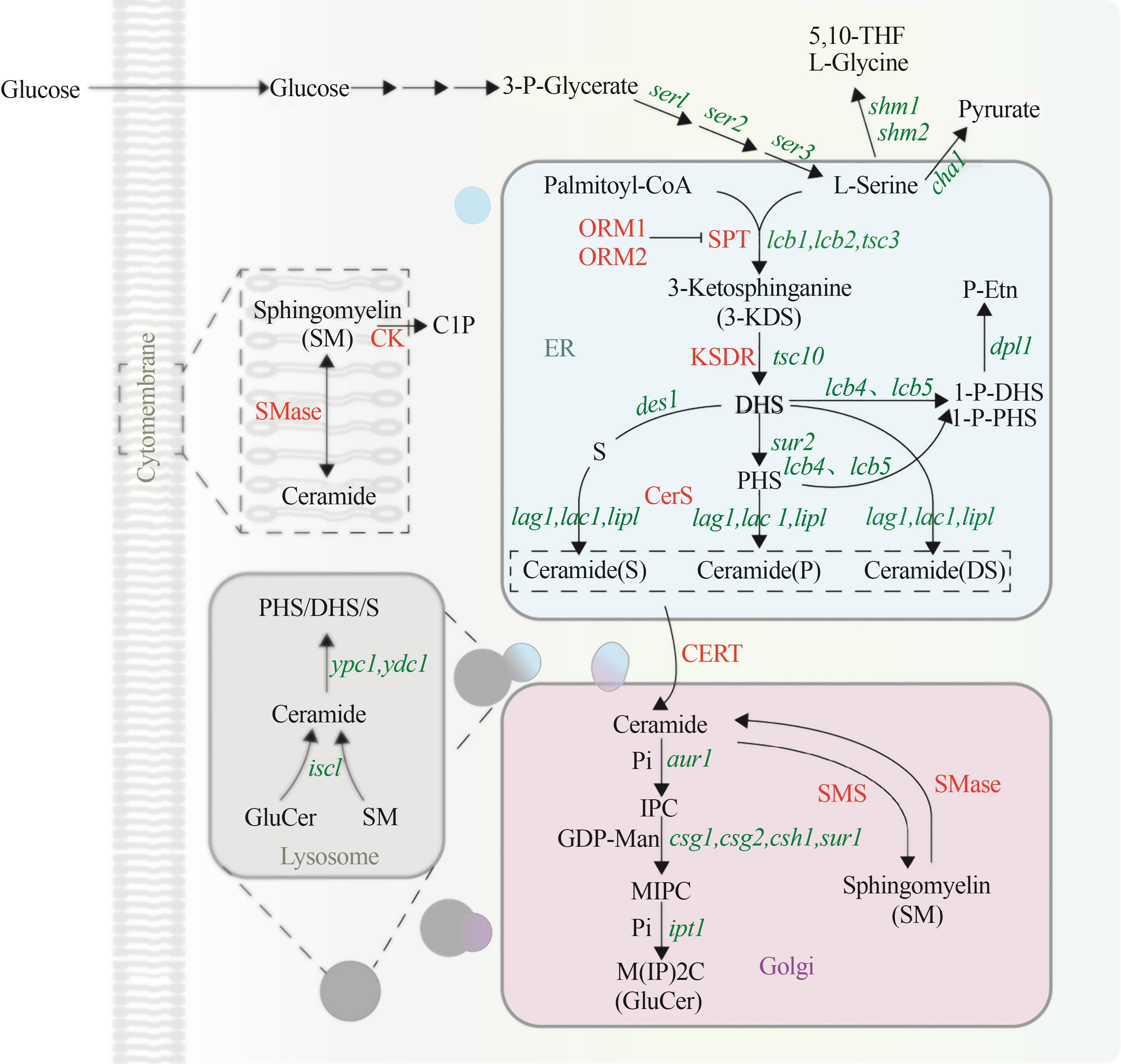
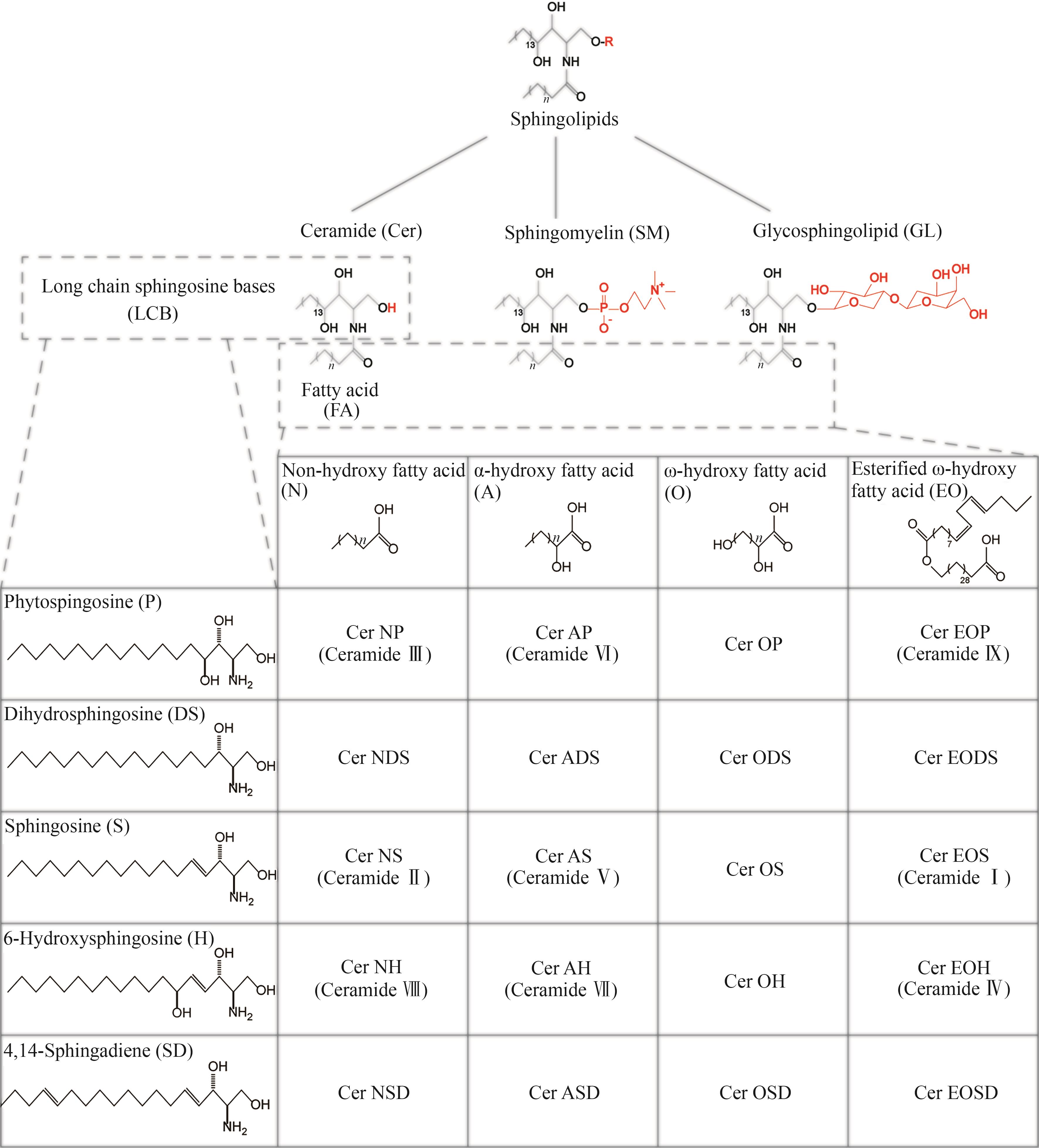
Fig. 3 Metabolic pathway of sphingolipid in yeast(Green represents the coding gene, red represents the enzyme. 5,10-THF—5,10-dimethyltetrahydrofolate; 3-KDS—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine; DHS—dihydrosphingosine; PHS—phytosphingosine; S—S phingosine; 1-P-DHS—dihydrosphingosine-1-phosphate; 1-P-PHS—phytosphingosine-1-phosphate; P-Etn—phosphoryl ethanolamine; Pi—phosphate group; IPC—inositol phosphorylceramide; GDP-Man—GDP mannose; MIPC—mannosyl-inositol phosphorylceramide; M(IP)2C—mannosyl-diinositol phosphorylceramide; GlcCer—glucosylceramide; SM—sphingomyelin; C1P—ceramide-1phosphate; ser1—3-phosphoserine aminotransferase encoding gene; ser2—phosphoserine phosphatase in the phosphoglycerate pathway encoding gene; ser3—3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase encoding gene; shm1, shm2—L-serine hydroxymethyltransferase encoding gene; cha1—L-serine deaminase encoding gene; lcb1, lcb2, tsc3—serine palmitoyltransferase encoding gene; tsc10—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase encoding gene; des1—sphingolipid Δ4-desaturase encoding gene; lcb4, lcb5—sphingosine kinase encoding gene; dpl1—sphingobase-1-phosphate lyase encoding gene; sur2—C4 hydroxylase encoding gene; lag1, lac1, lip1—ceramide synthase encoding gene; aur1—ceramide phosphoinositide transferase encoding gene; csg1, csg2, csh1, sur1—mannosylinositol phosphorylceramide synthase encoding gene; ipt1—inositol phosphotransferase encoding gene; isc1—complex sphingolipid headgroup hydrolase encoding gene; ypc1, ydc1—alkaline ceramidase encoding gene; ORM1, ORM2—mediate sphingolipid homeostasis protein; SPT—serine palmitoyl transferase; KDSR—3-ketodihydrosphingosine reductase; CerS—ceramide synthase; CERT—ceramide transfer protein; SMS—sphingomyelin synthase; SMase—sphingomyelinase; CK—ceramide kinase; ER—endoplasmic reticulum)
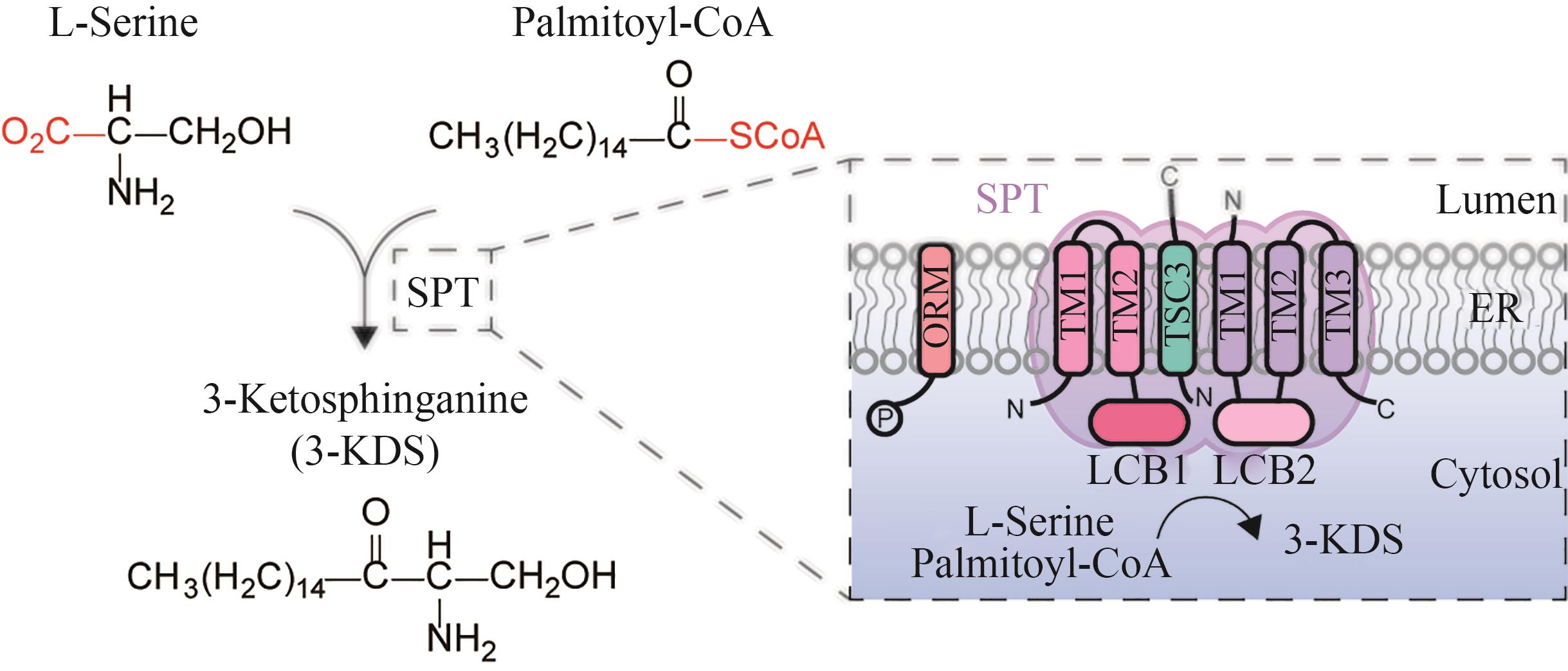
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram for the catalytic synthesis of 3-KDS by serine palmitoyl transferase(SPT—serine palmitoyl transferase; ORM—mediate sphingolipid homeostasis protein;3-KDS—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine; TM—Transmembrane; LCB1, LCB2, TSC3—subunits of serine palmitoyltransferase; ER—endoplasmic reticulum)
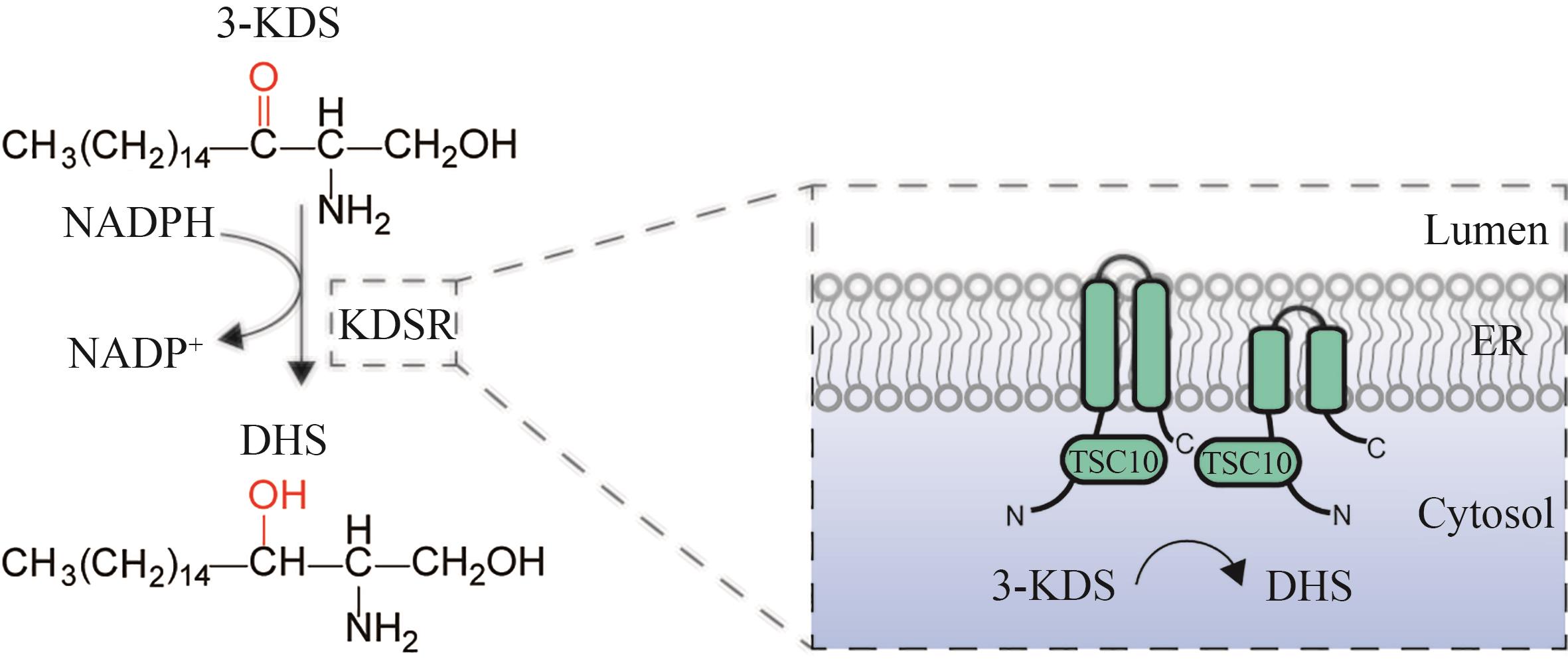
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram for the catalytic synthesis of DHS by 3-ketodihydrosphingosine reductase(3-KDS—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine; KDSR—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase; TSC10—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase; DHS—dihydrosphingosine; ER—endoplasmic reticulum)
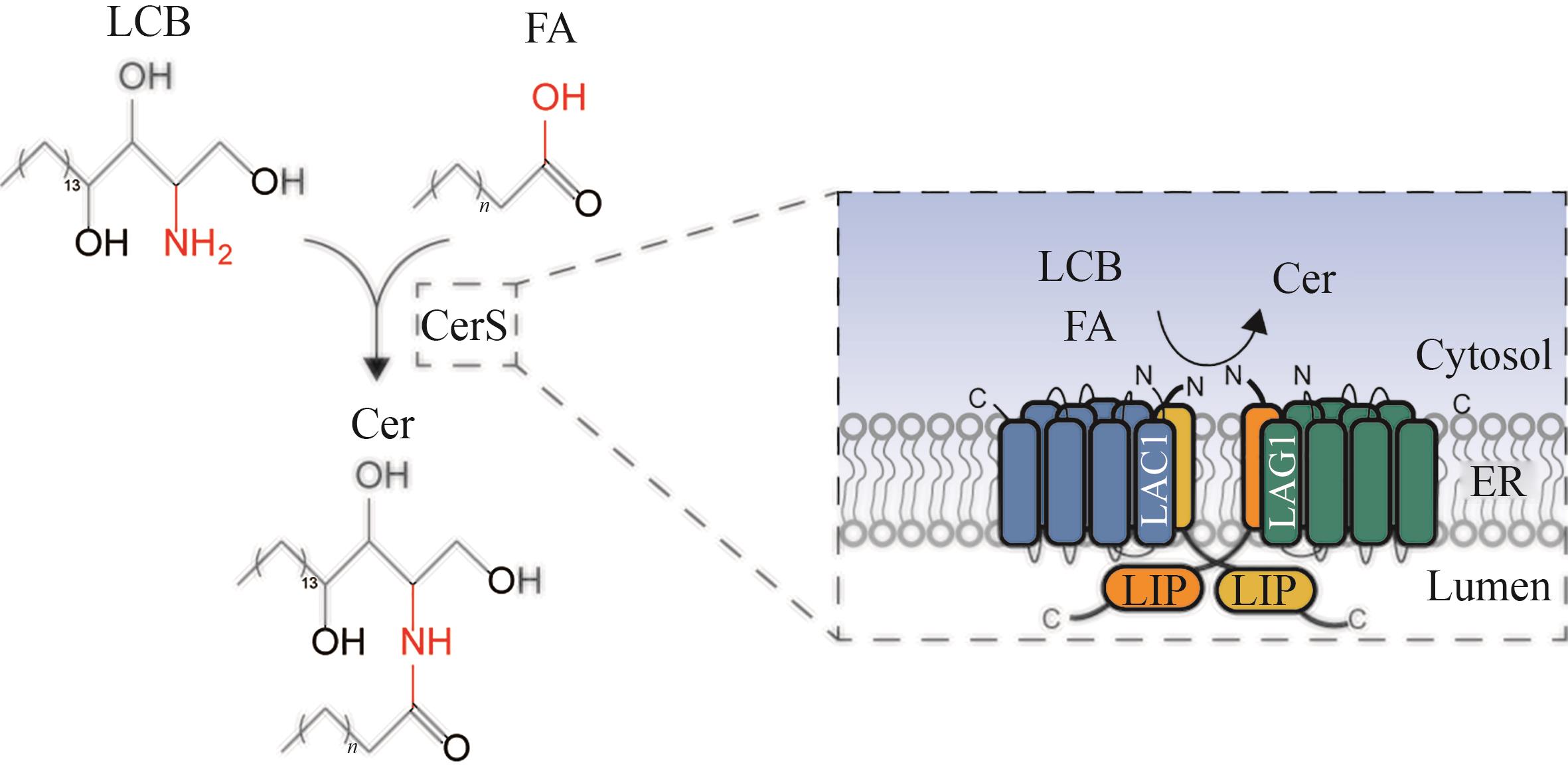
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram for the catalytic synthesis of ceramide by ceramide synthase(LCB—long chain sphingosine bases; FA—fatty acid; CerS—ceramide synthase; Cer—ceramide; LAG1, LAC1, LIP1—subunits of ceramide synthase; ER—endoplasmic reticulum)
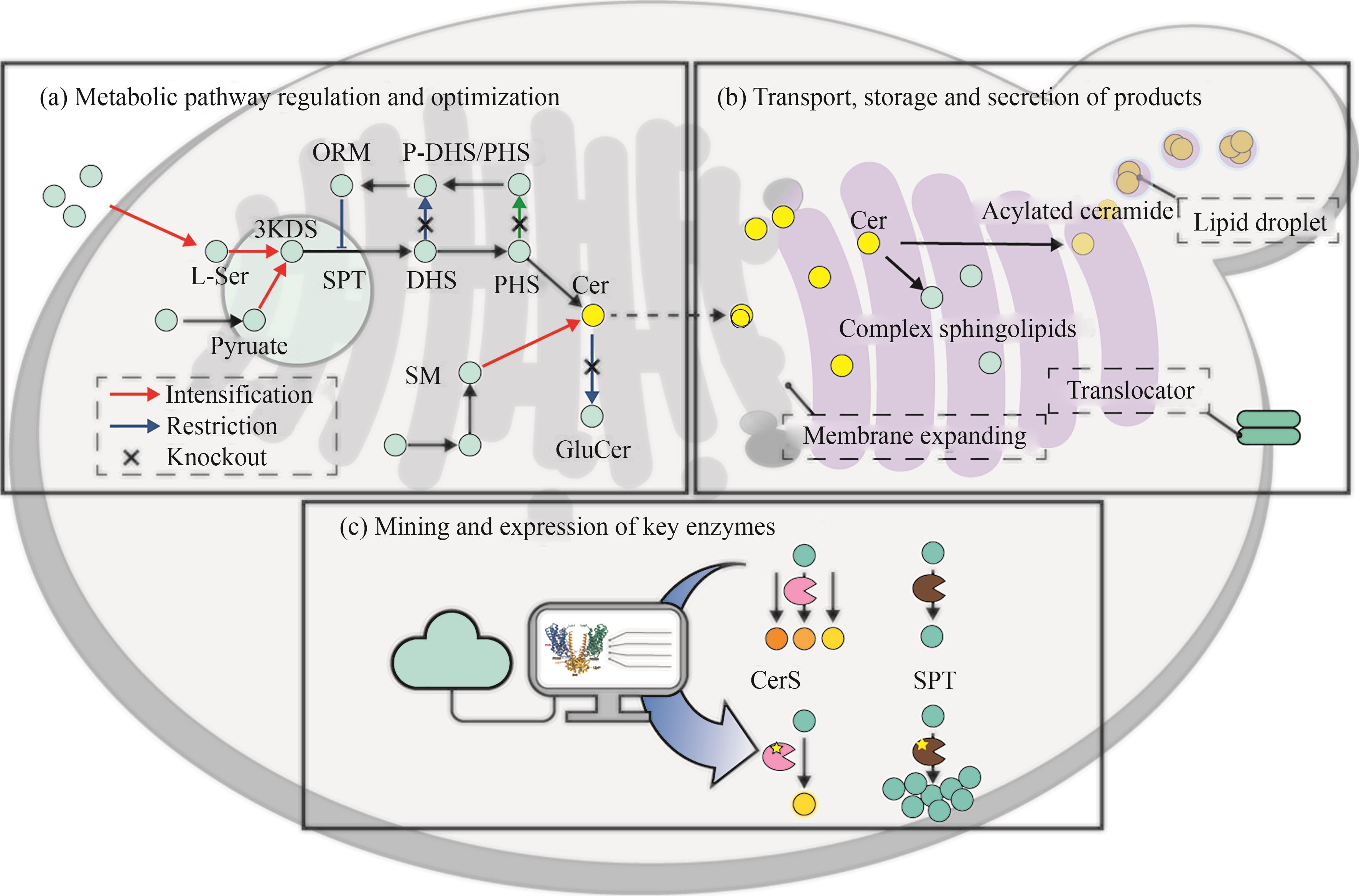
Fig. 7 Strategy for the modification of the ceramide biosynthetic pathway(3-KDS—3-keto-dihydrosphingosine; ORM—mediate sphingolipid homeostasis protein; SPT—serine palmitoyl transferase; DHS—dihydrosphingosine; PHS—phytosphingosine; Cer—ceramide; GlcCer—glucosylceramide; SM—sphingomyelin; CerS—ceramide synthase)
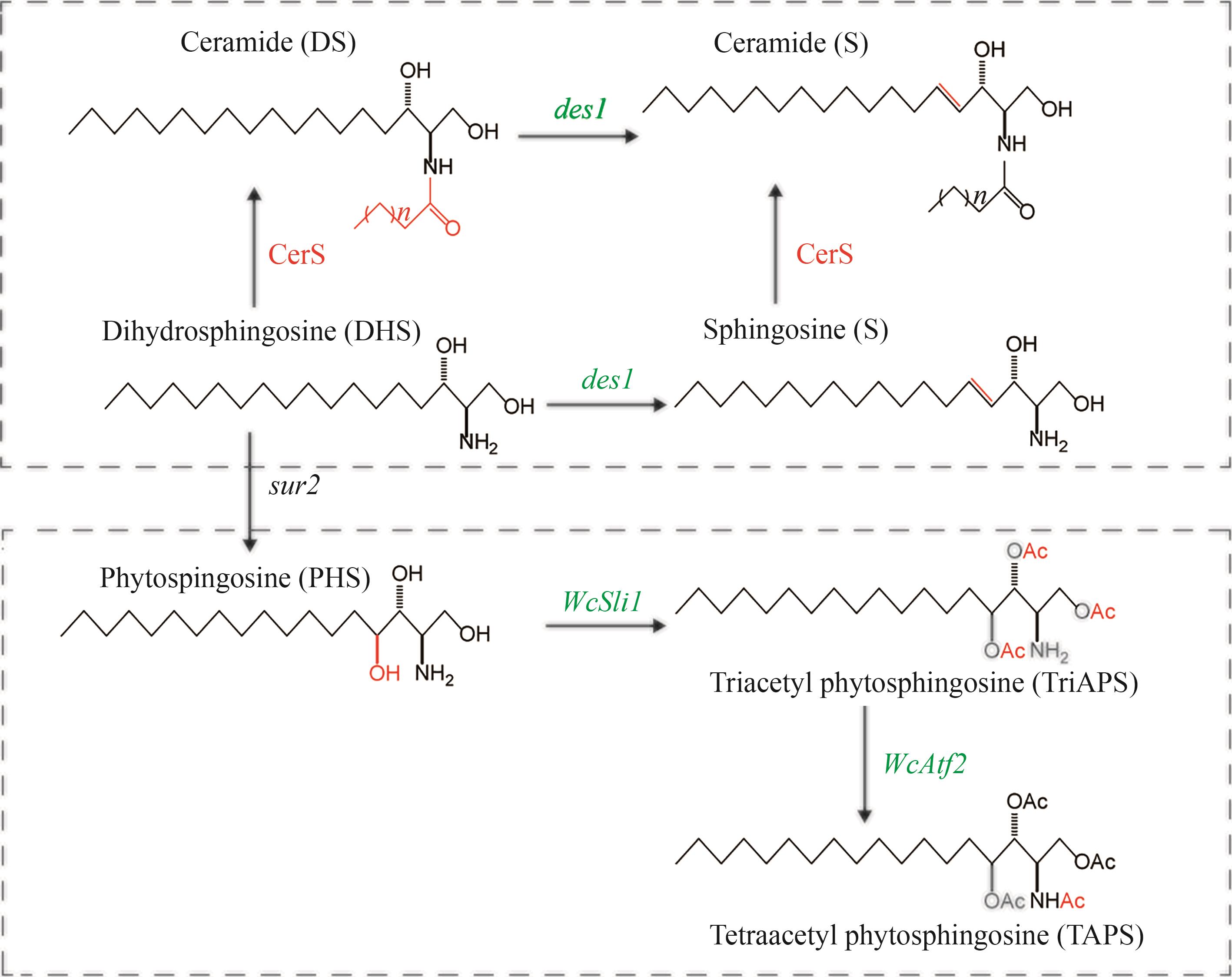
Fig. 8 Diagram for the catalytic synthesis of ceramides by DES1、SLI1 and ATF2(CerS—Ceramide synthase; des1—Human sphingolipid desaturase encoding gene; WcSli1, WcAtf2—Wickhamomyces ciferrii sphingobase N/O-acetyltransferase encoding genes)
| 1 | MURPHY B, GRIMSHAW S, HOPTROFF M, et al. Alteration of barrier properties, stratum corneum ceramides and microbiome composition in response to lotion application on cosmetic dry skin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 5223. |
| 2 | FUJII M. The pathogenic and therapeutic implications of ceramide abnormalities in atopic dermatitis[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2386. |
| 3 | SCHMITT T, NEUBERT R H H. State of the art in stratum corneum research: the biophysical properties of ceramides[J]. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 2018, 216: 91-103. |
| 4 | CHA H J, HE C F, ZHAO H, et al. Intercellular and intracellular functions of ceramides and their metabolites in skin (Review)[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2016, 38(1): 16-22. |
| 5 | FEINGOLD K R. Thematic review series: Skin Lipids. The role of epidermal lipids in cutaneous permeability barrier homeostasis[J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2007, 48(12): 2531-2546. |
| 6 | VAN SMEDEN J, HOPPEL L, VAN DER HEIJDEN R, et al. LC/MS analysis of stratum corneum lipids: ceramide profiling and discovery[S][J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2011, 52(6): 1211-1221. |
| 7 | MASUKAWA Y, NARITA H, SHIMIZU E, et al. Characterization of overall ceramide species in human stratum corneums [J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2008, 49(7): 1466-1476. |
| 8 | T’KINDT R, JORGE L, DUMONT E, et al. Profiling and characterizing skin ceramides using reversed-phase liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(1): 403-411. |
| 9 | LI X, YANG Q, ZHENG J, et al. Efficacy and safety of a topical moisturizer containing linoleic acid and ceramide for mild-to-moderate psoriasis vulgaris: a multicenter randomized controlled trial[J]. Dermatologic Therapy, 2020, 33(6): e14263. |
| 10 | SHIN K O, MIHARA H, ISHIDA K, et al. Exogenous ceramide serves as a precursor to endogenous ceramide synthesis and as a modulator of keratinocyte differentiation[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(11): 1742. |
| 11 | UCHIDA Y, PARK K. Ceramides in skin health and disease: an update[J]. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 2021, 22(6): 853-866. |
| 12 | SPADA F, HARRISON I P, BARNES T M, et al. A daily regimen of a ceramide-dominant moisturizing cream and cleanser restores the skin permeability barrier in adults with moderate eczema: a randomized trial[J]. Dermatologic Therapy, 2021, 34(4): e14970. |
| 13 | CAO Y, ZHANG X H, HE X F, et al. Efficacy of ceramide-containing sunscreen on skin barrier[J]. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 2024, 23(2): 525-528. |
| 14 | ZHENG Y, HUNT R L, VILLARUZ A E, et al. Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis contributes to skin barrier homeostasis by generating protective ceramides[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2022, 30(3): 301-313.e9. |
| 15 | KIM D S, KIM S Y, CHUNG J H, et al. Delayed ERK activation by ceramide reduces melanin synthesis in human melanocytes[J]. Cellular Signalling, 2002, 14(9): 779-785. |
| 16 | PHILIPS N, TUASON M, CHANG T, et al. Differential effects of ceramide on cell viability and extracellular matrix remodeling in keratinocytes and fibroblasts[J]. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 2009, 22(3): 151-157. |
| 17 | FISCHER C L, DRAKE D R, DAWSON D V, et al. Antibacterial activity of sphingoid bases and fatty acids against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2012, 56(3): 1157-1161. |
| 18 | BIBEL D J, ALY R, SHINEFIELD H R. Antimicrobial activity of sphingosines[J]. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 1992, 98(3): 269-273. |
| 19 | DONGFACK M D J, LALLEMAND M C, KUETE V, et al. A new sphingolipid and furanocoumarins with antimicrobial activity from Ficus exasperata [J]. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2012, 60(8): 1072-1075. |
| 20 | BECAM J, WALTER T, BURGERT A, et al. Antibacterial activity of ceramide and ceramide analogs against pathogenic Neisseria [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 17627. |
| 21 | 戚建华, 边凌林, 罗燕, 等. 一种神经酰胺类化合物和应用: CN106631871A[P]. 2017-05-10. |
| QI J H, BIAN L L, LUO Y, et al. A ceramide compound and application thereof: CN106631871A[P]. 2017-05-10. | |
| 22 | OHTA K, HIRAKI S, MIYANABE M, et al. Appearance of intact molecules of dietary ceramides prepared from soy sauce lees and rice glucosylceramides in mouse plasma[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(32): 9188-9198. |
| 23 | MORAD S A F, CABOT M C. Ceramide-orchestrated signalling in cancer cells[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2013, 13(1): 51-65. |
| 24 | CASTRO B M, PRIETO M, SILVA L C. Ceramide: a simple sphingolipid with unique biophysical properties[J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 2014, 54: 53-67. |
| 25 | ZHANG Y H, VASKO M R, NICOL G D. Ceramide, a putative second messenger for nerve growth factor, modulates the TTX-resistant Na+ current and delayed rectifier K+ current in rat sensory neurons[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 2002, 544(2): 385-402. |
| 26 | ASHLEY COWART L, OBEID L M. Yeast sphingolipids: recent developments in understanding biosynthesis, regulation, and function[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2007, 1771(3): 421-431. |
| 27 | NICHOLSON R J, NORRIS M K, POSS A M, et al. The lard works in mysterious ways: ceramides in nutrition-linked chronic disease[J]. Annual Review of Nutrition, 2022, 42: 115-144. |
| 28 | OHTA K, HIRAKI S, MIYANABE M, et al. Dietary ceramide prepared from soy sauce lees improves skin barrier function in hairless mice[J]. Journal of Oleo Science, 2021, 70(9): 1325-1334. |
| 29 | ZHU F F, ZHAO B, HU B, et al. Review of available “extraction + purification” methods of natural ceramides and their feasibility for sewage sludge analysis[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(26): 68022-68053. |
| 30 | 张可青, 王建华, 于姝燕, 等. 植物中神经酰胺类化合物提取工艺研究进展[J]. 内蒙古中医药, 2022, 41(6): 131-133. |
| ZHANG K Q, WANG J H, YU S Y, et al. Research progress on extraction technology of ceramides from plants[J]. Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 41(6): 131-133. | |
| 31 | YAHYA N A, ATTAN N, WAHAB R A. An overview of cosmeceutically relevant plant extracts and strategies for extraction of plant-based bioactive compounds[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 2018, 112: 69-85. |
| 32 | OJHA K S, AZNAR R, O’DONNELL C, et al. Ultrasound technology for the extraction of biologically active molecules from plant, animal and marine sources[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 122: 115663. |
| 33 | WILD R, SCHMIDT R R. Sphingosine and phytosphingosine from D-threose synthesis of a 4-keto-ceramide[J]. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1994, 5(11): 2195-2208. |
| 34 | TORSSELL S, SOMFAI P. A practical synthesis of D-erythro-sphingosine using a cross-metathesis approach[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2004, 2(11): 1643-1646. |
| 35 | CHAUDHARI V D, AJISH KUMAR K S, DHAVALE D D. An efficient synthesis of D-erythro- and D-threo-sphingosine from D-glucose: olefin cross-metathesis approach[J]. Organic Letters, 2005, 7(26): 5805-5807. |
| 36 | YAMAMOTO T, HASEGAWA H, HAKOGI T, et al. Versatile synthetic method for sphingolipids and functionalized sphingosine derivatives via olefin cross metathesis[J]. Organic Letters, 2006, 8(24): 5569-5572. |
| 37 | YANG H, LIEBESKIND L S. A concise and scalable synthesis of high enantiopurity (–)-D-erythro-sphingosine using peptidyl thiol ester-boronic acid cross-coupling[J]. Organic Letters, 2007, 9(16): 2993-2995. |
| 38 | 禹柄英, 张元僖, 朱泳协, 等. 新型的类神经酰胺化合物其及其制备方法: CN104854081A[P]. 2015-08-19. |
| WOO B Y, JANG W H, JOO Y H, et al. The invention discloses a novel ceramide-like compound and a preparation method thereof: CN104854081A[P]. 2015-08-19. | |
| 39 | 刘希望. 神经酰胺类似化合物的合成及其生物活性研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. |
| LIU X W. Synthesis and bioactivity of ceramide-like compounds [D]. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, 2010. | |
| 40 | CRITCHLEY P, RAWLINGS A V, SCOTT I R. Synthetic pseudoceramide and cosmetic compositions thereof: US5206020A[P]. 1993-04-27. |
| 41 | MOTION K R, JANOUSEK A, WATKINS S D. Hydroxy alkyl amides of dicarboxylic acids and their use in cosmetic compositions: US5656668A[P]. 1997-08-12. |
| 42 | BAIK I S, LEE J G, PARK B D, et al. Pseudoceramides, and dermatologic external preparations containing the same: US6221371B1 [P]. 2001-04-24. |
| 43 | PARK B D, LEE K M, PARK I J, et al. Novel pseudoceramides and their synthesis using alkyl ketene dimer[J]. Journal of the Society of Cosmetic Scientists of Korea, 1997, 23: 92-96. |
| 44 | 杨超文, 叶柳. 含共轭羧酸的神经酰胺类化合物及其制备方法和应用: CN115433100A[P]. 2022-12-06. |
| YANG C W, YE L. Ceramide compounds containing conjugated carboxylic acids, preparation method and application thereof: CN115433100A[P]. 2022-12-06. | |
| 45 | 吴江, 张伟, 朱纯银. 一种酰胺的合成方法及其在神经酰胺3制备上的应用: CN 110078635 A[P]. 2019-08-02. |
| WU J, ZHANG W, ZHU C Y. An amide synthesis method and its application in the preparation of ceramide 3: CN 110078635 A[P]. 2019-08-02. | |
| 46 | M.F.埃克施泰因, M.D.范洛格切姆, H.H.文克, 等. 制备鞘脂的方法: CN110317840A[P]. 2019-10-11. |
| ECKSTEIN M F, VAN LOGCHEM M D, WENK H H, et al. Method for preparing sphingolipid: CN110317840A[P]. 2019-10-11. | |
| 47 | F.霍尔曼, O.图姆, P.格热比克, 等. 使用脂肪酶和脂肪酸甘油酯通过溶性鞘脂的酶促N-酰化反应制备鞘脂的方法: CN102057050B[P]. 2014-06-11. |
| HOLMANN F, TUM O, GRZEBYK P, et al. Method of preparing sphingolipid by enzymatic N-acylation of soluble sphingolipid using lipase and fatty acid glyceride: CN102057050B[P]. 2014-06-11. | |
| 48 | ZHANG X Y, MA Y J, OUYANG B, et al. Efficient lipase-catalyzed synthesis of ceramide Ⅲ series compounds in an eco-friendly solvent[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2024, 558: 114006. |
| 49 | HE L, BYUN H S, BITTMAN R. Stereoselective preparation of ceramide and its skeleton backbone modified analogues via cyclic thionocarbonate intermediates derived by catalytic asymmetric dihydroxylation of α,β-unsaturated ester precursors[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2000, 65(22): 7627-7633. |
| 50 | RAI A N, BASU A. Synthesis of the glycosphingolipid β-galactosyl ceramide and analogues via olefin cross metathesis[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2005, 70(20): 8228-8230. |
| 51 | NAKAMURA T, SHIOZAKI M. Stereoselective synthesis of D-erythro-sphingosine and L-lyxo-phytosphingosine[J]. Tetrahedron, 2001, 57(44): 9087-9092. |
| 52 | LU X Q, BITTMAN R. Efficient and versatile synthesis of (2S,3R)-sphingosine and its 2-azido-3-O-benzylsphingosine analogue[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2005, 46(11): 1873-1875. |
| 53 | DUCLOS R I. The total syntheses of D-erythro-sphingosine, N-palmitoylsphingosine (ceramide), and glucosylceramide (cerebroside) via an azidosphingosine analog[J]. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 2001, 111(2): 111-138. |
| 54 | 朴尽五, 李知愿, 全圣贤, 等. 新型类神经酰胺化合物及其用途: CN111201216A[P]. 2020-05-26. |
| PARK J O, LEE J W, JEON S H, et al. Novel ceramide-like compounds and their applications: CN111201216A[P]. 2020-05-26. | |
| 55 | F.霍尔曼, O.图姆, C.特勒, 等. 使用真菌脂肪酶和脂肪酸烷基酯通过溶性鞘脂的酶促N-酰化反应制备鞘脂的方法: CN102057049B[P]. 2014-10-01. |
| HOLMANN F, TUM O, TELLERET C, et al. Sphingolipid is prepared by enzymatic N-acylation of soluble sphingolipid using fungal lipase and fatty acid alkyl ester: CN102057049B[P]. 2014-10-01. | |
| 56 | WICKERHAM L J, STODOLA F H. Formation of extracellular sphingolipides by microorganisms.Ⅰ. Tetraacetylphyto-sphingosine from Hansenula ciferri [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1960, 80(4): 484-491. |
| 57 | SCHORSCH C, KÖHLER T, ANDREA H, et al. High-level production of tetraacetyl phytosphingosine (TAPS) by combined genetic engineering of sphingoid base biosynthesis and L-serine availability in the non-conventional yeast Pichia ciferrii [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2012, 14(2): 172-184. |
| 58 | VELD F TER, WOLFF D, SCHORSCH C, et al. Production of tetraacetyl phytosphingosine (TAPS) in Wickerhamomyces ciferrii is catalyzed by acetyltransferases Sli1p and Atf2p[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(19): 8537-8546. |
| 59 | PARK S B, TRAN Q G, RYU A J, et al. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting-mediated directed evolution of Wickerhamomyces ciferrii for enhanced production of tetraacetyl phytosphingosine[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 39(4): 1004-1010. |
| 60 | HAN C, JANG M, KIM M J, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for de novo production of tetraacetyl phytosphingosine[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2021, 130(6): 1981-1992. |
| 61 | CHOI J Y, HWANG H J, CHO W Y, et al. Differences in the fatty acid profile, morphology, and tetraacetylphytosphingosine-forming capability between wild-type and mutant Wickerhamomyces ciferrii [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 662979. |
| 62 | 纪晓俊, 崔柳伟, 王凯峰, 等. 一株高产四乙酰基植物鞘氨醇的菌株及其应用: CN117070382A[P]. 2023-11-17. |
| JI X J, CUI L W, WANG K F, et al. A strain with high yield of tetraacetyl phytosphingosine and its application: CN117070382A[P]. 2023-11-17. | |
| 63 | PARK C S, JEONG J H, HONG S Y, et al. Yeast Pichia ciferrii : US6194196B1[P]. 2001-02-27. |
| 64 | 张天萌, 刘金钊, 朱倩倩, 等. 一种高产鞘脂类微生物菌株、它的筛选方法和它的用途: CN114736815A[P]. 2022-07-12. |
| ZHANG T M, LIU J Z, ZHU Q Q, et al. A high-yielding sphingolipid microbial strain, its screening method and its use: CN114736815A[P]. 2022-07-12. | |
| 65 | 孙杰, 谢朋天, 魏春, 等. 一种高产植物鞘氨醇的酿酒酵母菌株: CN116103176A[P]. 2023-05-12. |
| SUN J, XIE P T, WEI C, et al. A strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with high yield of sphingosine: CN116103176A[P]. 2023-05-12. | |
| 66 | M. 施瓦布, M. 巴鲍, D. 费希尔, 等. 生产植物鞘氨醇或二氢神经鞘氨醇的方法: CN108473968A[P]. 2018-08-31. |
| SCHWAB M, BABAU M, FISCHER D, et al. Method for producing phytosphingosine or dihydrosphingosine: CN108473968A[P]. 2018-08-31. | |
| 67 | KWUN K H, LEE J H, RHO K H, et al. Production of ceramide with Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2006, 133(3): 203-210. |
| 68 | KIM S K, NOH Y H, KOO J R, et al. Effect of expression of genes in the sphingolipid synthesis pathway on the biosynthesis of ceramide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 20(2): 356-362. |
| 69 | KIM S K, NOH Y H, KOO J R, et al. Effects of expression of lcb1/lcb2 and lac1/lag1 genes on the biosynthesis of ceramides[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2011, 16(1): 1-6. |
| 70 | MURAKAMI S, SHIMAMOTO T, NAGANO H, et al. Producing human ceramide-NS by metabolic engineering using yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 16319. |
| 71 | 黄铭, 吴佳欣, 张目, 等. 毕赤酵母PAS_chr4_0427基因敲除促进神经酰胺合成[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2024, 50(17): 17-22. |
| HUANG M, WU J X, ZHANG M, et al. Knockout of PAS_chr4_0427 promotes ceramide synthesis in Pichia pastoris [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(17): 17-22. | |
| 72 | KURTZMAN C P. Phylogeny of the ascomycetous yeasts and the renaming of Pichia anomala to Wickerhamomyces anomalus [J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2011, 99(1): 13-23. |
| 73 | MAISTER H G, ROGOVIN S P, STODOLA F H, et al. Formation of extracellular sphingolipids by microorganisms: Ⅳ. Pilot-plant production of tetraacetylphytosphingosine by Hansenula ciferrii [J]. Applied Microbiology, 1962, 10(5): 401-406. |
| 74 | S.舍费尔, M.A.范登贝尔赫, D.博尔格尔, 等. 使用遗传工程化的微生物菌株的改进的鞘氨醇类碱的生产: CN101490260A[P]. 2009-07-22. |
| SCHAFFER S, VAN DEN BERGH M A, BOERGEL D, et al. Improved production of sphingoid bases using genetically engineered microbial strains: CN101490260A[P]. 2009-07-22. | |
| 75 | OLEA-OZUNA R J, POGGIO S, EDBERGSTRÖM, et al. Five structural genes required for ceramide synthesis in Caulobacter and for bacterial survival[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 23(1): 143-159. |
| 76 | FURUYA H, IDE Y, HAMAMOTO M, et al. Isolation of a novel bacterium, Blautia glucerasei sp. nov., hydrolyzing plant glucosylceramide to ceramide[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2010, 192(5): 365-372. |
| 77 | HALAMKA T A, GARCIA A, EVANS T W, et al. Occurrence of ceramides in the Acidobacterium solibacter usitatus: implications for bacterial physiology and sphingolipids in soils[J]. Frontiers in Geochemistry, 2024, 2: 1400278. |
| 78 | STANKEVICIUTE G, TANG P J, ASHLEY B, et al. Convergent evolution of bacterial ceramide synthesis[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(3): 305-312. |
| 79 | BROWN E M, KE X B, HITCHCOCK D, et al. Bacteroides-derived sphingolipids are critical for maintaining intestinal homeostasis and symbiosis[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2019, 25(5): 668-680.e7. |
| 80 | YAMAJI T, HANADA K. Sphingolipid metabolism and interorganellar transport: localization of sphingolipid enzymes and lipid transfer proteins[J]. Traffic, 2015, 16(2): 101-122. |
| 81 | CINGOLANI F, FUTERMAN A H, CASAS J. Ceramide synthases in biomedical research[J]. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 2016, 197: 25-32. |
| 82 | SAWAI H, OKAMOTO Y, LUBERTO C, et al. Identification of ISC1 (YER019w) as inositol phosphosphingolipid phospholipase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(50): 39793-39798. |
| 83 | DICKSON R C. Roles for sphingolipids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2010, 688: 217-231. |
| 84 | ANDO H, KOMURA N. Recent progress in the synthesis of glycosphingolipids[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2024, 78: 102423. |
| 85 | WENNEKES T, VAN DEN BERG R J B H N, BOOT R G, et al. Glycosphingolipids-nature, function, and pharmacological modulation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(47): 8848-8869. |
| 86 | HARRISON P J, DUNN T M, CAMPOPIANO D J. Sphingolipid biosynthesis in man and microbes[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2018, 35(9): 921-954. |
| 87 | YARD B A, CARTER L G, JOHNSON K A, et al. The structure of serine palmitoyltransferase; gateway to sphingolipid biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2007, 370(5): 870-886. |
| 88 | HANADA K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2003, 1632(1-3): 16-30. |
| 89 | GABLE K, HAN G S, MONAGHAN E, et al. Mutations in the yeast LCB1 and LCB2 genes, including those corresponding to the hereditary sensory neuropathy typeⅠmutations, dominantly inactivate serine palmitoyltransferase*[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(12): 10194-10200. |
| 90 | GABLE K, SLIFE H, BACIKOVA D, et al. Tsc3p is an 80-amino acid protein associated with serine palmitoyltransferase and required for optimal enzyme activity[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(11): 7597-7603. |
| 91 | REN J H, SAIED E M, ZHONG A, et al. Tsc3 regulates SPT amino acid choice in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by promoting alanine in the sphingolipid pathway[J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2018, 59(11): 2126-2139. |
| 92 | SCHÄFER J H, KÖRNER C, ESCH B M, et al. Structure of the ceramide-bound SPOTS complex[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 6196. |
| 93 | BEELER T, BACIKOVA D, GABLE K, et al. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae TSC10/YBR265w gene encoding 3-ketosphinganine reductase is identified in a screen for temperature-sensitive suppressors of the Ca2+-sensitive csg2Δ mutant[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273(46): 30688-30694. |
| 94 | BRESLOW D K, COLLINS S R, BODENMILLER B, et al. Orm family proteins mediate sphingolipid homeostasis[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7284): 1048-1053. |
| 95 | LIU Q, CHAN A K N, CHANG W H, et al. 3-Ketodihydrosphingosine reductase maintains ER homeostasis and unfolded protein response in leukemia[J]. Leukemia, 2022, 36(1): 100-110. |
| 96 | ZHAO P Q, ZHUANG Z W, GUAN X Y, et al. Crystal structure of the 3-ketodihydrosphingosine reductase TSC10 from Cryptococcus neoformans [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2023, 670: 73-78. |
| 97 | SCHORLING S, VALLÉE B, BARZ W P, et al. Lag1p and Lac1p are essential for the acyl-CoA-dependent ceramide synthase reaction in Saccharomyces cerevisae [J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2001, 12(11): 3417-3427. |
| 98 | GUILLAS I, KIRCHMAN P A, CHUARD R, et al. C26-CoA-dependent ceramide synthesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is operated by Lag1p and Lac1p[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2001, 20(11): 2655-2665. |
| 99 | SCHÄFER J H, CLAUSMEYER L, KÖRNER C, et al. Structure of the yeast ceramide synthase[J/OL]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. (2024-11-11)[2024-11-11]. . |
| 100 | ZHANG M M, LI Z Y, LIU Y W, et al. The ceramide synthase (CERS/LASS) family: functions involved in cancer progression[J]. Cellular Oncology, 2023, 46(4): 825-845. |
| 101 | XIE T, FANG Q, ZHANG Z K, et al. Structure and mechanism of a eukaryotic ceramide synthase complex[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2023, 42(24): e114889. |
| 102 | COWART L A, HANNUN Y A. Selective substrate supply in the regulation of yeast de novo sphingolipid synthesis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(16): 12330-12340. |
| 103 | HANADA K, HARA T, NISHIJIMA M. Purification of the serine palmitoyltransferase complex responsible for sphingoid base synthesis by using affinity peptide chromatography techniques[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(12): 8409-8415. |
| 104 | SCHWAB M, BABAU M, FISCHER D, et al. Method for producing phytosphingosine or sphinganine: US20180179562[P]. 2021-09-07. |
| 105 | HAN S M, LONE M A, SCHNEITER R, et al. Orm1 and Orm2 are conserved endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins regulating lipid homeostasis and protein quality control[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(13): 5851-5856. |
| 106 | LIU M, HUANG C J, POLU S R, et al. Regulation of sphingolipid synthesis through Orm1 and Orm2 in yeast[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2012, 125(Pt 10): 2428-2435. |
| 107 | RODRIGUEZ-GALLARDO S, KUROKAWA K, SABIDO-BOZO S, et al. Ceramide chain length-dependent protein sorting into selective endoplasmic reticulum exit sites[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(50): eaba8237. |
| 108 | LIU L K, CHOUDHARY V, TOULMAY A, et al. An inducible ER-Golgi tether facilitates ceramide transport to alleviate lipotoxicity[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 2017, 216(1): 131-147. |
| 109 | IKEDA A, SCHLARMANN P, KUROKAWA K, et al. Tricalbins are required for non-vesicular ceramide transport at ER-Golgi contacts and modulate lipid droplet biogenesis[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(10): 101603. |
| 110 | ZELNIK I D, VENTURA A E, KIM J L, et al. The role of ceramide in regulating endoplasmic reticulum function[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2020, 1865(1): 158489. |
| 111 | LIU P T, SUN L, SUN Y X, et al. Decreased fluidity of cell membranes causes a metal ion deficiency in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing carotenoids[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43(4): 525-535. |
| 112 | BU X, LIN J Y, CHENG J, et al. Engineering endogenous ABC transporter with improving ATP supply and membrane flexibility enhances the secretion of β-carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2020, 13: 168. |
| [1] | SHENG Zhouhuang, CHEN Zhixian, ZHANG Yan. Research progress of yeast mannoproteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [2] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [3] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [4] | TANG Chuan′gen, WANG Jing, ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Haoning, KANG Zhen. Advances in synthesis and mining strategies for functional peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| [5] | ZHONG Quanzhou, SHAN Yiyi, PEI Qingyun, JIN Yanyun, WANG Yihan, MENG Luyuan, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Yuxin, LIU Kunyuan, WANG Huizhong, FENG Shangguo. Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [6] | ZHU Fanghuan, CEN Xuecong, CHEN Zhen. Research progress of diols production by microbes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [7] | LIU Yining, PU Wei, YANG Jinxing, WANG Yu. Recent advances in the biosynthesis of ω-amino acids and lactams [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [8] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [9] | CHENG Xiaolei, LIU Tiangang, TAO Hui. Recent research progress in non-canonical biosynthesis of terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [10] | LIU Zijian, MU Baiyang, DUAN Zhiqiang, WANG Xuan, LU Xiaojie. Advances in the development of DNA-compatible chemistries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [11] | ZHANG Shouqi, WANG Tao, KONG Yao, ZOU Jiasheng, LIU Yuanning, XU Zhengren. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of natural products: evolution of synthetic methodology and strategy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [12] | XIE Xiangqian, GUO Wen, WANG Huan, LI Jin. Biosynthesis and chemical synthesis of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides containing aminovinyl cysteine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [13] | TANG Zhijun, HU Youcai, LIU Wen. Enzymatic (4+2)- and (2+2)-cycloaddition reactions: fundamentals and applications of regio- and stereoselectivity [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jun, JIN Shixue, YUN Qian, QU Xudong. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [15] | CHEN Xiwei, ZHANG Huaran, ZOU Yi. Biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of fungal non-ribosomal peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||