Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (5): 1243-1254.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-057
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Design and practice of plant synthetic biology theme in the International Genetically Engineered Machine Competition
HE Yangyu1, YANG Kai1, WANG Weilin1, HUANG Qian2, QIU Ziying1, SONG Tao1, HE Liushang1, YAO Jinxin3, GAN Lu3, HE Yuchi1
- 1.College of Life Sciences,Hubei University,Wuhan 430062,Hubei,China
2.Hubei University Library,Wuhan 430062,Hubei,China
3.College of Chemical and Environmental Engineering,Hanjiang Normal University,Shiyan 442000,Hubei,China
-
Received:2025-06-09Revised:2025-08-26Online:2025-11-05Published:2025-10-31 -
Contact:GAN Lu, HE Yuchi
国际基因工程机器大赛中植物合成生物学主题的设计与实践
何杨昱1, 杨凯1, 王玮琳1, 黄茜2, 丘梓樱1, 宋涛1, 何流赏1, 姚金鑫3, 甘露3, 何玉池1
- 1.湖北大学生命科学学院,湖北 武汉 430062
2.湖北大学图书馆,湖北 武汉 430062
3.汉江师范学院化学与环境工程学院,湖北 十堰 442000
-
通讯作者:甘露,何玉池 -
作者简介:何杨昱 (2003—),男,本科,湖北大学生物工程专业在读。研究方向为植物合成生物学。E-mail:1210037876@qq.com甘露 (1985—),女,博士,讲师。研究方向为植物合成生物学与代谢工程。E-mail:ganlu@hjnu.edu.cn何玉池 (1974—),女,博士,二级教授,国家级实验教学示范中心主任。研究方向为植物合成生物学与代谢工程。E-mail:hyc@hubu.edu.cn -
基金资助:湖北省重点研发计划(20220BBA032);汉江师范学院校级教学改革研究项目(2021C09)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HE Yangyu, YANG Kai, WANG Weilin, HUANG Qian, QIU Ziying, SONG Tao, HE Liushang, YAO Jinxin, GAN Lu, HE Yuchi. Design and practice of plant synthetic biology theme in the International Genetically Engineered Machine Competition[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1243-1254.
何杨昱, 杨凯, 王玮琳, 黄茜, 丘梓樱, 宋涛, 何流赏, 姚金鑫, 甘露, 何玉池. 国际基因工程机器大赛中植物合成生物学主题的设计与实践[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1243-1254.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-057
| 创新维度 | 技术突破点示例 | 应用场景靶点 |
|---|---|---|
| 底盘系统改造 | 叶绿体/线粒体合成工厂构建[ | 高附加值天然产物生产 |
| 代谢网络重构 | 跨物种萜类合成途径的移植[ | 抗逆作物开发(抗旱/耐盐) |
| 智能调控装置 | 光控CRISPR开关的系统设计[ | 环境污染物实时监测与修复 |
| 细胞通信工程 | 根系植物-微生物群体系统[ | 智能施肥/病虫害预警 |
| 植物营养强化 | 多营养协同强化[ | 复合营养作物培育 |
Table 1 Selection dimension matrix
| 创新维度 | 技术突破点示例 | 应用场景靶点 |
|---|---|---|
| 底盘系统改造 | 叶绿体/线粒体合成工厂构建[ | 高附加值天然产物生产 |
| 代谢网络重构 | 跨物种萜类合成途径的移植[ | 抗逆作物开发(抗旱/耐盐) |
| 智能调控装置 | 光控CRISPR开关的系统设计[ | 环境污染物实时监测与修复 |
| 细胞通信工程 | 根系植物-微生物群体系统[ | 智能施肥/病虫害预警 |
| 植物营养强化 | 多营养协同强化[ | 复合营养作物培育 |
| 维度 | 评估指标 | 验证方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 科学原创性 | 是否提出新机制/新理论(如植物新型信号传导路径设计等) | 文献分析、专利检索等 |
| 技术独特性 | 是否开发新元件/新思路(如植物特异的CRISPR-Cas12f系统等) | 对比现有技术(Benchling元件库比对)、元件功能实验验证等 |
| 应用颠覆性 | 是否开辟新模式/新场景(如海水稻可实现在盐碱地生长等) | 行业需求分析(PEST分析模型)等 |
| 系统复杂性 | 是否实现多层次调控(如结合基因回路+代谢调控等) | 计算机分析(Cobra框架建模、Cell Designer) |
Table 2 Matrix of dimensions for assessing the innovativeness of selected topics
| 维度 | 评估指标 | 验证方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 科学原创性 | 是否提出新机制/新理论(如植物新型信号传导路径设计等) | 文献分析、专利检索等 |
| 技术独特性 | 是否开发新元件/新思路(如植物特异的CRISPR-Cas12f系统等) | 对比现有技术(Benchling元件库比对)、元件功能实验验证等 |
| 应用颠覆性 | 是否开辟新模式/新场景(如海水稻可实现在盐碱地生长等) | 行业需求分析(PEST分析模型)等 |
| 系统复杂性 | 是否实现多层次调控(如结合基因回路+代谢调控等) | 计算机分析(Cobra框架建模、Cell Designer) |
| 底盘植物 | 生长周期 | 转化效率 | 应用场景 | 元件兼容性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烟草 | 苗床期约60天,大田期约100天[ | 农杆菌浸润法效率达60%~80%[ | 常用于瞬时表达系统,适合重组蛋白生产 | 具有高度兼容性,对多种标准化载体适配良好[ |
| 拟南芥 | 约6周 | 农杆菌介导浸花法效率可达30%~50%[ | 常用于基础代谢通路解析 | 适配多数标准化载体,对iGEM元件库有较好的适配能力[ |
| 水稻 | 营养生长约90天,生殖生长约70天[ | 农杆菌介导法效率为10%~20%[ | 常用于作物性状改良 | 在启动子等元件选择上具有一定的特异性[ |
| 浮萍 | 约30天 | 因株系而异,瞬时转染效率较高,而稳定转化的效率很低[ | 常作为生物反应器生产外源蛋白 | 目前针对浮萍兼容性的研究相对较少,需要进一步探索其适配性 |
Table 3 A lateral comparison of various plant-based materials
| 底盘植物 | 生长周期 | 转化效率 | 应用场景 | 元件兼容性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烟草 | 苗床期约60天,大田期约100天[ | 农杆菌浸润法效率达60%~80%[ | 常用于瞬时表达系统,适合重组蛋白生产 | 具有高度兼容性,对多种标准化载体适配良好[ |
| 拟南芥 | 约6周 | 农杆菌介导浸花法效率可达30%~50%[ | 常用于基础代谢通路解析 | 适配多数标准化载体,对iGEM元件库有较好的适配能力[ |
| 水稻 | 营养生长约90天,生殖生长约70天[ | 农杆菌介导法效率为10%~20%[ | 常用于作物性状改良 | 在启动子等元件选择上具有一定的特异性[ |
| 浮萍 | 约30天 | 因株系而异,瞬时转染效率较高,而稳定转化的效率很低[ | 常作为生物反应器生产外源蛋白 | 目前针对浮萍兼容性的研究相对较少,需要进一步探索其适配性 |
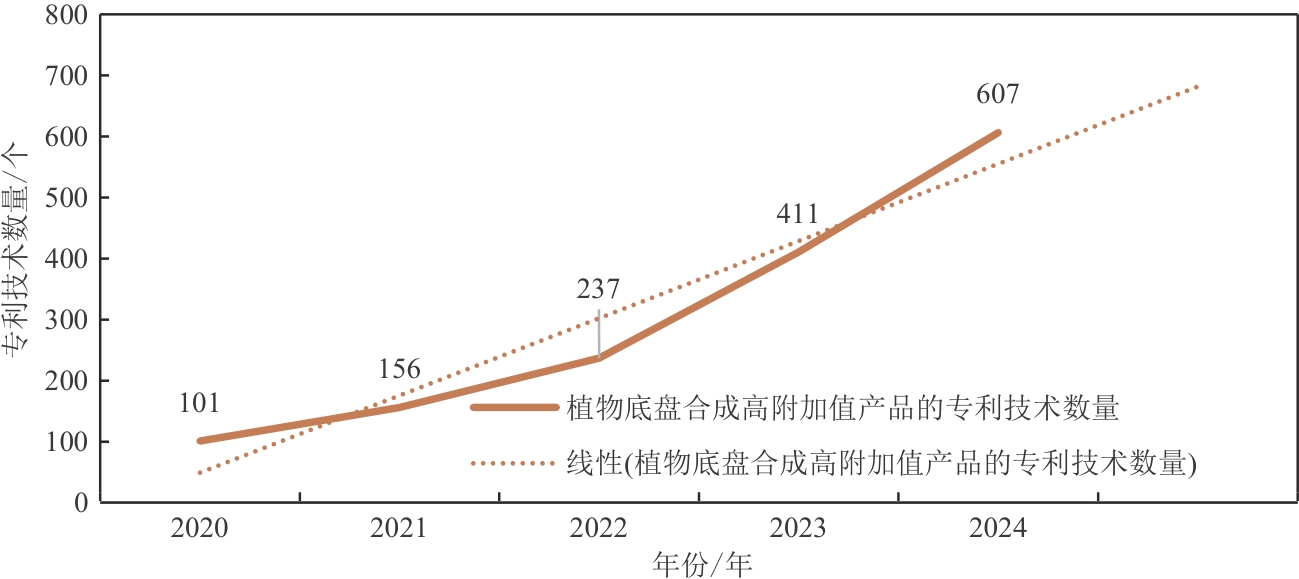
Fig. 1 The changes in the number of patents for high-value-added products synthesized using plant chassis technology in China over the past five years
| 申请号 | 申请日期 | 专利名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN202411992792.5 | 2024-12-31 | 一种氧甲基转移酶及其在生物合成异嗪皮啶和嗪皮啶中的应用 | 基于申请的氧甲基转移酶,结合异嗪皮啶的代谢途径,可以在藻类和植物底盘中实现异嗪皮啶的合成 | [ |
| CN202310573134.1 | 2023-05-18 | 一种利用多基因共表达在植物中异源合成人参皂苷Rg3的方法 | 为利用植物底盘合成稀有人参皂苷Rg3提供了一种可行的技术 | [ |
| CN202211273337.0 | 2022-10-18 | 一种可提升广藿香醇合成量的融合基因及方法 | 以番茄果实为底盘,在其细胞质体的MEP通路中重构广藿香醇合成通路,显著提升广藿香醇的合成量 | [ |
| CN202210565180.2 | 2022-05-23 | 一种黄酮合酶Ⅰ/黄烷酮-3-羟化酶及在黄酮类化合物合成领域的应用 | PnFNSⅠ/F3H基因可用于在大肠杆菌和植物底盘中生产黄酮和黄酮醇类化合物,具有较高的应用价值 | [ |
| CN202010435008.6 | 2020-05-21 | 一种高效人工根际联合固氮体系 | 根据合成生物学理论与方法构建的高效人工根际联合固氮体系 | [ |
Table 4 Parts of patent technology based on plant platforms
| 申请号 | 申请日期 | 专利名称 | 描述 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN202411992792.5 | 2024-12-31 | 一种氧甲基转移酶及其在生物合成异嗪皮啶和嗪皮啶中的应用 | 基于申请的氧甲基转移酶,结合异嗪皮啶的代谢途径,可以在藻类和植物底盘中实现异嗪皮啶的合成 | [ |
| CN202310573134.1 | 2023-05-18 | 一种利用多基因共表达在植物中异源合成人参皂苷Rg3的方法 | 为利用植物底盘合成稀有人参皂苷Rg3提供了一种可行的技术 | [ |
| CN202211273337.0 | 2022-10-18 | 一种可提升广藿香醇合成量的融合基因及方法 | 以番茄果实为底盘,在其细胞质体的MEP通路中重构广藿香醇合成通路,显著提升广藿香醇的合成量 | [ |
| CN202210565180.2 | 2022-05-23 | 一种黄酮合酶Ⅰ/黄烷酮-3-羟化酶及在黄酮类化合物合成领域的应用 | PnFNSⅠ/F3H基因可用于在大肠杆菌和植物底盘中生产黄酮和黄酮醇类化合物,具有较高的应用价值 | [ |
| CN202010435008.6 | 2020-05-21 | 一种高效人工根际联合固氮体系 | 根据合成生物学理论与方法构建的高效人工根际联合固氮体系 | [ |
| [1] | 潘俊慧, 周凯钰太, 王素春, 等. 合成生物学概述及其在兽医领域的应用前景展望[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2025, 42(2): 57-65. |
| PAN J H, ZHOU K Y T, WANG S C, et al. Introduction to synthetic biology and its prospective application in veterinary field[J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2025, 42(2): 57-65. | |
| [2] | YIN Y, WEN J L, WEN M, et al. The design strategies for CRISPR-based biosensing: target recognition, signal conversion, and signal amplification[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2024, 246: 115839. |
| [3] | YANG Z R, CAO Y B, SHI Y T, et al. Genetic and molecular exploration of maize environmental stress resilience: toward sustainable agriculture[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(10): 1496-1517. |
| [4] | 邹奇, 潘炜松, 邱健, 等. 植物生物反应器优化策略与最新应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2023, 43(1): 71-86. |
| ZOU Q, PAN W S, QIU J, et al. Recent advances in optimization strategies and applications of plant bioreactors[J]. China Biotechnology, 2023, 43(1): 71-86. | |
| [5] | XU H, YUE C, ZHANG Y, et al. Forestation at the right time with the right species can generate persistent carbon benefits in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(41): e2304988120. |
| [6] | 张先恩. 中国合成生物学发展回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2019, 49(12): 1543-1572. |
| ZHANG X E. Synthetic biology in China: review and prospects[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2019, 49(12): 1543-1572. | |
| [7] | 赵国华, 浦佳丽, 唐北沙. ZFN、TALEN 和 CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术在疾病研究及基因治疗中的应用[J]. 中华医学遗传学杂志, 2016, 33(6): 857-862. |
| ZHAO G H, PU J L, TANG B S. Applications of ZFN TALEN and CRISPR/Cas9 techniques in disease modeling and gene therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Genetics, 2016, 33(6): 857-862. | |
| [8] | LAN T L, CHEN L G, WANG Y, et al. Genome synthesis in plants[J]. Nature Reviews Bioengineering, 2025: 326. |
| [9] | TIAN C F, LI J H, WANG Y. From qualitative to quantitative: the state of the art and challenges for plant synthetic biology[J]. Quantitative Biology, 2023, 11(3): 214-230. |
| [10] | MILLER T E, BENEYTON T, SCHWANDER T, et al. Light-powered CO2 fixation in a chloroplast mimic with natural and synthetic parts[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6491): 649-654. |
| [11] | DEMURTAS O C, NICOLIA A, DIRETTO G. Terpenoid transport in plants: how far from the final picture?[J]. Plants, 2023, 12(3): 634. |
| [12] | LIU J L, ZHANG R X, CHAI N, et al. Programmable genome engineering and gene modifications for plant biodesign[J]. Plant Communications, 2025, 6(8): 101427. |
| [13] | BAI B, LIU W D, QIU X Y, et al. The root microbiome: community assembly and its contributions to plant fitness[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(2): 230-243. |
| [14] | CHAI N, XU J, ZHANG R X, et al. Synthetic metabolic engineering of functional crops: boosting nutrition and human health[J/OL]. The Crop Journal, 2025. (2025-07-04)[2025-08-01]. . |
| [15] | 宋凯. 合成生物学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 172. |
| SONG K. Introduction to synthetic biology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 172. | |
| [16] | LAWSON C E, HARCOMBE W R, HATZENPICHLER R, et al. Common principles and best practices for engineering microbiomes[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2019, 17(12): 725-741. |
| [17] | FUENTES P, ZHOU F, ERBAN A, et al. A new synthetic biology approach allows transfer of an entire metabolic pathway from a medicinal plant to a biomass crop[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e13664. |
| [18] | SANTOYO G. How plants recruit their microbiome? New insights into beneficial interactions[J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2022, 40: 45-58. |
| [19] | MCCANTS C B, WOLTZ W G. Growth and mineral nutrition of tobacco[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 1967, 19: 211-265. |
| [20] | ZHANG Y J, CHEN M X, SIEMIATKOWSKA B, et al. A highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated method for transient gene expression and functional studies in multiple plant species[J]. Plant Communications, 2020, 1(5): 100028. |
| [21] | LIU C Y, CHEN Q, QU Y, et al. The plant platform for natural products synthesis: tobacco[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2025, 225: 120605. |
| [22] | CLOUGH S J, BENT A F. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. The Plant Journal, 1998, 16(6): 735-743. |
| [23] | HOLLAND C K, JEZ J M. Arabidopsis: the original plant chassis organism[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2018, 37(10): 1359-1366. |
| [24] | MOHAPATRA P K, SARKAR R K, PANDA D, et al. Staging of rice plant growth and development[M/OL]//Tillering behavior of rice plant. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2025: 105-139. (2025-01-24)[2025-08-01]. . |
| [25] | MOHAMMED S, SAMAD A A, RAHMAT Z. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice: constraints and possible solutions[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(3): 133-146. |
| [26] | SHIMAMOTO K. The molecular biology of rice[J]. Science, 1995, 270(5243): 1772-1773. |
| [27] | YANG G L, FANG Y, XU Y L, et al. Frond transformation system mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens for Lemna minor [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2018, 98(4): 319-331. |
| [28] | 吴荣荣, 汪阳忠, 潘晓璐, 等. 烟草瞬时表达技术的多途径应用研究进展[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2024, 45(5): 114-120. |
| WU R R, WANG Y Z, PAN X L, et al. Advances and prospects of research on multi-pathway applications of tobacco transient expression technology[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2024, 45(5): 114-120. | |
| [29] | 郎宸用. 拟南芥MEP途径关键酶及代谢中间产物对萜类化合物生物合成的调控[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016. |
| LANG C Y. Regulation of key enzymes and metabolic intermediates in MEP pathway on terpenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016. | |
| [30] | ADAMS J P, ADELI A, HSU C Y, et al. Plant-based FRET biosensor discriminates environmental zinc levels[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2012, 10(2): 207-216. |
| [31] | 邓接楼, 王爱斌, 涂晓虹. 秋水仙素对杂交水稻发芽率及主要农艺性状的影响[J]. 上饶师范学院学报, 2014, 34(3): 53-59. |
| DENG J L, WANG A B, TU X H. Effects of colchicine on germination rate and major agronomic traits of hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Shangrao Normal University, 2014, 34(3): 53-59. | |
| [32] | SONG Y J, HU Z L, LIU S Z, et al. Utilization of microalgae and duckweed as sustainable protein sources for food and feed: nutritional potential and functional applications[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2025, 73(8): 4466-4482. |
| [33] | 唐娅丽, 于昌江, 刘宇, 等. 浮萍合成生物学研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2020, 32(2): 100-109. |
| TANG Y L, YU C J, LIU Y, et al. Advances in synthetic biology of duckweed[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2020, 32(2): 100-109. | |
| [34] | 中国农业科学院深圳农业基因组研究所(岭南现代农业科学与技术广东省实验室深圳分中心). 一种氧甲基转移酶及其在生物合成异嗪皮啶和嗪皮啶中的应用: CN202411992792.5[P]. 2025-04-04. |
| Shenzhen Institute of Agricultural Genomics, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(Shenzhen Branch Center of Lingnan Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Guangdong Laboratory). An oxymethyltransferase and its application in the biosynthesis of isoxaziridine and ziridine: CN202411992792.5[P]. 2025-04-04. | |
| [35] | 浙江大学. 一种利用多基因共表达在植物中异源合成人参皂苷Rg3的方法: CN202310573134.1[P]. 2023-09-05. |
| Zhejiang University. A method for heterologous synthesis of ginsenoside Rg3 in plants using multi-gene co-expr: CN202310573134.1[P]. 2023-09-05. | |
| [36] | 重庆大学. 一种可提升广藿香醇合成量的融合基因及方法: CN202211273337.0[P] .2024-09-17. |
| Chongqing University. A fusion gene and method to enhance patchouli alcohol synthesis: CN202211273337.0[P]. 2024-09-17. | |
| [37] | 山东大学. 一种黄酮合酶Ⅰ/黄烷酮-3-羟化酶及在黄酮类化合物合成领域的应用: CN202210565180.2[P]. 2023-08-22. |
| Shandong University. A flavonoid synthase Ⅰ/flavanone-3-hydroxylase and its application in flavonoid synthesis: CN202210565180.2[P]. 2023-08-22. | |
| [38] | 中国农业科学院生物技术研究所. 一种高效人工根际联合固氮体系: CN202010435008.6[P]. 2020-05-21. |
| Institute of Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. An efficient artificial rhizosphere combined nitrogen fixation system: CN202010435008.6[P]. 2020-05-21. | |
| [39] | SMITH J K, SCHLOSS J V, MAZUR B J. Functional expression of plant acetolactate synthase genes in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1989, 86(11): 4179-4183. |
| [40] | CAPARCO A A, GONZÁLEZ-GAMBOA I, CHANG-LIAO S, et al. A plug-and-play strategy for agrochemical delivery using a plant virus nanotechnology[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2024, 26(12): 280. |
| [41] | TIAN C F, LI J H, WU Y H, et al. An integrative database and its application for plant synthetic biology research[J]. Plant Communications, 2024, 5(5): 100827. |
| [42] | NIELSEN A A K, DER B S, SHIN J, et al. Genetic circuit design automation[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6281): aac7341. |
| [43] | BANF M, RHEE S Y. Computational inference of gene regulatory networks: approaches, limitations and opportunities[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 2017, 1860(1): 41-52. |
| [44] | MENG X Y, ZHANG H X, MEZEI M, et al. Molecular docking: a powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery[J]. Current Computer-Aided Drug Design, 2011, 7(2): 146-157. |
| [45] | KONG C, YANG Y, QI T C, et al. Predictive genetic circuit design for phenotype reprogramming in plants[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 715. |
| [46] | 朱新广, 常天根, 宋青峰, 等. 数字植物: 科学内涵、瓶颈及发展策略[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 285-297. |
| ZHU X G, CHANG T G, SONG Q F, et al. ePlant: scientific connotations, bottlenecks, and development strategies[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 285-297. | |
| [47] | 李星坤, 潘慧, 李攀, 等. 基于CRISPR/Cas9系统的拟南芥ugt84a1/ugt84a2双突变体制作及突变位点分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(20): 49-55. |
| LI X K, PAN H, et al. Construction of Arabidopsis ugt84a1/ugt84a2 double mutant and analysis of mutation site based on CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(20): 49-55. | |
| [48] | 蔡波, 李晓晓, 张凌寒, 等. CRISPR/Cas9技术联合脂质体转染子宫内膜癌细胞单质粒基因敲除方法首次编辑免疫相关基因HLA-DRA[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(15): 2356-2362. |
| CAI B, LI X X, ZHANG L H, et al. Editing immune-related gene HLA-DRA for the first time by CRISPR/Cas9 technology combined with liposome transfection of endometrial cancer cells with single-plasmid gene knockout method[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2356-2362. | |
| [49] | 李淑萍. 农杆菌T-DNA导入植物基因组的分子机理[J]. 河南农业科学, 2005, 34(4): 16-21. |
| LI S P. Molecular mechanisms of Agrobacterium T-DNA integration into plant genomes[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 34(4): 16-21. | |
| [50] | OZYIGIT I I, YUCEBILGILI KURTOGLU K. Particle bombardment technology and its applications in plants[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(12): 9831-9847. |
| [51] | ALTPETER F, BAISAKH N, BEACHY R, et al. Particle bombardment and the genetic enhancement of crops: myths and realities[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2005, 15(3): 305-327. |
| [52] | KESHAVAREDDY G, KUMAR A R V, RAMU V S. Methods of plant transformation- a review[J]. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 2018, 7(7): 2656-2668. |
| [53] | GAD A E, ROSENBERG N, ALTMAN A. Liposome-mediated gene delivery into plant cells[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 1990, 79(1): 177-183. |
| [54] | SU W B, XU M Y, RADANI Y, et al. Technological development and application of plant genetic transformation[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(13): 10646. |
| [55] | KAEPPLER H F, GU W, SOMERS D A, et al. Silicon carbide fiber-mediated DNA delivery into plant cells[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 1990, 9(8): 415-418. |
| [56] | SHIVASHAKARAPPA K, MARRIBOINA S, DUMENYO K, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated gene delivery techniques in plant systems[J]. Frontiers in Nanotechnology, 2025, 7: 1516180. |
| [57] | DENG X W, CAO M J, ZHANG J K, et al. Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of MiR-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(14): 4333-4344. |
| [58] | LV Z Y, JIANG R, CHEN J F, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated gene transformation strategies for plant genetic engineering[J]. The Plant Journal, 2020, 104(4): 880-891. |
| [59] | HAMERS R J. Nanomaterials and global sustainability[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50(3): 633-637. |
| [60] | CUNNINGHAM F J, GOH N S, DEMIRER G S, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery towards advancing plant genetic engineering[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 882-897. |
| [1] | YU Wenwen, LV Xueqin, LI Zhaofeng, LIU Long. Plant synthetic biology and bioproduction of human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 992-997. |
| [2] | YAN Zhaotao, ZHOU Pengfei, WANG Yangzhong, ZHANG Xin, XIE Wenyan, TIAN Chenfei, WANG Yong. Plant synthetic biology: new opportunities for large-scale culture of plant cells [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1107-1125. |
| [3] | ZHAO Xinyu, SHENG Qi, LIU Kaifang, LIU Jia, LIU Liming. Construction of microbial cell factories for aspartate-family feed amino acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1184-1202. |
| [4] | LIU Jie, GAO Yu, MA Yongshuo, SHANG Yi. Progress and challenges of synthetic biology in agriculture [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 998-1024. |
| [5] | ZHENG Lei, ZHENG Qiteng, ZHANG Tianjiao, DUAN Kun, ZHANG Ruifu. Engineering rhizosphere synthetic microbial communities to enhance crop nutrient use efficiency [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1058-1071. |
| [6] | HUANG Yuqing, WU Han, LI Xiaobin, LIU Junyu, MA Shaohua, GE Jun, XING Xinhui, ZHANG Canyang. Recent advancements in non-biological component-augmented synthetic bio-hybrid systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 764-788. |
| [7] | CHEN Yingying, LIU Yang, SHI Junjie, MA Junying, JU Jianhua. CRISPR/Cas systems and their applications in gene editing with filamentous fungi [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 672-693. |
| [8] | XU Zhimeng, XIE Zhen. Research progress and biotechnological applications of the prime editing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 1-15. |
| [9] | CHEN Yaru, CAO Yingxiu, SONG Hao. Advances and applications of gene editing and transcriptional regulation in electroactive microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1281-1299. |
| [10] | LIN Jicong, ZOU Gen, LIU Hongmin, WEI Yongjun. Application of CRISPR/Cas genome editing technology in the synthesis of secondary metabolites of filamentous fungi [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 738-755. |
| [11] | LIU Ke, LIN Guihong, LIU Kun, ZHOU Wei, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Mining, engineering and functional expansion of CRISPR/Cas systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 47-66. |
| [12] | LIANG Liya, LIU Rongming. Protein engineering of DNA targeting type Ⅱ CRISPR/Cas systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| [13] | LIU Jiaxin, CHENG Chi, LI Xinqi, WANG Chaojun, ZHANG Ying, XUE Chuang. Recent progress in the molecular genetic modification tools of Clostridium [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1201-1217. |
| [14] | YANG Jianzhao, ZHU Xinguang. Plant synthetic biology for carbon peak and carbon neutrality [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 847-869. |
| [15] | BI Jiacheng, TIAN Zhigang. Synthetic immunology and future NK cell immunotherapy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(1): 22-34. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||