Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (5): 1107-1125.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-095
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Plant synthetic biology: new opportunities for large-scale culture of plant cells
YAN Zhaotao1,2,3, ZHOU Pengfei4, WANG Yangzhong1, ZHANG Xin1, XIE Wenyan1, TIAN Chenfei1,2, WANG Yong2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Cigarette Smoke in Tobacco Industry,Shanghai Tobacco Group Co. ,Ltd,Shanghai 201315,China
2.Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology,CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences,Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 200032,China
3.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
4.School of Basic Medical Sciences,Guangdong Medical University,Dongguan 523808,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2024-12-18Revised:2025-02-24Online:2025-10-31Published:2025-10-31 -
Contact:TIAN Chenfei, WANG Yong
植物合成生物学:植物细胞大规模培养的新机遇
颜钊涛1,2,3, 周鹏飞4, 汪阳忠1, 张鑫1, 谢雯燕1, 田晨菲1,2, 王勇2
- 1.上海烟草集团有限责任公司烟草行业卷烟烟气重点实验室,上海 201315
2.中国科学院分子植物科学卓越创新中心,植物生理生态研究所,中国科学院合成生物学重点实验室,上海 200032
3.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
4.广东医科大学基础医学院,广东 东莞 523808
-
通讯作者:田晨菲,王勇 -
作者简介:颜钊涛 (1998—),男,硕士研究生。主要研究方向为植物合成生物学及植物细胞培养。E-mail:yanzhaotao@cemps.ac.cn田晨菲 (1995—),女,博士后。研究方向为植物合成生物学。E-mail:tianchenfei@cemps.ac.cn王勇 (1974—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为天然产物合成生物学,通过解析天然产物的生物合成途径,运用合成生物学的思想和方法,基于工程化的设计和建构,改进复杂天然产物的生物合成效率和其生产方式,开发天然的或非天然的复杂天然产物活性成分。E-mail:yongwang@cemps.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(SQ2024YFA1700126);上海市市级重大专项(24HC2820400);上海烟草集团有限责任公司行业卷烟烟气重点实验室开放性课题(K2023-1-044P)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YAN Zhaotao, ZHOU Pengfei, WANG Yangzhong, ZHANG Xin, XIE Wenyan, TIAN Chenfei, WANG Yong. Plant synthetic biology: new opportunities for large-scale culture of plant cells[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1107-1125.
颜钊涛, 周鹏飞, 汪阳忠, 张鑫, 谢雯燕, 田晨菲, 王勇. 植物合成生物学:植物细胞大规模培养的新机遇[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(5): 1107-1125.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-095
| 产品 | 物种 | 应用 | 制造商 | 参考资料 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 紫杉醇 | Taxus chinensis L. | 药物,抗癌 | Phyton Biotech | https://phytonbiotech.com/about-pcf/ |
| 迷迭香酸 | Melissa axillaris L. | 药物,抗氧化 | Aethera Biotech | https://www.aetherabiotech.it/en/ |
| 可可粉 | Theobroma cacao L. | 食品成分 | California Cultured | https://www.cacultured.com/ |
| 黄烷醇 | Theobroma cacao L. | 医药、保健品成分 | AyanaBio | http://www.ayanabio.com |
| 海茴香细胞提取物 | Crithmummaritimum L. | 化妆品成分,抗氧化 | Ancelbio | http://ancelbio.cn/ |
| 火绒草细胞提取物 | Leontopodium alpinum L. | 化妆品成分,抗皱 | Ancelbio | http://ancelbio.cn/ |
| GBL-Skin1 | Glycyrrhizauralensis L. | 化妆品原料,乳化剂 | Green Bioactives | https://greenbioactives.com/ |
| 白藜芦醇 | Graptoveria amethorum L. | 化妆品、保健品成分 | Bioharvest Science | https://bioharvest.com/ |
| Elelyso | Daucus carota L. | 戈谢病治疗性蛋白 | Protalix BioThera | http://protalix.comhttps://clinicaltrials.gov |
| OPRX-100 | Daucus carota L. | 溃疡性结肠炎治疗性蛋白 | Protalix BioThera | http://protalix.comhttps://clinicaltrials.gov |
| PRX-102 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 法布里病治疗性蛋白 | Protalix BioThera | http://protalix.comhttps://clinicaltrials.gov |
| 新城疫疫苗 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 新城疫疫苗 | Dow AgroSciences | https://www.dow.com/ |
| MOSS-FH | Physcomitriumpatens L. | 溶血性尿毒症综合征治疗性蛋白 | Greenovation Biotech GmbH | http://www.greenovation.com/ developmental-pipeline.html |
Table 1 Commercial cases of mass production of plant cells
| 产品 | 物种 | 应用 | 制造商 | 参考资料 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 紫杉醇 | Taxus chinensis L. | 药物,抗癌 | Phyton Biotech | https://phytonbiotech.com/about-pcf/ |
| 迷迭香酸 | Melissa axillaris L. | 药物,抗氧化 | Aethera Biotech | https://www.aetherabiotech.it/en/ |
| 可可粉 | Theobroma cacao L. | 食品成分 | California Cultured | https://www.cacultured.com/ |
| 黄烷醇 | Theobroma cacao L. | 医药、保健品成分 | AyanaBio | http://www.ayanabio.com |
| 海茴香细胞提取物 | Crithmummaritimum L. | 化妆品成分,抗氧化 | Ancelbio | http://ancelbio.cn/ |
| 火绒草细胞提取物 | Leontopodium alpinum L. | 化妆品成分,抗皱 | Ancelbio | http://ancelbio.cn/ |
| GBL-Skin1 | Glycyrrhizauralensis L. | 化妆品原料,乳化剂 | Green Bioactives | https://greenbioactives.com/ |
| 白藜芦醇 | Graptoveria amethorum L. | 化妆品、保健品成分 | Bioharvest Science | https://bioharvest.com/ |
| Elelyso | Daucus carota L. | 戈谢病治疗性蛋白 | Protalix BioThera | http://protalix.comhttps://clinicaltrials.gov |
| OPRX-100 | Daucus carota L. | 溃疡性结肠炎治疗性蛋白 | Protalix BioThera | http://protalix.comhttps://clinicaltrials.gov |
| PRX-102 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 法布里病治疗性蛋白 | Protalix BioThera | http://protalix.comhttps://clinicaltrials.gov |
| 新城疫疫苗 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 新城疫疫苗 | Dow AgroSciences | https://www.dow.com/ |
| MOSS-FH | Physcomitriumpatens L. | 溶血性尿毒症综合征治疗性蛋白 | Greenovation Biotech GmbH | http://www.greenovation.com/ developmental-pipeline.html |
| 植物物种 | 拉丁名 | 蛋白名称 | 细胞材料 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 人骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP2) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 21.5 μg/mL培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 人类生长激素(hGH) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 57 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 合成牛胰蛋白酶原(synthetic bovine trypsinogen) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 15 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 酸性葡萄糖苷酶(GAA) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 37 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 血管内皮生长因子(VEGF) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 19 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 包膜糖蛋白(envelope glycoprotein) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 18.5 μg/g | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 贝伐单抗(Bevacizumab monoclonal antibody) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 160.7~242.8 mg/kg | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 人抗胰蛋白酶(human α1-antitrypsin) | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 34.7 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 人生长激素(human growth hormone) | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 5.2%总可溶蛋白 | [ |
Table 2 Heterologous synthesis of recombinant proteins in plant cells
| 植物物种 | 拉丁名 | 蛋白名称 | 细胞材料 | 产量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 人骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP2) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 21.5 μg/mL培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 人类生长激素(hGH) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 57 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 合成牛胰蛋白酶原(synthetic bovine trypsinogen) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 15 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 酸性葡萄糖苷酶(GAA) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 37 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 血管内皮生长因子(VEGF) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 19 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 包膜糖蛋白(envelope glycoprotein) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 18.5 μg/g | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 贝伐单抗(Bevacizumab monoclonal antibody) | 水稻愈伤组织细胞 | 160.7~242.8 mg/kg | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 人抗胰蛋白酶(human α1-antitrypsin) | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 34.7 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 人生长激素(human growth hormone) | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 5.2%总可溶蛋白 | [ |
| 物种 | 外植体部位 | 类型 | 激素 | 培养基 | 周期 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 | 胚乳 | 愈伤组织 | 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D; 1.0 mg/L 6BA | N6培养基 | 6个月 | [ |
| 葡萄 | 叶片 | 愈伤组织 | 0.05 mg/L NAA; 0.5 mg/L 2,4-D; 2.0 mg/L KT | B5培养基 | 21天 | [ |
| 胡萝卜 | 茎段 | 愈伤组织 | 0.5 mg/L 2,4-D | MS培养基 | 14天 | [ |
| 红豆杉 | 胚乳 | 愈伤组织 | 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D; 0.5 mg/L 6BA | B5培养基 | 15天 | [ |
| 人参 | 根部 | 愈伤组织 | 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D; 0.1 mg/L KT | MS培养基 | 90天 | [ |
| 地黄 | 根部 | 形成层干细胞 | 2.0 mg/L NAA; 2.0 mg/L 6BA | MS培养基 | 14天 | [ |
Table 3 Common induction conditions of plant cell lines in vitro
| 物种 | 外植体部位 | 类型 | 激素 | 培养基 | 周期 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻 | 胚乳 | 愈伤组织 | 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D; 1.0 mg/L 6BA | N6培养基 | 6个月 | [ |
| 葡萄 | 叶片 | 愈伤组织 | 0.05 mg/L NAA; 0.5 mg/L 2,4-D; 2.0 mg/L KT | B5培养基 | 21天 | [ |
| 胡萝卜 | 茎段 | 愈伤组织 | 0.5 mg/L 2,4-D | MS培养基 | 14天 | [ |
| 红豆杉 | 胚乳 | 愈伤组织 | 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D; 0.5 mg/L 6BA | B5培养基 | 15天 | [ |
| 人参 | 根部 | 愈伤组织 | 1.0 mg/L 2,4-D; 0.1 mg/L KT | MS培养基 | 90天 | [ |
| 地黄 | 根部 | 形成层干细胞 | 2.0 mg/L NAA; 2.0 mg/L 6BA | MS培养基 | 14天 | [ |
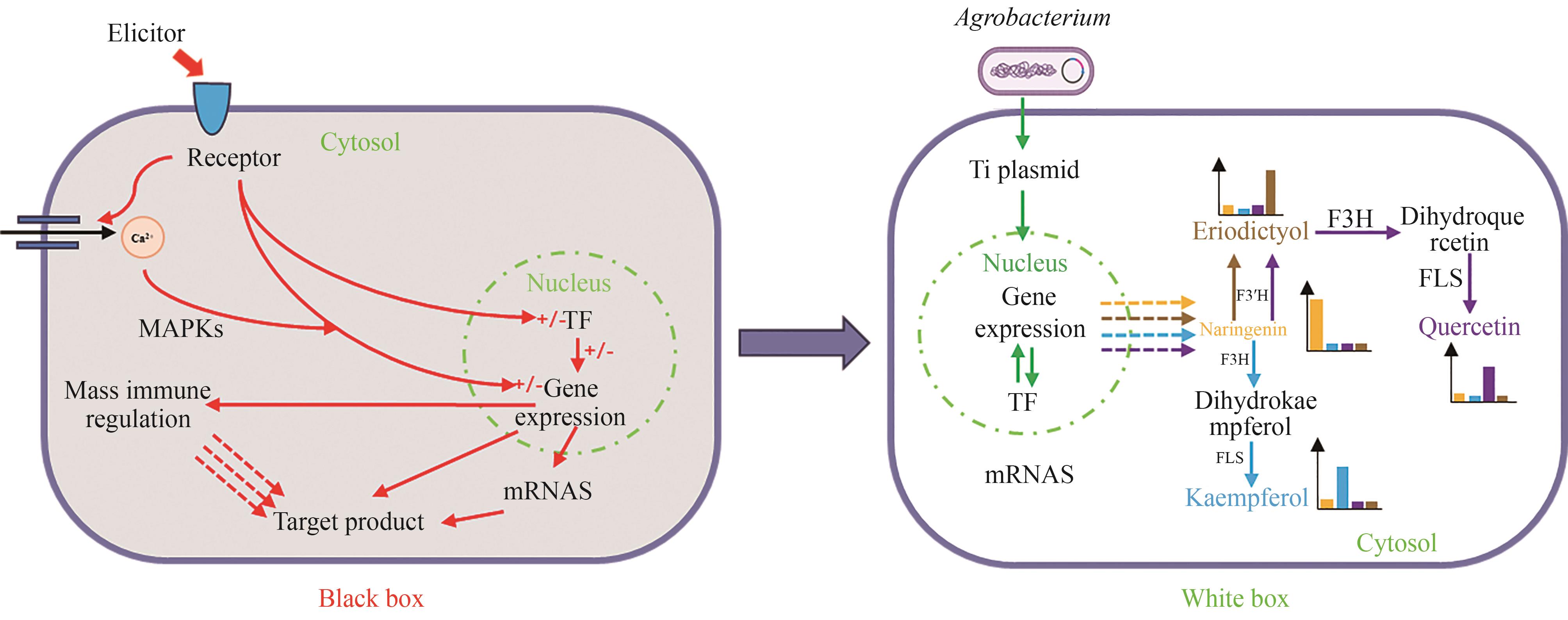
Fig. 2 Strategies for increasing plant cell yield from “Black box” to “White box”[89](In the “Black box”, the mechanism of the inducer to increase the yield of the target product has not been fully defined; in the “White box”, the yield of target products can be increased precisely with different gene circuits)
| 植物物种 | 改造策略 | 细胞材料 | 化合物类别 | 作用效果 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山葡萄 | Vitis amurensis Rupr. | 过表达VaCPK29 | 悬浮细胞 | 多酚类 | 白藜芦醇1.39 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 柑橘 | Citrusreticulata L. | 过表达CsMADS6、PSY、PDS和CCD1 | 愈伤组织细胞 | 类胡萝卜素 | 类胡萝卜素23 µg/g DW | [ |
| 加州藜芦 | Veratrum californicum var. | 过表达VnOSC1 | 愈伤组织细胞 | 生物碱 | 环巴胺6.14 mg/g DW | [ |
| 红豆杉 | Taxus baccata L. | 过表达NINV | 悬浮细胞 | 二萜类 | 紫杉醇94 μg/g FW | [ |
| 红豆杉 | Taxus baccata L. | 过表达BAPT、DBTNBT | 悬浮细胞 | 二萜类 | 紫杉醇310 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 灌木状辣椒 | Capsicum frutescens L. | 过表达VpVAN | 悬浮细胞 | 芳香族化合物 | 香兰素(573.39±120.70) µg/g组织 | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达转录因子AmRos1和AmDel | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 黄酮类 | 花青素30 mg/g DW | [ |
| 甜菜 | Beta vulgaris L. | 过表达VpVAN | 毛状根 | 芳香族化合物 | 香兰素(0.0430 ±0.003) mg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达HCHL | 悬浮细胞 | 黄酮类 | 花青素(75.4±6.1) µmol/g FW | [ |
| 竹 | Phyllostachys nigra L. | 过表达PpHCH | 悬浮细胞 | 酚类 | 4-羟基苯甲醇1.7 g/L培养液 | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达CqCYP76AD1、CqDODA、CqCDOPA5GT和CqAmaSy | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 苷类 | 苋菜苷(13.67±4.13) µmol/L;甜菜苷(26.60±1.53) µmol/L | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达CqCYP76AD1-1和CqDODA-1 | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 类黄酮 | 甜菜苷(19.53±8.60) µmol/L | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达VoGES | 悬浮细胞 | 单萜类 | 香叶醇16 µg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达PgDDS | 悬浮细胞 | 三萜类 | 达玛烯二醇-Ⅱ 573 µg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达PgDDS和CYP716A47 | 悬浮细胞 | 三萜类 | 原人参二醇980.9 µg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | CRISPRi抑制NtC4H | 悬浮细胞 | 苯丙素类 | 绿原酸1799.69 ng/mL培养液; 乔松酮384.19 ng/mL培养液; 柚皮素597.53 ng/mL培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 修饰近靶顺式作用元件,激活PHYTOENE SYNTHASE 1启动子 | 愈伤组织细胞 | 类胡萝卜素 | 八氢番茄红素7.13 µg/g DW | [ |
| 水飞蓟 | Silybum marianum L. | 过表达STS | 悬浮细胞 | 多酚类 | 白藜芦醇50 ng/g FW | [ |
| 连翘 | Forsythia koreana L. | 过表达CYP81Q1;RNAi抑制UGT71A18和PLR | 悬浮细胞 | 木质素 | 芝麻素(10.83±0.35) µg/g DW | [ |
Table 4 Cases of secondary metabolites synthesized by plant cells
| 植物物种 | 改造策略 | 细胞材料 | 化合物类别 | 作用效果 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山葡萄 | Vitis amurensis Rupr. | 过表达VaCPK29 | 悬浮细胞 | 多酚类 | 白藜芦醇1.39 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 柑橘 | Citrusreticulata L. | 过表达CsMADS6、PSY、PDS和CCD1 | 愈伤组织细胞 | 类胡萝卜素 | 类胡萝卜素23 µg/g DW | [ |
| 加州藜芦 | Veratrum californicum var. | 过表达VnOSC1 | 愈伤组织细胞 | 生物碱 | 环巴胺6.14 mg/g DW | [ |
| 红豆杉 | Taxus baccata L. | 过表达NINV | 悬浮细胞 | 二萜类 | 紫杉醇94 μg/g FW | [ |
| 红豆杉 | Taxus baccata L. | 过表达BAPT、DBTNBT | 悬浮细胞 | 二萜类 | 紫杉醇310 mg/L培养液 | [ |
| 灌木状辣椒 | Capsicum frutescens L. | 过表达VpVAN | 悬浮细胞 | 芳香族化合物 | 香兰素(573.39±120.70) µg/g组织 | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达转录因子AmRos1和AmDel | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 黄酮类 | 花青素30 mg/g DW | [ |
| 甜菜 | Beta vulgaris L. | 过表达VpVAN | 毛状根 | 芳香族化合物 | 香兰素(0.0430 ±0.003) mg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达HCHL | 悬浮细胞 | 黄酮类 | 花青素(75.4±6.1) µmol/g FW | [ |
| 竹 | Phyllostachys nigra L. | 过表达PpHCH | 悬浮细胞 | 酚类 | 4-羟基苯甲醇1.7 g/L培养液 | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达CqCYP76AD1、CqDODA、CqCDOPA5GT和CqAmaSy | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 苷类 | 苋菜苷(13.67±4.13) µmol/L;甜菜苷(26.60±1.53) µmol/L | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达CqCYP76AD1-1和CqDODA-1 | BY-2悬浮细胞 | 类黄酮 | 甜菜苷(19.53±8.60) µmol/L | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达VoGES | 悬浮细胞 | 单萜类 | 香叶醇16 µg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达PgDDS | 悬浮细胞 | 三萜类 | 达玛烯二醇-Ⅱ 573 µg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | 过表达PgDDS和CYP716A47 | 悬浮细胞 | 三萜类 | 原人参二醇980.9 µg/g DW | [ |
| 烟草 | Nicotiana tabacum L. | CRISPRi抑制NtC4H | 悬浮细胞 | 苯丙素类 | 绿原酸1799.69 ng/mL培养液; 乔松酮384.19 ng/mL培养液; 柚皮素597.53 ng/mL培养液 | [ |
| 水稻 | Oryza sativa L. | 修饰近靶顺式作用元件,激活PHYTOENE SYNTHASE 1启动子 | 愈伤组织细胞 | 类胡萝卜素 | 八氢番茄红素7.13 µg/g DW | [ |
| 水飞蓟 | Silybum marianum L. | 过表达STS | 悬浮细胞 | 多酚类 | 白藜芦醇50 ng/g FW | [ |
| 连翘 | Forsythia koreana L. | 过表达CYP81Q1;RNAi抑制UGT71A18和PLR | 悬浮细胞 | 木质素 | 芝麻素(10.83±0.35) µg/g DW | [ |
| [1] | MURTHY H N, LEE E J, PAEK K Y. Production of secondary metabolites from cell and organ cultures: strategies and approaches for biomass improvement and metabolite accumulation[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2014, 118(1): 1-16. |
| [2] | NAGATA T, KUMAGAI F. Plant cell biology through the window of the highly synchronized tobacco BY-2 cell line[J]. Methods in Cell Science, 1999, 21(2): 123-127. |
| [3] | RAHMAN Z A, AHMAD SEMAN Z, OTHMAN A N, et al. Efficient callus induction and plant regeneration of Malaysian indica rice MR219 using anther culture[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2021, 31: 101865. |
| [4] | LI Y L, HUANG S W, ZHANG J Y, et al. A protocol of homozygous haploid callus induction from endosperm of Taxus chinensis Rehd. var. mairei [J]. SpringerPlus, 2016, 5(1): 659. |
| [5] | OBAE S G, KLANDORF H, WEST T P. Growth characteristics and ginsenosides production of in vitro tissues of American ginseng, Panax quinquefolius L[J]. HortScience, 2011, 46(8): 1136-1140. |
| [6] | LE V, SUKHIKH A, LARICHEV T, et al. Isolation of the main biologically active substances and phytochemical analysis of Ginkgo biloba callus culture extracts[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(4): 1560. |
| [7] | EIBL R, MEIER P, STUTZ I, et al. Plant cell culture technology in the cosmetics and food industries: current state and future trends[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(20): 8661-8675. |
| [8] | EMMANUEL D B, ISHAKU G A, ANDREW F P, et al. Callus culture for the production of therapeutic compounds[J]. American Journal of Plant Biology, 2019, 4(4): 76. |
| [9] | NETT R S, LAU W, SATTELY E S. Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2020, 584(7819): 148-153. |
| [10] | MAEDA H A. Harnessing evolutionary diversification of primary metabolism for plant synthetic biology[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2019, 294(45): 16549-16566. |
| [11] | MEYER H P, SCHMIDHALTER D R. Industrial scale suspension culture of living cells[M/OL]. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley Blackwell, 2014. (2014-06-18)[2024-12-01]. . |
| [12] | DIRISALA V R, NAIR R R, SRIRAMA K, et al. Recombinant pharmaceutical protein production in plants: unraveling the therapeutic potential of molecular pharming[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 39(1): 18. |
| [13] | ARYA S S, ROOKES J E, CAHILL D M, et al. Next-generation metabolic engineering approaches towards development of plant cell suspension cultures as specialized metabolite producing biofactories[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 45: 107635. |
| [14] | HUSSAIN M S, FAREED S, ANSARI S, et al. Current approaches toward production of secondary plant metabolites[J]. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences, 2012, 4(1): 10-20. |
| [15] | RAMIREZ-ESTRADA K, VIDAL-LIMON H, HIDALGO D, et al. Elicitation, an effective strategy for the biotechnological production of bioactive high-added value compounds in plant cell factories[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(2): 182. |
| [16] | NAGEGOWDA D A, GUPTA P. Advances in biosynthesis, regulation, and metabolic engineering of plant specialized terpenoids[J]. Plant Science, 2020, 294: 110457. |
| [17] | FONSECA-SANTOS B, CORRÊA M A, CHORILLI M. Sustainability, natural and organic cosmetics: consumer, products, efficacy, toxicological and regulatory considerations[J]. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2015, 51(1): 17-26. |
| [18] | GOMORD V, FAYE L. Posttranslational modification of therapeutic proteins in plants[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2004, 7(2): 171-181. |
| [19] | GHAG S B, ADKI V S, GANAPATHI T R, et al. Plant platforms for efficient heterologous protein production[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2021, 26(4): 546-567. |
| [20] | SINGH A A, PILLAY P, TSEKOA T L. Engineering approaches in plant molecular farming for global health[J]. Vaccines, 2021, 9(11): 1270. |
| [21] | WU J P, ZHANG J X, HAO X Y, et al. Establishment of an efficient callus transient transformation system for Vitis vinifera cv. ‘Chardonnay’[J]. Protoplasma, 2024, 261(2): 351-366. |
| [22] | CORTESE E, CARRARETTO L, BALDAN B, et al. Arabidopsis photosynthetic and heterotrophic cell suspension cultures[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2021, 2200: 167-185. |
| [23] | LI B, TAKAHASHI D, KAWAMURA Y, et al. Plasma membrane proteome analyses of Arabidopsis thaliana suspension-cultured cells during cold or ABA treatment: relationship with freezing tolerance and growth phase[J]. Journal of Proteomics, 2020, 211: 103528. |
| [24] | SEGEČOVÁ A, ČERVENÝ J, ROITSCH T. Advancement of the cultivation and upscaling of photoautotrophic suspension cultures using Chenopodium rubrum as a case study[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2018, 135(1): 37-51. |
| [25] | THORPE T A. History of plant tissue culture[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2007, 37(2): 169-180. |
| [26] | SRBA M, ČERNÍKOVÁ A, OPATRNÝ Z, et al. Practical guidelines for the characterization of tobacco BY-2 cell lines[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2016, 60(1): 13-24. |
| [27] | IKEDA N, KAMIMURA M, UESUGI K, et al. Choline chloride and N-allylglycine promote plant growth by increasing the efficiency of photosynthesis[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2024, 89(1): 51-61. |
| [28] | LEE E K, JIN Y W, PARK J H, et al. Cultured cambial meristematic cells as a source of plant natural products[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(11): 1213-1217. |
| [29] | ZHOU P F, LI H H, LIN Y J, et al. Omics analyses of Rehmannia glutinosa dedifferentiated and cambial meristematic cells reveal mechanisms of catalpol and indole alkaloid biosynthesis[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23(1): 463. |
| [30] | PATRA N, SRIVASTAVA A K. Artemisinin production by plant hairy root cultures in gas- and liquid-phase bioreactors[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2016, 35(1): 143-153. |
| [31] | HA L T, PAWLICKI-JULLIAN N, PILLON-LEQUART M, et al. Hairy root cultures of Panax vietnamensis, a promising approach for the production of ocotillol-type ginsenosides[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2016, 126(1): 93-103. |
| [32] | PERASSOLO M, CARDILLO A B, MUGAS M L, et al. Enhancement of anthraquinone production and release by combination of culture medium selection and methyl jasmonate elicitation in hairy root cultures of Rubia tinctorum [J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2017, 105: 124-132. |
| [33] | NGUYEN T M, WU P Y, CHANG C H, et al. High-yield BMP2 expression in rice cells via CRISPR and endogenous αAmy3 promoter[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2024, 108(1): 206. |
| [34] | KIM T G, BAEK M Y, LEE E K, et al. Expression of human growth hormone in transgenic rice cell suspension culture[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2008, 27(5): 885-891. |
| [35] | KIM N S, YU H Y, CHUNG N D, et al. Production of functional recombinant bovine trypsin in transgenic rice cell suspension cultures[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2011, 76(1): 121-126. |
| [36] | JUNG J W, KIM N S, JANG S H, et al. Production and characterization of recombinant human acid α-glucosidase in transgenic rice cell suspension culture[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 226: 44-53. |
| [37] | CHUNG N D, KIM N S, VAN GIAP D, et al. Production of functional human vascular endothelial growth factor 165 in transgenic rice cell suspension cultures[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2014, 63: 58-63. |
| [38] | KIM T G, KIM M Y, TIEN N Q D, et al. Dengue virus E glycoprotein production in transgenic rice callus[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2014, 56(12): 1069-1078. |
| [39] | CHEN L, YANG X Y, LUO D, et al. Efficient production of a bioactive bevacizumab monoclonal antibody using the 2A self-cleavage peptide in transgenic rice callus[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1156. |
| [40] | ZHANG N N, WRIGHT T, CARAWAY P, et al. Enhanced secretion of human α1-antitrypsin expressed with a novel glycosylation module in tobacco BY-2 cell culture[J]. Bioengineered, 2019, 10(1): 87-97. |
| [41] | XU J F, OKADA S, TAN L, et al. Human growth hormone expressed in tobacco cells as an Arabinogalactan-protein fusion glycoprotein has a prolonged serum life[J]. Transgenic Research, 2010, 19(5): 849-867. |
| [42] | GENGENBACH B B, KEIL L L, OPDENSTEINEN P, et al. Comparison of microbial and transient expression (tobacco plants and plant-cell packs) for the production and purification of the anticancer mistletoe lectin viscumin[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(9): 2236-2249. |
| [43] | RATNER M. Genzyme resumes shipping as Sanofi-aventis hovers[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(10): 994. |
| [44] | MIHALIAK C A, FANTON M J, MCMILLEN J K. Preparation of vaccine master cell lines using recombinant plant suspension cultures: US2006/041305[P]. 2010-01-14. |
| [45] | HANANIA U, ARIEL T, TEKOAH Y, et al. Establishment of a tobacco BY2 cell line devoid of plant-specific xylose and fucose as a platform for the production of biotherapeutic proteins[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(9): 1120-1129. |
| [46] | HUANG T K, MCDONALD K A. Bioreactor systems for in vitro production of foreign proteins using plant cell cultures[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(2): 398-409. |
| [47] | ALCALDE M A, PEREZ-MATAS E, ESCRICH A, et al. Biotic elicitors in adventitious and hairy root cultures: a review from 2010 to 2022[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(16): 5253. |
| [48] | CHODISETTI B, RAO K, GANDI S, et al. Improved gymnemic acid production in the suspension cultures of Gymnema sylvestre through biotic elicitation[J]. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 2013, 7(4): 519-525. |
| [49] | LIANG C X, CHEN C, ZHOU P F, et al. Effect of Aspergillus flavus fungal elicitor on the production of terpenoid indole alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus cambial meristematic cells[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(12): 3276. |
| [50] | NAMDEO A G. Plant cell elicitation for production of secondary metabolites: a review[J]. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 2007, 1(1): 69-79. |
| [51] | AN Y, FENG S, XU Y, et al. ChemInform abstract: hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of a new potassium phosphatoantimonate, K8Sb8P2O29×8 H2O[J]. ChemInform, 1996, 27(21): 199621020. |
| [52] | EFFERTH T. Biotechnology applications of plant callus cultures[J]. Engineering, 2019, 5(1): 50-59. |
| [53] | ZHANG Z J, SUN Y H, LI Y. Plant rejuvenation: from phenotypes to mechanisms[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2020, 39(10): 1249-1262. |
| [54] | TAKEDA T, MIZUKAMI M, MATSUOKA H. Characterization of two-step direct somatic embryogenesis in carrot[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 38(2): 206-211. |
| [55] | LU Y, LIU Z Y, LYU M L, et al. Characterization of JsWOX1 and JsWOX4 during callus and root induction in the shrub species Jasminum sambac [J]. Plants, 2019, 8(4): 79. |
| [56] | FENG M, ZHANG A, NGUYEN V, et al. A conserved graft formation process in Norway spruce and Arabidopsis identifies the PAT gene family as central regulators of wound healing[J]. Nature Plants, 2024, 10(1): 53-65. |
| [57] | CAO H F, ZHANG X, LI F, et al. Glucosinolate O-methyltransferase mediated callus formation and affected ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2024, 30(1): 109-121. |
| [58] | SU Y H, TANG L P, ZHAO X Y, et al. Plant cell totipotency: insights into cellular reprogramming[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(1): 228-243. |
| [59] | XU C Y, CHANG P J, GUO S Q, et al. Transcriptional activation by WRKY23 and derepression by removal of bHLH041 coordinately establish callus pluripotency in Arabidopsis regeneration[J]. The Plant Cell, 2023, 36(1): 158-173. |
| [60] | YANG W T, ZHAI H W, WU F M, et al. Peptide REF1 is a local wound signal promoting plant regeneration[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(12): 3024-3038.e14. |
| [61] | 张博, 马永硕, 尚轶, 等. 植物合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 121-140. |
| ZHANG B, MA Y S, SHANG Y, et al. Recent advances in plant synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(2): 121-140. | |
| [62] | YOOSEFZADEH-NAJAFABADI M, TORABI S, TULPAN D, et al. Genome-wide association studies of soybean yield-related hyperspectral reflectance bands using machine learning-mediated data integration methods[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 777028. |
| [63] | RAMEZANPOUR M R, FARAJPOUR M. Application of artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm to predict and optimize greenhouse banana fruit yield through nitrogen, potassium and magnesium[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(2): e0264040. |
| [64] | HESAMI M, ALIZADEH M, JONES A M P, et al. Machine learning: its challenges and opportunities in plant system biology[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 106(9-10): 3507-3530. |
| [65] | JAFARI M, DANESHVAR M H. Prediction and optimization of indirect shoot regeneration of Passiflora caerulea using machine learning and optimization algorithms[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2023, 23(1): 27. |
| [66] | FALLAH ZIARANI M, TOHIDFAR M, NAVVABI M. Modeling and optimizing in vitro percentage and speed callus induction of carrot via Multilayer Perceptron-Single point discrete GA and radial basis function[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2022, 22(1): 34. |
| [67] | REZAEI H, MIRZAIE-ASL A, ABDOLLAHI M R, et al. Enhancing Petunia tissue culture efficiency with machine learning: a pathway to improved callogenesis[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(11): e0293754. |
| [68] | GRIGOREVA E I, SIDORCHUK Y V, DEINEKO E V. Aggregates’ formation in higher plants’ cell culture: the role of cell wall components[J]. Biology Bulletin Reviews, 2022, 12(2): S182-S194. |
| [69] | KOLEWE M E, HENSON M A, ROBERTS S C. Analysis of aggregate size as a process variable affecting paclitaxel accumulation in Taxus suspension cultures[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2011, 27(5): 1365-1372. |
| [70] | PATIL R A, KOLEWE M E, ROBERTS S C. Cellular aggregation is a key parameter associated with long term variability in paclitaxel accumulation in Taxus suspension cultures[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2013, 112(3): 303-310. |
| [71] | NYON M P, DU L Y, TSENG C K, et al. Engineering a stable CHO cell line for the expression of a MERS-coronavirus vaccine antigen[J]. Vaccine, 2018, 36(14): 1853-1862. |
| [72] | BISSINGER T, WU Y X, MARICHAL-GALLARDO P, et al. Towards integrated production of an influenza A vaccine candidate with MDCK suspension cells[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(10): 3996-4013. |
| [73] | SHEN C F, GUILBAULT C, LI X L, et al. Development of suspension adapted Vero cell culture process technology for production of viral vaccines[J]. Vaccine, 2019, 37(47): 6996-7002. |
| [74] | LEE N, SHIN J, PARK J H, et al. Targeted gene deletion using DNA-free RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease accelerates adaptation of CHO cells to suspension culture[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(11): 1211-1219. |
| [75] | MOHNEN D. Pectin structure and biosynthesis[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2008, 11(3): 266-277. |
| [76] | YEH B J, RUTIGLIANO R J, DEB A, et al. Rewiring cellular morphology pathways with synthetic guanine nucleotide exchange factors[J]. Nature, 2007, 447(7144): 596-600. |
| [77] | GLEBA Y Y, TUSÉ D, GIRITCH A. Plant viral vectors for delivery by Agrobacterium [M/OL]//PALMER K, GLEBA Y. Plant viral vectors. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013, 375: 155-192. (2013-08-15)[2024-12-14]. . |
| [78] | HESAMI M, ALIZADEH M, NADERI R, et al. Forecasting and optimizing Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation via ensemble model-fruit fly optimization algorithm: a data mining approach using chrysanthemum databases[J]. PloS One, 2020,15(9); e0239901. |
| [79] | JIANG T, ZHANG Y, ZUO G G, et al. Transcription factor PgNAC72 activates DAMMARENEDIOL SYNTHASE expression to promote ginseng saponin biosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2024, 195(4): 2952-2969. |
| [80] | ZHAO Y, CHENG P, LIU Y, et al. A highly efficient soybean transformation system using GRF3-GIF1 chimeric protein[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2025, 67(1): 3-6. |
| [81] | JHA P, KUMAR V. BABY BOOM (BBM): a candidate transcription factor gene in plant biotechnology[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2018, 40(11): 1467-1475. |
| [82] | LOWE K, WU E, WANG N, et al. Morphogenic regulators baby boom and wuschel improve monocot transformation[J]. The Plant Cell, 2016, 28(9): 1998-2015. |
| [83] | KOBERCOVÁ E, SRBA M, FISCHER L. Sulfadiazine and phosphinothricin selection systems optimised for the transformation of tobacco BY-2 cells[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2023, 42(3): 535-548. |
| [84] | HE Y B, ZHANG T, SUN H, et al. A reporter for noninvasively monitoring gene expression and plant transformation[J]. Horticulture Research, 2020, 7: 152. |
| [85] | TIAN C F, ZHANG Y X, LI J H, et al. Benchmarking intrinsic promoters and terminators for plant synthetic biology research[J]. Biodesign Research, 2022, 2022: 9834989. |
| [86] | YAMASAKI S, SUZUKI A, YAMANO Y, et al. Identification of 5'-untranslated regions that function as effective translational enhancers in monocotyledonous plant cells using a novel method of genome-wide analysis[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2018, 35(4): 365-373. |
| [87] | HUANG L F, TAN C C, YEH J F, et al. Efficient secretion of recombinant proteins from rice suspension-cultured cells modulated by the choice of signal peptide[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): e0140812. |
| [88] | WOJCIK S, KRIECHBAUMER V. Go your own way: membrane-targeting sequences[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 185(3): 608-618. |
| [89] | SELMA S, SANMARTÍN N, ESPINOSA-RUIZ A, et al. Custom-made design of metabolite composition in N. benthamiana leaves using CRISPR activators[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(8): 1578-1590. |
| [90] | PEREZ-MATAS E, HIDALGO-MARTINEZ D, MOYANO E, et al. Overexpression of BAPT and DBTNBT genes in Taxus baccata in vitro cultures to enhance the biotechnological production of paclitaxel[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 22(1): 233-247. |
| [91] | ZUO A Q, HE D, SUN C R, et al. Integration of induction, system optimization and genetic transformation in Veratrum californicum var. vitro cultures to enhance the production of cyclopamine and veratramine[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 216: 109087. |
| [92] | CHU M Y, PEDREÑO M A, ALBURQUERQUE N, et al. A new strategy to enhance the biosynthesis of trans-resveratrol by overexpressing stilbene synthase gene in elicited Vitis vinifera cell cultures[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2017, 113: 141-148. |
| [93] | LI J H, MUTANDA I, WANG K B, et al. Chloroplastic metabolic engineering coupled with isoprenoid pool enhancement for committed taxanes biosynthesis in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4850. |
| [94] | SHI Y S, WANG D, LI R S, et al. Engineering yeast subcellular compartments for increased production of the lipophilic natural products ginsenosides[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 67: 104-111. |
| [95] | KARLSON C K S, MOHD NOOR S N, KHALID N, et al. CRISPRi-mediated down-regulation of the cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H) gene enhances the flavonoid biosynthesis in Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Biology, 2022, 11(8): 1127. |
| [96] | ZHANG W H, ZHANG J Z, FAN Y D, et al. RNA sequencing analysis reveals PgbHLH28 as the key regulator in response to methyl jasmonate-induced saponin accumulation in Platycodon grandiflorus [J]. Horticulture Research, 2024, 11(5): uhae058. |
| [97] | KARPPINEN K, LAFFERTY D J, ALBERT N W, et al. MYBA and MYBPA transcription factors co-regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in blue-coloured berries[J]. New Phytologist, 2021, 232(3): 1350-1367. |
| [98] | APPELHAGEN I, WULFF-VESTER A K, WENDELL M, et al. Colour bio-factories: towards scale-up production of anthocyanins in plant cell cultures[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 48: 218-232. |
| [99] | JIA E T, LI H, HE F, et al. Metabolic engineering of artificially modified transcription factor SmMYB36-VP16 for high-level production of tanshinones and phenolic acids[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2024, 86: 29-40. |
| [100] | GE C, YU Z, SHENG H K, et al. Redesigning regulatory components of quorum-sensing system for diverse metabolic control[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2182. |
| [101] | WU J J, BAO M J, DUAN X G, et al. Developing a pathway-independent and full-autonomous global resource allocation strategy to dynamically switching phenotypic states[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5521. |
| [102] | KURZBACH E, STRIEKER M, WITTSTOCK U. Production of benzylglucosinolate in genetically engineered carrot suspension cultures[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2022, 39(3): 241-250. |
| [103] | VASILEV N, SCHMITZ C, GRÖMPING U, et al. Assessment of cultivation factors that affect biomass and geraniol production in transgenic tobacco cell suspension cultures[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e104620. |
| [104] | CHUN J H, ADHIKARI P B, PARK S B, et al. Production of the dammarene sapogenin (protopanaxadiol) in transgenic tobacco plants and cultured cells by heterologous expression of PgDDS and CYP716A47 [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2015, 34(9): 1551-1560. |
| [105] | MURATA J, MATSUMOTO E, MORIMOTO K, et al. Generation of triple-transgenic Forsythia cell cultures as a platform for the efficient, stable, and sustainable production of lignans[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(12): e0144519. |
| [106] | LU S W, ZHANG Y, ZHU K J, et al. The Citrus transcription factor CsMADS6 modulates carotenoid metabolism by directly regulating carotenogenic genes[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176(4): 2657-2676. |
| [107] | DONG Y S, DUAN W L, HE H X, et al. Enhancing taxane biosynthesis in cell suspension culture of Taxus chinensis by overexpressing the neutral/alkaline invertase gene[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(4): 651-660. |
| [108] | CHEE M J Y, LYCETT G W, KHOO T J, et al. Bioengineering of the plant culture of Capsicum frutescens with vanillin synthase gene for the production of vanillin[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2017, 59(1): 1-8. |
| [109] | HUSAIN Z, WARSI Z I, KHAN S, et al. Metabolic engineering of hairy root cultures in beta vulgaris for enhanced production of vanillin, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, and vanillyl alcohol[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2024, 12: 1435190. |
| [110] | MAYER M J, NARBAD A, PARR A J, et al. Rerouting the plant phenylpropanoid pathway by expression of a novel bacterial enoyl-CoA hydratase/lyase enzyme function[J]. The Plant Cell, 2001, 13(7): 1669-1682. |
| [111] | KITAOKA N, NOMURA T, OGITA S, et al. Bioproduction of glucose conjugates of 4-hydroxybenzoic and vanillic acids using bamboo cells transformed to express bacterial 4-hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA hydratase/lyase[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2020, 130(1): 89-97. |
| [112] | IMAMURA T, ISOZUMI N, HIGASHIMURA Y, et al. Isolation of amaranthin synthetase from Chenopodium quinoa and construction of an amaranthin production system using suspension-cultured tobacco BY-2 cells[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(5): 969-981. |
| [113] | HAN J Y, WANG H Y, CHOI Y E. Production of dammarenediol-Ⅱ triterpene in a cell suspension culture of transgenic tobacco[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33(2): 225-233. |
| [114] | SOBRINO-MENGUAL G, ALVAREZ D, TWYMAN R M, et al. Activation of the native PHYTOENE SYNTHASE 1 promoter by modifying near-miss cis-acting elements induces carotenoid biosynthesis in embryogenic rice callus[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2024, 43(5): 118. |
| [115] | HIDALGO D, GEORGIEV M, MARCHEV A, et al. Tailoring tobacco hairy root metabolism for the production of stilbenes[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 17976. |
| [116] | DEUS-NEUMANN B, ZENK M H. Instability of indole alkaloid production in Catharanthus roseus cell suspension cultures[J]. Planta Medica, 1984, 50(5): 427-431. |
| [117] | ISHCHUK O P, DOMENZAIN I, SÁNCHEZ B J, et al. Genome-scale modeling drives 70-fold improvement of intracellular heme production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(30): e2108245119. |
| [118] | CRISTIANA GOMES DE OLIVEIRA DAL’MOLIN L Q. AraGEM, a genome-scale reconstruction of the primary metabolic network in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 152(2): 579-589. |
| [119] | MURALI S, IBRAHIM M, RAJENDRAN H, et al. Genome-scale metabolic model led engineering of Nothapodytes nimmoniana plant cells for high camptothecin production[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1207218. |
| [120] | LAKSHMANAN M, LIM S H, MOHANTY B, et al. Unraveling the light-specific metabolic and regulatory signatures of rice through combined in silico modeling and multiomics analysis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(4): 3002-3020. |
| [121] | CHOWDHURY N B, SIMONS-SENFTLE M, DECOUARD B, et al. A multi-organ maize metabolic model connects temperature stress with energy production and reducing power generation[J]. iScience, 2023, 26(12): 108400. |
| [122] | YUAN H L, MAURICE CHEUNG C Y, POOLMAN M G, et al. A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and its application to photorespiratory metabolism[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 85(2): 289-304. |
| [123] | CUNHA E, SILVA M, CHAVES I, et al. The first multi-tissue genome-scale metabolic model of a woody plant highlights suberin biosynthesis pathways in Quercus suber [J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2023, 19(9): e1011499. |
| [124] | ARANO-VARELA H, FERNÁNDEZ F J, ESTRADA-ZÚÑIGA M E, et al. Verbascoside production in long-term Buddleja cordata Kunth cell suspension cultures[J]. 3 Biotech, 2020, 10(6): 245. |
| [125] | TREJO-TAPIA G, BALCAZAR-AGUILAR J B, MARTÍNEZ-BONFIL B, et al. Effect of screening and subculture on the production of betaxanthins in Beta vulgaris L. var. ‘Dark Detroit’ callus culture[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2008, 9(1): 32-36. |
| [126] | COPPEDE J S, PINA E S, PAZ T A, et al. Cell cultures of Maytenus ilicifolia Mart. are richer sources of quinone-methide triterpenoids than plant roots in natura[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2014, 118(1): 33-43. |
| [127] | ZHU X F, MOHSIN A, ZAMAN W Q, et al. Development of a novel noninvasive quantitative method to monitor Siraitia grosvenorii cell growth and browning degree using an integrated computer-aided vision technology and machine learning[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(10): 4092-4104. |
| [1] | SONG Kainan, ZHANG Liwen, WANG Chao, TIAN Pingfang, LI Guangyue, PAN Guohui, XU Yuquan. Advances in small-molecule biopesticides and their biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1203-1223. |
| [2] | YU Wenwen, LV Xueqin, LI Zhaofeng, LIU Long. Plant synthetic biology and bioproduction of human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 992-997. |
| [3] | HE Yangyu, YANG Kai, WANG Weilin, HUANG Qian, QIU Ziying, SONG Tao, HE Liushang, YAO Jinxin, GAN Lu, HE Yuchi. Design and practice of plant synthetic biology theme in the International Genetically Engineered Machine Competition [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1243-1254. |
| [4] | LIU Dan, WANG Jianyu, JIANG Zhengqiang. Research progress and development trends in the biosynthesis of neutral core human milk oligosaccharides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(5): 1126-1144. |
| [5] | WANG Mingpeng, CHEN Lei, ZHAO Yiran, ZHANG Yimin, ZHENG Qifan, LIU Xinyang, WANG Yixue, WANG Qinhong. Halogenases in biocatalysis: advances in mechanism elucidation, directed evolution, and green manufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 728-763. |
| [6] | HU Die, XU Daozhu, LU Zhiyi, TANG Wei, FAN Bo, HE Yucai. Biosynthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat straw xylan through the synergistic hydrolysis by xylanase Xyn11A and arabinofuranosidase Abf62A [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 972-986. |
| [7] | SHENG Zhouhuang, CHEN Zhixian, ZHANG Yan. Research progress of yeast mannoproteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [8] | LU Jinchang, WU Yaokang, LV Xueqin, LIU Long, CHEN Jian, LIU Yanfeng. Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 422-444. |
| [9] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [10] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [11] | TANG Chuan′gen, WANG Jing, ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Haoning, KANG Zhen. Advances in synthesis and mining strategies for functional peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| [12] | LIU Xiaoyue, WANG Pandi, WU Gang, LIU Fang. Efficient biosynthesis of glucoraphanin in Brassicaceae crops by genetic engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 136-156. |
| [13] | ZHONG Quanzhou, SHAN Yiyi, PEI Qingyun, JIN Yanyun, WANG Yihan, MENG Luyuan, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Yuxin, LIU Kunyuan, WANG Huizhong, FENG Shangguo. Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [14] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [15] | ZHU Fanghuan, CEN Xuecong, CHEN Zhen. Research progress of diols production by microbes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||