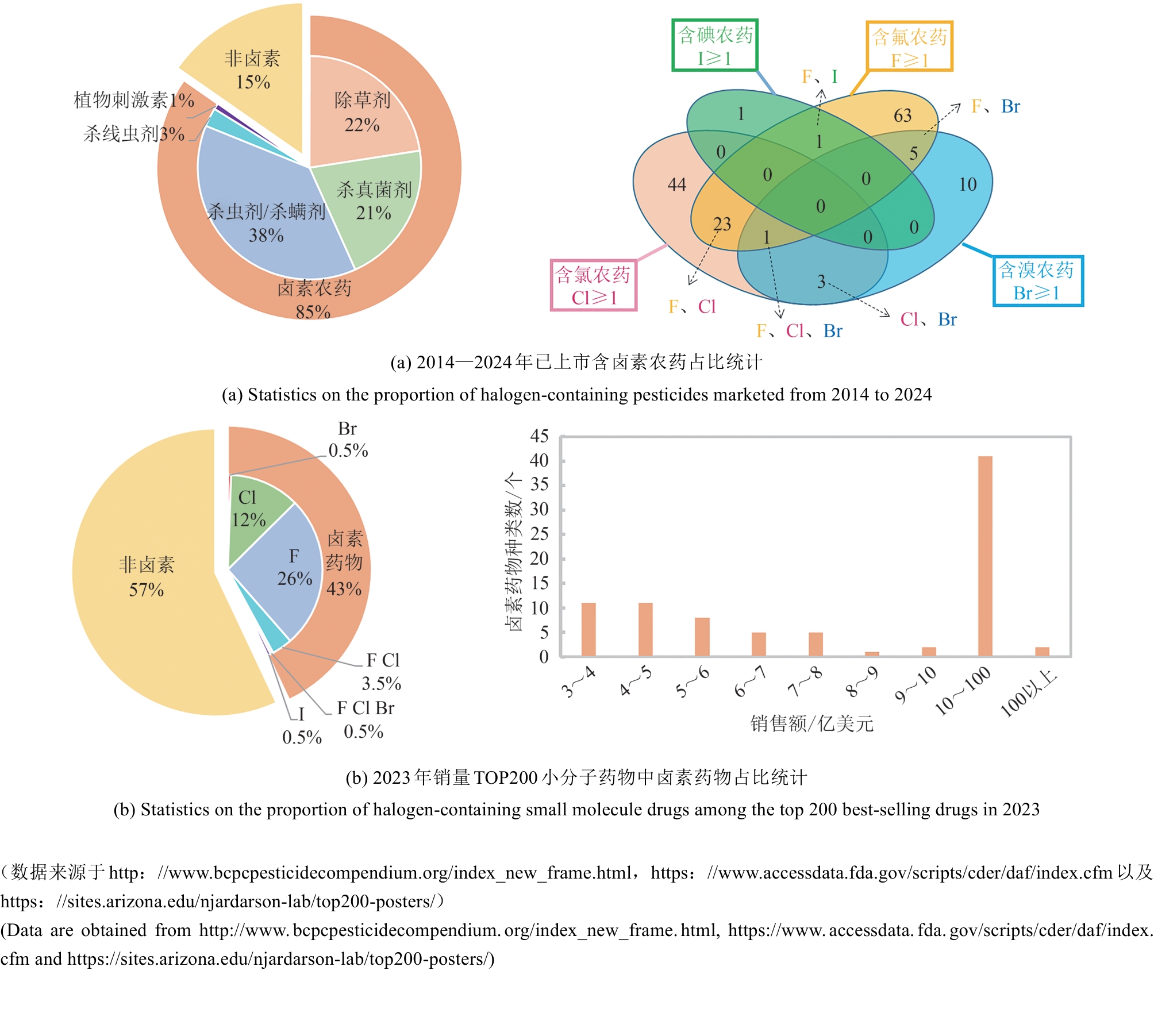
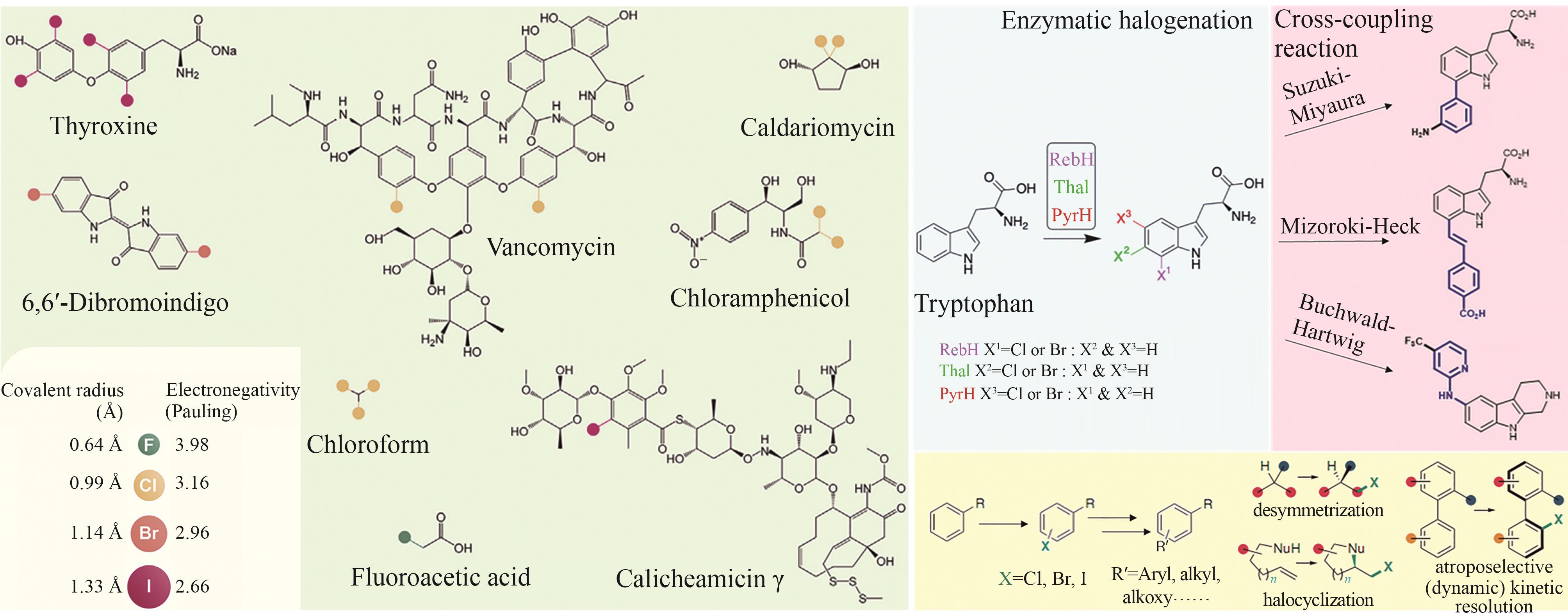
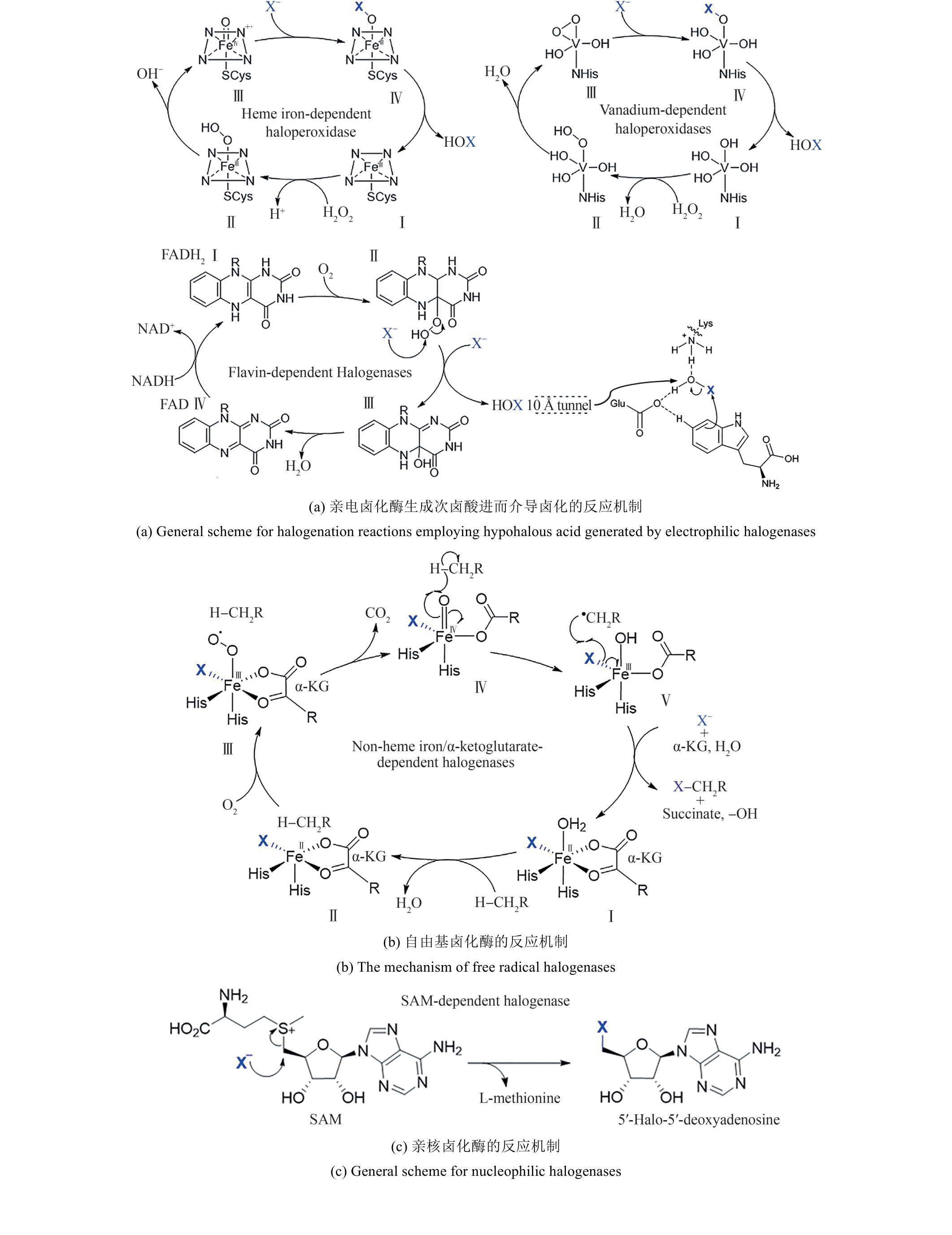
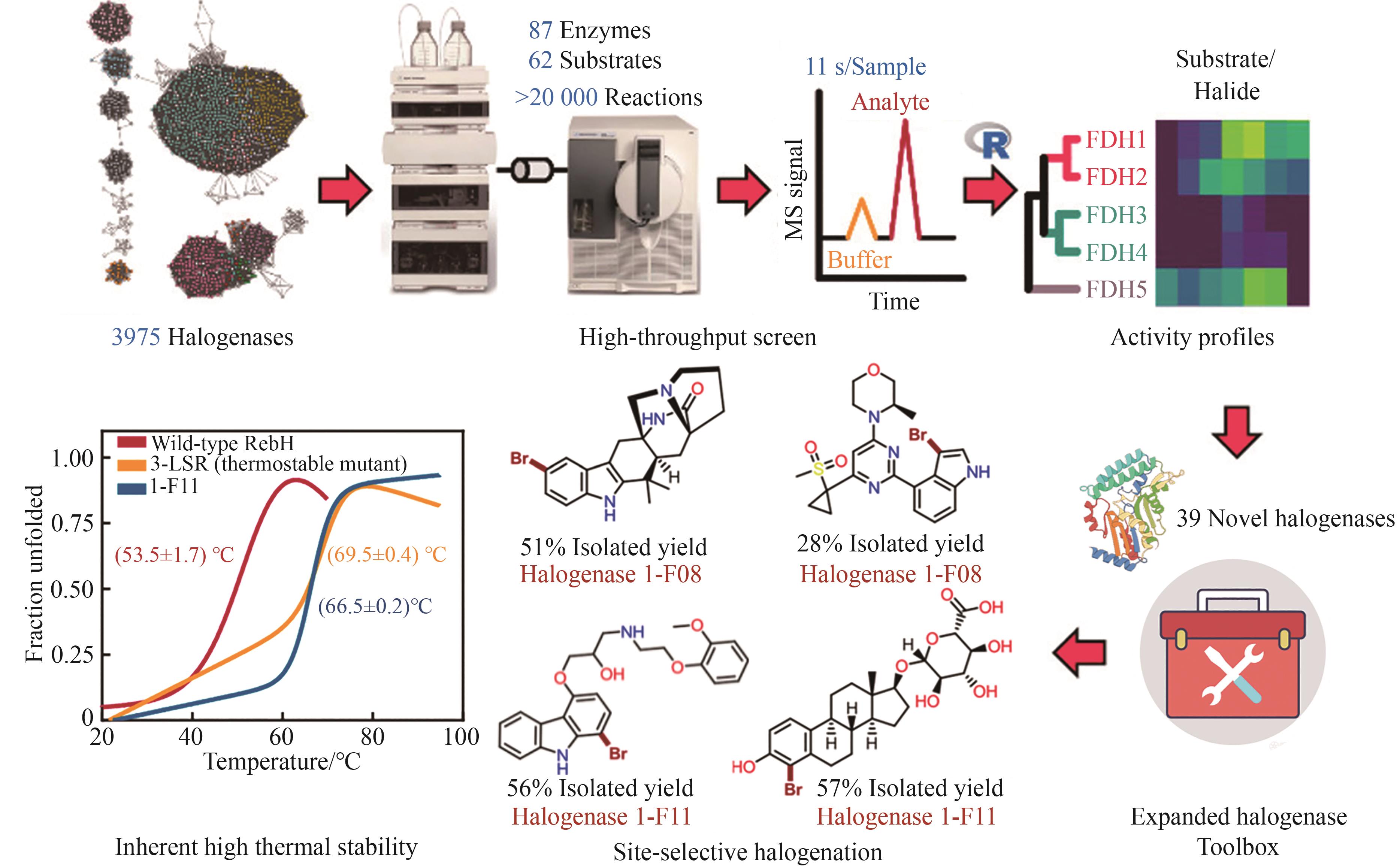
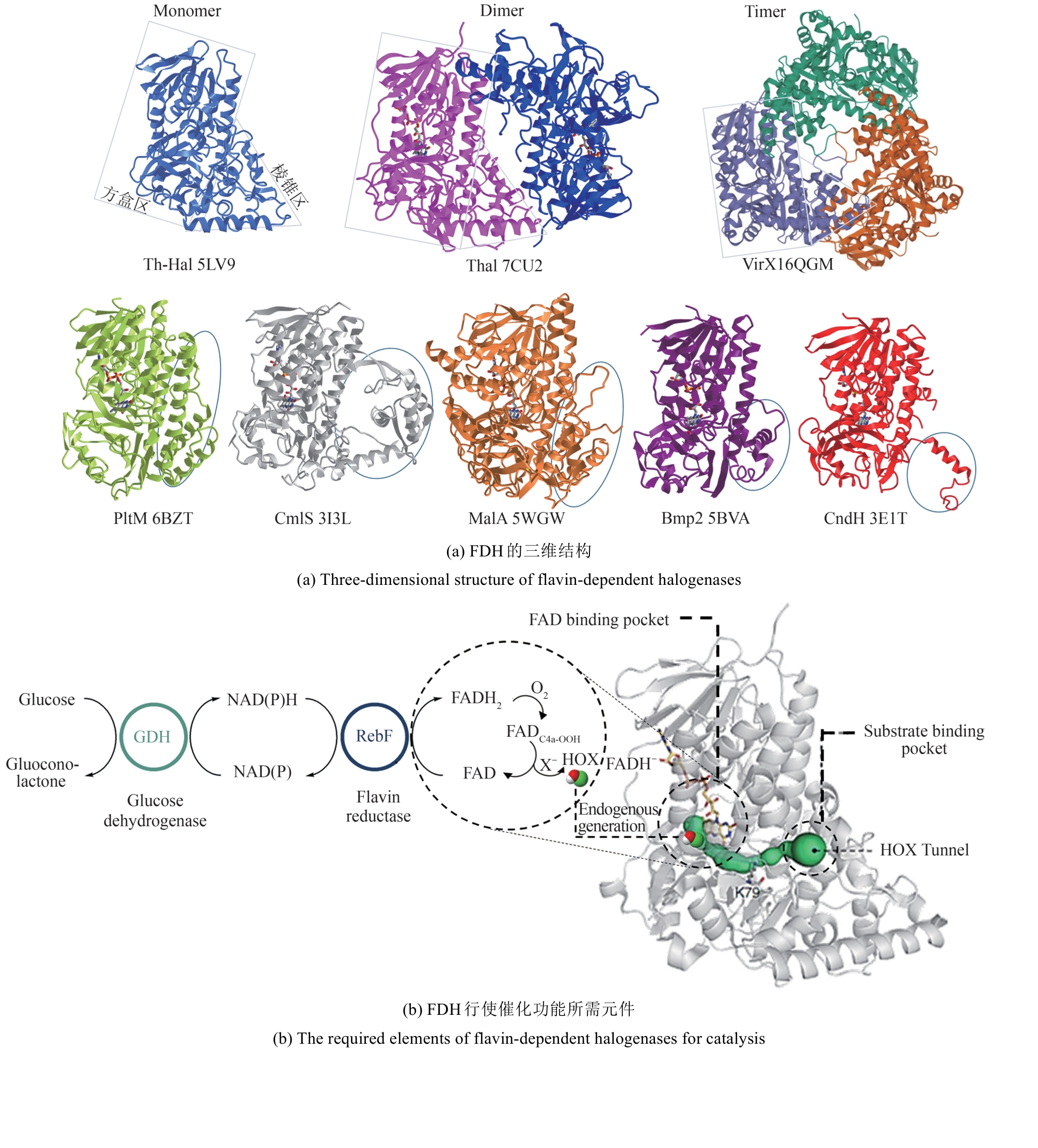
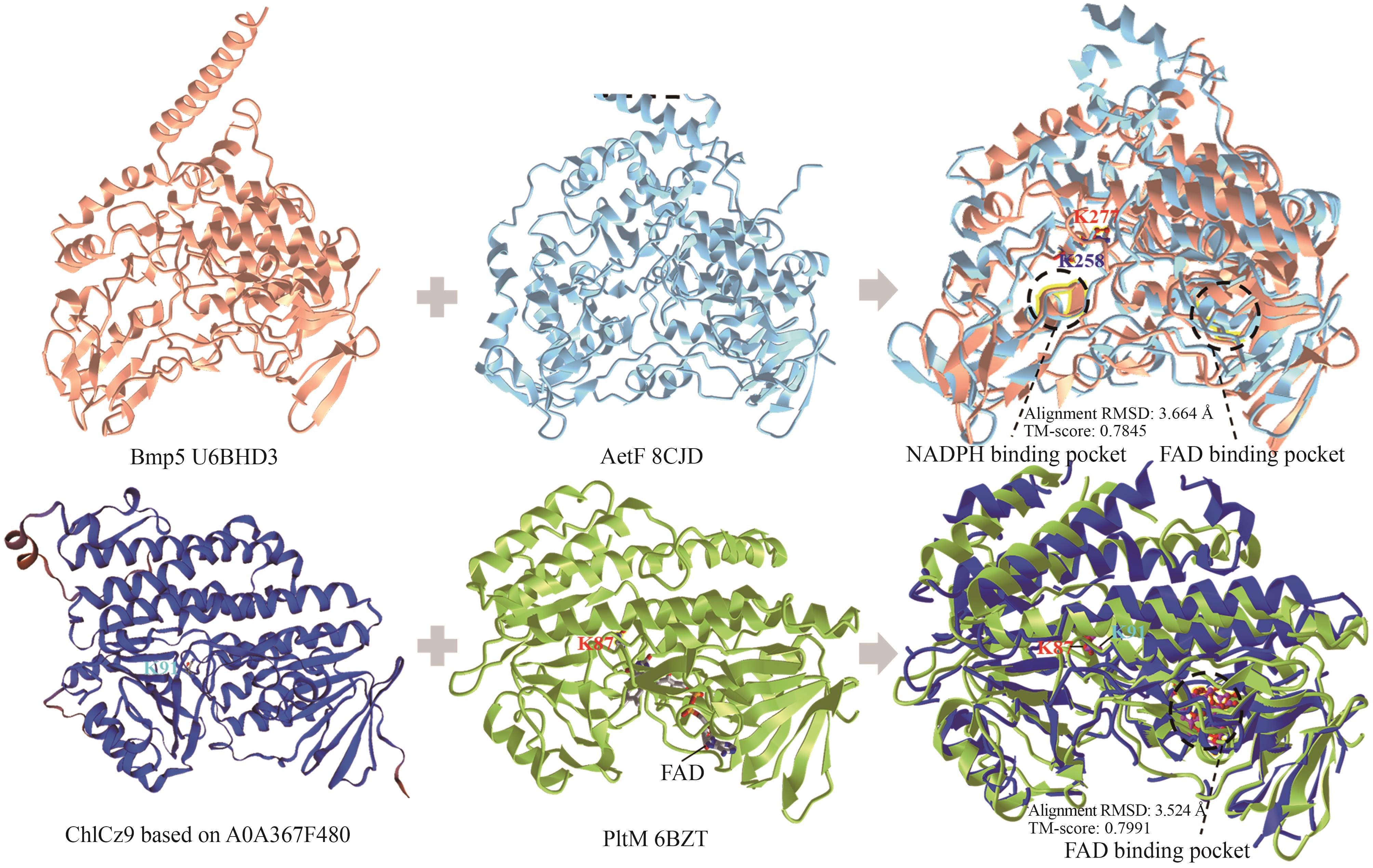
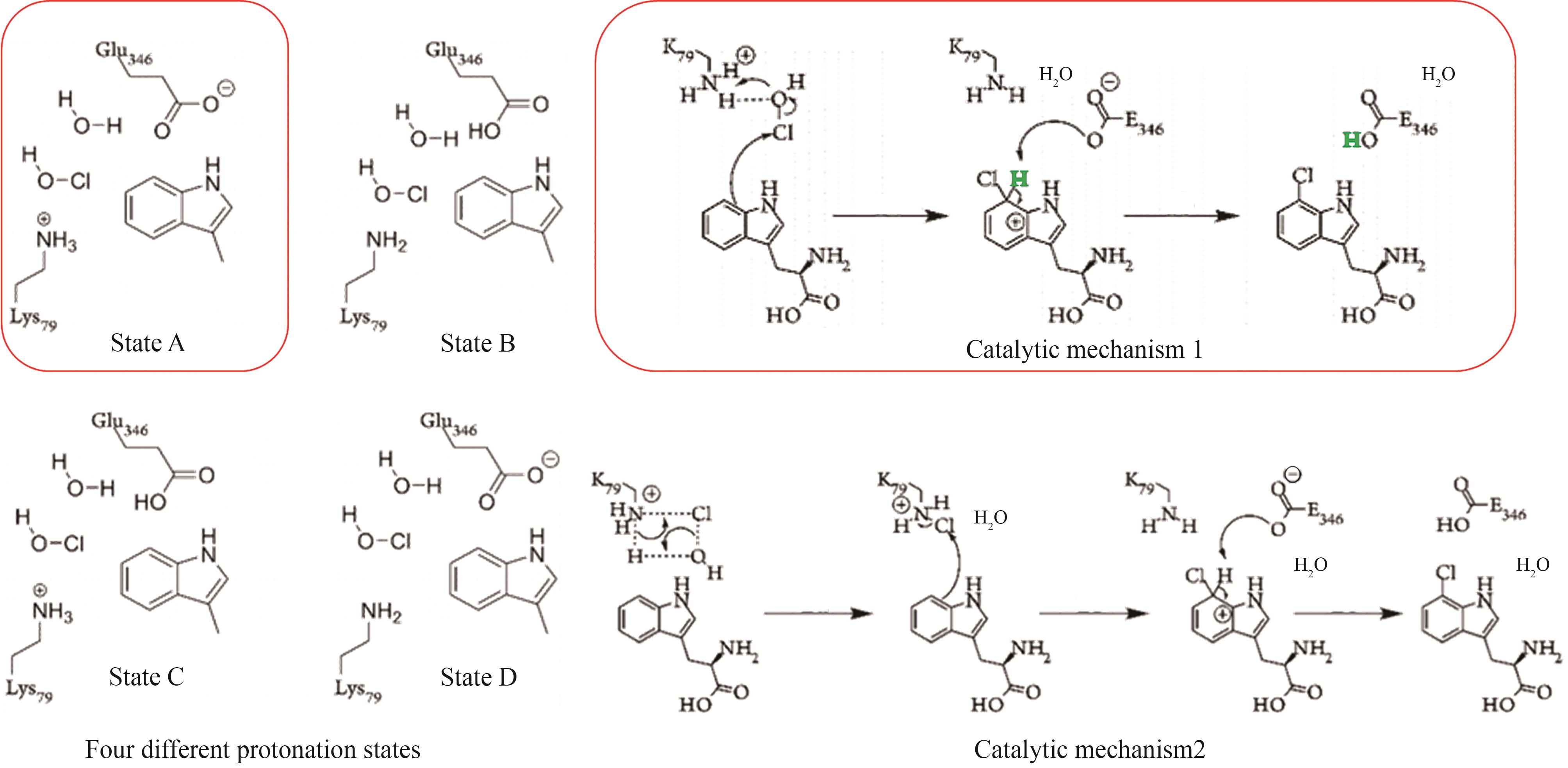
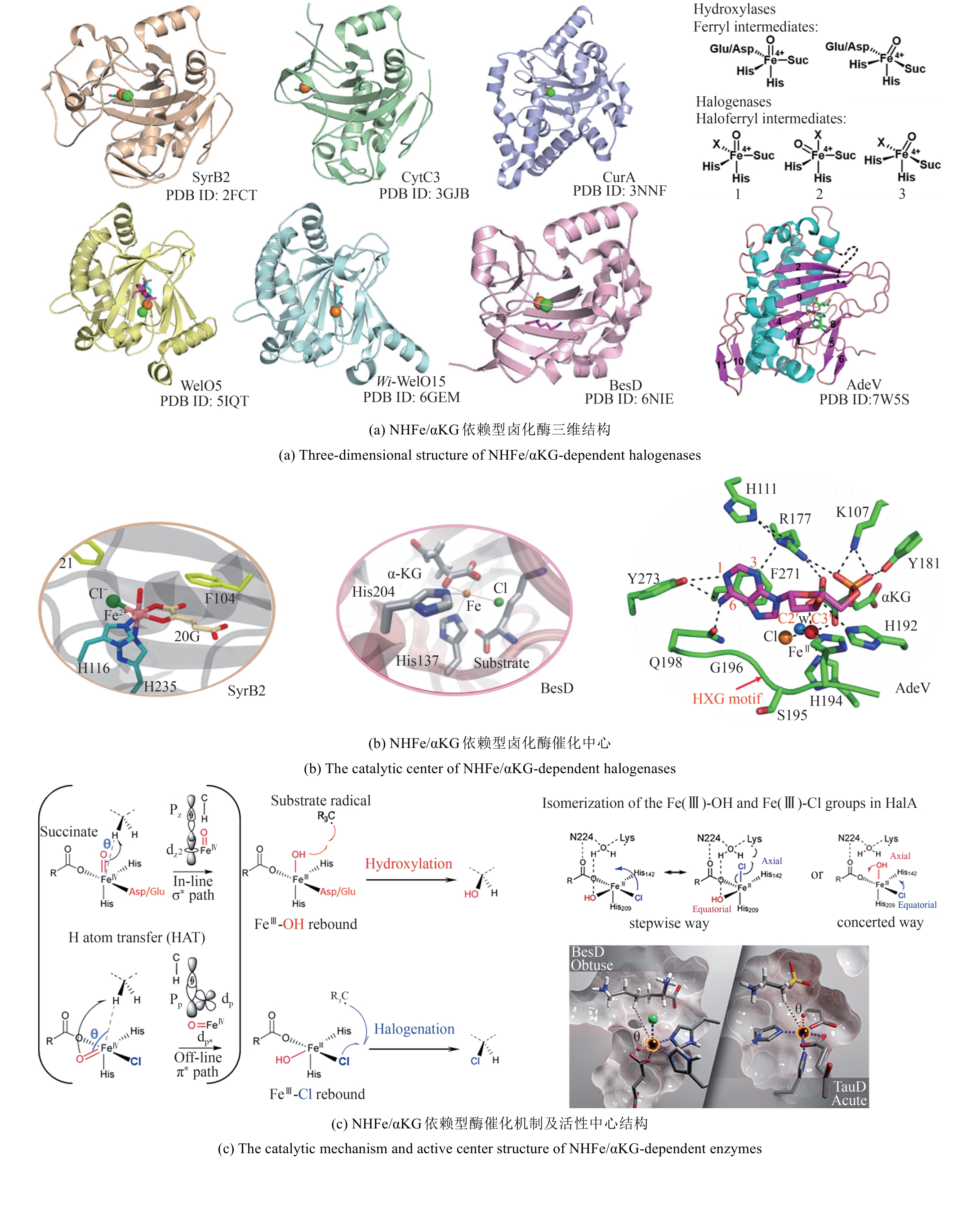
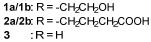Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 728-763.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-091
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Halogenases in biocatalysis: advances in mechanism elucidation, directed evolution, and green manufacturing
WANG Mingpeng1,2,3, CHEN Lei1,2, ZHAO Yiran1, ZHANG Yimin1, ZHENG Qifan1, LIU Xinyang1, WANG Yixue1, WANG Qinhong2,3
- 1.School of Life Sciences,Qufu Normal University,Qufu 273100,Shandong,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
3.National Center of Technology Innovation for Synthetic Biology,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2024-12-03Revised:2025-04-14Online:2025-09-03Published:2025-08-31 -
Contact:WANG Qinhong
卤化酶在生物催化中的应用:机制解析、定向进化和绿色制造的进展
王明鹏1,2,3, 陈蕾1,2, 赵一冉1, 张祎慜1, 郑琪帆1, 刘馨阳1, 王毅学1, 王钦宏2,3
- 1.曲阜师范大学生命科学学院,山东 曲阜 273100
2.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,低碳合成工程生物学全国重点实验室,天津 300308
3.国家合成生物技术创新中心,天津 300308
-
通讯作者:王钦宏 -
作者简介:王明鹏 (1988—),男,博士后。研究方向为酶资源挖掘及定向进化。 E-mail:qsdwmp2018@qfnu.edu.cn;wangmp@tib.cas.cn王钦宏 (1974—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为微生物的进化与代谢工程,高性能微生物细胞工厂构建,芳香族化学品工业化生产等。E-mail:wang_qh@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2103300);国家重点研发计划(2024YFA0918000);山东省自然科学基金青年项目(ZR2023QC030);山东省自然科学基金面上项目(ZR2023MB039)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Mingpeng, CHEN Lei, ZHAO Yiran, ZHANG Yimin, ZHENG Qifan, LIU Xinyang, WANG Yixue, WANG Qinhong. Halogenases in biocatalysis: advances in mechanism elucidation, directed evolution, and green manufacturing[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 728-763.
王明鹏, 陈蕾, 赵一冉, 张祎慜, 郑琪帆, 刘馨阳, 王毅学, 王钦宏. 卤化酶在生物催化中的应用:机制解析、定向进化和绿色制造的进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 728-763.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-091
| 名称 | 来源 | 同源蛋白(相似性百分比) | 产物 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DarH | 藤黄紫假交替单胞菌 Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea | YpdA(<27%) | 溴化达罗巴汀
| 抗生素 | [ |
| AltN | 假交替单胞菌 Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain T1lg65 | Bmp2 | 溴化或双溴变色素
| 抗生素 | [ |
| SclC | 无刺蜜蜂青霉菌 Penicillium meliponae | AclH (63%) | 核丛青霉素中间产物
| 中间代谢物 | [ |
| ChlCz9 | 图巴塔哈链霉菌 Streptomyces tubbatahanensissp. nov. | 来自Streptomyces diacarni的 黄素依赖型氧化还原酶(95.1%) | 氯代咔唑生物碱
| 抗生素 | [ |
| SzoI | 黏细菌 Sandaracinus sp. MSr10575 | 未提及 | 桑达拉唑类Sandarazol
| 防御性化合物, 毒素 | [ |
| LutA | 塔拉霉属 Talaromyces sp. | GedL (56.7%) | 氯化阿扎菲酮类
| [ | |
| OrfA | 溶瘤链霉菌 Streptomyces tumemacerans JCM5050 | XanH (35%) LlpH (34%) | 卤化白真菌素
| 抗生素 | [ |
| PtlK | 杜鹃花拟盘多毛孢菌 Pestalotiopsis rhododendri LF-19-12 | GedL (51%) | 氯化二苯甲酮衍生物
| 抗生素 | [ |
| DnHal | 黑囊基地衣属 Dirinaria sp. | RadH (65%) | 氯化赤星衣酸甲酯
| 中间代谢物, 有机合成骨架 | [ |
| Tal-halo | 嗜松塔拉霉菌 Talaromyces pinophilus LD‑7 | RadH (56%) | 氯化异香豆素
| 中间代谢物, 有机合成骨架 | [ |
Table 1 Examples of halogenase discovered by genome mining
| 名称 | 来源 | 同源蛋白(相似性百分比) | 产物 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DarH | 藤黄紫假交替单胞菌 Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea | YpdA(<27%) | 溴化达罗巴汀
| 抗生素 | [ |
| AltN | 假交替单胞菌 Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain T1lg65 | Bmp2 | 溴化或双溴变色素
| 抗生素 | [ |
| SclC | 无刺蜜蜂青霉菌 Penicillium meliponae | AclH (63%) | 核丛青霉素中间产物
| 中间代谢物 | [ |
| ChlCz9 | 图巴塔哈链霉菌 Streptomyces tubbatahanensissp. nov. | 来自Streptomyces diacarni的 黄素依赖型氧化还原酶(95.1%) | 氯代咔唑生物碱
| 抗生素 | [ |
| SzoI | 黏细菌 Sandaracinus sp. MSr10575 | 未提及 | 桑达拉唑类Sandarazol
| 防御性化合物, 毒素 | [ |
| LutA | 塔拉霉属 Talaromyces sp. | GedL (56.7%) | 氯化阿扎菲酮类
| [ | |
| OrfA | 溶瘤链霉菌 Streptomyces tumemacerans JCM5050 | XanH (35%) LlpH (34%) | 卤化白真菌素
| 抗生素 | [ |
| PtlK | 杜鹃花拟盘多毛孢菌 Pestalotiopsis rhododendri LF-19-12 | GedL (51%) | 氯化二苯甲酮衍生物
| 抗生素 | [ |
| DnHal | 黑囊基地衣属 Dirinaria sp. | RadH (65%) | 氯化赤星衣酸甲酯
| 中间代谢物, 有机合成骨架 | [ |
| Tal-halo | 嗜松塔拉霉菌 Talaromyces pinophilus LD‑7 | RadH (56%) | 氯化异香豆素
| 中间代谢物, 有机合成骨架 | [ |
Table 2 The uniqueness and superiority of the CLEAN algorithm framework
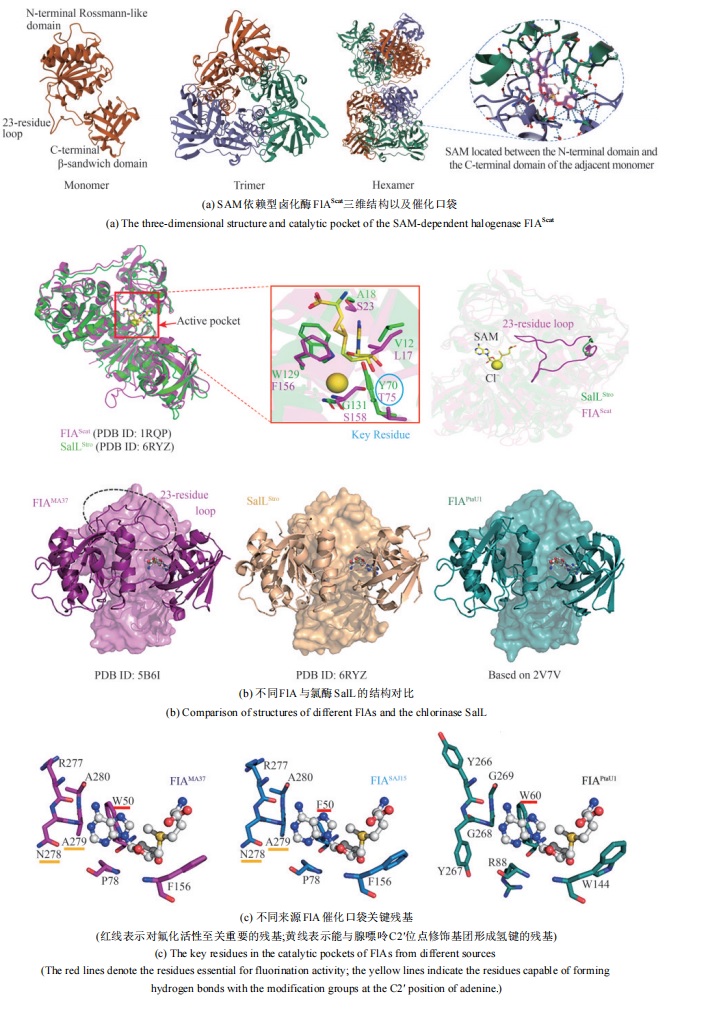
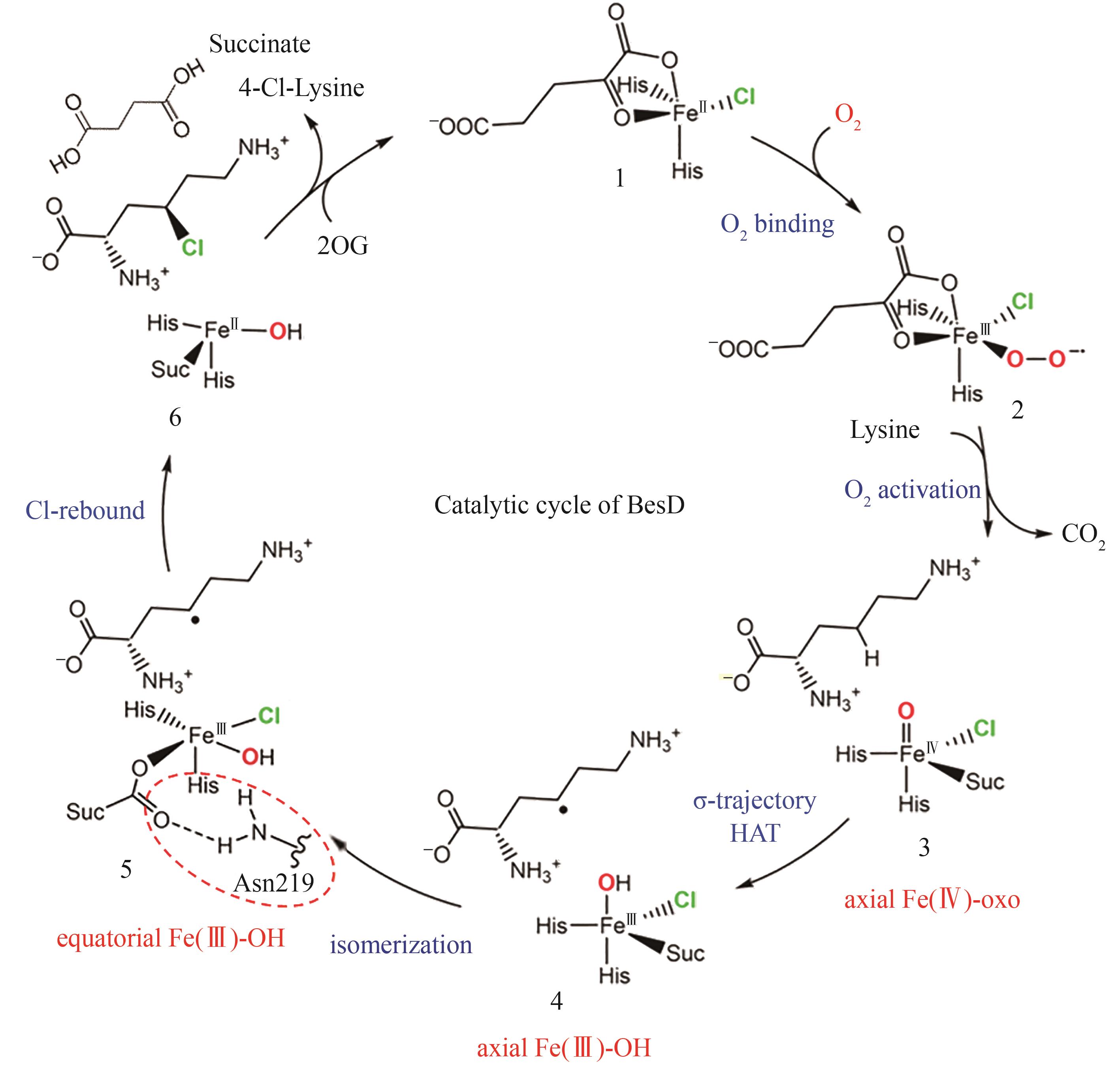
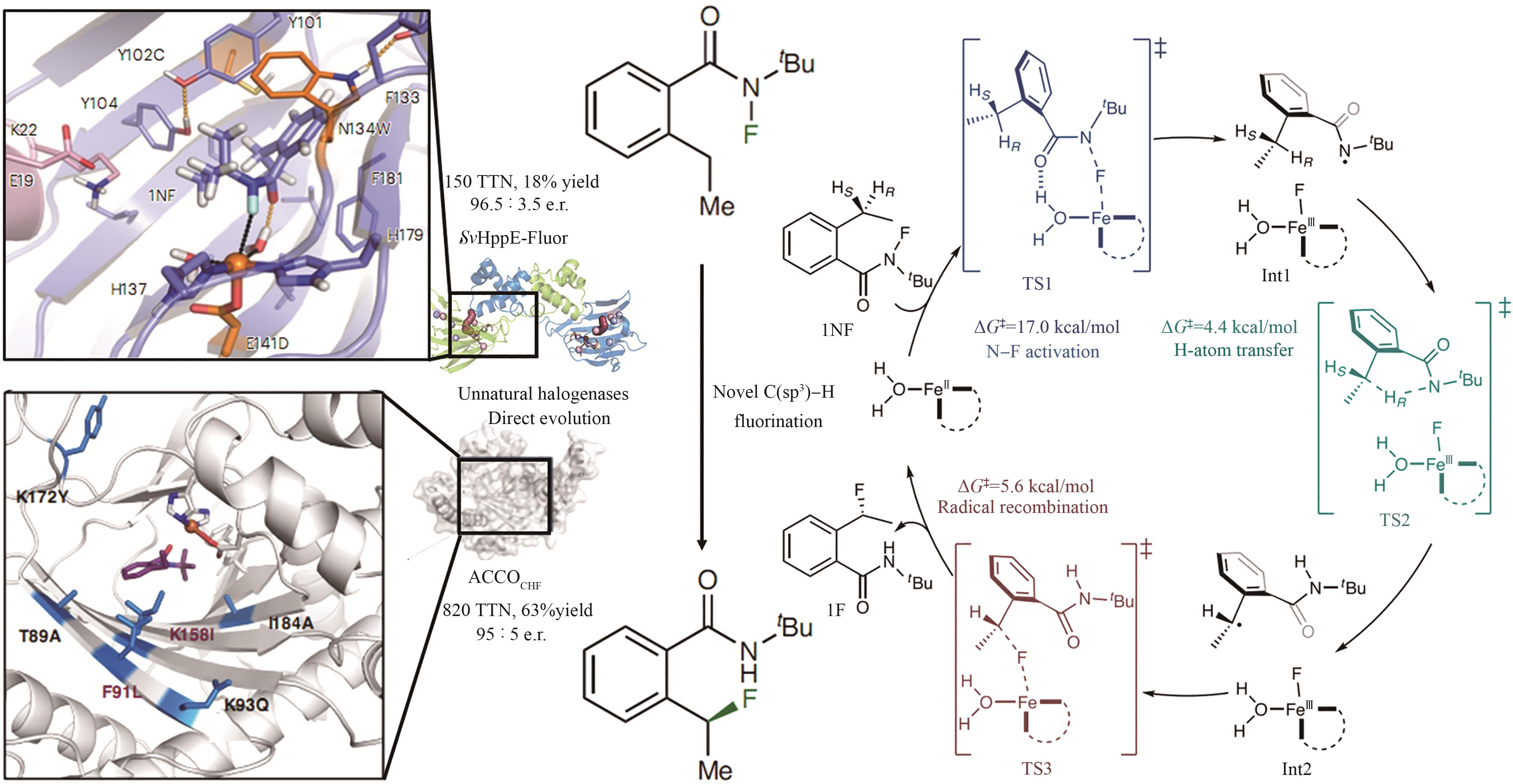
Fig. 13 The typical structure SAM-dependent halogenase [84-91](The red lines denote the residues essential for fluorination activity; the yellow lines indicate the residues capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the modification groups at the C2′ position of adenine.)
| 改造策略 | 技术路线 | 典型研究案例 | 酶活改变 | 动力学参数 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反应条件优化 | 可溶性表达系统; 温度/pH优化 | PrnC在最适条件下实现1 h内对天然底物的100%转化生成氨基吡咯菌素(APRN),显著优于化学合成方法(10%转化率,副产物大量积累) | >600倍 | KM = (14.40 ± 1.20) µmol/L kcat = (1.66 ± 0.02) min-1 | [ |
| 定向进化 | 底物结合口袋及C端帽状区域关键残基定点突变 | 多位点卤化酶FasV通过定点突变实现对底物特异性和区域选择性的可控催化 | 未提及 | KM: (24.1±14.2)~(205.9± 124.5) µmol/L kcat: (11.3±2.4)×10-2~(67.2±25.0)×10-2 min-1 | [ |
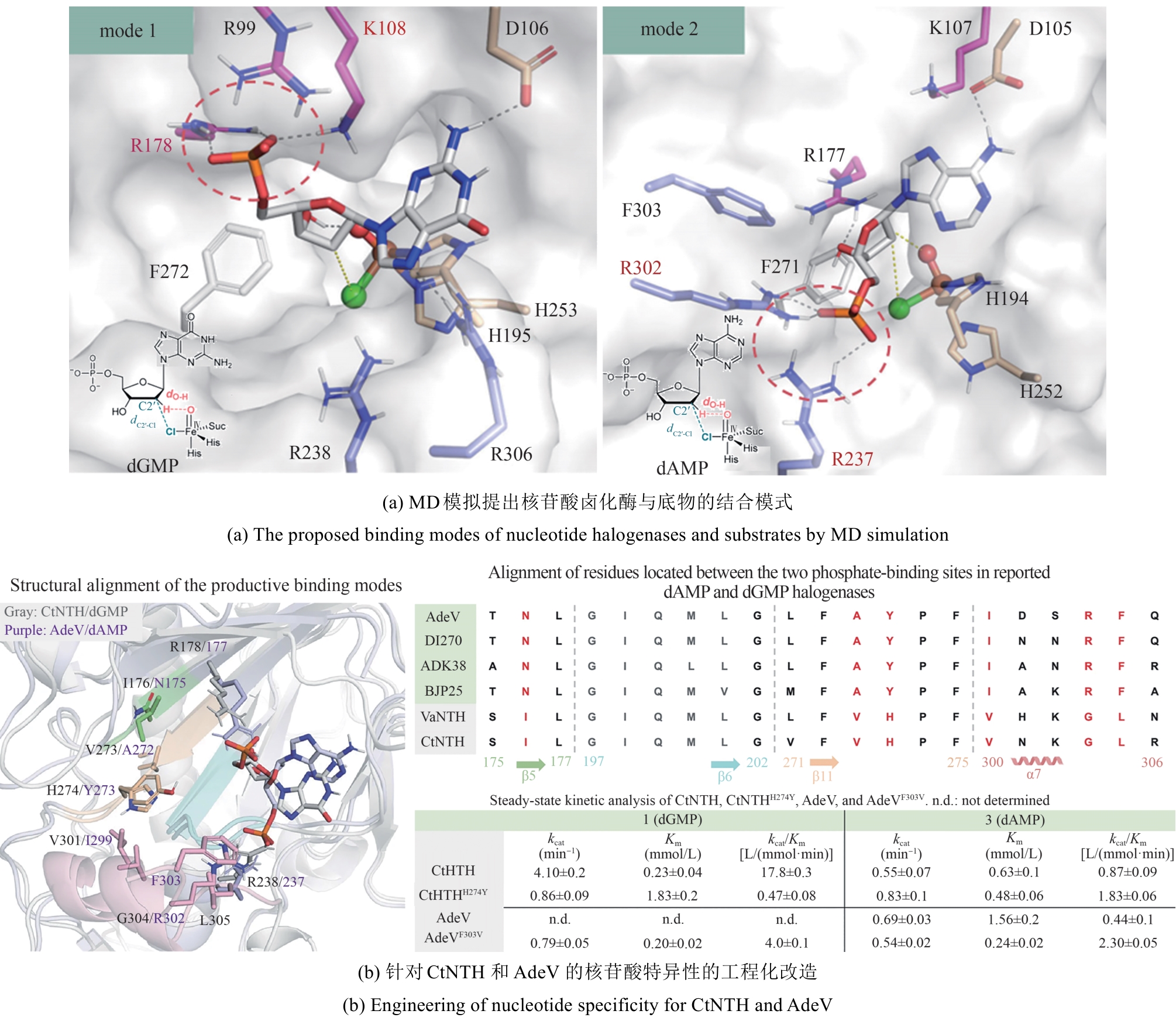
| 计算辅助 | 序列比对;分子对接; MD模拟;定点突变 | 核苷酸卤化酶CtNTH通过工程化磷酸结合位点关键残基簇(H247Y),成功实现底物选择性的定向切换 | 38倍 | KM = (0.23 ± 0.04) mmol/L kcat = (4.1±0.2) min-1 | [ |
| 光催化辅因子再生 | 蓝光照射光催化蛋白质内部氧化型FAD还原再生; 时间分辨紫外-可见光谱 | W281F突变使PrnH的量子转化效率提升41%,光还原速率接近游离FADox的57.5%,为光催化应用提供了优化方向 | 未提及 | 未提及 | [ |
| 机器学习辅助理性设计 | 智能文库设计; ML指导虚拟筛选 | ML指导下筛选的WelO5* VLA突变体催化大环内酯类非天然底物,TTN提高300倍以上, | >62倍 | KM = (0.44±0.03) mmol/L kcat = (1.96 ± 0.51) min-1 | [ |
| 多酶自组装 | 三酶组装元件构建; 自组装纳米簇(TESNC); 固定化 | 与游离酶相比,TESNC表现出更高的热稳定性和转化效率,6-Cl-L-Trp产量增加2.1倍;且固定化TESNC后,6-Cl-L-Trp产量进一步提高4.2倍 | 2倍 | KM = (42.88 ± 12.22) µmol/L kcat = (0.64 ± 0.03) min-1 | [ |
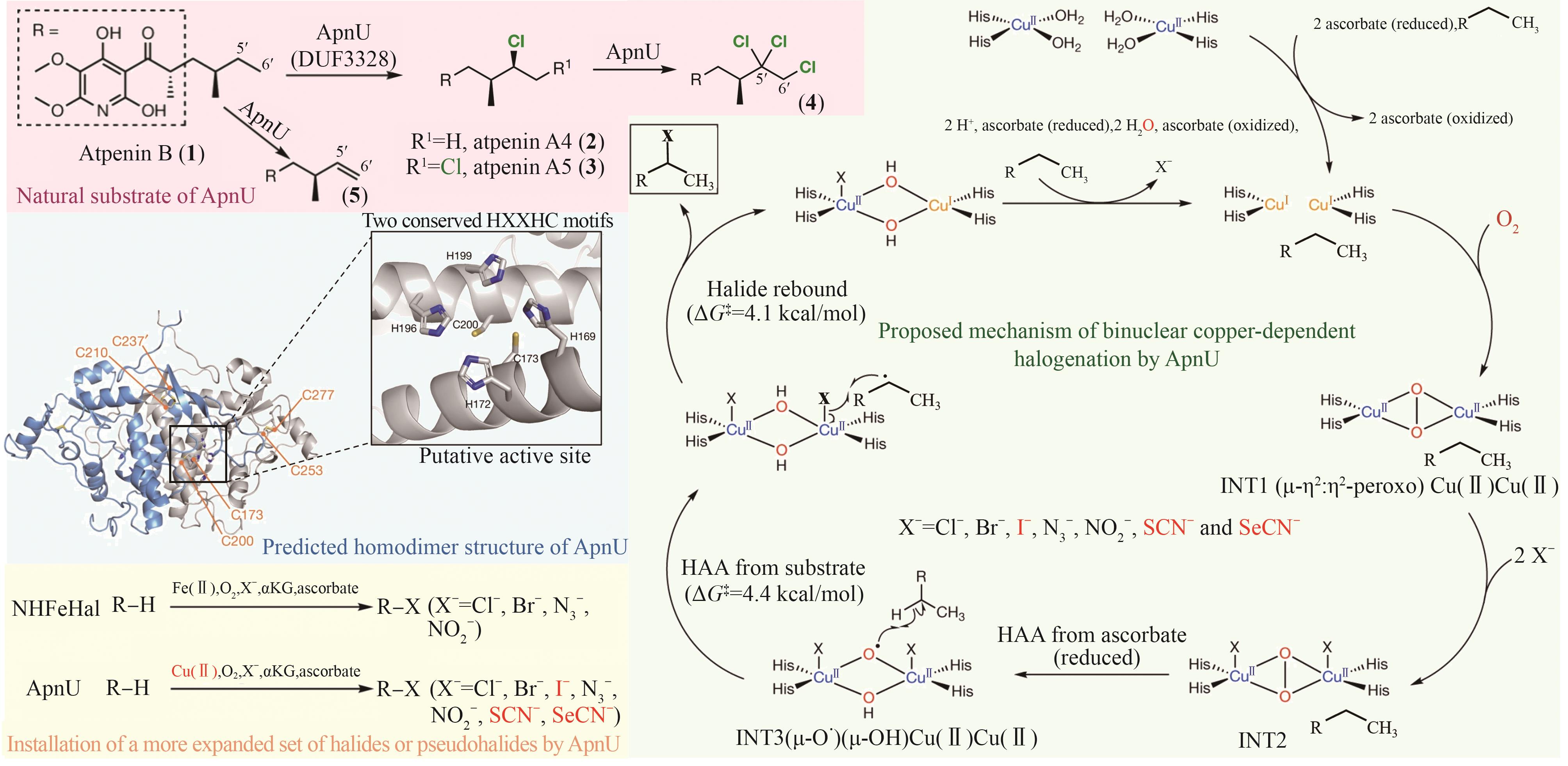
Table 3 Typical engineering cases of natural halogenase in recent years
| 改造策略 | 技术路线 | 典型研究案例 | 酶活改变 | 动力学参数 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反应条件优化 | 可溶性表达系统; 温度/pH优化 | PrnC在最适条件下实现1 h内对天然底物的100%转化生成氨基吡咯菌素(APRN),显著优于化学合成方法(10%转化率,副产物大量积累) | >600倍 | KM = (14.40 ± 1.20) µmol/L kcat = (1.66 ± 0.02) min-1 | [ |
| 定向进化 | 底物结合口袋及C端帽状区域关键残基定点突变 | 多位点卤化酶FasV通过定点突变实现对底物特异性和区域选择性的可控催化 | 未提及 | KM: (24.1±14.2)~(205.9± 124.5) µmol/L kcat: (11.3±2.4)×10-2~(67.2±25.0)×10-2 min-1 | [ |
| 计算辅助 | 序列比对;分子对接; MD模拟;定点突变 | 核苷酸卤化酶CtNTH通过工程化磷酸结合位点关键残基簇(H247Y),成功实现底物选择性的定向切换 | 38倍 | KM = (0.23 ± 0.04) mmol/L kcat = (4.1±0.2) min-1 | [ |
| 光催化辅因子再生 | 蓝光照射光催化蛋白质内部氧化型FAD还原再生; 时间分辨紫外-可见光谱 | W281F突变使PrnH的量子转化效率提升41%,光还原速率接近游离FADox的57.5%,为光催化应用提供了优化方向 | 未提及 | 未提及 | [ |
| 机器学习辅助理性设计 | 智能文库设计; ML指导虚拟筛选 | ML指导下筛选的WelO5* VLA突变体催化大环内酯类非天然底物,TTN提高300倍以上, | >62倍 | KM = (0.44±0.03) mmol/L kcat = (1.96 ± 0.51) min-1 | [ |
| 多酶自组装 | 三酶组装元件构建; 自组装纳米簇(TESNC); 固定化 | 与游离酶相比,TESNC表现出更高的热稳定性和转化效率,6-Cl-L-Trp产量增加2.1倍;且固定化TESNC后,6-Cl-L-Trp产量进一步提高4.2倍 | 2倍 | KM = (42.88 ± 12.22) µmol/L kcat = (0.64 ± 0.03) min-1 | [ |
| 卤化酶 | 动力学参数 | 产物 | 对映体催化类型 | 对映体比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RebH 4V | 未提及 | 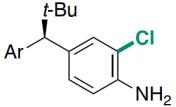 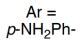 | 去对称化反应 | 99∶1 |
| RebH 3-T | KM: 0.002 mmol/L kcat: 0.03 min-1 | 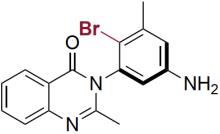 | 阻转选择性卤化 | >99.5∶0.5 |
| RebH 4V+S | KM: 0.47 mmol/L kcat: 0.36 min-1 | 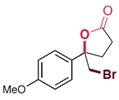 | 卤代环化反应 | 96∶4 |
| RebH 4PL | 未提及 | 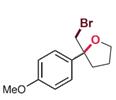 | 卤代环化反应 | 91∶9 |
| AetF | 未提及 | 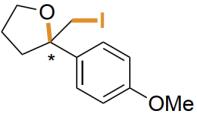 | 卤代环化反应 | 99∶1 |
Table 4 Examples of FDHs catalyzing enantioselective reactions[125-127]
| 卤化酶 | 动力学参数 | 产物 | 对映体催化类型 | 对映体比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
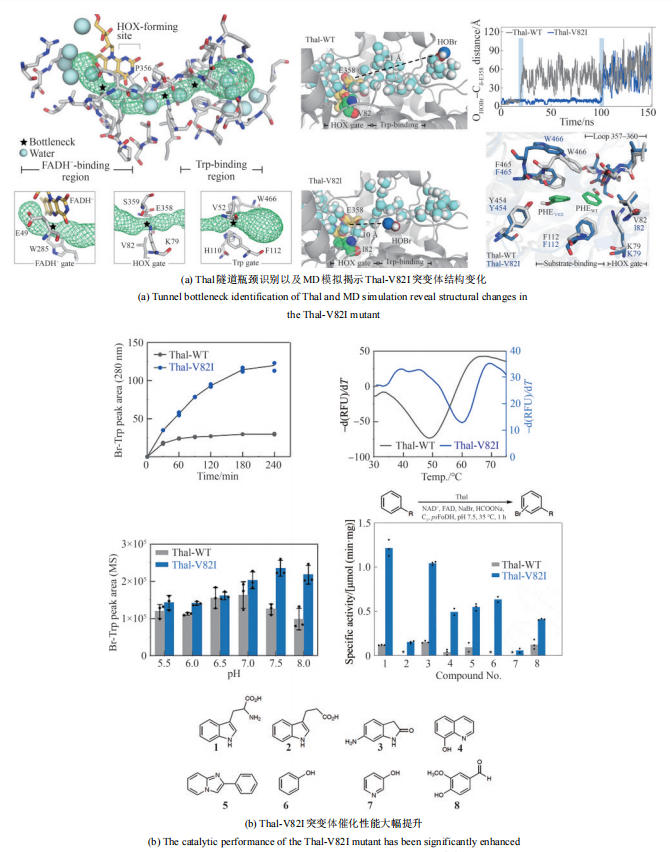
| RebH 4V | 未提及 |  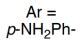 | 去对称化反应 | 99∶1 |
| RebH 3-T | KM: 0.002 mmol/L kcat: 0.03 min-1 |  | 阻转选择性卤化 | >99.5∶0.5 |
| RebH 4V+S | KM: 0.47 mmol/L kcat: 0.36 min-1 |  | 卤代环化反应 | 96∶4 |
| RebH 4PL | 未提及 |  | 卤代环化反应 | 91∶9 |
| AetF | 未提及 |  | 卤代环化反应 | 99∶1 |
| 卤化酶 | 技术路线 | 生产工艺或优化策略 | 生产规模 | 产品种类及产量 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RebH | 异源共表达色氨酸酶/卤化酶/脱羧酶;谷氨酸棒状杆菌底盘 | 补料分批发酵 | 2 L | 7-溴色胺: 0.36 g/L | [ |
| RebH 3-LSR | 偶联L-氨基酸脱氨酶(L-AAD) 构建FAD/FADH2再生系统 | 纯酶或全细胞催化的7 -氯色氨酸和吲哚丙酮酸(IPA)的联合生产 | 5L | 7-Cl-Trp: 170 mg/L IPA: 193 mg/L | [ |
Thal RebH PyrH | 构建具有磷酸基脱氢酶和黄素还原酶活性的双功能融合酶用于FAD辅酶再生;共表达融合酶、卤化酶及双加氧酶;多酶固定化 | 在单次培养条件下,高效实现一锅式固定化酶级联反应,用于大规模连续生产神经药物前药 L-4-氯犬尿氨酸(L-4-Cl-Kyn)及其非天然类似物 L-4-溴犬尿氨酸(L-4-Br-Kyn) | 2.5 L | L-4-Cl-Kyn: 701 mg L-4-Br-Kyn: 805 mg | [ |
RebH PrnA SttH PyrH | 卤化酶催化的卤代反应与钯催化的氰化反应相结合以及随后与腈水合酶或腈水解酶进行级联反应 | 生物-化学交叉偶联催化用于区域选择性碳氢键官能化以合成腈、酰胺和羧酸等基团,实现药物分子的克级制备 | 30 mL~1 L | 芳酰胺类化合物8a: 1.98g | [ |
| WelO5*及其突变体 | 算法辅助的理性设计与改造 | 异源表达卤化酶;细胞裂解液催化广谱抗真菌剂索拉芬A(soraphen A)等大环内酯类化合物的卤化 | 2 L | 氯化索拉芬2a(总转化数): 91.8±22.0 | [ |
Table 5 Recent cases and key data pertaining to the potential industrial application of halogenases
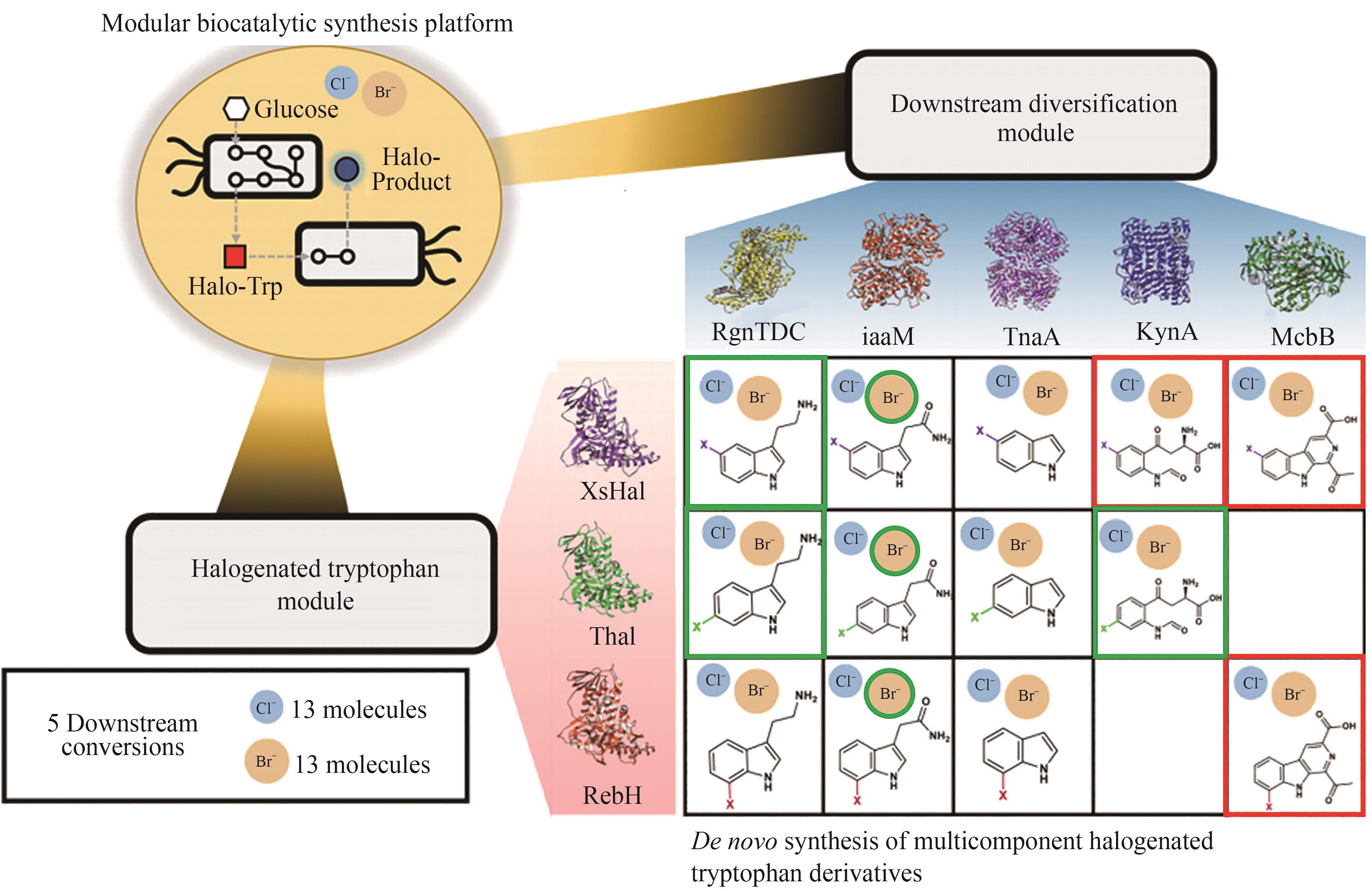
| 卤化酶 | 技术路线 | 生产工艺或优化策略 | 生产规模 | 产品种类及产量 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RebH | 异源共表达色氨酸酶/卤化酶/脱羧酶;谷氨酸棒状杆菌底盘 | 补料分批发酵 | 2 L | 7-溴色胺: 0.36 g/L | [ |
| RebH 3-LSR | 偶联L-氨基酸脱氨酶(L-AAD) 构建FAD/FADH2再生系统 | 纯酶或全细胞催化的7 -氯色氨酸和吲哚丙酮酸(IPA)的联合生产 | 5L | 7-Cl-Trp: 170 mg/L IPA: 193 mg/L | [ |
Thal RebH PyrH | 构建具有磷酸基脱氢酶和黄素还原酶活性的双功能融合酶用于FAD辅酶再生;共表达融合酶、卤化酶及双加氧酶;多酶固定化 | 在单次培养条件下,高效实现一锅式固定化酶级联反应,用于大规模连续生产神经药物前药 L-4-氯犬尿氨酸(L-4-Cl-Kyn)及其非天然类似物 L-4-溴犬尿氨酸(L-4-Br-Kyn) | 2.5 L | L-4-Cl-Kyn: 701 mg L-4-Br-Kyn: 805 mg | [ |
RebH PrnA SttH PyrH | 卤化酶催化的卤代反应与钯催化的氰化反应相结合以及随后与腈水合酶或腈水解酶进行级联反应 | 生物-化学交叉偶联催化用于区域选择性碳氢键官能化以合成腈、酰胺和羧酸等基团,实现药物分子的克级制备 | 30 mL~1 L | 芳酰胺类化合物8a: 1.98g | [ |
| WelO5*及其突变体 | 算法辅助的理性设计与改造 | 异源表达卤化酶;细胞裂解液催化广谱抗真菌剂索拉芬A(soraphen A)等大环内酯类化合物的卤化 | 2 L | 氯化索拉芬2a(总转化数): 91.8±22.0 | [ |
| [1] | LATHAM J, BRANDENBURGER E, SHEPHERD S A, et al. Development of halogenase enzymes for use in synthesis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(1): 232-269. |
| [2] | NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(3): 770-803. |
| [3] | XU Z J, YANG Z, LIU Y T, et al. Halogen bond: its role beyond drug-target binding affinity for drug discovery and development[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2014, 54(1): 69-78. |
| [4] | CROWE C, MOLYNEUX S, SHARMA S V, et al. Halogenases: a palette of emerging opportunities for synthetic biology-synthetic chemistry and C—H functionalisation[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(17): 9443-9481. |
| [5] | SUN C H, MA B D, LI G J, et al. Engineering the substrate specificity of a P450 dimerase enables the collective biosynthesis of heterodimeric tryptophan-containing diketopiperazines[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(25): e202304994. |
| [6] | YAN X L, ZHANG J, TAN H Q, et al. A pair of atypical KAS Ⅲ homologues with initiation and elongation functions program the polyketide biosynthesis in asukamycin[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(19): e202200879. |
| [7] | CHRÉTIEN J M, ZAMMATTIO F, LE GROGNEC E, et al. Polymer-supported organotin reagents for regioselective halogenation of aromatic amines[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2005, 70(7): 2870-2873. |
| [8] | INKPEN M S, DU S R, DRIVER M, et al. Oxidative purification of halogenated ferrocenes[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2013, 42(8): 2813-2816. |
| [9] | CANTILLO D, KAPPE C O. Halogenation of organic compounds using continuous flow and microreactor technology[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 2(1): 7-19. |
| [10] | HENDERSON S H, WEST R A, WARD S E, et al. Metal-free selective mono-halodecarboxylation of heteroarenes under mild conditions[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2018, 5(6): 180333. |
| [11] | PAUNOVIĆ V, PÉREZ-RAMÍREZ J. Catalytic halogenation of methane: a dream reaction with practical scope?[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(17): 4515-4530. |
| [12] | BERGER G, FRANGVILLE P, MEYER F. Halogen bonding for molecular recognition: new developments in materials and biological sciences[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(37): 4970-4981. |
| [13] | MINGES H, SEWALD N. Recent advances in synthetic application and engineering of halogenases[J]. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(18): 4450-4470. |
| [14] | CROS A, ALFARO-ESPINOZA G, DE MARIA A, et al. Synthetic metabolism for biohalogenation[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 74: 180-193. |
| [15] | SENN H M. Insights into enzymatic halogenation from computational studies[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2014, 2: 98. |
| [16] | RUIZ-CASTILLO P, BUCHWALD S L. Applications of palladium-catalyzed C—N cross-coupling reactions[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(19): 12564-12649. |
| [17] | MENON B R K, RICHMOND D, MENON N. Halogenases for biosynthetic pathway engineering: toward new routes to naturals and non-naturals[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2022, 64(3): 533-591. |
| [18] | JIANG Y H, LEWIS J C. Asymmetric catalysis by flavin-dependent halogenases[J]. Chirality, 2023, 35(8): 452-460. |
| [19] | ANDORFER M C, LEWIS J C. Understanding and improving the activity of flavin-dependent halogenases via random and targeted mutagenesis[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2018, 87: 159-185. |
| [20] | BÜCHLER J, PAPADOPOULOU A, BULLER R. Recent advances in flavin-dependent halogenase biocatalysis: sourcing, engineering, and application[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(12): 1030. |
| [21] | ZENG J, ZHAN J X. Chlorinated natural products and related halogenases[J]. Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 59(5): 387-402. |
| [22] | COCHEREAU B, MESLET-CLADIÈRE L, POUCHUS Y F, et al. Halogenation in fungi: what do we know and what remains to be discovered?[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(10): 3157. |
| [23] | LUDEWIG H, MOLYNEUX S, FERRINHO S, et al. Halogenases: structures and functions[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2020, 65: 51-60. |
| [24] | 郑哲麟, 胡文达, 何亚文. 微生物卤化酶及其应用研究进展[J]. 微生物前沿, 2020, 9(4): 141-155. |
| ZHENG Z L, HU W D, HE Y W. Research progress in microbial halogenases and their industrial applications[J]. Advances in Microbiology, 2020, 9(4): 141-155. | |
| [25] | 王汇滨, 车昌丽, 游松. Fe/α-酮戊二酸依赖型卤化酶在绿色卤化反应中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 545-566. |
| WANG H B, CHE C L, YOU S. Recent advances of enzymatic synthesis of organohalogens catalyzed by Fe/αKG-dependent halogenases[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 545-566. | |
| [26] | YEH E, BLASIAK L C, KOGLIN A, et al. Chlorination by a long-lived intermediate in the mechanism of flavin-dependent halogenases[J]. Biochemistry, 2007, 46(5): 1284-1292. |
| [27] | FLECKS S, PATALLO E, ZHU X F, et al. New insights into the mechanism of enzymatic chlorination of tryptophan[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(49): 9533-9536. |
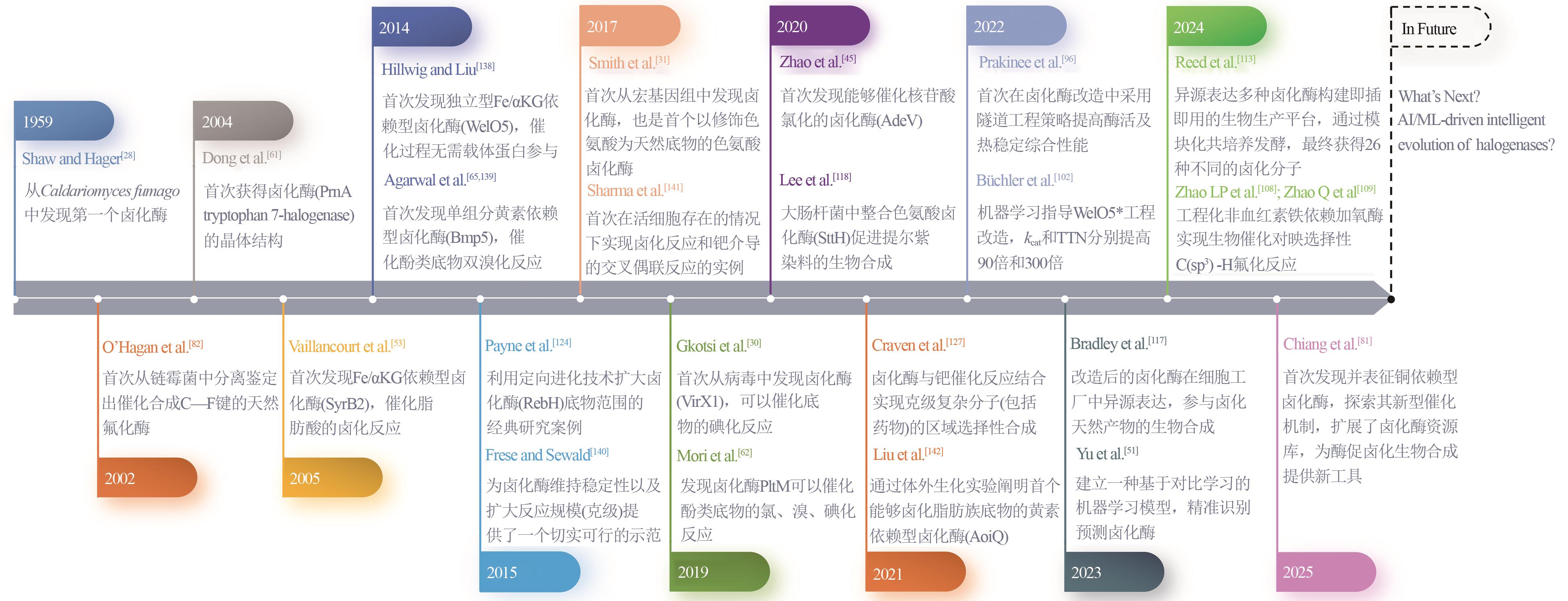
| [28] | SHAW P D, HAGER L P. Biological chlorination. Ⅳ. peroxidative nature of enzymatic chlorination1 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1959, 81(24): 6527-6528. |
| [29] | JEON J, LEE J, JUNG S M, et al. Genomic determinants encode the reactivity and regioselectivity of flavin-dependent halogenases in bacterial genomes and metagenomes[J]. mSystems, 2021, 6(3): e00053-21. |
| [30] | GKOTSI D S, LUDEWIG H, SHARMA S V, et al. A marine viral halogenase that iodinates diverse substrates[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(12): 1091-1097. |
| [31] | SMITH D R M, URIA A R, HELFRICH E J N, et al. An unusual flavin-dependent halogenase from the metagenome of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei WA[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12(5): 1281-1287. |
| [32] | NEUBAUER P R, PIENKNY S, WESSJOHANN L, et al. Predicting the substrate scope of the flavin-dependent halogenase BrvH[J]. ChemBioChem, 2020, 21(22): 3282-3288. |
| [33] | LAVECCHIA A, FOSSO B, ENGELEN A H, et al. Macroalgal microbiomes unveil a valuable genetic resource for halogen metabolism[J]. Microbiome, 2024, 12(1): 47. |
| [34] | FISHER B F, SNODGRASS H M, JONES K A, et al. Site-selective C—H halogenation using flavin-dependent halogenases identified via family-wide activity profiling[J]. ACS Central Science, 2019, 5(11): 1844-1856. |
| [35] | BÖHRINGER N, KRAMER J C, DE LA MORA E, et al. Genome- and metabolome-guided discovery of marine BamA inhibitors revealed a dedicated darobactin halogenase[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2023, 30(8): 943-952.e7. |
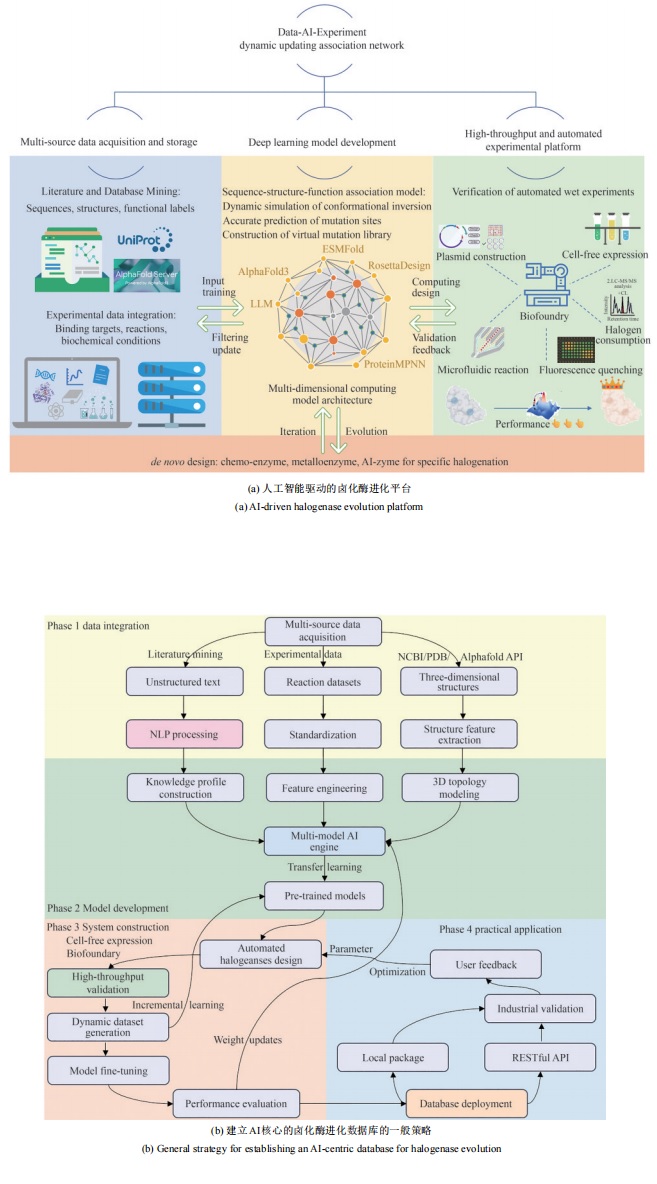
| [36] | REN Y X, LIU R Y, ZHENG Y F, et al. Biosynthetic mechanism of the yellow pigments in the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain T1lg65[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2024, 90(2): e01779-23. |
| [37] | SOUSA T F, DE ARAÚJO JÚNIOR M B, PERES E G, et al. Discovery of dual PKS involved in sclerotiorin biosynthesis in Penicillium meliponae using genome mining and gene knockout[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2023, 205(2): 75. |
| [38] | TENEBRO C P, TRONO D J V L, BALIDA L A P, et al. Synergy between genome mining, metabolomics, and bioinformatics uncovers antibacterial chlorinated carbazole alkaloids and their biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces tubbatahanensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from Sulu Sea, Philippines[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2023, 11(2): e03661-22. |
| [39] | PANTER F, BADER C D, MÜLLER R. The sandarazols are cryptic and structurally unique plasmid-encoded toxins from a rare myxobacterium[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(15): 8081-8088. |
| [40] | HUANG X L, LI D, LONG B, et al. Activation of a silent gene cluster from the endophytic fungus Talaromyces sp. unearths cryptic azaphilone metabolites[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(28): 15801-15810. |
| [41] | WANG Z C, LO I W, LIN K H, et al. Genetic and biochemical characterization of halogenation and drug transportation genes encoded in the albofungin biosynthetic gene cluster[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2022, 88(17): e00806-22. |
| [42] | LUO M N, WANG M Y, CHANG S S, et al. Halogenase-targeted genome mining leads to the discovery of (±) pestalachlorides A1a, A2a, and their atropisomers[J]. Antibiotics, 2022, 11(10): 1304. |
| [43] | HASAN N S, LING J G, BAKAR M F ABU, et al. The lichen flavin-dependent halogenase, DnHal: identification, heterologous expression and functional characterization[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2023, 195(11): 6708-6736. |
| [44] | REN M, LI Z, WANG Z X, et al. Antiviral chlorinated drimane meroterpenoids from the fungus Talaromyces pinophilus LD-7 and their biosynthetic pathway[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2024, 87(8): 2034-2044. |
| [45] | ZHAO C H, YAN S, LI Q, et al. An Fe2+- and α-ketoglutarate-dependent halogenase acts on nucleotide substrates[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(24): 9478-9484. |
| [46] | NI J, ZHUANG J Y, SHI Y M, et al. Discovery and substrate specificity engineering of nucleotide halogenases[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 5254. |
| [47] | BAUMGARTNER J T, MCKINNIE S M K. Regioselective halogenation of lavanducyanin by a site-selective vanadium-dependent chloroperoxidase[J]. Organic Letters, 2024, 26(27): 5725-5730. |
| [48] | The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D480-D489. |
| [49] | JIANG K, CHEN X, YAN X L, et al. An unusual aromatase/cyclase programs the formation of the phenyldimethylanthrone framework in anthrabenzoxocinones and fasamycin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(11): e2321722121. |
| [50] | RADIVOJAC P, CLARK W T, ORON T R, et al. A large-scale evaluation of computational protein function prediction[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(3): 221-227. |
| [51] | YU T H, CUI H Y, LI J C, et al. Enzyme function prediction using contrastive learning[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6639): 1358-1363. |
| [52] | ADAK S, MOORE B S. Cryptic halogenation reactions in natural product biosynthesis[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(10): 1760-1774. |
| [53] | VAILLANCOURT F H, YEH E, VOSBURG D A, et al. Cryptic chlorination by a non-haem iron enzyme during cyclopropyl amino acid biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7054): 1191-1194. |
| [54] | GU L C, WANG B, KULKARNI A, et al. Metamorphic enzyme assembly in polyketide diversification[J]. Nature, 2009, 459(7247): 731-735. |
| [55] | YAMANAKA K, RYAN K S, GULDER T A M, et al. Flavoenzyme-catalyzed atropo-selective N, C-bipyrrole homocoupling in marinopyrrole biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(30): 12434-12437. |
| [56] | MARCHAND J A, NEUGEBAUER M E, ING M C, et al. Discovery of a pathway for terminal-alkyne amino acid biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7748): 420-424. |
| [57] | NAKAMURA H, HAMER H A, SIRASANI G, et al. Cylindrocyclophane biosynthesis involves functionalization of an unactivated carbon center[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(45): 18518-18521. |
| [58] | NAKAMURA H, SCHULTZ E E, BALSKUS E P. A new strategy for aromatic ring alkylation in cylindrocyclophane biosynthesis[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(8): 916-921. |
| [59] | GLASSER N R, CUI D T, RISSER D D, et al. Accelerating the discovery of alkyl halide-derived natural products using halide depletion[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2024, 16(2): 173-182. |
| [60] | REED K B, D’OELSNITZ S, BROOKS S M, et al. Fluorescence-based screens for engineering enzymes linked to halogenated tryptophan[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(4): 1373-1381. |
| [61] | DONG C J, KOTZSCH A, DORWARD M, et al. Crystallization and X-ray diffraction of a halogenating enzyme, tryptophan 7-halogenase, from Pseudomonas fluorescens [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D: Biological Crystallography, 2004, 60(8): 1438-1440. |
| [62] | MORI S, PANG A H, THAMBAN CHANDRIKA N, et al. Unusual substrate and halide versatility of phenolic halogenase PltM[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1255. |
| [63] | GAMAL A EL, AGARWAL V, DIETHELM S, et al. Biosynthesis of coral settlement cue tetrabromopyrrole in marine bacteria by a uniquely adapted brominase-thioesterase enzyme pair[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(14): 3797-3802. |
| [64] | PODZELINSKA K, LATIMER R, BHATTACHARYA A, et al. Chloramphenicol biosynthesis: the structure of CmlS, a flavin-dependent halogenase showing a covalent flavin-aspartate bond[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2010, 397(1): 316-331. |
| [65] | AGARWAL V, GAMAL A A EL, YAMANAKA K, et al. Biosynthesis of polybrominated aromatic organic compounds by marine bacteria[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(8): 640-647. |
| [66] | ADAK S, LUKOWSKI A L, SCHÄFER R J B, et al. From tryptophan to toxin: nature’s convergent biosynthetic strategy to aetokthonotoxin[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(7): 2861-2866. |
| [67] | MINGES H. Engineering of halogenases towards synthetic applications: increasing the thermostability and investigations on a marine brominase Bmp5[M/OL]. Wiesbaden: Springer Spektrum Wiesbaden, 2017[2024-12-01]. . |
| [68] | GÄFE S, NIEMANN H H. Structural basis of regioselective tryptophan dibromination by the single-component flavin-dependent halogenase AetF[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology, 2023, 79(7): 596-609. |
| [69] | BARKER R D, YU Y Q, DE MARIA L, et al. Mechanism of action of flavin-dependent halogenases[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(24): 15352-15360. |
| [70] | DAI L H, ZHANG X, HU Y M, et al. Structural and functional insights into a nonheme iron- and α-ketoglutarate-dependent halogenase that catalyzes chlorination of nucleotide substrates[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2022, 88(9): e02497-21. |
| [71] | WILSON R H, CHATTERJEE S, SMITHWICK E R, et al. Role of secondary coordination sphere residues in halogenation catalysis of non-heme iron enzymes[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(17): 10913-10924. |
| [72] | LI R N, CHEN S L. Mechanism for the halogenation and azidation of lysine catalyzed by non-heme iron BesD enzyme[J]. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2022, 17(17): e202200438. |
| [73] | KASTNER D W, NANDY A, MEHMOOD R, et al. Mechanistic insights into substrate positioning that distinguish non-heme Fe(Ⅱ)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent halogenases and hydroxylases[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(4): 2489-2501. |
| [74] | PAPADOPOULOU A, MEYER F, BULLER R M. Engineering Fe(Ⅱ)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent halogenases and desaturases[J]. Biochemistry, 2023, 62(2): 229-240. |
| [75] | C R Ⅲ ZWICK, RENATA H. Overview of amino acid modifications by iron- and α-ketoglutarate-dependent enzymes[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(7): 4853-4865. |
| [76] | SMITHWICK E R, WILSON R H, CHATTERJEE S, et al. Electrostatically regulated active site assembly governs reactivity in nonheme iron halogenases[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(20): 13743-13755. |
| [77] | KISSMAN E N, KIPOUROS I, SLATER J W, et al. Dynamic metal coordination controls chemoselectivity in radical halogenases[J]. bioRxiv, 2024: 2024.09.19.613983. |
| [78] | KISSMAN E N, NEUGEBAUER M E, SUMIDA K H, et al. Biocatalytic control of site-selectivity and chain length-selectivity in radical amino acid halogenases[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(12): e2214512120. |
| [79] | KULIK H J, DRENNAN C L. Substrate placement influences reactivity in non-heme Fe(Ⅱ) halogenases and hydroxylases[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(16): 11233-11241. |
| [80] | ZHANG J Y, LI Y F, YUAN W L, et al. Conformational isomerization of the Fe(Ⅲ)-OH species enables selective halogenation in carrier-protein-independent halogenase BesD and hydroxylase-evolved halogenase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(12): 9342-9353. |
| [81] | CHIANG C Y, OHASHI M, LE J, et al. Copper-dependent halogenase catalyses unactivated C-H bond functionalization[J]. Nature, 2025, 638(8049): 126-132. |
| [82] | O’HAGAN D, SCHAFFRATH C, COBB S L, et al. Biosynthesis of an organofluorine molecule[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6878): 279. |
| [83] | DONG C J, HUANG F L, DENG H, et al. Crystal structure and mechanism of a bacterial fluorinating enzyme[J]. Nature, 2004, 427(6974): 561-565. |
| [84] | EUSTÁQUIO A S, POJER F, NOEL J P, et al. Discovery and characterization of a marine bacterial SAM-dependent chlorinase[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2008, 4(1): 69-74. |
| [85] | DENG H, O’HAGAN D. The fluorinase, the chlorinase and the duf-62 enzymes[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2008, 12(5): 582-592. |
| [86] | BUTLER A, SANDY M. Mechanistic considerations of halogenating enzymes[J]. Nature, 2009, 460(7257): 848-854. |
| [87] | O’HAGAN D, DENG H. Enzymatic fluorination and biotechnological developments of the fluorinase[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(2): 634-649. |
| [88] | PARDO I, BEDNAR D, CALERO P, et al. A nonconventional archaeal fluorinase identified by in silico mining for enhanced fluorine biocatalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(11): 6570-6577. |
| [89] | JIANG Y X, YAO M D, NIU H R, et al. Enzyme engineering renders chlorinase the activity of fluorinase[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(2): 1203-1212. |
| [90] | LOWE P T, LÜDDECKE I, O’HAGAN D. Exploring fluorinase substrate tolerance at C-2 of SAM[J]. ChemBioChem, 2025, 26(1): e202400861. |
| [91] | HE K, YAN Y, FENG S T, et al. Two fluorinases prioritized from protein families of fluorinase, SAM-dependent chlorinase and hydroxide adenosyltransferase[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2025, 23(2): 318-322. |
| [92] | LIN Y Q, XUE W Q, LI H C, et al. Advances in enzymatic incorporation of small fluorine modules[J]. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 27(17): e202400003. |
| [93] | LIU H Y, QIAN F, ZHANG H M, et al. Tri-enzyme fusion of tryptophan halogenase achieves a concise strategy for coenzyme self-sufficiency and the continuous halogenation of L-tryptophan[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 19(4): 2300557. |
| [94] | KOKKONEN P, BEDNAR D, PINTO G, et al. Engineering enzyme access tunnels[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(6): 107386. |
| [95] | PHINTHA A, PRAKINEE K, JARUWAT A, et al. Dissecting the low catalytic capability of flavin-dependent halogenases[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2021, 296: 100068. |
| [96] | PRAKINEE K, PHINTHA A, VISITSATTHAWONG S, et al. Mechanism-guided tunnel engineering to increase the efficiency of a flavin-dependent halogenase[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5(6): 534-544. |
| [97] | DAI L H, LI H, DAI S, et al. Structural and functional insights into the self-sufficient flavin-dependent halogenase[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 260: 129312. |
| [98] | BESSE C, NIEMANN H H, SEWALD N. Increasing the stability of flavin-dependent halogenases by disulfide engineering[J]. ChemBioChem, 2024, 25(1): e202300700. |
| [99] | GEBAUER J, PIETRUSZKA J, CLASSEN T. Expression and characterization of PrnC—a flavin-dependent halogenase from the pyrrolnitrin biosynthetic pathway of Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5[J]. Frontiers in Catalysis, 2023, 3: 1231765. |
| [100] | HU Y, PENG S Y, MA X Y, et al. Functional characterization and molecular basis of a multi-site halogenase in naphthacemycin biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(7): e202418843. |
| [101] | DIEPOLD N, REESE F, PRIOR T, et al. Balance between photoreduction efficiency, cofactor affinity, and allosteric coupling of halogenase flavoenzymes[J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2025, 24(1): 37-51. |
| [102] | BÜCHLER J, MALCA S H, PATSCH D, et al. Algorithm-aided engineering of aliphatic halogenase WelO5* for the asymmetric late-stage functionalization of soraphens[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 371. |
| [103] | LIU H Y, NING P, QIAN F, et al. Protein scaffold-mediated multi-enzyme self-assembly and ordered co-immobilization of flavin-dependent halogenase-coenzyme cycle system for efficient biosynthesis of 6-Cl-L-Trp[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2025, 122(2): 395-404. |
| [104] | PRAKINEE K, LAWAN N, PHINTHA A, et al. On the mechanisms of hypohalous acid formation and electrophilic halogenation by non-native halogenases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(24): e202403858. |
| [105] | SZPERA R, MOSELEY D F J, SMITH L B, et al. The fluorination of C-H bonds: developments and perspectives[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(42): 14824-14848. |
| [106] | LEIBLER I N M, GANDHI S S, TEKLE-SMITH M A, et al. Strategies for nucleophilic C(sp3)-(radio)fluorination[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(18): 9928-9950. |
| [107] | HAYASHI T, LIGIBEL M, SAGER E, et al. Evolved aliphatic halogenases enable regiocomplementary C-H functionalization of a pharmaceutically relevant compound[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(51): 18535-18539. |
| [108] | ZHAO L P, MAI B K, CHENG L D, et al. Biocatalytic enantioselective C(sp3)-H fluorination enabled by directed evolution of non-haem iron enzymes[J]. Nature Synthesis, 2024, 3(8): 967-975. |
| [109] | ZHAO Q, CHEN Z H, SOLER J, et al. Engineering non-haem iron enzymes for enantioselective C(sp3)—F bond formation via radical fluorine transfer[J]. Nature Synthesis, 2024, 3(8): 958-966. |
| [110] | JIANG Y X, YAO M D, FENG J Q, et al. Molecular insights into converting hydroxide adenosyltransferase into halogenase[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(22): 12685-12695. |
| [111] | YU K, ZHANG K L, JAKOB R P, et al. An artificial nickel chlorinase based on the biotin-streptavidin technology[J]. Chemical Communications, 2024, 60(14): 1944-1947. |
| [112] | MILNE N, SÁEZ-SÁEZ J, NIELSEN A M, et al. Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the de novo production of halogenated tryptophan and tryptamine derivatives[J]. ChemistryOpen, 2023, 12(4): e202200266. |
| [113] | REED K B, BROOKS S M, WELLS J, et al. A modular and synthetic biosynthesis platform for de novo production of diverse halogenated tryptophan-derived molecules[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 3188. |
| [114] | PUTRI V R M, JUNG M H, LEE J Y, et al. Fermentative aminopyrrolnitrin production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2024, 23(1): 147. |
| [115] | PEH G R, TAY T, TAN L L, et al. Site-selective chlorination of pyrrolic heterocycles by flavin dependent enzyme PrnC[J]. Communications Chemistry, 2024, 7: 7. |
| [116] | MOWZOON-MOGHARRABI R, STOUT C N, RENATA H. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of 7-chloro-4-dimethylallyl-L-tryptophan, a fragment of krisynomycin[J]. Tetrahedron, 2024, 162: 134127. |
| [117] | BRADLEY S A, LEHKA B J, HANSSON F G, et al. Biosynthesis of natural and halogenated plant monoterpene indole alkaloids in yeast[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(12): 1551-1560. |
| [118] | LEE J C, KIM J W, SONG J E, et al. Production of Tyrian purple indigoid dye from tryptophan in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2021, 17(1): 104-112. |
| [119] | LI F F, CHEN Q, DENG H X, et al. One-pot selective biosynthesis of Tyrian purple in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2024, 81: 100-109. |
| [120] | YI B, LEE B W, YU K, et al. Production of halogenated indigo by Escherichia coli whole-cell conversion system with novel halogenase derived from Pseudoalteromonas nigrifaciens [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2024, 29(5): 806-814. |
| [121] | MONTUA N, THYE P, HARTWIG P, et al. Enzymatic peptide and protein bromination: the BromoTrp tag[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(5): e202314961. |
| [122] | GUO Y M, CHENG L Q, HU Y, et al. Biosynthesis of halogenated tryptophans for protein engineering using genetic code expansion[J]. ChemBioChem, 2024, 25(20): e202400366. |
| [123] | SAHA N, VIDYA F N U, XIE R, et al. Halogenase-assisted alkyne/aryl bromide sonogashira coupling for ribosomally synthesized peptides[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(44): 30009-30013. |
| [124] | PAYNE J T, POOR C B, LEWIS J C. Directed evolution of RebH for site-selective halogenation of large biologically active molecules[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 127(14): 4300-4304 |
| [125] | MONDAL D, FISHER B F, JIANG Y H, et al. Flavin-dependent halogenases catalyze enantioselective olefin halocyclization[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3268. |
| [126] | SNODGRASS H M, MONDAL D, LEWIS J C. Directed evolution of flavin-dependent halogenases for site- and atroposelective halogenation of 3-aryl-4(3H)-quinazolinones via kinetic or dynamic kinetic resolution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(36): 16676-16682. |
| [127] | CRAVEN E J, LATHAM J, SHEPHERD S A, et al. Programmable late-stage C-H bond functionalization enabled by integration of enzymes with chemocatalysis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(5): 385-394. |
| [128] | JIANG Y H, SNODGRASS H M, ZUBI Y S, et al. The single-component flavin reductase/flavin-dependent halogenase AetF is a versatile catalyst for selective bromination and iodination of arenes and olefins[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2022, 134(51): e202214610. |
| [129] | JIANG Y H, MONDAL D, LEWIS J C. Expanding the reactivity of flavin dependent halogenases toward olefins via enantioselective intramolecular haloetherification and chemoenzymatic oxidative rearrangements[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(21): 13501-13505. |
| [130] | JIANG Y H, KIM A, OLIVE C, et al. Selective C-H halogenation of alkenes and alkynes using flavin-dependent halogenases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(13): e202317860. |
| [131] | LUKOWSKI A L, HUBERT F M, NGO T E, et al. Enzymatic halogenation of terminal alkynes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(34): 18716-18721. |
| [132] | WILSON R H, CHATTERJEE S, SMITHWICK E R, et al. Controllable multi-halogenation of a non-native substrate by SyrB2 iron halogenase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(17): 13209-13218. |
| [133] | BARBER V, MIELKE T, CARTWRIGHT J, et al. Unspecific peroxygenase (UPO) can be tuned for oxygenation or halogenation activity by controlling the reaction pH[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2024, 30(40): e202401706. |
| [134] | BÜCHLER J, HEGARTY E, SCHROER K, et al. A collaborative journey towards the late-stage functionalization of added-value chemicals using engineered halogenases[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 2023, 106(1): e202200128. |
| [135] | KERBS A, BURGARDT A, VELDMANN K H, et al. Fermentative production of halogenated tryptophan derivatives with Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing tryptophanase or decarboxylase genes[J]. ChemBioChem, 2022, 23(9): e202200007. |
| [136] | HOU Y, ZHAO W Y, DING X C, et al. Co-production of 7-chloro-tryptophan and indole pyruvic acid based on an efficient FAD/FADH2 regeneration system[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(15): 4873-4885. |
| [137] | MONTUA N, SEWALD N. Extended biocatalytic halogenation cascades involving a single-polypeptide regeneration system for diffusible FADH2 [J]. ChemBioChem, 2023, 24(22): e202300478. |
| [138] | HILLWIG M L, LIU X Y. A new family of iron-dependent halogenases acts on freestanding substrates[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(11): 921-923. |
| [139] | AGARWAL V, MOORE B S. Enzymatic synthesis of polybrominated dioxins from the marine environment[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2014, 9(9): 1980-1984. |
| [140] | FRESE M, SEWALD N. Enzymatic halogenation of tryptophan on a gram scale[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(1): 298-301. |
| [141] | SHARMA S V, TONG X X, PUBILL-ULLDEMOLINS C, et al. Living GenoChemetics by hyphenating synthetic biology and synthetic chemistry in vivo [J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 229. |
| [142] | LIU M T, OHASHI M, HUNG Y S, et al. AoiQ catalyzes geminal dichlorination of 1,3-diketone natural products[J]. Jourmal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(19): 7267-7271. |
| [143] | ABRAMSON J, ADLER J, DUNGER J, et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3[J]. Nature, 2024, 630(8016): 493-500. |
| [144] | WEI G Z, DUAN B R, ZHOU T P, et al. A nucleobase-driven P450 peroxidase system enables regio- and stereo-specific formation of C─C and C─N bonds[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(46): e2412890121. |
| [145] | BAEK M Y, ANISHCHENKO I, HUMPHREYS I R, et al. Efficient and accurate prediction of protein structure using RoseTTAFold2[EB/OL]. bioRxiv,2023: 2023.05.24.542179. (2023-05-25)[2024-12-01]. . |
| [146] | ANISHCHENKO I, KIPNIS Y, KALVET I, et al. Modeling protein-small molecule conformational ensembles with ChemNet[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2024: 2024.09.25.614868. (2024-09-25)[2024-12-01]. . |
| [147] | ZHANG Z X, SHEN W X, LIU Q, et al. Efficient generation of protein pockets with PocketGen[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2024, 6(11): 1382-1395. |
| [148] | MUELLERS S N, ALLEN K N, WHITTY A. MEnTaT: a machine-learning approach for the identification of mutations to increase protein stability[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(49): e2309884120. |
| [149] | WANG T, HE X H, LI M Y, et al. Ab initio characterization of protein molecular dynamics with AI2BMD[J]. Nature, 2024, 635(8040): 1019-1027. |
| [150] | KORTEMME T. De novo protein design-from new structures to programmable functions[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(3): 526-544. |
| [151] | YEH A H W, NORN C, KIPNIS Y, et al. De novo design of luciferases using deep learning[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7949): 774-780. |
| [152] | WANG J, LISANZA S, JUERGENS D, et al. Scaffolding protein functional sites using deep learning[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6604): 387-394. |
| [153] | WATSON J L, JUERGENS D, BENNETT N R, et al. De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion[J]. Nature, 2023, 620(7976): 1089-1100. |
| [154] | KRISHNA R, WANG J, AHERN W, et al. Generalized biomolecular modeling and design with RoseTTAFold All-Atom[J]. Science, 2024, 384(6693): eadl2528. |
| [155] | DAUPARAS J, ANISHCHENKO I, BENNETT N, et al. Robust deep learning-based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6615): 49-56. |
| [156] | DAUPARAS J, LEE G R, PECORARO R, et al. Atomic context-conditioned protein sequence design using LigandMPNN[J]. Nature Methods, 2025, 22: 717-723. |
| [157] | ZHOU J X, ZHANG B, LI G W, et al. An AI agent for fully automated multi-omic analyses[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(44): 2407094. |
| [158] | MERLICEK L P, NEUMANN J, LEAR A, et al. AI.zymes-a modular platform for evolutionary enzyme design [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(27): e202507031. |
| [159] | ZHANG Q, CHEN W Y, QIN M, et al. Integrating protein language models and automatic biofoundry for enhanced protein evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 1553. |
| [160] | LANDWEHR G M, BOGART J W, MAGALHAES C, et al. Accelerated enzyme engineering by machine-learning guided cell-free expression[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 865. |
| [161] | HUANG H Z, SHI X G, LEI H Y, et al. ProtChat: an AI multi-agent for automated protein analysis leveraging GPT-4 and protein language model[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2025, 65(1): 62-70. |
| [1] | MA Muqing, WU Yan, QU Maohua, LU Xiafeng, CAO Min, DU Feng, JI Rongtao, DONG Leichi, LUO Zhibo. Extracellular multi-enzyme assembly and biocatalytic cascade: advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 920-939. |
| [2] | HU Die, XU Daozhu, LU Zhiyi, TANG Wei, FAN Bo, HE Yucai. Biosynthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat straw xylan through the synergistic hydrolysis by xylanase Xyn11A and arabinofuranosidase Abf62A [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 972-986. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [4] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [5] | SHENG Zhouhuang, CHEN Zhixian, ZHANG Yan. Research progress of yeast mannoproteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [6] | LU Jinchang, WU Yaokang, LV Xueqin, LIU Long, CHEN Jian, LIU Yanfeng. Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 422-444. |
| [7] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [8] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [9] | TANG Chuan′gen, WANG Jing, ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Haoning, KANG Zhen. Advances in synthesis and mining strategies for functional peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| [10] | ZHONG Quanzhou, SHAN Yiyi, PEI Qingyun, JIN Yanyun, WANG Yihan, MENG Luyuan, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Yuxin, LIU Kunyuan, WANG Huizhong, FENG Shangguo. Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [11] | ZHU Fanghuan, CEN Xuecong, CHEN Zhen. Research progress of diols production by microbes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [12] | LIU Yining, PU Wei, YANG Jinxing, WANG Yu. Recent advances in the biosynthesis of ω-amino acids and lactams [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [13] | FU Yu, ZHONG Fangrui. Recent advances in chemically driven enantioselective photobiocatalysis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [14] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [15] | CHENG Xiaolei, LIU Tiangang, TAO Hui. Recent research progress in non-canonical biosynthesis of terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||