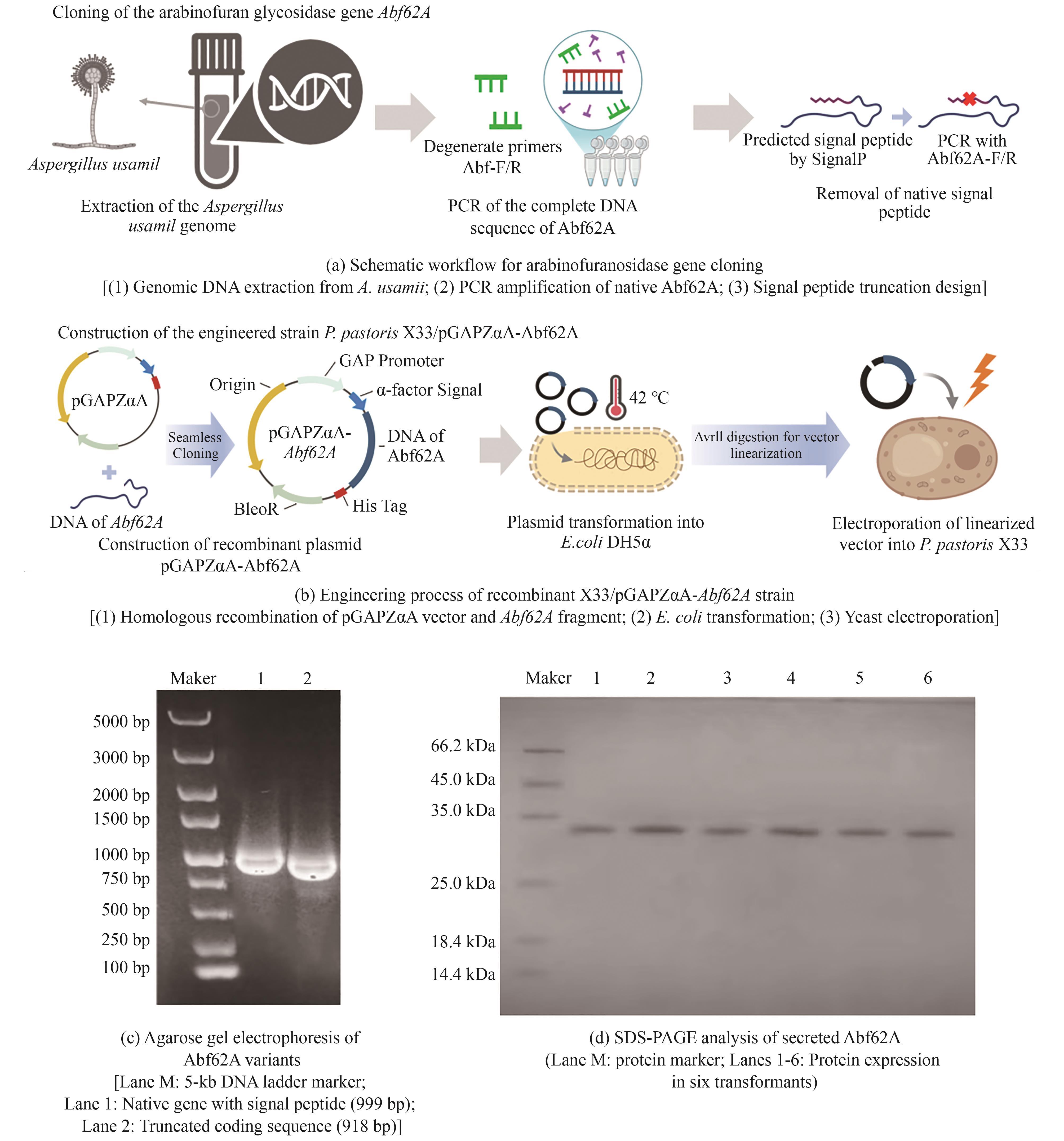
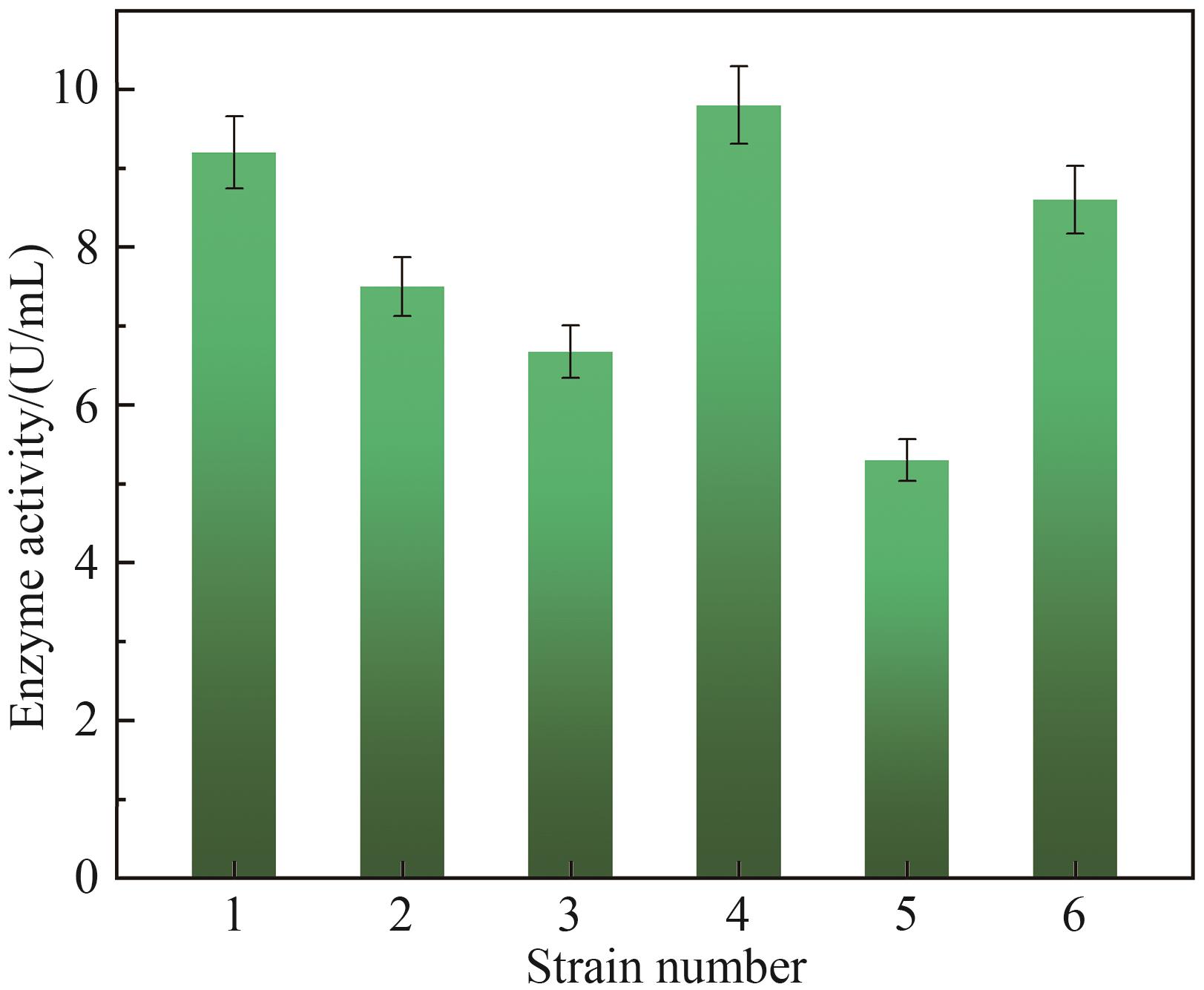
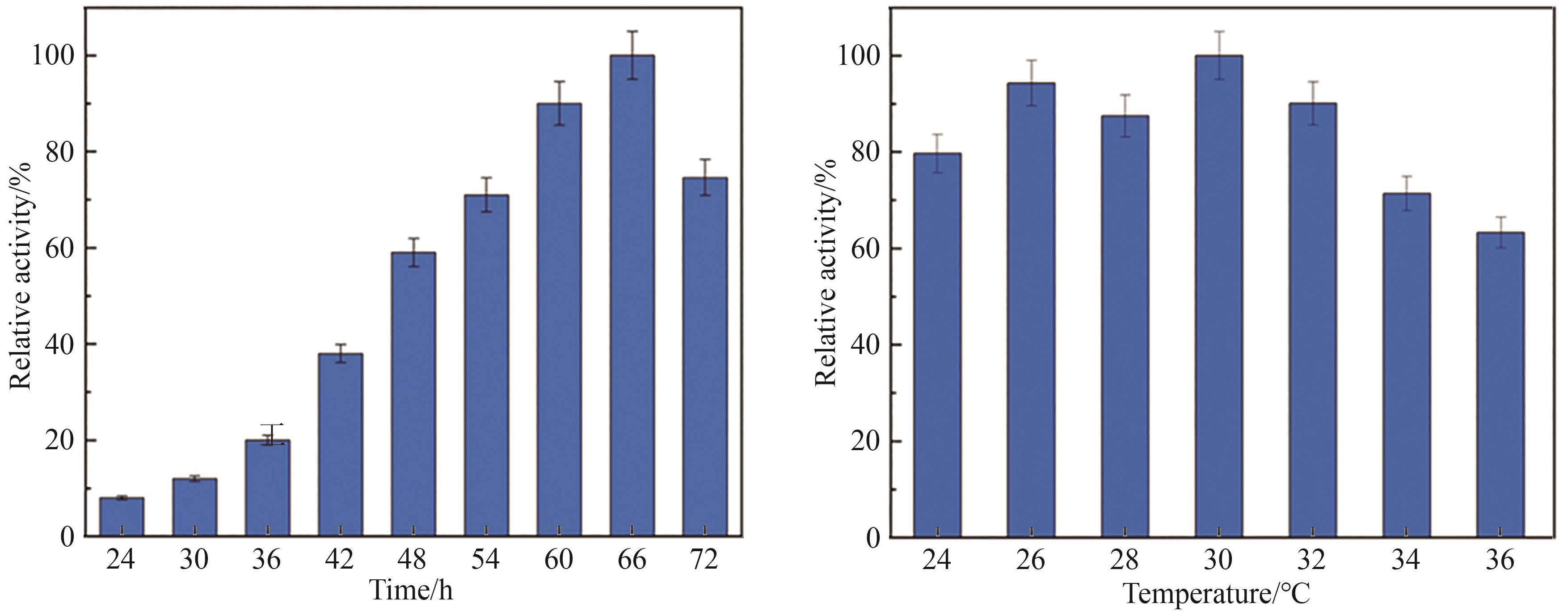
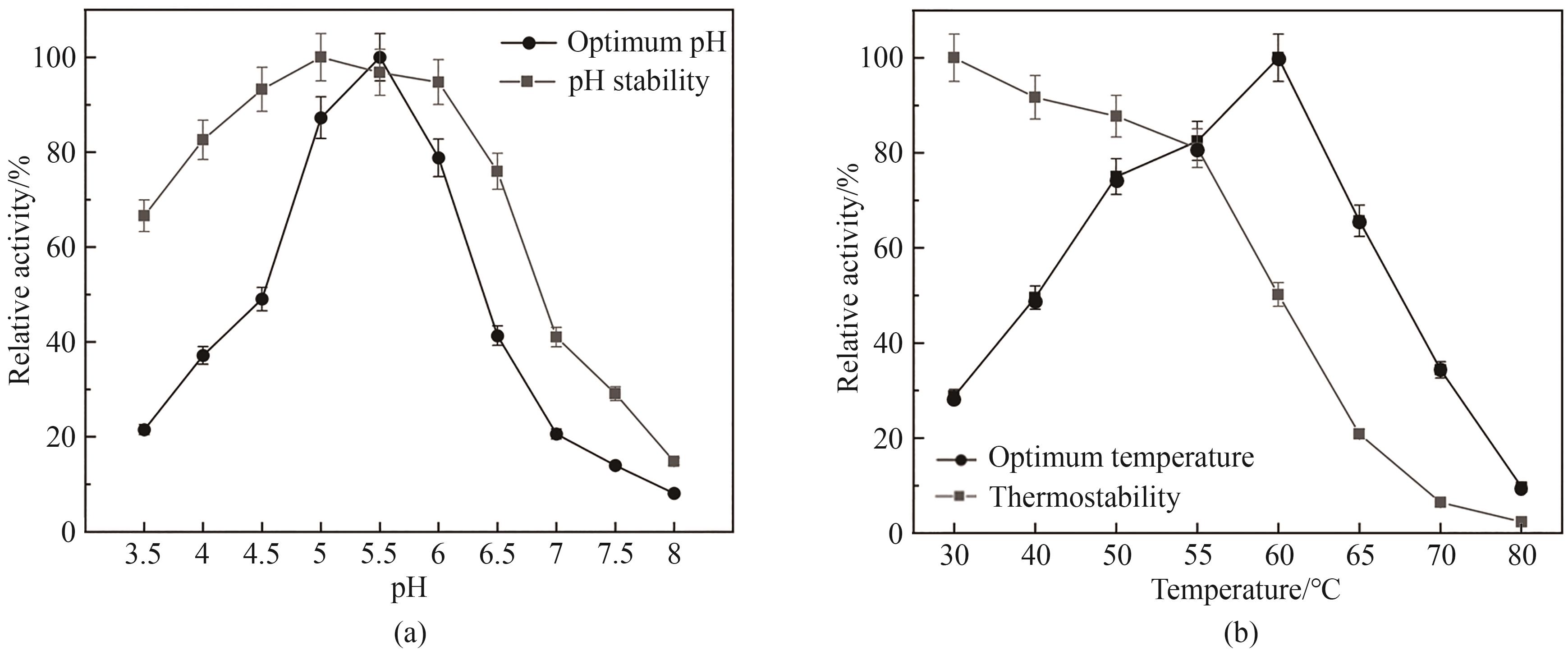
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 972-986.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-037
• Research Article • Previous Articles
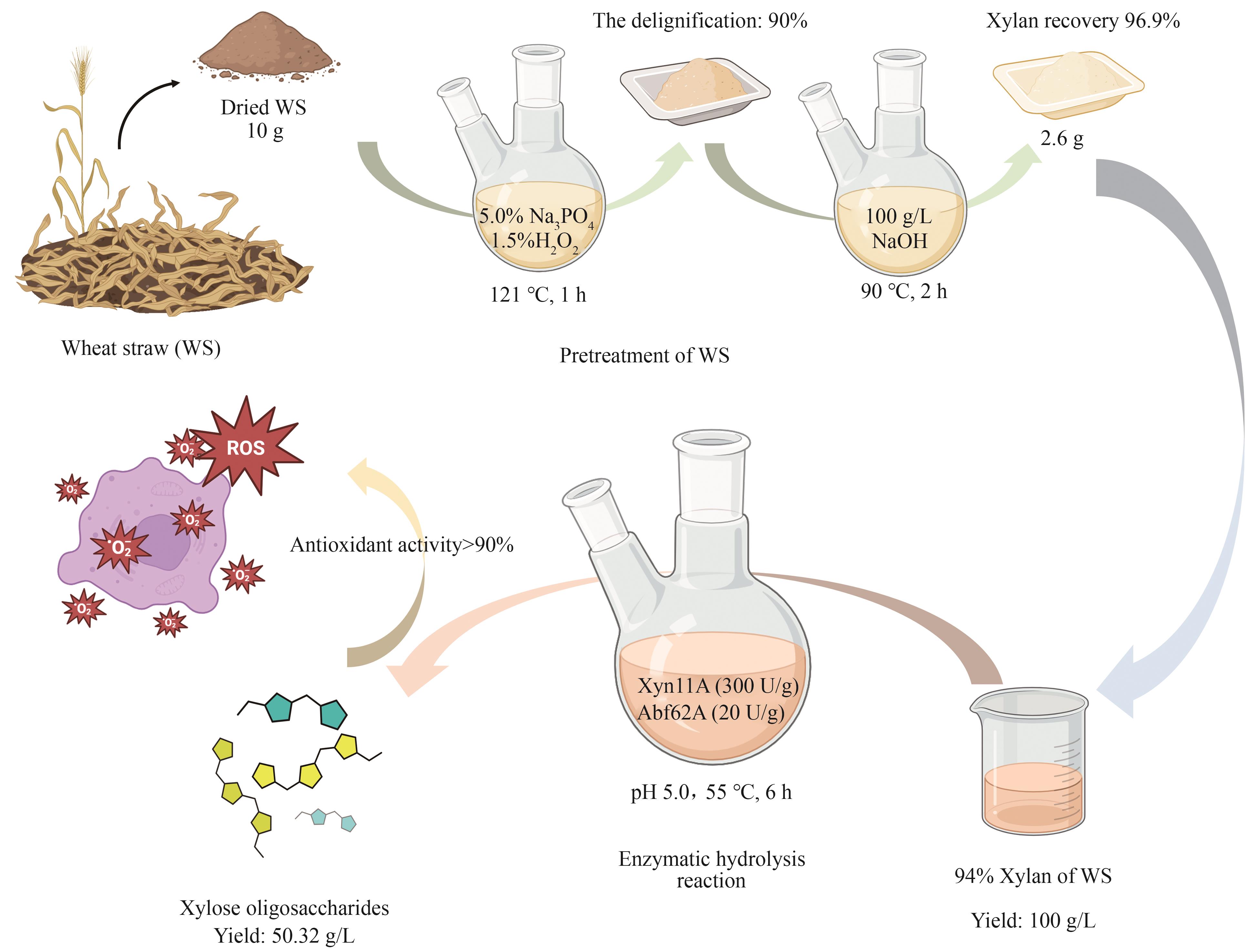
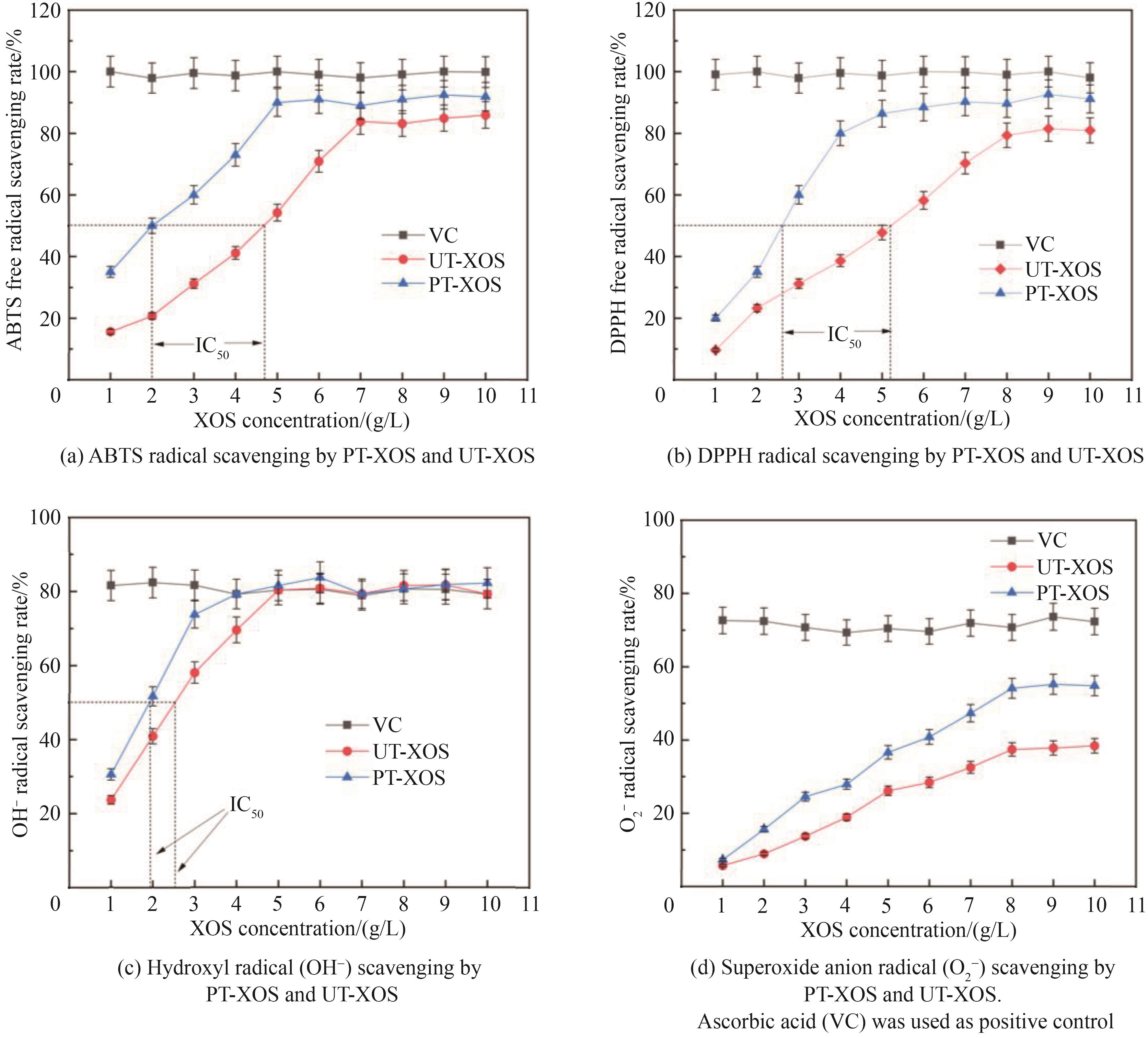
Biosynthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat straw xylan through the synergistic hydrolysis by xylanase Xyn11A and arabinofuranosidase Abf62A
HU Die, XU Daozhu, LU Zhiyi, TANG Wei, FAN Bo, HE Yucai
- School of Pharmacy & School of Biological and Food Engineering,Changzhou University,Changzhou 213164,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2025-04-29Revised:2025-07-03Online:2025-09-03Published:2025-08-31 -
Contact:HE Yucai
木聚糖酶Xyn11A与阿拉伯呋喃糖苷酶Abf62A协同水解麦秆木聚糖生物合成低聚木糖
胡蝶, 徐道铸, 鲁志毅, 唐卫, 樊博, 何玉财
- 常州大学,药学院 生物与食品工程学院,江苏 常州 213164
-
通讯作者:何玉财 -
作者简介:胡蝶 (1988—),女,博士,助理研究员,硕士生导师。研究方向为酶工程与酶分子设计。 E-mail:Butterflystudy@163.com何玉财 (1979—), 男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为合成生物学和生物质能源。E-mail:heyucai2001@126.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(22208031)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HU Die, XU Daozhu, LU Zhiyi, TANG Wei, FAN Bo, HE Yucai. Biosynthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat straw xylan through the synergistic hydrolysis by xylanase Xyn11A and arabinofuranosidase Abf62A[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 972-986.
胡蝶, 徐道铸, 鲁志毅, 唐卫, 樊博, 何玉财. 木聚糖酶Xyn11A与阿拉伯呋喃糖苷酶Abf62A协同水解麦秆木聚糖生物合成低聚木糖[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 972-986.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-037
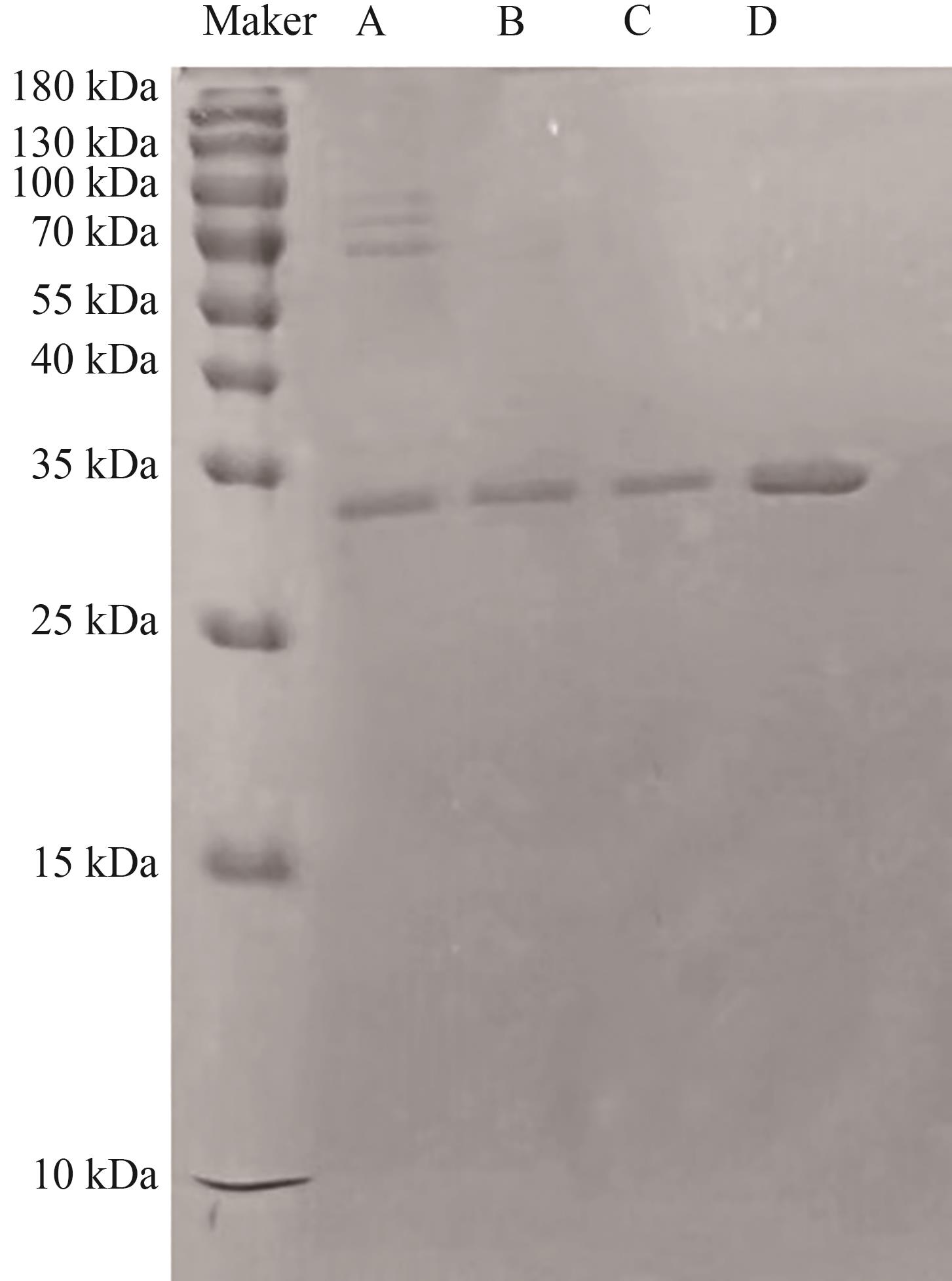
Fig. 4 SDS-PAGE results Abf62A protein(Lane A: Abf62A fermentation liquor; Lane B: Abf62A flow-through solution; Lane C: Abf62A eluate solution; Lane D: Abf62A pure enzyme solution)
| Product | UTX | PTX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | |
| Xylose | 0.63 | 3.08 | 1.37 | 3.97 |
| Xylobiose | 11.69 | 57.16 | 20.85 | 60.45 |
| Xylotriose | 7.61 | 37.21 | 11.44 | 33.17 |
| Xylotetraose | 0.41 | 2.01 | 1.13 | 3.28 |
| Xylopentaose | 0.26 | 1.27 | 1.0 | 2.90 |
| Arabinose | 0.17 | 0.83 | 0.43 | 1.25 |
| Glucose | 0.35 | 1.71 | 0.4 | 1.16 |
Table 1 Analysis of Xyn11A enzymatic hydrolysis products of different WS xylan
| Product | UTX | PTX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | |
| Xylose | 0.63 | 3.08 | 1.37 | 3.97 |
| Xylobiose | 11.69 | 57.16 | 20.85 | 60.45 |
| Xylotriose | 7.61 | 37.21 | 11.44 | 33.17 |
| Xylotetraose | 0.41 | 2.01 | 1.13 | 3.28 |
| Xylopentaose | 0.26 | 1.27 | 1.0 | 2.90 |
| Arabinose | 0.17 | 0.83 | 0.43 | 1.25 |
| Glucose | 0.35 | 1.71 | 0.4 | 1.16 |
| Product | UTX | PTX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | |
| Xylose | 0.55 | 2.35 | 1.43 | 2.63 |
| Xylobiose | 12.38 | 52.79 | 31.71 | 58.22 |
| Xylotriose | 8.35 | 35.61 | 15.92 | 29.23 |
| Xylotetraose | 0.62 | 2.64 | 1.65 | 3.03 |
| Xylopentaose | 0.47 | 2.01 | 1.04 | 1.91 |
| Arabinose | 0.62 | 2.64 | 2.34 | 4.30 |
| Glucose | 0.46 | 1.96 | 0.38 | 0.70 |
Table 2 Sugar content and proportion in xylan hydrolysates of different WS
| Product | UTX | PTX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | Concentration/(g/L) | Proportion/% | |
| Xylose | 0.55 | 2.35 | 1.43 | 2.63 |
| Xylobiose | 12.38 | 52.79 | 31.71 | 58.22 |
| Xylotriose | 8.35 | 35.61 | 15.92 | 29.23 |
| Xylotetraose | 0.62 | 2.64 | 1.65 | 3.03 |
| Xylopentaose | 0.47 | 2.01 | 1.04 | 1.91 |
| Arabinose | 0.62 | 2.64 | 2.34 | 4.30 |
| Glucose | 0.46 | 1.96 | 0.38 | 0.70 |
| [1] | SANTIBÁÑEZ L, HENRÍQUEZ C, CORRO-TEJEDA R, et al. Xylooligosaccharides from lignocellulosic biomass: a comprehensive review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 251: 117118. |
| [2] | GIBSON G R, HUTKINS R, SANDERS M E, et al. Expert consensus document: the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2017, 14(8): 491-502. |
| [3] | YAN F, TIAN S Q, DU K, et al. Preparation and nutritional properties of xylooligosaccharide from agricultural and forestry byproducts: a comprehensive review[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2022, 9: 977548. |
| [4] | LIU Z X, LIU M H, MENG J, et al. A review of the interaction between diet composition and gut microbiota and its impact on associated disease[J]. Journal of Future Foods, 2024, 4(3): 221-232. |
| [5] | ZHOU J M, WU S G, QI G H, et al. Dietary supplemental xylooligosaccharide modulates nutrient digestibility, intestinal morphology, and gut microbiota in laying hens[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2021, 7(1): 152-162. |
| [6] | CHEN W W, GUO C, HUSSAIN S, et al. Role of xylo-oligosaccharides in protection against salinity-induced adversities in Chinese cabbage[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(2): 1254-1264. |
| [7] | CARRILLO I, MENDONÇA R T, AGO M, et al. Comparative study of cellulosic components isolated from different Eucalyptus species[J]. Cellulose, 2018, 25(2): 1011-1029. |
| [8] | POLETTO P, PEREIRA G N, MONTEIRO C R M, et al. Xylooligosaccharides: transforming the lignocellulosic biomasses into valuable 5-carbon sugar prebiotics[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2020, 91: 352-363. |
| [9] | KUMAR P, BARRETT D M, DELWICHE M J, et al. Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(8): 3713-3729. |
| [10] | KUMAR R, PRAKASH O. Experimental investigation on effect of season on the production of bioethanol from wheat-stalk (WS) using simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) method[J]. Fuel, 2023, 351: 128958. |
| [11] | ZHANG L M, LARSSON A, MOLDIN A, et al. Comparison of lignin distribution, structure, and morphology in wheat straw and wood[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 187: 115432. |
| [12] | SUN M X, XU X B, WANG C D, et al. Environmental burdens of the comprehensive utilization of straw: wheat straw utilization from a life-cycle perspective[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 259: 120702. |
| [13] | BRENELLI L B, FIGUEIREDO F L, DAMASIO A, et al. An integrated approach to obtain xylo-oligosaccharides from sugarcane straw: from lab to pilot scale[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 313: 123637. |
| [14] | HIDAYATULLAH I M, HUSNA M D AL, RADIYAN H, et al. Combining biodelignification and hydrothermal pretreatment of oil palm empty fruit bunches (OPEFB) for monomeric sugar production[J]. Bioresource Technology Reports, 2021, 15: 100808. |
| [15] | ZHAO J Y, BIAN B, WANG X K, et al. Integrating ball milling assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of bamboo cellulose for controllable production of xylo-oligosaccharides, monosaccharides and cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2024, 209: 118024. |
| [16] | MANISHA, YADAV S K. Technological advances and applications of hydrolytic enzymes for valorization of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245(Pt B): 1727-1739. |
| [17] | CARVALHO A F A, DE OLIVA NETO P, SILVA D F DA, et al. Xylo-oligosaccharides from lignocellulosic materials: chemical structure, health benefits and production by chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Food Research International, 2013, 51(1): 75-85. |
| [18] | ZHANG H M, LI J F, WANG J Q, et al. Determinants for the improved thermostability of a mesophilic family 11 xylanase predicted by computational methods[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2014, 7(1): 3. |
| [19] | KULATHUNGA J, ISLAM S. Wheat arabinoxylans: insight into structure-function relationships[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2025, 348: 122933. |
| [20] | WILKENS C, ANDERSEN S, DUMON C, et al. GH62 Arabinofuranosidases: structure, function and applications[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(6): 792-804. |
| [21] | PETUSHKOVA A I, ZAMYATNIN A A. Redox-mediated post-translational modifications of proteolytic enzymes and their role in protease functioning[J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(4): 650. |
| [22] | PORIA V, SAINI J K, SINGH S, et al. Arabinofuranosidases: characteristics, microbial production, and potential in waste valorization and industrial applications[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 304: 123019. |
| [23] | LIU X Q, GAO F, WANG Y R, et al. Characterization of a novel thermostable α-L-arabinofuranosidase for improved synergistic effect with xylanase on lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis without prior pretreatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 394: 130177. |
| [24] | YAN R Y, WANG W J, VUONG T V, et al. Structural characterization of the family GH115 α-glucuronidase from Amphibacillus xylanus yields insight into its coordinated action with α-arabinofuranosidases[J]. New Biotechnology, 2021, 62: 49-56. |
| [25] | AYTAŞ Z G, TUNÇER M, KUL Ç S, et al. Partial characterization of β-glucosidase, β-xylosidase, and α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Jiangella alba DSM 45237 and their potential in lignocellulose-based biorefining[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 2023, 31: 100900. |
| [26] | LI P H, YANG C, JIANG Z W, et al. Lignocellulose pretreatment by deep eutectic solvents and related technologies: a review[J]. Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, 2023, 8(1): 33-44. |
| [27] | 康里奇, 谈攀, 洪亮. 人工智能时代下的酶工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. |
| KANG L Q, TAN P, HONG L. Enzyme engineering in the age of artificial intelligence[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. | |
| [28] | 丁明珠, 李炳志, 王颖, 等. 合成生物学重要研究方向进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| DING M Z, LI B Z, WANG Y, et al. Significant research progress in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. | |
| [29] | 阮青云, 黄莘, 孟子钧, 等. 蛋白质稳定性计算设计与定向进化前沿工具[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. |
| RUAN Q Y, HUANG X, MENG Z J, et al. Computational design and directed evolution strategies for optimizing protein stability[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. | |
| [30] | SELLÉS VIDAL L, ISALAN M, HEAP J T, et al. A primer to directed evolution: current methodologies and future directions[J]. RSC Chemical Biology, 2023, 4(4): 271-291. |
| [31] | 祁延萍, 朱晋, 张凯, 等. 定向进化在蛋白质工程中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. |
| QI Y P, ZHU J, ZHANG K, et al. Recent development of directed evolution in protein engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. | |
| [32] | MCLURE R J, RADFORD S E, BROCKWELL D J. High-throughput directed evolution: a golden era for protein science[J]. Trends in Chemistry, 2022, 4(5): 378-391. |
| [33] | YANG Q Z, FAN B, HE Y C. Combination of solid acid and solvent pretreatment for co-production of furfural, xylooligosaccharide and reducing sugars from Phyllostachys edulis [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 395: 130398. |
| [34] | TANG Z Y, FAN B, TANG W, et al. Comprehensive understanding of co-producing fermentable sugar, furfural, and xylo-oligosaccharides through the pretreatment with CTAB-based deep eutectic solvent containing Brønsted and Lewis acid[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 150637. |
| [35] | ALVAREZ V M Z, FERNÁNDEZ P V, CIANCIA M. Structure-antioxidant activity relationship of xylooligosaccharides obtained from carboxyl-reduced glucuronoarabinoxylans from bamboo shoots[J]. Food Chemistry, 2024, 455: 139761. |
| [36] | KRISTENSEN J B, THYGESEN L G, FELBY C, et al. Cell-wall structural changes in wheat straw pretreated for bioethanol production[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2008, 1(1): 5. |
| [37] | CHEN Y, TANG Z Y, TANG W, et al. Exploration of biomass fractionation and lignin removal for enhancing enzymatic digestion of wheat-stalk through deep eutectic solvent Cetyl trimethyl ammonium chloride: lactic acid treatment[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 306: 141460. |
| [38] | CHANDIMALI N, BAK S G, PARK E H, et al. Free radicals and their impact on health and antioxidant defenses: a review[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2025, 11: 19. |
| [1] | WANG Mingpeng, CHEN Lei, ZHAO Yiran, ZHANG Yimin, ZHENG Qifan, LIU Xinyang, WANG Yixue, WANG Qinhong. Halogenases in biocatalysis: advances in mechanism elucidation, directed evolution, and green manufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 728-763. |
| [2] | SHENG Zhouhuang, CHEN Zhixian, ZHANG Yan. Research progress of yeast mannoproteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [3] | LU Jinchang, WU Yaokang, LV Xueqin, LIU Long, CHEN Jian, LIU Yanfeng. Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 422-444. |
| [4] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [5] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [6] | TANG Chuan′gen, WANG Jing, ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Haoning, KANG Zhen. Advances in synthesis and mining strategies for functional peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| [7] | ZHONG Quanzhou, SHAN Yiyi, PEI Qingyun, JIN Yanyun, WANG Yihan, MENG Luyuan, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Yuxin, LIU Kunyuan, WANG Huizhong, FENG Shangguo. Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [8] | ZHU Fanghuan, CEN Xuecong, CHEN Zhen. Research progress of diols production by microbes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [9] | LIU Yining, PU Wei, YANG Jinxing, WANG Yu. Recent advances in the biosynthesis of ω-amino acids and lactams [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHENG Xiaolei, LIU Tiangang, TAO Hui. Recent research progress in non-canonical biosynthesis of terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [12] | LIU Zijian, MU Baiyang, DUAN Zhiqiang, WANG Xuan, LU Xiaojie. Advances in the development of DNA-compatible chemistries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [13] | ZHANG Shouqi, WANG Tao, KONG Yao, ZOU Jiasheng, LIU Yuanning, XU Zhengren. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of natural products: evolution of synthetic methodology and strategy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [14] | XIE Xiangqian, GUO Wen, WANG Huan, LI Jin. Biosynthesis and chemical synthesis of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides containing aminovinyl cysteine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [15] | TANG Zhijun, HU Youcai, LIU Wen. Enzymatic (4+2)- and (2+2)-cycloaddition reactions: fundamentals and applications of regio- and stereoselectivity [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||