Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (3): 685-700.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-079
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective
ZHANG Yiqing1,2, LIU Gaowen1
- 1.Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Synthetic Genomics,Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Synthetic Genomics,Key Laboratory of Quantitative Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2024-11-11Revised:2025-02-20Online:2025-06-27Published:2025-06-30 -
Contact:LIU Gaowen
合成生物学视角下的基因功能探索与酵母工程菌株文库构建
章益蜻1,2, 刘高雯1
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,深圳合成基因组学重点实验室,广东省合成基因组学重点实验室,定量合成生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
-
通讯作者:刘高雯 -
作者简介:章益蜻 (2001—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为合成生物学与系统基因组学。E-mail:yq.zhang3@siat.ac.cn刘高雯 (1987—),女,副研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为酵母系统基因组学与适应性进化。E-mail:gaowen.liu@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:广东省合成基因组学重点实验室资助项目(2023B1212060054);深圳合成基因组学重点实验室资助项目(ZDSYS201802061806209)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700.
章益蜻, 刘高雯. 合成生物学视角下的基因功能探索与酵母工程菌株文库构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 685-700.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-079
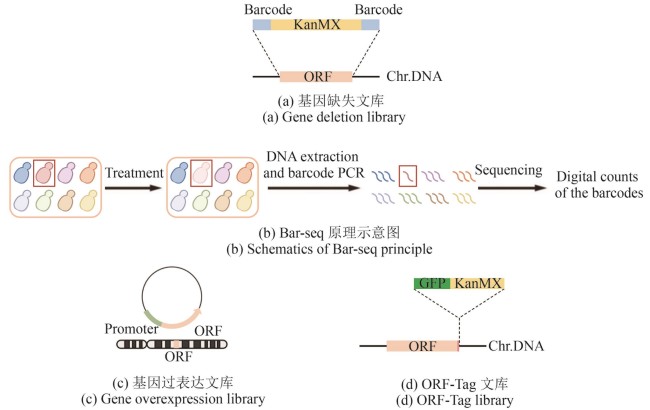
Fig. 1 Schematics for constructing classical libraries (created by biorender)[(a) In the gene deletion library, the ORF (orange fragment) of target gene is replaced by the KanMX (kanamycin resistance selection marker, yellow fragment), flanked by unique barcodes (blue fragments). Chr.DNA: chromosomal DNA.(b) Schematic diagram of the Bar-seq principle. Under specific treatment conditions, the target strain (red) shows reduced growth (light pink), which is reflected by a lower read count of its corresponding barcode during sequencing (fewer red lines compared to others).(c) In the gene overexpression library, the ORF (orange fragment) of target gene is not only expressed from its endogenous locus but is also additionally expressed from a plasmid, driven by a constitutive promoter (light green fragment).(d) In the ORF-Tag library, the C-terminus of the target gene ORF (orange fragment), with its stop codon removed, is fused to the fluorescent protein GFP (dark green fragment) and the selection marker KanMX (yellow fragment).]
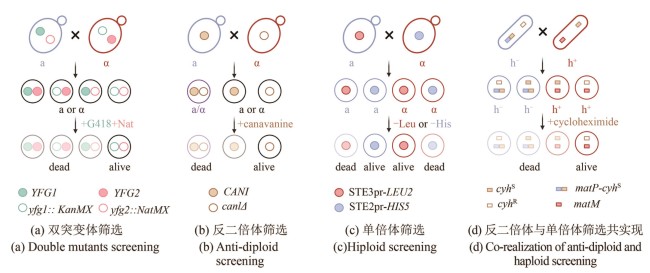
Fig. 2 Schematics for SGA and PEM methods (created by biorender)[(a) Double mutant selection strategy. Two mating-type cells each carry different resistance markers at their respective mutation sites: KanMX (green hollow circle) and NatMX (pink hollow circle). These allow for the selection of double mutant progeny (outlined in black). YFG (your favorite gene): target gene of interest.(b) Counter-diploid selection strategy. Haploid cells carrying a wild-type CAN1 gene (blue, a-type) and diploid cells (purple) can uptake the toxic analog canavanine and are killed, while can1Δ mutants cannot transport canavanine and thus survive (outlined in black).(c) Haploid selection strategy. A mating-type-specific promoter is used to drive the expression of a nutritional selection marker in the opposite mating type, allowing selection of haploid progeny of a specific mating type. For example, when an a-type parent cell (blue), harboring a gene cassette expressing STE3pr-LEU2 (red solid circle) — which is only active in α-type cell — mates with another cell, only the α-type progeny that inherit this construct (outlined in red with a red solid circle) will survive.(d) Combined counter-diploid and haploid selection strategy. A dominant-lethal resistance gene, cyhS (brown solid square), is inserted near the mat1 mating-type locus to link its expression with a specific haploid phenotype. For example, insertion near matP (blue square) in h- cells (blue) leads to the death of cyhS -containing h- haploids and diploids, enabling selection of h+ haploids.]
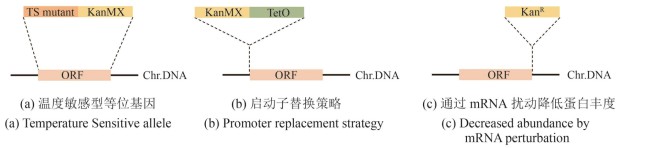
Fig. 3 Construction of conditional allele libraries (created by biorender)[(a) In the temperature-sensitive (TS) allele strategy, the ORF (orange fragment) of target gene is replaced with a corresponding TS mutant (dark orange fragment) and tagged with a KanMX resistance marker (yellow fragment). Chr.DNA: chromosomal DNA.(b) In the promoter replacement strategy, an inducible promoter (green fragment) and a KanMX resistance marker (yellow fragment) is inserted upstream of the start codon of the target gene ORF (orange fragment). Chr.DNA: chromosomal DNA.(c) In the DAmP (Decreased Abundance by mRNA Perturbation) strategy, the 3′UTR of the target gene ORF (orange fragment) is disrupted by insertion of a KanR resistance cassette (yellow fragment) to reduce transcript stability and protein abundance. Chr.DNA: chromosomal DNA.]
| 1 | PRZYBYLA L, GILBERT L A. A new era in functional genomics screens[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2022, 23(2): 89-103. |
| 2 | GALANIE S, THODEY K, TRENCHARD I J, et al. Complete biosynthesis of opioids in yeast[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6252): 1095-1100. |
| 3 | RUNGUPHAN W, KEASLING J D. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of fatty acid-derived biofuels and chemicals[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 21: 103-113. |
| 4 | SHENG J Y, FENG X Y. Metabolic engineering of yeast to produce fatty acid-derived biofuels: bottlenecks and solutions[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 554. |
| 5 | SAMAL S K, PREETAM S. Synthetic biology: refining human health[M/OL]//SUAR M, MISRA N, DASH C. Microbial engineering for therapeutics. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2022: 57-70 [2024-11-01]. . |
| 6 | TSAI C S, KWAK S, TURNER T L, et al. Yeast synthetic biology toolbox and applications for biofuel production[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2015, 15(1): 1-15. |
| 7 | GOFFEAU A, BARRELL B G, BUSSEY H, et al. Life with 6000 genes[J]. Science, 1996, 274(5287): 546-567. |
| 8 | ARITA Y, KIM G, LI Z J, et al. A genome-scale yeast library with inducible expression of individual genes[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2021, 17(6): e10207. |
| 9 | WOOD V, GWILLIAM R, RAJANDREAM M A, et al. The genome sequence of Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6874): 871-880. |
| 10 | GREWAL S I S, JIA S T. Heterochromatin revisited[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2007, 8(1): 35-46. |
| 11 | ROGUEV A, RYAN C J, HARTSUIKER E, et al. High-throughput quantitative genetic interaction mapping in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2018, 2018(2): pdb.top079905. |
| 12 | ZHANG W, GENG A L. Improved ethanol production by a xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strain constructed through a modified genome shuffling method[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2012, 5(1): 46. |
| 13 | BOTSTEIN D, FINK G R. Yeast: an experimental organism for 21st century biology[J]. Genetics, 2011, 189(3): 695-704. |
| 14 | RODRIGUEZ A, STRUCKO T, STAHLHUT S G, et al. Metabolic engineering of yeast for fermentative production of flavonoids[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 1645-1654. |
| 15 | MYBURGH M W, FAVARO L, VAN ZYL W H, et al. Engineered yeast for the efficient hydrolysis of polylactic acid[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 378: 129008. |
| 16 | CHEN J S, BECKLEY J R, MCDONALD N A, et al. Identification of new players in cell division, DNA damage response, and morphogenesis through construction of Schizosaccharomyces pombe deletion strains[J]. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics, 2015, 5(3): 361-370. |
| 17 | TURCO G, CHANG C, WANG R Y, et al. Global analysis of the yeast knockout phenome[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(21): eadg5702. |
| 18 | KIM D U, HAYLES J, KIM D, et al. Analysis of a genome-wide set of gene deletions in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2010, 28(6): 617-623. |
| 19 | SCHERENS B, GOFFEAU A. The uses of genome-wide yeast mutant collections[J]. Genome Biology, 2004, 5(7): 229. |
| 20 | GIAEVER G, NISLOW C. The yeast deletion collection: a decade of functional genomics[J]. Genetics, 2014, 197(2): 451-465. |
| 21 | SOPKO R, HUANG D Q, PRESTON N, et al. Mapping pathways and phenotypes by systematic gene overexpression[J]. Molecular Cell, 2006, 21(3): 319-330. |
| 22 | MATSUYAMA A, ARAI R, YASHIRODA Y, et al. ORFeome cloning and global analysis of protein localization in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006, 24(7): 841-847. |
| 23 | TONG A H, EVANGELISTA M, PARSONS A B, et al. Systematic genetic analysis with ordered arrays of yeast deletion mutants[J]. Science, 2001, 294(5550): 2364-2368. |
| 24 | ROGUEV A, WIREN M, WEISSMAN J S, et al. High-throughput genetic interaction mapping in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Nature Methods, 2007, 4(10): 861-866. |
| 25 | GIAEVER G, CHU A M, NI L, et al. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome[J]. Nature, 2002, 418(6896): 387-391. |
| 26 | HWANG Y C, LIN C C, CHANG J Y, et al. Predicting essential genes based on network and sequence analysis[J]. Molecular BioSystems, 2009, 5(12): 1672-1678. |
| 27 | JEONG H, MASON S P, BARABÁSI A L, et al. Lethality and centrality in protein networks[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6833): 41-42. |
| 28 | LI Z J, VIZEACOUMAR F J, BAHR S, et al. Systematic exploration of essential yeast gene function with temperature-sensitive mutants[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29(4): 361-367. |
| 29 | SHORTLE D, NOVICK P, BOTSTEIN D. Construction and genetic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutant alleles of the yeast actin gene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(15): 4889-4893. |
| 30 | BEN-AROYA S, COOMBES C, KWOK T, et al. Toward a comprehensive temperature-sensitive mutant repository of the essential genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Molecular Cell, 2008, 30(2): 248-258. |
| 31 | POULTNEY C S, BUTTERFOSS G L, GUTWEIN M R, et al. Rational design of temperature-sensitive alleles using computationalstructure prediction[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e23947. |
| 32 | CHAKSHUSMATHI G, MONDAL K, LAKSHMI G S, et al. Design of temperature-sensitive mutants solely from amino acid sequence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(21): 7925-7930. |
| 33 | TAN G H, CHEN M, FOOTE C, et al. Temperature-sensitive mutations made easy: generating conditional mutations by using temperature-sensitive inteins that function within different temperature ranges[J]. Genetics, 2009, 183(1): 13-22. |
| 34 | WIDLUND P O, DAVIS T N. A high-efficiency method to replace essential genes with mutant alleles in yeast[J]. Yeast, 2005, 22(10): 769-774. |
| 35 | KOFOED M, MILBURY K L, CHIANG J H, et al. An updated collection of sequence barcoded temperature-sensitive alleles of yeast essential genes[J]. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics, 2015, 5(9): 1879-1887. |
| 36 | MNAIMNEH S, DAVIERWALA A P, HAYNES J, et al. Exploration of essential gene functions via titratable promoter alleles[J]. Cell, 2004, 118(1): 31-44. |
| 37 | BRESLOW D K, CAMERON D M, COLLINS S R, et al. A comprehensive strategy enabling high-resolution functional analysis of the yeast genome[J]. Nature Methods, 2008, 5(8): 711-718. |
| 38 | SCHULDINER M, COLLINS S R, THOMPSON N J, et al. Exploration of the function and organization of the yeast early secretory pathway through an epistatic miniarray profile[J]. Cell, 2005, 123(3): 507-519. |
| 39 | LIU G W, YONG M Y J, YURIEVA M, et al. Gene essentiality is a quantitative property linked to cellular evolvability[J]. Cell, 2015, 163(6): 1388-1399. |
| 40 | GUO Y B, PARK J M, CUI B W, et al. Integration profiling of gene function with dense maps of transposon integration[J]. Genetics, 2013, 195(2): 599-609. |
| 41 | EVERTTS A G, PLYMIRE C, CRAIG N L, et al. The Hermes transposon of Musca domestica is an efficient tool for the mutagenesis of Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Genetics, 2007, 177(4): 2519-2523. |
| 42 | PARK J M, EVERTTS A G, LEVIN H L. The Hermes transposon of Musca domestica and its use as a mutagen of Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Methods, 2009, 49(3): 243-247. |
| 43 | GANGADHARAN S, MULARONI L, FAIN-THORNTON J, et al. DNA transposon Hermes inserts into DNA in nucleosome-free regions in vivo [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(51): 21966-21972. |
| 44 | CAIN A K, BARQUIST L, GOODMAN A L, et al. A decade of advances in transposon-insertion sequencing[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2020, 21(9): 526-540. |
| 45 | MICHEL A H, HATAKEYAMA R, KIMMIG P, et al. Functional mapping of yeast genomes by saturated transposition[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e23570. |
| 46 | BLAKE BILLMYRE R, EICKBUSH M T, CRAIG C J, et al. Genome-wide quantification of contributions to sexual fitness identifies genes required for spore viability and health in fission yeast[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2022, 18(10): e1010462. |
| 47 | ADAMES N R, GALLEGOS J E, PECCOUD J. Yeast genetic interaction screens in the age of CRISPR/Cas[J]. Current Genetics, 2019, 65(2): 307-327. |
| 48 | LI L, LIU X C, WEI K K, et al. Synthetic biology approaches for chromosomal integration of genes and pathways in industrial microbial systems[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(5): 730-745. |
| 49 | GASIUNAS G, BARRANGOU R, HORVATH P, et al. Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(39): E2579-E2586. |
| 50 | QI L S, LARSON M H, GILBERT L A, et al. Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression[J]. Cell, 2021, 184: 844. |
| 51 | LIAN J Z, HAMEDIRAD M, HU S M, et al. Combinatorial metabolic engineering using an orthogonal tri-functional CRISPR system[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 1688. |
| 52 | GUO X G, CHAVEZ A, TUNG A, et al. High-throughput creation and functional profiling of DNA sequence variant libraries using CRISPR-Cas9 in yeast[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(6): 540-546. |
| 53 | SI T, CHAO R, MIN Y H, et al. Automated multiplex genome-scale engineering in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15187. |
| 54 | SAKAI A, SHIMIZU Y, HISHINUMA F. Integration of heterologous genes into the chromosome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a delta sequence of yeast retrotransposon Ty[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1990, 33(3): 302-306. |
| 55 | DICARLO J E, CONLEY A J, PENTTILÄ M, et al. Yeast oligo-mediated genome engineering (YOGE)[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(12): 741-749. |
| 56 | BARBIERI E M, MUIR P, AKHUETIE-ONI B O, et al. Precise editing at DNA replication forks enables multiplex genome engineering in eukaryotes[J]. Cell, 2017, 171(6): 1453-1467.e13. |
| 57 | JAKOČIŪNAS T, RAJKUMAR A S, ZHANG J, et al. CasEMBLR: Cas9-facilitated multiloci genomic integration of in vivo assembled DNA parts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(11): 1226-1234. |
| 58 | LIU R M, LIANG L Y, CHOUDHURY A, et al. Multiplex navigation of global regulatory networks (MINR) in yeast for improved ethanol tolerance and production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 51: 50-58. |
| 59 | KUZMIN E, VANDERSLUIS B, NGUYEN BA A N, et al. Exploring whole-genome duplicate gene retention with complex genetic interaction analysis[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6498): eaaz5667. |
| 60 | PENG J R. Gene redundancy and gene compensation: an updated view[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2019, 46(7): 329-333. |
| 61 | MERZ S, WESTERMANN B. Genome-wide deletion mutant analysis reveals genes required for respiratory growth, mitochondrial genome maintenance and mitochondrial protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Genome Biology, 2009, 10(9): R95. |
| 62 | LOUCA S, POLZ M F, MAZEL F, et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2018, 2(6): 936-943. |
| 63 | BIDLINGMAIER S, LIU B. Construction of yeast surface-displayed cDNA libraries[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2011, 729: 199-210. |
| 64 | LIU Z H, TYO K E J, MARTÍNEZ J L, et al. Different expression systems for production of recombinant proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2012, 109(5): 1259-1268. |
| 65 | SMITH V, BOTSTEIN D, BROWN P O. Genetic footprinting: a genomic strategy for determining a gene’s function given its sequence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1995, 92(14): 6479-6483. |
| 66 | SMITH V, CHOU K N, LASHKARI D, et al. Functional analysis of the genes of yeast chromosome Ⅴ by genetic footprinting[J]. Science, 1996, 274(5295): 2069-2074. |
| 67 | HAN T X, XU X Y, ZHANG M J, et al. Global fitness profiling of fission yeast deletion strains by barcode sequencing[J]. Genome Biology, 2010, 11(6): R60. |
| 68 | STEINMETZ L M, SCHARFE C, DEUTSCHBAUER A M, et al. Systematic screen for human disease genes in yeast[J]. Nature Genetics, 2002, 31(4): 400-404. |
| 69 | WARRINGER J, ERICSON E, FERNANDEZ L, et al. High-resolution yeast phenomics resolves different physiological features in the saline response[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(26): 15724-15729. |
| 70 | BIRRELL G W, BROWN J A, IRENE WU H, et al. Transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to DNA-damaging agents does not identify the genes that protect against these agents[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(13): 8778-8783. |
| 71 | CHANG M, BELLAOUI M, BOONE C, et al. A genome-wide screen for methyl methanesulfonate-sensitive mutants reveals genes required for S phase progression in the presence of DNA damage[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(26): 16934-16939. |
| 72 | PARSONS A B, BROST R L, DING H M, et al. Integration of chemical-genetic and genetic interaction data links bioactive compounds to cellular target pathways[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(1): 62-69. |
| 73 | PARSONS A B, LOPEZ A, GIVONI I E, et al. Exploring the mode-of-action of bioactive compounds by chemical-genetic profiling in yeast[J]. Cell, 2006, 126(3): 611-625. |
| 74 | ENYENIHI A H, SAUNDERS W S. Large-scale functional genomic analysis of sporulation and meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Genetics, 2003, 163(1): 47-54. |
| 75 | MATECIC M, SMITH D L, PAN X W, et al. A microarray-based genetic screen for yeast chronological aging factors[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2010, 6(4): e1000921. |
| 76 | ROMILA C A, TOWNSEND S, MALECKI M, et al. Barcode sequencing and a high-throughput assay for chronological lifespan uncover ageing-associated genes in fission yeast[J]. Microbial Cell, 2021, 8(7): 146-160. |
| 77 | FERRARI S, BERETTA S, JACOB A, et al. BAR-Seq clonal tracking of gene-edited cells[J]. Nature Protocols, 2021, 16(6): 2991-3025. |
| 78 | RALLIS C, LÓPEZ-MAURY L, GEORGESCU T, et al. Systematic screen for mutants resistant to TORC1 inhibition in fission yeast reveals genes involved in cellular ageing and growth[J]. Biology Open, 2014, 3(2): 161-171. |
| 79 | KENNEDY P J, VASHISHT A A, HOE K L, et al. A genome-wide screen of genes involved in cadmium tolerance in Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2008, 106(1): 124-139. |
| 80 | RODRÍGUEZ-LÓPEZ M, BORDIN N, LEES J, et al. Broad functional profiling of fission yeast proteins using phenomics and machine learning[J]. eLife, 2023, 12: RP88229. |
| 81 | NI L, SNYDER M. A genomic study of the bipolar bud site selection pattern in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2001, 12(7): 2147-2170. |
| 82 | KELLY F D, NURSE P. Spatial control of Cdc42 activation determines cell width in fission yeast[J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2011, 22(20): 3801-3811. |
| 83 | NAVARRO F J, NURSE P. A systematic screen reveals new elements acting at the G2/M cell cycle control[J]. Genome Biology, 2012, 13(5): R36. |
| 84 | BLYTH J, MAKRANTONI V, BARTON R E, et al. Genes important for Schizosaccharomyces pombe meiosis identified through a functional genomics screen[J]. Genetics, 2018, 208(2): 589-603. |
| 85 | DESHPANDE G P, HAYLES J, HOE K L, et al. Screening a genome-wide S. pombe deletion library identifies novel genes and pathways involved in genome stability maintenance[J]. DNA Repair, 2009, 8(5): 672-679. |
| 86 | PAN X, LEI B K, ZHOU N, et al. Identification of novel genes involved in DNA damage response by screening a genome-wide Schizosaccharomyces pombe deletion library[J]. BMC Genomics, 2012, 13: 662. |
| 87 | COSTANZO M, VANDERSLUIS B, KOCH E N, et al. A global genetic interaction network maps a wiring diagram of cellular function[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6306): aaf1420. |
| 88 | ROSS-MACDONALD P, COELHO P S, ROEMER T, et al. Large-scale analysis of the yeast genome by transposon tagging and gene disruption[J]. Nature, 1999, 402(6760): 413-418. |
| 89 | WHITE W H, JOHNSON D I. Characterization of synthetic-lethal mutants reveals a role for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae guanine-nucleotide exchange factor Cdc24p in vacuole function and Na+ tolerance[J]. Genetics, 1997, 147(1): 43-55. |
| 90 | HUH W K, FALVO J V, GERKE L C, et al. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast[J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6959): 686-691. |
| 91 | RAZDAIBIEDINA A, BRECHALOV A, FRIESEN H, et al. PIFiA: self-supervised approach for protein functional annotation from single-cell imaging data[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2024, 20(5): 521-548. |
| 92 | CHONG Y T, KOH J L Y, FRIESEN H, et al. Yeast proteome dynamics from single cell imaging and automated analysis[J]. Cell, 2015, 161: 1413-1424 |
| 93 | HAYASHI A, DING D Q, TSUTSUMI C, et al. Localization of gene products using a chromosomally tagged GFP-fusion library in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Genes to Cells, 2009, 14(2): 217-225. |
| 94 | JIA B, WU Y, LI B Z, et al. Precise control of SCRaMbLE in synthetic haploid and diploid yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1933. |
| 95 | SI T, LUO Y Z, BAO Z H, et al. RNAi-assisted genome evolution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for complex phenotype engineering[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(3): 283-291. |
| 96 | ZENG W Z, GUO L K, XU S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 888-906. |
| 97 | RUGBJERG P, SOMMER M O A. Overcoming genetic heterogeneity in industrial fermentations[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(8): 869-876. |
| 98 | WEHRS M, TANJORE D, ENG T, et al. Engineering robust production microbes for large-scale cultivation[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2019, 27(6): 524-537. |
| 99 | JAKOČIŪNAS T, BONDE I, HERRGÅRD M, et al. Multiplex metabolic pathway engineering using CRISPR/Cas9 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 28: 213-222. |
| 100 | LI Y H, MOLYNEAUX N, ZHANG H T, et al. A multiplexed, three-dimensional pooling and next-generation sequencing strategy for creating barcoded mutant arrays: construction of a Schizosaccharomyces pombe transposon insertion library[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(17): e102. |
| 101 | COOPE R J N, MATIC N, PANDOH P K, et al. Automated library construction and analysis for high-throughput nanopore sequencing of SARS-CoV-2[J]. The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine, 2022, 7(5): 1025-1036. |
| 102 | SANTACRUZ D, ENANE F O, FUNDEL-CLEMENS K, et al. Automation of high-throughput mRNA-seq library preparation: a robust, hands-free and time efficient methodology[J]. SLAS Discovery, 2022, 27(2): 140-147. |
| 103 | VAN DEVENTER J A, WITTRUP K D. Yeast surface display for antibody isolation: library construction, library screening, and affinity maturation[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2014, 1131: 151-181. |
| 104 | YOFE I, WEILL U, MEURER M, et al. One library to make them all: streamlining the creation of yeast libraries via a SWAp-tag strategy[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(4): 371-378. |
| 105 | COSTANZO M, HOU J, MESSIER V, et al. Environmental robustness of the global yeast genetic interaction network[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6542): eabf8424. |
| 106 | KUZMIN E, VANDERSLUIS B, WANG W, et al. Systematic analysis of complex genetic interactions[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6386): eaao1729. |
| 107 | PENNISI E. Building the ultimate yeast genome[J]. Science, 2014, 343(6178): 1426-1429. |
| 108 | ZHAO Y, COELHO C, HUGHES A L, et al. Debugging and consolidating multiple synthetic chromosomes reveals combinatorial genetic interactions[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(24): 5220-5236.e16. |
| 109 | SCHINDLER D, WALKER R S K, JIANG S Y, et al. Design, construction, and functional characterization of a tRNA neochromosome in yeast[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(24): 5237-5253.e22. |
| 110 | ZHANG W M, LAZAR-STEFANITA L, YAMASHITA H, et al. Manipulating the 3D organization of the largest synthetic yeast chromosome[J]. Molecular Cell, 2023, 83(23): 4424-4437.e5. |
| 111 | DAI J B, BOEKE J D, LUO Z Q, et al. Sc3.0: revamping and minimizing the yeast genome[J]. Genome Biology, 2020, 21(1): 205. |
| 112 | SHAO Y Y, LU N, WU Z F, et al. Creating a functional single-chromosome yeast[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 331-335. |
| 113 | WANG P, LIN Y, ZOU C J, et al. Construction and screening of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol protein deletion library in Pichia pastoris [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2020, 20(1): 262. |
| [1] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [2] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [3] | LI Yongzhu, CHEN Yu. Advances and prospects in genome-scale models of yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 585-602. |
| [4] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [5] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [6] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [7] | GAO Qi, XIAO Wenhai. Advances in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes by yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 357-372. |
| [8] | SHENG Zhouhuang, CHEN Zhixian, ZHANG Yan. Research progress of yeast mannoproteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [9] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [11] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [12] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [13] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [14] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| [15] | ZUO Yimeng, ZHANG Jiaojiao, LIAN Jiazhang. Enabling technology for the biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 233-253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||