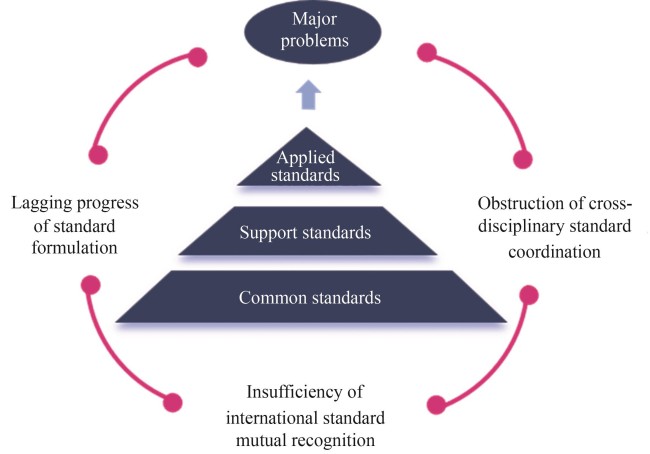
Biomanufacturing represents a strategic frontier in the global technological revolution and industrial transformation, disruptively reshaping how we produce various products such as biofuels, bioenergy, biobased chemicals, and biomaterials through the convergence of synthetic biology, artificial intelligence, and other cutting-edge technologies. However, the persistent lack of comprehensive standardization frameworks in this emerging field poses significant challenges. Standardization in biomanufacturing is essential for accelerating scientific discovery, enhancing production efficiency, and ensuring sustainable industry growth. Therefore, major global economies have prioritized biomanufacturing standardization as a critical element of national competitiveness. The United States, through the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), has established itself as a global leader in developing standards for data, metrology, intelligent algorithms, and automated facilities. NIST spearheads numerous ISO standards in biotechnology and biomanufacturing that shape international practices. In the United Kingdom, the Centre for Engineering Biology Metrology and Standards formulates roadmaps to guide the development of metrology and standards for engineering biological species. The European Union fosters the standards in metrology, chassis, yeast, and other eukaryotic systems through the International Cooperation for Synthetic Biology Standardization Project (BioRoBoost). The European Committee for Standardization has been particularly active in developing and updating standards for biomaterials and biobased products including wood-derived products, while establishing corresponding product classification rules. Since launching its 14th Five-Year Plan, China has strategically prioritized the development of standardization for biomanufacturing across the entire value chain, including key components such as sensors, production equipment like bioreactors, and operational processes such as production technical specifications. Furthermore, China has implemented a series of standards for product quality control, testing methods, and evaluation procedures across various biomanufacturing application sectors, including food, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and others. This article presents a comprehensive assessment on the development of biomanufacturing standardization worldwide and in China. At the international level, we focus on standards issued by major international organizations in three major categories: basic commonalities, enabling technologies, and application fields. At the domestic level, our analysis is based on systematic data mining from China Standards Service Network. Our findings reveal several notable patterns. First, the distribution of standard types shows a clear hierarchical structure, with association standards comprising the majority, which highlights the pivotal role of professional organizations in driving technical integration and standardization. Second, we observed substantial variations in standardization maturity across application sectors. Biobased materials currently possess the most comprehensive portfolio with standards for standardization, followed by rapid progress in biobanking and active pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturing. Based on the current status, we identifies major challenges including the lagging of standard formulation, the obstruction of cross-disciplinary standard coordination, and the insufficiency of mutual recognition for international standards, through multi-dimensional analysis encompassing technological development, industrial ecosystem, and international collaboration. To address these challenges, we propose a strategic framework for developing biomanufacturing standards, including the construction of a dynamic standard transformation mechanism, the establishment of a cross-sector standard coordination platform, and the implementation of a standard internationalization plan. These recommendations provide both theoretical foundations and decision-making references for accelerating the development of biomanufacturing standardization system in China. By facilitating the transition from technology-driven to standard-led development in biomanufacturing, this framework aims to help secure China’s competitiveness in the global economy.