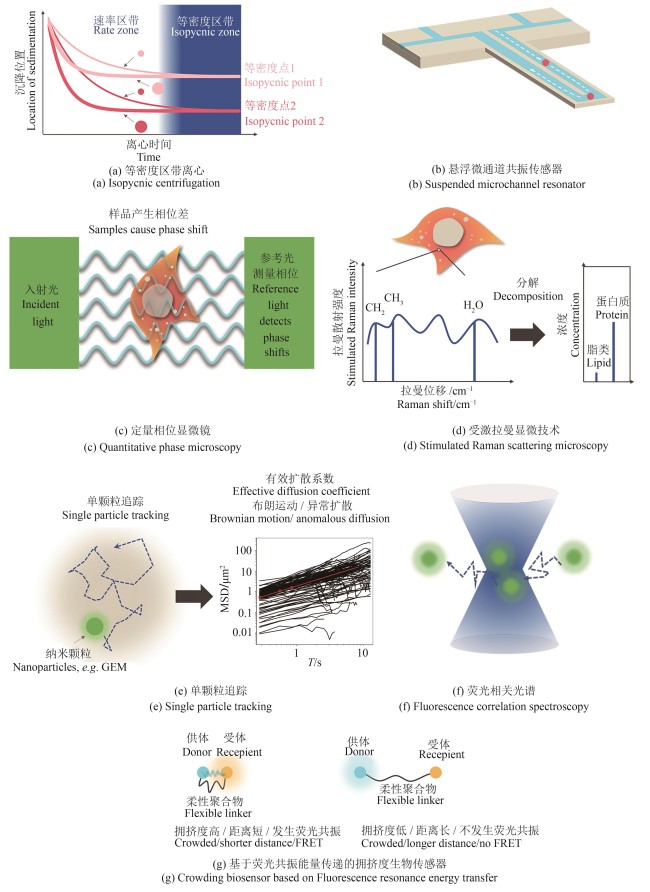
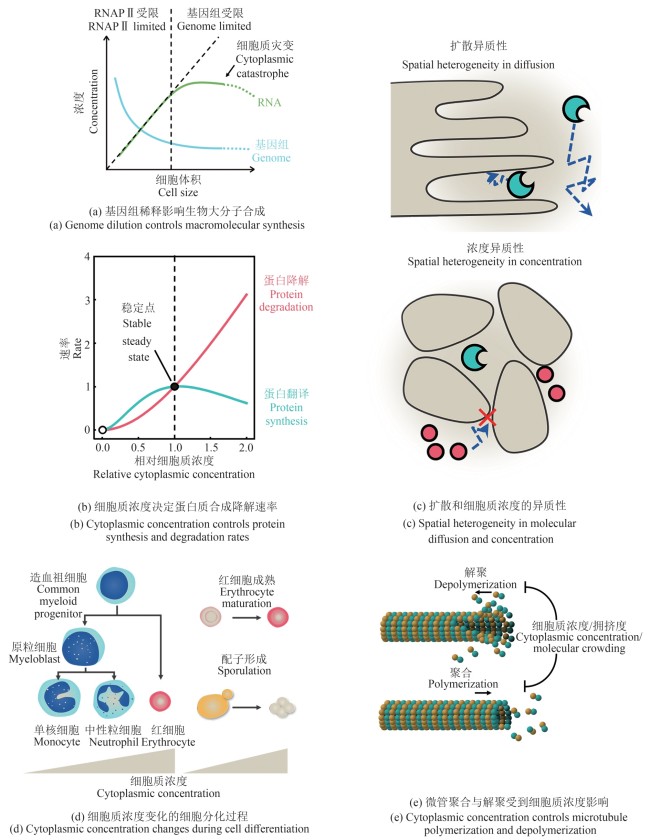
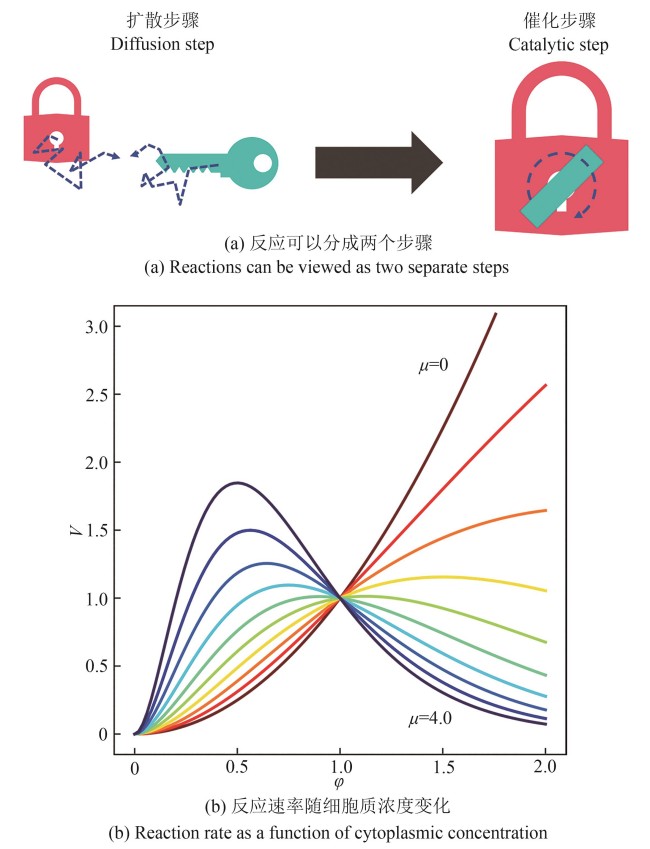
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (3): 497-515.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-086
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cytoplasmic concentration: an old question and a new parameter in cell biology
LI Qian1, FERRELL JR. James E.2,3, CHEN Yuping1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Quantitative Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.Department of Chemical and Systems Biology,School of Medicine,Stanford University,Stanford 94305,California,USA
3.Department of Biochemistry,School of Medicine,Stanford University,Stanford 94305,California,USA
-
Received:2024-12-02Revised:2025-03-04Online:2025-06-27Published:2025-06-30 -
Contact:CHEN Yuping
细胞质浓度:细胞生物学的老问题、新参数
李倩1, FERRELL JR.James E.2,3, 陈于平1
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,定量合成生物学全国重点实验室,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,广东 深圳 518055
2.斯坦福大学医学院化学与系统生物学系,美国 加利福尼亚州 斯坦福 94305
3.斯坦福大学医学院生物化学系,美国 加利福尼亚州 斯坦福 94305
-
通讯作者:陈于平 -
作者简介:李倩 (1998—),女,科研助理。研究方向为细胞质浓度稳态调控。E-mail:qian.li2@siat.ac.cn陈于平 (1990—),男,副研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为细胞质稳态调控。 E-mail:yp.chen3@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2024YFA0919600);深圳合成生物学研究所启动经费项目(HSE49901)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Qian, FERRELL JR. James E., CHEN Yuping. Cytoplasmic concentration: an old question and a new parameter in cell biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 497-515.
李倩, FERRELL JR.James E., 陈于平. 细胞质浓度:细胞生物学的老问题、新参数[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 497-515.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-086
| 细胞生理 | 细胞质浓度 (变化前为100%) | 浓度变化原因 | 后果 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有丝分裂肿胀 | 80%~90% | 未知 | 未知 | [ |
| 配子成熟 | 增加 | 排水 | 配子抗逆性增加 | [ |
| 血细胞成熟 | 增加或减少;血红细胞细胞质浓度最大;单核细胞其次 | 血红细胞:血红蛋白大量合成 | 血红细胞携氧量增加 | [ |
| [ | ||||
| 渗透压 | 64%~155% | 渗透压改变 | 微管聚合速率变化范围64%~477%;微管解聚速率变化范围42%~645% | [ |
| 翻译/降解 | 10%~200% | 人工浓缩、稀释 | 翻译速度先增加后降低,降解速度增加 | [ |
| 基因组稀释 | cdc28-13突变体:66% | 限制温度培养,细胞周期停滞,细胞体积增加 | 基因表达激活停滞;基因组稳定性降低 | [ |
| 衰老 | hTERT-RPE1细胞:降低(体积增至588%);MCF7细胞:降低(体积增至262%) | Palbociclib处理,细胞体积增加 | 激活p53-p21信号传导;53BP1不再修复DNA损伤;有丝分裂失败;基因组不稳定性;细胞周期永久退出 | [ |
Table 1 Physiological processes affecting cytoplasmic concentration
| 细胞生理 | 细胞质浓度 (变化前为100%) | 浓度变化原因 | 后果 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有丝分裂肿胀 | 80%~90% | 未知 | 未知 | [ |
| 配子成熟 | 增加 | 排水 | 配子抗逆性增加 | [ |
| 血细胞成熟 | 增加或减少;血红细胞细胞质浓度最大;单核细胞其次 | 血红细胞:血红蛋白大量合成 | 血红细胞携氧量增加 | [ |
| [ | ||||
| 渗透压 | 64%~155% | 渗透压改变 | 微管聚合速率变化范围64%~477%;微管解聚速率变化范围42%~645% | [ |
| 翻译/降解 | 10%~200% | 人工浓缩、稀释 | 翻译速度先增加后降低,降解速度增加 | [ |
| 基因组稀释 | cdc28-13突变体:66% | 限制温度培养,细胞周期停滞,细胞体积增加 | 基因表达激活停滞;基因组稳定性降低 | [ |
| 衰老 | hTERT-RPE1细胞:降低(体积增至588%);MCF7细胞:降低(体积增至262%) | Palbociclib处理,细胞体积增加 | 激活p53-p21信号传导;53BP1不再修复DNA损伤;有丝分裂失败;基因组不稳定性;细胞周期永久退出 | [ |
| 1 | WILSON E B. The Cell in development and inheritance[M]. New York: The MacMillan Company, 1896. |
| 2 | MILO R, PHILLIPS R. Cell biology by the numbers[M/OL]. New York: Garland Science, 2015. (2015-12-07)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 3 | NATHANS D, SMITH H O. Restriction endonucleases in the analysis and restructuring of DNA molecules[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 1975, 44: 273-293. |
| 4 | CHIEN A, EDGAR D B, TRELA J M. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from the extreme thermophile Thermus aquaticus [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1976, 127(3): 1550-1557. |
| 5 | ALBERTS B. Molecular biology of the cell[M/OL]. New York: Garland Science, 2017. (2017-08-07)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 6 | JACKSON D A, SYMONS R H, BERG P. Biochemical method for inserting new genetic information into DNA of Simian virus 40: circular SV40 DNA molecules containing lambda phage genes and the galactose operon of Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1972, 69(10): 2904-2909 |
| 7 | PRASHER D C, ECKENRODE V K, WARD W W, et al. Primary structure of the Aequorea victoria green-fluorescent protein[J]. Gene, 1992, 111(2): 229-233. |
| 8 | JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6096): 816-821. |
| 9 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 10 | TRUNNELL N B, POON A C, KIM S Y, et al. Ultrasensitivity in the regulation of Cdc25C by Cdk1[J]. Molecular Cell, 2011, 41(3): 263-274. |
| 11 | PARDEE A B, JACOB F, MONOD J. The genetic control and cytoplasmic expression of “Inducibility” in the synthesis of β-galactosidase by E. coli [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1959, 1(2): 165-178. |
| 12 | KANEHISA M. Enzyme annotation and metabolic reconstruction using KEGG[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2017, 1611: 135-145. |
| 13 | CHEN Y P, HUANG J H, PHONG C, et al. Viscosity-dependent control of protein synthesis and degradation[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 2149. |
| 14 | ALRIC B, FORMOSA-DAGUE C, DAGUE E, et al. Macromolecular crowding limits growth under pressure[J]. Nature Physics, 2022, 18(4): 411-416. |
| 15 | MOLINES A T, LEMIÈRE J, GAZZOLA M, et al. Physical properties of the cytoplasm modulate the rates of microtubule polymerization and depolymerization[J]. Developmental Cell, 2022, 57(4): 466-479.e6. |
| 16 | WEBB B A, CHIMENTI M, JACOBSON M P, et al. Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2011, 11(9): 671-677. |
| 17 | ELOWITZ M B, SURETTE M G, WOLF P E, et al. Protein mobility in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1999, 181(1): 197-203. |
| 18 | BEGASSE M L, LEAVER M, VAZQUEZ F, et al. Temperature dependence of cell division timing accounts for a shift in the thermal limits of C. elegans and C. briggsae [J]. Cell Reports, 2015, 10(5): 647-653. |
| 19 | PERSSON L B, AMBATI V S, BRANDMAN O. Cellular control of viscosity counters changes in temperature and energy availability[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(6): 1572-1585.e16. |
| 20 | MINTON A P. Implications of macromolecular crowding for protein assembly[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2000, 10(1): 34-39. |
| 21 | HARRIS R F. Effect of water potential on microbial growth and activity[M/OL]//PARR J F, GARDNER W R, ELLIOTT L F. Water potential relations in soil microbiology. New York: Wiley, 2015: 23-95. (2015-10-25)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 22 | CHAKRABARTI B, RACHH M, SHVARTSMAN S Y, et al. Cytoplasmic stirring by active carpets[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(30): e2405114121. |
| 23 | BRANGWYNNE C P, KOENDERINK G H, MACKINTOSH F C, et al. Cytoplasmic diffusion: molecular motors mix it up[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 2008, 183(4): 583-587. |
| 24 | BRANGWYNNE C P, KOENDERINK G H, MACKINTOSH F C, et al. Intracellular transport by active diffusion[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 2009, 19(9): 423-427. |
| 25 | NEUROHR G E, AMON A. Relevance and regulation of cell density[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 2020, 30(3): 213-225. |
| 26 | DILL K A, GHOSH K, SCHMIT J D. Physical limits of cells and proteomes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(44): 17876-17882. |
| 27 | ELLIS R J. Macromolecular crowding: obvious but underappreciated[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2001, 26(10): 597-604. |
| 28 | GUO M, PEGORARO A F, MAO A, et al. Cell volume change through water efflux impacts cell stiffness and stem cell fate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(41): E8618-E8627. |
| 29 | CADART C, BARTZ J, OAKS G, et al. Polyploidy in Xenopus lowers metabolic rate by decreasing total cell surface area[J]. Current Biology, 2023, 33(9): 1744-1752.e7. |
| 30 | CADART C, VENKOVA L, RECHO P, et al. The physics of cell-size regulation across timescales[J]. Nature Physics, 2019, 15(10): 993-1004. |
| 31 | MINTON A P. The influence of macromolecular crowding and macromolecular confinement on biochemical reactions in physiological media[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(14): 10577-10580. |
| 32 | LEMIÈRE J, REAL-CALDERON P, HOLT L J, et al. Control of nuclear size by osmotic forces in Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. eLife, 2022, 11: e76075. |
| 33 | HARTWELL L H. Periodic density fluctuation during the yeast cell cycle and the selection of synchronous cultures[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1970, 104(3): 1280-1285. |
| 34 | RAHMAN Y E, ELSON D L, CERNY E A. Studies on the mechanism of erythrocyte aging and destruction. Ⅰ. Separation of rat erythrocytes according to age by Ficoll gradient centrifugation[J]. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 1973, 2(2): 141-150. |
| 35 | SEGAL A W, FORTUNATO A, HERD T. A rapid single centrifugation step method for the separation of erythrocytes, granulocytes and mononuclear cells on continous density gradients of percoll[J]. Journal of Immunological Methods, 1980, 32(3): 209-214. |
| 36 | CATSIMPOOLAS N. Methods of cell separation[M/OL]. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. (2012-12-06)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 37 | KRUGER N J. The Bradford method for protein quantitation[M/OL]//WALKER J M. The protein protocols handbook. Springer protocols handbooks. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2009: 17-24 [2024-12-01]. . |
| 38 | NOBLE J E, BAILEY M J A. Chapter 8 quantitation of protein[M/OL]//BURGESS R R, DEUTSCHER M P. Methods in enzymology. New York: Academic Press, 2009, 463(C): 73-95. (2009-11-03)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 39 | PETERSON M S, PATKAR A Y, SEO J H. Flow cytometric analysis of total protein content and size distributions of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology Techniques, 1992, 6(3): 203-206. |
| 40 | CRISSMAN H A, STEINKAMP J A. Rapid, simultaneous measurement of DNA, protein, and cell volume in single cells from large mammalian cell populations[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1973, 59(3): 766-771. |
| 41 | ROTH B L, POOT M, YUE S T, et al. Bacterial viability and antibiotic susceptibility testing with SYTOX green nucleic acid stain[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1997, 63(6): 2421-2431. |
| 42 | NASH R, TOKIWA G, ANAND S, et al. The WHI1+gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog[J]. EMBO Journal, 1988, 7(13): 4335-4346. |
| 43 | ROSEBROCK A P. Analysis of the budding yeast cell cycle by flow cytometry[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2017, 2017(1): pdb.prot088740. |
| 44 | BLATTER L A. Cell volume measurements by fluorescence confocal microscopy: theoretical and practical aspects[M/OL]//Methods in enzymology. New York: Academic Press, 1999, 307: 274-295 [2024-12-01]. . |
| 45 | XIE S C, SKOTHEIM J M. A G1 sizer coordinates growth and division in the mouse epidermis[J]. Current Biology, 2020, 30(5): 916-924.e2. |
| 46 | ZLOTEK-ZLOTKIEWICZ E, MONNIER S, CAPPELLO G, et al. Optical volume and mass measurements show that mammalian cells swell during mitosis[J]. Journal of Cell Biology, 2015, 211(4): 765-774. |
| 47 | GROVER W H, BRYAN A K, DIEZ-SILVA M, et al. Measuring single-cell density[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(27): 10992-10996. |
| 48 | SON S M, KANG J H, OH S E, et al. Resonant microchannel volume and mass measurements show that suspended cells swell during mitosis[J]. Journal of Cell Biology, 2015, 211(4): 757-763. |
| 49 | ICHA J, WEBER M, WATERS J C, et al. Phototoxicity in live fluorescence microscopy, and how to avoid it[J]. BioEssays, 2017, 39(8): 1700003. |
| 50 | DEMCHENKO A P. Photobleaching of organic fluorophores: quantitative characterization, mechanisms, protection[J]. Methods and Applications in Fluorescence, 2020, 8(2): 022001. |
| 51 | PARK Y, DEPEURSINGE C, POPESCU G. Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine[J]. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12(10): 578-589. |
| 52 | CURL C L, BELLAIR C J, HARRIS T, et al. Refractive index measurement in viable cells using quantitative phase-amplitude microscopy and confocal microscopy[J]. Cytometry Part A, 2005, 65A(1): 88-92. |
| 53 | BON P, MAUCORT G, WATTELLIER B, et al. Quadriwave lateral shearing interferometry for quantitative phase microscopy of living cells[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(15): 13080-13094. |
| 54 | CREATH K, GOLDSTEIN G. Dynamic quantitative phase imaging for biological objects using a pixelated phase mask[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2012, 3(11): 2866-2880. |
| 55 | GARDINER D J. Introduction to Raman scattering[M/OL]//Practical Raman spectroscopy. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1989: 1-12 [2024-12-01]. . |
| 56 | FREUDIGER C W, MIN W, SAAR B G, et al. Label-free biomedical imaging with high sensitivity by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5909): 1857-1861. |
| 57 | CHENG J X, XIE X S. Vibrational spectroscopic imaging of living systems: an emerging platform for biology and medicine[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6264): aaa8870. |
| 58 | HILL A H, MANIFOLD B, FU D. Tissue imaging depth limit of stimulated Raman scattering microscopy[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11(2): 762-774. |
| 59 | FU D, LU F K, ZHANG X, et al. Quantitative chemical imaging with multiplex stimulated Raman scattering microscopy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(8): 3623-3626. |
| 60 | OH S E, LEE C H, YANG W L, et al. Protein and lipid mass concentration measurement in tissues by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(17): e2117938119. |
| 61 | GARNER R M, MOLINES A T, THERIOT J A, et al. Vast heterogeneity in cytoplasmic diffusion rates revealed by nanorheology and Doppelgänger simulations[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2023, 122(5): 767-783. |
| 62 | HUANG W Y C, CHENG X R, FERRELL J E JR. Cytoplasmic organization promotes protein diffusion in Xenopus extracts[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 5599. |
| 63 | PHILLIPS R, KONDEV J, THERIOT J, et al. Physical biology of the cell[M/OL]. 2nd Edition. New York: Garland Science, 2012. (2012-10-29)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 64 | DELARUE M, BRITTINGHAM G P, PFEFFER S, et al. mTORC1 controls phase separation and the biophysical properties of the cytoplasm by tuning crowding[J]. Cell, 2018, 174(2): 338-349.e20. |
| 65 | SHU T, MITRA G, ALBERTS J, et al. Mesoscale molecular assembly is favored by the active, crowded cytoplasm[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2023: 2023.09.19.558334. (2023-09-21)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 66 | KRICHEVSKY O, BONNET G. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: the technique and its applications[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2002, 65(2): 251-297. |
| 67 | HUANG W Y C, BOXER S G, FERRELL J E JR. Membrane localization accelerates association under conditions relevant to cellular signaling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(10): e2319491121. |
| 68 | AXELROD D, KOPPEL D E, SCHLESSINGER J, et al. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics[J]. Biophysical Journal, 1976, 16(9): 1055-1069. |
| 69 | ZHOU H X, RIVAS G, MINTON A P. Macromolecular crowding and confinement: biochemical, biophysical, and potential physiological consequences[J]. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2008, 37: 375-397. |
| 70 | WEISS M, ELSNER M, KARTBERG F, et al. Anomalous subdiffusion is a measure for cytoplasmic crowding in living cells[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2004, 87(5): 3518-3524. |
| 71 | RIVAS G, MINTON A P. Macromolecular crowding in vitro, in vivo, and in between[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2016, 41(11): 970-981. |
| 72 | ALGAR W R, HILDEBRANDT N, VOGEL S S, et al. FRET as a biomolecular research tool: understanding its potential while avoiding pitfalls[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(9): 815-829. |
| 73 | BOERSMA A J, ZUHORN I S, POOLMAN B. A sensor for quantification of macromolecular crowding in living cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(3): 227-229. |
| 74 | LIU X L, OH S E, KIRSCHNER M W. The uniformity and stability of cellular mass density in mammalian cell culture[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2022, 10: 1017499. |
| 75 | PLANTE S, MOON K M, LEMIEUX P, et al. Breaking spore dormancy in budding yeast transforms the cytoplasm and the solubility of the proteome[J]. PLoS Biology, 2023, 21(4): e3002042. |
| 76 | SHARMA R, AGARWAL A. Spermatogenesis: an overview[M/OL]//ZINI A, AGARWAL A. Sperm chromatin. New York: Springer New York, 2011: 19-44. (2011-06-30)[2024-12-01]. . |
| 77 | MAURER F, JOHN T, MAKHRO A, et al. Continuous percoll gradient centrifugation of erythrocytes-explanation of cellular bands and compromised age separation[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(8): 1296. |
| 78 | COOPER K L, OH S E, SUNG Y J, et al. Multiple phases of chondrocyte enlargement underlie differences in skeletal proportions[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 375-378. |
| 79 | NEUROHR G E, TERRY R L, LENGEFELD J, et al. Excessive cell growth causes cytoplasm dilution and contributes to senescence[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(5): 1083-1097.e18. |
| 80 | MANOHAR S, ESTRADA M E, ULIANA F, et al. Genome homeostasis defects drive enlarged cells into senescence[J]. Molecular Cell, 2023, 83(22): 4032-4046.e6. |
| 81 | MIETTINEN T P, KANG J H, YANG L F, et al. Mammalian cell growth dynamics in mitosis[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e44700. |
| 82 | ZHURINSKY J, LEONHARD K, WATT S, et al. A coordinated global control over cellular transcription[J]. Current Biology, 2010, 20(22): 2010-2015. |
| 83 | SWAFFER M P, MARINOV G K, ZHENG H, et al. RNA polymerase Ⅱ dynamics and mRNA stability feedback scale mRNA amounts with cell size[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(24): 5254-5268.e26. |
| 84 | CHEN Y P, ZHAO G, ZAHUMENSKY J, et al. Differential scaling of gene expression with cell size may explain size control in budding yeast[J]. Molecular Cell, 2020, 78(2): 359-370.e6. |
| 85 | LANZ M C, ZATULOVSKIY E, SWAFFER M P, et al. Increasing cell size remodels the proteome and promotes senescence[J]. Molecular Cell, 2022, 82(17): 3255-3269.e8. |
| 86 | BRANGWYNNE C P, ECKMANN C R, COURSON D S, et al. Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5935): 1729-1732. |
| 87 | MOLLIEX A, TEMIROV J, LEE J H, et al. Phase separation by low complexity domains promotes stress granule assembly and drives pathological fibrillization[J]. Cell, 2015, 163(1): 123-133. |
| 88 | LUO Y, NA Z K, SLAVOFF S A. P-bodies: composition, properties, and functions[J]. Biochemistry, 2018, 57(17): 2424-2431. |
| 89 | LAFONTAINE D L J, RIBACK J A, BASCETIN R, et al. The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021, 22(3): 165-182. |
| 90 | HE J N, HUO X R, PEI G F, et al. Dual-role transcription factors stabilize intermediate expression levels[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(11): 2746-2766.e25. |
| 91 | CHEN Y P, FERRELL J E JR. C. elegans colony formation as a condensation phenomenon[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 4947. |
| 92 | ALBERTI S, HYMAN A A. Biomolecular condensates at the nexus of cellular stress, protein aggregation disease and ageing[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2021, 22(3): 196-213. |
| 93 | MINTON A P. The effect of volume occupancy upon the thermodynamic activity of proteins: some biochemical consequences[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 1983, 55(2): 119-140. |
| 94 | KLOSIN A, OLTSCH F, HARMON T, et al. Phase separation provides a mechanism to reduce noise in cells[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6476): 464-468. |
| 95 | LUBY‐PHELPS K. Cytoarchitecture and physical properties of cytoplasm: volume, viscosity, diffusion, intracellular surface area[M/OL]//International review of cytology: microcompartmentation and phase separation in cytoplasm. New York: Academic Press, 1999(192): 189-221 [2024-12-01]. . |
| 96 | MINTON A P. Influence of excluded volume upon macromolecular structure and associations in “crowded” media[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 1997, 8(1): 65-69. |
| 97 | HU Z, CHEN K F, XIA Z, et al. Nucleosome loss leads to global transcriptional up-regulation and genomic instability during yeast aging[J]. Genes & Development, 2014, 28(4): 396-408. |
| 98 | NEUROHR G E, TERRY R L, SANDIKCI A, et al. Deregulation of the G1/S-phase transition is the proximal cause of mortality in old yeast mother cells[J]. Genes & Development, 2018, 32(15-16): 1075-1084. |
| 99 | CHEN Y P, FUTCHER B. Scaling gene expression for cell size control and senescence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Current Genetics, 2021, 67(1): 41-47. |
| 100 | AOKI K, TAKAHASHI K, KAIZU K, et al. A quantitative model of ERK MAP kinase phosphorylation in crowded media[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 1541. |
| 101 | HUANG J H, CHEN Y P, HUANG W Y C, et al. Robust trigger wave speed in Xenopus cytoplasmic extracts[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 5782. |
| 102 | JIANG H D, SONG C Y, CHEN C C, et al. Quantitative 3D imaging of whole, unstained cells by using X-ray diffraction microscopy[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(25): 11234-11239. |
| 103 | BROUHARD G J, RICE L M. Microtubule dynamics: an interplay of biochemistry and mechanics[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2018, 19(7): 451-463. |
| 104 | MIESCH J, WIMBISH R T, VELLUZ M C, et al. Phase separation of +TIP networks regulates microtubule dynamics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(35): e2301457120. |
| 105 | FULTON A B. How crowded is the cytoplasm?[J]. Cell, 1982, 30(2): 345-347. |
| 106 | CAMERON I L, KANAL K M, KEENER C R, et al. A mechanistic view of the non-ideal osmotic and motional behavior of intracellular water[J]. Cell Biology International, 1997, 21(2): 99-113. |
| 107 | BAR-EVEN A, NOOR E, SAVIR Y, et al. The moderately efficient enzyme: evolutionary and physicochemical trends shaping enzyme parameters[J]. Biochemistry, 2011, 50(21): 4402-4410. |
| 108 | MAVROVOUNIOTIS M L, STEPHANOPOULOS G, STEPHANOPOULOS G. Estimation of upper bounds for the rates of enzymatic reactions[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1990, 93(1): 211-236. |
| 109 | STEITZ T A, SHOHAM M, BENNETT W S JR. Structural dynamics of yeast hexokinase during catalysis[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 1981, 293(1063): 43-52. |
| 110 | KOSHLAND D E JR. The key-lock theory and the induced fit theory[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 1995, 33(23-24): 2375-2378. |
| 111 | HOPFIELD J J. Kinetic proofreading: a new mechanism for reducing errors in biosynthetic processes requiring high specificity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1974, 71(10): 4135-4139. |
| 112 | CHOI A A, XU K. Single-molecule diffusivity quantification unveils ubiquitous net charge-driven protein-protein interaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(15): 10973-10978. |
| 113 | CHOI A A, ZHOU C Y, TABO A, et al. Single-molecule diffusivity quantification in Xenopus egg extracts elucidates physicochemical properties of the cytoplasm[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(50): e2411402121. |
| 114 | AN S, KUMAR R, SHEETS E D, et al. Reversible compartmentalization of de novo purine biosynthetic complexes in living cells[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5872): 103-106. |
| 115 | CHAUDHURI P K, LOW B C, LIM C T. Mechanobiology of tumor growth[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(14): 6499-6515. |
| 116 | ALIBERT C, GOUD B, MANNEVILLE J B. Are cancer cells really softer than normal cells?[J]. Biology of the Cell, 2017, 109(5): 167-189. |
| 117 | DESSARD M, MANNEVILLE J B, BERRET J F. Cytoplasmic viscosity is a potential biomarker for metastatic breast cancer cells[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2024, 6(6): 1727-1738. |
| [1] | LIU Xiangshi, WU Yilu, ZHAN Peng, HUANG Tianhao, CAI Di, QIN Peiyong. State-of-the-art for alcohol dehydrogenase development and the prospect of its applications in bio-based furan compounds valorization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(6): 1122-1139. |
| [2] | LIU Wanqiu, JI Xiangyang, XU Huiling, LU Yicong, LI Jian. Cell-free protein synthesis system enables rapid and efficient biosynthesis of restriction endonucleases [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 840-851. |
| [3] | TANG Shiming, HU Jiyuan, ZHENG Suiping, HAN Shuangyan, LIN Ying. Designing, building and rapid prototyping of biosynthesis module based on cell-free system [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1250-1261. |
| [4] | HOU Jiaqi, JIANG Nan, MA Lianju, LU Yuan. Cell-free protein synthesis: from basic research to engineering applications [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 465-486. |
| [5] | YANG Xinyu, ZHU Tong, LI Ruifeng, WU Bian. Enzymatic ligation technologies for the synthesis of pharmaceutical peptides and proteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(1): 33-45. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||