Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (3): 651-668.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-082
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and prospect of live cell DNA-based molecular recorders in cell lineage tracing
JIANG Baiyi, QIAN Long
- Center for Quantitative Biology,Peking University,Beijing 100871,China
-
Received:2024-11-27Revised:2025-03-03Online:2025-06-27Published:2025-06-30 -
Contact:QIAN Long
活细胞记录器在细胞谱系追踪中的应用和前景
姜百翼, 钱珑
- 北京大学定量生物学中心,北京 100871
-
通讯作者:钱珑 -
作者简介:姜百翼 (2000—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为哺乳动物细胞合成生物学。E-mail:2201111972@stu.pku.edu.cn钱珑 (1985—),女,副研究员。研究方向为DNA分子信息存储、合成生物学元件的大数据挖掘与设计、合成基因线路的可预测设计、基因组科学和基因组进化。E-mail:long.qian@pku.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2020YFA0906900)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIANG Baiyi, QIAN Long. Application and prospect of live cell DNA-based molecular recorders in cell lineage tracing[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 651-668.
姜百翼, 钱珑. 活细胞记录器在细胞谱系追踪中的应用和前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 651-668.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-082
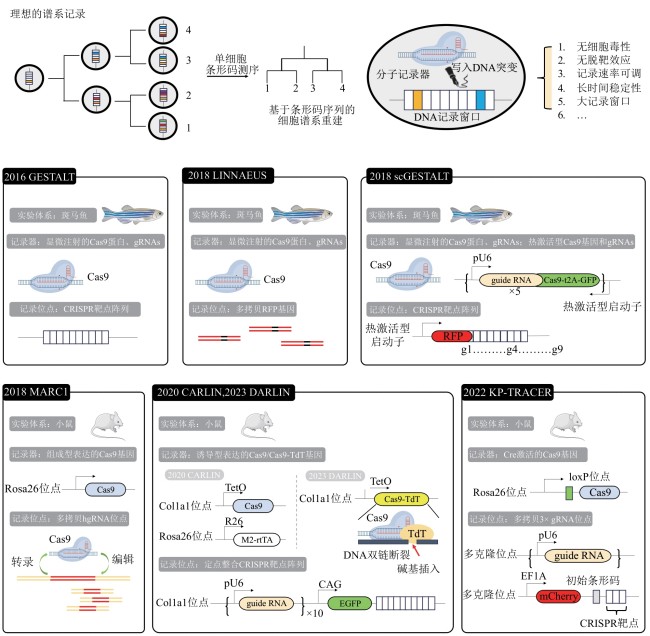
Fig. 1 Ideal molecular recorders [42-44] and representative studies of Cas9-based molecular recorders[41-42,45-49][Rosa26, Col1a1: landing pad sites on genome, for site-specific integration of exogenous genes. R26, pU6, CAG, EFIA: constitutive promoters. TetO: inducible promoter, activated by rtTA. M2-rtTA: inducible system, activated by doxycycline(dox) inducer]
| 名称 | 分子记录器 | 记录窗口 大小/bp | 靶点数量 /site | 主要突变类型 | 追踪时间① /d | 物种 | 是否稳 定整合② | 研究领域 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GESTALT | Cas9 | 266 | 10 | 碱基删除 | 3 | 斑马鱼 | 否 | 发育 | [ |
| scGESTALT | Cas9 | 363 | 10 | 碱基删除 | 23~25 | 斑马鱼 | 否 | 发育 | [ |
| MARC1 | Cas9 | 240 | 约20 | 碱基删除 | 19~21 | 小鼠 | 是 | 发育 | [ |
| LINNAEUS | Cas9 | 75 | 16~32 | 碱基删除 | 5 | 斑马鱼 | 否 | 发育 | [ |
| CHYRON | Cas9+TdT | 100 | 5 | 碱基插入 | 22 | HEK293T细胞系 | 是 | — | [ |
| CARLIN | Cas9 | 276 | 10 | 碱基删除 | 7 | 小鼠 | 是 | 发育 | [ |
| DARLIN | Cas9+TdT | 828 | 30 | 碱基插入 | 7 | 小鼠 | 是 | 发育 | [ |
| 2021年的一项研究 | Cas9 | — | 约30 | 碱基删除 | 54 | 小鼠 | 是(仅肿瘤) | 肿瘤 | [ |
| KP-TRACER | Cas9 | — | 30~90 | 碱基删除 | 150~180 | 小鼠 | 是(嵌合体) | 肿瘤 | [ |
Table 1 Summary of the characteristics of Cas9-based molecular recorders
| 名称 | 分子记录器 | 记录窗口 大小/bp | 靶点数量 /site | 主要突变类型 | 追踪时间① /d | 物种 | 是否稳 定整合② | 研究领域 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GESTALT | Cas9 | 266 | 10 | 碱基删除 | 3 | 斑马鱼 | 否 | 发育 | [ |
| scGESTALT | Cas9 | 363 | 10 | 碱基删除 | 23~25 | 斑马鱼 | 否 | 发育 | [ |
| MARC1 | Cas9 | 240 | 约20 | 碱基删除 | 19~21 | 小鼠 | 是 | 发育 | [ |
| LINNAEUS | Cas9 | 75 | 16~32 | 碱基删除 | 5 | 斑马鱼 | 否 | 发育 | [ |
| CHYRON | Cas9+TdT | 100 | 5 | 碱基插入 | 22 | HEK293T细胞系 | 是 | — | [ |
| CARLIN | Cas9 | 276 | 10 | 碱基删除 | 7 | 小鼠 | 是 | 发育 | [ |
| DARLIN | Cas9+TdT | 828 | 30 | 碱基插入 | 7 | 小鼠 | 是 | 发育 | [ |
| 2021年的一项研究 | Cas9 | — | 约30 | 碱基删除 | 54 | 小鼠 | 是(仅肿瘤) | 肿瘤 | [ |
| KP-TRACER | Cas9 | — | 30~90 | 碱基删除 | 150~180 | 小鼠 | 是(嵌合体) | 肿瘤 | [ |
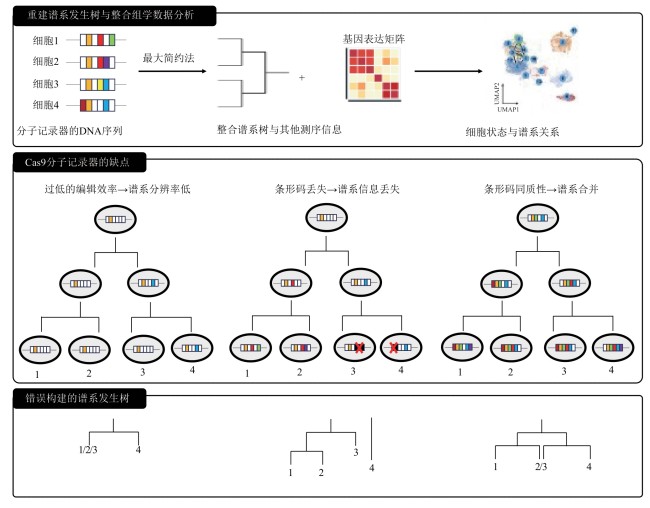
Fig. 2 Reconstructed phylogeny trees and integrated omics data analysis[43,49] as well as shortcomings of Cas9-based molecular recorders and errors in reconstructing phylogeny trees [3,42,49]
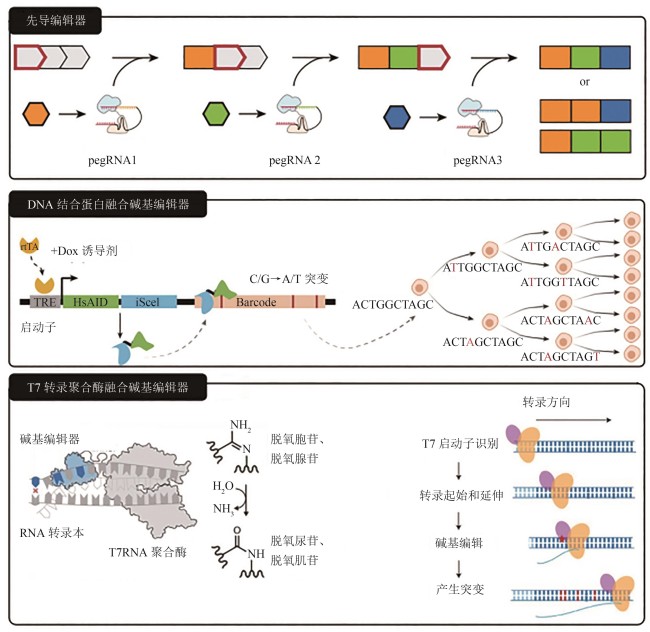
Fig. 3 Working principles for three novel molecular recorders[61-64](pegRNA—prime editing guide RNA;TRE—a promoter that can be activated by rtTA in the presence of DOX; HsAID—base-editor;iSceI—DNA binding protein; rtTA—inducible system)
| 分子记录器 | 稳定性 | 时序写入 | 特异性 | 编辑窗口大小 | 编辑效率 | 技术发展程度 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 | 易丢失 | 否 | 易脱靶 | 窄 | — | 高 | [ |
| 先导编辑 | 高 | 是 | 易脱靶 | 窄 | 低于Cas9 | 中 | [ |
| DNA结合蛋白 | 高 | 否 | 强 | 宽 | 高于Cas9 | 中 | [ |
| Muta-T7 | 高 | 否 | 强 | 可调节 | 未知 | 低 | [ |
Table 2 Comparative analysis of novel molecular recorders and the Cas9-based molecular recorder
| 分子记录器 | 稳定性 | 时序写入 | 特异性 | 编辑窗口大小 | 编辑效率 | 技术发展程度 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 | 易丢失 | 否 | 易脱靶 | 窄 | — | 高 | [ |
| 先导编辑 | 高 | 是 | 易脱靶 | 窄 | 低于Cas9 | 中 | [ |
| DNA结合蛋白 | 高 | 否 | 强 | 宽 | 高于Cas9 | 中 | [ |
| Muta-T7 | 高 | 否 | 强 | 可调节 | 未知 | 低 | [ |
| 1 | KESTER L, VAN OUDENAARDEN A. Single-cell transcriptomics meets lineage tracing[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(2): 166-179. |
| 2 | WAGNER D E, KLEIN A M. Lineage tracing meets single-cell omics: opportunities and challenges[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2020, 21(7): 410-427. |
| 3 | WEINREB C, RODRIGUEZ-FRATICELLI A, CAMARGO F D, et al. Lineage tracing on transcriptional landscapes links state to fate during differentiation[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6479): eaaw3381. |
| 4 | VANHORN S, MORRIS S A. Next-generation lineage tracing and fate mapping to interrogate development[J]. Developmental Cell, 2021, 56(1): 7-21. |
| 5 | SANKARAN V G, WEISSMAN J S, ZON L I. Cellular barcoding to decipher clonal dynamics in disease[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6616): eabm5874. |
| 6 | WANG Y Q, ZHANG X, WANG Z. Cellular barcoding: from developmental tracing to anti-tumor drug discovery[J]. Cancer Letters, 2023, 567: 216281. |
| 7 | FENG J, PUCELLA J N, JANG G, et al. Clonal lineage tracing reveals shared origin of conventional and plasmacytoid dendritic cells[J]. Immunity, 2022, 55(3): 405-422.e11. |
| 8 | VAN EGEREN D, ESCABI J, NGUYEN M, et al. Reconstructingthe lineage histories and differentiation trajectories of individual cancer cells in myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(3): 514-523.e9. |
| 9 | AALAM S M M, NGUYEN L V, RITTING M L, et al. Clonal tracking in cancer and metastasis[J]. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 2024, 43(2): 639-656. |
| 10 | PORTA-PARDO E, VALENCIA A, GODZIK A. Understandingoncogenicity of cancer driver genes and mutations in the cancer genomics era[J]. FEBS Letters, 2020, 594(24): 4233-4246. |
| 11 | KAKIUCHI N, OGAWA S. Clonal expansion in non-cancer tissues[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2021, 21(4): 239-256. |
| 12 | SINKALA M. Mutational landscape of cancer-driver genes across human cancers[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 12742. |
| 13 | TARKOWSKI A K. Mouse chimaeras developed from fused eggs[J]. Nature, 1961, 190: 857-860. |
| 14 | MINTZ B. Genetic mosaicism in adult mice of quadriparental lineage[J]. Science, 1965, 148(3674): 1232-1233. |
| 15 | LIVET J, WEISSMAN T A, KANG H, et al. Transgenic strategies for combinatorial expression of fluorescent proteins in the nervous system[J]. Nature, 2007, 450(7166): 56-62. |
| 16 | SNIPPERT H J, VAN DER FLIER L G, SATO T, et al. Intestinal crypt homeostasis results from neutral competition between symmetrically dividing Lgr5 stem cells[J]. Cell, 2010, 143(1): 134-144. |
| 17 | WEISSMAN T A, PAN Y A. Brainbow: new resources and emerging biological applications for multicolor genetic labeling and analysis[J]. Genetics, 2015, 199(2): 293-306. |
| 18 | NADALIN F, MARZI M J, PIRRA PISCAZZI M, et al. Multi-omic lineage tracing predicts the transcriptional, epigenetic and genetic determinants of cancer evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 7609. |
| 19 | OREN Y, TSABAR M, CUOCO M S, et al. Cycling cancer persister cells arise from lineages with distinct programs[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 576-582. |
| 20 | RENZ P F, GHOSHDASTIDER U, BAGHAI SAIN S, et al. In vivo single-cell CRISPR uncovers distinct TNF programmes in tumour evolution[J]. Nature, 2024, 632(8024): 419-428. |
| 21 | YU C N, MANNAN A M, YVONE G M, et al. High-throughput identification of genotype-specific cancer vulnerabilities in mixtures of barcoded tumor cell lines[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(4): 419-423. |
| 22 | CORSELLO S M, NAGARI R T, SPANGLER R D, et al. Discovering the anti-cancer potential of non-oncology drugs by systematic viability profiling[J]. Nature Cancer, 2020, 1(2): 235-248. |
| 23 | XIA Y F, JI X D, JANG I S, et al. Genetic and pharmacological interrogation of cancer vulnerability using a multiplexed cell line screening platform[J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4(1): 834. |
| 24 | MARTÍNEZ-JIMÉNEZ F, MUIÑOS F, SENTÍS I, et al. A compendium of mutational cancer driver genes[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2020, 20(10): 555-572. |
| 25 | PARK S Y, MALI N M, KIM R, et al. Clonal dynamics in early human embryogenesis inferred from somatic mutation[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7876): 393-397. |
| 26 | SPENCER CHAPMAN M, RANZONI A M, MYERS B, et al. Lineage tracing of human development through somatic mutations[J]. Nature, 2021, 595(7865): 85-90. |
| 27 | COORENS T H H, MOORE L, ROBINSON P S, et al. Extensive phylogenies of human development inferred from somatic mutations[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7876): 387-392. |
| 28 | SHETH R U, WANG H H. DNA-based memory devices for recording cellular events[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(11): 718-732. |
| 29 | JANG H, YIM S S. Toward DNA-based recording of biological processes[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(17): 9233. |
| 30 | SUN J L, RAMOS A, CHAPMAN B, et al. Clonal dynamics of native haematopoiesis[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7522): 322-327. |
| 31 | FIGUERES-OÑATE M, SÁNCHEZ-GONZÁLEZ R, LÓPEZ-MASCARAQUE L. Deciphering neural heterogeneity through cell lineage tracing[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2021, 78(5): 1971-1982. |
| 32 | WOODWORTH M B, GIRSKIS K M, WALSH C A. Building a lineage from single cells: genetic techniques for cell lineage tracking[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2017, 18(4): 230-244. |
| 33 | PEI W K, FEYERABEND T B, RÖSSLER J, et al. Polylox barcoding reveals haematopoietic stem cell fates realized in vivo [J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7668): 456-460. |
| 34 | PEI W K, WANG X, RÖSSLER J, et al. Using Cre-recombinase-driven Polylox barcoding for in vivo fate mapping in mice[J]. Nature Protocols, 2019, 14(6): 1820-1840. |
| 35 | CHOW K K, BUDDE M W, GRANADOS A A, et al. Imaging cell lineage with a synthetic digital recording system[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6538): eabb3099. |
| 36 | WAGNER D E, WEINREB C, COLLINS Z M, et al. Single-cell mapping of gene expression landscapes and lineage in the zebrafish embryo[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6392): 981-987. |
| 37 | CONG L, RAN F A, COX D, et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819-823. |
| 38 | RAN F A, HSU P D, WRIGHT J, et al. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(11): 2281-2308. |
| 39 | SANDER J D, JOUNG J K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(4): 347-355. |
| 40 | WANG J Y, DOUDNA J A. CRISPR technology: a decade of genome editing is only the beginning[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6629): eadd8643. |
| 41 | MCKENNA A, FINDLAY G M, GAGNON J A, et al. Whole-organism lineage tracing by combinatorial and cumulative genome editing[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6298): aaf7907. |
| 42 | LI L, BOWLING S, MCGEARY S E, et al. A mouse model with high clonal barcode diversity for joint lineage, transcriptomic, and epigenomic profiling in single cells[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(23): 5183-5199.e22. |
| 43 | CHAN M M, SMITH Z D, GROSSWENDT S, et al. Molecular recording of mammalian embryogenesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 570(7759): 77-82. |
| 44 | FARZADFARD F, LU T K. Emerging applications for DNA writers and molecular recorders[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6405): 870-875. |
| 45 | SPANJAARD B, HU B, MITIC N, et al. Simultaneous lineage tracing and cell-type identification using CRISPR-Cas9-induced genetic scars[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(5): 469-473. |
| 46 | KALHOR R, KALHOR K, MEJIA L, et al. Developmental barcoding of whole mouse via homing CRISPR[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6405): eaat9804. |
| 47 | RAJ B, WAGNER D E, MCKENNA A, et al. Simultaneous single-cell profiling of lineages and cell types in the vertebrate brain[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(5): 442-450. |
| 48 | BOWLING S, SRITHARAN D, OSORIO F G, et al. An engineered CRISPR-Cas9 mouse line for simultaneous readout of lineage histories and gene expression profiles in single cells[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(6): 1410-1422.e27. |
| 49 | YANG D, JONES M G, NARANJO S, et al. Lineage tracing reveals the phylodynamics, plasticity, and paths of tumor evolution[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(11): 1905-1923.e25. |
| 50 | LOVELESS T B, GROTTS J H, SCHECHTER M W, et al. Lineage tracing and analog recording in mammalian cells by single-site DNA writing[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2021, 17(6): 739-747. |
| 51 | QUINN J J, JONES M G, OKIMOTO R A, et al. Single-cell lineages reveal the rates, routes, and drivers of metastasis in cancer xenografts[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6532): eabc1944. |
| 52 | WANG R, ZHANG R, KHODAVERDIAN A, et al. Theoretical guarantees for phylogeny inference from single-cell lineage tracing[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(12): e2203352120. |
| 53 | SALVADOR-MARTÍNEZ I, GRILLO M, AVEROF M, et al. Is it possible to reconstruct an accurate cell lineage using CRISPR recorders?[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e40292. |
| 54 | FORROW A, SCHIEBINGER G. LineageOT is a unified framework for lineage tracing and trajectory inference[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 4940. |
| 55 | ZAFAR H, TZEN A, NAVIN N, et al. SiFit: inferring tumor trees from single-cell sequencing data under finite-sites models[J]. Genome Biology, 2017, 18(1): 178. |
| 56 | ZAFAR H, LIN C, BAR-JOSEPH Z. Single-cell lineage tracing by integrating CRISPR-Cas9 mutations with transcriptomic data[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3055. |
| 57 | KIM I S. DNA barcoding technology for lineage recording and tracing to resolve cell fate determination[J]. Cells, 2023, 13(1): 27. |
| 58 | BARON C S, VAN OUDENAARDEN A. Unravelling cellular relationships during development and regeneration using genetic lineage tracing[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2019, 20(12): 753-765. |
| 59 | CHEN M Y, FU R J, CHEN Y Q, et al. High-resolution, noninvasive single-cell lineage tracing in mice and humans based on DNA methylation epimutations[J]. Nature Methods, 2025,22:488-498. |
| 60 | JONES M G, KHODAVERDIAN A, QUINN J J, et al. Inference of single-cell phylogenies from lineage tracing data using Cassiopeia[J]. Genome Biology, 2020, 21(1): 92. |
| 61 | CHOI J, CHEN W, MINKINA A, et al. A time-resolved, multi-symbol molecular recorder via sequential genome editing[J]. Nature, 2022, 608(7921): 98-107. |
| 62 | LU Z L, MO S L, XIE D, et al. Polyclonal-to-monoclonal transition in colorectal precancerous evolution[J]. Nature, 2024, 636(8041): 233-240. |
| 63 | MENGISTE A A, MCDONALD J L, NGUYEN TRAN M T, et al. MutaT7GDE: a single chimera for the targeted, balanced, efficient, and processive installation of all possible transition mutations in vivo [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2024, 13(9): 2693-2701. |
| 64 | CHEN H Q, LIU S, PADULA S, et al. Efficient, continuous mutagenesis in human cells using a pseudo-random DNA editor[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(2): 165-168. |
| 65 | LIAO H N, CHOI J, SHENDURE J. Molecular recording using DNA typewriter[J]. Nature Protocols, 2024, 19(10): 2833-2862. |
| 66 | CHEN W, CHOI J, LI X Y, et al. Symbolic recording of signalling and cis-regulatory element activity to DNA[J]. Nature, 2024, 632(8027): 1073-1081. |
| 67 | LIU K H, DENG S J, YE C, et al. Mapping single-cell-resolution cell phylogeny reveals cell population dynamics during organ development[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(12): 1506-1514. |
| 68 | LIU Z, ZENG H, XIANG H M, et al. Achieving single-cell-resolution lineage tracing in zebrafish by continuous barcoding mutations during embryogenesis[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2024, 51(9): 947-956. |
| 69 | MOLINA R S, RIX G, MENGISTE A A, et al. In vivo hypermutation and continuous evolution[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2022, 2: 37. |
| 70 | BUTT H, RAMIREZ J L M, MAHFOUZ M. Synthetic evolution of herbicide resistance using a T7 RNAP-based random DNA base editor[J]. Life Science Alliance, 2022, 5(12): e202201538. |
| 71 | CRAVENS A, JAMIL O K, KONG D Z, et al. Polymerase-guided base editing enables in vivo mutagenesis and rapid protein engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1579. |
| 72 | ANZALONE A V, RANDOLPH P B, DAVIS J R, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| 73 | CHEN P J, LIU D R. Prime editing for precise and highly versatile genome manipulation[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2023, 24(3): 161-177. |
| 74 | NELSON J W, RANDOLPH P B, SHEN S P, et al. Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(3): 402-410. |
| 75 | KOCAK D D, JOSEPHS E A, BHANDARKAR V, et al. Increasing the specificity of CRISPR systems with engineered RNA secondary structures[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(6): 657-666. |
| 76 | COELHO M A, DE BRAEKELEER E, FIRTH M, et al. CRISPR GUARD protects off-target sites from Cas9 nuclease activity using short guide RNAs[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4132. |
| 77 | LI A, MITSUNOBU H, YOSHIOKA S, et al. Cytosine base editing systems with minimized off-target effect and molecular size[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 4531. |
| 78 | CABRERA A, EDELSTEIN H I, GLYKOFRYDIS F, et al. The sound of silence: transgene silencing in mammalian cell engineering[J]. Cell Systems, 2022, 13(12): 950-973. |
| 79 | ALLSHIRE R C, MADHANI H D. Ten principles of heterochromatin formation and function[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2018, 19(4): 229-244. |
| 80 | ALHAJI S Y, NGAI S C, ABDULLAH S. Silencing of transgene expression in mammalian cells by DNA methylation and histone modifications in gene therapy perspective[J]. Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering Reviews, 2019, 35(1): 1-25. |
| 81 | LYKO F. The DNA methyltransferase family: a versatile toolkit for epigenetic regulation[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(2): 81-92. |
| 82 | HUGHES A L, KELLEY J R, KLOSE R J. Understanding the interplay between CpG island-associated gene promoters and H3K4 methylation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 2020, 1863(8): 194567. |
| 83 | LI X Y, CHEN W, MARTIN B K, et al. Chromatin context-dependent regulation and epigenetic manipulation of prime editing[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(10): 2411-2427.e25. |
| 84 | FONFARA I, CURTH U, PINGOUD A, et al. Creating highly specific nucleases by fusion of active restriction endonucleases and catalytically inactive homing endonucleases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(2): 847-860. |
| 85 | HWANG B, LEE W, YUM S Y, et al. Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1234. |
| 86 | ZHANG X H, ZHU B Y, CHEN L, et al. Dual base editor catalyzes both cytosine and adenine base conversions in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 856-860. |
| 87 | YE L J, ZHAO D D, LI J, et al. Glycosylase-based base editors for efficient T-to-G and C-to-G editing in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2024, 42(10): 1538-1547. |
| 88 | CHEN Z H, SCHNEIDER T D. Information theory based T7-like promoter models: classification of bacteriophages and differential evolution of promoters and their polymerases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, 33(19): 6172-6187. |
| 89 | DIETZ A, WEISSER H J, KÖSSEL H, et al. The gene for Klebsiella bacteriophage K11 RNA polymerase: sequence and comparison with the homologous genes of phages T7, T3, and SP6[J]. Molecular & General Genetics, 1990, 221(2): 283-286. |
| 90 | WANG W Y, LI Y, WANG Y Q, et al. Bacteriophage T7 transcription system: an enabling tool in synthetic biology[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(8): 2129-2137. |
| 91 | RIO D C. Expression and purification of active recombinant T7 RNA polymerase from E. coli [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2013, 2013(11): pdb.prot078527. |
| 92 | LEE S S, KANG C. Two base pairs at-9 and-8 distinguish between the bacteriophage T7 and SP6 promoters[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1993, 268(26): 19299-19304. |
| 93 | IMBURGIO D, RONG M, MA K, et al. Studies of promoter recognition and start site selection by T7 RNA polymerase using a comprehensive collection of promoter variants[J]. Biochemistry, 2000, 39(34): 10419-10430. |
| 94 | ZONG Y Q, ZHANG H M, LYU C, et al. Insulated transcriptional elements enable precise design of genetic circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 52. |
| 95 | MOORE C L, PAPA L J 3 RD, SHOULDERS M D. A processive protein chimera introduces mutations across defined DNA regions in vivo [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(37): 11560-11564. |
| 96 | PARK H J, KIM S H. Gene-specific mutagenesis enables rapid continuous evolution of enzymes in vivo [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(6): e32. |
| 97 | SEO D J, KOH B H, EOM G E, et al. A dual gene-specific mutator system installs all transition mutations at similar frequencies in vivo [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(10): e59. |
| 98 | MENGISTE A A, WILSON R H, WEISSMAN R F, et al. Expanded MutaT7 toolkit efficiently and simultaneously accesses all possible transition mutations in bacteria[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(6): e31. |
| 99 | DIONISI S, PIERA K, BAUMSCHLAGER A, et al. Implementation of a novel optogenetic tool in mammalian cells based on a split T7 RNA polymerase[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(8): 2650-2661. |
| 100 | GHADERI M, SABAHI F, SADEGHI-ZADEH M, et al. Construction of an eGFP expression plasmid under control of T7 promoter and IRES sequence for assay of T7 RNA polymerase activity in mammalian cell lines[J]. Iranian Journal of Cancer Prevention, 2014, 7(3): 137-141. |
| 101 | QIN C R, XIANG Y H, LIU J, et al. Precise programming of multigene expression stoichiometry in mammalian cells by a modular and programmable transcriptional system[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1500. |
| 102 | AKHTAR W, DE JONG J, PINDYURIN A V, et al. Chromatin position effects assayed by thousands of reporters integrated in parallel[J]. Cell, 2013, 154(4): 914-927. |
| 103 | VANHILLE L, GRIFFON A, MAQBOOL M A, et al. High-throughput and quantitative assessment of enhancer activity in mammals by CapStarr-seq[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6905. |
| 104 | VAN ARENSBERGEN J, FITZPATRICK V D, DE HAAS M, et al. Genome-wide mapping of autonomous promoter activity in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(2): 145-153. |
| 105 | ANDERSSON R, SANDELIN A. Determinants of enhancer and promoter activities of regulatory elements[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2020, 21(2): 71-87. |
| [1] | XIAO He, YAO Mingju, QIAO Xue. Advances in the biosynthesis of long sugar-chain saponins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-7. |
| [2] | LI Mingchen, ZHONG Bozitao, YU Yuanxi, JIANG Fan, ZHANG Liang, TAN Yang, YU Huiqun, FAN Guisheng, HONG Liang. DeepSeek model analysis and its applications in AI-assistant protein engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 636-650. |
| [3] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [4] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [5] | LI Qian, FERRELL JR. James E., CHEN Yuping. Cytoplasmic concentration: an old question and a new parameter in cell biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 497-515. |
| [6] | ZHANG Chengxin. Challenges and opportunities in text mining-based protein function annotation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 603-616. |
| [7] | WANG Ke, CHEN Wenhui, LEI Chunyang, NIE Zhou. Advances in the Application of CRISPR/Cas Systems in Molecular Diagnostics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-27. |
| [8] | GAN Mudan, ZUO Jingrui, CAO Youzhi. Biocontainment strategies of engineered bacteria [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-14. |
| [9] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| [10] | GAO Qi, XIAO Wenhai. Advances in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes by yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 357-372. |
| [11] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [12] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [13] | FANG Xinyi, SUN Lichao, HUO Yixin, WANG Ying, YUE Haitao. Trends and challenges in microbial synthesis of higher alcohols [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-25. |
| [14] | SU Juanjuan, ZHENG Jiawen, MIAO Runze, HAN Peng, WANG Shi’an, LI Fuli. Biosynthesis and manufacture of microbial oils and vegetable oils [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-17. |
| [15] | WEN Yanhua, LIU Hedong, CAO Chunlai, WU Ruibo. Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||