Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (3): 636-650.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-041
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
DeepSeek model analysis and its applications in AI-assistant protein engineering
LI Mingchen1,2, ZHONG Bozitao1, YU Yuanxi1, JIANG Fan1, ZHANG Liang1, TAN Yang1,2, YU Huiqun2, FAN Guisheng2, HONG Liang1
- 1.Zhangjiang Institute for Advanced Study,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 201203,China
2.School of Information Science and Engineering,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
-
Received:2025-05-01Revised:2025-06-03Online:2025-06-27Published:2025-06-30 -
Contact:HONG Liang
DeepSeek模型分析及其在AI辅助蛋白质工程中的应用
李明辰1,2, 钟博子韬1, 余元玺1, 姜帆1, 张良1, 谭扬1,2, 虞慧群2, 范贵生2, 洪亮1
- 1.上海交通大学张江高等研究院,上海 201203
2.华东理工大学信息科学与工程学院,上海 200237
-
通讯作者:洪亮 -
作者简介:李明辰 (1998—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为人工智能。 E-mail:lmc@mail.ecust.edu.cn洪亮 (1981—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为分子生物物理,人工智能功能蛋白质设计以及药物分子设计。 E-mail:hongl3liang@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:上海市2023年度“科技创新行动计划”计算生物学重点专项(23JS1400600)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Mingchen, ZHONG Bozitao, YU Yuanxi, JIANG Fan, ZHANG Liang, TAN Yang, YU Huiqun, FAN Guisheng, HONG Liang. DeepSeek model analysis and its applications in AI-assistant protein engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 636-650.
李明辰, 钟博子韬, 余元玺, 姜帆, 张良, 谭扬, 虞慧群, 范贵生, 洪亮. DeepSeek模型分析及其在AI辅助蛋白质工程中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(3): 636-650.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-041
| 模型 | 架构 | 参数量 | 预训练任务 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UniRep[ | LSTM | 18.2 M | 自回归生成 | 理解 |
| ESM-2[ | Transformer | 650 M/15 B | 自回归生成 | 理解 |
| ESM-3[ | Transformer | 98 B | 掩码预测 | 生成 |
| ProGEN[ | Transformer | 6.4 B | 自回归生成 | 生成 |
| xTrimoPGLM[ | Transformer | 100 B | 掩码预测 & 自回归生成 | 生成 |
| ProtT5[ | Transformer | 11 B | 掩码预测 | 理解 |
| SaProt[ | Transformer | 650 M | 掩码预测 | 理解 |
| ProSST[ | Transformer | 110 M | 掩码预测 | 理解 |
| ESM-1v[ | Transformer | 650 M | 掩码预测 | 突变预测 |
| Tranception[ | Transformer | 700 M | 自回归生成 | 突变预测 |
Table 1 Architecture, parameter count, pre-training task, and application scenario of currently available protein language models
| 模型 | 架构 | 参数量 | 预训练任务 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UniRep[ | LSTM | 18.2 M | 自回归生成 | 理解 |
| ESM-2[ | Transformer | 650 M/15 B | 自回归生成 | 理解 |
| ESM-3[ | Transformer | 98 B | 掩码预测 | 生成 |
| ProGEN[ | Transformer | 6.4 B | 自回归生成 | 生成 |
| xTrimoPGLM[ | Transformer | 100 B | 掩码预测 & 自回归生成 | 生成 |
| ProtT5[ | Transformer | 11 B | 掩码预测 | 理解 |
| SaProt[ | Transformer | 650 M | 掩码预测 | 理解 |
| ProSST[ | Transformer | 110 M | 掩码预测 | 理解 |
| ESM-1v[ | Transformer | 650 M | 掩码预测 | 突变预测 |
| Tranception[ | Transformer | 700 M | 自回归生成 | 突变预测 |
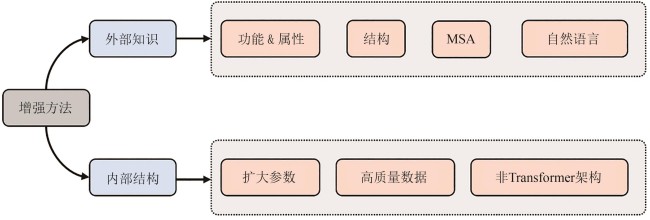
| 模型 | 引入的外部知识 | 模型整合的方式 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ProteinBERT[ | 结构、功能 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| PromptProtein[ | 结构、属性 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| OntoProtein[ | 结构 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| MELT[ | 功能 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| Regression Transformer[ | 功能、属性 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| Prime[ | 温度 | 训练目标 | 突变设计 |
| PeTriBERT[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| MIF-ST[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProteinMPNN[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 生成(逆折叠) |
| ESM-IF[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 生成(逆折叠) |
| ESM-S[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProstT5[ | 结构 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| LM-Design[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 生成 |
| SaProt[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| PST[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| SES-Adapter[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProSST[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| AlphaMissense[ | 结构、MSA | 训练目标 | 突变设计 |
| PoET[ | 结构、MSA | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProMEP[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 突变设计 |
Table 2 Protein language models enhanced by introducing external knowledge
| 模型 | 引入的外部知识 | 模型整合的方式 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ProteinBERT[ | 结构、功能 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| PromptProtein[ | 结构、属性 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| OntoProtein[ | 结构 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| MELT[ | 功能 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| Regression Transformer[ | 功能、属性 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| Prime[ | 温度 | 训练目标 | 突变设计 |
| PeTriBERT[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| MIF-ST[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProteinMPNN[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 生成(逆折叠) |
| ESM-IF[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 生成(逆折叠) |
| ESM-S[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProstT5[ | 结构 | 训练目标 | 理解 |
| LM-Design[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 生成 |
| SaProt[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| PST[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| SES-Adapter[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProSST[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| AlphaMissense[ | 结构、MSA | 训练目标 | 突变设计 |
| PoET[ | 结构、MSA | 额外输入 | 理解 |
| ProMEP[ | 结构 | 额外输入 | 突变设计 |
| 1 | 余元玺, 钟博子韬, 洪亮. 人工智能的诺奖时刻: 重塑科学的未来[J]. 物理, 2025, 54(01): 25-29. |
| 2 | FAN W Q, ZHOU Y, WANG S J, et al. Computational protein science in the era of large language models (LLMs)[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2025: 2501.10282. (2025-01-25)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 3 | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C/OL]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), 2017: 5998-6008 [2025-06-03]. |
| 4 | DeepSeek-AI, LIU A X, FENG B, et al. DeepSeek-V3 technical report[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2412.19437v1. (2024-12-27)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 5 | GUO D Y, YANG D J, ZHANG H W,et al. DeepSeek-R1: incentivizing reasoning capability in LLMs via reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2025: 2501.12948. (2025-01-22)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 6 | JAECH A, KALAI A, LERER A, et al. Openai o1 system card [EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2412.16720. (2024-12-21)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 7 | BI X, CHEN D L, CHEN G T, et al. DeepSeek LLM: scaling open-source language models with longtermism[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2401.02954. (2024-01-05)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 8 | GUO D Y, ZHU Q H, YANG D J, et al. DeepSeek-Coder: when the large language model meets programming—the rise of code intelligence[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2401.14196. (2024-01-26)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 9 | DAI D M, DENG C Q, ZHAO C G, et al. DeepSeekMoE: towards ultimate expert specialization in mixture-of-experts language models[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: ACL, 2024: 1280-1297 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 10 | TOUVRON H, MARTIN L, STONE K, et al. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2023: 2307.09288. (2023-07-18)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 11 | SHAO Z H, WANG P Y, ZHU Q H, et al. DeepSeekMath: pushing the limits of mathematical reasoning in open language models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2402.03300. (2024-02-05)[2025-06-03].. |
| 12 | DEEPSEEK-AI, LIU A X, FENG B, et al. DeepSeek-V2: a strong, economical, and efficient mixture-of-experts language model[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2405.04434. (2024-06-19)[2025-06-03].. |
| 13 | DeepSeek-V2.5: a new open-source model combining general and coding capabilities[EB/OL]. (2024-09-05)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 14 | ZHAO W X, ZHOU K, LI J Y, et al. A survey of large language models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2023: 2303.18223. (2025-03-11)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 15 | KWON W, LI Z H, ZHUANG S Y, et al. Efficient memory management for large language model serving with PagedAttention[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 29th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles. October 23-26, 2023, Koblenz, Germany. ACM, 2023: 611-626 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 16 | SHAZEER N. Fast transformer decoding: one write-head is all you need[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2019: 1911.02150. (2019-11-06)[2025-06-03].. |
| 17 | AINSLIE J, LEE-THORP J, DE JONG M, et al. GQA: training generalized multi-query transformer models from multi-head checkpoints[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Singapore, 2023: 4895-4901 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 18 | DEVLIN J, CHANG M, LEE K, et al. Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding [C/OL]// Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers). Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA: ACL, 2019: 4171-4186 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 19 | LIN Z M, AKIN H, RAO R, et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6637): 1123-1130. |
| 20 | KAPLAN J, MCCANDLISH S, HENIGHAN T, et al. Scaling laws for neural language models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2020: 2001.08361. (2020-01-23)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 21 | HOFFMANN J, BORGEAUD S, MENSCH A, et al. Training compute-optimal large language models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2022: 2203.15556. (2022-03-29)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 22 | JACOBS R A, JORDAN M I, NOWLAN S J, et al. Adaptive mixtures of local experts[J]. Neural Computation, 1991, 3(1): 79-87. |
| 23 | JORDAN M I, XU L. Convergence results for the EM approach to mixtures of experts architectures[J]. Neural Networks, 1995, 8(9): 1409-1431. |
| 24 | SHAZEER N, MIRHOSEINI A, MAZIARZ K, et al. Outrageously large neural networks: the sparsely-gated mixture-of-experts layer[C/OL]// 5th International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR 2017. (2017-02-06)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 25 | WEI MING T. DeepSeek V3 Training cost: here’s how it compares to Llama 3.1 (405B)[EB/OL]. (2025-01-26)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 26 | KAHAN W. IEEE standard 754 for binary floating-point arithmetic[EB/OL]. Lecture Notes on the Status of IEEE, 1996, 754(94720-1776): 11[2025-06-03]. . |
| 27 | MICIKEVICIUS P, STOSIC D, BURGESS N, et al. FP8 formats for deep learning[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2022: 2209.05433. (2022-09-12)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 28 | ZAMIRAI P, ZHANG J, ABERGER C R, et al. Revisiting BFloat16 training[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2020: 2010.06192. (2020-10-13)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 29 | FUJII K, NAKAMURA T, YOKOTA R. Balancing speed and stability: the trade-offs of FP8 vs. BF16 training in LLMs[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2411.08719. (2024-11-01)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 30 | ALLEY E C, KHIMULYA G, BISWAS S, et al. Unified rational protein engineering with sequence-based deep representation learning[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(12): 1315-1322. |
| 31 | HAYES T, RAO R, AKIN H, et al. Simulating 500 million years of evolution with a language model[J]. Science, 2025, 387(6736): 850-858. |
| 32 | MADANI A, KRAUSE B, GREENE E R, et al. Large language models generate functional protein sequences across diverse families[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(8): 1099-1106. |
| 33 | CHEN B, CHENG X Y, LI P, et al. xTrimoPGLM: unified 100-billion-parameter pretrained transformer for deciphering the language of proteins[J]. Nature Methods, 2025, 22(5): 1028-1039. |
| 34 | ELNAGGAR A, HEINZINGER M, DALLAGO C, et al. ProtTrans: toward understanding the language of life through self-supervised learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(10): 7112-7127. |
| 35 | SU J, HAN C C, ZHOU Y Y, et al. SaProt: protein language modeling with structure-aware vocabulary[C/OL]// The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR 2024, 2024[2025-06-03]. . |
| 36 | LI M C, TAN Y, MA X Z, et al. ProSST: protein language modeling with quantized structure and disentangled attention[C/OL]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 2024: 35700-35726 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 37 | MEIER J, RAO R, VERKUIL R, et al. Language models enable zero-shot prediction of the effects of mutations on protein function[C/OL]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (NeurIPS 2021), 2021: 29287-29303 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 38 | NOTIN P, DIAS M, FRAZER J, et al. Tranception: protein fitness prediction with autoregressive transformers and inference-time retrieval[C/OL]// Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, 2022, 162:16990-17017 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 39 | LUTZ I D, WANG S Z, NORN C, et al. Top-down design of protein architectures with reinforcement learning[J]. Science, 2023, 380(6642): 266-273. |
| 40 | WANG Y, TANG H, HUANG L C, et al. Self-play reinforcement learning guides protein engineering[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2023, 5(8): 845-860. |
| 41 | WEI J, TAY Y, BOMMASANI R, et al. Emergent abilities of large language models[J/OL]. Transactions on Machine Learning Research, 2022. (2022-08-31)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 42 | CHENG X Y, CHEN B, LI P, et al. Training compute-optimal protein language models[C/OL]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 37 (NeurIPS 2024), 2024[2025-06-03]. . |
| 43 | HESSLOW D, ZANICHELLI N, NOTIN P, et al. RITA: a study on scaling up generative protein sequence models[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2022: 2205.05789. (2022-07-14)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 44 | VIEIRA L C, HANDOJO M L, WILKE C O. Scaling down for efficiency: medium-sized protein language models perform well at transfer learning on realistic datasets[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2025: 2024.11.22.624936. (2025-05-08)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 45 | GAN W S, WAN S C, YU P S. Model-as-a-service (MaaS): a survey[C/OL]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData). December 15-18, 2023, Sorrento, Italy. IEEE, 2023: 4636-4645 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 46 | GOLDFARB T, KODALI V K, PUJAR S, et al. NCBI RefSeq: reference sequence standards through 25 years of curation and annotation[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53(D1): D243-D257. |
| 47 | DYER S C, AUSTINE-ORIMOLOYE O, AZOV A G, et al. Ensembl 2025[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53(D1): D948-D957. |
| 48 | The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2025[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53(D1): D609-D617. |
| 49 | FOURNIER Q, VERNON R M, VAN DER SLOOT A, et al. Protein language models: is scaling necessary?[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2024: 09.23.614603. (2024-09-23)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 50 | BRANDES N, OFER D, PELEG Y, et al. ProteinBERT: a universal deep-learning model of protein sequence and function[J]. Bioinformatics, 2022, 38(8): 2102-2110. |
| 51 | WANG Z Y, ZHANG Q, HU S W, et al. Multi-level protein structure pre-training via prompt learning[C/OL]// The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR 2023. (2023-02-02)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 52 | ZHANG N Y, BI Z, LIANG X Z, et al. OntoProtein: protein pretraining with gene ontology embedding[C/OL]// The Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR 2022. (2022-01-29)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 53 | GELMAN S, JOHNSON B, FRESCHLIN C, et al. Biophysics-based protein language models for protein engineering[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2025: 2024.03.15.585128. (2025-04-24)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 54 | BORN J, MANICA M. Regression transformer enables concurrent sequence regression and generation for molecular language modelling[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2023, 5(4): 432-444. |
| 55 | JIANG F, LI M C, DONG J J, et al. A general temperature-guided language model to design proteins of enhanced stability and activity[J]. Science Advances, 2024, 10(48): eadr2641. |
| 56 | DUMORTIER B, LIUTKUS A, CARRÉ C, et al. PeTriBERT: augmenting BERT with tridimensional encoding for inverse protein folding and design[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2022: 08.10.503344. (2022-08-13)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 57 | YANG K K, ZANICHELLI N, YEH H. Masked inverse folding with sequence transfer for protein representation learning[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2022, 36: gzad015. |
| 58 | DAUPARAS J, ANISHCHENKO I, BENNETT N, et al. Robust deep learning-based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6615): 49-56. |
| 59 | HSU C, VERKUIL R, LIU J, et al. Learning inverse folding from millions of predicted structures[C/OL]// Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, 2022, 162: 8946-8970 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 60 | ZHENG Z X, DENG Y F, XUE D Y, et al. Structure-informed language models are protein designers[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2023: 2302.01649. (2023-02-09)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 61 | ZHANG Z B, LU J R, CHENTHAMARAKSHAN V, et al. Structure-informed protein language model[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2402.05856. (2024-02-07)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 62 | CHEN D X, HARTOUT P, PELLIZZONI P, et al. Endowing protein language models with structural knowledge[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024: 2401.14819.(2024-01-26)[2025-06-03]. . |
| 63 | TAN Y, LI M C, ZHOU B X, et al. Simple, efficient, and scalable structure-aware adapter boosts protein language models[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2024, 64(16): 6338-6349. |
| 64 | CHENG J, NOVATI G, PAN J, et al. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6664): eadg7492. |
| 65 | TRUONG T F JR, BEPLER T. PoET: a generative model of protein families as sequences-of-sequences[C/OL]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems(NeurIPS 2023), 2023: 77379-415 [2025-06-03]. . |
| 66 | CHENG P, MAO C, TANG J, et al. Zero-shot prediction of mutation effects with multimodal deep representation learning guides protein engineering[J]. Cell Research, 2024, 34(9): 630-647. |
| 67 | OLSEN T H, BOYLES F, DEANE C M. Observed antibody space: a diverse database of cleaned, annotated, and translated unpaired and paired antibody sequences[J]. Protein Science, 2022, 31(1): 141-146. |
| 68 | NGUYEN E, POLI M, DURRANT M G, et al. Sequence modeling and design from molecular to genome scale with Evo[J]. Science, 2024, 386(6723): eado9336. |
| 69 | RIESSELMAN A J, INGRAHAM J B, MARKS D S. Deep generative models of genetic variation capture the effects of mutations[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(10): 816-822. |
| 70 | YU Y X, JIANG F, ZHONG B, et al. Entropy-driven zero-shot deep learning model selection for viral proteins[J]. Physical Review Research, 2025, 7: 013229. |
| [1] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [2] | ZHANG Chengxin. Challenges and opportunities in text mining-based protein function annotation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 603-616. |
| [3] | ZHU Jingyong, LI Junxiang, LI Xuhui, ZHANG Jin, WU Wenjing. Advances in applications of deep learning for predicting sequence-based protein interactions [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 88-106. |
| [4] | CHEN Zhihang, JI Menglin, QI Yifei. Research progress of artificial intelligence in desiging protein structures [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 464-487. |
| [5] | SONG Yidong, YUAN Qianmu, YANG Yuedong. Application of deep learning in protein function prediction [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 488-506. |
| [6] | LYU Jingwei, DENG Zixin, ZHANG Qi, DING Wei. Identification of RiPPs precursor peptides and cleavage sites based on deep learning [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1262-1276. |
| [7] | WANG Ye, WANG Haochen, YAN Minghao, HU Guanhua, WANG Xiaowo. Design of biomolecular sequences by artificial intelligence [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(1): 1-14. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||