Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (1): 65-86.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-061
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry
WEN Yanhua1,2, LIU Hedong3, CAO Chunlai2,3, WU Ruibo1
- 1.School of Pharmaceutical Science,Sun Yat-Sen University,Guangzhou 510006,Guangdong,China
2.Zhuhai United Laboratories Co. ,Ltd,Zhuhai 519040,Guangdong,China
3.The United Biotechnology (Zhuhai Hengqin) Co. ,Ltd. ,Zhuhai 519031,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2024-08-05Revised:2024-10-16Online:2025-03-12Published:2025-02-28 -
Contact:CAO Chunlai, WU Ruibo
蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用
温艳华1,2, 刘合栋3, 曹春来2,3, 巫瑞波1
- 1.中山大学药学院,广东 广州 510006
2.珠海联邦制药股份有限公司,广东 珠海 519040
3.联邦生物科技(珠海横琴)有限公司,广东 珠海 519031
-
通讯作者:曹春来,巫瑞波 -
作者简介:温艳华 (1995—),女,中山大学药学院和珠海联邦制药股份有限公司联合培养博士后。研究方向为蛋白质工程、生物合成和新药研发。E-mail:wenyh37@mail.sysu.edu.cn曹春来 (1979—),男,硕士生导师,制药高级工程师,联邦生物科技(珠海横琴)有限公司总经理,珠海联邦制药股份有限公司生物研究所所长。研究方向为代谢疾病和自身免疫疾病的新药研发。E-mail:caocl@tul.com.cn巫瑞波 (1984—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为计算辅助的天然产物药效挖掘与生物合成。E-mail:wurb3@mail.sysu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(22473118)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WEN Yanhua, LIU Hedong, CAO Chunlai, WU Ruibo. Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 65-86.
温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-061
| 酶 | 来源 | 蛋白质工程策略 | 应用 | 效益 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转氨酶ATA-117 | Arthrobacter sp. | 底物游走、随机突变、ProSAR、理性设计 | 西格列汀酮→西格列汀[ | 收率↑,产量↑ 生产成本↓,废料↓ |
| 转氨酶S6 | Chromobacterium violaceum | 底物游走、迭代饱和突变、随机突变 | CGRP受体拮抗剂rimegepant中间体的合成[ | 活性↑,转化率↑ |
| 酰基转移酶LovD | Aspergillus terreus | ProSAR、半理性设计 | 莫那可林J→辛伐他汀[ | 活性↑,稳定性↑ 反应步骤↓,有毒试剂↓, 酰基供体用量↓ |
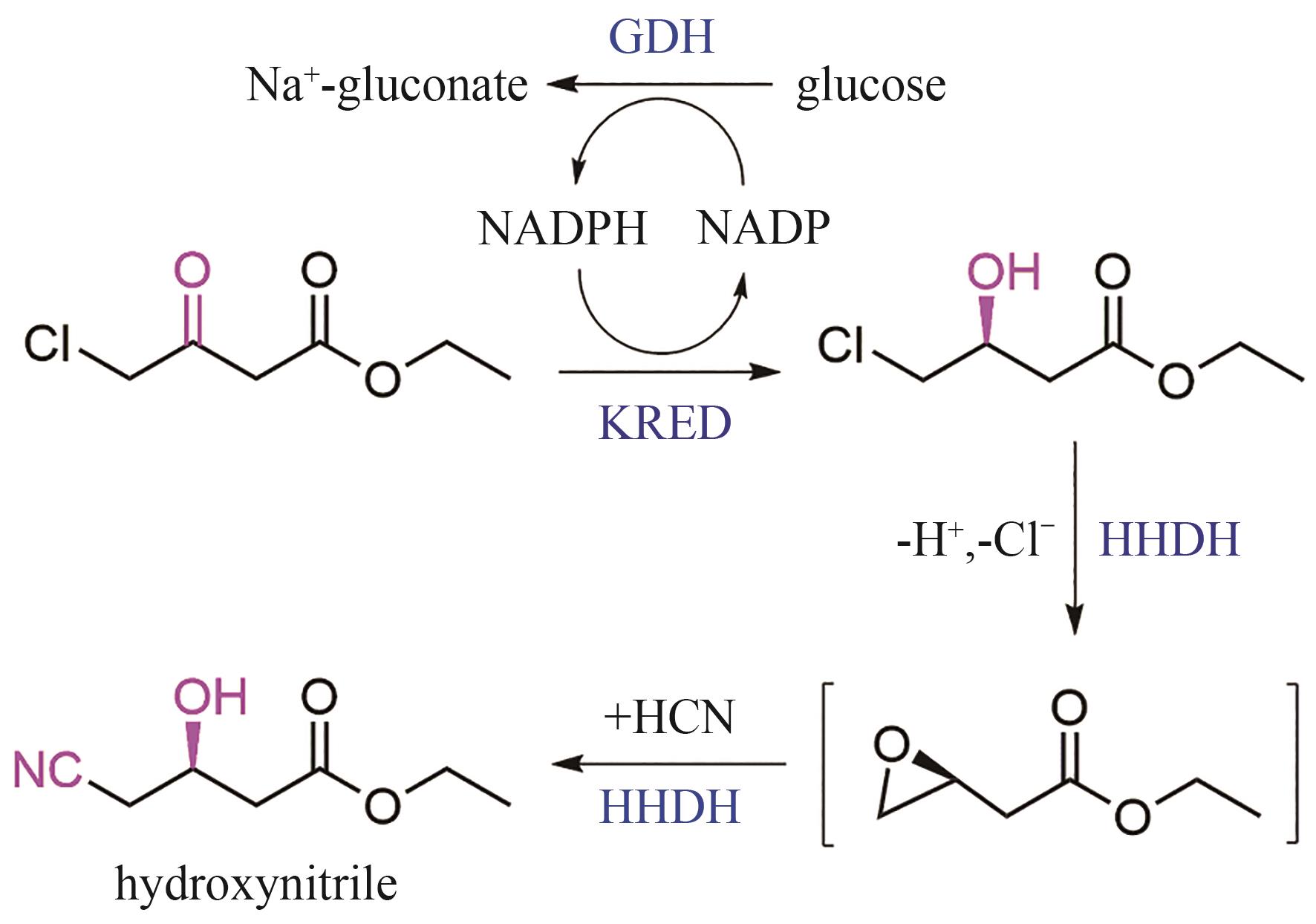
| 酮还原酶 | Candida magnoliae | DNA shuffling | 阿托伐他汀中间体 羟基腈的合成[ | 活性↑,稳定性↑,E因子↑, 体积生产率↑ |
| 葡萄糖脱氢酶 | Bacillus subtilis Bacillus megaterium | |||
| 卤代醇脱卤酶 | Agrobacterium sp. | |||
| 酰胺酶Pa-Ami | Pantoea sp. | 理性设计、通道改造 | 2-氯烟酰胺→2-氯烟酸[ | 底物载量↑,转化率↑, 时空收率↑ |
| 单胺氧化酶MAON | Aspergillus niger | 随机突变、半理性设计 | 抗病毒药波塞普韦中间体的合成[ | 活性↑,稳定性↑,收率↑ 原材料↓,用水量↓ |
Table 1 Applications of protein engineering in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients
| 酶 | 来源 | 蛋白质工程策略 | 应用 | 效益 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转氨酶ATA-117 | Arthrobacter sp. | 底物游走、随机突变、ProSAR、理性设计 | 西格列汀酮→西格列汀[ | 收率↑,产量↑ 生产成本↓,废料↓ |
| 转氨酶S6 | Chromobacterium violaceum | 底物游走、迭代饱和突变、随机突变 | CGRP受体拮抗剂rimegepant中间体的合成[ | 活性↑,转化率↑ |
| 酰基转移酶LovD | Aspergillus terreus | ProSAR、半理性设计 | 莫那可林J→辛伐他汀[ | 活性↑,稳定性↑ 反应步骤↓,有毒试剂↓, 酰基供体用量↓ |
| 酮还原酶 | Candida magnoliae | DNA shuffling | 阿托伐他汀中间体 羟基腈的合成[ | 活性↑,稳定性↑,E因子↑, 体积生产率↑ |
| 葡萄糖脱氢酶 | Bacillus subtilis Bacillus megaterium | |||
| 卤代醇脱卤酶 | Agrobacterium sp. | |||
| 酰胺酶Pa-Ami | Pantoea sp. | 理性设计、通道改造 | 2-氯烟酰胺→2-氯烟酸[ | 底物载量↑,转化率↑, 时空收率↑ |
| 单胺氧化酶MAON | Aspergillus niger | 随机突变、半理性设计 | 抗病毒药波塞普韦中间体的合成[ | 活性↑,稳定性↑,收率↑ 原材料↓,用水量↓ |
| 酶/抗体 | 来源 | 蛋白质工程策略 | 应用 | 效益 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青霉素G酰化酶 | Kluyvera cryocrescens | 定向进化 | 胰岛素特定位置的保护和脱保护[ | 位置选择性↑,催化活性↑ |
| 果糖肽氧化酶 | Eupenicillium terrenum | 理性设计、定点突变 | 糖尿病诊断[ | 催化活性↑,催化特异性↑ |
| 纤维蛋白溶解酶 | Homo sapiens | 丙氨酸扫描[ | 治疗急性心肌梗死的抗凝剂[ | 纤维蛋白特异性↑,耐受内源蛋白酶降解能力↑,半衰期↑ |
| 尿酸氧化酶 | mammals | DNA shuffling | 治疗高尿酸血症和痛风[ | 活性↑,免疫原性↓,半衰期↑ |
| 尿酸氧化酶 | Candida utilis | 理性设计 | 治疗高尿酸血症和痛风的候选口服药物[ | 胰酶和肠液稳定性↑,半衰期↑ |
| 纳米抗体K922 | 大羊驼免疫 噬菌体文库筛选 | DNA shuffling | 减少大肠杆菌引起的仔猪腹泻[ | 胃液和肠液稳定性↑ |
Table 2 Applications of protein engineering in the biopharmaceutical industry
| 酶/抗体 | 来源 | 蛋白质工程策略 | 应用 | 效益 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青霉素G酰化酶 | Kluyvera cryocrescens | 定向进化 | 胰岛素特定位置的保护和脱保护[ | 位置选择性↑,催化活性↑ |
| 果糖肽氧化酶 | Eupenicillium terrenum | 理性设计、定点突变 | 糖尿病诊断[ | 催化活性↑,催化特异性↑ |
| 纤维蛋白溶解酶 | Homo sapiens | 丙氨酸扫描[ | 治疗急性心肌梗死的抗凝剂[ | 纤维蛋白特异性↑,耐受内源蛋白酶降解能力↑,半衰期↑ |
| 尿酸氧化酶 | mammals | DNA shuffling | 治疗高尿酸血症和痛风[ | 活性↑,免疫原性↓,半衰期↑ |
| 尿酸氧化酶 | Candida utilis | 理性设计 | 治疗高尿酸血症和痛风的候选口服药物[ | 胰酶和肠液稳定性↑,半衰期↑ |
| 纳米抗体K922 | 大羊驼免疫 噬菌体文库筛选 | DNA shuffling | 减少大肠杆菌引起的仔猪腹泻[ | 胃液和肠液稳定性↑ |
| 1 | BORNSCHEUER U T, HUISMAN G W, KAZLAUSKAS R J, et al. Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7397): 185-194. |
| 2 | ABDELRAHEEM E M M, BUSCH H, HANEFELD U, et al. Biocatalysis explained: from pharmaceutical to bulk chemical production[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 4(11): 1878-1894. |
| 3 | TAO J H, XU J H. Biocatalysis in development of green pharmaceutical processes[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2009, 13(1): 43-50. |
| 4 | PRASAD S, ROY I. Converting enzymes into tools of industrial importance[J]. Recent Patents on Biotechnology, 2018, 12(1): 33-56. |
| 5 | FASAN R D, JENNIFER KAN S B, ZHAO H M. A continuing career in biocatalysis: Frances H. Arnold[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(11): 9775-9788. |
| 6 | 曲戈, 赵晶, 郑平, 等. 定向进化技术的最新进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(1): 1-11. |
| QU G, ZHAO J, ZHENG P, et al. Recent advances in directed evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 34(1): 1-11. | |
| 7 | HECKO S, SCHIEFER A, BADENHORST C P S, et al. Enlightening the path to protein engineering: chemoselective turn-on probes for high-throughput screening of enzymatic activity[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(6): 2832-2901. |
| 8 | TRAXLMAYR M W, OBINGER C. Directed evolution of proteins for increased stability and expression using yeast display[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2012, 526(2): 174-180. |
| 9 | AGRESTI J J, ANTIPOV E, ABATE A R, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(9): 4004-4009. |
| 10 | 杨建花, 苏晓岚, 朱蕾蕾. 高通量筛选系统在定向改造中的新进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. |
| YANG J H, SU X L, ZHU L L. Advances of high-throughput screening system in reengineering of biological entities[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(7): 2197-2210. | |
| 11 | REETZ M T, KAHAKEAW D, LOHMER R. Addressing the numbers problem in directed evolution[J]. ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(11): 1797-1804. |
| 12 | KILLE S, ACEVEDO-ROCHA C G, PARRA L P, et al. Reducing Codon redundancy and screening effort of combinatorial protein libraries created by saturation mutagenesis[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(2): 83-92. |
| 13 | SUN Z T, LONSDALE R, WU L, et al. Structure-guided triple-code saturation mutagenesis: efficient tuning of the stereoselectivity of an epoxide hydrolase[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(3): 1590-1597. |
| 14 | REETZ M T, BOCOLA M, CARBALLEIRA J D, et al. Expanding the range of substrate acceptance of enzymes: combinatorial active-site saturation test[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(27): 4192-4196. |
| 15 | REETZ M T, CARBALLEIRA J D. Iterative saturation mutagenesis (ISM) for rapid directed evolution of functional enzymes[J]. Nature Protocols, 2007, 2(4): 891-903. |
| 16 | LI D Y, WU Q, REETZ M T. Focused rational iterative site-specific mutagenesis (FRISM)[M/OL]//Methods in enzymology: enzyme engineering and evolution: general methods, 2020, 643: 225-242. (2020-09-04)[2024-06-25]. . |
| 17 | XU J, CEN Y X, SINGH W, et al. Stereodivergent protein engineering of a lipase to access all possible stereoisomers of chiral esters with two stereocenters[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(19): 7934-7945. |
| 18 | FOX R. Directed molecular evolution by machine learning and the influence of nonlinear interactions[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2005, 234(2): 187-199. |
| 19 | 蒋迎迎, 曲戈, 孙周通. 机器学习助力酶定向进化[J]. 生物学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 1-11. |
| JIANG Y Y, QU G, SUN Z T. Machine learning-assisted enzyme directed evolution[J]. Journal of Biology, 2020, 37(4): 1-11. | |
| 20 | 康里奇, 谈攀, 洪亮. 人工智能时代下的酶工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. |
| KANG L Q, TAN P, HONG L. Enzyme engineering in the age of artificial intelligence[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. | |
| 21 | 曲戈, 朱彤, 蒋迎迎, 等. 蛋白质工程: 从定向进化到计算设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. |
| QU G, ZHU T, JIANG Y Y, et al. Protein engineering: from directed evolution to computational design[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. | |
| 22 | FOX R J, DAVIS S C, MUNDORFF E C, et al. Improving catalytic function by ProSAR-driven enzyme evolution[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(3): 338-344. |
| 23 | ROMERO P A, KRAUSE A, ARNOLD F H. Navigating the protein fitness landscape with Gaussian processes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(3): E193-E201. |
| 24 | WU Z, JENNIFER KAN S B J, LEWIS R D, et al. Machine learning-assisted directed protein evolution with combinatorial libraries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(18): 8852-8858. |
| 25 | YANG K K, WU Z, ARNOLD F H. Machine-learning-guided directed evolution for protein engineering[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(8): 687-694. |
| 26 | HUANG P S, BOYKEN S E, BAKER D. The coming of age of de novo protein design[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7620): 320-327. |
| 27 | WOOLFSON D N. A brief history of de novo protein design: minimal, rational, and computational[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2021, 433(20): 167160. |
| 28 | JIANG L, ALTHOFF E A, CLEMENTE F R, et al. De novo computational design of Retro-Aldol enzymes[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5868): 1387-1391. |
| 29 | RÖTHLISBERGER D, KHERSONSKY O, WOLLACOTT A M, et al. Kemp elimination catalysts by computational enzyme design[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7192): 190-195. |
| 30 | SIEGEL J B, ZANGHELLINI A, LOVICK H M, et al. Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels-Alder reaction[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5989): 309-313. |
| 31 | 阮青云, 黄莘, 孟子钧, 等. 蛋白质稳定性计算设计与定向进化前沿工具[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. |
| RUAN Q Y, HUANG X, MENG Z J, et al. Computational design and directed evolution strategies for optimizing protein stability[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 5-29. | |
| 32 | SCHYMKOWITZ J, BORG J, STRICHER F, et al. The FoldX web server: an online force field[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, 33(Web Server issue): W382-W388. |
| 33 | WEINSTEIN J J, GOLDENZWEIG A, HOCH S, et al. PROSS 2: a new server for the design of stable and highly expressed protein variants[J]. Bioinformatics, 2021, 37(1): 123-125. |
| 35 | WIJMA H J, FLOOR R J, JEKEL P A, et al. Computationally designed libraries for rapid enzyme stabilization[J]. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 2014, 27(2): 49-58. |
| 36 | MUSIL M, STOURAC J, BENDL J, et al. FireProt: web server for automated design of thermostable proteins[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W393-W399. |
| 37 | CHOWDHURY R, MARANAS C D.From directed evolution to computational enzyme engineering—a review[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(3): e16847. |
| 38 | BULLER R, LUTZ S, KAZLAUSKAS R J, et al. From nature to industry: harnessing enzymes for biocatalysis[J]. Science, 2023, 382(6673): eadh8615. |
| 39 | REETZ M T, SUN Z T, QU G. Enzyme engineering: selective catalysts for applications in biotechnology, organic chemistry, and life science[M/OL]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2023. (2023-01-06)[2024-05-01]. . |
| 40 | ANASTAS P T, ALLEN D T. Twenty-five years of green chemistry and green engineering: the end of the beginning[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(11): 5820. |
| 41 | SHELDON R A. E factors, green chemistry and catalysis: an odyssey[J]. Chemical Communications, 2008(29): 3352-3365. |
| 42 | BECKER J, MANSKE C, RANDL S. Green chemistry and sustainability metrics in the pharmaceutical manufacturing sector[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2022, 33: 100562. |
| 43 | HAGEN T J, HELGREN T R. Chirality and drug discovery[M/OL]//Abraham D J. Burger’s medicinal chemistry, drug discovery and development. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2021: 1-45. (2021-04-26)[2024-05-01]. . |
| 44 | REETZ M T. Recent advances in directed evolution of stereoselective enzymes[M/OL]//Directed enzyme evolution: advances and applications. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 69-99. (2017-02-15)[2024-05-01]. . |
| 45 | MENTLEIN R, GALLWITZ B, SCHMIDT W E. Dipeptidyl-peptidase Ⅳ hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide, peptide histidine methionine and is responsible for their degradation in human serum[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1993, 214(3): 829-835. |
| 46 | VAHL T P, PATY B W, FULLER B D, et al. Effects of GLP-1-(7-36)NH2, GLP-1-(7-37), and GLP-1-(9-36)NH2 on intravenous glucose tolerance and glucose-induced insulin secretion in healthy humans[J]. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2003, 88(4): 1772-1779. |
| 47 | BROCKUNIER L L, HE J F, COLWELL L F JR, et al. Substituted piperazines as novel dipeptidyl peptidase Ⅳ inhibitors[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2004, 14(18): 4763-4766. |
| 48 | ANGELAUD R, ZHONG Y L, MALIGRES P, et al. Synthesis of a β-amino acid pharmacophore via a β-lactam intermediate[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2005, 70(5): 1949-1952. |
| 49 | HANSEN K B, BALSELLS J, DREHER S, et al. First generation process for the preparation of the DPP-Ⅳ inhibitor sitagliptin[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2005, 9(5): 634-639. |
| 50 | HANSEN K B, HSIAO Y, XU F, et al. Highly efficient asymmetric synthesis of sitagliptin[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(25): 8798-8804. |
| 51 | DESAI A A. Sitagliptin manufacture: a compelling tale of green chemistry, process intensification, and industrial asymmetric catalysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(9): 1974-1976. |
| 52 | EPA. Presidential green chemistry challenge: 2006 greener synthetic pathways award[EB/OL]. (2023-12-19)[2024-06-10]. . |
| 53 | GEN. Merck & Co. Licenses Codexis’ CodeEvolver® Platform[EB/OL]. [2024-06-10]. . |
| 54 | SAVILE C K, JANEY J M, MUNDORFF E C, et al. Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5989): 305-309. |
| 55 | KOHLS H, STEFFEN-MUNSBERG F, HÖHNE M. Recent achievements in developing the biocatalytic toolbox for chiral amine synthesis[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2014, 19: 180-192. |
| 56 | GUO F, BERGLUND P. Transaminase biocatalysis: optimization and application[J]. Green Chemistry, 2017, 19(2): 333-360. |
| 57 | KELLY S A, MIX S, MOODY T S, et al. Transaminases for industrial biocatalysis: novel enzyme discovery[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(11): 4781-4794. |
| 58 | IWASAKI A, YAMADA Y, KIZAKI N, et al. Microbial synthesis of chiral amines by (R)-specific transamination with Arthrobacter sp. KNK168[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 69(5): 499-505. |
| 59 | CHEN Z L, ZHAO H M. Rapid creation of a novel protein function by in vitro coevolution[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2005, 348(5): 1273-1282. |
| 60 | EPA. Presidential green chemistry challenge: 2010 greener reaction conditions award[EB/OL]. (2024-08-01)[2024-08-10]. . |
| 61 | MA Y L, JIAO X C, WANG Z J, et al. Engineering a transaminase for the efficient synthesis of a key intermediate for rimegepant[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2022, 26(7): 1971-1977. |
| 62 | KELLY S A, POHLE S, WHARRY S, et al. Application of ω-transaminases in the pharmaceutical industry[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(1): 349-367. |
| 63 | ENDO A. The discovery and development of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors[J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 1992, 33(11): 1569-1582. |
| 64 | MOL M J T M, WILLEM ERKELENS D, GEVERS LEUVEN J A, et al. Simvastatin (MK-733): a potent cholesterol synthesis inhibitor in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia[J]. Atherosclerosis, 1988, 69(2-3): 131-137. |
| 65 | HOYOS P, PACE V, ALCÁNTARA A R. Biocatalyzed synthesis of statins: a sustainable strategy for the preparation of valuable drugs[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(3): 260. |
| 66 | XIE X K, TANG Y. Efficient synthesis of simvastatin by use of whole-cell biocatalysis[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(7): 2054-2060. |
| 67 | XIE X K, WATANABE K, WOJCICKI W A, et al. Biosynthesis of lovastatin analogs with a broadly specific acyltransferase[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2006, 13(11): 1161-1169. |
| 68 | GAO X, XIE X K, PASHKOV I, et al. Directed evolution and structural characterization of a simvastatin synthase[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2009, 16(10): 1064-1074. |
| 69 | JAMES C S, LING T E, JOLY S, et al. Improved Lov-D acyltransferase mediated acylation: WO2011041233A1[P]. 2011-04-07. |
| 70 | LYNNE G, JAMES C S, JOLY S, et al. Variant LovD polypeptides and their uses: WO2011041231A1[P]. 2011-04-07. |
| 71 | JIMÉNEZ-OSÉS G, OSUNA S, GAO X, et al. The role of distant mutations and allosteric regulation on LovD active site dynamics[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(6): 431-436. |
| 72 | EPA. Presidential green chemistry challenge: 2012 greener synthetic pathways award[EB/OL]. (2024-06-06)[2024-06-10]. . |
| 73 | GARCÍA-MARQUINA G, NÚÑEZ-FRANCO R, PECCATI F, et al. Deconvoluting the directed evolution pathway of engineered acyltransferase LovD[J]. ChemCatChem, 2022, 14(4): e202101349. |
| 74 | LI Z N, YANG H D, LIU J Y, et al. Application of ketoreductase in asymmetric synthesis of pharmaceuticals and bioactive molecules: an update (2018—2020)[J]. The Chemical Record, 2021, 21(7): 1611-1630. |
| 75 | PATEL J M. Biocatalytic synthesis of atorvastatin intermediates[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 2009, 61(3-4): 123-128. |
| 76 | MA S K, GRUBER J, DAVIS C, et al. A green-by-design biocatalytic process for atorvastatin intermediate[J]. Green Chemistry, 2010, 12(1): 81-86. |
| 77 | DAVIS S C, GRATE J H, GRAY D R, et al. Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives: US7125693B2[P]. 2006-10-24. |
| 78 | DAVIS S C, GRATE J H, GRAY D R, et al. Enzymatic processes for the production of 4-substituted 3-hydroxybutyric acid derivatives and vicinal cyano, hydroxy substituted carboxylic acid esters: US7132267B2[P]. 2006-11-07. |
| 79 | BAUSCH M, SCHULTHEISS C, SIECK J B. Recommendations for comparison of productivity between fed-batch and perfusion processes[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 14(2): 1700721. |
| 80 | EPA. Presidential green chemistry challenge: 2006 greener reaction conditions award[EB/OL]. (2024-06-06)[2024-09-26]. . |
| 81 | QIAO L, LUO Z Y, CHEN H M, et al. Engineering ketoreductases for the enantioselective synthesis of chiral alcohols[J]. Chemical Communications, 2023, 59(49): 7518-7533. |
| 82 | SHANBHAG A P. Stairway to stereoisomers: engineering short- and medium-chain ketoreductases to produce chiral alcohols[J]. ChemBioChem, 2023, 24(6): e202200687. |
| 83 | SHARMA M, SHARMA N N, BHALLA T C. Amidases: versatile enzymes in nature[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2009, 8(4): 343-366. |
| 84 | WU Z M, LIU C F, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Amidase as a versatile tool in amide-bond cleavage: from molecular features to biotechnological applications[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 43: 107574. |
| 85 | ZHENG R C, JIN J Q, WU Z M, et al. Biocatalytic hydrolysis of chlorinated nicotinamides by a superior AS family amidase and its application in enzymatic production of 2-chloronicotinic acid[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry, 2018, 76: 81-87. |
| 86 | WU Z M, ZHENG R C, ZHENG Y G. Exploitation and characterization of three versatile amidase super family members from Delftia tsuruhatensis ZJB-05174[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2016, 86: 93-102. |
| 87 | RUAN L T, ZHENG R C, ZHENG Y G. Mining and characterization of two amidase signature family amidases from Brevibacterium epidermidis ZJB-07021 by an efficient genome mining approach[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2016, 126: 16-25. |
| 88 | JIN L Q, LIU Z Q, XU J M, et al. Efficient biocatalytic hydrolysis of 2-chloronicotinamide for production of 2-chloronicotinic acid by recombinant amidase[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2013, 38: 6-9. |
| 89 | TANG X L, JIN J Q, WU Z M, et al. Structure-based engineering of amidase from Pantoea sp. for efficient 2-chloronicotinic acid biosynthesis[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2019, 85(5): e02471-18. |
| 90 | GORA A, BREZOVSKY J, DAMBORSKY J. Gates of enzymes[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(8): 5871-5923. |
| 91 | WU Z M, XIE F, ZHENG W, et al. Structure-oriented engineering of amidase: modification of twisted access tunnel for efficient synthesis of 2-chloronicotinic acid[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(13): 9078-9089. |
| 92 | LI T, LIANG J, AMBROGELLY A, et al. Efficient, chemoenzymatic process for manufacture of the Boceprevir bicyclic [3.1.0] proline intermediate based on amine oxidase-catalyzed desymmetrization[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(14): 6467-6472. |
| 93 | ZHANG J, MA Y Q, ZHU F F, et al. Structure-guided semi-rational design of an imine reductase for enantio-complementary synthesis of pyrrolidinamine[J]. Chemical Science, 2023, 14(16): 4265-4272. |
| 94 | YUAN B, YANG D M, QU G, et al. Biocatalytic reductive aminations with NAD(P)H-dependent enzymes: enzyme discovery, engineering and synthetic applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2024, 53(1): 227-262. |
| 95 | 杨璐, 瞿旭东. 亚胺还原酶在手性胺合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 516-529. |
| YANG L, QU X D. Application of imine reductase in the synthesis of chiral amines[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 516-529. | |
| 96 | 熊亮斌, 宋璐, 赵云秋, 等. 甾体化合物绿色生物制造: 从生物转化到微生物从头合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. |
| XIONG L B, SONG L, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Green biomanufacturing of steroids: from biotransformation to de novo synthesis by microorganisms[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 942-963. | |
| 97 | 汤恒, 韩鑫, 邹树平, 等. 多酶催化体系在医药化学品合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 559-576. |
| TANG H, HAN X, ZOU S P, et al. Application of multi-enzyme catalytic system in the synthesis of pharmaceutical chemicals[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 559-576. | |
| 98 | EPA. Green chemistry challenge: 2022 greener synthetic pathways award[EB/OL]. (2024-05-02)[2024-06-10]. . |
| 99 | CRUZ G, ACOSTA J, DEL ARCO J, et al. Enzyme-mediated synthesis of molnupiravir: paving the way for the application of biocatalysis in pharmaceutical industry[J]. ChemCatChem, 2022, 14(13): e202200140. |
| 100 | ROSANGZUALA K, PATLOLLA R R, SHAIKH A, et al. Streamlined chemo-enzymatic synthesis of molnupiravir via lipase catalyst[J]. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(4): 4423-4428. |
| 101 | REETZ M T, QU G, SUN Z T. Engineered enzymes for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other high-value products[J]. Nature Synthesis, 2024, 3: 19-32. |
| 102 | WANG L, WANG N X, ZHANG W P, et al. Therapeutic peptides: current applications and future directions[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2022, 7(1): 48. |
| 103 | SHARMA K, SHARMA K K, SHARMA A, et al. Peptide-based drug discovery: current status and recent advances[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2023, 28(2): 103464. |
| 104 | ROSSINO G, MARCHESE E, GALLI G, et al. Peptides as therapeutic agents: challenges and opportunities in the green transition era[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(20): 7165. |
| 105 | MULLARD A. FDA approves 100th monoclonal antibody product[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(7): 491-495. |
| 106 | JIN B K, ODONGO S, RADWANSKA M, et al. NANOBODIES®: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic applications[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(6): 5994. |
| 107 | MUSAIMI O AL, SHAER D AL, ALBERICIO F, et al. 2022 FDA TIDES (peptides and oligonucleotides) harvest[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2023, 16(3): 336. |
| 108 | ZINSLI L V, STIERLIN N, LOESSNER M J, et al. Deimmunization of protein therapeutics - recent advances in experimental and computational epitope prediction and deletion[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19: 315-329. |
| 109 | CANTOR J R, PANAYIOTOU V, AGNELLO G, et al. Engineering reduced-immunogenicity enzymes for amino acid depletion therapy in cancer[M/OL]//Methods in enzymology. New York, USA: Elsevier Science & Technology, 2012, 502: 291-319. (2011-12-09)[2024-06-25]. . |
| 110 | FUHRMANN G, LEROUX J C. Improving the stability and activity of oral therapeutic enzymes-recent advances and perspectives[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 31(5): 1099-1105. |
| 111 | LAPUHS P, FUHRMANN G. Engineering strategies for oral therapeutic enzymes to enhance their stability and activity[M/OL]//LABROU N. Advances in experimental medicine and biology: therapeutic enzymes: function and clinical implications. Singapore: Springer, 2019, 1148: 151-172. (2019-09-04)[2024-06-25]. . |
| 112 | DEBON A, SIIROLA E, SNAJDROVA R. Enzymatic bioconjugation: a perspective from the pharmaceutical industry[J]. JACS Au, 2023, 3(5): 1267-1283. |
| 113 | FRYSZKOWSKA A, AN C H, ALVIZO O, et al. A chemoenzymatic strategy for site-selective functionalization of native peptides and proteins[J]. Science, 2022, 376(6599): 1321-1327. |
| 114 | MORIHARA K. Enzymatic semisynthesis of human insulin: an update[J]. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 1990, 3(5/6): 181-186. |
| 115 | LIU Y D, BEARDSLEY M I, YANG F. Expanding the analytical toolbox: developing new Lys-C peptide mapping methods with minimized assay-induced artifacts to fully characterize antibodies[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2023, 16(9): 1327. |
| 116 | SINGH R S, SINGH T, SINGH A K. Enzymes as diagnostic tools[M/OL]//Advances in enzyme technology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 225-271.(2019-02-15)[2024-06-25]. . |
| 117 | 周文娟, 吴云翔, 易军. 糖化血红蛋白标准化及其检测技术的发展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2015, 42(5): 443-456. |
| ZHOU W J, WU Y X, YI J. Standardization and technology development of measurement of glycated human hemoglobin[J]. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2015, 42(5): 443-456. | |
| 118 | SHAHBAZMOHAMMADI H, SARDARI S, LARI A, et al. Engineering an efficient mutant of Eupenicillium terrenum fructosyl peptide oxidase for the specific determination of hemoglobin A1c[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(4): 1725-1735. |
| 119 | TANDON S, SHARMA A, SINGH S, et al. Therapeutic enzymes: discoveries, production and applications[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2021, 63: 102455. |
| 120 | HENNIGAN J N, LYNCH M D. The past, present, and future of enzyme-based therapies[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2022, 27(1): 117-133. |
| 121 | DE LA FUENTE M, LOMBARDERO L, GÓMEZ-GONZÁLEZ A, et al. Enzyme therapy: current challenges and future perspectives[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(17): 9181. |
| 122 | MICHAILIDOU F. Engineering of therapeutic and detoxifying enzymes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(46): e202308814. |
| 123 | VICTORINO DA SILVA AMATTO I, GONSALES DA ROSA-GARZON N, ANTÔNIO DE OLIVEIRA SIMÕES F, et al. Enzyme engineering and its industrial applications[J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2022, 69(2): 389-409. |
| 124 | MENDIS S, DAVIS S, NORRVING B. Organizational update: the World Health Organization global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014; one more landmark step in the combat against stroke and vascular disease[J]. Stroke, 2015, 46(5): e121-e122. |
| 125 | VACHHER M, SEN A, KAPILA R, et al. Microbial therapeutic enzymes: a promising area of biopharmaceuticals[J]. Current Research in Biotechnology, 2021, 3: 195-208. |
| 126 | CRAIK C S, PAGE M J, MADISON E L. Proteases as therapeutics[J]. Biochemical Journal, 2011, 435(1): 1-16. |
| 127 | PAONI N F, CHOW A M, PEÑA L C, et al. Making tissue-type plasminogen activator more fibrin specific[J]. Protein Engineering, 1993, 6(5): 529-534. |
| 128 | KEYT B A, PAONI N F, REFINO C J, et al. A faster-acting and more potent form of tissue plasminogen activator[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(9): 3670-3674. |
| 129 | WU X W, LEE C C, MUZNY D M, et al. Urate oxidase: primary structure and evolutionary implications[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1989, 86(23): 9412-9416. |
| 130 | CAMMALLERI L, MALAGUARNERA M. Rasburicase represents a new tool for hyperuricemia in tumor Lysis syndrome and in gout[J]. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 2007, 4(2): 83-93. |
| 131 | NYBORG A C, WARD C, ZACCO A, et al. A therapeutic uricase with reduced immunogenicity risk and improved development properties[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0167935. |
| 132 | CHEN J, JIANG N, WANG T, et al. DNA shuffling of uricase gene leads to a more “human like” chimeric uricase with increased uricolytic activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 82: 522-529. |
| 133 | PIERZYNOWSKA K, DESHPANDE A, MOSIICHUK N, et al. Oral treatment with an engineered uricase, ALLN-346, reduces hyperuricemia, and uricosuria in urate oxidase-deficient mice[J]. Frontiers in Medicine, 2020, 7: 569215. |
| 134 | CHEN D, ZHAO Y J, LI M Y, et al. A general Fc engineering platform for the next generation of antibody therapeutics[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(4): 1901-1917. |
| 135 | CHIU M L, GILLILAND G L. Engineering antibody therapeutics[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2016, 38: 163-173. |
| 136 | DUCANCEL F, MULLER B H. Molecular engineering of antibodies for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes[J]. mAbs, 2012, 4(4): 445-457. |
| 137 | SHEN Z L, SANG Z, SHI Y. Nanobodies as a powerful platform for biomedicine[J]. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 2022, 28(11): 1006-1007. |
| 138 | HARMSEN M M, VAN SOLT C B, VAN ZIJDERVELD-VAN BEMMEL A M, et al. Selection and optimization of proteolytically stable llama single-domain antibody fragments for oral immunotherapy[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72(3): 544-551. |
| 139 | CHUNGYOUN M F, GRAY J J. AI models for protein design are driving antibody engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering, 2023, 28: 100473. |
| 140 | LIPPOW S M, WITTRUP K D, TIDOR B. Computational design of antibody-affinity improvement beyond in vivo maturation[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(10): 1171-1176. |
| 141 | SIRCAR A, GRAY J J. SnugDock: paratope structural optimization during antibody-antigen docking compensates for errors in antibody homology models[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2010, 6(1): e1000644. |
| 142 | WEITZNER B D, KURODA D, MARZE N, et al. Blind prediction performance of RosettaAntibody 3.0: grafting, relaxation, kinematic loop modeling, and full CDR optimization[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2014, 82(8): 1611-1623. |
| 143 | MARKS C, HUMMER A M, CHIN M, et al. Humanization of antibodies using a machine learning approach on large-scale repertoire data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2021, 37(22): 4041-4047. |
| 144 | KIM J, MCFEE M, FANG Q, et al. Computational and artificial intelligence-based methods for antibody development[J]. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2023, 44(3): 175-189. |
| 145 | BAILLY M, MIECZKOWSKI C, JUAN V, et al. Predicting antibody developability profiles through early stage discovery screening[J]. mAbs, 2020, 12(1): 1743053. |
| 146 | KERI D, WALKER M, SINGH I, et al. Next generation of multispecific antibody engineering[J]. Antibody Therapeutics, 2024, 7(1): 37-52. |
| 147 | HIE B L, SHANKER V R, XU D, et al. Efficient evolution of human antibodies from general protein language models[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2024, 42(2): 275-283. |
| 148 | SHANKER V R, BRUUN T U J, HIE B L, et al. Unsupervised evolution of protein and antibody complexes with a structure-informed language model[J]. Science, 2024, 385(6704): 46-53. |
| 149 | DAUPARAS J, ANISHCHENKO I, BENNETT N, et al. Robust deep learning-based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6615): 49-56. |
| 150 | BENNETT N R, WATSON J L, RAGOTTE R J, et al. Atomically accurate de novo design of single-domain antibodies[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2024: 2024.03.14.585103. (2024-05-18)[2024-06-25]. . |
| 151 | EBRAHIMI S B, SAMANTA D. Engineering protein-based therapeutics through structural and chemical design[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 2411. |
| 152 | BENNETT W F, PAONI N F, KEYT B A, et al. High resolution analysis of functional determinants on human tissue-type plasminogen activator[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1991, 266(8): 5191-5201. |
| 153 | KRISHNA R, WANG J, AHERN W, et al. Generalized biomolecular modeling and design with RoseTTAFold All-Atom[J]. Science, 2024, 384(6693): eadl2528. |
| 154 | ABRAMSON J, ADLER J, DUNGER J, et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3[J]. Nature, 2024, 630(8016): 493-500. |
| 155 | KROLL A, RANJAN S, ENGQVIST M K M, et al. A general model to predict small molecule substrates of enzymes based on machine and deep learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 2787. |
| 156 | KROLL A, ROUSSET Y, HU X P, et al. Turnover number predictions for kinetically uncharacterized enzymes using machine and deep learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 4139. |
| 157 | JANG Y J, QIN Q Q, HUANG S Y, et al. Accurate prediction of protein function using statistics-informed graph networks[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 6601. |
| 158 | WITTMANN B J, YUE Y S, ARNOLD F H. Informed training set design enables efficient machine learning-assisted directed protein evolution[J]. Cell Systems, 2021, 12(11): 1026-1045.e7. |
| 159 | CHEN L, ZHANG Z H, LI Z H, et al. Learning protein fitness landscapes with deep mutational scanning data from multiple sources[J]. Cell Systems, 2023, 14(8): 706-721.e5. |
| 160 | YU T H, BOOB A G, SINGH N, et al. In vitro continuous protein evolution empowered by machine learning and automation[J]. Cell Systems, 2023, 14(8): 633-644. |
| 161 | RAPP J T, BREMER B J, ROMERO P A. Self-driving laboratories to autonomously navigate the protein fitness landscape[J]. Nature Chemical Engineering, 2024, 1(1): 97-107. |
| 162 | NOTIN P, ROLLINS N, GAL Y, et al. Machine learning for functional protein design[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2024, 42(2): 216-228. |
| 163 | WATSON J L, JUERGENS D, BENNETT N R, et al. De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion[J]. Nature, 2023, 620(7976): 1089-1100. |
| 164 | MADANI A, KRAUSE B, GREENE E R, et al. Large language models generate functional protein sequences across diverse families[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(8): 1099-1106. |
| 165 | VÁZQUEZ TORRES S, LEUNG P J Y, VENKATESH P, et al. De novo design of high-affinity binders of bioactive helical peptides[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(7998): 435-442. |
| 166 | SILVA D A, YU S, ULGE U Y, et al. De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7738): 186-191. |
| 167 | AGUILERA-PUGA M D C, CANCELARICH N L, MARANI M M, et al. Accelerating the discovery and design of antimicrobial peptides with artificial intelligence[M/OL]//GORE M, JAGTAP U B. Methods in molecular biology: computational drug discovery and design. New York: Humana, 2024, 2714: 329-352. (2023-09-08)[2024-06-25]. . |
| 168 | ZAMBALDI V, LA D, CHU A E, et al. De novo design of high-affinity protein binders with AlphaProteo[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2024, 2409.08022. (2024-09-12)[2024-10-01]. . |
| 169 | JOHNSON S R, FU X Z, VIKNANDER S, et al. Computational scoring and experimental evaluation of enzymes generated by neural networks[J/OL]. Nature Biotechnology, 2024. (2024-04-23)[2024-05-01]. . |
| 170 | CHU A E, LU T Y, HUANG P S. Sparks of function by de novo protein design[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2024, 42(2): 203-215. |
| 171 | KOLLURI S, LIN J C, LIU R, et al. Machine learning and artificial intelligence in pharmaceutical research and development: a review[J]. The AAPS Journal, 2022, 24(1): 19. |
| 172 | HARRER S, SHAH P, ANTONY B, et al. Artificial intelligence for clinical trial design[J]. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2019, 40(8): 577-591. |
| [1] | DONG Ying, MA Mengdan, HUANG Weiren. Progress in the miniaturization of CRISPR-Cas systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [2] | WANG Ziyuan, YANG Lirong, WU Jianping, ZHENG Wenlong. A review on enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of chiral amino acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [3] | CHENG Feng, ZOU Shuping, XU Jianmiao, TANG Heng, XUE Yaping, ZHENG Yuguo. BioHPP®: a benchmark of biomanufacturing for high optically pure L-phosphinothricin [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [4] | FU Yu, ZHONG Fangrui. Recent advances in chemically driven enantioselective photobiocatalysis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [5] | ZHANG Shouqi, WANG Tao, KONG Yao, ZOU Jiasheng, LIU Yuanning, XU Zhengren. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of natural products: evolution of synthetic methodology and strategy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [6] | XI Mengyu, HU Yiling, GU Yucheng, GE Huiming. Genome mining-directed discovery for natural medicinal products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [7] | LEI Ru, TAO Hui, LIU Tiangang. Deep genome mining boosts the discovery of microbial terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| [8] | ZHU Jingyong, LI Junxiang, LI Xuhui, ZHANG Jin, WU Wenjing. Advances in applications of deep learning for predicting sequence-based protein interactions [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 88-106. |
| [9] | LAI Qilong, YAO Shuai, ZHA Yuguo, BAI Hong, NING Kang. Microbiome-based biosynthetic gene cluster data mining techniques and application potentials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 611-627. |
| [10] | CHEN Zhihang, JI Menglin, QI Yifei. Research progress of artificial intelligence in desiging protein structures [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 464-487. |
| [11] | MENG Qiaozhen, GUO Fei. Applications of foldability in intelligent enzyme engineering and design: take AlphaFold2 for example [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 571-589. |
| [12] | KANG Liqi, TAN Pan, HONG Liang. Enzyme engineering in the age of artificial intelligence [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 524-534. |
| [13] | WANG Sheng, WANG Zechen, CHEN Weihua, CHEN Ke, PENG Xiangda, OU Fafen, ZHENG Liangzhen, SUN Jinyuan, SHEN Tao, ZHAO Guoping. Design of synthetic biology components based on artificial intelligence and computational biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 422-443. |
| [14] | LIANG Liya, LIU Rongming. Protein engineering of DNA targeting type Ⅱ CRISPR/Cas systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 86-101. |
| [15] | Yanping QI, Jin ZHU, Kai ZHANG, Tong LIU, Yajie WANG. Recent development of directed evolution in protein engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1081-1108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||