Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (2): 233-253.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-070
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Enabling technology for the biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ZUO Yimeng1,2, ZHANG Jiaojiao2, LIAN Jiazhang1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education & National Key Laboratory of Biobased Transportation Fuel Technology,College of Chemical and Biological Engineering,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310027,Zhejiang,China
2. ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310000,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2024-09-02Revised:2024-11-04Online:2025-05-20Published:2025-04-30 -
Contact:LIAN Jiazhang
酿酒酵母使能技术在化妆品原料合成中的应用
左一萌1,2, 张姣姣2, 连佳长1,2
- 1. 浙江大学化学工程与生物工程学院,生物质化工教育部重点实验室,生物基运输燃料技术全国重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310027
2. 浙江大学杭州国际科创中心,浙江 杭州 310000
-
通讯作者:连佳长 -
作者简介:左一萌 (1997—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为植物天然产物合成生物学。E-mail:ymzuo@zju.edu.cn张姣姣 (1994—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为植物天然产物合成生物学。E-mail:L231459@zju.edu.cn连佳长 (1984—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为合成生物学的相关研究。E-mail:jzlian@zju.edu.cn
第一联系人:左一萌、张姣姣为共同第一作者 -
基金资助:浙江省属高校基本科研业务费专项资金(226-2023-00015);国家自然科学基金(22278361)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZUO Yimeng, ZHANG Jiaojiao, LIAN Jiazhang. Enabling technology for the biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 233-253.
左一萌, 张姣姣, 连佳长. 酿酒酵母使能技术在化妆品原料合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(2): 233-253.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-070
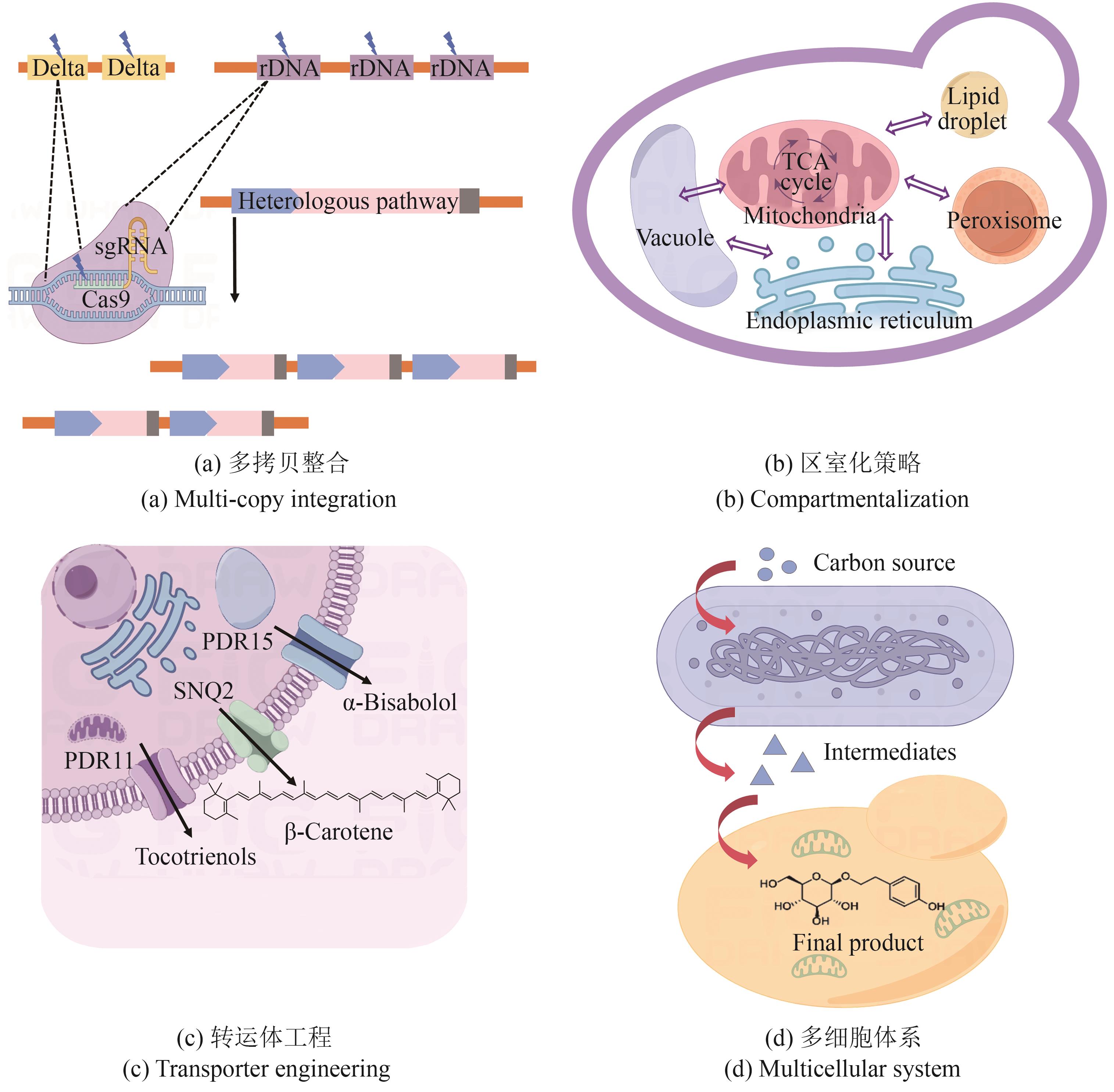
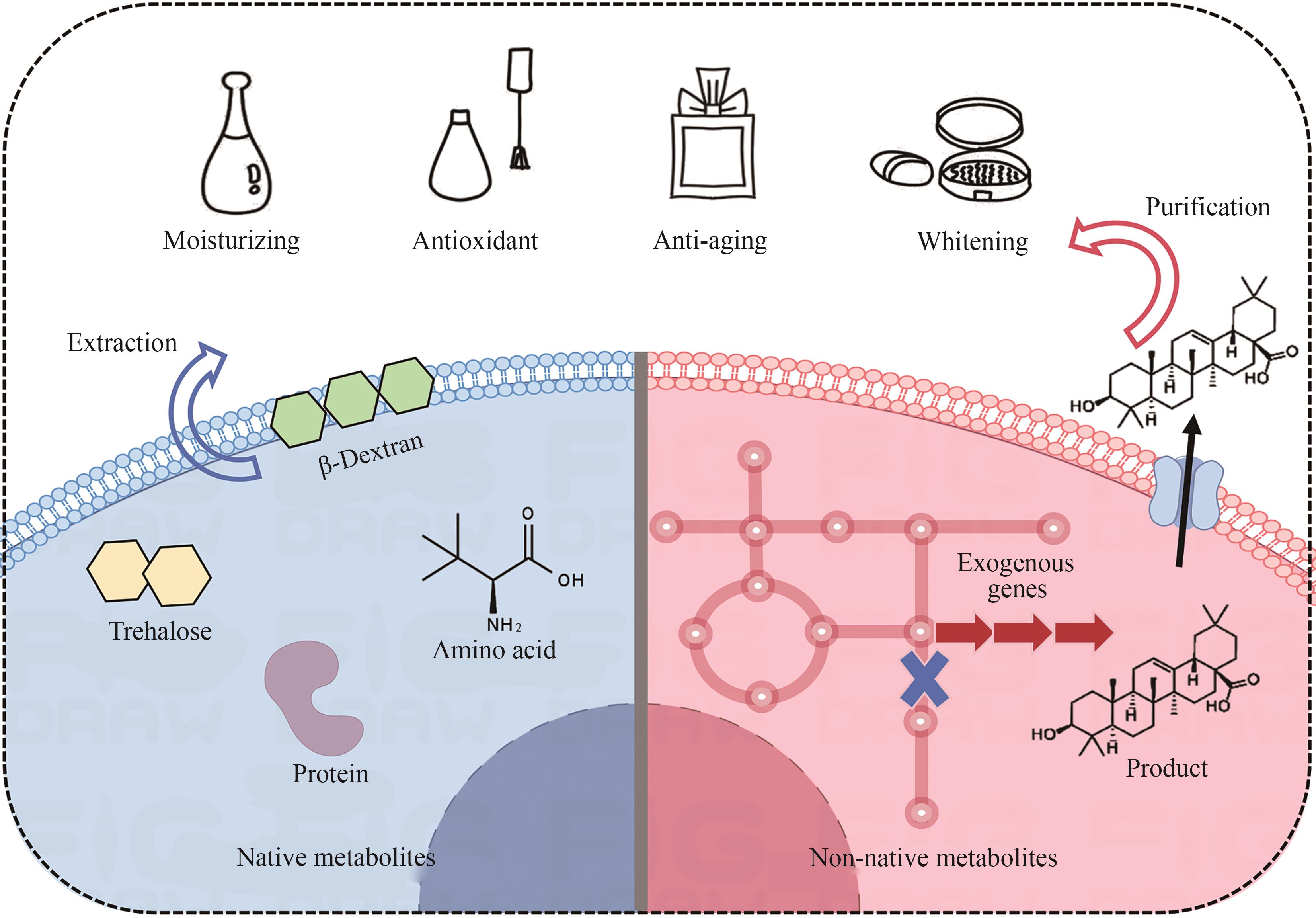
Fig. 2 Key enabling technologies for the synthesis of cosmetic active ingredients with S. cerevisiae (PDR11—pleiotropic drug-resistant transporter 11; PDR15—pleiotropic drug resistance transporter 15; SNQ2—sensitivity to 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide transporter 2)
| 物质 类别 | 物质 名称 | 英文名 | 分子式 | 功能 | 发酵 方式 | 产量 | 改造策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萜类 | α-红没药醇 | α-Bisabolol | C15H26O | 抗菌、抗炎、抗过敏 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 7.02 g/L | 引入MrBBS,替换内源ERG9启动子,融合表达ERG20和MrBBS,强化MVA途径,过表达内源转运蛋白PDR15 | [ |
| α-檀香醇 | α-Santalol | C15H24O | 加速伤口愈合、促进皮肤再生、减少红血丝、抗敏 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 1.18 g/L | 使用GAL启动子表达SaSSy、CYP736A167和SaCPR2,使用HXT1启动子替换酵母自身ERG9启动子,过表达tHMG1和UPC2-1 | [ | |
| 薄荷醇 | Menthol | C10H20O | 清凉、舒缓止痒、增强皮肤渗透性 | 摇瓶 | 6.28 mg/L | 强化MVA途径,动态调节ERG20基因 | [ | |
| 柠檬烯 | Limonene | C10H16 | 增香、抗氧化、镇定消炎作用 | 3 L 发酵罐 | 2.63 g/L | 引入柠檬烯合酶的截断突变体tLimS并优化其拷贝数,引入ERG20 抑制蛋白,强化MVA途径,优化NADPH供应并结合线粒体区室化策略 | [ | |
| 橙花叔醇 | Nerolidol | C15H26O | 抗炎、抗氧化、神经保护作用 | 摇瓶 | 2.54 g/L | 基于四环素抑制和37 °C诱导的GAL调控系统,用HAC1启动子控制人工转录因子表达 | [ | |
| 角鲨烯 | Squalene | C15H30 | 亲肤性、渗透性,化妆品中保湿及抗氧化作用 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 9.47 g/L | 过表达SpNADH-HMGR、ADH2、DzADA,增强乙醇耐受性 | [ | |
| 5 L 发酵罐 | 21.10 g/L | 过表达tHMG1、ERG20、ERG9,结合线粒体区室化工程 | [ | |||||
| 齐墩果酸 | Oleanolic acid | C30H48O3 | 改善真皮胶原蛋白,增加皮肤弹性,化妆品中抗炎、抗衰剂 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 1.23 g/L | 整合GgbAS、MtCYP716A12和MtCPR基因,建立GEM模型,结合FBA和OptKnock计算优化代谢途径 | [ | |
| 100 L 发酵罐 | 4.07 g/L | 引入植物源细胞色素b5,使用糖诱导启动子P ADH2 表达rSE | [ | |||||
| 熊果酸 | Ursolic acid | C30H48O3 | 镇静、抗炎、抗菌、抗氧化性,化妆品中抗衰成分 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 2.33 g/L | 组合优化ALD6和MPC2以及rHMGR、ADA和GAPC平衡乙酰辅酶A与NADH/NADPH供应 | [ | |
| 积雪草苷 | Asiaticoside | C48H78O19 | 润肤剂,改善皮肤红肿、炎症及伤口愈合 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 772.30 μg/L | 鉴定5种积雪草苷合成的C28糖基转移酶结合途径工程实现从头合成 | [ | |
| 人参皂苷Ro | Ginsenoside Ro | C48H76O19 | 提高角质层的含水量,化妆品中美白抗皱成分 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 0.53 g/L | 挖掘类纤维素合酶Pn022859,引入AtUGDH,筛选到2个糖基转移酶UGT73F3及UGT73P40,实现从头合成 | [ | |
| β-胡萝卜素 | β-Carotene | C40H56 | 天然抗氧化剂、清除自由基、抗炎 | 摇瓶 | 477.90 mg/L | 引入来自含油酵母脂肪酶LIP2、LIP7和LIP8,添加1%橄榄油 | [ | |
| 番茄红素 | Lycopene | C40H56 | 抗氧化、抗炎 | 7 L 发酵罐 | 8.15 g/L | 利用ARTP诱变结合H2O2诱导的适应性进化策略增强FPP供应,过表达crtE,引入工程化的crtI突变体(Y160F&N576S) | [ | |
| 虾青素 | Astaxanthin | C40H52O4 | 抗氧化 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 446.40 mg/L | 鉴定OPI3和HRD1作为新的工程目标,通过平衡β-胡萝卜素羟化酶和转酮酶、脂滴工程以及温度响应动态调控 | [ | |
| 维生素类 | 生育酚 (维生素 E,VE) | Tocopherol | C29H5O2 | 抗衰老 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 320.00 mg/L | GAL10和GAL1启动子驱动tHMG1、crtE、HPPD、tMPBQMT、SyHPT、tTMT和tTC等基因表达,增加SyHPT、tTMT和tTC拷贝数,引入温控系统GAL4M9 | [ |
| 视黄醇 (视黄醛,VA) | Retinol Retinal | C20H30O C20H28O | 增强表皮增殖和增加胶原蛋白的产生 | 3 L 发酵罐 | 视黄醇 1.26 g/L 视黄醛 2.10 g/L | 引入β-胡萝卜素合成途径和β-胡萝卜素15,15′-单加氧酶(BCMO)编码基因,采用两阶段发酵,维生素A滴度为3.35 g/L | [ | |
| 维生素C(VC,抗坏血酸) | Ascorbic acid | C6H8O6 | 预防皮肤色素沉着、刺激胶原蛋白形成 | 摇瓶 | 44.00 mg/L | 引入外源基因GME、VTC2、VTC4、GalDH和GLDH,融合表达L-GalDH和L-GLDH,增加VTC2拷贝,外源添加L-半乳糖或GSHVc | [ | |
| D-泛酸(VB5) | D-pantothenic acid | C9H17NO45 | 具有舒缓、修护作用 | 1 L 发酵罐 | 4.00 g/L | 构建异源β-丙氨酸异源合成途径,组合筛选泛酸合成关键酶(AHAS/KARI/DHAD/KPHMT/KPR),添加β-丙氨酸 | [ | |
| 烟酰胺 核糖核苷 | NMN | C11H15N2O8PP | 抗衰老、抚平皱纹 | 30 mL反应液 | 12.60 g/L | 构建NRK-2表面展示菌株,以NR为底物全细胞催化合成β-NMN | [ | |
| 多酚类 | 白藜芦醇 | Resveratrol | C14H12O3 | 防止光老化、清除自由基,化妆品中抗氧剂、抗菌剂和美白剂 | 3 L 发酵罐 | 4.10 g/L | 引入RtPAL/TAL,联合苯丙氨酸与酪氨酸途径重建白藜芦醇合成途径,过表达Pc4CL 、VvSTS,敲除 DPP1 | [ |
| 花青素 | Anthocyanin | C15H11ClO6 | 抗炎、抗衰老、美容,化妆品抗衰剂、抗敏剂 | — | 约150 μmol/L | 引入DFR、AtLDOX,证实ArGSTs的催化作用,实现从头合成 | [ | |
| 咖啡酸 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | 抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 5.5 g/L | 在咖啡酸生产菌株的基础上,增加前体供应,计酿酒酵母三种辅因子 | [ | |
| 黄腐酚 | Xanthohumol | C21H22O5 | 抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化,用于美白防晒类化妆品 | 摇瓶 | 0.14 mg/L | 过表达HlPT1L、HlOMT3sc,融合表达IDI1-HlPT1LΔ1-86 ,结合过氧化物酶体工程 | [ | |
| 白杨素 | Chrysin | C15H10O4 | 抗炎、抗氧化,用于美白、防晒、抗衰抗皱类化妆品 | 摇瓶 | 41.90 mg/L | 引入ZmPAL,融合表达PcFNSI-ScCPR-EbFNSI-1,过表达CIT、MAC1/3、CTP1、YHM2、RtME和MDH | [ | |
| 红景天苷 | Salidroside | C14H20O7 | 抗氧化、消炎,用于抗皱美白类化妆品 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 26.55 g/L | 引入ARO4K229L和ARO7G141S,过表达RKI1和TKL1,敲除PHA2和PDC1 | [ | |
| 蛋白、 多肽及 氨基酸类 | 超氧化物 歧化酶 | Superoxide dismutase | — | 抗氧化 | 摇瓶 | 513.74 U/mg | — | [ |
| 谷胱甘肽 | Glutathione | C10H17N3O6S | 抗氧化 | 摇瓶 | 64.00 mg/L | 过表达SER3、SHM2和CYS4 | [ | |
| 霉孢素类 氨基酸 | MAAs | — | 防晒,消炎 | 5 L 发酵罐 | Shinorine 1.53 g/L 卟啉-334 1.21 g/L | 整合木糖途径,引入三个编码DDGS基因和ATP抓取酶表达盒,敲除HXK2和TAL1,引入4个D-Ala-D-Ala连接酶,成功生产了三种双取代的MAA | [ | |
| 其他类 | 海藻糖 | Trehalose | C12H22O11 | 作为化妆品中的保湿、抗辐射成分 | 摇瓶 | 约140 mg/g | 过表达ARI1基因 | [ |
| 水杨酸 | Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | 去除角质、控制青春痘、淡化色素斑、缩小毛孔等作用 | 摇瓶 | 46.71 mg/L | 引入外源水杨酸合成基因entC和PfpchB,优化启动子,改造加强莽草酸途径并解除关键酶ARO4的反馈抑制,加强磷酸戊糖途径 | [ |
Table 1 Biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with S. cerevisiae
| 物质 类别 | 物质 名称 | 英文名 | 分子式 | 功能 | 发酵 方式 | 产量 | 改造策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萜类 | α-红没药醇 | α-Bisabolol | C15H26O | 抗菌、抗炎、抗过敏 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 7.02 g/L | 引入MrBBS,替换内源ERG9启动子,融合表达ERG20和MrBBS,强化MVA途径,过表达内源转运蛋白PDR15 | [ |
| α-檀香醇 | α-Santalol | C15H24O | 加速伤口愈合、促进皮肤再生、减少红血丝、抗敏 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 1.18 g/L | 使用GAL启动子表达SaSSy、CYP736A167和SaCPR2,使用HXT1启动子替换酵母自身ERG9启动子,过表达tHMG1和UPC2-1 | [ | |
| 薄荷醇 | Menthol | C10H20O | 清凉、舒缓止痒、增强皮肤渗透性 | 摇瓶 | 6.28 mg/L | 强化MVA途径,动态调节ERG20基因 | [ | |
| 柠檬烯 | Limonene | C10H16 | 增香、抗氧化、镇定消炎作用 | 3 L 发酵罐 | 2.63 g/L | 引入柠檬烯合酶的截断突变体tLimS并优化其拷贝数,引入ERG20 抑制蛋白,强化MVA途径,优化NADPH供应并结合线粒体区室化策略 | [ | |
| 橙花叔醇 | Nerolidol | C15H26O | 抗炎、抗氧化、神经保护作用 | 摇瓶 | 2.54 g/L | 基于四环素抑制和37 °C诱导的GAL调控系统,用HAC1启动子控制人工转录因子表达 | [ | |
| 角鲨烯 | Squalene | C15H30 | 亲肤性、渗透性,化妆品中保湿及抗氧化作用 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 9.47 g/L | 过表达SpNADH-HMGR、ADH2、DzADA,增强乙醇耐受性 | [ | |
| 5 L 发酵罐 | 21.10 g/L | 过表达tHMG1、ERG20、ERG9,结合线粒体区室化工程 | [ | |||||
| 齐墩果酸 | Oleanolic acid | C30H48O3 | 改善真皮胶原蛋白,增加皮肤弹性,化妆品中抗炎、抗衰剂 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 1.23 g/L | 整合GgbAS、MtCYP716A12和MtCPR基因,建立GEM模型,结合FBA和OptKnock计算优化代谢途径 | [ | |
| 100 L 发酵罐 | 4.07 g/L | 引入植物源细胞色素b5,使用糖诱导启动子P ADH2 表达rSE | [ | |||||
| 熊果酸 | Ursolic acid | C30H48O3 | 镇静、抗炎、抗菌、抗氧化性,化妆品中抗衰成分 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 2.33 g/L | 组合优化ALD6和MPC2以及rHMGR、ADA和GAPC平衡乙酰辅酶A与NADH/NADPH供应 | [ | |
| 积雪草苷 | Asiaticoside | C48H78O19 | 润肤剂,改善皮肤红肿、炎症及伤口愈合 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 772.30 μg/L | 鉴定5种积雪草苷合成的C28糖基转移酶结合途径工程实现从头合成 | [ | |
| 人参皂苷Ro | Ginsenoside Ro | C48H76O19 | 提高角质层的含水量,化妆品中美白抗皱成分 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 0.53 g/L | 挖掘类纤维素合酶Pn022859,引入AtUGDH,筛选到2个糖基转移酶UGT73F3及UGT73P40,实现从头合成 | [ | |
| β-胡萝卜素 | β-Carotene | C40H56 | 天然抗氧化剂、清除自由基、抗炎 | 摇瓶 | 477.90 mg/L | 引入来自含油酵母脂肪酶LIP2、LIP7和LIP8,添加1%橄榄油 | [ | |
| 番茄红素 | Lycopene | C40H56 | 抗氧化、抗炎 | 7 L 发酵罐 | 8.15 g/L | 利用ARTP诱变结合H2O2诱导的适应性进化策略增强FPP供应,过表达crtE,引入工程化的crtI突变体(Y160F&N576S) | [ | |
| 虾青素 | Astaxanthin | C40H52O4 | 抗氧化 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 446.40 mg/L | 鉴定OPI3和HRD1作为新的工程目标,通过平衡β-胡萝卜素羟化酶和转酮酶、脂滴工程以及温度响应动态调控 | [ | |
| 维生素类 | 生育酚 (维生素 E,VE) | Tocopherol | C29H5O2 | 抗衰老 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 320.00 mg/L | GAL10和GAL1启动子驱动tHMG1、crtE、HPPD、tMPBQMT、SyHPT、tTMT和tTC等基因表达,增加SyHPT、tTMT和tTC拷贝数,引入温控系统GAL4M9 | [ |
| 视黄醇 (视黄醛,VA) | Retinol Retinal | C20H30O C20H28O | 增强表皮增殖和增加胶原蛋白的产生 | 3 L 发酵罐 | 视黄醇 1.26 g/L 视黄醛 2.10 g/L | 引入β-胡萝卜素合成途径和β-胡萝卜素15,15′-单加氧酶(BCMO)编码基因,采用两阶段发酵,维生素A滴度为3.35 g/L | [ | |
| 维生素C(VC,抗坏血酸) | Ascorbic acid | C6H8O6 | 预防皮肤色素沉着、刺激胶原蛋白形成 | 摇瓶 | 44.00 mg/L | 引入外源基因GME、VTC2、VTC4、GalDH和GLDH,融合表达L-GalDH和L-GLDH,增加VTC2拷贝,外源添加L-半乳糖或GSHVc | [ | |
| D-泛酸(VB5) | D-pantothenic acid | C9H17NO45 | 具有舒缓、修护作用 | 1 L 发酵罐 | 4.00 g/L | 构建异源β-丙氨酸异源合成途径,组合筛选泛酸合成关键酶(AHAS/KARI/DHAD/KPHMT/KPR),添加β-丙氨酸 | [ | |
| 烟酰胺 核糖核苷 | NMN | C11H15N2O8PP | 抗衰老、抚平皱纹 | 30 mL反应液 | 12.60 g/L | 构建NRK-2表面展示菌株,以NR为底物全细胞催化合成β-NMN | [ | |
| 多酚类 | 白藜芦醇 | Resveratrol | C14H12O3 | 防止光老化、清除自由基,化妆品中抗氧剂、抗菌剂和美白剂 | 3 L 发酵罐 | 4.10 g/L | 引入RtPAL/TAL,联合苯丙氨酸与酪氨酸途径重建白藜芦醇合成途径,过表达Pc4CL 、VvSTS,敲除 DPP1 | [ |
| 花青素 | Anthocyanin | C15H11ClO6 | 抗炎、抗衰老、美容,化妆品抗衰剂、抗敏剂 | — | 约150 μmol/L | 引入DFR、AtLDOX,证实ArGSTs的催化作用,实现从头合成 | [ | |
| 咖啡酸 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | 抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 5.5 g/L | 在咖啡酸生产菌株的基础上,增加前体供应,计酿酒酵母三种辅因子 | [ | |
| 黄腐酚 | Xanthohumol | C21H22O5 | 抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化,用于美白防晒类化妆品 | 摇瓶 | 0.14 mg/L | 过表达HlPT1L、HlOMT3sc,融合表达IDI1-HlPT1LΔ1-86 ,结合过氧化物酶体工程 | [ | |
| 白杨素 | Chrysin | C15H10O4 | 抗炎、抗氧化,用于美白、防晒、抗衰抗皱类化妆品 | 摇瓶 | 41.90 mg/L | 引入ZmPAL,融合表达PcFNSI-ScCPR-EbFNSI-1,过表达CIT、MAC1/3、CTP1、YHM2、RtME和MDH | [ | |
| 红景天苷 | Salidroside | C14H20O7 | 抗氧化、消炎,用于抗皱美白类化妆品 | 5 L 发酵罐 | 26.55 g/L | 引入ARO4K229L和ARO7G141S,过表达RKI1和TKL1,敲除PHA2和PDC1 | [ | |
| 蛋白、 多肽及 氨基酸类 | 超氧化物 歧化酶 | Superoxide dismutase | — | 抗氧化 | 摇瓶 | 513.74 U/mg | — | [ |
| 谷胱甘肽 | Glutathione | C10H17N3O6S | 抗氧化 | 摇瓶 | 64.00 mg/L | 过表达SER3、SHM2和CYS4 | [ | |
| 霉孢素类 氨基酸 | MAAs | — | 防晒,消炎 | 5 L 发酵罐 | Shinorine 1.53 g/L 卟啉-334 1.21 g/L | 整合木糖途径,引入三个编码DDGS基因和ATP抓取酶表达盒,敲除HXK2和TAL1,引入4个D-Ala-D-Ala连接酶,成功生产了三种双取代的MAA | [ | |
| 其他类 | 海藻糖 | Trehalose | C12H22O11 | 作为化妆品中的保湿、抗辐射成分 | 摇瓶 | 约140 mg/g | 过表达ARI1基因 | [ |
| 水杨酸 | Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | 去除角质、控制青春痘、淡化色素斑、缩小毛孔等作用 | 摇瓶 | 46.71 mg/L | 引入外源水杨酸合成基因entC和PfpchB,优化启动子,改造加强莽草酸途径并解除关键酶ARO4的反馈抑制,加强磷酸戊糖途径 | [ |
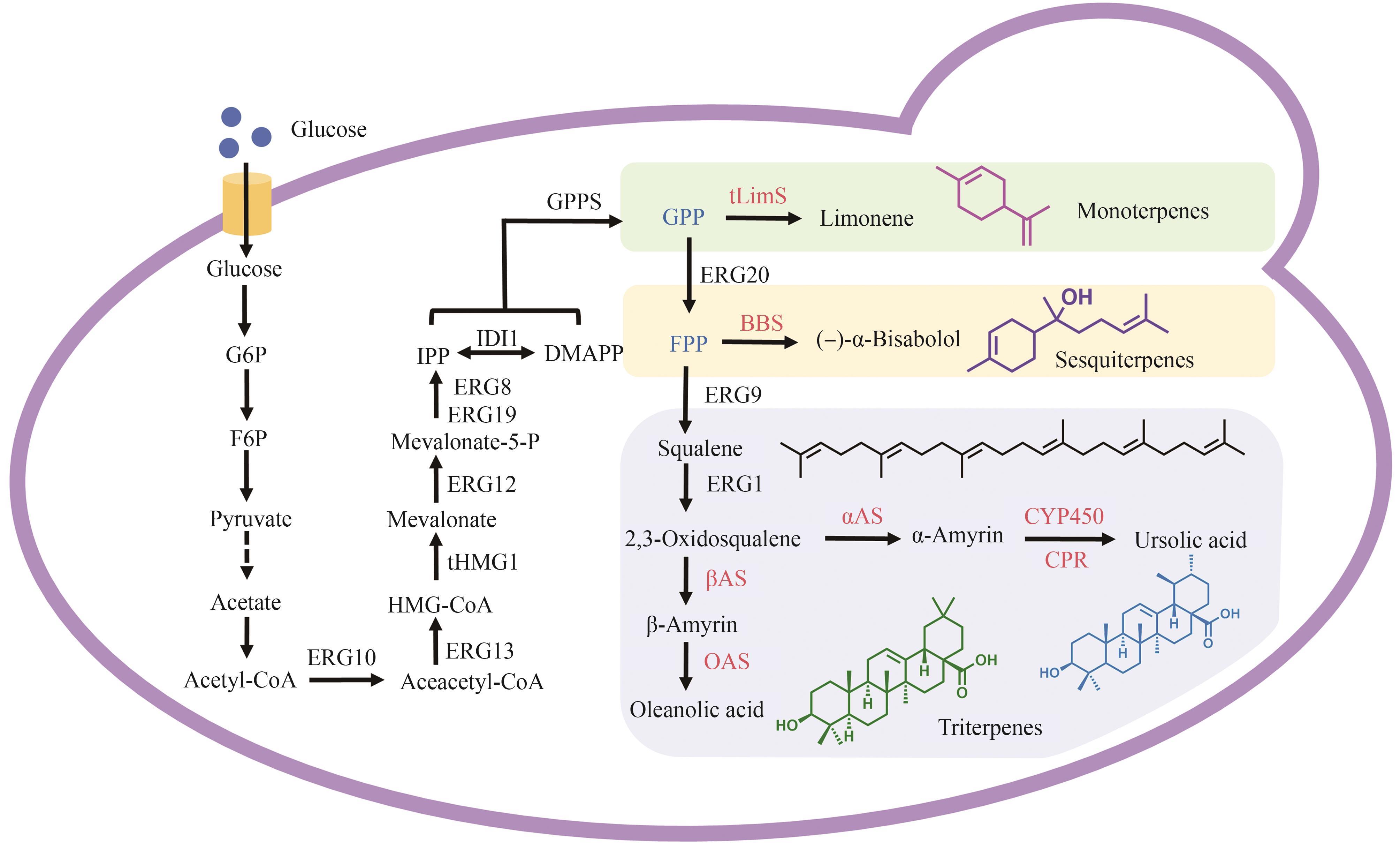
Fig. 3 Biosynthetic pathways for terpenoid-based cosmetic active ingredients with S. cerevisiae (The green module represents the synthesis of monoterpene compounds, the yellow module represents the synthesis of sesquiterpene compounds, and the blue module represents the synthesis of triterpene compounds. ERGs—terpenoid biosynthesis pathway sequential catalytic enzymes; tHMG1—truncated HMG-CoA reductase; IDI1—isoprene diphosphate isomerase; GPPS—geranyl pyrophosphate synthase; tLimS—truncated limonene synthase; BBS—(-)-α-bisabolol synthase; βAS—β-amyrin synthase; OAS—oleanolic acid synthase; αAS—α-amyrin synthase; CYP450—cytochrome P450 enzyme; CPR—cytochrome P450 reductase)
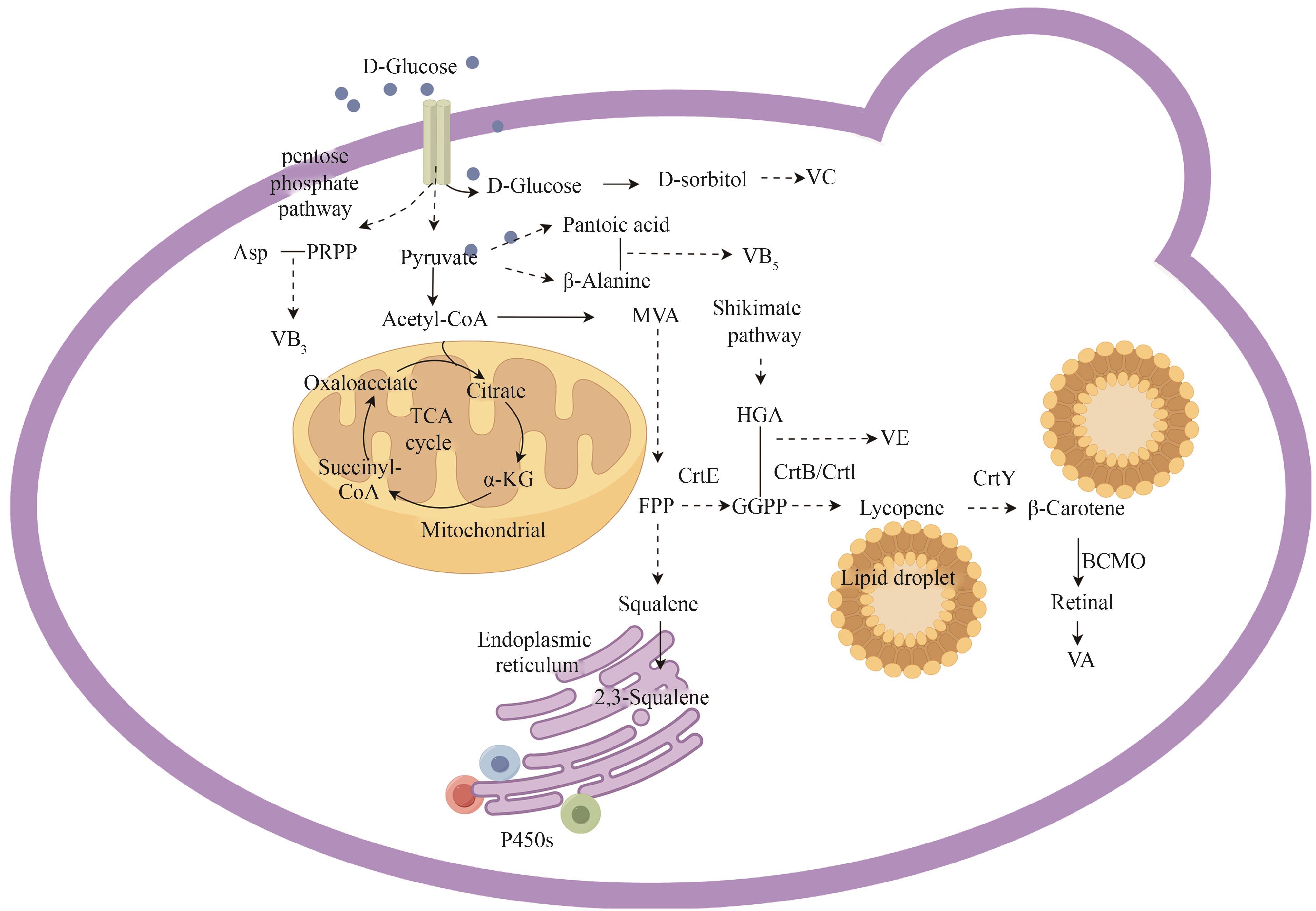
Fig. 4 Biosynthetic pathways for vitamin-based cosmetic active ingredients with S. cerevisiae (α-KG—α-ketoglutaric acid; VA—vitamin A; VB3—vitamin B3; VB5—vitamin B5; VC—vitamin C; VE—vitamin E; CrtE—GGPP synthetase; CrtB—octahydrolycopene synthase; CrtI—octahydrolycopene dehydrogenase; CrtY—lycopene cyclase; BCMO—β-Carotene 15,15′-monooxygenase)
| 1 | 丁明珠, 李炳志, 王颖, 等 . 合成生物学重要研究方向进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| DING M Z , LI B Z , WANG Y , et al . Significant research progress in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. | |
| 2 | LI Y F , LIN Z Q , HUANG C , et al . Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using CRISPR-Cas9 meditated genome editing[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 31: 13-21. |
| 3 | LI T , LIU G S , ZHOU W , et al . Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to overproduce squalene[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(7): 2132-2138. |
| 4 | JIANG Y K , XIA L , GAO S , et al . Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enhanced (-)-α-bisabolol production[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2023, 8(2): 187-195. |
| 5 | ZHA W L , AN T Y , LI T , et al . Reconstruction of the biosynthetic pathway of santalols under control of the GAL regulatory system in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(2): 449-456. |
| 6 | SHI S B , WANG Z H , SHEN L R , et al . Synthetic biology: a new frontier in food production[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(7): 781-803. |
| 7 | LI M J , KILDEGAARD K R , CHEN Y , et al . De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 32: 1-11. |
| 8 | LIU T , LIU Y Q , LI L , et al . De novo biosynthesis of polydatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(21): 5917-5925. |
| 9 | YANG S , CHEN R B , CAO X , et al . De novo biosynthesis of the hops bioactive flavonoid xanthohumol in yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 253. |
| 10 | SANTOS L O , SILVA P G P , LEMOS JUNIOR W J F , et al . Glutathione production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: current state and perspectives[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 106(5-6): 1879-1894. |
| 11 | OLIVEIRA A S , FERREIRA C , PEREIRA J O , et al . Spent brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a potential source of bioactive peptides: an overview[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 208: 1116-1126. |
| 12 | KRISDAPHONG T , TOIDA T , POPP M , et al . Evaluation of immunological and moisturizing activities of β-glucan isolated from molasses yeast waste[J]. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2018, 80(5): 795-801. |
| 13 | 江丽红, 董昌, 黄磊, 等 . 酿酒酵母代谢工程技术[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(5): 1578-1602. |
| JIANG L H , DONG C , HUANG L , et al . Metabolic engineering tools for Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(5): 1578-1602. | |
| 14 | HSU P D , LANDER E S , ZHANG F . Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(6): 1262-1278. |
| 15 | CONG L , RAN F ANN , COX D, et al . Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819-823. |
| 16 | JAKOČIŪNAS T , RAJKUMAR A S , ZHANG J , et al . CasEMBLR: Cas9-facilitated multiloci genomic integration of in vivo assembled DNA parts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(11): 1226-1234. |
| 17 | ZHANG N , LI X H , ZHOU Q , et al . Self-controlled in silico gene knockdown strategies to enhance the sustainable production of heterologous terpenoid by Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2024, 83: 172-182. |
| 18 | EAUCLAIRE S F , ZHANG J Z , RIVERA C G , et al . Combinatorial metabolic pathway assembly in the yeast genome with RNA-guided Cas9[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43(7): 1001-1015. |
| 19 | REIDER APEL A , D’ESPAUX L , WEHRS M , et al . A Cas9-based toolkit to program gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(1): 496-508. |
| 20 | LIU T F , GOU Y W , ZHANG B , et al . Construction of ajmalicine and sanguinarine de novo biosynthetic pathways using stable integration sites in yeast[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2022, 119(5): 1314-1326. |
| 21 | LEE M E , DELOACHE W C , CERVANTES B , et al . A highly characterized yeast toolkit for modular, multipart assembly[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(9): 975-986. |
| 22 | ALPER H , FISCHER C , NEVOIGT E , et al . Tuning genetic control through promoter engineering[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(8): 3006. |
| 23 | LIU H Y , TIAN Y J , ZHOU Y , et al . Multi-modular engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-titre production of tyrosol and salidroside[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2021, 14(6): 2605-2616. |
| 24 | LIAN J Z , JIN R , ZHAO H M . Construction of plasmids with tunable copy numbers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their applications in pathway optimization and multiplex genome integration[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(11): 2462-2473. |
| 25 | LIAN J Z , MISHRA S , ZHAO H M . Recent advances in metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: new tools and their applications[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 50: 85-108. |
| 26 | BLEYKASTEN-GROSSHANS C , FRIEDRICH A , SCHACHERER J . Genome-wide analysis of intraspecific transposon diversity in yeast[J]. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14: 399. |
| 27 | PETES T D . Yeast ribosomal DNA genes are located on chromosome Ⅻ[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1979, 76(1): 410-414. |
| 28 | ZHENG H H , WANG K , XU X X , et al . Highly efficient rDNA-mediated multicopy integration based on the dynamic balance of rDNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2022, 15(5): 1511-1524. |
| 29 | LIU L , LIU C , ZOU S L , et al . Expression of cellulase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via δ-integration subject to auxotrophic markers[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2013, 35(8): 1303-1307. |
| 30 | QI H , YU L , LI Y Z , et al . Developing multi-copy chromosomal integration strategies for heterologous biosynthesis of caffeic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 851706. |
| 31 | FANG C , WANG Q H , SELVARAJ J N , et al . High copy and stable expression of the xylanase XynHB in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by rDNA-mediated integration[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 8747. |
| 32 | RONDA C , MAURY J , JAKOČIUNAS T , et al . CrEdit: CRISPR mediated multi-loci gene integration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 97. |
| 33 | PENG B Y , ESQUIROL L , LU Z Y , et al . An in vivo gene amplification system for high level expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2895. |
| 34 | CUI H , NI X P , SHAO W , et al . Functional manipulations of the tetramycin positive regulatory gene ttmRIV to enhance the production of tetramycin A and nystatin A1 in Streptomyces ahygroscopicus [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2015, 42(9): 1273-1282. |
| 35 | SHI B , MA T , YE Z L , et al . Systematic metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for lycopene overproduction[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(40): 11148-11157. |
| 36 | LIU G S , LI T , ZHOU W , et al . The yeast peroxisome: a dynamic storage depot and subcellular factory for squalene overproduction[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 57: 151-161. |
| 37 | ARENDT P , MIETTINEN K , POLLIER J , et al . An endoplasmic reticulum-engineered yeast platform for overproduction of triterpenoids[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 40: 165-175. |
| 38 | KIM J E , JANG I S , SON S H , et al . Tailoring the Saccharomyces cerevisiae endoplasmic reticulum for functional assembly of terpene synthesis pathway[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 50-59. |
| 39 | PALAGE A M , WARD V C . Strategies for production of hydrophobic compounds[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2022, 75: 102681. |
| 40 | THIAM A R , BELLER M . The why, when and how of lipid droplet diversity[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2017, 130(2): 315-324. |
| 41 | SHI Y S , WANG D , LI R S , et al . Engineering yeast subcellular compartments for increased production of the lipophilic natural products ginsenosides[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 67: 104-111. |
| 42 | LIU X N , DING W T , JIANG H F . Engineering microbial cell factories for the production of plant natural products: from design principles to industrial-scale production[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 125. |
| 43 | BU X , LIN J Y , CHENG J , et al . Engineering endogenous ABC transporter with improving ATP supply and membrane flexibility enhances the secretion of β-carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2020, 13: 168. |
| 44 | JIAO X , SHEN B , LI M , et al . Secretory production of tocotrienols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(2): 788-799. |
| 45 | LI M , ZHOU P P , CHEN M K , et al . Spatiotemporal regulation of astaxanthin synthesis in S. cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(8): 2636-2649. |
| 46 | AULAKH S K , SELLÉS VIDAL L , SOUTH E J , et al . Spontaneously established syntrophic yeast communities improve bioproduction[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(8): 951-961. |
| 47 | PENG H D , DARLINGTON A P S , SOUTH E J , et al . A molecular toolkit of cross-feeding strains for engineering synthetic yeast communities[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2024, 9(3): 848-863. |
| 48 | CAMACHO-ZARAGOZA J M , HERNÁNDEZ-CHÁVEZ G , MORENO-AVITIA F , et al . Engineering of a microbial coculture of Escherichia coli strains for the biosynthesis of resveratrol[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 163. |
| 49 | LIU X , LI X B , JIANG J L , et al . Convergent engineering of syntrophic Escherichia coli coculture for efficient production of glycosides[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 243-253. |
| 50 | ZHOU X J , ZHANG X X , WANG D , et al . Efficient biosynthesis of salidroside via artificial in vivo enhanced UDP-glucose system using cheap sucrose as substrate[J]. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(20): 22386-22397. |
| 51 | HE N , LI D F , YU H W , et al . Construction of an artificial microbial consortium for green production of (-)-ambroxide[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(5): 1939-1948. |
| 52 | LV X Q , ZHOU X , MA J , et al . Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the de novo biosynthesis of (-)-menthol[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2022, 8(9): 982. |
| 53 | KONG X , WU Y K , YU W W , et al . Efficient synthesis of limonene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using combinatorial metabolic engineering strategies[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(20): 7752-7764. |
| 54 | PENG B Y , BANDARI N C , LU Z Y , et al . Engineering eukaryote-like regulatory circuits to expand artificial control mechanisms for metabolic engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Communications Biology, 2022, 5(1): 135. |
| 55 | ZHU Z T , DU M M , GAO B , et al . Metabolic compartmentalization in yeast mitochondria: burden and solution for squalene overproduction[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 68: 232-245. |
| 56 | CHENG X , PANG Y R , BAN Y L , et al . Application of multiple strategies to enhance oleanolic acid biosynthesis by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2024, 401: 130716. |
| 57 | JIA N , LI J Z , ZANG G W , et al . Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-efficient production of ursolic acid via cofactor engineering and acetyl-CoA optimization[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 203: 109189. |
| 58 | ZHAO X Y , WEI W Q , LI S , et al . Elucidation of the biosynthesis of asiaticoside and its reconstitution in yeast[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(10): 4028-4040. |
| 59 | REN S C , SUN Q Y , ZHANG L , et al . Sustainable production of rare oleanane-type ginsenoside Ro with an artificial glycosylation pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(21): 8302-8313. |
| 60 | FATHI Z , TRAMONTIN L R R , EBRAHIMIPOUR G , et al . Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of β-carotene from hydrophobic substrates[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2021, 21(1): foaa068. |
| 61 | ZHOU K , YU C , LIANG N , et al . Adaptive evolution and metabolic engineering boost lycopene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via enhanced precursors supply and utilization[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(8): 3821-3831. |
| 62 | SHEN B , ZHOU P P , JIAO X , et al . Fermentative production of vitamin E tocotrienols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under cold-shock-triggered temperature control[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5155. |
| 63 | SUN L , KWAK S , JIN Y S . Vitamin A production by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae from xylose via two-phase in situ extraction[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(9): 2131-2140. |
| 64 | PENG H D , CHEN R Q , SHAW W M , et al . Modular metabolic engineering and synthetic coculture strategies for the production of aromatic compounds in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(6): 1739-1749. |
| 65 | GUO J X , SUN X X , YUAN Y J , et al . Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for vitamin B5 production[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(19): 7408-7417. |
| 66 | HE Z H , YANG X S , TIAN X , et al . Yeast cell surface engineering of a nicotinamide riboside kinase for the production of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide via whole-cell catalysis[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(10): 3451-3459. |
| 67 | MENG L J , DIAO M X , WANG Q Y , et al . Efficient biosynthesis of resveratrol via combining phenylalanine and tyrosine pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22(1): 46. |
| 68 | EICHENBERGER M , SCHWANDER T , HÜPPI S , et al . The catalytic role of glutathione transferases in heterologous anthocyanin biosynthesis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2023, 6(10): 927-938. |
| 69 | CHEN R B , GAO J Q , YU W , et al . Engineering cofactor supply and recycling to drive phenolic acid biosynthesis in yeast[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(5): 520-529. |
| 70 | XU W Q , LIU M S , LI H B , et al . De novo synthesis of chrysin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(12): 6481-6490. |
| 71 | PINMANEE P , SOMPINIT K , JANTIMAPORN A , et al . Purification and immobilization of superoxide dismutase obtained from Saccharomyces cerevisiae TBRC657 on bacterial cellulose and its protective effect against oxidative damage in fibroblasts[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13(7): 1156. |
| 72 | KOBAYASHI J , SASAKI D , HARA K Y , et al . Metabolic engineering of the L-serine biosynthetic pathway improves glutathione production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 153. |
| 73 | KIM S J , PARK B G , JIN H B , et al . Efficient production of natural sunscreens shinorine, porphyra-334, and mycosporine-2-glycine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2023, 78: 137-147. |
| 74 | DIVATE N R , CHEN G H , DIVATE R D , et al . Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improvement in stresses tolerance[J]. Bioengineered, 2017, 8(5): 524-535. |
| 75 | RASOOL A , ZHANG G L , LI Z , et al . Engineering of the terpenoid pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-overproduces squalene and the non-terpenoid compound oleic acid[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 152: 457-467. |
| 76 | ZHOU C Y , LI M J , LU S R , et al . Engineering of cis-element in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient accumulation of value-added compound squalene via downregulation of the downstream metabolic flux[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(42): 12474-12484. |
| 77 | HUANG L L , LI J , YE H C , et al . Molecular characterization of the pentacyclic triterpenoid biosynthetic pathway in Catharanthus roseus [J]. Planta, 2012, 236(5): 1571-1581. |
| 78 | LU C Z , ZHANG C B , ZHAO F L , et al . Biosynthesis of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(11): 3794-3802. |
| 79 | JIN K , SHI X , LIU J H , et al . Combinatorial metabolic engineering enables the efficient production of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 374: 128819. |
| 80 | SHEN X Q , GUO M M , YU H Y , et al . Propionibacterium acnes related anti-inflammation and skin hydration activities of madecassoside, a pentacyclic triterpene saponin from Centella asiatica [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2019, 83(3): 561-568. |
| 81 | LI M K , MA M Y , WU Z K , et al . Advances in the biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of rare ginsenosides[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2023, 107(11): 3391-3404. |
| 82 | ZHAO Y J , ZHANG Y P , NIELSEN J , et al . Production of β-carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through altering yeast lipid metabolism[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(5): 2043-2052. |
| 83 | BU X , LIN J Y , DUAN C Q , et al . Dual regulation of lipid droplet-triacylglycerol metabolism and ERG9 expression for improved β-carotene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 3. |
| 84 | CHEN Y , XIAO W H , WANG Y , et al . Lycopene overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through combining pathway engineering with host engineering[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 113. |
| 85 | HUANG G X , LI J R , LIN J Y , et al . Multi-modular metabolic engineering and efflux engineering for enhanced lycopene production in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2024, 51: kuae015. |
| 86 | XIE W P , LV X M , YE L D , et al . Construction of lycopene-overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae by combining directed evolution and metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 30: 69-78. |
| 87 | MA J , YAN H H , QIN C Q , et al . Accumulation of astaxanthin by co-fermentation of Spirulina platensis and recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2022, 194(2): 988-999. |
| 88 | SJ S, VEERABHADRAPPA B , SUBRAMANIYAN S , et al . Astaxanthin enhances the longevity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by decreasing oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2019, 19(1): foy113. |
| 89 | ZHOU D W , FEI Z Y , LIU G N , et al . The bioproduction of astaxanthin: a comprehensive review on the microbial synthesis and downstream extraction[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 74: 108392. |
| 90 | ZHOU P P , XIE W P , LI A P , et al . Alleviation of metabolic bottleneck by combinatorial engineering enhanced astaxanthin synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2017, 100: 28-36. |
| 91 | ZHOU P P , YE L D , XIE W P , et al . Highly efficient biosynthesis of astaxanthin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by integration and tuning of algal crtZ and bkt [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(20): 8419-8428. |
| 92 | HU Q Y , ZHANG T L , YU H W , et al . Selective biosynthesis of retinol in S. cerevisiae [J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2022, 9(1): 22. |
| 93 | MADAAN P , SIKKA P , MALIK D S . Cosmeceutical aptitudes of niacinamide: a review[J]. Recent Advances in Anti-Infective Drug Discovery, 2021, 16(3): 196-208. |
| 94 | CHENG F , LI K X , WU S S , et al . Biosynthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide: synthesis method, enzyme, and biocatalytic system[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(7): 3302-3313. |
| 95 | ZHOU P P , YUE C L , SHEN B , et al . Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enhanced production of caffeic acid[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(14-15): 5809-5819. |
| 96 | LIU L Q , LIU H , ZHANG W , et al . Engineering the biosynthesis of caffeic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with heterologous enzyme combinations[J]. Engineering, 2019, 5(2): 287-295. |
| 97 | LI Y Z , MAO J W , LIU Q L , et al . De novo biosynthesis of caffeic acid from glucose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(4): 756-765. |
| 98 | TIPPELT A , NETT M . Saccharomyces cerevisiae as host for the recombinant production of polyketides and nonribosomal peptides[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 161. |
| 99 | KOBAYASHI J , SASAKI D , KONDO A . A procedure for precise determination of glutathione produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Bio-protocol Journal, 2018, 8(12): e2887. |
| 100 | HU X Y , SHEN X L , ZHU S , et al . Optimization of glutathione production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae HBSD-W08 using Plackett-Burman and central composite rotatable designs[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2023, 23(1): 11. |
| 101 | CHEN H L , CAO X T , ZHU N Q , et al . A stepwise control strategy for glutathione synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on oxidative stress and energy metabolism[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 36(8): 117. |
| 102 | GELSE K , PÖSCHL E , AIGNER T . Collagens: structure, function, and biosynthesis[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2003, 55(12): 1531-1546. |
| 103 | VAUGHN P R , GALANIS M , RICHARDS K M , et al . Production of recombinant hydroxylated human type Ⅲ collagen fragment in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. DNA and Cell Biology, 1998, 17(6): 511-518. |
| 104 | HENGARDI M T , LIANG C , MADIVANNAN K , et al . Reversing the directionality of reactions between non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway and glycolytic pathway boosts mycosporine-like amino acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2024, 23(1): 121. |
| 105 | VAN DER HOEK S A , RUSNÁK M , WANG G K , et al . Engineering precursor supply for the high-level production of ergothioneine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 70: 129-142. |
| 106 | 刘少奇 . 酿酒酵母中水杨酸生物合成研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2017. |
| LIU S Q . Study on the biosynthesis of salicylic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2017. | |
| 107 | TANG H T , LIN S M , DENG J L , et al . Engineering yeast for the de novo synthesis of jasmonates[J]. Nature Synthesis, 2024, 3: 224-235. |
| 108 | LOHMANN K J . A candidate magnetoreceptor[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15: 136-138. |
| 109 | IGNEA C , RAADAM M H , KOUTSAVITI A , et al . Expanding the terpene biosynthetic code with non-canonical 16 carbon atom building blocks[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 5188. |
| 110 | 曾涛, 巫瑞波 . 数据驱动的酶反应预测与设计[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 535-550. |
| ZENG T , WU R B . Data-driven prediction and design for enzymatic reactions[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 535-550. |
| [1] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [2] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [3] | LI Yongzhu, CHEN Yu. Advances and prospects in genome-scale models of yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 585-602. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [5] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [6] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [7] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [8] | GAO Qi, XIAO Wenhai. Advances in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes by yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 357-372. |
| [9] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [11] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [12] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [13] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [14] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| [15] | TANG Chuan′gen, WANG Jing, ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Haoning, KANG Zhen. Advances in synthesis and mining strategies for functional peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||