合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (2): 320-334.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-009
合成生物纳米酶
刘奇奇, 王春玉, 齐天翊, 朱明盛, 黄兴禄
- 南开大学生命科学学院,药物化学生物学国家重点实验室,生物活性材料教育部重点实验室,纳米酶联合实验室,天津 300071
-
收稿日期:2022-01-28修回日期:2022-03-31出版日期:2022-04-30发布日期:2022-05-11 -
通讯作者:黄兴禄 -
作者简介:刘奇奇 (1994—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为纳米生物材料的生物学效应及疾病治疗应用。 E-mail:450137842@qq.com黄兴禄 (1981—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学纳米材料、血管纳米生物学等。 E-mail:huangxinglu@nankai.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31870999);天津合成生物技术创新能力提升行动项目(TSBICIP-KJGG-014-03)
Synthetic biological nanozyme
LIU Qiqi, WANG Chunyu, QI Tianyi, ZHU Mingsheng, HUANG Xinglu
- State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology and Key Laboratory of Bioactive Materials for the Ministry of Education,Joint Laboratory of Nanozymes,College of Life Sciences,Nankai University,Tianjin 300071,China
-
Received:2022-01-28Revised:2022-03-31Online:2022-04-30Published:2022-05-11 -
Contact:HUANG Xinglu
摘要:
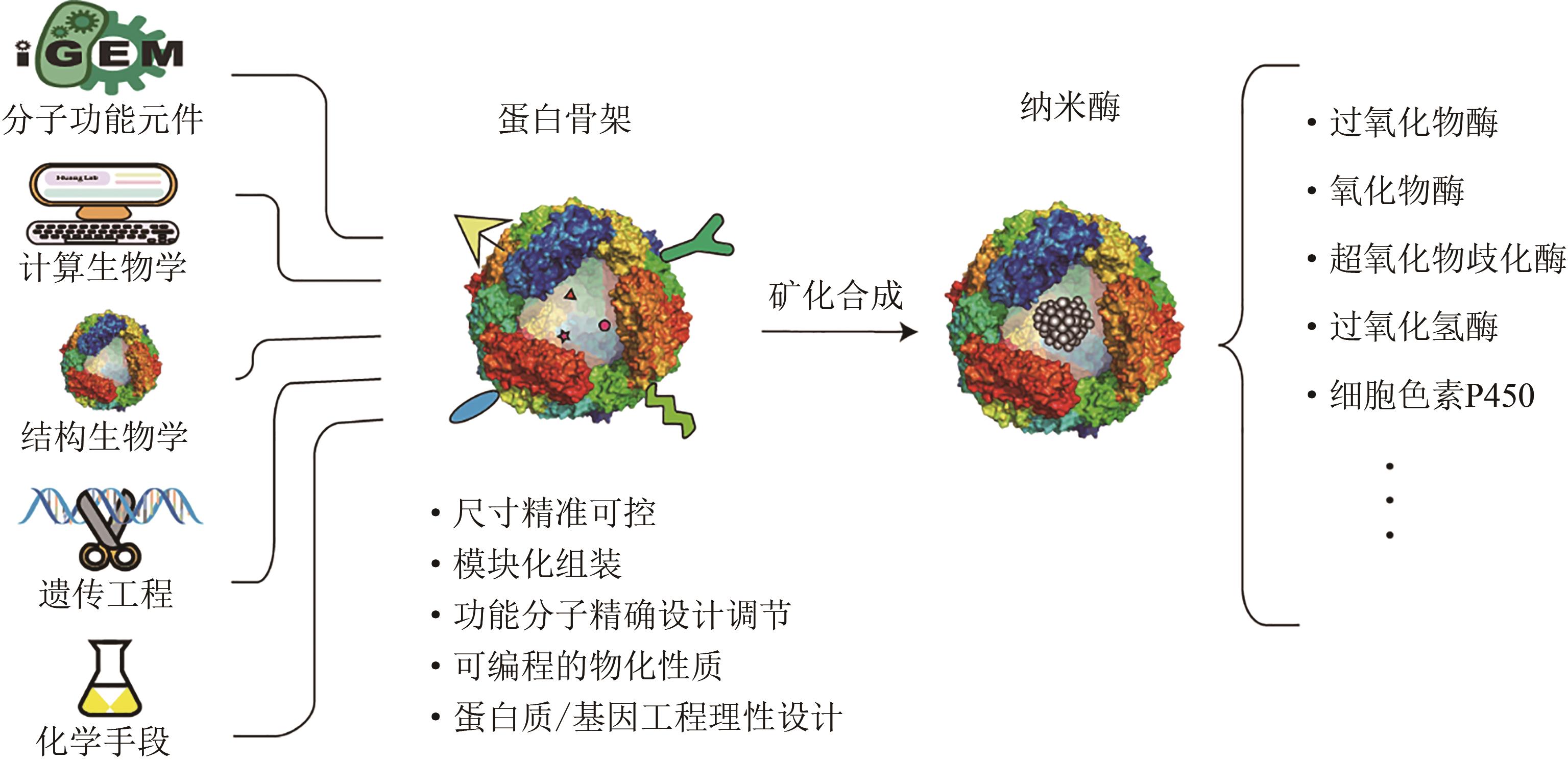
纳米酶是一类本身蕴含酶学特性的纳米材料,能够在生理条件下催化天然酶的底物及其介导的生化反应,表现出类似的反应动力学和催化机理。自2007年首次发现四氧化三铁纳米颗粒自身具有类过氧化物酶活性以来,成百上千种不同的纳米酶材料相继被开发出来,在生物医学、检测传感、环境工程等领域有着广泛的应用。近年来,以基因编辑或重组为基础的纳米酶材料开始出现。相比较其他纳米酶,这种纳米酶是基于合成生物学相关技术开发而来,在这里将其命名为合成生物纳米酶,其特点是以人为改造或从头设计的蛋白作为骨架,原位生长一些金属纳米颗粒,将蛋白骨架的功能和材料的催化融于一体。本文主要介绍了纳米酶的基本概况,例证了其在生物医学应用上的优势;概述了多种天然蛋白作为骨架制备纳米酶的原理,列举了其中的部分应用;简述了基因改造蛋白骨架方面的研究进展,并重点强调这种蛋白骨架在合成无机纳米颗粒方面的优势;在以上这些进展的基础上,提出了合成生物纳米酶的概念,并阐释了其中的内涵,最后也以基因重组铁蛋白纳米酶为例介绍了目前的一些设计及应用。未来,以合成生物纳米酶为代表的纳米酶,有可能会将计算生物学、结构生物学、蛋白/基因工程及化学等手段融为一体,在模拟酶的设计上更为理性,在赋予功能上更为多样化,并且有望进一步促进合成生物学与纳米生物学的深度融合。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘奇奇, 王春玉, 齐天翊, 朱明盛, 黄兴禄. 合成生物纳米酶[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 320-334.
LIU Qiqi, WANG Chunyu, QI Tianyi, ZHU Mingsheng, HUANG Xinglu. Synthetic biological nanozyme[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 320-334.
| 纳米酶 | 天然酶 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 优点 | 缺点 | 优点 | 缺点 |
| 高催化活性、成本低 | 活性类型有限 | 高催化活性 | 成本高 |
| 稳定性高 | 底物选择性有限 | 高底物选择性 | 稳定性有限 |
| 可长期存储 | 具有潜在的纳米毒性 | 良好的生物相容性 | 长期存储难 |
| 易于批量生产、可回收利用 | 催化机制不清楚 | 生物催化类型广泛 | 批量生产难、分离纯化耗时 |
| 多酶模拟活性、可控催化活性和类型 | 缺乏统一标准和参考资料 | 应用广泛 | 催化活性单一 |
| 易于多功能化(生物共轭表面积大)、可以通过外部刺激进行催化活性和催化类型控制(如光、超声、热、磁等) | 催化性能依赖于大小、形状、结构和成分等 | 通过基因和蛋白质工程进行理性设计 | |
| 适用于极端环境 | 在极端环境中使用难(如高温、极端pH、盐离子浓度、紫外线照射等) | ||
| 独特的物理化学性质(如荧光、电、顺磁性质等) | |||
表1 天然酶与纳米酶优缺点对比[9]
Tab. 1 Advantages and disadvantages of natural enzymes and nanozymes[9]
| 纳米酶 | 天然酶 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 优点 | 缺点 | 优点 | 缺点 |
| 高催化活性、成本低 | 活性类型有限 | 高催化活性 | 成本高 |
| 稳定性高 | 底物选择性有限 | 高底物选择性 | 稳定性有限 |
| 可长期存储 | 具有潜在的纳米毒性 | 良好的生物相容性 | 长期存储难 |
| 易于批量生产、可回收利用 | 催化机制不清楚 | 生物催化类型广泛 | 批量生产难、分离纯化耗时 |
| 多酶模拟活性、可控催化活性和类型 | 缺乏统一标准和参考资料 | 应用广泛 | 催化活性单一 |
| 易于多功能化(生物共轭表面积大)、可以通过外部刺激进行催化活性和催化类型控制(如光、超声、热、磁等) | 催化性能依赖于大小、形状、结构和成分等 | 通过基因和蛋白质工程进行理性设计 | |
| 适用于极端环境 | 在极端环境中使用难(如高温、极端pH、盐离子浓度、紫外线照射等) | ||
| 独特的物理化学性质(如荧光、电、顺磁性质等) | |||

图1 纳米酶试纸条的设计[24](a)标准胶体金试纸条;(b)纳米酶试纸条,利用纳米酶的活性,可以与底物发生显色反应,实现肉眼可见的增强信号
Fig. 1 Design for nanozyme-strips[24](a) Colloidal gold strips; (b) Nanozyme-strips. Probe with nanozyme activity generates a color reaction with substrates, which significantly enhances the signal so that it can be visualized by naked-eyes
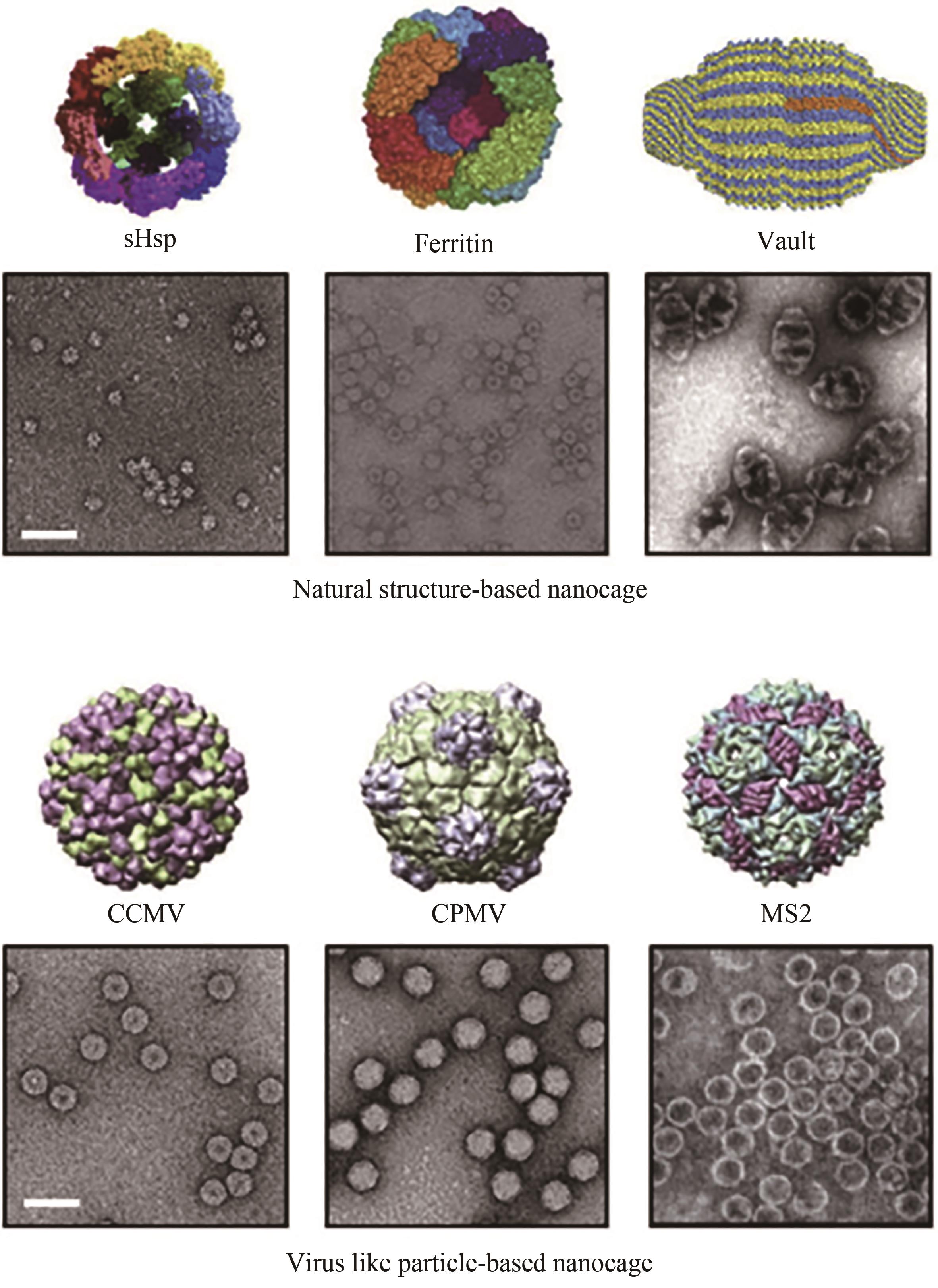
图3 各种基于笼状蛋白的结构示意图及其透射电镜图[52](比例尺= 50 nm。上图显示了基于天然结构的纳米笼,下图展示了基于病毒样颗粒的纳米笼)
Fig. 3 Schematic diagrams and TEM images of structures of various protein-based nanocages[52](Scale bar: 50 nm. Upper images show natural structure-based nanocages, and lower images show virus-like particles.)

图4 杂化铁蛋白纳米酶(mito-fenozyme)保护线粒体功能[88](a)mito-fenozyme制备示意图;(b)FTn的负染色TEM图;(c)MnO2 fenozyme TEM图;(d) mito-fenozyme TEM图(比例尺=20 nm);(e)在mito-fenozyme作用下细胞内自由基向非细胞毒性分子转化的示意图;(f)mito-fenozyme影响线粒体氧化损伤的共聚焦图像(上)和量化分析(下);(g) mito-fenozyme处理的细胞内氧化损伤自由基水平下降(比例尺=10 μm)
Fig. 4 Hybrid ferritin nanozyme (Mito-Fenozyme) protects mitochondrial functions[88](a) Schematic diagram for the preparation of Mito-Fenozyme. TEM images of the FTn protein shell (negative staining with 1% uranyl acetate) (b), MnO2 nanoparticles inside the FTn shell (c), and Mito-Fenozyme (d). Scale bar: 20 nm. (e) Schematic diagram for the intracellular conversion of free radicals to non-cytotoxic molecules under the catalysis of Mito-Fenozyme. (f) Confocal images (top) and quantitative analysis (bottom) for the effect of Mito-Fenozyme on mitochondrial oxidative damage. (g) Mito-Fenozyme reduced intracellular free radical levels in oxidatively damaged cells. Scale bar: 10 μm

图5 模块化组装思路构筑寡聚纳米酶[87](a)铁蛋白胞内重组胞外再重组构筑寡聚组装体示意图;(b)构筑的几种组装体的示意图(上)和TEM照片(下)。比例尺=20 nm
Fig. 5 Assembly of chain-like nanostructures[87](a) Schematic illustration for the preparation of FTn-Ner via a two-step self-assembly/post-assembly approach. The uniform FTn as motifs were obtained by the self-assembly of 24 FTn subunits expressed in E. coli. Subsequently, purified FTn motifs were further assembled to form different FTn-Ner by using two-armed PEG. (b) Representative TEM images of various assembled nanostructures. Scale bar: 20 nm
| 1 | DE PINA MARIZ B, CARVALHO S, BATALHA I L, et al. Artificial enzymes bringing together computational design and directed evolution[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2021, 19(9): 1915-1925. |
| 2 | MAK W S, SIEGEL J B. Computational enzyme design: transitioning from catalytic proteins to enzymes[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2014, 27: 87-94. |
| 3 | MURAKAMI Y, KIKUCHI J I, HISAEDA Y, et al. Artificial enzymes[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1996, 96(2): 721-758. |
| 4 | 高利增, 梁敏敏, 温涛, 等. 纳米酶标准术语[J]. 中国科技术语, 2020, 22(6): 21-24. |
| GAO L Z, LIANG M M, WEN T, et al. Standard vocabulary for nanozyme[J]. China Terminology, 2020, 22(6): 21-24. | |
| 5 | WEI H, GAO L Z, FAN K L, et al. Nanozymes: a clear definition with fuzzy edges[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 40: 101269. |
| 6 | WEI H, WANG E K. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(14): 6060-6093. |
| 7 | WU J J X, WANG X Y, WANG Q, et al. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (Ⅱ)[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(4): 1004-1076. |
| 8 | GAO L Z, ZHUANG J, NIE L, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2007, 2(9): 577-583. |
| 9 | LIANG M M, YAN X Y. Nanozymes: from new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(8): 2190-2200. |
| 10 | WANG X Y, GAO X J, QIN L, et al. eg occupancy as an effective descriptor for the catalytic activity of perovskite oxide-based peroxidase mimics[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 704. |
| 11 | 武江洁星, 魏辉. 浅谈纳米酶的高效设计策略[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(1): 42-51. |
| WU J J X, WEI H. Efficient design strategies for nanozymes[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(1): 42-51. | |
| 12 | LIN S C, WEI H. Design of high performance nanozymes: a single-atom strategy[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2019, 62(5): 710-712. |
| 13 | MENG X Q, ZARE I, YAN X Y, et al. Protein-protected metal nanoclusters: an emerging ultra-small nanozyme[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2020, 12(3): e1602. |
| 14 | ZHANG R F, FAN K L, YAN X Y. Nanozymes: created by learning from nature[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2020, 63(8): 1183-1200. |
| 15 | LI S R, ZHOU Z J, TIE Z X, et al. Data-informed discovery of hydrolytic nanozymes[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 827. |
| 16 | LIU Q W, ZHANG A M, WANG R H, et al. A review on metal-and metal oxide-based nanozymes: properties, mechanisms, and applications[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13(1): 154. |
| 17 | HUANG Y Y, REN J S, QU X G. Nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(6): 4357-4412. |
| 18 | SUN H J, ZHOU Y, REN J S, et al. Carbon nanozymes: enzymatic properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(30): 9224-9237. |
| 19 | LOPEZ-CANTU D O, GONZÁLEZ-GONZÁLEZ R B, MELCHOR-MARTÍNEZ E M, et al. Enzyme-mimicking capacities of carbon-dots nanozymes: properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications-a review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 194: 676-687. |
| 20 | WANG X Y, HU Y H, WEI H. Nanozymes in bionanotechnology: from sensing to therapeutics and beyond[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2016, 3(1): 41-60. |
| 21 | HU Y H, CHENG H J, ZHAO X Z, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering active gold nanoparticles with enzyme-mimicking activities for measuring glucose and lactate in living tissues[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(6): 5558-5566. |
| 22 | PRATSINIS A, KELESIDIS G A, ZUERCHER S, et al. Enzyme-mimetic antioxidant luminescent nanoparticles for highly sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensing[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(12): 12210-12218. |
| 23 | WEI H, WANG E K. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics and their applications in H2O2 and glucose detection[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(6): 2250-2254. |
| 24 | DUAN D M, FAN K L, ZHANG D X, et al. Nanozyme-strip for rapid local diagnosis of Ebola[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015, 74: 134-141. |
| 25 | CHANG M Y, HOU Z Y, WANG M, et al. Single-atom Pd nanozyme for ferroptosis-boosted mild-temperature photothermal therapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(23): 12971-12979. |
| 26 | CHEN Y, ZOU H, YAN B, et al. Atomically dispersed Cu nanozyme with intensive ascorbate peroxidase mimic activity capable of alleviating ROS-mediated oxidation damage[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(5): 2103977. |
| 27 | MEI L Q, ZHU S, LIU Y P, et al. An overview of the use of nanozymes in antibacterial applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 418: 129431. |
| 28 | FAN K L, XI J Q, FAN L, et al. In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1440. |
| 29 | ZHAO S, DUAN H X, YANG Y L, et al. Fenozyme protects the integrity of the blood-brain barrier against experimental cerebral malaria[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(12): 8887-8895. |
| 30 | REN E, ZHANG C, LI D F, et al. Leveraging metal oxide nanoparticles for bacteria tracing and eradicating[J]. View, 2020, 1(3): 20200052. |
| 31 | ATTAR F, SHAHPAR M G, RASTI B, et al. Nanozymes with intrinsic peroxidase-like activities[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 278: 130-144. |
| 32 | JIANG D W, NI D L, ROSENKRANS Z T, et al. Nanozyme: new horizons for responsive biomedical applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(14): 3683-3704. |
| 33 | SUN H J, GAO N, DONG K, et al. Graphene quantum dots-band-aids used for wound disinfection[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(6): 6202-6210. |
| 34 | TAINER J A, ROBERTS V A, GETZOFF E D. Protein metal-binding sites[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 1992, 3(4): 378-387. |
| 35 | CHAKRABARTI P. Geometry of interaction of metal ions with histidine residues in protein structures[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 1990, 4(1): 57-63. |
| 36 | BALA T, PRASAD B L V, SASTRY M, et al. Interaction of different metal ions with carboxylic acid group: a quantitative study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2007, 111(28): 6183-6190. |
| 37 | CHAKRABARTI P. Systematics in the interaction of metal ions with the main-chain carbonyl group in protein structures[J]. Biochemistry, 1990, 29(3): 651-658. |
| 38 | AN F F, ZHANG X H. Strategies for preparing albumin-based nanoparticles for multifunctional bioimaging and drug delivery[J]. Theranostics, 2017, 7(15): 3667-3689. |
| 39 | BAL W, SOKOŁOWSKA M, KUROWSKA E, et al. Binding of transition metal ions to albumin: sites, affinities and rates[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2013, 1830(12): 5444-5455. |
| 40 | LARSEN M T, KUHLMANN M, HVAM M L, et al. Albumin-based drug delivery: harnessing nature to cure disease[J]. Molecular and Cellular Therapies, 2016, 4: 3. |
| 41 | TAN Y L, HO H K. Navigating albumin-based nanoparticles through various drug delivery routes[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2018, 23(5): 1108-1114. |
| 42 | HUANG G N, ZANG J K, HE L Z, et al. Bioactive nanoenzyme reverses oxidative damage and endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurons under ischemic stroke[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(1): 431-452. |
| 43 | HAN L, ZHANG H J, CHEN D Y, et al. Protein-directed metal oxide nanoflakes with tandem enzyme-like characteristics: colorimetric glucose sensing based on one-pot enzyme-free cascade catalysis[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(17): 1800018. |
| 44 | CRIVELLI B, PERTEGHELLA S, BARI E L, et al. Silk nanoparticles: from inert supports to bioactive natural carriers for drug delivery[J]. Soft Matter, 2018, 14(4): 546-557. |
| 45 | YANG R H, FU S Y, LI R D, et al. Facile engineering of silk fibroin capped AuPt bimetallic nanozyme responsive to tumor microenvironmental factors for enhanced nanocatalytic therapy[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(1): 107-116. |
| 46 | WILLNER I, BARON R, WILLNER B. Growing metal nanoparticles by enzymes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2006, 18(9): 1109-1120. |
| 47 | ZENG D D, LUO W J, LI J, et al. Gold nanoparticles-based nanoconjugates for enhanced enzyme cascade and glucose sensing[J]. The Analyst, 2012, 137(19): 4435-4439. |
| 48 | LOSADA-GARCIA N, JIMENEZ-ALESANCO A, VELAZQUEZ-CAMPOY A, et al. Enzyme/nanocopper hybrid nanozymes: Modulating enzyme-like activity by the protein structure for biosensing and tumor catalytic therapy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(4): 5111-5124. |
| 49 | LI X Y, CAO Y F, LUO K, et al. Highly active enzyme-metal nanohybrids synthesized in protein-polymer conjugates[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(8): 718-725. |
| 50 | HERRERA ESTRADA L P, CHAMPION J A. Protein nanoparticles for therapeutic protein delivery[J]. Biomaterials Science, 2015, 3(6): 787-799. |
| 51 | SCHOONEN L, HEST J C M VAN. Functionalization of protein-based nanocages for drug delivery applications[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(13): 7124-7141. |
| 52 | LEE E J, LEE N K, KIM I S. Bioengineered protein-based nanocage for drug delivery[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 106: 157-171. |
| 53 | CHOI S H, KWON I C, HWANG K Y, et al. Small heat shock protein as a multifunctional scaffold: integrated tumor targeting and caspase imaging within a single cage[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2011, 12(8): 3099-3106. |
| 54 | MOON H, LEE J S, MIN J, et al. Developing genetically engineered encapsulin protein cage nanoparticles as a targeted delivery nanoplatform[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2014, 15(10): 3794-3801. |
| 55 | MIN J, KIM S, LEE J S, et al. Lumazine synthase protein cage nanoparticles as modular delivery platforms for targeted drug delivery[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(89): 48596-48600. |
| 56 | SAN B H, KIM S, MOH S H, et al. Platinum nanoparticles encapsulated by aminopeptidase: a multifunctional bioinorganic nanohybrid catalyst[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(50): 11924-11929. |
| 57 | DANIELS T R, DELGADO T, RODRIGUEZ J A, et al. The transferrin receptor part I: Biology and targeting with cytotoxic antibodies for the treatment of cancer[J]. Clinical Immunology, 2006, 121(2): 144-158. |
| 58 | MONTEMIGLIO L C, TESTI C, CECI P, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human ferritin-transferrin receptor 1 complex[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1121. |
| 59 | FAN K L, JIA X H, ZHOU M, et al. Ferritin nanocarrier traverses the blood brain barrier and kills glioma[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(5): 4105-4115. |
| 60 | XING R M, WANG X Y, ZHANG C L, et al. Characterization and cellular uptake of platinum anticancer drugs encapsulated in apoferritin[J]. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 2009, 103(7): 1039-1044. |
| 61 | LIU W, LIN Q, FU Y, et al. Target delivering paclitaxel by ferritin heavy chain nanocages for glioma treatment[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 323: 191-202. |
| 62 | ZHAO Y Z, LIANG M M, LI X, et al. Bioengineered magnetoferritin nanoprobes for single-dose nuclear-magnetic resonance tumor imaging[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(4): 4184-4191. |
| 63 | ZHEN Z P, TANG W, GUO C L, et al. Ferritin nanocages to encapsulate and deliver photosensitizers for efficient photodynamic therapy against cancer[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(8): 6988-6996. |
| 64 | ZHEN Z P, TANG W, CHEN H M, et al. RGD-modified apoferritin nanoparticles for efficient drug delivery to tumors[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(6): 4830-4837. |
| 65 | LI X, QIU L H, ZHU P, et al. Epidermal growth factor-ferritin H-chain protein nanoparticles for tumor active targeting[J]. Small, 2012, 8(16): 2505-2514. |
| 66 | KRAMER R M, LI C, CARTER D C, et al. Engineered protein cages for nanomaterial synthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(41): 13282-13286. |
| 67 | HOSEIN H A, STRONGIN D R, ALLEN M, et al. Iron and cobalt oxide and metallic nanoparticles prepared from ferritin[J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(23): 10283-10287. |
| 68 | BUTTS C A, SWIFT J, KANG S G, et al. Directing noble metal ion chemistry within a designed ferritin protein[J]. Biochemistry, 2008, 47(48): 12729-12739. |
| 69 | PENG T, PARAMELLE D, SANA B, et al. Designing non-native iron-binding site on a protein cage for biological synthesis of nanoparticles[J]. Small, 2014, 10(15): 3131-3138. |
| 70 | DOUGLAS T, STRABLE E, WILLITS D, et al. Protein engineering of a viral cage for constrained nanomaterials synthesis[J]. Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(6): 415-418. |
| 71 | GIESSEN T W, SILVER P A. Converting a natural protein compartment into a nanofactory for the size-constrained synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(12): 1497-1504. |
| 72 | ROHL C A, STRAUSS C E M, MISURA K M S, et al. Protein structure prediction using Rosetta[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2004, 383: 66-93. |
| 73 | KING N P, SHEFFLER W, SAWAYA M R, et al. Computational design of self-assembling protein nanomaterials with atomic level accuracy[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6085): 1171-1174. |
| 74 | DIVINE R, DANG H V, UEDA G, et al. Designed proteins assemble antibodies into modular nanocages[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6537): eabd9994. |
| 75 | GAO R M, TAN H, LI S S, et al. A prototype protein nanocage minimized from carboxysomes with gated oxygen permeability[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(5): e2104964119. |
| 76 | UCHIDA M, KANG S, REICHHARDT C, et al. The ferritin superfamily: supramolecular templates for materials synthesis[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2010, 1800(8): 834-845. |
| 77 | SUN X R, HONG Y L, GONG Y B, et al. Bioengineered ferritin nanocarriers for cancer therapy[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(13): 7023. |
| 78 | MOSCA L, FALVO E, CECI P, et al. Use of ferritin-based metal-encapsulated nanocarriers as anticancer agents[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(1): 101. |
| 79 | ZANG J C, ZHENG B W, ZHANG X Q, et al. Design and site-directed compartmentalization of gold nanoclusters within the intrasubunit interfaces of ferritin nanocage[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2019, 17(1): 79. |
| 80 | HUARD D J E, KANE K M, TEZCAN F A. re-engineering protein interfaces yields copper-inducible ferritin cage assembly[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2013, 9(3): 169-176. |
| 81 | JENKINS M C, LUTZ S. Encapsulin nanocontainers as versatile scaffolds for the development of artificial metabolons[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(4): 857-869. |
| 82 | MCCONNELL S A, CANNON K A, MORGAN C, et al. Designed protein cages as scaffolds for building multienzyme materials[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(2): 381-391. |
| 83 | JIANG B, FANG L, WU K M, et al. Ferritins as natural and artificial nanozymes for theranostics[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(2): 687-706. |
| 84 | HE J Y, FAN K L, YAN X Y. Ferritin drug carrier (FDC) for tumor targeting therapy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2019, 311/312: 288-300. |
| 85 | HUANG X L, CHISHOLM J, ZHUANG J, et al. Protein nanocages that penetrate airway mucus and tumor tissue[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(32): E6595-E6602. |
| 86 | HUANG X L, ZHUANG J, CHUNG S W, et al. Hypoxia-tropic protein nanocages for modulation of tumor- and chemotherapy-associated hypoxia[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(1): 236-247. |
| 87 | LIU Q Q, TIAN J W, LIU J J, et al. Modular assembly of tumor-penetrating and oligomeric nanozyme based on intrinsically self-assembling protein nanocages[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(39): 2103128. |
| 88 | ZHANG Y, KHALIQUE A, DU X C, et al. Biomimetic design of mitochondria-targeted hybrid nanozymes as superoxide scavengers[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(9): 2006570. |
| 89 | SUN Z Y, LIU Q Q, WANG X Y, et al. Bioorthogonal catalytic nanozyme-mediated lysosomal membrane leakage for targeted drug delivery[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(3): 1132-1147. |
| 90 | HU X Y, WANG X Y, LIU Q Q, et al. Nanozyme-powered giant unilamellar vesicles for mimicry and modulation of intracellular oxidative stress[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(18): 21087-21096. |
| 91 | CHEN J, PATIL S, SEAL S, et al. Rare earth nanoparticles prevent retinal degeneration induced by intracellular peroxides[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2006, 1(2): 142-150. |
| 92 | SHCHERBAKOV A B, ZHOLOBAK N M, SPIVAK N Y, et al. Advances and prospects of using nanocrystalline ceria in prolongation of lifespan and healthy aging[J]. Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 60(13): 1595-1625. |
| 93 | ZHAO H Q, ZHANG R F, YAN X Y, et al. Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: an emerging star for anti-oxidation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 9(35): 6939-6957. |
| 94 | GAO F L, WU J, GAO H Q, et al. Hypoxia-tropic nanozymes as oxygen generators for tumor-favoring theranostics[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 230: 119635. |
| 95 | CHOUCHANI E T, PELL V R, JAMES A M, et al. A unifying mechanism for mitochondrial superoxide production during ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Cell Metabolism, 2016, 23(2): 254-263. |
| 96 | FAN K L, CAO C Q, PAN Y X, et al. Magnetoferritin nanoparticles for targeting and visualizing tumour tissues[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(7): 459-464. |
| 97 | JIANG B, YAN L, ZHANG J L, et al. Biomineralization synthesis of the cobalt nanozyme in SP94-ferritin nanocages for prognostic diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(10): 9747-9755. |
| 98 | ORTIZ DE MONTELLANO P R. Cytochrome P450: structure, mechanism, and biochemistry [M]. 3rd ed. Springer, 2005. |
| 99 | SIES H, JONES D P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2020, 21(7): 363-83. |
| [1] | 梁晓声, 郭永超, 门冬, 张先恩. 病毒-纳米金杂合导电网络结构在电化学分析的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 415-427. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||